文章编号:1004-0609(2009)10-1802-07
W含量对(Mo1-x, Wx)Si2复合材料力学性能和
高温氧化性能的影响
彭 可,易茂中,冉丽萍,葛毅成,杨 琳
(中南大学 粉末冶金国家重点实验室,长沙 410083)
摘 要:以Mo、W和Si粉为原料,采用自蔓延热爆合成和热压工艺制备不同W含量的(Mo1-x, Wx)Si2复合材料,研究W含量对(Mo1-x, Wx)Si2复合材料的力学性能和高温抗氧化性能的影响。结果表明:随着W含量的增加, (Mo1-x, Wx)Si2复合材料的力学性能逐渐增加,氧化激活能逐渐降低;(Mo0.5,W0.5)Si2复合材料的室温抗弯强度、 1 200 ℃高温抗弯强度、硬度和断裂韧性分别为363 MPa、480 MPa、9.28 GPa和3.82 MPa?m1/2,与纯MoSi2比较,分别增加了40.7%、112.4%、12.1%和27.3%;(Mo1-x, Wx)Si2复合材料在1 673~1 873 K空气中能形成致密的氧化层,氧化增量符合抛物线规律。
关键词:二硅化钼;合金化;力学性能;氧化行为
中图法分类号: TG 148 文献标识码: A
Effect of W content on mechanical properties and high temperature oxidation behavior of (Mo1-x, Wx)Si2composites
PENG Ke, YI Mao-zhong, RAN Li-ping, GE Yi-cheng, YANG Lin
(State Key Laboratory of Powder Metallurgy, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China)
Abstract: (Mo1-x, Wx)Si2 composites were prepared by the thermal explosion mode of SHS followed by hot pressing using Mo, W and Si powders as raw materials. The effect of W content on the mechanical properties and high temperature oxidation behavior of (Mo1-x, Wx)Si2 composites were studied. The results show that with increasing W content, the mechanical properties of (Mo1-x, Wx)Si2 composites gradually increase, and the activation energies of (Mo1-x, Wx)Si2 composites gradually decrease. The room temperature bending strength, high-temperature flexural strength at 1 200 ℃, hardness and fracture toughness of (Mo0.5, W0.5)Si2 composite are 363 MPa, 480 MPa, 9.28 GPa and 3.82 MPa?m1/2, respectively, increased by 40.7%, 112.4%, 12.1% and 27.3% when compared with those of the monolithic MoSi2. (Mo1-x, Wx)Si2 composites can form compact oxidation layers in the air at 1673-1 873 K, and oxidation mass gain is accordance with parabolic law.
