定向凝固藕状多孔Si的孔结构
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2014年第11期
论文作者:杨倩倩 刘 源 李言祥 张 言
文章页码:3517 - 3523
关键词:藕状多孔Si;凝固速率;氢气压力;过热度;孔长度
Key words:lotus-type porous silicon; solidification speed; hydrogen pressure; superheat degree; pore length
摘 要:采用定向凝固的方法,在一定的氢压条件下制备具有长孔结构的藕状多孔Si。通过调整凝固速率和氢气压力,铸锭的孔隙率、孔径和孔长度能够得到有效控制。实验结果表明:当其他条件不变时,铸锭的面孔隙率几乎不随凝固速率发生变化,但随着氢气压力的增加而逐渐降低。采用理论模型获得的不同氢压条件下制备出的铸锭体孔隙率预测结果与实验结果吻合较好。随着凝固速率和氢气压力的降低,铸锭的平均孔长度和孔径均逐渐增加,长径比则基本保持不变。通过将熔体的过热度从200 K提高到300 K,制备得到的试样其平均孔径增加约0.3 mm,平均孔长度从7 mm提高至24 mm,平均长径比则由8提高至20。
Abstract: Lotus-type porous silicon with elongated pores was fabricated by unidirectional solidification under pressurized hydrogen. Porosity, pore diameter, and pore length can be adjusted by changing solidification speed and hydrogen pressure. The porosity of the ingot is nearly constant under different solidification speeds, but decreases with the increase of hydrogen pressure. The overall porosities of ingots fabricated at different hydrogen pressures were evaluated through a theoretical model. Findings are in good agreement with experimental values. The average pore diameter and pore length increase simultaneously while the average pore aspect ratio changes slightly with the decreases of solidification speed and hydrogen pressure. The average pore length is raised from 7 to 24 mm and the pore aspect ratio is raised from 8 to 20 respectively with the average pore diameter promoted by about 0.3 mm through improving the superheat degree of the melt from 200 to 300 K.
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 24(2014) 3517-3523
Qian-qian YANG1, Yuan LIU1,2, Yan-xiang LI1,2, Yan ZHANG1
1. School of Materials Science and Engineering, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China;
2. Key Laboratory for Advanced Materials Processing Technology, Ministry of Education, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China
Received 12 December 2013; accepted 28 April 2014
Abstract: Lotus-type porous silicon with elongated pores was fabricated by unidirectional solidification under pressurized hydrogen. Porosity, pore diameter, and pore length can be adjusted by changing solidification speed and hydrogen pressure. The porosity of the ingot is nearly constant under different solidification speeds, but decreases with the increase of hydrogen pressure. The overall porosities of ingots fabricated at different hydrogen pressures were evaluated through a theoretical model. Findings are in good agreement with experimental values. The average pore diameter and pore length increase simultaneously while the average pore aspect ratio changes slightly with the decreases of solidification speed and hydrogen pressure. The average pore length is raised from 7 to 24 mm and the pore aspect ratio is raised from 8 to 20 respectively with the average pore diameter promoted by about 0.3 mm through improving the superheat degree of the melt from 200 to 300 K.
Key words: lotus-type porous silicon; solidification speed; hydrogen pressure; superheat degree; pore length
1 Introduction
Porous and foamed materials have been widely used in aerospace, automotive, shipbuilding, and biomedical industries because of their characteristics that differ from those solid ones, such as lower density, larger specific surface area and energy absorption performance [1,2]. As a new type of porous materials, lotus-type porous metal (or semiconductor) with long cylindrical pores aligned in one direction has elicited much attention [3-7]. This material is fabricated by a unidirectional solidification method [8] based on the solubility difference of gas between liquid and solid phases, which is also called Gasar process [9]. This method is believed to be revolutionary because the pore structure could be well controlled by adjusting the processing parameters [10,11].
