DOI:10.19476/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2019.12.19
氰化黄铜矿表面活化剂的活化机理
邱廷省1, 2,严华山1,袁勤智1
(1. 江西理工大学 资源与环境工程学院,赣州341000;
2. 江西理工大学 江西省矿业工程重点实验室,赣州 341000)
摘 要:在氰化黄铜矿浮选试验的基础上,通过微量热法和X射线光电子能谱(XPS)研究次氯酸钠和焦亚硫酸钠对氰化黄铜矿的活化机理。结果表明:氰化黄铜矿不经活化难以浮选,而次氯酸钠和焦亚硫酸钠都对其具有明显的活化效果。丁基黄药在未经活化的氰化黄铜矿表面吸附时的表观活化能较高,而次氯酸钠和焦亚硫酸钠的作用可分别将丁基黄药在氰化黄铜矿表面吸附时的表观活化能减少76.64%和79.84%,大幅降低了捕收剂的吸附难度。次氯酸钠和焦亚硫酸钠的作用可大幅降低氰化黄铜矿表面的CuCN含量,并使表面S元素浓度分别升高43.83%和72.13%,显著改善氰化黄铜矿表面的硫亏损状态。
关键词:氰化渣;黄铜矿;微量热法;活化机理
文章编号:1004-0609(2019)-12-2860-08 中图分类号:TD952;TD923 文献标志码:A
氰化尾渣是氰化提金工艺中产生的尾渣。据统计,我国黄金矿山每年的氰化尾渣排放量达到2000万t以上[1]。巨量氰化尾渣的堆存不仅占用庞大土地面积,还造成了严重的环境污染问题。尾渣中残留的选矿药剂、氰化物以及重金属离子都严重破坏水体和土地质量[2-4]。同时,氰化尾渣中往往还残留有品位可观的金银以及铜、铅、锌、硫、铁等有价元素,如不加以回收利用,将造成严重的资源浪费。氰化尾渣的减量化、资源化和安全化研究已迫在眉睫。
虽然氰化尾渣中残留有数量可观的硫化矿矿物,但由于这些矿物颗粒细小,且在氰化提金过程中与氰化物长时间接触,其表面性质已经与新开采的矿物表面性质截然不同,导致其浮选回收难度大[5]。氰化物在硫化矿物表面化学吸附,另外还可溶解矿物表面的黄原酸盐薄膜,使其表面亲水而难以上浮[6-7]。许多学者对氰化尾渣中的有价元素的综合回收进行了探索[8-10],李正要等[11]对某氰化尾渣采用抑铜浮铅的浮选工艺流程回收铜、铅矿物,添加石灰抑制黄铁矿,利用残留氰化物抑制黄铜矿,浮铅尾矿以组合药剂NP作铜的活化剂,以FM作黄铁矿的抑制剂,以Z-200和丁胺黑药为铜的混合捕收剂,最终得到含铅45.24%的铅精矿和含铜19.28%的铜精矿。林俊领等[12]选用亚硫酸钠+硫酸锌为锌硫矿物的抑制剂,PAC为铜矿物的捕收剂,采用一粗一扫两精的流程,从氰化尾渣中浮选获得含铜15.27%、回收率80.55%的铜精矿。张亚莉等[13-14]开展了从氰化尾渣中回收有价铁的研究。杨秀丽等[15-16]进行了从氰化尾渣中浮选回收硫化铜锌矿的研究,并发现由于CN-在黄铜矿、铁闪锌矿表面的化学吸附而使其受到强烈抑制,而次氯酸钠、双氧水、焦亚硫酸钠和硫酸铜对其具有很好的活化作用。目前,氰化尾渣中有用硫化矿的回收利用研究主要为实践应用,而理论研究少见报道。
