具有梯度纳米/微米晶表层的工业纯钛变形和断裂机制
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2015年第3期
论文作者:尹雁飞 徐 巍 孙巧艳 肖 林 孙 军
文章页码:738 - 747
关键词:表面机械碾磨处理;工业纯钛;梯度纳米/微米晶;加工硬化;韧窝
Key words:surface mechanical grinding treatment; commercially pure titanium; gradient nano-to-micron grain; strain hardening; dimple
摘 要:通过室温表面机械碾磨处理(SMGT),获得从表面到基体具有梯度纳米/微米尺度晶粒的纯钛试样。与未处理纯钛相比,经表面机械碾磨处理(SMGT-treated)的纯钛强度有所提高,塑性介于超细晶与粗晶纯钛之间。表面机械碾磨处理纯钛的拉伸应力-应变曲线具有双加工硬化指数特性;同时,随着应变的增加,其加工硬化率逐渐减小,初始屈服阶段的变形由梯度纳米/微米晶表层主导,后期变形由粗晶心部支配。断口形貌分析表明,表面机械碾磨处理纯钛的变形机制属于韧性断裂并伴有大量韧窝。基于裂纹尖端的塑性区尺寸分析可知,梯度纳米/微米晶表层由于具有较高的加工硬化指数及强度,使韧窝尺寸比粗晶心部的更加细小。
Abstract: Titanium with gradient nano-to-micron scale grains from surface to matrix was fabricated by surface mechanical grinding treatment (SMGT) at room temperature. The SMGT-treated titanium shows higher strength than that of as-received one, but moderate ductility between those of ultra-fine grained (UFG) and coarse-grained titanium. Tensile stress-strain curves of SMGT-treated titanium show double strain hardening regimes. The strain hardening rate (dσ/dε) decreases with increasing strain in tensile deformation. The high strain hardening rate at initial yielding is attributed to nano-to-micron-grained surface layer. The low strain hardening rate at large plastic strain regime primarily results from coarse-grained matrix. The SMGT-treated titanium shows a ductile fracture mode with a large number of dimples. The small size of dimples in the treated surface layer is due to the combination of the high strength and strain hardening exponent. The difference between dimple size in nano-to-micron-grained surface layer and coarse-grained matrix is discussed in terms of plastic zone size at the tip of crack in the SMGT-treated titanium.
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 25(2015) 738-747
Yan-fei YIN1,2, Wei XU1, Qiao-yan SUN1, Lin XIAO1, Jun SUN1
1. State Key Laboratory for Mechanical Behavior of Materials, Xi’an Jiaotong University, Xi’an 710049, China;
2. Northwest Institute for Nonferrous Metals Research, Xi’an 710016, China
Received 9 April 2014; accepted 20 October 2014
Abstract: Titanium with gradient nano-to-micron scale grains from surface to matrix was fabricated by surface mechanical grinding treatment (SMGT) at room temperature. The SMGT-treated titanium shows higher strength than that of as-received one, but moderate ductility between those of ultra-fine grained (UFG) and coarse-grained titanium. Tensile stress-strain curves of SMGT-treated titanium show double strain hardening regimes. The strain hardening rate (dσ/dε) decreases with increasing strain in tensile deformation. The high strain hardening rate at initial yielding is attributed to nano-to-micron-grained surface layer. The low strain hardening rate at large plastic strain regime primarily results from coarse-grained matrix. The SMGT-treated titanium shows a ductile fracture mode with a large number of dimples. The small size of dimples in the treated surface layer is due to the combination of the high strength and strain hardening exponent. The difference between dimple size in nano-to-micron-grained surface layer and coarse-grained matrix is discussed in terms of plastic zone size at the tip of crack in the SMGT-treated titanium.
Key words: surface mechanical grinding treatment; commercially pure titanium; gradient nano-to-micron grain; strain hardening; dimple
1 Introduction
Grain refinement to submicron and nanometer scales can significantly enhance the strength of metals by introducing a great number of grain boundaries and crystal defects [1-10]. However, the uniform plastic deformation capability is dramatically restricted in the nano-grained (NG) and ultra-fine grained (UFG) metals [11-15]. Consequently, the brittleness, which has been attributed to the absence of strain hardening, is displayed since tiny NG/UFG grains have very low dislocation storage efficiency [16,17]. Dislocation slip in NG and UFG metals is more severely restricted than the coarse-grained ones due to the following two reasons. Firstly, nanoscale grains suppress dislocation slip but facilitate grain boundary sliding. However, the amount of plastic deformation in the latter is not large enough to accommodate the large plastic strain. Secondly, high density of dislocations or lattice distortions due to severe plastic deformation becomes strong barriers to dislocation slip. As a result, strain localization (necking instability) quickly occurs after yielding and little uniform elongation exhibits during tension. The brittleness of nano-grained and ultrafine-grained metals prepared by severe plastic deformation (SPD), which significantly restricts their wide application, has been considered to be intrinsic property [4].