Key words: molybdenum disilicide; alloying; mechanical properties; oxidation behavior
金属间化合物MoSi2因具有高熔点(2 030 ℃)、低密度(6.24×103 kg/m3)、良好的导热性和导电性以及 优异的高温抗氧化能力而被认为是最有前途的高温 结构材料,然而其低温脆性和高温蠕变限制了其实际应用[1-2]。合金化是强韧化MoSi2的一种有效方法,但由于MoSi2具有特殊的晶体结构,只有少数硅化物可作为其合金化组元,如WSi2、NbSi2、CoSi2、Mo5Si3和Ti5Si3等[3]。其中,WSi2与MoSi2具有相同的晶体结构和相近的点阵晶格常数,二者能以任何比例混合,形成合金化合物(Mo,W)Si2,其蠕变速率低于MoSi2[4-5]。(Mo0.5,W0.5)Si2固溶复合材料在1 500 ℃时的屈服强度要比纯MoSi2的屈服强度高8~10倍[3],且由WSi2合金化制备的MoSi2发热体具有更好的高温强度,可以在氧化条件下使用至1 900 ℃[4]。
本文作者以Mo、W和Si粉为原料,采用自蔓延热爆合成和热压工艺制备了致密的(Mo,W)Si2复合材料,研究W含量对(Mo,W)Si2复合材料力学性能及高温抗氧化性能的影响,为开发性能更优异的MoSi2基高温结构材料提供实验参考和理论依据。
1 实验
以Mo粉(平均粒度1 μm,纯度99.99%)、W粉(平均粒度1 μm,纯度99.99%)和Si粉(平均粒度5 μm,纯度99.0%)为原料,采用自蔓延热爆合成制备不同W含量的(Mo1-x,Wx)Si2复合粉末[6-7]。将热爆合成块体粗碎后,再经WL-1型行星球磨机粉碎研磨5 h,研磨后粉末的平均粒径约为5 μm,经干燥、过筛,在氩气保护下热压,热压模具为自制C/C复合材料模具,热压工艺为1 700 ℃,50 MPa,60 min。
采用Archimedes排水法测量试样的体积密度;室温和高温抗弯强度均采用三点弯曲法测定,试样尺寸为3 mm×4 mm×36 mm,跨距30 mm,测试加载速率为0.5 mm/min。采用直通切口三点弯曲梁(SENB)法测定断裂韧性,试样尺寸为5 mm×2.5 mm×30 mm,切口宽度约为0.20 mm,切口深度为2.50 mm,加载速率为0.05 mm/min。将试样表面抛光后,在HVS-120型维氏硬度计上采用100 N的压头载荷测试复合材料的硬度。
氧化实验样品尺寸为10 mm×10 mm×5 mm,用SiC砂纸抛光其表面后,浸入丙酮在超声波容器中清洗。在进行氧化实验前,先测量样品的尺寸,计算出样品的总表面积。氧化增量数据用单位面积上的增量来计算。循环氧化实验在温度为1 400~1 600 ℃的空气自然对流的箱式炉中进行,每隔一定的时间取出样品,自然冷却后采用天平(感应量1×10-4 g)称其质量,样品氧化时间累积为120 h。
通过MeF3A型光学金相显微镜观察试样的组织结构,并采用Q520图像分析软件测定晶粒大小;用JSM-6360LV型扫描电镜观察断口形貌及复合材料高温氧化后的截面形貌,用Rigaku-3014型X射线能谱仪对复合材料高温氧化表面进行成分分析。
2 结果及分析
2.1 复合材料的显微组织
图1所示为MoSi2及(Mo, W)Si2复合材料的偏光金相照片。在偏光下由于晶粒的各向异性而显示出不同颜色。MoSi2、(Mo0.9, W0.1)Si2、(Mo0.7, W0.3)Si2和(Mo0.5, W0.5)Si2试样的平均晶粒大小分别17.2、16.8、15.6和14.2 μm。随着W含量的增加,晶粒逐渐减小,表明W能抑制晶粒的长大[8]。通过Archimedes排水法测得各试样的相对密度大于98.0%。从图1可以看出,在晶粒的晶界及晶粒中分布着少量的黑色相,结合断口形貌SEM分析,黑色相为孔洞。
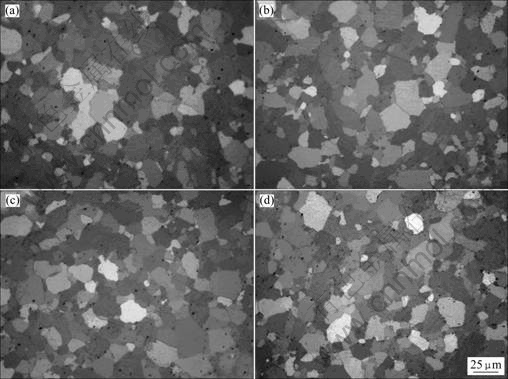
