基于改进的潜在生态风险指数的霞湾港底泥重金属生态风险评价
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2012年第6期
论文作者:祝慧娜 袁兴中 曾光明 蒋敏 梁婕 张长 尹娟 黄华军 刘智峰 江洪炜
文章页码:1470 - 1477
关键词:重金属;化学形态;改进的潜在生态风险指数;底泥;霞湾港
Key words:heavy metals; chemical speciation; modified potential ecological risk index; sediments; Xiawan Port
摘 要:基于潜在生态风险指数(RI)和风险评价代码(RAC),建立改进的潜在生态风险指数(MRI)。该方法考虑了单个重金属不同形态毒性的不同。以株洲霞湾港底泥为例,研究Cd、Cu、Pb、Zn的污染状况及其形态特征,并分别运用潜在生态风险指数、风险评价代码以及改进的潜在生态风险指数3种方法对霞湾港底泥进行风险评价。实验数据显示,霞湾港底泥的重金属污染严重。根据改进的潜在生态风险指数,重金属生态风险呈现Cd>Pb>Cu>Zn递减的顺序。通过对比得出,改进的生态风险评价综合了潜在生态风险指数和风险评价代码2种方法的优点,评价结果更加可靠,能够为风险管理提供一定的理论依据。
Abstract: Modified potential ecological risk index (MRI) was proposed based on the potential ecological risk index (RI) and risk assessment code (RAC) by modifying an index. The modified index was relevant to the chemical speciation of heavy metals. Xiawan Port, a typical region contaminated by industrial production, was selected as a case study area. The total concentrations and chemical speciation of heavy metals in sediments of Xiawan Port were analyzed. The experimental data indicate that Xiawan Port is seriously polluted by heavy metals, especially by Cd. The risks of heavy metals are evaluated by RI, RAC and MRI, respectively. The resluts of MRI show that the risks of heavy metals are in the decreasing order of Cd>Pb>Cu>Zn. Comparison of results by different methods reveals that MRI integrates the characters of RI and RAC. MRI is recognized to be useful for risk managemnt of heavy metals in sediments.

![]()

Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 22(2012) 1470-1477
ZHU Hui-na1, 2, YUAN Xing-zhong1, 2, ZENG Guang-ming1, 2, JIANG Min1, 2, LIANG Jie1, 2,
ZHANG Chang1, 2, YIN Juan3, HUANG Hua-jun1, 2, LIU Zhi-feng1, 2, JIANG Hong-wei1, 2
1. College of Environmental Science and Engineering, Hunan University, Changsha 410082, China;
2. Key Laboratory of Environmental Biology and Pollution Control (Hunan University),
Ministry of Education, Changsha 410082, China;
3. Department of Business Administration, Guangxi University of Finance and Economics,Nanning 530003, China
Received 30 June 2011; accepted 28 October 2011
Abstract: Modified potential ecological risk index (MRI) was proposed based on the potential ecological risk index (RI) and risk assessment code (RAC) by modifying an index. The modified index was relevant to the chemical speciation of heavy metals. Xiawan Port, a typical region contaminated by industrial production, was selected as a case study area. The total concentrations and chemical speciation of heavy metals in sediments of Xiawan Port were analyzed. The experimental data indicate that Xiawan Port is seriously polluted by heavy metals, especially by Cd. The risks of heavy metals are evaluated by RI, RAC and MRI, respectively. The resluts of MRI show that the risks of heavy metals are in the decreasing order of Cd>Pb>Cu>Zn. Comparison of results by different methods reveals that MRI integrates the characters of RI and RAC. MRI is recognized to be useful for risk managemnt of heavy metals in sediments.