WANG et al [18] proposed that a proper population of coarse grains embedded in fine grains could substantially enhance the strain hardening capacity and ductility of NG/UFG metals. The metals with bimodal grain size distribution can be expected to have an excellent combination of strength and ductility. Strain hardening induced by inhomogeneous microstructures can stabilize the tensile plastic deformation and result in a large tensile ductility (~65%) and uniform elongation (~30%) at a slight cost of yielding stress. The similar results were also obtained by RAJU et al [19] in Cu-Ag alloys. On the other hand, LU et al [20-22] found that NG copper film with a spatial gradient grains in a bulk coarse-grained (CG) copper exhibited superior mechanical properties as well. They proposed that coarse-grained substrate could suppress strain localization of nano-grained surface layer. Consequently, nano-grained surface layer, which has high strength, shows a comparable ductility with coarse-grained matrix of copper. The formation of nano-to-micron-grained surface layer in the severe deformation process was also discussed in detail [23,24]. The tensile properties of pure titanium after surface mechanical grinding treatment have been reported to be higher than those of coarse- grained titanium [25]. However, more experimental results are needed to reveal the effect of gradient nano-to-micron-structured surface layer on the deformation and fracture behavior of pure titanium, and the cooperation of nano-grained surface and coarse- grained matrix in strain hardening of titanium with such inhomogeneous microstructure. The objective of this work is to ascertain mechanical properties, strain hardening mechanism and fracture character on the severe deformed surface and undeformed matrix so as to obtain a better understanding on mechanical behavior of metals with nano-to-micron-grained surface layer.
2 Experimental
Commercially pure titanium bars (TA2) with 16 mm in diameter and 100 mm in length were chosen. The bars were annealed at 973 K for 1 h to obtain an average grain size of 20-30 μm. The annealed bars were mechanically machined to dog-bone shaped tensile bars with 30 mm in gauge length and 6 mm in diameter. The surface mechanical grinding treatment processing, which was reported by FANG et al [22], was performed at room temperature on titanium with the sample rotation speed of 600 r/min on a lathe. The penetration depth of one pass is 50 μm. The treating pass is an important parameter for formation of nano-to-micron scale grains in surface layer. Ten passes are found to be the maximum pass because treatment with more than 10 passes causes surface damage. And 5 passes are taken as a middle parameter to show the effect of passes on the formation of surface layer and the properties as well. The deformed microstructures were observed with an optical microscopy (OM) and a JEM-200CX transmission electron microscope (TEM). Tensile tests were carried out on the INSTRON1195 electron-tensile tester at a displacement rate of 1 mm/min. Fracture surfaces were observed with a Hitachi S-2700 type scanning electron microscope (SEM). Microhardness at different depths was measured using the Tukon-R2100B microhardness tester with a load of 20 g and the holding time of 10 s. The distance between two measuring points is around 30 μm.
3 Results
3.1 Microstructural characterization of SMGT-treated titanium
Figure 1 shows the microstructures from surface to the center on the cross section of a SMGT-treated titanium (titanium bars with surface mechanical grinding treatment). Figure 1(a) shows a typical gradient NG- UFG-CG microstructure. The original grain boundaries are obscure and hardly identified due to severe deformation in the surface layer with depth of 200 μm. Beyond 200 μm from surface, deformed grains with mechanical twins were observed. The effect of surface mechanical grinding treatment becomes little beyond 300 μm depth from surface. TEM images show the details of twins, subgrains or dislocation cells in deformed area at depth from 20 to 110 μm from the surface, as shown in Figs. 1(b)-(e). Twins were observed in the surface layer, as shown in Fig. 1(b) (110 μm from surface). On a close examination, subgrain embryo was formed inside twins, as indicated by an arrow of A in Fig. 1(b). Some twins were broken due to severe strain, as indicated by circle in Fig. 1(b). However, twins were seldom observed in NG and UFG areas closer to surface layer, as shown in Figs. 1(c)-(e). The elongated subgrains formed in this area, as indicated by arrow B in Fig. 1(c). Selected-area electron diffraction analysis showed nano-to-micron-grains in treated surface layer (Fig. 1(d)). The equiaxed nanograins and submicron grains were observed apparently. In the depth of 20 μm, the lower dislocation density and nano-sized grains with random crystallographic orientations were observed, due to dynamic recovery and dynamic recrystallization in the outmost layer as reported in Refs. [26-28]. Consequently, inhomogeneous microstructure in SMGT-treated titanium bar can be divided into four regions from surface to center: NG region, UFG region, strain-affected region and strain-free matrix.
The results show that the treating passes have apparent effect on the thickness of deformed surface layer. The thickness is about 320 and 150 μm for samples with 10 and 5 passes, respectively. In outmost surface layer, the deformation is observed much severer in the sample with 10 passes than 5 passes, as seen in Fig. 2.