Compared with the traditional porous materials, lotus-type porous metal (or semiconductor) presents unique thermal performance. As the heat dissipation problem has become a major problem which restricts the development of electronic chips and powered devices towards high integration and miniaturization, a high heat transfer system is in urgent need. Lotus-type porous structure is expected to exhibit prospective cooling performance with smoother inner surface of the pore, smaller pressure drop and higher effective thermal conductivity as a special kind of micro channel structure [12,13]. OGUSHI et al [14,15] and ZHANG et al [16] have tested the heat transfer coefficient of lotus-type porous copper and the maximum value of 9 W/(cm2·K) was obtained. In view of the high thermal conductivity, lotus-type porous silicon is a potential candidate for high performance heat sink system with much lower thermal expansion coefficient and density than copper.
So far, numerous efforts have been made to fabricate lotus-type porous materials. ZHANG et al [17] has established the pressure condition of hydrogen for obtaining uniform porous structure. IDE et al [18] successfully fabricated porous aluminum by continuous casting technique with extremely low solidification speed of 0.5 to 0.9 mm/min, while the mold casting process merely obtained spherical pores [19]. In contrast, the regular porous stainless steel [20] was fabricated by continuous zone melting technique at a higher solidification speed instead of mold casting method which only gained the coarse ellipsoidal pores owing to the lower thermal conductivity. PARK et al [21] also found that a critical solidification speed should be achieved to produce regular porous copper with long cylindrical pores. These experiments all indicate that solidification speed is a crucial parameter for producing uniform porous structures. Lotus-type porous silicon has been fabricated by NAKAHATA et al [22] under different pressure conditions. In their study, a series of porous silicons with porosity of 34% to 10% and pore size ranging from 1 mm to 10 μm were obtained. Nevertheless, the pore length was no more than 2 mm which was too short to be used in the heat sink system. According to the above analysis, inappropriate solidification speed may be the major reason for the short pores.
In this work, we firstly attempted to fabricate lotus-type porous silicon by unidirectional solidification method at different solidification speeds. The hydrogen pressure and superheat degree of the melt were also changed based on the proper solidification speed. Their effects on the pore structure, especially on the average pore length and pore aspect ratio were studied systematically. The porous silicon with an average pore length of 24 mm and a pore aspect ratio of 20 was fabricated successfully, which provided the structural foundation for the application of lotus-type porous silicon as heat sink system in the engineering field.
2 Experimental
Figure 1 shows the schematic drawing of a unidirectional solidification apparatus with an induction melting component. The apparatus consists of three parts: vacuum system, melting part, and solidification part. Pure silicon chips (99.99%, mass fraction) were melted in a graphite crucible (100 mm in inside diameter and 240 mm in height) surrounded by induction heating coils in vacuum. After melting, hydrogen was introduced into the vacuum chamber. The molten silicon was held in hydrogen atmosphere for 600 s to uniformly dissolve the hydrogen in the melt. Then, the melt was poured into the graphite solidification mold whose bottom was cooled with circulating water and solidified upward.
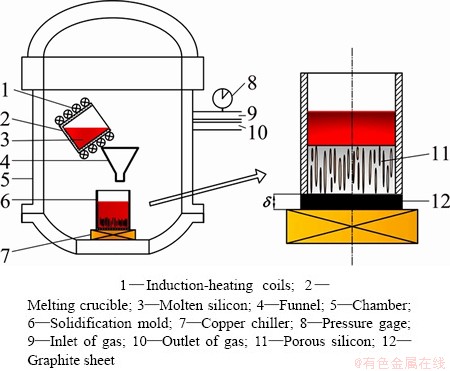
Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of solidification apparatus for lotus-type porous silicon
The thickness of the graphite sheet (δ in Fig. 1) between the mold and the copper chiller was set as 2, 5, and 15 mm, while the hydrogen pressure (pH2) was 0.2 MPa. When δ=15 mm, hydrogen pressure was changed from 0.1 to 0.4 MPa. Furthermore, a higher superheat degree (△T) of the melt (which was about 300 K, whereas those of others were 200 K) was adopted to fabricate the porous silicon when pH2=0.2 MPa and δ=15 mm. Meanwhile, a layer of boron nitride coating was used on both the upper and lower surfaces of the graphite solidification mold to further decrease the solidification speed during the experiments. The ingots obtained were about 100 mm in diameter and 120 to 150 mm in height depending on the porosity.
