
Influence of hydrogenation on microstructures and microhardness of Ti6Al4V alloy
ZHAO Jing-wei(赵敬伟)1, DING Hua(丁 桦)1, ZHAO Wen-juan(赵文娟)1,
TIAN Xue-feng(田学锋)1, HOU Hong-liang(侯红亮)2, WANG Yao-qi(王耀奇)2
1. School of Materials and Metallurgy, Northeastern University, Shenyang 110004, China;
2. Beijing Aeronautical Manufacturing Technology Research Institute, Beijing 100024, China
Received 26 June 2007; accepted 3 December 2007
Abstract: The microstructures of Ti6Al4V alloy after hydrogenation were investigated by optical microscopy(OM), X-ray diffraction(XRD) and transmission electron microscopy(TEM). The influence of hydrogenation on the hardness of α and β phases was analysed by microhardness testing. The influence of hydrogenation on alloying elements diffusion was studied by electron probe microanalysis(EPMA). The microstructural observation reveals that hydride δ (FCC structure) as well as large number of dislocations precipitate in the specimens with 0.278% and 0.514% hydrogen, and a lot of twins are found in the specimen with 0.514% hydrogen, simultaneously. The result of microhardness testing shows that the hardness of α and β phases increases synchronously with the increase of hydrogen and the hardness increment of β is larger than that of α. According to analysis of EPMA, the diffusion ability of alloy elements Al and V increases after hydrogenation. It is considered that hydrogen solution strengthening and V element diffusion are the main factors causing the hardness of α phase increase with the increase of hydrogen, and the formation of δ hydrides, lattice defects, hydrogen solution strengthening and Al element diffusion jointly cause the hardness of β phase increase with the increasing hydrogen.
Key words: Ti6Al4V alloy; hydrogenation; hydride; microhardness; defect; solution strengthening; diffusion
1 Introduction
High hydrogen content can remarkably degrade the mechanical properties of most engineering materials [1-2]. Furthermore, even relatively low concentration of hydrogen can lead to material failure if hydrogen is trapped around structural defects and local concentrations exceed a critical value[3-5]. However, in the 1950s, ZWIKCHER and SCHLEICHER found that the addition of proper quantity of hydrogen in cast ingots of titanium alloys could strongly enhance the plasticity and then improve the hot working properties considerably[6-7]. In the 1970s, scholars in former Soviet Union began to investigate the influences of hydrogen on processability of titanium alloys, and the conception of thermo hydrogen treatment(THT) was given then[8]. THT, or the use of hydrogen as a temporary alloying element, can strongly modify the microstructures and enhance the mechanical properties of titanium alloys[9-11].
Ti6Al4V is one of the most widely used titanium alloys in the aerospace industry[12]. The study on the influences of hydrogenation on the microstructures of Ti6Al4V alloy currently received much attention[13-14]. However, the influence of hydrogenation on microhardness especially on elements diffusion has been less investigated extensively. The objective of this work is to research the influences of hydrogenation on the microstructures and microhardness of Ti6Al4V alloy, with discussion on the influence mechanisms of hydrogenation on microhardness.
2 Experimental
The material used in this investigation was a Ti6Al4V alloy consisting of α and β phases. Prior to hydrogenation, 10 mm×15 mm×2 mm specimens were cut from Ti6Al4V plates, and the specimens were hydrogenated at 750 ℃ for 1 h followed by air-cooling to room temperature. Specimens with various contents of hydrogen in the range of 0-0.5 % (mass fraction) were obtained by controlling the hydrogen pressure. The actual hydrogen content in the specimens was determined by weighing the specimens before and after hydrogenation.