Based on the measurement of a number of TEM images, statistic distribution of grain (subgrain or cell) size at depths of 20, 50, 80 μm from surface is shown in Figs. 3(a)-(c), respectively. Grain size variation is observed in the range from 20 to 320 nm in the treated surface layer. Grain size with the highest frequency decreases from 160-180 to 60-70 nm with depth from 80 to 50 μm. The average grain size is about 100 nm in the layer of 20 μm under the surface, and variation of average grain size versus depth from the surface is shown in Fig. 3(d). It reveals a gradient nano- submicron-structured surface layer with thickness of ~320 μm, while the original coarse grains with size of 20-30 μm remain beyond ~320 μm to the center of the SMGT-treated titanium bars.

Fig. 1 Typical cross sectional OM image of SMGT-treated titanium sample (a) and TEM images of microstructure at different depths of 110, 80, 50, and 20 μm, respectively (b-e)
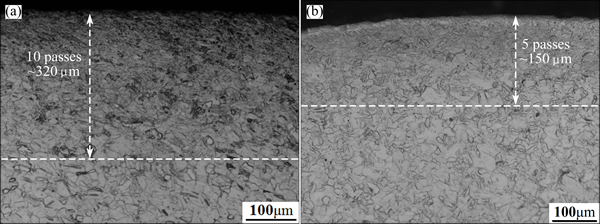
Fig. 2 OM images of SMGT-treated Ti samples with 10 (a) and 5 (b) passes
3.2 Mechanical behaviors of SMGT-treated titanium
Figure 4(a) shows the microhardness distribution on the cross section of SMGT-treated titanium. The hardness of coarse-grained matrix is HV 170. In comparison, the hardness in NG/UFG surface layer reaches HV 260. The increase of hardness is attributed to the grain refinement, twins, high density of dislocations in the treated surface layer. Below a certain depth, the strain is insufficient to refine grain but can still increase the microhardness. As a result, the hardness curves as a function of the depth gradually decrease, which is shown in Fig. 4(a).
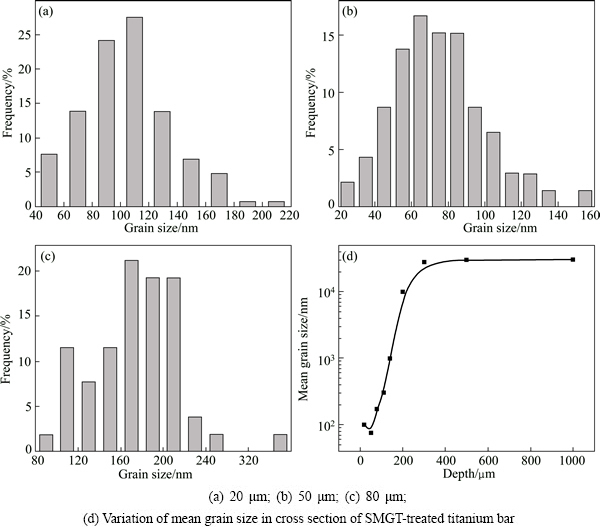
Fig. 3 Grain size distribution in SMGT-treated titanium bar at different depths from surface
The tensile engineering stress-strain curves of SMGT-treated titanium and as-received titanium samples are plotted in Fig. 4(b). The average yield strength and ultimate tensile strength (UTS) of as-received pure titanium are 323 and 460 MPa, respectively. The average yield strength and UTS of SMGT-treated titanium bars with 10 passes were measured to be 374 and 525 MPa, respectively. The elongation of SMGT-treated titanium bars is about 19%, which is lower than that of the CG Ti (~31%), but higher than that of UFG Ti by SPD (~10%) [15,24]. Furthermore, the reduction in area of SMGT- treated Ti sample with 10 passes is 53%, which is comparable to that of coarse-grained Ti (55%). Figure 4(c) shows the variation of strength of SMGT-treated titanium with treating passes. The yield strength and UTS increase with increasing passes due to increase of the thickness of treated surface layer.
Furthermore, double logarithmic true stress versus the true strain curves are shown in Fig. 5(a). According to the Ludwik-Hollomon law:
σ=Kεn (1)
where the strain hardening exponent (n) is defined as the slope of ln σ-ln ε curve. The double strain hardening exponents are observed in tension deformation of SMGT-treated Ti. The strain hardening exponents are: n1=0.34±0.01 when strain is less than 1.2% and n2=0.12±0.01 when strain is between 1.2% and 7.5%. While, an almost constant strain hardening exponent of 0.15±0.01 is observed in plastic deformation regime of as-received Ti, as shown in Fig. 5(a). The results show that SMGT-treated Ti exhibits a similar strain hardening characteristic as UFG Ti and CG titanium at initial plastic strain and the large plastic strain regime, respectively. It is worth noting that very high strain hardening exponent of 0.34±0.01 is observed at the beginning of plastic deformation, which is approximate to the hardening exponent of UFG Ti (n4=0.39±0.02) by repeat-rolling, as shown in Fig. 5(a). It can be reasonably assumed that the initial plastic strain hardening of SMGT-treated titanium results from the NG-UFG layer. Figure 5(b) shows the strain hardening rate (dσ/dε) strain curves of SMGT-treated titanium, as-received titanium and the UFG titanium. The strain hardening rate of SMGT-treated titanium is between that of CG titanium and UFG titanium at initial plastic deformation and is close to zero when the strain is larger than 0.03, as seen in Fig. 5(b).
