TiB2+TiC含量对等离子熔覆Ni55基复合材料涂层显微组织及耐磨性能的影响
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2019年第1期
论文作者:张新杰 崔洪芝 王佳峰 张国松 赵玉桥 孙康
文章页码:132 - 142
关键词:金属基复合材料涂层;等离子熔覆;显微组织;摩擦学行为;磨损机制
Key words:metal matrix composite coating; plasma cladding; microstructure; tribological behavior; wear mechanism
摘 要:采用等离子熔覆工艺,以不同比例的Ti、B4C和Ni55为原料原位制备TiB2-TiC强化Ni55基复合材料涂层,研究陶瓷相TiB2+TiC含量对涂层显微组织及耐磨性能的影响。结果表明:通过等离子熔覆合成TiB2和TiC陶瓷相,陶瓷相含量对涂层在不同载荷下的摩擦学性能和磨损机制有较大影响。在30 N磨损载荷下,复合陶瓷通过阻碍裂纹扩展抑制剥层磨损的作用;在60 N磨损载荷下,高硬度、高强度陶瓷可以有效降低磨粒磨损和黏着磨损的作用。另外,在高陶瓷含量的涂层磨痕表面发现有压实层结构分布,有效降低摩擦因数和磨损率。在30 和60 N的磨损载荷下,TiB2-TiC复合陶瓷通过不同的磨损机制提高涂层的磨损性能。
Abstract: TiB2-TiC reinforced Ni55 matrix composite coatings were in-situ fabricated via plasma cladding on steels using Ti, B4C, and Ni55 as precursor materials at different proportions. Effects of TiB2+TiC content of ceramics phase on the microstructure and wear resistance were studied. The results showed that ceramic phases TiB2 and TiC were in-situ synthesized by plasma cladding, and the ceramic phase content significantly affected tribological performance and the wear mechanism of coatings under different loads. The composite ceramics protected coatings from further delamination wear by crack-resistance under a load of 30 N. Severe abrasive wear and adhesive wear were prevented when the load increased to 60 N because of the high hardness and strength of ceramic phases. Moreover, a compacted layer appeared on the wear surface of coatings with high content of ceramic phases, which effectively decreased the friction coefficient and wear rate. The TiB2-TiC composite ceramics significantly improved the wear performance of metal matrix composite coatings by different mechanisms under loads of 30 and 60 N.
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 29(2019) 132-142
Xin-jie ZHANG, Hong-zhi CUI, Jia-feng WANG, Guo-song ZHANG, Yu-qiao ZHAO, Kang SUN
School of Materials Science and Engineering, Shandong University of Science and Technology, Qingdao 266590, China
Received 13 October 2017; accepted 16 April 2018
Abstract: TiB2-TiC reinforced Ni55 matrix composite coatings were in-situ fabricated via plasma cladding on steels using Ti, B4C, and Ni55 as precursor materials at different proportions. Effects of TiB2+TiC content of ceramics phase on the microstructure and wear resistance were studied. The results showed that ceramic phases TiB2 and TiC were in-situ synthesized by plasma cladding, and the ceramic phase content significantly affected tribological performance and the wear mechanism of coatings under different loads. The composite ceramics protected coatings from further delamination wear by crack-resistance under a load of 30 N. Severe abrasive wear and adhesive wear were prevented when the load increased to 60 N because of the high hardness and strength of ceramic phases. Moreover, a compacted layer appeared on the wear surface of coatings with high content of ceramic phases, which effectively decreased the friction coefficient and wear rate. The TiB2-TiC composite ceramics significantly improved the wear performance of metal matrix composite coatings by different mechanisms under loads of 30 and 60 N.
Key words: metal matrix composite coating; plasma cladding; microstructure; tribological behavior; wear mechanism
1 Introduction
Metallic matrix composite (MMC) coatings have been widely employed in engineering (such as surface enhancement of pick and chute in the mining industry) because of their high hardness and excellent wear resistance [1-3]. There are many techniques to produce MMC coatings, such as plasma spraying [4], mag-netron sputtering [5], laser cladding [6-8], surface welding [9,10], and plasma cladding [11-14]. Of these methods, plasma cladding is a versatile technique to produce MMC coatings on mining picks and chutes, because of its good metallurgical bonding, low cost, and high efficiency [14-16]. The coating with excellent wear resistance can be prepared by plasma cladding technology.
