
Hydrogen storage behaviors and microstructure of MF3 (M=Ti, Fe)-doped magnesium hydride
PENG Shu-ke(彭书科), XIAO Xue-zhang(肖学章), XU Rui-juan(许瑞娟), LI Luo(李 骆),
WU Fan(吴 凡), LI Shou-quan(李寿权), WANG Qi-dong(王启东), CHEN Li-xin(陈立新)
Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310027, China
Received 12 October 2009; accepted 6 April 2010
Abstract: MgH2+10%MF3 (M=Ti, Fe) (mass fraction) composites were prepared by ball-milling in hydrogen atmosphere, and their hydrogen storage behaviors and microstructure were investigated systematically. The results show that the hydriding and dehydriding kinetics of MgH2 are markedly improved by doping TiF3 and FeF3 fluorides. At 573 K, the two composites can absorb 5.67%-6.07% (mass fraction) hydrogen within 5 min under an initial hydrogen pressure of 3.5 MPa, and desorb 5.34%-6.02% hydrogen within 6 min. Furthermore, the composites can absorb hydrogen rapidly in moderate temperature range of 313-473 K. In comparison, TiF3-doped sample has a better hydriding-dehydriding kinetics than FeF3-doped sample. The microstructure analysis shows that some active particles including MgF2, TiH2 and Fe could be formed in the hydriding-dehydriding processes of the MF3-doped composites. From the Kissinger’s plot, the apparent activation energies for the hydrogen desorption of the composites are estimated to be 74.1 kJ/mol for TiF3-doped composite and 77.6 kJ/mol for FeF3-doped composite, indicating MgH2 is significantly activated due to the catalytic effect of the doping of MF3.
Key words: Mg-based composites; TiF3; FeF3; hydrogen storage properties; microstructure
1 Introduction
Among metal hydrides studied as possible solid-state hydrogen storage materials, magnesium hydride is one of the most promising candidates for hydrogen storage due to its high hydrogen storage capacity (7.6% in MgH2), low cost and abundance. However, its practical application for hydrogen storage is hampered by its high thermodynamic stability and sluggish hydriding-dehydriding kinetics. A great deal of research has shown that the hydrogen storage performance of MgH2 could be improved by adding other hydrogen storage materials[1] and doping with appropriate catalysts by ball-milling, such as transition metals[2-5], transition metal oxides[6-8] and transition metal fluorides[9-12]. XIAO et al[13] reported that Mg+ xLaMg2Ni (x=5%-20%, mass fraction, the same below if not mentioned) composites milled for 6 h can absorb about 5% hydrogen in 200 s at 453 K. VARIN et al[2] found that the 2% micro-Ni doped MgH2 synthesized by controlled reactive mechanical milling desorbs about 5% hydrogen in 1 000 s at 573 K. LUO et al[9] reported that MgH2+2%NbF5 (mole fraction) milled for 5 h can desorb 5% hydrogen in 60 min at 573 K. Among them, the addition of transition metal fluorides to MgH2 by mechanical milling seems to be one of the most promising methods for the improvement of the hydrogen sorption properties. However, little investigation on understanding the improvement of hydrogen storage properties of MgH2 by doping transition metal fluorides has been done.
In this work, MgH2+10%MF3 (M=Ti, Fe) composites were prepared by ball-milling in hydrogen atmosphere. The influence of doping TiF3 and FeF3 fluorides on the hydrogen storage behaviors and microstructure of the composites was investigated systematically. In addition, the reason why the hydrogen storage properties of above composites are improved has been also discussed.
2 Experimental
MgH2 powder (98%), TiF3 (99%) and FeF3 (98%) were purchased from Aldrich Co. The MgH2+10% MF3 (M=Ti, Fe) composite samples were mechanically milled under supra-pure hydrogen of 1 MPa for 15 h by using a QM-3SP4J planetary mill at 400 r/min. The ball-to-powder mass ratio was about 40:1. For comparison, MgH2 was mechanically milled under identical conditions. All the sample handling was performed in an Ar-filled glove-box equipped with purification system.