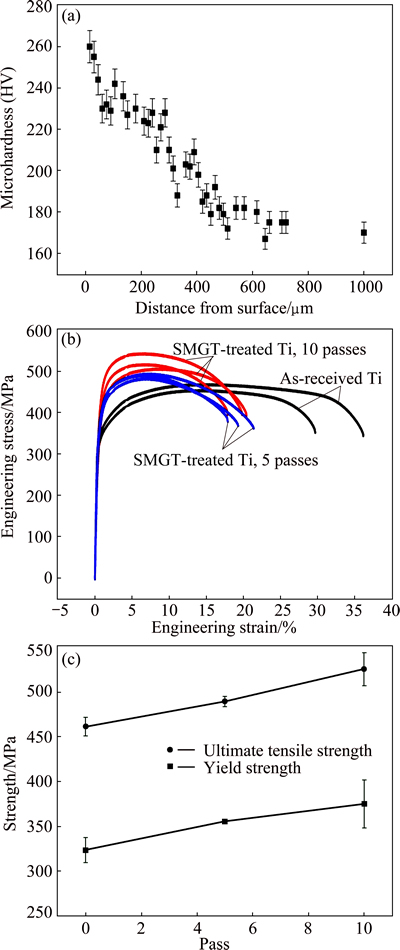
Fig. 4 Variation of microhardness with distance from treated surface (a), engineering stress-strain curves between as-received and SMGT-treated titanium bars with 5 and 10 passes (b), and variation of YS and UTS with pass (c)
3.3 Fracture of SMGT-treated titanium
A plenty of dimples are observed on fracture surfaces of SMGT-treated titanium sample, as seen in Fig. 6(a). Dimple size varies from 800 nm in the treated surface layer to 23 μm in the strain-free matrix on fracture surface of SMGT-treated titanium. The similar fracture character was observed by other researchers [24,28]. Besides, a few of parabolic dimples are observed in the area of 20 μm below the surface of SMGT-treated titanium, as shown in Fig. 6(b), which means that failure occurs under shear stress state in this surface layer instead of triaxial stress. Large dimples with an average size of 23 μm are observed in the CG titanium, as shown in Fig. 6(c).

Fig. 5 Strain hardening exponent (a) and strain hardening rate (b) of SMGT-treated titanium, as-received titanium and repeat-rolling (RR) UFG titanium
3.4 Microstructures of fractured SMGT-treated titanium
In order to reveal dislocation structures in the deformed titanium with nano-grained surface layer, TEM observations were conducted on the treated surface layer and coarse-grained matrix in a fractured sample. Figure 7(a) shows the substructure in the depth of 20-70 μm from the surface. Shear band is observed, as indicated by zone A in Fig. 7(a). Figure 7(b) shows the dislocation configuration in this layer. Few shear bands are observed with increasing depth to 100-150 μm from the surface. Dislocation debris and tangles are observed in this area, as shown in Fig. 7(c). Figure 7(d) shows a local dislocation tangles and a few of twins indicated by zone B in the coarse-grained matrix. The results indicate that the deformation mode of NG/UFG surface layer is different from that of CG matrix in SMGT-treated titanium.
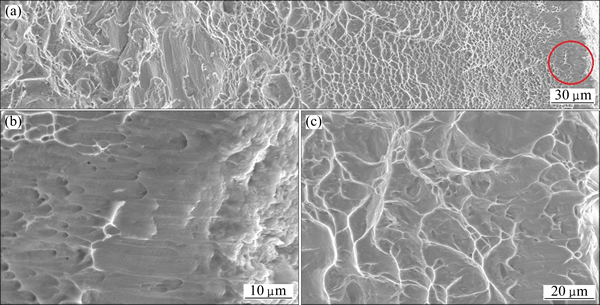
Fig. 6 SEM images of fracture surfaces in SMGT-treated titanium sample (a, b) and as-received titanium sample (c) ((b) is magnified image indicated by red circle in (a))

Fig. 7 Shear band in deformation in zone A (a) and dislocation cells in treated surface layer at depth of 20-70 μm (b), dislocation debris and tangles at depth of 100-150 μm (c) and twins in coarse-grained matrix (d)
4 Discussion
4.1 Strengthening of SMGT-treated titanium
A rule-of-mixture is suggested to estimate strength of copper with nano-grained surface layer by SMGT [22]. In the surface layer of SMGT-treated titanium, the strain decreases with increasing depth from surface, so the deformed surface layer is divided into NG/UFG layer and the dislocation-structured (DS) layer, which are principally strengthened by high-angle boundaries (HABs) and low-angle boundaries (LABs), respectively [29,30]. Figure 8 shows the schematic illustration of strengthening mechanisms in NG/UFG and DS layers. According to the microstructure of the treated surface layer, the thickness of NG/UFG layer is about 50 μm, where nanoscale and submicron-sized grains are observed frequently. Dislocation tangles and bands predominate in DS layer with thickness of about 150 μm. The rule-of-mixture of strength (σy) is as follows:
 (2)
(2)
where s1, s2 and m stand for NG/UFG layer, DS layer and matrix, respectively; V is volume fraction; σys1 and σys2 are the yield stresses of NG/UFG layer and DS layer, respectively; σym is the yield stress of coarse-grained matrix. According to the microstructure at different depths from surface, Vs1, Vs2 and Vm are 3.31%, 9.58% and 87.11%, respectively.