The microstructures of the specimens were investigated by optical microscopy(OM) using OLYMPUS GX51 microscope. The phase constituents were measured by X-ray diffraction(XRD) using Cu Kα radiation at 40 kV and 40 mA. Disc samples with a diameter of 3 mm were used for TEM studies. The TEM samples were prepared by electropolishing in an electrolyte of 6% HCLO4+34% C4H9OH+60% CH3OH (volume fraction), and the operating conditions were -35 to -40 ℃, 50-55 V and 30-35 mA. TEM observations were carried out on a TECNAL G2 20 microscope operated at 200 kV. The microhardness was tested on an FM-700 microhardness tester with dwelling force 0.1 N and dwelling time 10 s. The composition of various phases in the alloys was determined by EPMA-1600 electron probe microanalyser(EPMA) with a beam diameter of 1 μm and a voltage of 15 kV, and the characteristic radiations used were Ti Kα, Al Kα and V Lα.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Microstructural observation and analysis
The microstructures of Ti6Al4V alloy with different hydrogen contents are shown in Fig.1. It can be seen that the specimen without hydrogen shows a rolled α+β dual phase structure, with an average prior-α grain size of 14 μm and an area fraction of 81% (Fig.1(a)). After 0.107% hydrogen is charged in the alloy, the microstructure changes unconspicuously (Fig.1(b)). The microstructures of the specimens with 0.278% and 0.514% hydrogen have two regions (Figs.1(c) and (d)), one is white, which indicates α phase, and the other is alternate with black and white phases, which indicate β phase (black) as well as hydride δ (black) and α phase after eutectoid reaction βH→α+δ.
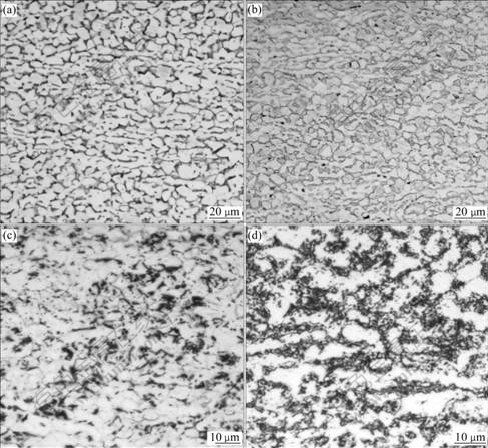
Fig.1 Microstructures of Ti6Al4V alloy hydrogenated at 750 ℃: (a) 0.0% H; (b) 0.107% H; (c) 0.278% H; (d) 0.514% H
The XRD patterns of Ti6Al4V alloy hydrogenated at 750 ℃ with different hydrogen contents are shown in Fig.2. The XRD pattern indicates that the specimen without hydrogen contains primary α phase and a small quantity of β phase. After hydrogenation, the XRD patterns change obviously. The relative intensities of β phase diffraction peaks increase gradually with the increase of hydrogen, which shows that the phase transformation α→β happens when hydrogenated at 750 ℃, then leading to the reduction of α and the increase of β. The peaks of α″ appear in the specimens with 0.107%, 0.278% and 0.514% hydrogen, and the δ peaks appear in the specimens with 0.278% and 0.514% hydrogen. The results indicate that the martensitic phase transformation β→α″ and the eutectoid reaction βH→α+δ happen when hydrogenated at 750 ℃ for 1 h followed by air-cooling to room temperature. Additionally, the β peaks move to lower angles gradually with the increase of hydrogen. According to the results of HUNG et al[15], the radius of hydrogen atom is only 0.046 nm, which inclines to occupy the tetrahedral interstitial sites in titanium alloy. β phase is a body-centered cubic(BCC) lattice which consists of 12 tetrahedral interstices and 6 octahedron interstices, and hydrogen has high solubility in β phase. After hydrogenation, hydrogen atoms occupy the interstitial sites of β unit cell and thus expand the lattice spacing, which leads to the reduction of Bragg diffraction angle. Contrastively, there are only 4 tetrahedral interstices and 2 octahedron interstices in α (close-packed hexagonal, HCP) lattice, and the solubility of hydrogen in α phase is far less than that in β phase. So hydrogen has little influence on the lattice of α phase, and the α peaks change unconspicuously with the increase of hydrogen.