The structure and morphology of the samples were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD, Thermo Electron ARL X’TRA) with Cu Kα radiation, and scanning electron microscopy (SEM, FEI FSEM SIRION-100), respectively. Calorimetric measurements were carried out with a differential scanning calorimetry (DSC, TA-SDT Q600) under a flow rate of Ar (120 mL/min) with a heating rate of 2, 5, 10 and 20 K/min from room temperature to 773 K. The dehydriding- hydriding properties of the samples with a typical amount of around 500 mg were examined by using a Sievert-type apparatus. Absorption measurements were performed at desired temperatures under an initial hydrogen pressure of 3.5 MPa. Desorption measurements were carried out at desired temperatures under an initial hydrogen pressure of 0.01 MPa. To allow a practical evaluation for the hydrogen storage capability of the composite, the mass of MF3 fluorides was taken into account in the determination of hydrogen storage capacity.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Hydriding and dehydriding properties
A comparison of the hydrogen absorption- desorption between the samples doped with 10% MF3 (M=Ti, Fe) and the undoped samples prepared under identical conditions are shown in Fig.1. It can be clearly seen that the pronounced catalytic enhancement arising upon adding MF3 (M=Ti, Fe) is observed on the hydriding and dehydriding aspect. The as-milled MgH2 absorbs 1.29% hydrogen within 5 min at 473 K, however, the samples doped with 10% MF3 (M=Ti, Fe) display a remarkable improvement in the hydriding kinetics of the composite. The TiF3-doped composite can absorb 4.20% hydrogen and the FeF3-doped composite can absorb 4.03% hydrogen within 5 min. For hydrogen desorption, the catalytic effect of MF3 (M=Ti, Fe) is also impressive. At 573 K, only 0.04% hydrogen can be desorbed within 8 min for the as-milled MgH2 sample, but the samples doped with 10% MF3 (M=Ti, Fe) can desorb 6.04% hydrogen for TiF3-doped composite and 5.92% hydrogen for FeF3-doped composite within 8 min.
The effect of temperature on the hydriding- dehydriding properties of MgH2+10% MF3 (M=Ti, Fe) composites was further investigated. Fig.2 shows the hydriding curves of MgH2+10% MF3 (M=Ti, Fe) composites at different temperatures under an initial hydrogen pressure of 3.5 MPa. It should be pointed out that all samples were directly measured after initial dehydrogenation at 573 K without any pre-activation. It is found that the two samples show good hydriding kinetics and can absorb hydrogen rapidly at a moderate temperature range from 313 to 473 K. At 573 K, under an initial hydrogen pressure of 3.5 MPa, the MgH2+10% TiF3 composite absorbs 5.22% hydrogen within 60 s and 6.27% hydrogen within 30 min. At 393 and 373 K, 4.33% hydrogen and 3.63% hydrogen can be absorbed within 10 min, respectively. The composite can absorb
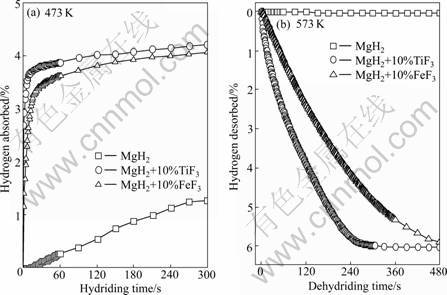
Fig.1 Hydriding (a) and dehydriding (b) curves of MgH2+10% MF3 (M=Ti, Fe) composites and as-milled MgH2
2.91% hydrogen even at 313 K within 30 min. For the MgH2+10% FeF3 composite, it absorbs 5.57% hydrogen within 60 s and 6.33% hydrogen within 30 min at 573 K. At 473 and 373 K, 4.28% hydrogen and 2.85% hydrogen are absorbed within 10 min, respectively. At 313 K, the composite can absorb 1.31% hydrogen within 30 min. In comparison, it is obvious that the MgH2+10% MF3 (M=Ti, Fe) composites almost have the same hydriding kinetics at 573 K, however, the TiF3-doped sample has better hydriding kinetics than FeF3-doped sample in a moderate temperature range from 313 K to 473 K, which is attributed to catalytic effect of TiF3 on MgH2 better than FeF3.