The porous silicon ingots were cut using a spark-erosion wire-cutting machine. Each ingot was firstly sectioned into two parts along the center axis. Then, one part was cut into several pieces perpendicular to the pore axis direction at heights of 20, 40, and 60 mm. Each section was polished with a series of emery papers. Pore structure images in both directions perpendicular and parallel to the pore axis direction were obtained by a scanner. The porosity (εf) and average pore diameter (D) of each cross-section were measured through an image analysis system. Overall porosity εb was evaluated using the following expression based on Archimedes’ principle:
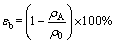 (1)
(1)
where ρA and ρ0 are the density of the porous silicon and the solid nonporous silicon, respectively. For the sample fabricated at △T=200 K, A rectangular specimen with dimensions of 30 mm (length)×20 mm (width)×30 mm (height, 40 mm for △T=300 K) was cut off at the height of 25 to 55 mm (20 to 60 mm for △T=300 K) along the pore axis direction from each ingot. Slices were cut off every 2 mm height from the top of the rectangular sample. The average pore length of each ingot was obtained by measuring the number of penetrating pores and the pore length at different solidification heights.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Pore morphology
Figures 2 and 3 show the longitudinal and cross-sectional views of the lotus-type porous silicon fabricated by mold casting technique under different thicknesses of graphite sheet (different solidification speeds, Fig. 2) and hydrogen pressures (Fig. 3). The thickness of the graphite sheet (δ) has remarkable influence on the pore morphology of porous silicon. Overall, a higher δ leads to lower average solidification speed and bigger pore diameter. With increasing thickness of the graphite sheet, the pores grow longer and smoother. A uniform pore size from the bottom to the top of the sample is only achieved at the lowest solidification speed (i.e., for a graphite sheet thickness of 15 mm). With increasing hydrogen pressure, the pores grow smaller due to the increase of growth resistance. In addition, the pore size changes periodically along the pore axis direction when pH2=0.1 MPa, indicating the existence of a periodical fluctuation of solute content in the melt ahead of the gas pores.
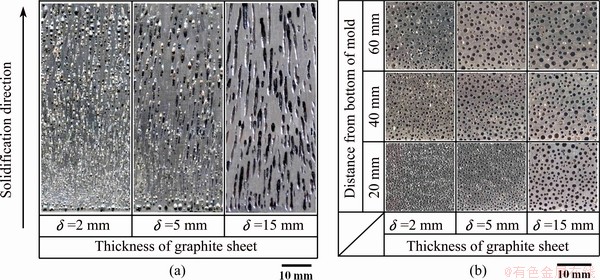
Fig. 2 Longitudinal (a) and cross-sectional (b) views of lotus-type porous silicon ingots produced at different solidification speeds (pH2=0.2 MPa, △T=200 K)
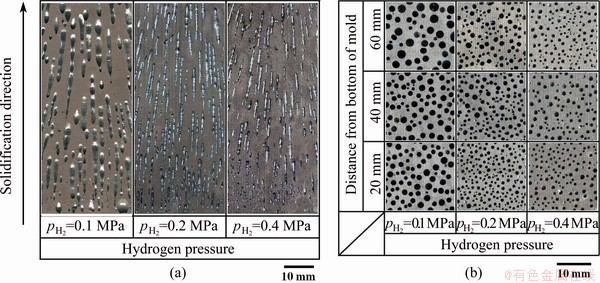
Fig. 3 Longitudinal (a) and cross-sectional (b) views of lotus-type porous silicon ingots produced at different hydrogen pressures (δ=15 mm, △T=200 K)
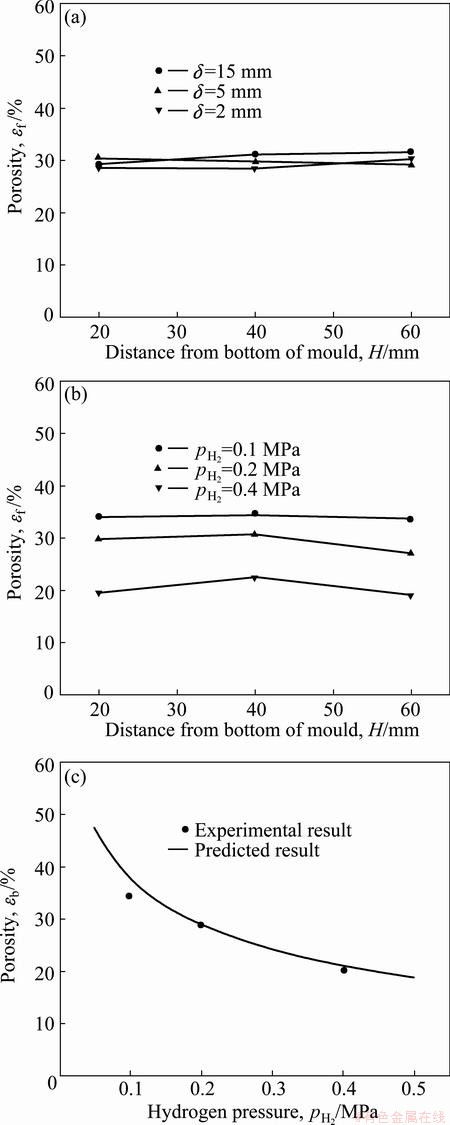