微量热法[17-18]是利用微热量热计研究热动力学规律的一种方法,它可连续、准确地监测和记录一个反应过程的热动力学曲线,原位、实时和无损地同时提供热力学和动力学信息,已在生物化学,物理化学,有机化学等许多领域广泛应用。早些年,有人利用微量热法测定了几种捕收剂在方铅矿、辉钼矿、黄铁矿等硫化矿表面吸附热[19-21]。近年来,陈建华等[22]采用微量热法研究了黄药、黑药和硫氮在方铅矿、黄铁矿表面的吸附,发现黑药和硫氮在两种矿物表面的吸附热和吸附动力学参数差异很大,而黄药则差异较小,认为在进行两种矿物的浮选分离时,黑药和硫氮要比黄药具有更好的选择性。赵翠华等[23]利用密度泛函理论和微量热法研究了水在矿物表面的吸附。计算结果表明,方铅矿和辉钼矿是疏水性的,而黄铁矿和闪锌矿是亲水的。热动力学分析表明,吸附热大小呈黄铁矿、闪锌矿、方铅矿和辉钼矿依次降低,与计算结果吻合较好,闪锌矿表面水分吸附量大于黄铁矿表面。蓝丽红等[24]采用微量热法对纯方铅矿和合成的六种不同掺杂方铅矿表面吸附黄药的过程进行了研究,结果表明含杂质方铅矿的吸附热与浮选回收率成正比关系。陈家玮等[25-26]用微量热法研究了几种矿物的溶解反应规律。目前,微量热法在选矿理论研究中的应用还不多,且这些研究都只是简单地对反应热效应、速率常数和反应级数等参数进行分析,并未进一步对反应活化能进行研究。
本文作者以实验室模拟氰化浸金工艺制得的受到氰化物长时间作用而被强烈抑制的黄铜矿(简称“氰化黄铜矿”)为研究对象,采用次氯酸钠、焦亚硫酸钠为活化剂,在单矿物浮选试验的基础上,通过微量热法和XPS等分析测试方法,考察氰化黄铜矿活化前后的浮选和活化行为,并从捕收剂在矿物表面吸附过程的热力学以及矿物表面改性的角度揭示其活化机理。
1 实验
1.1 实验材料
试验所用黄铜矿单矿物取自江西某矿山,矿样纯度为98.58%,其XRD谱如图1所示。试验所用氰化黄铜矿样品是在实验室模拟氰化浸金工艺制得,制取方法如下:以1:9的固液比例将黄铜矿样品与0.8%的氰化钠溶液加入密封的烧杯中,在pH值为12,转速为1200 r/min条件下搅拌24 h,过滤后真空干燥。

图1 黄铜矿单矿物的XRD谱
Fig. 1 XRD pattern of chalcopyrite monomineral
试验所用次氯酸钠、焦亚硫酸钠活化后的黄铜矿样品制取方法如下,取若干氰化黄铜矿样品置于XFG-Ⅱ浮选机的40 mL有机玻璃槽中,分别加入适量的3 mL/L的次氯酸钠溶液、1.5×10-3 mol/L的焦亚硫酸钠溶液,在pH值为10、转速为1800 r/min条件下搅拌6 min,过滤后真空干燥。
丁基黄药,纯度大于95%,实验室自制;次氯酸钠、焦亚硫酸钠、氢氧化钠、氰化钠,分析纯,2#油,工业纯,国药集团化学试剂有限公司。
1.2 单矿物浮选
单矿物浮选试验在XFG-Ⅱ浮选机(吉林探矿机械厂)的40 mL有机玻璃槽中进行。每次试验用2 g矿样,用超声波清洗矿样后置于浮选槽内,依次添加蒸馏水、pH调整剂、活化剂、捕收剂及起泡剂并搅拌,搅拌时间为1、2、3、3和2 min后,人工刮泡浮选4 min。将所得泡沫产品及槽内尾矿过滤、晾干、称取质量,按质量百分比计算回收率。
1.3 微量热法
在RD496-2000型微热量热计(中国工程物理研究院)上完成了测量温度分别为298.15、301.15、304.15 K的量热试验,量热常数分别为66.67、66.38、66.27 μV/mW。微热量热计由量热炉体(包括量热容器、热电堆以及温度控制等功能部件组成)、测控仪(包括数据采集和控制量输出以及通讯接口等部分)、计算机(包括控制软件和数据处理软件)以及配件工具等构成。