The dehydriding curves of MgH2+10% MF3 (M=Ti, Fe) composites at different temperatures are presented in Fig.3. At 573 K, the TiF3-doped sample desorbs 5.98% hydrogen and the FeF3-doped sample desorbs 4.82% hydrogen within 300 s. At 553 K, the TiF3-doped composite desorbs 5.46% hydrogen and the FeF3-doped composite desorbs 4.59% hydrogen within 450 s. It is also obvious that the TiF3-doped sample has better dehydriding kinetics than FeF3-doped sample.
3.2 Microstructure characterization and thermal analysis
XRD patterns of MgH2+10% MF3 (M=Ti, Fe) composite samples are shown in Fig.4 and Fig.5. After ball-milling for 15 h, the diffraction peaks of β-MgH2 in the composites broaden significantly, which is attributed to the reduction of MgH2 crystallite size resulting from plastic deformation, recrystallisation, fracturing and cold welding of material [14]. Besides, the formation of a little γ-MgH2 is observed. The formation of this metastable high-pressure phase is attributed to high compressive stresses resulting form impact loading during mechanical ball-milling. Small peaks of MgO are observed in all samples due to the oxidation of samples in the XRD test. Additionally, for the as-milled samples, the most intense diffraction peaks of the XRD patterns can be identified to come from the starting materials, i.e.
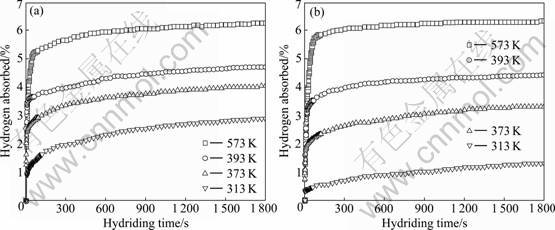
Fig.2 Hydriding curves of MgH2+10% MF3 (M=Ti, Fe) composites at different temperatures: (a) MgH2+10%TiF3; (b) MgH2+ 10%FeF3
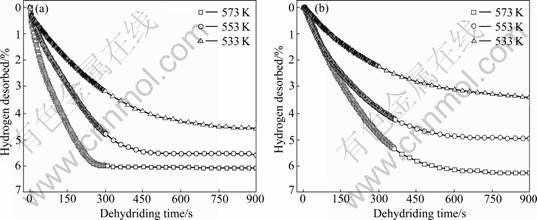
Fig.3 Dehydriding curves of MgH2+10% MF3 (M=Ti, Fe) composites at different temperatures: (a) MgH2+10%TiF3; (b) MgH2+ 10%FeF3
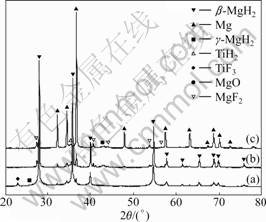
Fig.4 XRD patterns of MgH2+10% TiF3 composite: (a) As- milled; (b) After hydrogenation at 573 K for 2 h in 10th cycle; (c) After dehydrogenation at 573 K for 2 h in 10th cycle
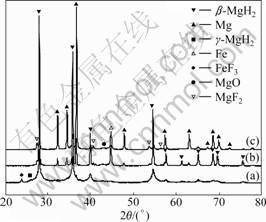
Fig.5 XRD patterns of MgH2+10% FeF3 composite: (a) As- milled; (b) After hydrogenation at 573 K for 2 h in 10th cycle; (c) After dehydrogenation at 573 K for 2 h in 10th cycle
MgH2 and TiF3 or FeF3, and no reactant from MgH2 and MF3 (M=Ti, Fe) is identified. However, this situation changes during the dehydriding-hydriding processes of the samples. As shown in Fig.4, after hydrogenation under 3.5 MPa hydrogen pressure and dehydrogenation at 573 K for 2 h in the 10th cycle, no diffraction peak of TiF3 is definitely identified, while MgF2 and TiH2 are accordingly identified. As shown in Fig.5, for the hydrided and dehydrided MgH2+10%FeF3 samples, FeF3 phase disappears, and MgF2 and Fe phases occur. This indicates that the fluorides have reacted with MgH2. Judging from the thermodynamic potentials of the various possible reaction pathways, the formation of MgF2 and TiH2 should follow reaction (1); the formation of MgF2 and Fe should follow reaction (2):
MgH2+2/3TiF3→MgF2+2/3TiH2+1/2H2