Fig. 4 Porosity evolution along height direction of silicon ingots fabricated at different solidification speeds (pH2=0.2 MPa, △T=200 K) (a), different hydrogen pressures (δ=15 mm, △T=200 K) (b) and comparison between predicted average porosities of ingot and experimental results (△T=200 K, pAr=0 MPa) (c)
3.2 Porosity
Porosity is a very important structural parameter that characterizes the gas content of porous silicon. Figure 4 shows the effects of solidification speed and hydrogen pressure on the porosity of the porous silicon. Based on Figs. 4(a) and (b), although a visible fluctuation exists, the porosity has a uniform distribution along the pore axis direction.
In addition, Fig. 4 shows that solidification speed has almost no effect on porosity under the experimental conditions while the porosity deceases with increasing hydrogen pressure. LIU et al [23] and ZHANG et al [24] established a theoretical model to predict the porosities of Mg/H2 and Cu/H2 systems. We also used this model to calculate the porosities of porous silicon ingots for comparison with the experimental results.
The model is shown in the following formula:
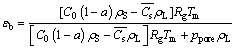 (2)
(2)
where εb is the theoretical overall porosity, Rg is the gas constant, and Tm is the melting point of silicon (1685 K). ρS and ρL are the densities (kg/m3) of the solid and liquid silicon, respectively. ppore is the gas pressure (MPa) in the pore which is equal to the furnace atmosphere (pH2+pAr, neglecting the hydrostatic pressure of the melt above the pore and the capillary pressure). 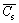 is the average hydrogen concentration (mol/m3) in the solid silicon, and can be solved via the following equation:
is the average hydrogen concentration (mol/m3) in the solid silicon, and can be solved via the following equation:
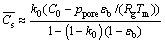 (3)
(3)
where k0 is the partition coefficient of hydrogen in the liquid and solid silicon. The estimated value of k0 is 0.72, according to the report of NAKAJIMA et al [22]. C0 is the initial hydrogen concentration in the liquid silicon (mol/m3), which can be calculated from Sievert’s law [25]
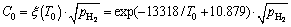 (4)
(4)
where T0 is the initial temperature (K) of the liquid silicon.
In our calculation, a is the escape coefficient which is equal to the ratio of the escaping hydrogen and the original hydrogen concentration in the liquid silicon. The expression is as follows [26]:
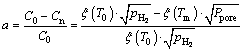 (5)
(5)
As the silicon ingots were fabricated under pure hydrogen atmosphere, the value of a is determined only by the superheat degree of the melt. By submitting Eq. (4) into Eq. (5), 0.57 is obtained as the value of a when the superheat degree of the melt is 200 K.