The strengthening in NG/UFG layer is dominated by HABs, namely grain boundaries. Therefore, yield stress σys1 can be expressed as Eq. (3) [29,30]. While in the DS layer LABs of dislocation cells and bands (here called dislocation boundaries) play an important role in the strengthening. The yield stress σys2 can be expressed as Eq. (4) [29,30]:
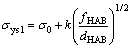 (3)
(3)
 (4)
(4)
where σ0 (=134.2 MPa) and k (=0.671 MPa×m1/2) are the Hall-Petch parameters of titanium [24,28]; G (=45 GPa) is the shear modulus of titanium; b (=2.95×10-10m) is the Burgers vector of a-type dislocation; ρ0(about 1×10-10m-2) is the average dislocation density of annealed pure metal. fHAB and fLAB are the densities of high angle boundaries in the NG/UFG and low angle boundaries in DS layer measured by EBSD, which are about 0.90 and 0.30, respectively [31]. dHAB and d′HAB are the boundary spacing, approximately equal to the mean grain size in the NG/UFG layer and cell size in DS layer, which are about 100 nm and 5 μm respectively according to Fig. 3(d). The parameter α for titanium is 1 according to Ref. [28], and average degree of θLAB is taken as 8° according to Ref. [31]. M is Taylor factor which is 3.07 according to Ref. [30]. Yield stress of the NG/UFG layer is calculated to be 2147 MPa, and that of the DS layer is 510 MPa. The yield strength of coarse-grained matrix is measured to be about 320 MPa. Therefore, the yield strength of titanium with NG/UFG- grained surface layer, DS layer and coarse-grained matrix is calculated to be 399 MPa for 10 passes samples, which is close to (374±27) MPa, the average yield strength of the measured data.
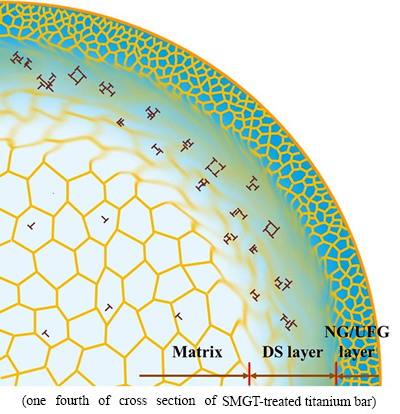
Fig. 8 Schematic illustration of strengthening mechanisms in NG/UFG and DS layer
It is reported that the compressive residual stress induced during SMGT can improve the fatigue properties of the samples effectively, because the compressive residual stress acts as the closure stress for the short fatigue cracks on the surface, and constrains the plastic deformation developed at the crack tip [32-36]. While in the tension of SMGT-treated titanium the primary cracks nucleate in the center of sample and extend to the surface. It is considered that compressive residual stress has less effect on the strength than on fatigue life of the sample. However, some researchers proposed that residual compressive stress changes the stress state of the sample and can also bring about strengthening according to Refs. [37,38]. The calculation of residual stress strengthening is complicated and need more endeavor in future.
4.2 Strain hardening mechanisms of SMGT-treated titanium
In coarse-grained metals, strain hardening results from the formation of obstacles to dislocation movements in crystals, such as grain boundaries, dislocations jungle in nonslip planes and second phase particles. The micron-sized grains have enough space for dislocation interactions and sources nucleation, which sustain continuous strain hardening and undergo large homogeneous deformation before necking. While for nano-sized grains, once dislocation nucleates from sources, they are absorbed by dislocation sinks, such as grain boundaries. The space of nano-sized grains is too small to sustain dislocation multiplication. Consequently, the number of dislocation hardly increases during plastic deformation. This leads to the fact that nanocrystalline/ ultra-fine crystal material has low dislocation storage efficiency and tends to lose the strain hardening easily after yielding [18]. As for SMGT-treated titanium, the microstructures are composed of coarse grains of about 30 μm and a NG/UFG surface layer, which is similar to “composite” material. The strain hardening mechanism of SMGT-treated titanium is schematically illustrated in Fig. 9. In the NG/UFG surface layer, the strain hardening is predominantly governed by dislocation nucleation. There is less dislocation multiplication in nano-size grains, while in coarse-grained matrix strain hardening is attributed to dislocation interactions and multiplications inside grains.