量热炉体的测量部分由两个相同的热电堆组成,分别放置量热反应池与参考反应池。为尽可能消除其它干扰,试验中取两个反应池热效应之差作为所测反应过程的热效应。图2所示为量热反应池示意图。量热反应池准备步骤如下:取0.03 g矿样和1 mL蒸馏水置于一根玻璃外管中,往一根玻璃内管中加入适量捕收剂溶液,将玻璃内管放入玻璃外管中,随后将它们放入一根不锈钢管内,盖上有孔上端盖后,以孔用弹性挡圈紧固,将带有按压手柄与弹簧的钢针由上端盖的孔中插入玻璃内管中并调整好钢针的位置。参考反应池的玻璃内管中也为捕收剂溶液,而玻璃外管中则不加入矿物样品,其余准备步骤与量热反应池一致。这样进行试验时即可消除捕收剂溶液的稀释、玻璃内管被捅破以及两部分溶液混合等过程所产生的热效应的干扰。

图2 量热反应池示意图
Fig. 2 Schematic diagram of reaction cell of microcalorimeter
将准备好的两个反应池在量热炉体中放好之后,将实验室的温度恒温至20 ℃并设置好量热参数,等待基线稳定后,同时并快速地按压两个反应池的钢针,两个反应池中的玻璃内管即被捅破,捕收剂在矿物表面的吸附反应开始进行,两个反应池热效应差由测控仪转变为电信号被计算机记录下来并实时地呈现出量热曲线。
1.4 XPS测试
采用型号为ESCALAB 250的光电子能谱仪(Thermo Fisher Scientific Co., USA)进行矿样的XPS光谱测试,X射线源为单色化的Al Kα源,工作电压为12 kV,分析室真空度为2×10-7 Pa(打开X射线源的情况下),仪器误差为± 0.2 eV。测试样品的制取方法如下:取0.5g矿样置于试管中,加入适量的蒸馏水,用超声波清洗器震荡5 min后过滤,在40 ℃环境中真空干燥。
2 结果与分析
2.1 氰化黄铜矿的浮选行为
为研究氰化黄铜矿活化前后的浮选行为,并确定后续量热试验时所用丁基黄药溶液的浓度,详细考察了丁基黄药、次氯酸钠和焦亚硫酸钠对氰化黄铜矿浮选行为的影响,试验结果如图3所示。
由图3(a)可知,黄铜矿已被氰化钠强烈抑制,不经活化几乎很难上浮,其浮选回收率最高仅为25.34%。随着丁基黄药用量的增加,捕收剂吸附于更多的黄铜矿表面,因而其回收率逐渐升高;当用量超过1×10-4 mol/L后,丁基黄药已在黄铜矿表面基本达到饱和吸附,故继续增加用量也无法提高其回收率。综合以上分析,以浓度为1×10-4 mol/L的丁基黄药溶液进行量热试验较为合适。
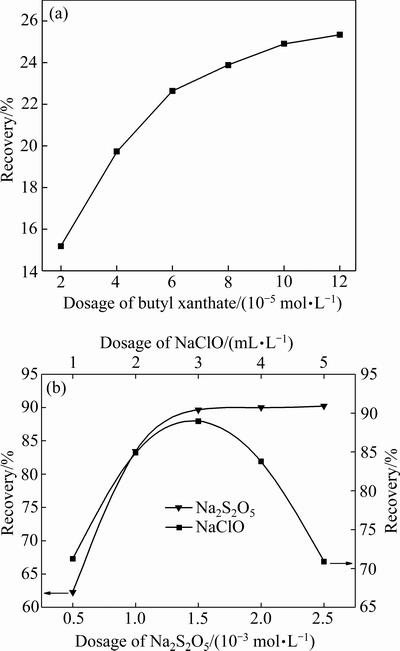
图3 丁基黄药用量和活化剂用量对氰化黄铜矿回收率的影响
Fig. 3 Effects of butyl xanthate(a) and activator(b) dosages on recovery of cyanide chalcopyrite
次氯酸钠为强氧化剂,当其用量较低时可优先对CN-起氧化作用[15],由图3(b)可看出,随着次氯酸钠用量的增加,受氰化黄铜矿表面的CN-被去除而露出新鲜矿物表面,因而黄铜矿回收率迅速升高。当次氯酸钠用量超过3 mL/L时,次氯酸钠开始将黄铜矿表面的低价态硫氧化为高价态硫,导致黄铜矿表面亲水,其浮选回收率急剧降低。次氯酸钠活化浮选时的最大回收率为88.9%。
焦亚硫酸钠水解生成的 可将CN-氧化为CNO-,破坏CN-的化学吸附,另一方面它亦可将S2-氧化为单质S,增强氰化黄铜矿表面的疏水性,从而起活化效果[16]。由图3(b)可知,随着焦亚硫酸钠用量的增加,氰化黄铜矿浮选回收率呈大幅升高的趋势,当焦亚硫酸钠用量大于1.5×10-3 mol/L时,黄铜矿浮选回收率达89.6%并保持平稳。