Recently, many efforts have been made to improve the tribological characteristics of MMC coatings, including adding or forming in-situ ceramic strengthening phases in the coating, such as TiB2, TiC, TiB, Al2O3, and WC [17-19]. FENG et al [20] have fabricated TiC-TiN reinforced Fe-based plasma cladding coatings using the plasma cladding method. The results indicated that the composite coatings exhibited excellent wear resistance and corrosion resistance, and high hardness. The wear resistance and corrosion resistance of the cladded coatings increased with the increase of Ti and B4C contents. SHARIFITABAR et al [12] have fabricated Fe-TiC-Al2O3 coatings on the surface of 1045 steel by gas tungsten arc. The hardness of the coatings increased to HV 830 due to the formation of TiC-Al2O3 reinforcing particles in the structure of the coatings, which improved the abrasive wear resistance of the substrate. MA et al [21] have fabricated Ni60/WC composite coatings by wide-band laser, and reported that fine ceramics greatly enhanced the wear resistance of composite coatings, but effects of large block ceramic particles on the wear resistance were limited. Of the above reinforcing ceramic phases, titanium carbide and boride demonstrated excellent compatibility, and greatly improved friction and wear performance [22,23]. WANG et al [24] have prepared (TiB2+TiC)/Fe composite coatings from a precursor of B4C, TiO2 and Al powders by laser cladding. The results showed that ceramic reinforcement particles could improve the wear resistance by inhibition of plastic deformation and plowing of soft substrate. Hard particles reduced the contact area of the matrix with the counterface, and minimized the smearing effect of the Fe-based coating on the counterface surface, thus lowering the the friction coefficient of composite coating. ZHANG et al [25] have produced TiC-TiB2 particle reinforced Fe-based composite coatings by laser cladding. The wear mechanisms of the substrate were plowing wear and adhesive wear. TiB2 and TiC reinforcements uniformly distributed in the coatings can overcome the effect of plowing and strengthen the substrate by the pinning effect, and the wear mechanism of composite coatings was abrasive wear by micro cutting. However, there are few detailed studies [26,27] on the effects of TiB2-TiC ceramic content on the resulting microstructures and dry sliding wear performance under different loads of MMC coatings applied via in-situ synthesis.
In the present study, TiB2-TiC reinforced MMC coatings were fabricated using Ti, B4C and NiCrBSi (Ni55, widely used as a precursor because it offers excellent wear and corrosion resistance [28,29]) as raw materials at different proportions by plasma cladding. The phase components and microstructures of the resulting materials were investigated. The dry sliding wear behaviors of the MMC coatings and pure Ni55 coating were characterized to investigate the influence of composite ceramic phases (TiB2-TiC) on the wear resistance of the coated materials under different loads.
2 Experimental
2.1 Raw materials and fabrication of plasma cladding coatings
The starting materials were commercial powders of Ti (≥99.7 wt.%, 48-75 μm), B4C (94 wt.%, 50-90 μm), and NiCrBSi (Ni55, 40-70 μm). Chemical composition of the Ni55 self-fluxing alloy powders is presented in Table 1 (the molar ratio of Ti/B4C was set to be 3:1 according to the chemical equation of 3Ti+B4C=2TiB2+ TiC [30]). Figure 1 shows the morphologies of the starting powders. The surfaces of Q235 mild carbon steel (with w(C)<0.2%) substrates (size: 100 mm × 30 mm × 10 mm) were polished with emery paper and ultrasonically cleaned in an alcohol bath. Four chemical compositions of the precursors are prepared as listed in Table 2.
Table 1 Chemical composition of Ni55 alloy (wt.%)

Table 2 Chemical compositions of mixtures used during plasma cladding process


Fig. 1 Morphologies of starting Ti (a), B4C (b) and Ni55 (c) powders
The cladding process was conducted using plasma cladding equipment with an output power of 4.5 kW, schematically described in Fig. 2. The specific plasma cladding parameters are as follows: operating welding current 80 A, welding voltage 30 V, cladding speed 300 mm/min, powder feeder gas flux 2.5 L/min, and overlap between adjacent cladding (overlapping ratio) approximately 30%. In order to prevent the melted pool from heavy oxidation, high-purity argon gas was used as a shielding gas applied through the coaxial nozzle at 10 L/min. The work distance between the plasma gun and the substrate surface was 10 mm.

Fig. 2 Schematic diagram of plasma cladding process
2.2 Microstructure characterization
In order to identify the phase components in the produced coatings, X-ray diffraction (XRD, D/ MAX2500PC, JAPAN) with Cu Kα radiation was performed at a scanning rate of 4 (°)/min and with scanning angles that ranged from 20° to 90°. Analysis of the microstructure of the coatings was performed using a field emission scanning electron microscope (FESEM, FEI Nova Nano SEM 450, USA) that allowed energy dispersive spectroscopy (EDS). The microhardness profile along the cross-section of the plasma cladding samples was measured using a microhardness tester (HVS-1000, FM-700, Japan) under a load of 500 g, a dwell time of 10 s, and an average distance between two points of 0.1 mm. The presented microhardness value of each sample at a certain depth is the average value of three parallel measurements on the cross-section.