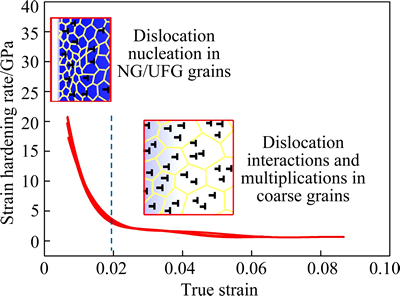
Fig. 9 Schematic illustration of strain hardening mechanism in SMGT-treated titanium
Strain hardening rate of SMGT-treated titanium is considered to be composed of treated surface layer and coarse-grained matrix. According to plastic deformation theory, deformation is stable in tension if the following formula is satisfied [16]:
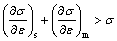 (5)
(5)
where σ is true stress; ε is true strain; m and s stand for matrix and surface, respectively. As for SMGT-treated titanium, the first item on the left of Eq. (5) is large at initial plastic deformation, while it decreases quickly and even becomes negative [15] with increasing plastic strain. The second item decreases slowly, which can make strain hardening of SMGT-treated titanium satisfy Eq. (5) and maintains the homogeneous deformation. If the coarse-grained matrix cannot undertake any strain hardening, the left side reaches a critical value for necking in Eq. (6):
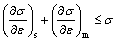 (6)
(6)
If Eq. (6) is satisfied in tension, the inhomogeneous deformation occurs and the sample fractures quickly. The coarse-grained matrix plays an important role in maintaining a homogeneous strain hardening for SMGT-treated titanium in this case.
4.3 Dimple size in SMGT-treated titanium
The dimples on the fracture surface indicate that the fracture of titanium with nano-grained surface layer is governed by nucleation and linkup of microvoids. Dimples are larger in coarse-grained matrix than those in the treated surface layer (Fig. 6(a)). The average dimple size is about 23 μm in the coarse-grained matrix, while it is 800 nm in the treated surface layer. The dimple size is several grains size in UG/UFG layer, which is agreement with that reported in nano-grained nickle [39]. The difference of dimple size is about 30 times between the coarse-grained matrix and the gradient nano-grained surface layer. Generally speaking, dimple size is affected by the second phase and strain hardening capacity of metals. There is no inclusion in the dimple of fracture surface in Fig. 6(a), so dimple size of pure titanium is related to local plastic strain. According to tension deformation theory, the true stress in the necked region is greater than that in the uniform deformation region, so the void formation and linkup are restricted to this region during fracture. A microcrack is assumed due to linkup of microvoids in the center of sample at the start of necking, and there is strong stress concentration at the tip of microcrack and results in the formation of plastic zone at crack tip. Severe plastic strain occurs in the plastic zone and a number of voids nucleate and grow in the plastic zone. The result shows that the most area is flat on facture surface and shear lip of surface is very thin, as shown in Fig. 6(a). It is considered that fracture in tension is in plane strain condition for SMGT-treated titanium. Therefore, the plastic zone size (ry) can be calculated as
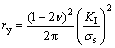 (7)
(7)
where KI is the stress intensity factor; σs is the yield strength of matrix; and ν is the Poisson ratio. For a given value of KI, ry is inversely proportional to the square of yield strength σs. The same number of microvoids is assumed in the plastic zone of matrix and treated surface layer for the above calculation. The dimple size ratio of coarse-grained matrix (dm) and NG/UFG surface layer (ds) can be expressed as
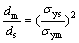 (8)
(8)
where m and s stand for matrix and surface layer. In addition, the dimple size decreases with increasing strain hardening exponent [40]. The parameter, ω, can be used to evaluate difference in strain hardening exponents between the matrix and the treated surface layer, and Eq. (8) can be rewritten as
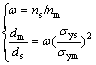 (9)
(9)
where nm and ns are the strain hardening exponents of surface layer and matrix, respectively.
The average strength (σys) of surface layer composed of NG/UFG and DS layers is calculated to be 930 MPa with strength of NG/UFG layer and DS layer based on rule of mixture, and σym is 320 MPa for the coarse-grained matrix. ω=ns/nm=2.83 (ns=0.34, nm=0.12). Substituting of σys, σym and ω into Eq. (9), dm/ds ratio is calculated to be about 24, which is close to experimental ratio (~30). According to void formation mechanism of nano-grained metals in Ref. [39], grain boundaries (GB) and GB slides promote void formation, which leads to much smaller dimple size in the treated surface layer than in coarse-grained matrix.
5 Conclusions
1) Gradient nano-to-micron-grained layer of about 320 μm in thickness was fabricated in titanium bars by surface mechanical grinding treatment at room temperature. The microstructures are composed of NG/UFG surface layer, strain-affected zone with mechanical twins and strain-free matrix of coarse grains.
2) SMGT-treated titanium shows an increase of 30-80 MPa in the yield strength compared with that of as-received titanium, while the elongation of 18%-21% is between those of UFG and CG titanium.
3) At the initial yielding strain hardening is governed by NG/UFG surface layer, while in large plastic strain regime dislocation interaction and multiplication in coarse-grained matrix predominate strain hardening. Double-n strain hardening behavior was observed in tensile deformation of SMGT-treated titanium.
4) Dimple size shows a gradient tendency from 800 nm in the treated surface layer to 23 μm in the coarse-grained matrix. Smaller dimples in the treated surface layer mainly arise from high strength and large initial strain hardening exponent in NG/UFG surface layer.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Professor Zhi-rui WANG from University of Toronto, Canada, for useful discussion on calculation of the strength and dimple size difference of SMGT-treated titanium.