图1 MoSi2和(Mo, W)Si2复合材料的偏光金相照片
Fig.1 Polarizing optical micrographs of MoSi2 and (Mo, W)Si2 composites: (a) MoSi2; (b) (Mo0.9, W0.1)Si2; (c) (Mo0.7, W0.3)Si2; (d) (Mo0.5, W0.5)Si2
2.2 复合材料的力学性能
W含量对(Mo1-x, Wx)Si2复合材料力学性能的影响如图2所示。从图2可以看出,随着W含量的增加,(Mo1-x, Wx)Si2复合材料的室温抗弯强度、1 200 ℃高温抗弯强度、硬度和断裂韧性均逐渐增加,其中(Mo0.5,W0.5)Si2复合材料的室温抗弯强度、1 200 ℃高温抗弯强度、硬度和断裂韧性分别为363 MPa、480 MPa、9.28 GPa和3.82 MPa?m1/2。与纯MoSi2比较,分别增加了40.7%、112.4%、12.1%和27.3%。INUI等[9]研究发现,采用高温熔炼法制备的(Mo1-x, Wx)Si2固溶体的强度和硬度均随W含量的增加而增加,而且随着温度的升高,固溶体强度的增加更为显著。
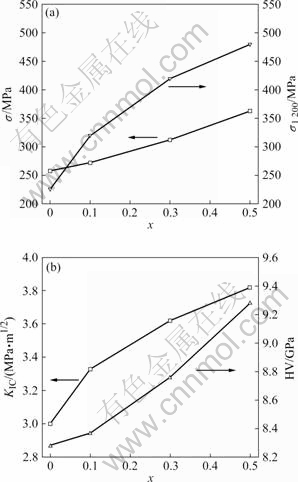
图2 W含量对复合材料室温抗弯强度、1 200 ℃高温抗弯强度、硬度和断裂韧性的影响
Fig.2 Effect of W content on room temperature bending strength, high-temperature flexural strength at 1 200 ℃ (a) and hardness, fracture toughness (b) for composites
本文作者根据固体与分子经验电子理论(EET),对MoSi2和WSi2的价电子结构进行了定量计算,并利用平均原子模型对(Mo1-x, Wx)Si2固溶体进行了价电子结构分析[10-13]。根据EET理论,材料的强度可以由η(共价电子总数占总的价电子数的比)表示,该指标越大,则材料的强度越大[14]。共价电子数的大小反映了原子的结合力,其结合越强,结合能越高,宏观上表现为硬度越高[14-16]。研究表明,在C11b型体心正方结构的(Mo1-x, Wx)Si2固溶体中,沿<331>位向分布的Mo(W)-Si原子键最强,随着W含量的增加,固溶体最强键上共价电子数、最强键键能和η值升高,表明随着W含量的增加,固溶体的硬度和强度逐渐增 加[11]。这从晶体的价电子结构解释了随着W含量的增加,材料硬度和强度随之增加的本质原因。另外,随着W含量的增加,复合材料的平均晶粒逐渐减小,对材料也起到了细晶增强增韧作用。
图3所示为MoSi2和(Mo0.5, W0.5)Si2的断口形貌。从图3可以看出,MoSi2和(Mo0.5, W0.5)Si2的断裂方式均为解理断裂。MoSi2和(Mo0.5, W0.5)Si2的断口形貌的“解理台阶”均非常明显,较大颗粒上也可见较为细密的解理台阶,它们都是裂纹沿着一族相互平行而高度不同的解理面扩展而形成的。由众多台阶汇集形成解理断口最典型的河流花样特征,其形貌如图3(b)和 (d)所示。
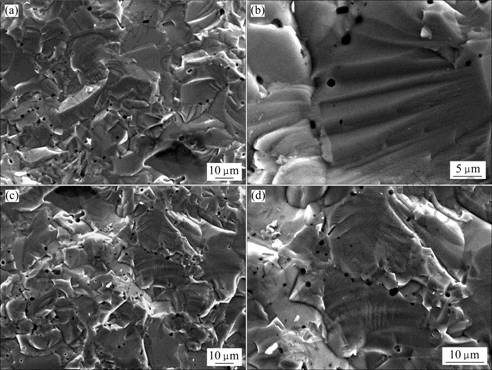
图3 MoSi2和(Mo0.5,W0.5)Si2的断口形貌
Fig.3 Fractural morphologies of MoSi2 ((a), (b)) and (Mo0.5,W0.5)Si2((c), (d))
2.3 复合材料的高温氧化动力学曲线
图4所示为不同W含量的(Mo, W)Si2复合材料在不同温度下流动空气中氧化得到的氧化增量与时间的关系。从图4可以看出,试样的氧化增量与氧化时间呈抛物线规律,氧化反应初期氧化增量较快随后增量减慢,可以用式(1)表达,且在相同的氧化温度下,氧化增量随着W含量的提高而增加,

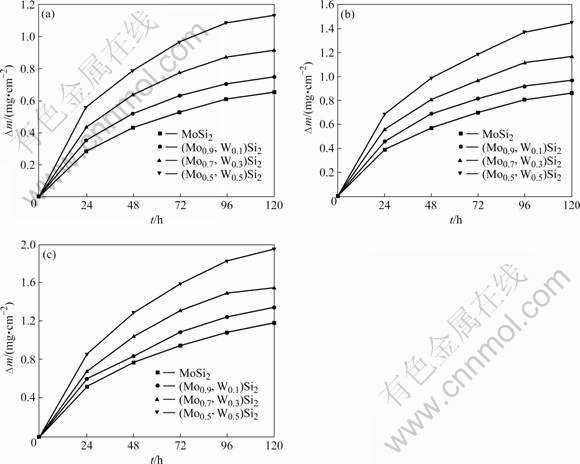