2.3 Wear testing
Figure 3 shows the schematic diagram of wear test process and wear volume of tracks on the coatings. The dry sliding wear tests were performed under room temperature conditions with a ball-on-disk model using a micro-tribometer (UMT-3, CETR, USA) with loads of 30 and 60 N for 2 h. An Al2O3 ball with a diameter of 9.525 mm, a hardness of HRA 92, and a surface roughness of around 50 nm was used as a counter body. The wear volume was determined by the depth and width of wear scars measured via a 3D profiler (Zeta-20, Zeta, USA). The wear volume was calculated by Eq. (1) [31]:
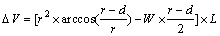 (1)
(1)
where W, d and L are the width, depth and length of the wear scar, respectively, and r is the outer radius of the wear ball. The wear rate was calculated by Eq. (2):
 (2)
(2)
where ω is the wear rate, D is the wear distance, and P is the load.

Fig. 3 Schematic diagram of wear test process (a) and wear volume of tracks (b) on coatings
After the wear test, the worn surfaces of MMC coatings were studied by FESEM.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Phase component
Figure 4 depicts the typical XRD patterns of the coatings with different ceramic contents. The coating of Ni55 mainly contained three phases: γ-Ni, CrFeB, and Fe2B. When 10% (Ti+B4C) was added to the reaction system, TiC and CrB appeared in the XRD patterns. With the continuous increase of Ti+B4C content up to 20%, diffraction peaks of TiB2 began to emerge. For C30 coating, TiB2 peaks increased greatly. The XRD patterns of C40 coating are similar to those of C30 coating. No peak corresponding to Ti and B4C phases is visible in the XRD pattern of the MMC coatings, which confirms that TiB2 and TiC can be synthesized in-situ by the reaction: 3Ti+B4C=2TiB2+TiC.

Fig. 4 XRD patterns of coatings with different ceramic phase contents
3.2 Microstructure
Figures 5(a-e) show the microstructures of Ni55 and MMC coatings prepared with different amounts of Ti+B4C. More detailed morphology about the micro- structure of C30 coating is presented in Fig. 5(f), and EDS mapping analysis corresponding to Fig. 5(f) is shown in Fig. 6. From the EDS results, we can see that there are mainly three kinds of particles, rectangular, square, and strip-shaped particles in the C30 coating. The Ti is concentrated in rectangular and square areas, B is concentrated in rectangular and strip areas, and C is concentrated in square areas. The areas of strip shape in the coating are rich in Cr, and there is no significant decrease of Fe in these areas. Combined with the data provided by the XRD patterns shown in Fig. 4, we can deduce that the rectangular particulates are TiB2, the square phases are TiC, and the strip areas are CrFeB. The hexagonal shape phases shown in Figs. 5(c) and (e) are TiB2 according to previous research [32], and TiB2 has a hexagonal AlB2-type structure with a P6/mm space group involving alternating planes of Ti and B atoms [33]. The size and volume fraction of TiB2 particles increased with the increase of the mixing ratio of Ti to B4C, and the size of TiC first increased and then decreased. The size of CrFeB became smaller because the increase of the TiB2 particles occupied more B element. In addition, more TiB2 particles limited the growth of CrFeB and TiC.
Figure 7(a) shows the cross-section typical micro- structure of coating in the interface region of the material prepared with 30% (Ti+B4C). The coating is free from pores and cracks, and has good metallurgical adhesion with the substrate. The microstructure of the coating near the substrate is composed of a small amount of well-developed columnar crystal phases growing in the direction of the heat flow [34]. The element distribution obtained by EDS line scan analysis corresponding to Fig. 7(a) is presented in Fig. 7(b). It can be seen that the Fe element is diffused into the coating and shows a decreasing trend, and the trend of Ni element is opposite.