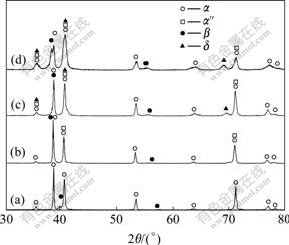
Fig.2 XRD patterns of Ti6Al4V alloy hydrogenated at 750℃: (a) 0.0% H; (b) 0.107% H; (c) 0.278% H; (d) 0.514% H
The TEM micrographs of Ti6Al4V alloy with 0.278% and 0.514% hydrogen are shown in Fig.3 and Fig.4, respectively. It can be seen that hydrides δ as well as large number of dislocations appear in the specimens with 0.278% and 0.514% hydrogen. As it is shown, hydride δ and eutectoid α are all lamellar which distribute alternatively, and the lamellar hydrides are approximately parallel. It can be presumed that hydride δ and eutectoid α nucleate on each other’s surface and then grow up when the eutectoid reaction βH→α+δ happens, and then the lamellar hydride δ and eutectoid α form alternatively with the beneficiation and leanness of hydrogen content in the βH till all the βH is exhausted. The corresponding selected-area electron diffraction (SAED) patterns suggest FCC structure for the hydride δ with [110] zone axis (Fig.4(b)). The chemical formula of δ hydride is TiHx, where the values of x are in the range of 1.50-1.94, and the hydride δ has a CaF2 type structure with titanium atoms on a face centered cubic(FCC) lattice and hydrogen atoms randomly occupying tetrahedral interstitial sites[16]. Fig.4(c) shows a TEM micrograph of β matrix and δ phase in the specimen with 0.514% hydrogen. The corresponding SAED pattern is shown in Fig.4(d), from which the orientation relationship between β and δ could be directly identified as: [120]β//[011]δ,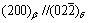 . In addition, a lot of twins in β phase are found in the specimen with 0.514% hydrogen (Fig.4(f)).
. In addition, a lot of twins in β phase are found in the specimen with 0.514% hydrogen (Fig.4(f)).
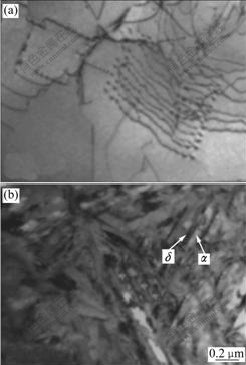
Fig.3 TEM micrographs of Ti6Al4V alloy with 0.278% hydrogen: (a) Hydride δ; (b) Dislocations
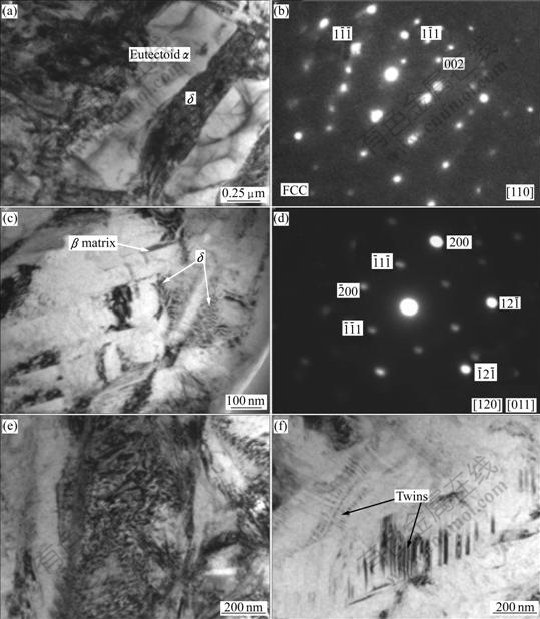

Fig.4 TEM micrographs of Ti6Al4V alloy with 0.514% hydrogen: (a) Hydride δ; (b) Corresponding SAED pattern of δ phase; (c) Matrix and δ phase; (d) SAED pattern of β and δ phases; (e) Dislocations; (f) Twins in β phase
3.2 Microhardness testing
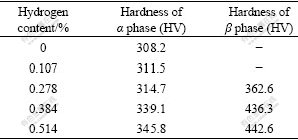
Since the content of β phase is relatively low, it is difficult to test its hardness directly. The hardness values of α phase were tested only in the specimens with 0.0% and 0.107% hydrogen. The microhardness values of Ti6Al4V alloy with different hydrogen contents are shown in Table 1. It can be seen that the hardness values of α and β phases increase synchronously with the increase of hydrogen. Moreover, the hardness value of β is higher than that of α at the same hydrogen content. In addition, when the hydrogen content is less than 0.278%, the hardness values of α phase increase slightly, and when the hydrogen content is between 0.278% and 0.514%, the hardness values of α phase increase faster with the increase of hydrogen, but the increment is obviously less than that of β phase (the hardness increment value of α phase is HV 31.1 and that of β phase is HV 80).