图4 不同W含量(Mo1-x,Wx)Si2复合材料在不同温度下氧化增量与时间的关系
Fig.4 Relationship between oxidation increment and time of (Mo1-x,Wx)Si2 composites with different W contents at different temperatures: (a) 1 673 K; (b) 1 773 K; (c) 1 873 K
从式(3)可以看出对lnkp与1/T作图,由直线斜率即可确定氧化激活能Q的值,从而可以推断不同反应的难易。因此,对不同WSi2含量的复合材料在1 673~ 1 873 K氧化速率常数的对数lnkp与1/T作图(见图5),进一步计算出氧化激活能,其结果如表1所列。从表1可以看出,激活能随着W含量的增加逐渐降低,从而,所需要越过的能垒也随之降低,抗氧化性能有所降低。
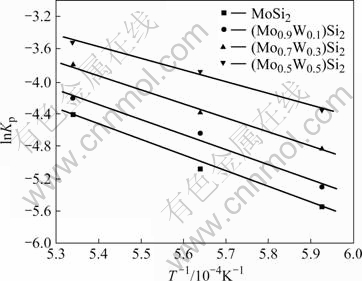
图5 不同W含量(Mo1-x,Wx)Si2复合材料的氧化速度常数与温度的关系
Fig.5 Relationship between oxidation speed constant and temperature of (Mo1-x,Wx)Si2 composites with different W contents
表1 不同W含量的(Mo1-x, Wx)Si2复合材料的活化能
Table 1 Activate energy of (Mo1-x, Wx)Si2 composites with different W contents

2.4 氧化产物的相组成与形貌分析
图6分别所示为MoSi2和(Mo0.5,W0.5)Si2复合材料在不同温度氧化3 h后表面氧化膜的XRD谱。MoSi2在1 673、1 773和1 873 K氧化3 h后表面成分均为MoSi2、Mo5Si3和SiO2;(Mo0.5,W0.5)Si2复合材料在1 673、1 773和1 873 K氧化3 h后表面成分均为(Mo0.5,W0.5)Si2、(Mo0.5,W0.5)5Si3和SiO2。MoSi2在高温下的氧化反应如下:
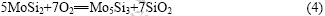
从XRD结果可以推断(Mo0.5,W0.5)Si2的高温氧化反应如下:

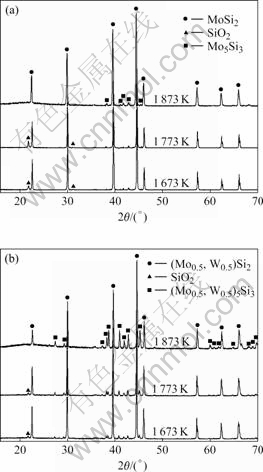
图6 MoSi2和(Mo0.5, W0.5)Si2在不同温度氧化3 h后表面氧化膜的XRD谱
Fig.6 XRD patterns of oxidation coatings formed on MoSi2 (a) and (Mo0.5,W0.5)Si2 (b) oxided at different temperatures for 3 h
Mo5Si3和(Mo0.5,W0.5)5Si3峰的强度均随着氧化温度的升高而增强,表明随着氧化温度的升高,试样表面的Mo5Si3或(Mo0.5,W0.5)5Si3含量增加。SiO2在不同温度下,结晶状态不一样,1 873 K生成的SiO2为非晶态。在对SiC高温氧化性能的研究中也发现,当温度在1 773 K以上氧化后,冷却到室温时存在非晶态的SiO2;而当温度在1 773 K以下时,氧化物均为晶态SiO2[17]。图7所示为MoSi2和(Mo0.5,W0.5)Si2复合材料在1 773 K氧化120 h后表面成分的XRD谱。由图7可以看出,经过120样h长时间氧化后,SiO2为非晶态。
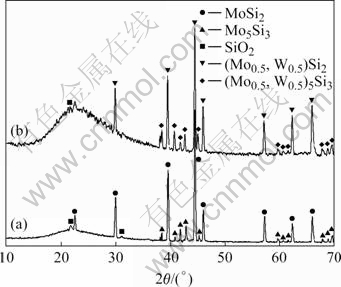
图7 MoSi2和(Mo0.5,W0.5)Si2在1 773 K氧化120 h后表面氧化膜的XRD谱
Fig.7 XRD patterns of coating formed on MoSi2 (a) and (Mo0.5,W0.5)Si2 (b) oxided at 1 773 K for 120 h