Fig. 5 Microstructures of Ni55 (a), C10 (b), C20 (c), C30 (d), C40 (e) coatings and high magnification image of area A in C30 coating (f)
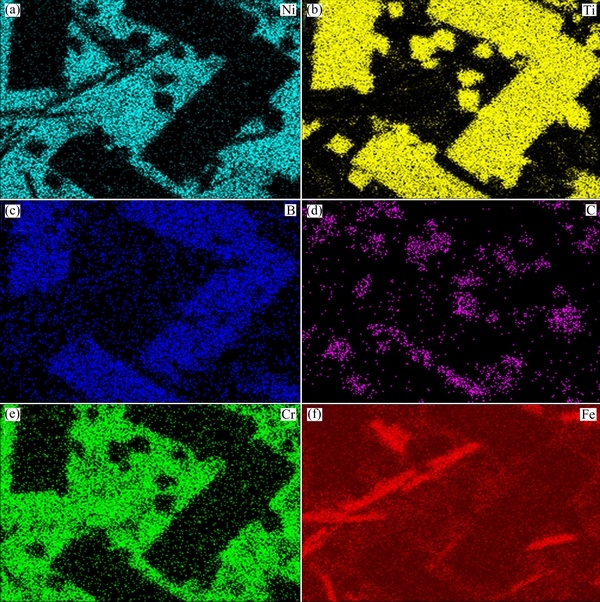
Fig. 6 EDS mapping analysis results of region A shown in Fig. 5(d)
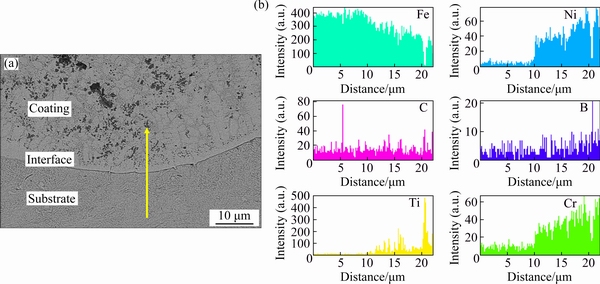
Fig. 7 SEM image of C30 coating interface region (a) and EDS line scan analysis results (b)
The distribution caused a gradual variation in the mechanical properties along the thickness direction of the material [35]. The gradient structure clearly indicates that sound metallurgical bonding to the Q235 substrate is obtained by the plasma cladding process.
3.3 Microhardness
Figure 8 presents the microhardness distribution of coatings with different ceramic contents along the depth direction. A dilution layer in the profile shows a lower microhardness than the rest of the coating. The average microhardness of the MMC coating (HV0.5 1000-1300) is about 2 times as much as that of the Ni55 coating (approximately HV0.5 550), and increases to the maximum of approximately HV0.5 1350 for the C40 coating. It can be deduced that the formation of ceramic compounds such as TiB2 and TiC with high hardness increases the overall microhardness of the coatings.
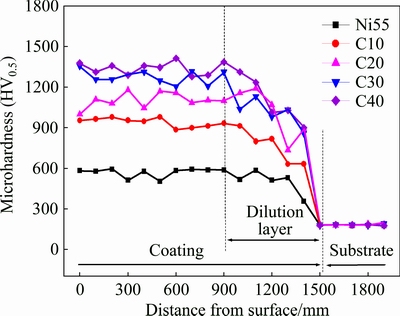
Fig. 8 Microhardness distribution of coatings with different ceramic contents along depth direction
3.4 Dry sliding wear behavior
3.4.1 Wear profiles and volume loss
The 3D profiles of the wear track of the coatings are shown in Fig. 9. Obviously, as additions of Ti and B4C increased, the wear scar on the coating tended to become lighter and smoother at loads of 30 and 60 N. Differences were observed in the width and length of the wear tracks obtained at different contact loads. The volume wear rate was calculated using data from these profiles and applying Eqs. (1) and (2).

Fig. 9 3D profiles of wear tracks

Fig. 10 Wear rate (a) and COF (b) of (TiB2+TiC)/Ni and Ni55 coatings under loads of 30 and 60 N
The wear rate and coefficient of friction (COF) of the (TiB2+TiC)/Ni and Ni55 coatings were determined and the values are presented in Fig. 10. In general, the coating with higher hardness exhibits better wear resistance as shown in Fig. 10(a), corresponding to the observed results of microhardness discussed above. As can be seen, the Ni55 coating exhibits the highest volume loss because of its relatively low hardness. Compared with the Ni55 coating, all coatings strengthened by TiB2+TiC ceramic phases exhibit a decreased wear rate. The wear rate of the coatings decreases obviously with the increasing content of ceramic phase under loads of 30 and 60 N. This indicates that the enhancement of hardness caused by ceramic phases can improve the wear resistance of the materials. The decrease of wear rate was more obvious with increasing ceramic content under a load of 60 N compared with that under a load of 30 N. HUANG et al [36] have studied the dry friction and wear behavior of 7075 Al alloy reinforced with SiC (a 3D continuous ceramic network). They found that the decrease of wear rate was more obvious with increasing ceramic content under high load, which is consistent with the results here. They explained this result as follows: under low load, the composite with low volume fraction of ceramic reinforcement exhibits better wear resistance due to the homogeneous reinforcement distribution with small pore size; in contrast, under high load, the composite with high reinforcement volume fraction exhibits better wear resistance because of the coarse frame size.