Table 1 Microhardness values of α and β phases
3.3 Discussion
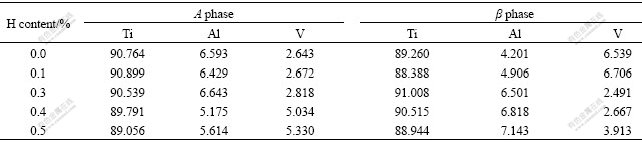
Usually, α phase can be seen as a hard phase in Ti6Al4V alloy, whose hardness is higher than that of β phase[17]. But, the hardness of β phase is higher than that of α phase after hydrogenation in the present work. For better understanding the influence mechanisms of hydrogenation on α and β phases hardness, the micro- area components of Ti6Al4V alloy with different hydrogen contents were determined by EPMA (Table 2). As it is shown, after hydrogenation at 750 ℃, the content of V in α phase increases evidently with the increase of hydrogen, while the contents of Ti and Al change unconspicuously. The content of Ti in β phase has little change, too, but the contents of Al and V change remarkably, and the content of Al increases evidently with the increase of hydrogen while the content of V decreases observably after hydrogenation.
Table 2 Micro-area components of Ti6Al4V alloy(mass fraction, %)
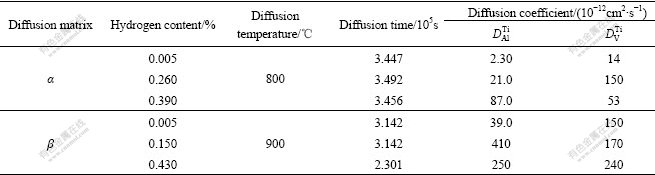
Decohesion theory[18] suggests that hydrogen exists in the form of H+ in metals. After being added into metal, hydrogen can enhance the repulsive force of metal ion and weaken the linkage action among atoms. And the diffusion coefficients of alloy elements will increase, which is a manifestation that self-diffusion ability of metal atoms and diffusion ability of solute atoms enhance synchronously after hydrogenation. The diffusion coefficients of Al and V in α and β phases are shown in Table 3[19]. As shown in Table 3, the diffusion coefficient of Al increases in both α and β phases, and the increment of diffusion coefficient of V in α phase is obviously larger than that in β phase. Combining with the results of EPMA (Table 2), when hydrogenated at 750 ℃, the content of V increases with the increase of hydrogen, which is a manifestation that the hydrogen added into α phase can increase the diffusion coefficient of V and then enhance its diffusion ability. And the hydrogen added into β phase has remarkable influence on Al, which causes the content of Al increase with the increase of hydrogen. The changes after element diffusion will cause main alloying elements Al and V redistribute in α and β phases and then influence the hardness values.
Table 3 Diffusion coefficients of Al and V in α and β phases[19]
According to the results analysed above, the microhardness change after hydrogenation in Ti6Al4V alloys is attributed to following reasons.
3.3.1 Reasons of α hardness increasing
1) There will be small quantities of hydrogen entered the interstitial sites of α phase after hydrogenation, although the solubility of hydrogen in α phase is relatively low. And then interstitial solid solution is formed, which functions as solution strengthening and causes α phase hardness increase with the increase of hydrogen.
2) The diffusion ability of V in α phase is enhanced after hydrogenation, and the increase of V in α phase is another important factor leading to α hardness increasing with the increase of hydrogen.
3.3.2 Reasons of β hardness increasing
1) The eutectoid reaction βH→α+δ is caused after hydrogenation, and then a new phase δ is formed. Because the specific volume of δ is different from that of β matrix, stress fields are generated when δ precipitates from β matrix, and then the distortion of lattices is caused, which leads to the appearance of large number of dislocations around δ.
2) Martensitic phase transformation β→α″ happens when hydrogenated at 750 ℃ followed by air-cooling to room temperature. During the martensitic phase transformation, lattice defects, such as dislocations and twins, are caused and then retained in β phase.
3) After hydrogenation, a large number of hydrogen atoms enter the interstitial sites of β phase and function as solution strengthening.
4) The diffusion ability of Al in β phase is enhanced after hydrogenation, and the content of Al increases with the increasing of hydrogen.
These four factors above jointly cause β hardness increase with the increasing of hydrogen.
The influence mechanisms of hydrogenation on the microhardness of Ti6Al4V alloy is shown in Fig.5.
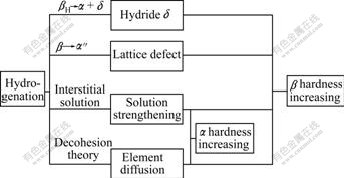
Fig.5 Influence mechanisms of hydrogenation on micro- hardness of Ti6Al4V alloy
4 Conclusions
1) Lamellar hydrides with FCC structure as well as large number of dislocations exist in the specimens with 0.278% and 0.514% hydrogen. Simultaneously, a lot of twins are found in specimen with 0.514% hydrogen.
