
Electrochemical characteristics of stainless steel using
impressed current cathodic protection in seawater
Seok-Ki JANG, Min-Su HAN, Seong-Jong KIM
Division of Marine Engineering, Mokpo Maritime University, Mokpo-City, Jeonnam, 530-729, Korea
Received 18 June 2008; accepted 10 March 2009
Abstract: Stainless steels such as STS 304, 316 and 630 are frequently used as shaft materials in small fiber reinforced polymer (FRP) fishing boats. If the shaft material is exposed to a severely corrosive environment such as seawater, it should be protected using appropriate methods. The impressed current cathodic protection was used to inhibit corrosion in shaft materials. In anodic polarization, passivity was remarkably more evident in STS 316 stainless steel than in STS 304 and STS 630. The pitting potentials of STS 304, 316, and 630 stainless steels were 0.30, 0.323, and 0.260 V, respectively. The concentration polarization due to oxygen reduction and activation polarization due to hydrogen generation were evident in the cathodic polarization trends of all three stainless steeds. STS 316 had the lowest current densities in all potential ranges, and STS 630 had the highest. Tafel analysis showed that STS 316 was the most noble in the three. In addition, the corrosion current density was the lowest for STS 316.
Key words: stainless steel; shaft material; impressed current cathodic protection; passivity
1 Introduction
The shaft system material in a fiber reinforced polymer(FRP) vessel is made of stainless steel, such as STS 304, 316, or 630. STS 304 is more commonly used due to its greater corrosion resistance and lower cost. In marine environments, extreme corrosion occurs in all types of stainless steel, including STS 304, which can lead to serious problems if it occurs intensively in a vessel that does not have a stern tube cooling system on the surface of the propeller shaft in the stern tube, or in the clearance between the stern tubes and the surrounding wood[1-2]. Intense corrosion can occur due to lack of resistance to galvanic, crevice, or stray current corrosion. Comprehensive investigations have been performed to determine an appropriate corrosion counter measure. Attempts have been made to protect stainless steel shaft systems from corrosion by installing grounding plates on the hull or using anticorrosive paint. However, the by-problem still exists and a definitive alternative technology has not yet been established. Pitted and cracked shafts must be repaired in dry docks by grinding and welding[1-2]. Differences of opinion often exist between an inspector certifying the repairs and the companies performing the repairs due to ambiguities in the regulations. People dealing with small shipyards do not have the resources to question these decisions. As a result, they become indifferent to the safety of their vessels in stormy weather, resulting in human and material losses. This investigation was performed to examine the impressed cathode current protection method[3-10] for stainless steel shaft systems on small FRP vessels.
We determined the optimum corrosion protection conditions, regardless of hydrogen embrittlement and stress corrosion cracking, and identified an optimum shaft system material.
2 Experimental
Tables 1 and 2 give the mechanical properties and chemical compositions of stainless steel STS 304, 316, and 630 commonly used for the shaft systems. The hardness was measured with a micro-Vickers hardness tester (Mitutoyo, Kawasaki, Japan) for an applied load of 9.807 N, an upkeep time of 10 s, and a measuring distance of 1 mm. The mean value of 20 measurements was used. For the electrochemical experiments, the STS 304, 316, and 630 specimens were mounted in an epoxy resin so as to leave an exposed area of 100 mm2 that was polished with 600# emery paper. Each specimen was carefully degreased with acetone and distilled water. Corrosion potential measurements were recorded over a period of 250 h at room temperature in natural seawater. Anodic polarization experiments were carried out at room temperature using an electrochemical apparatus consisting of a Pt coil as the counter-electrode and a Ag/AgCl-saturated KCl as reference electrode. A scan rate of 2 mV/s was executed from an open circuit potential(OCP) to a voltage 3.0 V. Cathodic polarization experiments were performed from an OCP to -2.0 V. Tafel analysis was performed under both anodic and cathodic conditions from an OCP to ±0.25 V under aerated conditions. The corrosion potential and corrosion current density were compared with Tafel analytical results obtained from various reference specimens. Potentiostatic experiments at an applied potential of 0.4 V were also performed and the resulting surface morphologies were examined and compared.