The data presented in Fig. 10(b) show that the COF of (TiB2+TiC)/Ni coatings is lower than that of the Ni55 coating. TiB2 and TiC decrease the COF between the coatings and the counter-bodies by obviously improving the hardness of coatings and reducing the practical area of contact when coatings are rubbed with Al2O3 [37]. However, the COF of the (TiB2+TiC)/Ni coatings shows an increasing trend with increasing additions of Ti and B4C. The change is more obvious under 60 N than that under 30 N. The explanation for this phenomenon is often described as a “stick and slip” mechanism [38]. The asperities adhere during wear, causing the moving parts to stick, leading to a high friction value. The coatings with high content ceramic phases exhibit lower COF values under a load of 60 N, suggesting that the corresponding wear mechanisms may be different.
3.4.2 Wear surface morphology
Figure 11 shows SEM images of the worn surfaces of the coatings under a load of 30 N. Figure 12 shows the schematic diagrams of wear mechanisms of coatings under a load of 30 N. Some scars are observed on the worn surface of the Ni55 coating. Crack initiation and propagation can occur by work hardening, and partial layer-stripping traces are observed on the surface of the Ni55 coating. This indicates that the main wear mechanism of the Ni55 coating is delamination wear. The delamination decreases with addition of 10% (Ti+B4C). This is due to the effect of ceramic compounds such as TiC with high hardness to increase the overall microhardness and strength of the coating. The worn surface morphology of C20 coating is very similar to that of the C10 coating, but the scars are lighter. Delamination is the predominant mechanism for C10 and C20 coatings (described in Fig. 12(a)).

Fig. 11 SEM images of worn surfaces of Ni55 (a), C10 (b), C20 (c), C30 (d) and C40 (e) coatings under load of 30 N
For the C30 coating, the worn surface is comparatively smooth. Some furrows are observed on the worn surface, with delamination near the ceramic phase. It can be inferred that more serious delamination wear is prevented by the crack-resisting of ceramic phases with the synthesis of larger size TiB2 particles. The worn surface morphology of the C40 coating is very similar to that of the C30 coating, but the furrows are shallower. In the dry sliding wear stage, the softer matrix wears out faster compared to the hard reinforcement, causing the reinforcement to protrude over the worn surface, protecting the coating from additional wear and removal [39]. This indicates that the main wear mechanism for C30 and C40 coatings is micro-cutting (described in Fig. 12(b)). Overall, the ceramic phases act good protection against wear. The worn surface morphology of the coatings and the wear mechanism correspond well to the observed changes in microhardness of the coatings caused by the presence of the ceramic hard reinforcements.

Fig. 12 Schematic diagrams of wear mechanisms of Ni55, C10, C20 (a) and C30, C40 (b) coatings at load of 30 N

Fig. 13 SEM images of worn surfaces of Ni55 (a), C10 (b), C20 (c), C30 (d), C40 (e) coatings under load of 60 N and high magnification image of area B in C30 coating (f)
Figure 13 shows SEM images of the worn surfaces of coatings under a load of 60 N. The load caused an increase in the temperature of wear surface during friction wear. Slight plastic deformation and adhesion to the worn surface were very easily generated, which might hinder the relative motion. Many grooves and adhesion traces can be seen on the worn surface of Ni55 coating, indicating that the wear mechanism is a combination of abrasive wear and adhesive wear. A smoother surface with fewer grooves is observed for C10 and C20 coatings because high hardness and strength of ceramic phases confer resistance of the composite coatings to abrasive wear and metallic adhesion during dry sliding wear. For the C30 and C40 coatings, the compacted layers appear on the worn surface, and are connected together in the C40 coating. Data in Figs. 13(d) and (e) show the EDS results of the surface of the compacted layer. There are O and Al elements on the worn surface, indicating material transfer and severe oxidation during the wear process.