The average porosity of the ingot can be calculated through iterative method by incorporating Eqs. (3)-(5) into Eq. (2). Finally, we obtain the comparison between the predicted average porosity and the experimental results, as shown in Fig. 4(c). The average porosity decreases with increasing hydrogen pressure. The predicted average porosities are in good agreement with the experimental results. Therefore, the theoretical model is still applicable for Si/H2 systems.
3.3 Pore diameter, pore length and pore aspect ratio
The average pore diameter is closely tied to the solidification speed and hydrogen pressure. Lower solidification speed makes the diffusion of hydrogen into the pores much more efficient and eventually bigger pores are obtained, as shown in Fig. 5(a). The hydrogen in the chamber has two effects: one is to dissolve into the melt as working gas and the other is to control the pore diameter as the growth resistance of pores. Though the melt possesses higher solute concentration under higher hydrogen pressure, the gas pressure inside the pores (i.e., the growth resistance of pores) is higher as well. Consequently, it is regarded that there is only a little difference in the amount of hydrogen diffused into the pore under different hydrogen pressures. According to the ideal gas law: pV=nRgTm, where p and V are the hydrogen pressure inside the pore and the volume of the pore, respectively; n is the amount of hydrogen diffused into the pore which is almost the same. Finally, smaller pores form under larger hydrogen pressure (Fig. 5(b)).
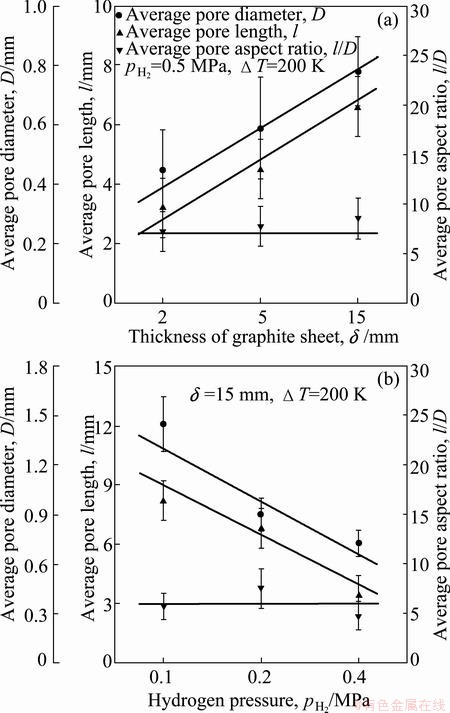
Fig. 5 Average pore diameter, pore length and pore aspect ratio fabricated at different solidification speeds (a) and different hydrogen pressures (b)
The average pore length and pore aspect ratio (the average pore length divided by average pore diameter) are the key structure parameters that affect the cooling performance of lotus-type porous structure. The average pore length can be promoted effectively by reducing the solidification speed and hydrogen pressure (Fig. 5). However, the average pore diameter is elevated as well. The average pore aspect ratio shows little change under these conditions.
The superheat degree of the melt exhibits a predominant effect on all the three structure parameters (the average pore diameter, pore length and pore aspect ratio) unlike the above process variables. As shown in Figs. 6(a) and (b), with the average pore diameter promoted by about 0.3 mm through increasing the superheat degree of the melt from 200 to 300 K, the average pore length increases from about 7 to 24 mm and the corresponding pore aspect ratio is elevated from about 8 to 20, which is a remarkable modification. The pore length is also enhanced by 12-fold of the longest pore in Nakahata’s study, which is approximately 2 mm [26]. Therefore, the superheat degree of the melt has much more significant effect on the pore length and pore aspect ratio of lotus-type porous silicon compared with the solidification speed and hydrogen pressure.