2) The hardness value of β is higher than that of α at the same hydrogen content. The hardness values of α and β increase synchronously with the increase of hydrogen, and the hardness increment of β is obviously larger than that of α.
3) It is considered that hydrogen solution strengthening and V element diffusion are the main factors causing α hardness increase with the increase of hydrogen, and the formation of δ hydrides, lattice defects, hydrogen solution strengthening and Al alloying element diffusion jointly cause β hardness increase with the increase of hydrogen.
References
[1] LOUTHAN M R, CASKEY G R, DONOVAN J A, RAWL D E. Hydrogen embrittlement of metals [J]. Materials Science and Engineering, 1972, 10: 357-368.
[2] CHEREPANOV G P. On the crack growth owing to hydrogen embrittlement [J]. Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 1973, 5(4): 1041-1050.
[3] PRESSOUYRE G M. Trap theory of hydrogen embrittlement [J]. Acta Metallurgica, 1980, 28(7): 895-911.
[4] HASUI A. Friction welding of titanium and SUS304L austenitic stainless steel [J]. Welding International, 1990(10): 768-774.
[5] BRIANT C L, WANG Z F, CHOLLOCOOP N. Hydrogen embrittlement of commercial purity titanium [J]. Corrosion Science, 2002, 44: 1875-1888.
[6] ILYIN A A, POLKIN I S, MOAMONOV A M. Thermohydrogen treatment—The base of hydrogen technology of titanium alloys [C]// BLENKINSON P A, EVANS W J, FLOWER H M. Titanium 95: Science and Technology. UK: Cambridge University Press, 1996: 2462-2469.
[7] HAN Ming-chen. Thermohydrogen treatment of titanium alloys [J]. Aerospace Materials and Technology, 1999(1): 23-27.
[8] KOLACHEV B A, MALKOV A V, VOROBYOV I A. The effect of hydrogen alloying on workability of titanium alloys [C]// FROES F H, CAPLAN I L. Titanium’92: Science and Technology. Warrendale, PA, USA: TMS, 1993: 861-869.
[9] MAHAJAN Y, NADIV S, KERR W R. Studies of hydrogenation in Ti-6Al-4V alloy[J]. Scripta Metallurgica, 1979, 13(8): 695-699.
[10] SENKOV O N, FROES F H. Thermohydrogen processing of titanium alloys [J]. Int J Hydrogen Energy, 1999, 24: 565-576.
[11] ELIEZER D, ELIAZ N, SENKOV O N, FROES F H. Positive effects of hydrogen in metals [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2000, 280: 220-224.
[12] DING R, GUO Z X, WILSON A. Microstructural evolution of a Ti-6Al-4V alloy during thermomechanical processing [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2002, 327: 233-245.
[13] QAZI J I, SENKOV O N, RAHIM J, (Sam) FROES F H. Kinetics of martensite decomposition in Ti-6Al-4V-xH alloys [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2003, 359: 137-149.
[14] LUO Liang-shun, SU Yan-qing, GUO Jing-jie, FU Heng-zhi. Formation of titanium hydride in Ti-6Al-4V alloy [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2006, 425: 140-144.
[15] HUANG Gang, CAO Xiao-hua, LONG Xing-gui. Physical and chemical properties of titanium-hydrogen system [J]. Materials Review, 2006, 20(10): 128-131.
[16] SCHUR D V, ZAGINAICHENKO S Y. Phase transformations in titanium hydrides [J]. Int J Hydrogen Energy, 1996, 21(11/12): 1121-1124.
[17] XIN She-wei, ZHAO Yong-qing. Discussion about the heat treatment and precipitated phases of titanium alloy [J]. Transactions of Metal Heat Treatment, 2006, 31(9): 39-42. (in Chinese)
[18] ORIANI R A, JOSEOGUC P H. Equilibrium aspects of hydrogen-induced cracking of steels [J]. Acta Mettallurgica, 1974, 22: 1065-1074.
[19] HOU Hong-liang, LI Zhi-qiang, WANG Ya-jun, GUAN Qiao. Technology of hydrogen treatment for titanium alloy and its application prospect [J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metal, 2003, 13(3): 533-549. (in Chinese)
Foundation item: Project supported by the Great Foundation Research Project of National Security
Corresponding author: ZHAO Jing-wei; Tel: +86-24-83687746; E-mail: jwzhaocn@gmail.com
(Edited by YUAN Sai-qian)