Table 1 Chemical compositions of STS 304, 316 and 630 (mass fraction, %)

Table 2 Mechanical properties of STS 304, 316 and 630
3 Results and discussion
The hardness of stainless steels STS 304, 316, and 630 were HV 149.4, 152.0, and 330.4, respectively. The hardness values of STS 304 and 316 are lower since they are austenite steel, whereas STS 630, whose carbon content is especially high, has a tensile strength twice that of austenite stainless steel. STS 304 is widely used due to its high corrosion and thermal resistance, and its high strength at low temperatures. However, in seawater solution, STS 304 becomes corroded due to the destruction of the passivity film by Cl- ions, resulting in pitting and intergranular corrosion. Therefore, corrosion protection facilities must be provided if STS 304 is used in a seawater environment. STS 316 has excellent pitting resistance characteristics in seawater and salinity solution environments due to the higher contents of Mo (2%-3%) and Ni[11]. Although STS 630 with additional copper has an excellent tensile strength, its anticorrosion properties are inferior to those of the other stainless steels. However, it is still widely used in shaft systems and turbines.
Fig.1 shows the potentials of stainless steels in sea water. The potential of STS 304 was initially -0.214 V; and it shifted in the positive direction after 4 000 s with the formation of a passivity film. The film was destroyed by the Cl- ions with time increasing, so the potential moved in the negative direction after approximately 20 000 s. Thereafter, a restored passivity film shifted the potential in the positive direction to -0.24 V. This value was maintained until the end of the test. The potential of STS 630 shifted in the positive direction in the early stages of test, and the highest potential occurred at approximately 15 000 s, after which the potential slowly shifted in the negative direction. The potential again shifted in the positive direction after approximately 180 000 s, followed by a shift in the negative direction at 210 000 s. Small fluctuations were observed after this point. The highest potential of STS 316 was -0.06 V, which occurred in the early stage of the test. Fluctuations were observed until 70 000 s, after which the potential remained stable. Among the three tested stainless steels, STS 316 had the most stable electrochemical behavior, and STS 630 had the lowest potential and the largest fluctuations, suggesting that STS 316 has the best corrosion resistance in seawater.
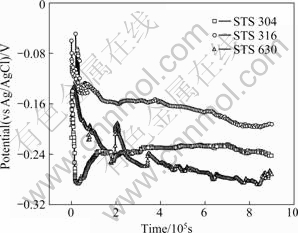
Fig.1 Potentials of various stainless steels in seawater
Fig.2 presents the anodic polarization curves for the stainless steels in seawater. STS 316 was passive in the early stage of the test. Passivity trends were present in the anodic polarization curves for STS 304 and 630, during which the current density gradually increased. Sharp increases in the current densities were observed at some potentials when the current was concentrated due to pitting corrosion. The pitting potentials for STS 304, 316, and 630 were 0.300, 0.323, and 0.260 V, respectively. The current density steadily increased after the pitting potential reached.
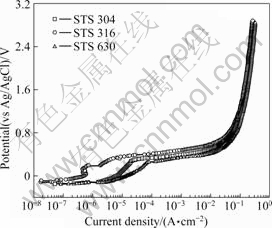
Fig.2 Anodic polarization curves for stainless steels in seawater
The lowest current density values with potential were obtained for STS 316, followed by STS 304 and 630, suggesting that STS 316 has the best resistance properties for stress corrosion cracking due to anodic dissolution reactions. Pitting at the specimen morphologies after the anodic polarization experiments was sporadically generated in STS 304 at several locations. The current density increased with the potential increasing, eventually causing pitting. Only a small amount of shallow pitting was observed in STS 316. Large grooves were present in the STS 630 specimen caused by extensive pitting, resulting in a damaged specimen. These results confirm that STS 630 has poor electrochemical properties, while STS 316 shows the best corrosion resistance characteristics.
Fig.3 gives specimen observations during the potentiostatic experiments with applied potential of 0.4 V in seawater. This potential is above the pitting potential of each specimen. When the specimens were cleaned off corrosion matter, a clean surface was observed on STS 304 after 200 s, but the surface was somewhat damaged after 400 s. Small pits were observed after 600 s, which grew into larger pits after 900 s. Numerous pits were present after 1 200 s. In contrast, the STS 316 surface remained clean for 900 s, and only one pit was observed on an otherwise clean surface after 1 200 s. The STS 630 surface remained clean for 100 s. Some damage and shallow pitting were observed after 150-200 s, and pitting was present on the entire surface after 400-1200 s. Therefore, STS 630 has the most damaged surface, while STS 316 has the cleanest surface and thus the best electrochemical behavior.