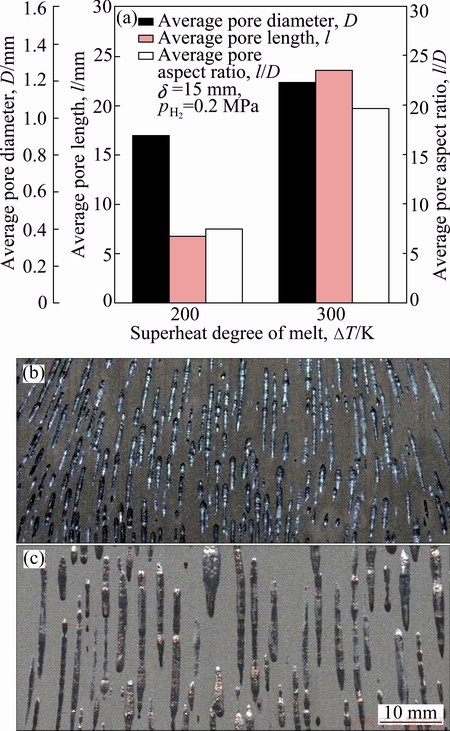
Fig. 6 Average pore diameter, pore length and pore aspect ratio fabricated at different superheat degrees of melt (a) and longitudinal section of lotus-type porous silicon ingot produced at △T=200 K (b) and △T=300 K (c)
The interruption phenomenon determines the final pore length. After the bubble nucleates, the cooling contraction of hydrogen occurs along with the whole growth process of the pore and much hydrogen is needed to maintain its growth owing to the temperature gradient existing in it. Once the supply of hydrogen is insufficient to keep its growth with the original size, the pore diameter begins to decrease. As smaller pores possess larger capillary pressure (2σlg/R, σlg is the interfacial energy of the liquid/gas phase and R is the curvature radius of the pore), the diffusion of hydrogen from liquid phase to the pores becomes much more difficult and eventually leads to the pore’s interruption. That is the reason why bigger pores tend to have a larger length and smaller ones interrupt much easier.
For the situation of higher superheat degree of the melt which has much longer pores and bigger pore aspect ratio, the probable reasons for the elongation of the pores are regarded as follows:
1) Most of the pores distribute at the grain boundaries for porous silicon [27]. The grains are more inclined to grow parallel to the solidification direction at higher superheat degree of the melt. The formation of the vertical and slender grains ensures the growth of pores with a larger length.
2) The heat stored in the melt with higher temperature compensates the heat dissipation of melt in the vicinity of pores (the inclined striped area in Fig. 7) due to the convection of hydrogen in the pores. The melt in this area is difficult to solidify in advance and delays the pores’ interruption.
3) The larger concentration of hydrogen possessed by the higher temperature of the melt makes the diffusion of hydrogen into the pores much more efficient (as shown in Fig. 7) and restrains the interruption of pores owing to the cooling shrinkage of hydrogen.
Although many efforts have been exerted to investigate the influence of processing parameters on the pore length and several reasons have been proposed to explain the interruption and elongation of the pores, the root factor for this phenomenon is an urgent question that requires further investigation.
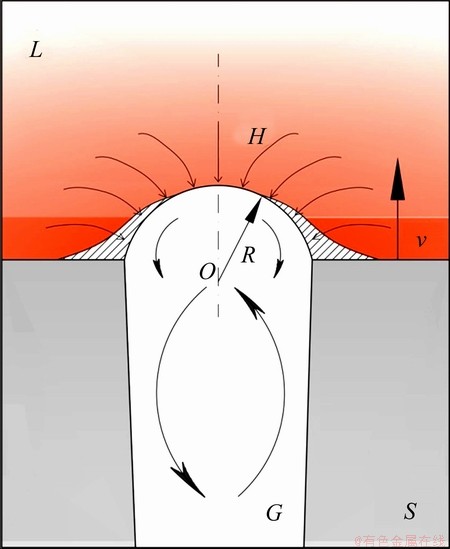
Fig. 7 Schematic diagram of diffusion and heat convection of hydrogen
4 Conclusions
1) Lotus-type porous silicon with elongated pores was fabricated successfully by unidirectional solidification.