MoSi2和(Mo0.5,W0.5)Si2复合材料在1 773 K空气中恒温氧化3和120 h的氧化层截面形貌如图8所示。从图8可以看出,MoSi2和(Mo0.5,W0.5)Si2复合材料在1 773 K空气中恒温氧化3和120 h后,氧化层均比较致密,且与基体的附着性很好,因此形成较好的阻挡氧扩散进入的障碍。在相同试验条件下,(Mo0.5,W0.5)Si2复合材料表面氧化层厚度要大于纯MoSi2材料,这进一步证实了前面氧化动力学曲线分析所得到的结论。
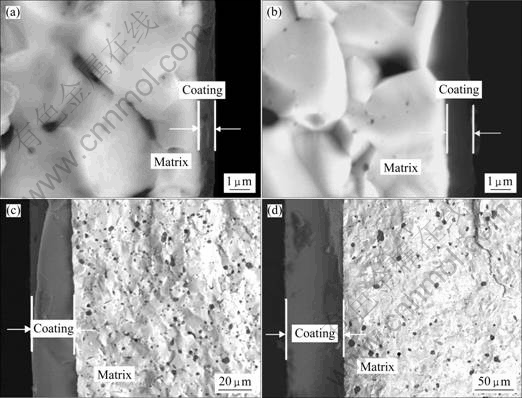
图8 MoSi2和(Mo0.5, W0.5)Si2复合材料在1 773 K空气中恒温氧化3 h和120 h的氧化层截面形貌
Fig.8 Cross-sectional morphologies of coatings formed on MoSi2 and (Mo0.5,W0.5)Si2 oxided at 1 773 K for 3 h and 120 h: (a) MoSi2, 3 h; (b) (Mo0.5,W0.5)Si2, 3 h; (c) MoSi2, 120 h; (d) (Mo0.5,W0.5)Si2, 120 h
3 结论
1) 采用热爆合成和热压烧结制备了致密的(Mo1-x,Wx)Si2复合材料。
2) 随着W含量的增加,(Mo1-x,Wx)Si2复合材料的室温抗弯强度、1 200 ℃高温抗弯强度、硬度和断裂韧性均逐渐增加,其中(Mo0.5,W0.5)Si2复合材料的室温抗弯强度、1 200 ℃高温抗弯强度、硬度和断裂韧性比MoSi2分别提高了40.7%、112.4%、12.1%和27.3%。(Mo1-x,Wx)Si2复合材料的断裂方式为解理断裂。
3) 不同W含量的(Mo1-x,Wx)Si2复合材料在 1 400~1 600 ℃空气中的能形成致密的氧化层,氧化增量符合抛物线规律。随着W含量的增加,(Mo1-x,Wx)Si2复合材料的氧化激活能逐渐降低。
REFERENCES
[1] MITRA R. Mechanical behaviour and oxidation resistance of structural silicides[J]. International Materials Reviews, 2006, 51(1): 13-64.
[2] PETROVIC J J, VASUDEVAN A K. Key developments in high temperature structural silicides[J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 1999, 261(1/2): 1-5.
[3] PETROVIC J J, HONNELL R E. SiC reinforced-MoSi2/WSi2 alloy matrix composites[J]. Ceramic Engineering and Science Proceedings, 1990, 11(7/8): 734-744.
[4] 金志浩, 李世斌, 高积强. MoSi2基复相材料的研究进展[J]. 西安交通大学学报, 2001, 35(2): 199-202.
JIN Zhi-hao, LI Shi-bin, GAO Ji-qiang. Research progress of MoSi2 matrix composites[J]. Journal of Xi’an Jiaotong University, 2001, 35(2): 199-202.
[5] PETROVIC J J. Toughening strategies for MoSi2-based high temperature structural silicides[J]. Intermetallics, 2000, 8(9/11): 1175-1182.