Key words: heavy metals; chemical speciation; modified potential ecological risk index; sediments; Xiawan Port
1 Introduction
Heavy metal contamination has become an environmental problem today in both developing and developed countries throughout the world [1,2]. Heavy metals are of considerable environmental concern due to their toxicity, wide sources, non-biodegradable properties and accumulative behaviors [3]. With the rapid industrialization and economic development in watershed region, the pollution of water body sediment has become very widespread in China [4,5]. Depending on hydrodynamics, biogeochemical processes and environmental conditions of rivers, sediments act as an important sink of heavy metals, as well as a potential non-point pollution source which may directly affect overlying waters [6,7]. To some extent, heavy metal contents in sediments can reflect the quality of water body. Although sediments act as one of the ultimate sinks for heavy metals input into the aquatic environment, they cannot fix heavy metals permanently [3]. Adsorbed heavy metals may desorb from sediments and result in some secondary pollution problems when environmental conditions change [8]. Taking into account the importance of sediments and the toxicity of heavy metals in them, related researches have been done to understand the effects of heavy metals on ecological systems [9,10]. The risk assessment of heavy metals would provide a certain theory support for risk management.
Risk assessment code (RAC) is a method for risk assessment of heavy metals. It classifies the risk levels based on the chemical speciation of heavy metals [11]. Potential ecological risk index (RI) is a methodology developed by HAKANSON [12] to evaluate the ecological risks of heavy metals in sediments. In terms of RAC, the toxic-response factors for different heavy metals are ignored. Although RI considers both the toxicities and total contents of heavy metals, the chemical speciation is neglected. Significant differences of noxious properties exist in different chemical speciations of heavy metals [13]. Most of recently reported studies dealing with the evaluation of heavy metal contamination in sediments use only the total content of heavy metal as a criterion for determining their potential effect on the environments. However, the total concentrations of heavy metals provide inadequate information for assessing their bioavailability or toxicity [14]. In this study, RI was modified by multiplying a toxic index corresponding to different chemical speciations of heavy metals, which were related to RAC. The chemical speciations of heavy metals in sediments could be obtained from a sequential extraction technique. In the modified potential ecological risk index (MRI) model, the toxicity and chemical speciation of heavy metals were considered simultaneously. In this work, MRI model was applied to evaluating the risk of heavy metals in sediments of Xiawan Port. The assessment conclusions would be beneficial for the management and control of heavy metal pollution in sediments of Xiawan Port.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Study area and sampling
Xiawan Port is located in Zhuzhou city of Hunan province, China. It is the receptor of urban and industrial sewage of Qingshuitang industry zone. It is also one of the main pollution sources of Xiangjiang River. The total length of Xiawan Port is about 6.0 km, and the drainage area is 11.8 km2. Xiawan Port originates from Ganhantang which is located in the northwest of Zhuzhou city, flows through Qingshuitang from the north to the south and finally runs into Xiangjiang River. The heavy metal pollution is very severe in Xiawan Port, which significantly threatens ecological systems and human health. In addition, long-term wastewater pollution results in serious sediment contamination. Therefore, it is necessary to analyze the potential ecological risk of heavy metals in sediments of Xiawan Port.
Considering the representativeness of heavy metal pollution in Xiawan Port, five sampling sites were chosen near the outlets of industry companies. Five locations were Zhuzhou chemical plant, Zhuzhou smelting works, Tongxia road, Zhuzhou sewage disposal work and the outfall of Xiawan Port, which were designed as Site 1, Site 2, Site 3, Site 4 and Site 5, respectively. The locations of sample points are shown in Fig. 1.
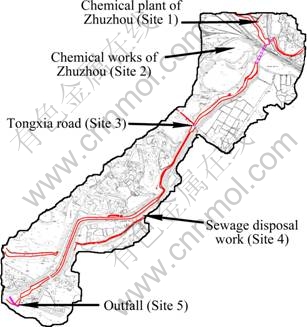
Fig. 1 Map of sampling sites in Xiawan Port
2.2 Sample analysis
For the analysis of total heavy metal concentrations (Cd, Cu, Zn and Pb), 0.1 g sample was placed in Teflon tube and digested with HNO3, HF, and HClO4. Then the solutions were dissolved with 2% (volume fraction) HNO3 to a final volume of 50 mL, and analyzed with an atomic absorption spectrophotometer (AAnalyst700, Perkin- Elmer Inc, US).
The chemical speciation of heavy metals was obtained through a sequential extraction procedure proposed by AKCAY et al [15] and TESSIER [16]. This sequential extraction procedure was widely used in analysis of heavy metals’ speciation distribution [17-19].