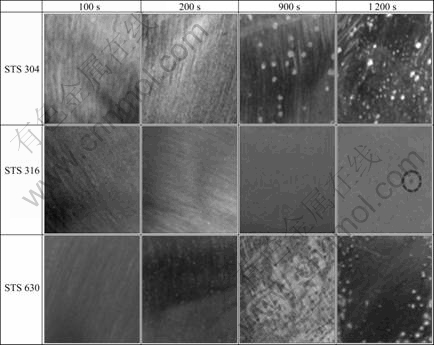
Fig.3 Specimen observation during potentiostatic experiment with potential of 0.4 V in seawater
Fig.4 presents the cathodic polarization curves for the stainless steels in seawater. The cathodic polarization trends for all three stainless steels showed the effects of concentration polarization due to an oxygen reduction reaction (O2+2H2O+4e-→4OH-) and activation polarization due to hydrogen generation (2H2O+2e-→H2 +2OH-)[12]. The cathodic polarization behavior of STS 304 and 316 showed similar trends for an OCP of approximately -0.4 V. STS 630 had the highest current density; while the current density at the potential for which concentration polarization occurred was the lowest for STS 316. The current density at the corrosion protection potential of metal, which has a potential range corresponding to the concentration polarization of the cathodic polarization curve, is very important. The ranges of the protection potential for STS 304, 316, and 630 were from -0.4 to -0.912, from -0.4 to -0.912, and from -0.4 to -1.07 V, respectively. The hydrogen embrittlement generation potentials were -0.912, -0.912, and -1.07 V, respectively.
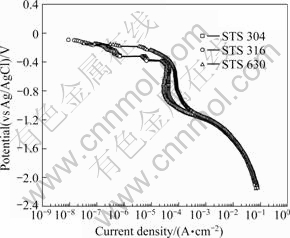
Fig.4 Cathodic polarization curves for stainless steels in seawater
The turning point between the concentration polarization due to the oxygen reduction reaction and the activation polarization due to hydrogen gas generation is the limit potential, which determines the corrosion protection potential. The turning point of STS 630 was the lowest, while the turning points of STS 304 and 316 were similar. However, the current density corresponding to the same potential in STS 316 was lower than that in STS 304. Therefore, STS 316 has the best corrosion resistance for cathodic protection applications. Although STS 630 has excellent mechanical properties due to the additional carbon and copper, its corrosion resistance is poor due to the residual stress increments in the metal resulting from the increase in strength[2].
The specimen morphologies after the cathodic polarization experiments, the anodic polarization and potentiostatic experiments at the anodic polarized potential, indicated the possibility of stress corrosion cracking, because the current density abruptly increased due to pitting caused by the destruction of the passivity film. The cathodic polarization trends showed the concentration polarization and activation polarization. The concentration polarization range for the dissolved oxygen reduction reaction was not affected by the specimen surface because it occurred while the surface was still protected. The activation polarization range for hydrogen gas generation differed from the concentration polarization range, but specimen morphologies did not indicate damage and the differences between the specimens were small, unlike the anodic polarization trends. Hydrogen embrittlement in high-tensile stainless steel is caused by permeation of hydrogen gas due to overprotection[7]. Anodic corrosion protection is performed at a potential lower than the pitting potential, while cathodic corrosion protection is performed at a potential higher than the hydrogen gas generation potential. The current density in the protection potential range for cathodic protection is greater than that for anodic protection, which implies that anodic protection is more beneficial than cathodic protection from an economic point of view.
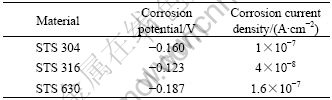
Fig.5 shows the results of the Tafel analysis used to determine the corrosion potential and corrosion current density of the specimens in seawater. Similar behaviors were observed for the three stainless steels. The current densities for the anodic polarization and cathodic polarization suddenly increased by 6.6×10-7 A/cm2 and 3.0×10-7 A/cm2, respectively. STS 316 had the highest corrosion potential, followed by STS 304 and 630. The corrosion current density ranked similarly. The results of the Tafel analysis are listed in Table 3.