2) The porosity decreases by increasing hydrogen pressure, but nearly remains constant by changing solidification speed under our experimental conditions. The predicted values of porosity are in good agreement with the experimental results.
3) The average pore length and pore diameter increase simultaneously, and the average pore aspect ratio changes slightly with decreasing the solidification speed and hydrogen pressure. The superheat degree of the melt has much more significant effect on the average pore length and pore aspect ratio compared with the solidification speed and hydrogen pressure. The average pore length increases from 7 to 24 mm and the corresponding pore aspect ratio increases from 8 to 20 by increasing the superheat degree of the melt from 200 to 300 K.
References
[1] WANG Xiao-hua, LI Jin-shan, HU Rui, KOU Hong-chao, ZHOU Lian. Mechanical properties of porous titanium with different distributions of pore size [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2013, 23(8): 2317-2322.
[2] BANHART J. Manufacture, characterisation and application of cellular metals and metal foams [J]. Progress in Materials Science, 2001, 46(6): 559-632.
[3] SHAPOVALOV V I, BOYKO L. Gasar–A new class of porous materials [J]. Advanced Engineering Materials, 2004, 6(6): 407-410.
[4] IDE T, TANE M, NAKAJIMA H. Effect of solidification condition and alloy composition on formation and shape of pores in directionally solidified Ni-Al alloys [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2013, 44(9): 4257-4265.
[5] LIU Yuan, LI Yan-xiang, WAN Jiang, ZHANG Hua-wei. Metal–gas eutectic growth during unidirectional solidification [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2006, 37(9): 2871-2878.
[6] LIU Xin-hua, LIU Xue-feng, JIANG Yan-bin, XIE Jian-xin. Effect of casting temperature on porous structure of lotus-type porous copper [J]. Procedia Engineering, 2012, 27: 490-501.
[7] JIN Qing-lin, LI Zhen-hua, LI Zai-jiu, YANG Tian-wu, ZHOU Rong. Fabrication of lotus-type porous copper with a continuous casting technique [J]. Foundry Technology, 2011, 32(3): 306-309. (in Chinese)
[8] PENG Peng, LI Xin-zhong, SU Yan-qing, LIU Dong-mei, GUO Jing-jie, FU Heng-zhi. Characterization of microstructural length scales in directionally solidified Sn-35%Ni peritectic alloy [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2013, 23(8): 2446-2453.
[9] SHAPOVALOV V I. Method of manufacture of porous articles: USA, 5181549 [P]. 1993-06-23.
[10] HYUN S K, NAKAJIMA H. Effect of solidification velocity on pore morphology of lotus-type porous copper fabricated by unidirectional solidification [J]. Materials Letters, 2003, 57(21): 3149-3154.
[11] JIANG Guang-rui, LI Yan-xiang, LIU Yuan. Influence of solidification mode on pore structure of directionally solidified porous Cu-Mn alloy [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2011, 21(1): 88-95.
[12] OGUSHI T, CHIBA H, NAKAJIMA H, IKEDA T. Measurement and analysis of effective thermal conductivities of lotus-type porous copper [J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2004, 95(10): 5843-5847.
[13] MURAMATSU K, IDE T, NAKJIMA H, EATON J K. Heat transfer and pressure drop of lotus-type porous metals [J]. Journal of Heat Transfer, 2013, 135(7): 072601.
[14] OGUSHI T, CHIBA H, NAKAJIMA H. Development of lotus-type porous copper heat sink [J]. Materials Transactions, 2006, 47(9): 2240-2247.
[15] CHIBA H, OGUSHI T, NAKAJIMA H, IKEDA T. Heat transfer capacity of lotus–type porous copper heat sink [J]. JSME International Journal: Series B, Fluids and Thermal Engineering, 2004, 47(3): 516-521.
[16] ZHANG Hua-wei, CHEN Liu-tao, LIU Yuan, LI Yan-xiang. Experimental study on heat transfer performance of lotus-type porous copper heat sink [J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2013, 56(1-2): 172-180.