2.3 Risk assessment code
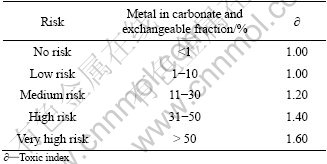
It is evident that the heavy metals in sediments are distributed in different fractions with different strengths, which give a clear connection with the presence of heavy metals in related aquatic environment [14]. Different extents of risk corresponding to different fractions could be expressed and regulated by RAC [13]. RAC determines the availability of heavy metals in sediments by applying a scale to the percentage of heavy metals in the exchangeable and carbonate fractions [11,14]. According to the RAC guideline, for any metal, when the total ratio of the exchangeable and carbonate fractions is less than 1%, the environment can be seen as secure; when the total ratio is more than 50%, the hazard is very high, and the heavy metals are very easy to enter the food chain [20]. The classification of risk has been categorized in terms of RAC and is tabulated in Table 1.
Table 1 Classification of RAC [21] and values of ?
2.4 Potential ecological risk index
RI is introduced to assess the ecological risk degree of heavy metals in soil or sediments, which was originally proposed by HAKANSON and widely used [22,23]. The value of RI can be calculated by the following formulas [12]:
![]() (1)
(1)
![]() (2)
(2)
![]() (3)
(3)
where RI is the sum of potential risk of individual heavy metal; ![]() is the potential risk of individual heavy metal;
is the potential risk of individual heavy metal; ![]() is the toxic-response factor for a given heavy metal;
is the toxic-response factor for a given heavy metal; ![]() is the contamination coefficient;
is the contamination coefficient; ![]() is the present concentration of heavy metals in sediments;
is the present concentration of heavy metals in sediments; ![]() is the pre-industrial record of heavy metal concentration in sediments.
is the pre-industrial record of heavy metal concentration in sediments.
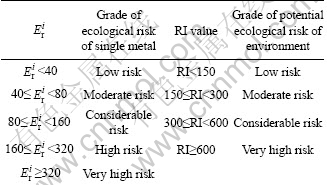
Based on the HAKANSON approach, the toxic-response factors for Pb, Cu, Cd and Zn are 5, 5, 30 and 1, respectively. In this study area, the pre-industrial concentration records for Cd, Cu, Pb and Zn are 0.2, 26, 35, and 94 mg/kg, respectively [24]. HAKANSON [12] defined five categories of ![]() , and four categories of RI, as shown in Table 2.
, and four categories of RI, as shown in Table 2.
Table 2 Indices and grades of potential ecological metals contamination [9]
2.5 Modified potential ecological risk index
The risk of heavy metal pollution depends on not only the total content of heavy metals, but also their chemical speciation. The researches about the relationship between heavy metal speciation and bioavailability certified that heavy metals’ speciation could greatly affect their bioavailability [25,26]. But so far,the chemical speciation of heavy metals was not considered in the risk assessment models which only considered their total concentrations [5,23].
In this study, different toxic indexes were given to different percentages of exchangeable and carbonate fractions in risk analysis. The calculation formulas of MRI are shown as follows:
![]() (4)
(4)
![]() (5)
(5)
![]() (6)
(6)
![]() (7)
(7)
![]() (8)
(8)
where ![]() ,
,![]() ,
,![]() , and MRI are the modified forms of
, and MRI are the modified forms of ![]() ,
,![]() ,
,![]() ,and RI, respectively; Ω is the modified index of heavy metal concentration; A is the percentage of exchangeable and carbonate fraction; B is the value of 1-A; ? is the toxic index corresponding to different ratios of exchangeable and carbonate fraction. The value of ? listed in Table 1 was obtained according to RAC and expert consultation.