References
[1] TERADA D, INOUE S, TSUJI N. Microstructure and mechanical properties of commercial purity titanium severely deformed by ARB process [J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2007, 5: 1673-1681.
[2] UEJI R, TSUJI N, MINAMINO Y, KOIZUMI Y. Ultragrain refinement of plain low carbon steel by cold-rolling and annealing of martensite [J]. Acta Materialia, 2002, 50: 4177-4189.
[3] HEBESBERGER T, STYWE H P, VORHAUER A, WETSCHER F, PIPPAN R. Structure of Cu deformed by high pressure torsion [J]. Acta Materialia, 2005, 53: 393-402.
[4] MEYERS M A, MISHRA A, BENSON D J. Mechanical properties of nanocrystalline materials [J]. Progress in Materials Science, 2006, 51: 427-556.
[5] WANG C T, GAO N, GEE M G, WOOD R J K, LANGDON T G. Tribology testing of ultrafine-grained Ti processed by high-pressure torsion with subsequent coating [J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2013, 13: 4742-4748.
[6] TAO N R, SUI M L, LU J, LU K. Surface nanocrystallization of iron induced by ultrasonic shot peening [J]. NanoStructured Materials, 1999, 11(4): 433-440.
[7] KRAL P, DVORAK J, ZHEREBTSOV S, SALISHCHEV G, KVAPILOVA M, SKLENICKA V. Effect of severe plastic deformation on creep behavior of a Ti-6Al-4V alloy [J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2013, 13: 4789-4795.
[8] KWAN C C F, WANG Z R. A composite nature of cyclic strain accommodation mechanisms of accumulative roll bonding (ARB) processed Cu sheet materials [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2011, 528: 2042-2048.
[9] WANG K, TAO N R, LIU G, LU J, LU K. Plastic strain-induced grain refinement at the nanometer scale in copper [J]. Acta Materialia, 2006, 54: 5281-5291.
[10] WEI Y L, GODFREY A, LIU W, LIU Q, HUANG X, HANSEN N, WINTHER G. Dislocations, boundaries and slip systems in cube grains of rolled aluminium [J]. Scripta Materialia, 2011, 65: 355-358.
[11] YOUSSEF K, SAKALIYSKA M, BAHMANPOUR H, SCATTERGOOD R, KOCH C. Effect of stacking fault energy on mechanical behavior of bulk nanocrystalline Cu and Cu alloys [J]. Acta Materialia, 2011, 59: 5758-5764.
[12] CHEN X H, LU J, LU L, LU K. Tensile properties of a nanocrystalline 316L austenitic stainless steel [J]. Scripta Materialia, 2005, 52: 1039-1044.
[13] RIKA Y, KOSUKE S, TAKATOSHI M, DAISUKE T, NOBUHIRO T. Formability of ultrafine-grained interstitial-free steel fabricated by accumulative roll-bonding and subsequent annealing [J]. Scripta Materialia, 2011, 65: 175-178.
[14] HASE K, TSUJI N. Effect of initial microstructure on ultrafine grain formation through warm deformation in medium-carbon steels [J]. Scripta Materialia, 2011, 65: 404-407.
[15] KO Y G, SHIN D H, PARK K T, LEE C S. An analysis of the strain hardening behavior of ultra-fine grain pure titanium [J]. Scripta Materialia, 2006, 54: 1785-1789.
[16] HART E W. Theory of tensile test [J]. Acta Metallurgica, 1967, 15: 351-355.
[17] JIA D, WANG Y M, RAMESH K T, MA E, ZHU Y T. Deformation behavior and plastic instabilities of ultrafine-grained titanium [J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2001, 79(5): 611-613.
[18] WANG Y M, CHEN M W, ZHOU F H, MA E. High tensile ductility in a nanostructured metal [J]. Nature, 2002, 419: 912-915.
[19] RAJU K S, SARMA V S, KAUFFMANN A, HEGEDUS Z, GUBICZA J, PETERLECHNER M, FREUDENBERGER J, WILDE G. High strength and ductile ultrafine-grained Cu-Ag alloy through bimodal grain size, dislocation density and solute distribution [J]. Acta Materialia, 2013, 61: 228-238.
[20] LU K, LU J. Nanostructured surface layer on metallic materials induced by surface mechanical attrition treatment [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2004, 375: 38-45.
[21] LI W L, TAO N R, LU K. Fabrication of a gradient nano-micro- structured surface layer on bulk copper by means of a surface mechanical grinding treatment [J]. Scripta Materialia, 2008, 59: 546-549.
[22] FANG T H, LI W L, TAO N R, LU K. Revealing extraordinary intrinsic tensile plasticity in gradient nano-grained copper [J]. Science, 2011, 331: 1587-1590.
[23] ZHU K Y, VASSEL A, BRISSET F, LU K, LU J. Nanostructure formation mechanism of α-titanium using SMAT [J]. Acta Materialia, 2004, 52: 4101-4110.