[17] ZHANG Hua-wei, LI Yan-xiang, LIU Yuan. Gas pressure condition for obtaining uniform lotus-type porous structure by gasar process [J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2006, 42(11): 1171-1176. (in Chinese)
[18] IDE T, IIO Y, NAKAJIMA H. Fabrication of porous aluminum with directional pores through continuous casting technique [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2013, 43(13): 5140-5152.
[19] ZHANG Hua-wei, LI Yan-xiang, LIU Yuan. Fabricating porous aluminium with directional solidification of Al-H system [J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2007, 43(1): 11-16. (in Chinese)
[20] NAKAJIMA H. Fabrication, properties and application of porous metals with directional pores [J]. Progress in Materials Science, 2007, 52(7): 1091-1173.
[21] PARK J S, HYUN S K, SUZUKI S, NAKAJIMA H. Effect of transference velocity and hydrogen pressure on porosity and pore morphology of lotus-type porous copper fabricated by a continuous casting technique [J]. Acta Materialia, 2007, 55(16): 5646-5654.
[22] NAKAHATA T, NAKAJIMA H. Fabrication of lotus-type porous silicon by unidirectional solidification in hydrogen [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2004, 384(1-2): 373-376.
[23] LIU Yuan, LI Yan-xiang, WAN Jiang, ZHANG Hua-wei. Evaluation of porosity in lotus-type porous magnesium fabricated by metal/gas eutectic unidirectional solidification [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2005, 402(1-2): 47-54.
[24] ZHANG Hua-wei, LI Yan-xiang, LIU Yuan. Evaluation of porosity in lotus-type porous Cu fabricated with gasar process [J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2006, 42(11): 1165-1170. (in Chinese)
[25] KOSTINA T K, BAUM B A, KUROCHKIN K T. Solubility of hydrogen in silicon [J]. Izvestiya Akademii Nauk SSSR, Neorganicheskie Materialy, 1970, 6(1): 117. (in Russian)
[26] ZHANG Hua-wei. Theoretical and experimental study on unidirectional solidification of metal–gas eutectics [D]. Beijing: Department of Mechanical Engineering, Tsinghua University, 2006: 31-39. (in Chinese)
[27] YANG Qian-qian, LIU Yuan, LI Yan-xiang. Fabrication of lotus–type porous silicon by unidirectional solidification in pressurized hydrogen atmosphere [C]//HAN Y, LIU X,  G H. Materials Performance, modeling and simulation. Taiyuan: Trans Tech Publications Ltd, 2013: 217-222.
G H. Materials Performance, modeling and simulation. Taiyuan: Trans Tech Publications Ltd, 2013: 217-222.
杨倩倩,刘 源,李言祥,张 言
1. 清华大学 材料学院,北京 100084;
2. 清华大学 先进成形制造教育部重点实验室,北京 100084
摘 要:采用定向凝固的方法,在一定的氢压条件下制备具有长孔结构的藕状多孔Si。通过调整凝固速率和氢气压力,铸锭的孔隙率、孔径和孔长度能够得到有效控制。实验结果表明:当其他条件不变时,铸锭的面孔隙率几乎不随凝固速率发生变化,但随着氢气压力的增加而逐渐降低。采用理论模型获得的不同氢压条件下制备出的铸锭体孔隙率预测结果与实验结果吻合较好。随着凝固速率和氢气压力的降低,铸锭的平均孔长度和孔径均逐渐增加,长径比则基本保持不变。通过将熔体的过热度从200 K提高到300 K,制备得到的试样其平均孔径增加约0.3 mm,平均孔长度从7 mm提高至24 mm,平均长径比则由8提高至20。
关键词:藕状多孔Si;凝固速率;氢气压力;过热度;孔长度
(Edited by Yun-bin HE)
Foundation item: Project (51271096) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project (NCET-12-0310) supported by the Program for New Century Excellent Talents in University, China
Corresponding author: Yuan LIU; Tel: +86-10-62789328; E-mail: yuanliu@tsinghua.edu.cn
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(14)63496-8