[6] 彭 可, 易茂中, 冉丽萍. 自蔓延热爆合成MoSi2-WSi2复合粉末[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2005, 15(6): 870-875.
PENG Ke, YI Mao-zhong, RAN Li-ping. Synthesis of MoSi2-WSi2 composite powders by thermal explosion mode of SHS[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2005, 15(6): 870-875.
[7] 彭 可, 易茂中, 冉丽萍. MoSi2-WSi2复合材料自蔓延热爆合成反应热力学[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2006, 35(4): 554-558.
PENG Ke, YI Mao-zhong, RAN Li-ping. Reaction thermodynamics of MoSi2-WSi2 composites in the thermal explosion mode of SHS[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2006, 35(4): 554-558.
[8] 张荣军, 杨延清, 刘红梅. SiCp-WSi2/MoSi2复合材料的室温力学性能[J]. 材料科学与工程学报, 2008, 26(1): 101-103.
ZHANG Rong-jun, YANG Yan-qing, LIU Hong-mei. Room-temperature mechanical properties of SiCp-WSi2/MoSi2 composites[J]. Journal of Materials Science and Engineering, 2008, 26(1): 101-103.
[9] INUI H, NAKAMOTO T, ISHIKAWA K, YAMAGUCHI M. Plastic deformation of single crystals of (Mo1-x,Wx)Si2 with the C11b structure[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 1999, 261(1/2): 131-138.
[10] 彭 可, 易茂中, 陶辉锦, 冉丽萍. MoSi2价电子结构及结合能计算[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2007. 17(2): 216-221.
PENG Ke, YI Mao-zhong, TAO Hui-jin, RAN Li-ping. Valence electronic structure analysis and cohesive energy calculation of MoSi2[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2007. 17(2): 216-221.
[11] 彭 可. 合金化和纳米复合化制备(Mo,W)Si2-SiC材料及其性能研究[D]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2008: 20-62.
PENG Ke. Investigation of fabrication and properties of alloying and nano-particle compositing (Mo, W)Si2-SiC[D]. Changsha: Central South University, 2008: 20-62.
[12] 彭 可, 易茂中, 冉丽萍. WSi2的价电子结构及其性能研究[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2007, 36(10): 1154-1158.
PENG Ke, YI Mao-zhong, RAN Li-ping. Study on the valence electronic structure and properties of WSi2 phases[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2007, 36(10): 1154-1158.
[13] 彭 可, 易茂中, 冉丽萍. MoSi2和WSi2的价电子结构及性能分析[J]. 金属学报, 2006, 42(11): 1125-1129.
PENG Ke, YI Mao-zhong, RAN Li-ping. Analysis of valence electronic structures and properties of MoSi2 and WSi2[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2006, 42(11): 1125-1129.
[14] 张瑞林. 固体与分子经验电子理论[M]. 吉林: 吉林科学技术出版社, 1993: 231-333.
ZHANG Rui-lin. Empirical electron theory of solid and molecules[M]. Jilin: Jilin Science and Technology Press, 1993: 231-333.
[15] 杜晓东, 丁厚福, 宣天鹏. CrB价电子结构对其性能的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2005, 12: 1980-1985.
DU Xiao-dong, DING Hou-fu, XUAN Tian-peng. Effect of valence electron structure on property of CrB[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2005, 12: 1980-1985.
[16] 郑 勇, 熊惟皓, 宗校军. Ti(C, N)固熔体的价电子结构及其与硬度和塑性间的关系[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2002, 31(1): 13-16.
ZHENG Yong, XIONG Wei-hao, ZONG Xiao-jun. On the valence electron structure of Ti(C, N) solid solution and its relationship with hardness and plasticity[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2002, 31(1): 13-16.
[17] 常 春, 陈传忠, 刘仲泉. 反应结合SiC电热材料的高温氧化特性[J]. 硅酸盐学报, 2004, 32(8): 1040-1044.
CHANG Chun, CHEN Chuan-zhong, LIU Zhong-quan. Oxidation characteristics of reaction-bonded silicon carbide electroheating material at high temperature[J]. Journal of The Chinese Ceramic Society, 2004, 32(8): 1040-1044.
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(50472078);教育部博士点基金资助项目(20040533006)
收稿日期:2008-11-21;修订日期:2009-04-28
通信作者:易茂中,教授,博士;电话:0731-8830894;Email: yimaozhong@126.com
(编辑 龙怀中)