可将CN-氧化为CNO-,破坏CN-的化学吸附,另一方面它亦可将S2-氧化为单质S,增强氰化黄铜矿表面的疏水性,从而起活化效果[16]。由图3(b)可知,随着焦亚硫酸钠用量的增加,氰化黄铜矿浮选回收率呈大幅升高的趋势,当焦亚硫酸钠用量大于1.5×10-3 mol/L时,黄铜矿浮选回收率达89.6%并保持平稳。
次氯酸钠和焦亚硫酸钠对氰化黄铜矿都具有很好的活化效果,其中焦亚硫酸钠的活化效果略好于次氯酸钠。
2.2 丁基黄药在氰化黄铜矿表面吸附的热力学分析
捕收剂与目的矿物作用的难易及强弱程度是矿物浮选过程的关键,作者采用对热效应十分灵敏的微热量热计监测并记录捕收剂在氰化黄铜矿表面吸附的过程,旨在从热力学角度阐释次氯酸钠和焦亚硫酸钠活化浮选氰化黄铜矿的机理。
2.2.1 量热曲线
用微热量热计分别记录了丁基黄药在不同活化程度的氰化黄铜矿表面吸附过程的量热曲线(见图4)。图4中,横坐标轴为时间,表示吸附过程时间长短;纵坐标轴为热电势,代表吸附过程的瞬时热量大小;量热曲线与t轴所围的积分面积则代表整个吸附过程所放出的总量热值,也就是吸附热(Q);此外,一般而言量热曲线为正时代表所测反应为放热过程,反之则为吸热过程。
图4中所有量热曲线为正值,这表明丁基黄药的吸附是一个放热过程;相同的吸附条件下,随着测量温度的升高,丁基黄药吸附的量热曲线整体向左移(即反应时间缩短),峰的面积减小,意味着反应速率增大而吸附热减少。此外,与未经活化的氰化黄铜矿相比,丁基黄药在经两种活化剂作用后的氰化黄铜矿表面的吸附热有明显的增加。这表明这两种活化剂已经大幅度消除了氰化黄铜矿表面的CN-,使其显露出新鲜疏水表面。
2.2.2 热力学参数
根据文献[23, 27]叙述的方法,对图4中的量热曲线进行处理,通过相关公式即可求得丁基黄药在不同黄铜矿表面吸附过程对应的热力学参数,见表1。
表1中:T为测量温度;Q为吸附热;lnA为指前因子;Ea为表观活化能;r为相关系数。表1中所有相关系数均较接近于1,计算结果较为可靠。
某个反应的活化能值可表征发生该反应的难易程度,一般而言,活化能值越小意味着该反应越容易发生。由表1可知,活化剂作用前后,丁基黄药在氰化黄铜矿表面吸附的表观活化能大小有明显的差异,丁基黄药在氰化黄铜矿、次氯酸钠作用的氰化黄铜矿以及焦亚硫酸钠作用的氰化黄铜矿表面吸附的表观活化能分别为164.96、38.54、33.26 kJ/mol,意味着丁基黄药的吸附难度依次降低,因而黄铜矿的可浮性依次升高。经次氯酸钠、焦亚硫酸钠作用后,丁基黄药在氰化黄铜矿表面吸附的表观活化能分别降低了76.64%和 79.84%,这说明次氯酸钠和焦亚硫酸钠都能大幅降低丁基黄药在氰化黄铜矿表面吸附的难度,从而起到活化作用。
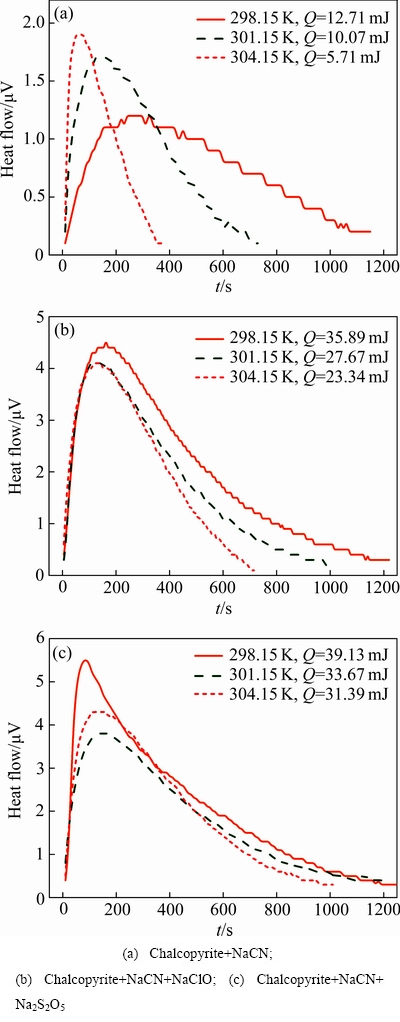
图4 丁基黄药在氰化黄铜矿表面吸附过程的量热曲线
Fig. 4 Caloric curves of butyl xanthate adsorption on surface of cyanide chalcopyrite
表1 丁基黄药在黄铜矿表面吸附过程的热力学参数
Table 1 Thermodynamic parameters of butyl xanthate adsorption on surfaces of cyanide chalcopyrite

2.3 氰化黄铜矿表面的XPS分析
为查明氰化黄铜矿活化前后的表面性质变化,对活化前的氰化黄铜矿,以及分别被次氯酸钠和焦亚硫酸钠活化后的氰化黄铜矿表面进行了XPS测试,其XPS全谱图、Cu元素窄谱图及元素浓度分别见图6、图7和表2。