Figure 14 shows the COF curves of the coatings under a load of 60 N. The COF of Ni55 coating displayed a high value under a load of 60 N. Coatings strengthened by ceramic phases exhibited a lower COF compared with the Ni55 coating because of the high hardness, the elastic modulus, and the chemical stability of the in-situ synthesized ceramic phases (TiB2 and TiC). Obviously, the COF of the C40 coating became very small. In the initial stage, the softer matrix would wear out faster, allowing protrusion of the reinforcements over the worn surface to protect the coating from serious wear damage (Fig. 13(f)). Under high load, adhesive wear and abrasive wear could accelerate material transfer. Because of the hindrance of TiB2 particles, the transferred material would agglomerate around the TiB2. The compacted layer appeared on the worn surface after the process of fracture, welding, rewelding, and repetitive rolling when the Ti+B4C content was 30% and 40%, respectively. A continuously compacted layer appeared on the wear surface of the C40 coating because a large size ceramic phase was better for blocking material transfer (corresponding to the microstructure shown in Fig. 5(e)). CHI et al [40] also observed this phenomenon for the dry sliding friction and wear behavior of (TiB2+h-BN)/2024Al composites, and found that the existence of the compacted layer had a significant effect on the friction coefficient and wear rate. The large area of the compacted layer hindered the adhesive and abrasive activities, eventually reducing the COF (as shown in Fig. 14) and wear rate. The results suggested that the ceramic content and wear load affected the tribological behavior of coatings through different wear mechanisms.

Fig. 14 COF curves of coatings under load of 60 N
4 Conclusions
(1) After plasma cladding, TiB2 and TiC ceramic phases were in-situ synthesized and homogenously distributed in TiB2 and TiC reinforced Ni55-based MMC coatings.
(2) The microhardness of the cladded coatings with Ti+B4C was about 2 times as high as that of the Ni55 coating due to the formation of re-enforcements such as TiB2 and TiC with high hardness.
(3) Cladded coatings reinforced by TiB2 and TiC exhibited a much better wear resistance than the Ni55 coating. Serious delamination wear was prevented because the in-situ synthesized ceramic phases TiB2 and TiC provided high hardness and prevented crack extension during dry sliding wear under a load of 30 N. At a load of 60 N, the ceramic phases significantly improved the tribological properties of coatings by providing resistance to abrasive wear and metallic adhesion. Compacted layers appeared on the worn surface of coatings with high content ceramic phases (C30 and C40), which effectively decreased the friction coefficient and wear rate. Ceramic content and wear load affected the tribological behavior of coatings through different wear mechanisms.
References
[1] AKBARI M K, BAHARVANDI H R, SHIRVANIMOGHADDAM K. Tensile and fracture behavior of nano/micro TiB2, particle reinforced casting A356 aluminum alloy composites [J]. Materials & Design, 2015, 66: 150-161.
[2] DIAO Yun-hua, ZHANG Ke-min. Microstructure and corrosion resistance of TC2 Ti alloy by laser cladding with Ti/TiC/TiB2 powders [J]. Applied Surface Science, 2015, 352: 163-168.
[3] TAN H, LUO Z, LI Y, YAN F, DUAN R, HUANG Y. Effect of strengthening particles on the dry sliding wear behavior of Al2O3-M7C3/Fe metal matrix composite coatings produced by laser cladding [J]. Wear, 2015, 324-325: 36-44.
[4] XU Jia-ying, ZOU Bing-lin, TAO Shun-yan, ZHANG Meng-xian, CAO Xue-qian. Fabrication and properties of Al2O3-TiB2-TiC/Al metal matrix composite coatings by atmospheric plasma spraying of SHS powders [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2016, 672: 251-259.
[5] DAI Ming-jiang, WEI Chun-bei, ZHOU Ke-song, ZHU Min, HOU Hui-jun, LIN Song-sheng, TONG Xin. Properties of W/DLC/W-S-C composite films fabricated by magnetron sputtering [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2015, 25: 3002-3011.
[6] LIU Kun, LI Ya-jiang, WANG Juan. In-situ reactive fabrication and effect of phosphorus on microstructure evolution of Ni/Ni-Al intermetallic composite coating by laser cladding [J]. Materials & Design, 2016, 105: 171-178.
[7] FARAHMAND P, KOVACEVIC R. Corrosion and wear behavior of laser cladded Ni-WC coatings [J]. Surface & Coatings Technology, 2015, 276: 121-135.
[8] WENG Fei, YU Hui-jun, CHEN Chuan-zhong, DAI Jing-jie. Microstructures and wear properties of laser cladding Co-based composite coatings on Ti-6Al-4V [J]. Materials & Design, 2015, 80: 174-181.
[9] LIU Y F, MU J S, XU X Y, YANG S Z. Microstructure and dry-sliding wear properties of TiC-reinforced composite coating prepared by plasma-transferred arc weld-surfacing process [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2007, 458(1-2): 366-370.
[10] WANG Li-mei, LIU Jun-bo, YUAN Chi. Fe-Cr-C-TiC high-chromium Fe-based ceramic composite coating prepared by PTA weld-surfacing process [J]. Materials Science Forum, 2011, 675-677: 783-787.
[11] CAO H T, DONG X P, PAN Z, WU X W, HUANG Q W, PEI Y T. Surface alloying of high-vanadium high-speed steel on ductile iron using plasma transferred arc alloying technique: microstructure and wear properties [J]. Materials & Design, 2016, 100: 223-234.