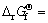 -196.83 kJ/mol (1)
-196.83 kJ/mol (1)
MgH2+2/3FeF3→MgF2+2/3Fe+1/2H2
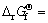 -434.45 kJ/mol (2)
-434.45 kJ/mol (2)
The standard Gibbs free energies,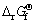 of MgH2, TiF3, MgF2, TiH2, and FeF3 are -35.97, -1361.66, -1 070.59, -104.97, and -900.22 kJ/mol[15], respectively, so the total change
of MgH2, TiF3, MgF2, TiH2, and FeF3 are -35.97, -1361.66, -1 070.59, -104.97, and -900.22 kJ/mol[15], respectively, so the total change 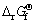 associated with reaction (1) would be -196.83 kJ/mol of MgH2 and reaction (2) would be -434.45 kJ/mol of MgH2.
associated with reaction (1) would be -196.83 kJ/mol of MgH2 and reaction (2) would be -434.45 kJ/mol of MgH2.
Fig.6 and Fig.7 show the SEM micrographs of MgH2+10% MF3 (M=Ti, Fe) composite samples ball-milled for 15 h, and subsequent hydrogenated- dehydrogenated at 573 K for 2 h in the 10th cycle. The results indicate that the particle size of MgH2 is effectively decreased after ball-milling. The doping of TiF3 or FeF3 leads to substantial refinement of the powder particles during milling. It is found that many small particles distribute on the surface of the composite matrix. The decrease of particles size can enhance the rates of dehydrogenation-hydrogenation.
It has been claimed by HANADA et al[4] that the behavior of the first-order reaction is universal for

Fig.6 SEM images of MgH2+10% TiF3 composite: (a) As- milled; (b) After hydrogenation at 573 K for 2 h in 10th cycle; (c) After dehydrogenation at 573 K for 2 h in 10th cycle

Fig.7 SEM images of MgH2+10% FeF3 samples: (a) As-milled; (b) After hydrogenation at 573 K for 2 h in 10th cycle; (c) After dehydrogenation at 573 K for 2 h in 10th cycle
H-desorption of the ball-milled MgH2 with some catalysts. In order to understand the fast H-sorption kinetics arising upon the doping of TiF3 and FeF3, quantitative estimation of kinetics barrier was then carried out by the determination of the apparent activation energy (Ea) with Kissinger’s method[16]:
 (3)
(3)
where β is the heating rate in K/min, Tm is the absolute temperature for the maximum desorption rate, and R is the gas constant. Table 1 presents the Tm that is extracted from the kinetic dehydrogenation curves at variable heating rates as shown in Fig.8. The plot of ln(Tm2) versus 1 000/Tm is shown in Fig.9. From the slope of these straight lines, Ea of MgH2 doped with TiF3 composite and MgH2 doped with FeF3 composite were estimated to be approximately 74.1 and 77.6 kJ/mol for the first-order dehydrogenation of MgH2, respectively. The value of Ea of as-milled pure MgH2 was estimated
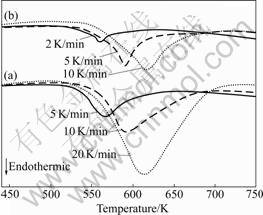
Fig.8 DSC curves of MgH2+10% MF3 (M=Ti, Fe) composites at various heating rates: (a) MgH2+10%TiF3; (b) MgH2+ 10%FeF3
Table 1 Tm corresponding to two samples at different heating rates