,and RI, respectively; Ω is the modified index of heavy metal concentration; A is the percentage of exchangeable and carbonate fraction; B is the value of 1-A; ? is the toxic index corresponding to different ratios of exchangeable and carbonate fraction. The value of ? listed in Table 1 was obtained according to RAC and expert consultation.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Contamination evaluation of heavy metals
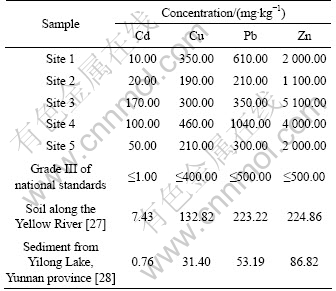
The total concentrations of Cd, Cu, Pb and Zn in sediments of Xiawan Port are presented in Table 3. It is obvious that higher concentrations of heavy metals were detected at Site 3 and Site 4 which were located at lower reaches of Xiawan Port. The contents of Cd and Zn seriously exceeded Grade III standard of China environmental quality standard for soil (GB15618—1995). In particular, Cd was considered to be the critical polluting substance in this study area. The concentrations of Cd and Zn in all samples transcended the standard values by 10-170 times and 2.2-10.2 times, respectively. The concentrations of Pb at Site 1 and Site 4 exceeded the standard value by 1.22 and 2.08 times, respectively. And Cu transcended the standard value at Site 4 by 1.4 times. Compared with the contents of heavy metals in other sites around China (Table 3), the concentrations of Cd, Cu, Pb and Zn in sediments of Xiawan Port were relatively high. In a word, the sediments of Xiawan Port were contaminated seriously by heavy metals.
Combined pollution index (CPI) was used to evaluate the pollution level of heavy metals. There are two steps in this assessment process [29].
Table 3 Concentrations of heavy metals in sediments of Xiawan Port
First step: Contamination coefficient of heavy metal is obtained by:
![]() (9)
(9)
Second step: combined pollution index is obtained by:
![]() (10)
(10)
where ![]() is the contamination coefficient of heavy metal; Ci is the concentration of heavy metal in sediment;
is the contamination coefficient of heavy metal; Ci is the concentration of heavy metal in sediment; ![]() is the background value. In Hunan province, the background values of Cd, Cu, Pb and Zn are 0.20, 26, 35 and 94 mg/kg, respectively [24]; m is the number of heavy metals; CPI is the combined pollution index.
is the background value. In Hunan province, the background values of Cd, Cu, Pb and Zn are 0.20, 26, 35 and 94 mg/kg, respectively [24]; m is the number of heavy metals; CPI is the combined pollution index.
When the CPI<1, sediment is un-polluted; when the CPI≥1, sediment is contaminated by heavy metals, and the pollution extent increases with the increment of CPI.
Contamination coefficients for four heavy metals in all sites are summarized in Table 4. According to this table, it is clear that all contamination coefficients exceed the critical value “1”. The contamination coefficients of Cd and Zn in Site 3 are 850 and 54.26, respectively. It could be concluded that the contamination degrees of heavy metals in this study area were ranked in the order of: Cd>Zn>Pb>Cu.
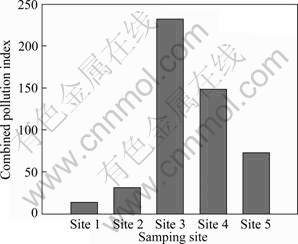
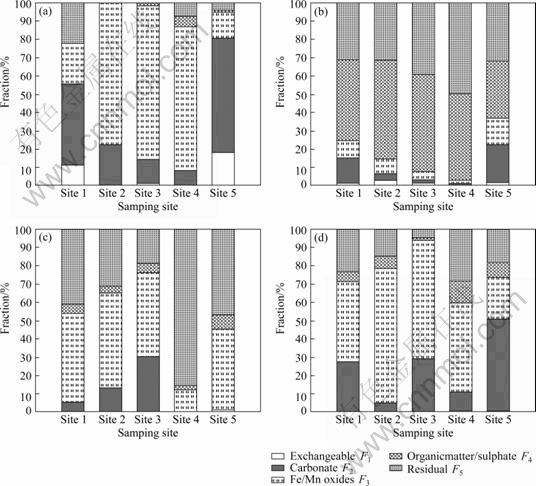
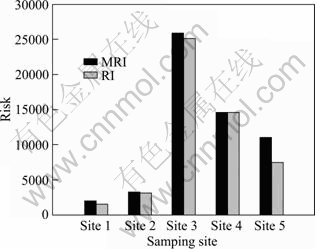
Figure 2 illustrates the CPI of heavy metals in sediment samples. The values of CPI increased in the order of Site 1(25.54) Table 4 Contamination coefficient of heavy metals Fig. 2 Combined pollution index of heavy metals in sediments of Xiawan Port 3.2 Results of RAC The distributions of heavy metals in various geochemical fractions are depicted in Fig. 3. The results of the sequential extraction (Fig. 3(a)) reveal that Cd at Site 1 and Site 5 posed a very high risk to the environ- ment for its higher ratios of F1 and F2 ((F1+F2)Cd,site1= 55.56%, (F1+F2)Cd,site5=80.61%). Furthermore, the proportions of Cd at Site 2 and Site 3 bound to F1 and F2 were 