[12] SHARIFITABAR M, KHAKI J V, SABZEVAR M H. Microstructure and wear resistance of in-situ TiC-Al2O3 particles reinforced Fe-based coatings produced by gas tungsten arc cladding [J]. Surface & Coatings Technology, 2016, 285: 47-56.
[13] ZHANG D K, LIU Y, YIN Y. Preparation of plasma cladding gradient wear-resistant layer and study on its impact fatigue properties [J]. Journal of Thermal Spray Technology, 2016, 25(3): 1-11.
[14] JIN G, LI Y, CUI H Y, CUI X F, CAI Z B. Microstructure and tribological properties of in situ synthesized TiN reinforced Ni/Ti alloy clad layer prepared by plasma cladding technique [J]. Journal of Materials Engineering & Performance, 2016, 25(6): 2412-2419.
[15] XIE Guo-zhi, SONG Xiao-long, ZHANG Dong-jie, WU Yu-ping, LIN Ping-hua. Microstructure and corrosion properties of thick WC composite coating formed by plasma cladding [J]. Applied Surface Science, 2010, 256(21): 6354-6358.
[16] ZHAO Cheng, TIAN Feng, PENG Hong-rui, HOU Jun-ying. Non-transferred arc plasma cladding of stellite Ni60 alloy on steel [J]. Surface & Coatings Technology, 2002, 155(1): 80-84.
[17] ZHOU S F, DAI X Q. Laser induction hybrid rapid cladding of WC particles reinforced NiCrBSi composite coating [J]. Applied Surface Science, 2010, 256(14): 4708-4714.
[18] YU T, DENG Q L, ZHENG J F, DONG G, YANG J G. Microstructure and wear behaviour of laser clad NiCrBSi+Ta composite coating [J]. Surface Engineering, 2013, 28(5): 357-363.
[19] HE Long, TAN Ye-fa, WANG Xiao-long, JING Qi-feng, HONG Xiang. Tribological properties of laser cladding TiB2 particles reinforced Ni-base alloy composite coatings on aluminum alloy [J]. Rare Metals, 2015, 34(11): 1-8.
[20] FENG Zai-qiang, TANG Ming-qi, LIU Yu-qiang, YAN Zhen-wei, LI Gang, ZHANG Rui-zhu. In situ synthesis of TiC-TiN-reinforced Fe-base plasma cladding coatings [J]. Surface Engineering, 2017, 34: 1-7.
[21] MA Qun-shuang, LI Ya-jiang, WANG Juan, LIU Kun. Microstructure evolution and growth control of ceramic particles in wide-band laser clad Ni60/WC composite coatings [J]. Materials & Design, 2016, 92: 897-905.
[22] DU Bao-shuai, PAITAL S R, DAHOTRE N B. Phase constituents and microstructure of laser synthesized TiB2-TiC reinforced composite coating on steel [J]. Scripta Materialia, 2008, 59(10): 1147-1150.
[23] TANG Jing-ming. Mechanical and tribological properties of the TiC-TiB2 composite coating deposited on 40Cr-steel by electro spark deposition [J]. Applied Surface Science, 2016, 365: 202-208.
[24] WANG X H, ZHANG M, DU B S, LI S. Microstructure and wear properties of laser clad (TiB2+TiC)/Fe composite coating [J]. Surface Review & Letters, 2012, 19(5): 295-234
[25] ZHANG M, QU K L, LUO S X, LIU S S. Effect of Cr on the microstructure and properties of TiC-TiB2 particles reinforced Fe-based composite coatings [J]. Surface & Coatings Technology, 2017: 316: 131-137.
[26] LI Xiu-qing, GAO Yi-min, PAN Wu, ZHONG Zhi-chao, SONG Lian-cheng, CHEN Wei, YANG Qing-xia. Effect of hBN content on the friction and wear characteristics of B4C-hBN ceramic composites under dry sliding condition [J]. Ceramics International, 2014, 41(3): 3918-3926.
[27] XU Jia-zi, LI Cheng-di, ZHU Feng, SHEN Yan, XU Tao, XU Jiu-jun. Ceramic particles content on friction and wear behavior of Cr-Al2O3 piston rings by composite plating [J]. China Surface Engineering, 2016, 29(1): 80-86. (in Chinese)
[28] HUANG Shi-ming, SUN Da-qian, WANG Wen-quan, XU Hong-yong. Microstructures and properties of in-situ TiC particles reinforced Ni-based composite coatings prepared by plasma spray welding [J]. Ceramics International, 2015, 41(9): 12202-12210.