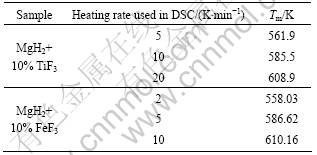
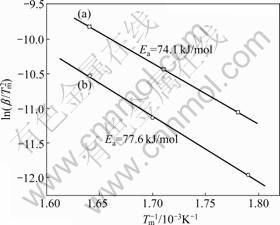
Fig.9 Kissinger’s plots of first-order dehydrogenation of MgH2+10% MF3 (M=Ti, Fe) composites at various heating rates: (a) MgH2+10%TiF3; (b) MgH2+10%FeF3
to be about 120 kJ/mol, reported by LUO et al[9]. This demonstrates the pronounced catalytic effect of TiF3 and FeF3 on the desorption process of MgH2.
The enhancement of hydrogen storage characteristics of MgH2 doped with MF3 (M=Ti, Fe) by ball-milling can be explained as follows. XRD and SEM analysis results show that the size of crystal grains of the composites is reduced and the abundant defects are formed by ball-milling under hydrogen atmosphere, which can create more fresh surfaces and active locations to accelerate the diffusion of hydrogen. Some MgF2 and TiH2 or Fe active particles form in the hydriding- dehydriding processes of the MF3-doped composites, making catalytic effect on the hydrogen absorption- desorption of MgH2. Besides, from the Kissinger’s plot, the values of the apparent activation energies for the hydrogen desorption composites are 74.1 kJ/mol for TiF3-doped composite and 77.6 kJ/mol for FeF3-doped composite, respectively. This indicates that MgH2 is significantly activated due to the catalytic effect of doping MF3 (M=Ti, Fe).
4 Conclusions
1) The hydriding-dehydriding kinetics of MgH2 are markedly improved by doping TiF3 and FeF3. At 573 K, under an initial hydrogen pressure of 3.5 MPa, the two composites can absorb 5.22% and 5.57% hydrogen within 60 s and 6.27% and 6.33% hydrogen within 30 min, respectively. Furthermore, the two composites can absorb hydrogen rapidly in moderate temperature range from 313 to 473 K. At 573 K, the two composites can desorb 5.34%-6.02% hydrogen within 6 min. In comparison, TiF3-doped sample has a better hydriding- dehydriding kinetics than FeF3-doped sample.
2) The microstructure analysis results show that some MgF2 and TiH2 or Fe active particles form in the hydriding-dehydriding processes of the MF3-doped composites. From the Kissinger’s plot, the values of the apparent activation energies for the hydrogen desorption of the composites are 74.1 kJ/mol for TiF3-doped composite and 77.6 kJ/mol for FeF3-doped composite, respectively. This clearly demonstrates the pronounced catalytic effect of doping TiF3 and FeF3 on the dehydriding process of MgH2.
References
[1] ZHANG Y, TIAN Q F, LIU S S, SUN L X. The destabilization mechanism and de/re-hydrogenation kinetics of MgH2-LiAlH4 hydrogen storage system [J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2008, 185(2): 1514-1518.
[2] VARIN R A, CZUJKO T, WASMUND E B, WRONSK Z S. Catalytic effects of various forms of nickel on the synthesis rate and hydrogen desorption properties of nanocrystalline magnesium hydride (MgH2) synthesized by controlled reactive mechanical milling (CRMM) [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2007, 432(1/2): 217-231.