2.3.1 XPS全谱图
图5中,氰化黄铜矿表面的XPS全谱图中电子结合能位于160、710、930 eV附近处的峰分别为S 2p、Fe 2p、Cu 2p元素的特征峰;可以看到在电子结合能位于285、530 eV附近处均分别出现了明显的C 1s、O 1s元素的特征峰,这要归因于测试过程的碳、氧污染,并不一定表明矿样原本含碳、氧。此外,氰化黄铜矿表面的XPS全谱图在电子结合能为400 eV附近处都出现有N 1s元素的特征峰,但相比于活化前的氰化黄铜矿,经过两种活化剂作用后的氰化黄铜矿表面的N 1s元素特征峰已大幅减弱,几乎很难看出。这表明次氯酸钠和焦亚硫酸钠均可消除氰化黄铜矿表面大量化学吸附的CN-,而起活化作用。

图5 氰化黄铜矿表面的XPS全谱图
Fig. 5 XPS full spectra of surface of cyanide chalcopyrite
2.3.2 Cu元素窄谱图
图6中,氰化黄铜矿表面的Cu元素窄谱图中电子结合能位于931.8、932.5、933.1 eV附近处的峰分别为CuFeS2、CuS、CuCN中的Cu特征峰。
由图6(a)可知,氰化黄铜矿表面的Cu元素主要形式为CuFeS2与CuCN,CuCN的峰面积甚至高于CuFeS2的峰面积,这表明CuCN是CN-化学吸附在黄铜矿表面的主要产物。另外,氰化黄铜矿表面还存在少量CuS。由图6(b)和(c)可以看出,次氯酸钠、焦亚硫酸钠活化后的氰化黄铜矿表面Cu的主要形式均为CuFeS2,部分为CuCN,少量的为CuS;且相比于活化前的氰化黄铜矿表面,经过两种活化剂的作用后的氰化黄铜矿表面的CuFeS2峰面积大幅增加,而CuCN峰面积则大幅度减少。CuCN峰面积由大到小依次为氰化黄铜矿、次氯酸钠活化后的氰化黄铜矿、焦亚硫酸钠活化后的氰化黄铜矿,这与它们的可浮性规律相符。
2.3.3 表面元素情况
表2中,由于CuCN的大量存在,氰化黄铜矿表面S元素浓度仅18.73%,而N元素浓度则高达7.63%;经过次氯酸钠、焦亚硫酸钠的作用后,黄铜矿表面S元素浓度分别升高至26.94%、32.24%,相对于活化前的增幅分别达43.83%、72.13%,而N元素浓度则分别大幅降低为0.83%、0.71%。
纯黄铜矿表面的元素比率应为n(Cu):n(Fe):n(S)= 1:1:2,由表2可知,氰化黄铜矿表面元素比率n(Cu):n(Fe):n(S)=1:0.6:1.07,呈现为严重的硫亏损状态,这不利于捕收剂在其表面的吸附;而经过次氯酸钠、焦亚硫酸钠的作用后,氰化黄铜矿表面元素比Cu、Fe与S的摩尔比分别变为1:0.86:1.83、1:0.94:1.91,这更接近于纯黄铜矿表面的元素比。
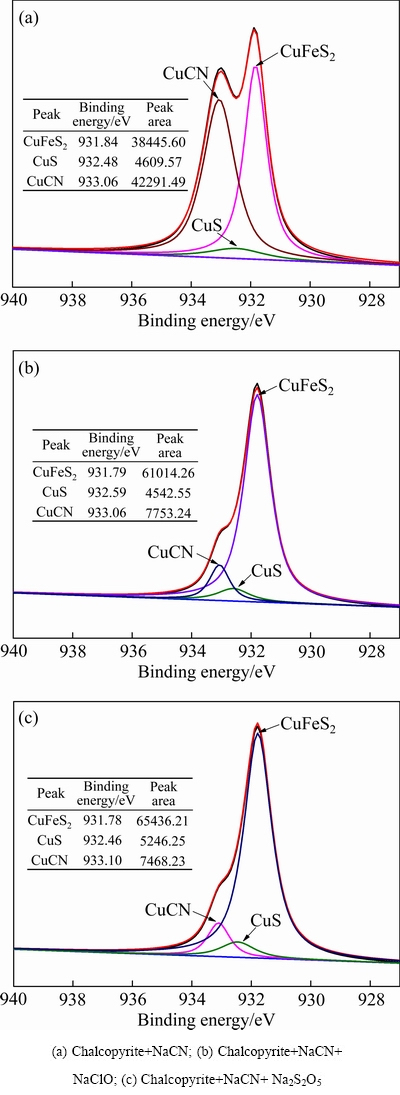
图6 氰化黄铜矿表面的Cu元素窄谱图
Fig. 6 Narrow spectra of Cu on surfaces of cyanide chalcopyrite
两种活化剂都能有效消除氰化黄铜矿表面CN-而增加S元素浓度,并大幅改善黄铜矿表面严重硫亏损的状态,其中焦亚硫酸钠效果要略好于次氯酸钠。
表2 氰化黄铜矿表面的元素浓度及比率
Table 2 Concentration and ratio of elements on surfaces of cyanide chalcopyrite

3 结论
1) 氰化黄铜矿未经活化时很难上浮,次氯酸钠和焦亚硫酸钠对氰化黄铜矿都具有明显的活化效果。