11.41% and 22.50%, respectively, indicating the medium risk category. In addition, the RAC value for Cd at Site 4 was below 10%, suggesting a relatively low risk. All in all, except at Site 4, Cd could easily enter the food chain and pose serious threat to the ecosystem for its higher toxicity and availability. The chemical partitions of Cu and Pb are plotted in Figs. 3(b) and (c), respectively. For Cu and Pb, sediment samples may be classified as no risk ((F1+F2)Cu,site4= 0.88%, (F1+F2)Pd,site4=0.00%, (F1+F2)Pd,site5=0.70%), low risk ((F1+F2)Cu,site2=6.29%, (F1+F2)Cu,site3=2.67%, (F1+F2)Pd,site1=4.80%), and medium risk ((F1+F2)Cu,site1= 14.83%, (F1+F2)Cu,site5=22.17%, (F1+F2)Pd,site2= 12.89%, (F1+F2)Pd,site3=29.68%). The authors’ findings of 50.27% show carbonate and exchangeable Zn fractions placed at site 5 in the very high risk category. Sites 1, 3 and 4 show medium risk category by Zn ((F1+F2)Zn,site1=27.37%, (F1+ F2)Zn,site3=29.01%, (F1+F2)Zn,site4=10.59%). In addition, at Site 2, Zn posed low risk to the environment ((F1+F2)Zn,site2= 4.79%), as shown in Fig. 3(d). Fig. 3 Partitioning patterns of Cd, Cu, Pb and Zn in sediments of Xiawan port: (a) Cd; (b) Cu; (c) Pb; (d) Zn On the basis of above analysis, these heavy metals are considered to be easily dissolved into the water by acidity. The relative amounts of easily dissolved phase of heavy metals in the sediments are in the order of Cd>Zn>Cu>Pb. According to RAC, the risks of Cd and Zn were very high. So, Cd and Zn should be recognized as priority pollutants in the sediments of Xiawan Port. 3.3 Results of MRI and RI According to Formula (4) and Table 1, toxic indexes of heavy metals were calculated and illustrated in Table 5. The values of toxic indexes were related to the chemical speciation of heavy metals. Compared with other metals, the toxic indexes of Cd and Zn were higher due to their higher percentages present in exchangeable and carbonate fractions. The ecological risk assessment results of toxic heavy metals in sediments of Xiawan Port are summarized in Table 6. It is found that the risk indices ( Table 5 Toxic indexes (Ω) of heavy metals In order to quantify the overall potential ecological risk of observed heavy metals in sediments of Xiawan Port, the values of MRI are shown in Fig. 4. MRI in five samples ranged from 1975.33 to 25850.81, with an average of 11328.90. All of MRI values in five samples were higher than 600, indicating very high potential ecological risk. In Site 3, the overall risk caused by four heavy metals was the highest as 25695.00. The overall risks of four heavy metals in five sites under MRI were in declining order of Site 3>Site 4>Site 5>Site 2>Site 1. Table 6 Fig. 4 Comparison of total risk under MRI and RI MRI could characterize sensitivity of local ecosystem to the toxic heavy metals and represent ecological risk resulting from the overall contamination [30]. The contribution percent of individual heavy metal to overall potentially ecological risk could be calculated by The risks of each heavy metal based on MRI and RI were different, especially for Cd. The possible reason may be the higher values of Ω for Cd. Comparisons of total risks of heavy metals in sediments of Xiawan Port calculated by methods of MRI and RI are presented in Fig. 4. It is shown that the total risk under MRI was higher than that under RI. Especially, the total risk of heavy metals in Site 5 under MRI was about 1.50 times that under RI. 4 Conclusions 1) Contamination assessment based on CPI shows that the four heavy metals in the study area appear to be “heavily contaminated” with the CPI>1. Cd appears to be “very heavily contaminated”. Meanwhile, other three heavy metals could be characterized as “heavily contaminated”. The overall pollution degrees of heavy metals are in the order of Cd>Zn>Pb>Cu. 2) According to RAC, Cd