[29] DESCHUYTENEER D, PETIT F, GONON M, CAMBIER F. Influence of large particle size-up to 1.2 mm and morphology on wear resistance in NiCrBSi/WC laser cladded composite coatings [J]. Surface & Coatings Technology, 2017, 311: 365-373.
[30] OUYANG J H, YANG Z L, LIU Z G, LIANG X S. Friction and wear properties of reactive hot-pressed TiB2-TiN composites in sliding against Al2O3 ball at elevated temperatures [J]. Wear, 2011, 271(9-10): 1966-1973.
[31] WEI N, CUI H Z, MA L, SONG X J, LIU W, HOU N. Porous TiC-TiB-NiAl composites and effect of NiAl contents on pore structure and microstructure [J]. Powder Metallurgy, 2015, 58(4): 273-280.
[32] CUI Hong-zhi, MA Li, CAO Li-li, TENG Fang-lei, CUI Ning. Effect of NiAl content on phases and microstructures of TiC-TiB2-NiAl composites fabricated by reaction synthesis [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2014, 24: 346-353.
[33] CUI Hong-zhi, ZHANG Yan-feng, ZHANG Guo-song, LIU Wei, SONG Xiao-jie, WEI Na. Pore and microstructure change induced by SiC whiskers and particles in porous TiB2-TiC-Ti3SiC2 composites [J]. Ceramics International, 2016, 42(7): 8376-8384.
[34] DU Bao-shuai, ZOU Zeng-da, WANG Xin-hong, LI Qing-ming. In situ synthesis of TiC-TiB2 reinforced FeCrSiB composite coating by laser cladding [J]. Surface Review & Letters, 2007, 14(2): 315-319.
[35] WEN Bian-ying, WU Gang, YU Jian. A flat polymeric gradient material: Preparation, structure and property [J]. Polymer, 2004, 45(10): 3359-3365.
[36] HUANG Dan, CHEN Wei-ping, ZHANG Shao-yan, HE Zeng-xian. Dry friction and wear performance of SiC 3D continuous ceramic frame reinforced 7075Al alloy [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2010, 20: 54-58.
[37] WANG X H, ZHANG M, LIU X M, QU S Y, ZOU Z D. Microstructure and wear properties of TiC/FeCrBSi surface composite coating prepared by laser cladding [J]. Surface & Coatings Technology, 2008, 202(15): 3600-3606.
[38] LACEY P, TORRANCE A A. The calculation of wear coefficients for plastic contacts [J]. Wear, 1991, 145(2): 367-383.
[39] LI Jun, YU Zhi-hui, WANG Hui-ping. Wear behaviors of an (TiB+TiC)/Ti composite coating fabricated on Ti6Al4V by laser cladding [J]. Thin Solid Films, 2011, 519(15): 4804-4808.
[40] CHI Hai-tao, JIANG Long-tao, CHEN Guo-qin, KANG Peng-chao, LIN Xiu, WU Gao-hui. Dry sliding friction and wear behavior of (TiB2+h-BN)/2024Al composites [J]. Materials & Design, 2015, 87: 960-968.
张新杰,崔洪芝,王佳峰,张国松,赵玉桥,孙 康
山东科技大学 材料科学与工程学院,青岛 266590
摘 要:采用等离子熔覆工艺,以不同比例的Ti、B4C和Ni55为原料原位制备TiB2-TiC强化Ni55基复合材料涂层,研究陶瓷相TiB2+TiC含量对涂层显微组织及耐磨性能的影响。结果表明:通过等离子熔覆合成TiB2和TiC陶瓷相,陶瓷相含量对涂层在不同载荷下的摩擦学性能和磨损机制有较大影响。在30 N磨损载荷下,复合陶瓷通过阻碍裂纹扩展抑制剥层磨损的作用;在60 N磨损载荷下,高硬度、高强度陶瓷可以有效降低磨粒磨损和黏着磨损的作用。另外,在高陶瓷含量的涂层磨痕表面发现有压实层结构分布,有效降低摩擦因数和磨损率。在30 和60 N的磨损载荷下,TiB2-TiC复合陶瓷通过不同的磨损机制提高涂层的磨损性能。
关键词:金属基复合材料涂层;等离子熔覆;显微组织;摩擦学行为;磨损机制
(Edited by Wei-ping CHEN)
Foundation item: Project (51772176) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project (tspd20161006) supported by Taishan Scholarship of Climbing Plan, China; Project (2015AA034404) supported by National High-tech Research and Development Program of China
Corresponding author: Hong-zhi CUI; Tel: +86-532-86057929; E-mail: cuihongzhi1965@163.com
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(18)64922-2