[24] WEN M, LIU G, GU J F, GUAN W M, LU J. Dislocation evolution in titanium during surface severe plastic deformation [J]. Applied Surface Science, 2009, 255: 6097-6102.
[25] WEN M, LIU G, GU J F, GUAN W M, LU J. The tensile properties of titanium processed by surface mechanical attrition treatment [J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2008, 202: 4728-4733.
[26] WANG Z B, LU K, WILDE G, DIVINSKI S V. Interfacial diffusion in Cu with a gradient nanostructured surface layer [J]. Acta Materialia, 2010, 58: 2376-2386.
[27] SUN H Q, SHI Y N, ZHANG M X, LU K. Plastic strain-induced grain refinement in the nanometer scale in a Mg alloy [J]. Acta Materialia, 2007, 55: 975-982.
[28] ZHU Y T, HUANG J Y, GUBICZA J, UNGAR T, WANG Y M, MA E, VALIEV R Z. Nanostructures in Ti processed by severe plastic deformation [J]. Journal of Materials Research, 2003, 18(8): 1908-1917.
[29] HANSEN N. Boundary strengthening in undeformed and deformed polycrystals [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2005, 409: 39-45.
[30] CABIBBO M. Microstructure strengthening mechanisms in different equal channel angular pressed aluminum alloys [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2013, 560: 413-432.
[31] WANG Q, YIN Y F, SUN Q Y, XIAO L, SUN J. Gradient nano microstructure and its formation mechanism in pure titanium produced by surface rolling treatment [J]. Journal of Material Research, 2014, 29: 569-577.
[32] YANG L, TAO N R, LU K, LU L. Enhanced fatigue resistance of Cu with a gradient nanograined surface layer [J]. Scripta Materialia, 2013, 68: 801-804.
[33] JIANG X P, MAN C S, SHEPARD M J, ZHAI T. Effects of shot-peening and re-shot-peening on four-point bend fatigue behavior of Ti-6Al-4V [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2007, 468-470: 137-143.
[34] KIM T, LEE J H, LEE H, CHEONG S K. An area-average approach to peening residual stress under multi-impacts using a three-dimensional symmetry-cell finite element model with plastic shots [J]. Materials and Design, 2010, 31: 50-59.
[35] LEE H, MAIL S. Stress relaxation behaviour of short-penned Ti-6Al-4V under fretting fatigue at elevated temperature [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2004, 366: 412-420.
[36] CHEN Guo-qing, JIAO Yan, TIAN Tang-yong, ZHANG Xin-hua, LI Zhi-qiang, ZHOU Wen-long. Effect of wet shot peening on Ti-6Al-4V alloy treated by ceramic beads [J].Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2014, 24: 690-696.
[37] WU X L, JIANG P, CHEN L, ZHANG J F, YUAN F P, ZHU Y T. Synergetic strengthening by gradient structure [J]. Materials Research Letters, 2014, 2: 185-191.
[38] WU X L, JIANG P, CHEN L, YUAN F P, and ZHU Y T. Extraordinary strain hardening by gradient structure [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of the Sciences of the United States of America, 2014, 111: 7197-7201.
[39] KUMAR K S, SURESH S, CHISHOLM M F, HORTON J A, WANG P. Deformation of electrodeposited nanocrystalline nickel [J]. Acta Materialia, 2003, 51: 387-405.
[40] MAJUMDAR S, RAY K K. Effect of prestrain on the ductile fracture behavior of an interstitial-free steel [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2006, 37: 3541-3553.
尹雁飞1,2,徐 巍1,孙巧艳1,肖 林1,孙 军1
1. 西安交通大学 金属材料强度国家重点实验室,西安 710049;
2. 西北有色金属研究院,西安 710016
摘 要:通过室温表面机械碾磨处理(SMGT),获得从表面到基体具有梯度纳米/微米尺度晶粒的纯钛试样。与未处理纯钛相比,经表面机械碾磨处理(SMGT-treated)的纯钛强度有所提高,塑性介于超细晶与粗晶纯钛之间。表面机械碾磨处理纯钛的拉伸应力-应变曲线具有双加工硬化指数特性;同时,随着应变的增加,其加工硬化率逐渐减小,初始屈服阶段的变形由梯度纳米/微米晶表层主导,后期变形由粗晶心部支配。断口形貌分析表明,表面机械碾磨处理纯钛的变形机制属于韧性断裂并伴有大量韧窝。基于裂纹尖端的塑性区尺寸分析可知,梯度纳米/微米晶表层由于具有较高的加工硬化指数及强度,使韧窝尺寸比粗晶心部的更加细小。
关键词:表面机械碾磨处理;工业纯钛;梯度纳米/微米晶;加工硬化;韧窝
(Edited by Wei-ping CHEN)
Foundation item: Project (2014CB644003) supported by the National Basic Research Program of China; Project (51321003) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project (B06025) supported by “111” Project of China
Corresponding author: Qiao-yan SUN; Tel/Fax: +86-29-82665125; E-mail: qysun@mail.xjtu.edu.cn
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(15)63659-7