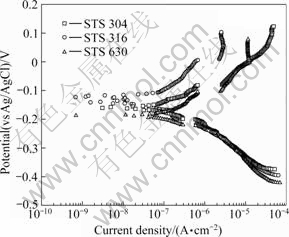
Fig.5 Polarization curves for Tafel analysis of stainless steels in seawater
Table 3 Results obtained from Tafel analysis of STS 304, 316 and 630 stainless steel in seawater
4 Conclusions
The corrosion protection offered by impressed current cathodic protection was examined for the stainless steel of shaft systems found in small vessels, and three types of stainless steels were evaluated to determine the material that provided the best corrosion resistance.
Among the three tested stainless steels, STS 316 had the most stable electrochemical behavior and STS 630 had the lowest potential and the largest fluctuations, suggesting that STS 316 has the best corrosion resistance in seawater. In anodic polarization, passivity was remarkably more evident in STS 316 than in STS 304 and STS 630. The pitting potentials of 304, 316, and 630 stainless steels were 0.300, 0.323, and 0.260 V, respectively. The concentration polarization due to oxygen reduction and activation polarization due to hydrogen generation were evident in the cathodic polarization trends of all three steels. STS 316 had the lowest current densities in all potential ranges, and STS 630 had the highest. Tafel analysis showed that STS 316 was the most noble of the three. In addition, the corrosion current density was lowest in STS 316.
References
[1] KIM S J, WOO Y B, HAN M S, JANG S K, KIM J I. Development of corrosion protection technology by thermal spray coating for STS 304 in sea water [C]//Proceedings of the Korean Marine Engineering Autumn Conference. 2006: 73-74.
[2] KIM S J, WOO Y B, KIM J I. Evaluation of electrochemical characteristics of shaft system materials for small vessel[C]// Proceedings of the Korean Marine Engineering Spring Conference. 2007: 61-62.
[3] KIM S J, KO J Y. Electrochemical properties of Al and Al alloys relevant to corrosion protection in seawater environments [J]. The Korean Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2006, 23(5): 847-853.
[4] KIM S J, KO J Y, HAN M S. Evaluation of the characteristics using slow strain rate tests of 5456 Al-Mg alloy for ship construction [J]. The Korean Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2006, 23(6): 1028- 1033.
[5] KIM S J, MOON K M. Hydrogen embrittlement properties of heat affected zone of high strength steel in shielded metal arc welding [J]. Metals and Materials International, 2002, 8(4): 395-401.
[6] KIM S J, MOON K M. The relationship between corrosion protection and hydrogen embrittlement properties of HAZ in flux core arc welding [J]. Metals and Materials International, 2002, 8(4): 387-393.
[7] KIM S J, OKIDO M, MOON K M. An electrochemical study of cathodic protection of steel used for marine structures [J]. The Korean Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2003, 20(3): 560-565.
[8] KIM S J, OKIDO M, MOON K M. The electrochemical study on mechanical and hydrogen embrittlement properties of HAZ part as a function of post-weld heat treatment in SMAW [J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2003, 169/170: 163-167.
[9] MOON K M, LEE M H, KIM K J, KIM S J. The effect of post-weld heat treatment affecting corrosion resistance and hydrogen embrittlement of HAZ part in FCAW [J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2003, 169/170: 675-678.
[10] KIM S J, JANG S K, KIM J I. Electrochemical study of hydrogen embrittlement and optimum cathodic protection potential of welded high strength steel [J]. Metals and Materials International, 2005, 11(1): 63-69.
[11] SEDRIKS J. Corrosion of stainless steels [M]. Wiley-Interscience Publication, 1996: 14.
[12] KIM S J, JANG S K, KIM J I. Electrochemical properties and corrosion protection of stainless steel for hot water tank [J]. The Korean Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2004, 21(3): 739-745.
Corresponding author: Min-Su HAN; Tel: +82-61-2407226; Fax: +82-61-2407201; E-mail: mp949@mmu.ac.kr
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(08)60380-5
(Edited by YUAN Sai-qian)