2) 丁基黄药在氰化黄铜矿表面的吸附为放热过程;丁基黄药在未经活化的氰化黄铜矿表面吸附时,吸附热较小而表观活化能较高;经次氯酸钠和焦亚硫酸钠分别作用后,丁基黄药的吸附热明显增加,且表观活化能分别降低了76.64%和79.84%,这表明次氯酸钠和焦亚硫酸钠都能大幅降低丁基黄药在氰化黄铜矿表面吸附的难度,从而起活化作用。
3) XPS分析表明,氰化黄铜矿表面存在大量的CuCN,呈严重的硫亏损状态,不利于捕收剂的吸附因而被抑制;次氯酸钠和焦亚硫酸钠的作用可大幅降低氰化黄铜矿表面的CuCN含量,并使表面S元素浓度分别升高43.83%和72.13%,显著改善了氰化黄铜矿表面的硫亏损状态,从而大大恢复了氰化黄铜矿的可浮性。
REFERENCES
[1] 李 婷, 尹艳芬, 方夕辉, 邱廷省. 从金氰化尾渣中回收铜、铅、锌、硫的工艺技术现状[J].现代矿业, 2011, 27(4): 28-29.
LI Ting, YIN Yan-fen, FANG Xi-hui, QIU Ting-sheng. Technological status of recovering copper, lead, zinc, sulfur from gold cyaniding tailings[J]. Modern Mining, 2011, 27(4): 28-29.
[2] LAITOS J G. Cyanide, mining, and the environment[J]. Pace Environmental Law Review, 2013, 30(3): 869-1278.
[3] DONATO D, NICHOLS O, POSSINGHAM H, MOORE M, RICCI P, NOLLER B. A critical review of the effects of gold cyanide-bearing tailings solutions on wildlife[J]. Environ. Int., 2007, 33(7): 974-984.
[4] MUDDER T, BOTZ M. Cyanide and society: A critical review[J]. European Journal of Mineral Processing and Environmental Protection, 2004, 4(1): 62-74.
[5] 吕翠翠, 丁 剑, 付国燕, 刘 娅, 鲁永刚, 钱 鹏, 叶树峰. 氰化尾渣中有价元素回收现状与展望[J]. 化工学报, 2016, 67(4): 1079-1089.
Lü Cui-cui, DING Jian, FU Guo-yan, LIU Ya, LU Yong-gang, QIAN Peng, YE Shu-feng. Present situation and prospect of recovering valuable elements from cyanidation tailing[J]. Journal of Chemical Industry and Engineering, 2016, 67(4): 1079-1089.
[6] GUO Bao, PENG Yong-jun, RODOLFO E G. Cyanide chemistry and its effect on mineral flotation[J]. Minerals Engineering, 2014, 66/68: 25-32.