[3] LI S L, LIU Y, VARIN R A, LIU H F, CUI J M, CHEN S Q. Effect of ball milling methods on synthesis and desorption properties of nanocrystalline Mg2FeH6 hydrogen storage materials [J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2008, 18(1): 42-47. (in Chinese)
[4] HANADA N, ICHIKAWA T, FUJII H. Catalytic effect of nanoparticle 3d-transition metals on hydrogen storage properties in magnesium hydride MgH2 prepared by mechanical milling [J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2005, 109(15): 7188-7194.
[5] BASSETTI A, BONETTI E, PASQUINI L, MONTONE A, GRBOVIC J, VITTOR ANTISAR M. Hydrogen desorption from ball milled MgH2 catalyzed with Fe [J]. The European Physical Journal B: Condensed Matter and Complex Systems, 2005, 43(1): 19-27.
[6] PATAH A, TAKASAKI A, SZMYD J S. Influence of multiple oxide (Cr2O3/Nb2O5) addition on the sorption kinetics of MgH2 [J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2009, 34(7): 3032-3037.
[7] GUPTA R, AGRESTI F, RUSSO S L, MADDALENA A, PALADE P, PRINCIPI G. Structure and hydrogen storage properties of MgH2 catalysed with La2O3 [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2008, 450(1/2): 310-313.
[8] FRIEDRICHS O, AGUEY-ZINSOU K F, FEMANDEZ J R A, SANCHEZ-LOPEZ J C, JUSTO A, KLASSEN T, BORMANN R, FEMANDEZ A. MgH2 with Nb2O5 as additive, for hydrogen storage: Chemical, structural and kinetic behavior with heating [J]. Acta Materialia, 2006, 54(1): 105-110.
[9] LUO Y, WANG P, MA L P, CHENG H M. Hydrogen sorption kinetics of MgH2 catalyzed with NbF5 [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2008, 453(1/2): 138-142.
[10] MA L P, WANG P, CHENG H M. Improving hydrogen sorption kinetics of MgH2 by mechanical milling with TiF3 [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2007, 432(1/2): L1-L4.
[11] XIE L, LIU Y, WANG Y T, ZHENG J, LI X G. Superior hydrogen storage kinetics of MgH2 nanoparticles doped with TiF3 [J]. Acta Materialia, 2007, 55(13): 4585-4591.
[12] JIN S A, SHIM J H, CHO Y W, YI K W. Dehydrogenation and hydrogenation characteristics of MgH2 with transition metal fluorides [J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2007, 172(2): 859-862.
[13] XIAO X Z, LIU G C, PENG S K, YU K R, LI S Q, CHEN C P, CHEN L X. Microstructure and hydrogen storage characteristics of nanocrystalline Mg+xwt% LaMg2Ni (x=0-30) composites [J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2010, 35: 2786-2790.
[14] AGUEY-ZINSOU K F, ARES FEMANDEZ J R, KLASSEN T, BOMANN R. Effect of Nb2O5 on MgH2 properties during mechanical milling [J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2007, 32(13): 2400-2407.
[15] DEAN J A. Lange’s chemistry handbook, 13th version [M]. SHANG J F, transl. Beijing: Science Press, 1991. (in Chinese)
[16] KISSINGER H E. Reaction kinetics in differential thermal analysis [J]. Analytical Chemistry, 1957, 29(11): 1702-1706.
(Edited by LI Xiang-qun)
Foundation item: Project(2006AA05Z144) supported by the National High-tech Research and Development Program of China; Project(2007CB209701) supported by the National Basic Research Program of China; Project(NCET-07-0741) supported by the Program for New Century Excellent Talents in University, China; Project(2006C11233) supported by the Science and Technology Program of Zhejiang Province, China
Corresponding author: CHEN Li-xin; Tel/Fax: +86-571-87951152; E-mail: lxchen@zju.edu.cn
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(09)60389-7