[7] 赵洪冬, 顾帼华. 氰化尾渣综合回收铜铅锌研究现状及展望[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2013, 34(5): 1-4.
ZHAO Hong-dong, GU Guo-hua. Status and prospect of research on comprehensive recovering copper, lead and zinc from cyaniding residues[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2013, 34(5): 1-4.
[8] 刘春龙. 银矿氰渣多金属综合回收试验研究[J]. 有色金属(选矿部分), 2016, 68(3): 38-42.
LIU Chun-long. Comprehensive polymetallic recovery from silver cyanide slag[J]. Nonferrous Metals (Mineral Processing Section), 2016, 68(3): 38-42.
[9] 谢 昆, 邹 尚, 陈 俊, 彭 竣. 氰化尾渣中金的回收及无害化处理试验研究[J]. 黄金, 2016, 37(11): 58-61.
XIE Kun, ZOU Shang, CHEN Jun, PENG Jun. Experimental study on recovering gold from cyanidation tailings and biosafety disposal[J]. Gold, 2016, 37(11): 58-61.
[10] 杨俊彦, 陈 萍, 徐兴保, 李雪林, 范凌雯, 徐忠敏. 胶东地区低品位氰化尾渣中铜铅锌综合回收利用研究[J]. 黄金, 2016, 37(2): 68-71.
YANG Jun-yan, CHEN Ping, XU Xing-bao, LI Xue-lin, FAN Ling-wen, XU Zhong-min. Experimental research on comprehensive recovery of copper, lead and zinc from low grade cyanide tailings in Jiaodong region[J]. Gold, 2016, 37(2): 68-71.
[11] 李正要, 汪 莉, 于艳红, 魏鹏程. 金精矿氰化尾渣铅和铜的回收[J]. 北京科技大学学报, 2009, 31(10): 1231-1234.
LI Zheng-yao, WANG Li, YU Yan-hong, WEI Peng-cheng. Recovery of lead and copper from cyanide tailings[J]. Journal of University of Science and Technology Beijing, 2009, 31(10): 1231-1234.
[12] 林俊领, 李增华, 卢冀伟, 王奉水, 李艳军. 新疆某金矿氰化尾渣回收铜的试验研究[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2013, 34(2): 28-32.
LIN Jun-ling, LI Zeng-hua, LU Ji-wei, WANG Feng-shui, LI Yan-jun. Research on recovering copper from cyanide tailing of a gold ore in Xinjiang[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2013, 34(2): 28-32.
[13] 张亚莉, 于先进, 李小斌, 张丽鹏, 李德刚. 氰化渣磁化焙烧过程中铁化合物反应行为的热力学分析[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2011, 42(12): 3623-3629.
ZHANG Ya-li, YU Xian-jin, LI Xiao-bin, ZHANG Li-peng, LI De-gang. Thermodynamics analysis of ferric compound during roasting-preparing process of cyanide tailings[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2011, 42(12): 3623-3629.
[14] ZHANG Ya-li, LI Huai-mei, YU Xian-jin. Fe extraction from high-silicon and aluminum cyanide tailings by magnetic separation pretreatment of water leaching before magnetic separation[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2013, 23(4): 1165-1173.
[15] YANG Xiu-li, HUANG Xiong, QIU Ting-sheng. Recovery of zinc from cyanide tailings by flotation[J]. Minerals Engineering, 2015, 84: 100-105.
[16] 杨秀丽, 黄 雄, 邱廷省. 焦亚硫酸钠在氰化尾渣中硫化铜锌矿表面的活化作用[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2016, 26(9): 1982-1989.
YANG Xiu-li, HUANG Xiong, QIU Ting-sheng. Activation of sodium metabisulfite on surfaces of copper-zinc sulfide ore in cyanidation tailings[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2016, 26(9): 1982-1989.
[17] 陈家玮, 鲍征宇. 量热学和热动力学研究进展概况[J]. 地质通报, 2007, 26(12): 1564-1568.
CHEN Jia-wei, BAO Zheng-yu. Advances in the calorimetry and the thermokinetic study[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2007, 26(12): 1564-1568.
[18] 杨 奇, 陈三平, 谢 钢, 刘向荣, 刘明艳, 朱之轮, 贾青生, 高胜利. RD496微热量计的研制及其应用[J]. 中国科学: 化学, 2014, 44(6): 889-914.
YANG Qi, CHEN San-ping, XIE Gang, LIU Xiang-rong, LIU Ming-yan, ZHU Zhi-lun, JIA Qing-sheng, GAO Sheng-li. Development and application of RD496 microcalorimeter[J]. Scientia Sinica Chimica, 2014, 44(6): 889-914.
[19] MELLGREN O. Heat of adsorption and surface reactions of potassium ethyl xanthate on galena[J]. Transactions Society of Mining Engineers, 1966, 235: 46-59.
[20] HAUNG H H, MILLER J D. Kinetics and thermochemistry of amyl xanthate adsorption by pyrite and marcasite[J]. International Journal of Mineral Processing, 1978, 5(3): 241-266.
[21] MAIER G S, QIU X, DOBIAS B. New collectors in the flotation of sulphide minerals: A study of the electrokinetic, calorimetric and flotation properties of sphalerite, galena and chalcocite[J]. Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 1997, 122: 207-225.
[22] CHEN Jian-hua, LAN Li-hong, CHEN Ye. Computational simulation of adsorption and thermodynamic study of xanthate, dithiophosphate and dithiocarbamate on galena and pyrite surfaces[J]. Mineral Engineering, 2013, 46/47: 136-143.
[23] ZHAO Cui-hua, CHEN Jian-hua, LONG Xian-hao, GUO Jin. Study of H2O adsorption on sulfides surfaces and thermokinetic analysis[J]. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 2014, 20(2): 605-609.
[24] LAN Li-hong, CHEN Jian-hua, LI Yu-qiong, LAN Ping, YANG Zhuo, AI Guang-yong. Microthermokinetic study of xanthate adsorption on impurity-doped galena[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2016, 25(1): 272-281.
[25] CHEN Jia-wei, BAO Zheng-yu, MEI Yan-Ping. Experimental study on mineral dissolution reaction by microcalorimetry[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 2007, 26(S1): 496-497.
[26] 刘祥文, 陈家玮, 鲍征宇. 几种矿物溶解热动力学与晶体缺陷的关系[J]. 电子显微学报, 2002, 21(5): 751-752.
LIU Xiang-wen, CHEN Jia-wei, BAO Zheng-yu. The relation between the dissolution thermokinetics of some minerals and their crystal defects[J]. Journal of Chinese Electron Microscopy Society, 2002, 21(5): 751-752.
[27] 高胜利, 陈三平, 胡荣祖, 李焕勇, 史启祯. 化学反应的热动力学方程及其应用[J]. 无机化学学报, 2002, 18(4): 362-366.
GAO Sheng-li, CHEN San-ping, HU Rong-zu, LI Huan-yong, SHI Qi-zheng. Derivation and application of thermodynamic equations[J]. Chinese Journal of Inorganic Chemistry, 2002, 18(4): 362-366.
Activation mechanism of activator on cyanide chalcopyrite surfaces
QIU Ting-sheng1, 2, YAN Hua-shan1, YUAN Qin-zhi1
(1. Faculty of Resource and Environmental Engineering, Jiangxi University of Science and Technology, Ganzhou 341000, China;
2. Jiangxi Key Laboratory of Mining Engineering, Jiangxi University of Science and Technology, Ganzhou 341000, China)
Abstract: Based on the monomineral flotation test, the activation mechanism of chloros and sodium metabisulfite on cyanide chalcopyrite surfaces was investigated by microcalorimetry and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS).The results show that the cyanide chalcopyrite is difficult to be floated without activation, and it can be effectively activated by chloros and sodium metabisulfite. When the butyl xanthate is adsorbed on the cyanide chalcopyrite surfaces before activation, the apparent activation energy is higher. After the treatment with chloros and sodium metabisulfite, the apparent activation energy decreases by 76.64% and 79.84%, respectively, which is beneficial to the adsorption of collectors. The effect of chloros and sodium metabisulfite can significantly reduce the CuCN content on the surface of cyanide chalcopyrite and increase the S concentration by 43.83% and 72.13%, respectively, which significantly improves the sulfur loss on the surface of cyanide chalcopyrite.
Key words: cyanide tailings; chalcopyrite; microcalorimetry; activation mechanism
Foundation item: Project(51474114) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China
Received date: 2017-11-01; Accepted date: 2019-11-09
Corresponding author: QIU Ting-sheng; Tel: +86-797-8312008; E-mail: qiutingsheng@163.com
(编辑 李艳红)
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(51474114)
收稿日期:2017-11-01;修订日期:2019-11-09
通信作者:邱廷省,教授,博士;电话:0797-8312008;E-mail:qiutingsheng@163.com