poses very high risk to the ecosystem due to its higher toxicity and percentage in the exchangeable and carbonate fractions which poses an adverse impact on aquatic biota. The overall risks levels of heavy metals are in the declining order of Cd>Zn>Cu>Pb. 3) Based on the chemical speciation and bioavailability of heavy metals, MRI was established and used to analyze the risk of heavy metals in Xiawan Port. The results show that Cd is the only metal posing a very high risk to the environments. The risks of four heavy metals under MRI are in a declining order of Cd>Pb>Cu>Zn. The overall risk indexes caused by the four toxic heavy metals rang from 1975.33 to 25850.81, corresponding to very high risk. The overall risks of four heavy metals in five sites are in the declining order: Site 3>Site 4>Site 5>Site 2>Site 1. Cd is the priority pollutant in the sediments of Xiawan Port, and Cd contributes most (average 97.07%) of the total overall ecological risk. 4) The comparison results of risk values of heavy metals based on different methods show that there are several disagreements. The main reason may be that RAC determines the risk level of heavy metals only focusing on the chemical speciation. And the toxic-response factors for different heavy metals are ignored. RI considers both the total concentration and toxic-response factors of heavy metals. But the toxic indexes corresponding to chemical speciation of heavy metals are neglected. 5) The chemical speciation and toxicities of heavy metals are both two significant factors in the risk assessment process. MRI established in this study integrates RAC and RI. The total concentration, chemical speciation and toxic response factor of individual heavy metal are considered simultaneously. Therefore, MRI, is recognized to be useful for improvement of ecological risk assessment and management of heavy metals in sediments. References [1] ZHANG Luo-ping, YE Xin, FENG Huan, JING You-hai, OUYANG Tong, YU Xing-tian, LIANG Rang-ruan, GAO Cheng-tie, CHEN Wei-qi. Heavy metal contamination in western Xiamen Bay sediments and its vicinity, China [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2007, 54(7): 974-982. [2] SUN Yue-bing, ZHOU Qi-xing, XIE Xiao-kui, LIU Rui. Spatial, sources and risk assessment of heavy metal contamination of urban soils in typical regions of Shenyang, China [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2010, 174: 455-462. [3] YU Rui-lian, YUAN Xing, ZHAO Yuan-hui, HU Gong-ren, TU Xiang-lin. Heavy metal pollution in intertidal sediments from Quanzhou Bay, China [J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2008, 20(6): 664-669. [4] WANG Shao-feng, JIA Yong-feng, WANG Shu-yin, WANG Xin, WANG He, ZHAO Zhi-xi, LIU Bing-zhu. Fractionation of heavy metals in shallow marine sediments from Jinzhou Bay China [J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2010, 22(1): 23-31. [5] NIU Hong-yi, DENG Wen-jing, WU Qun-he, CHEN Xin-geng. Potential toxic risk of heavy metals from sediment of the pearl river in south China [J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2009, 21(8): 1053-1058. [6] BRUCES W R, VANDAM L F, BELL R G, GREEN M O, KIM J P. Heavy metal and suspended sediment fluxes from a contaminated, intertidal inlet (Manukau Harbour, New Zealand) [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 1996, 32: 812-822. [7] SANTOS B J C, BELTR?N R, G?MEZ A J L. Spatial variations of heavy metals contamination in sediments from Odiel River (Southwest Spain) [J]. Environment International, 2003, 29: 69-77. [8] SEGURA R, ARANCIBIA V, Z??IGA M C, PAST?N P. Distribution of copper, zinc, lead and cadmium concentrations in stream sediments from the Mapocho River in Santiago, Chile [J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2006, 91: 71-80. [9] WU Yao-guo, XU You-ning, ZHANG Jiang-hua, HU Si-hai. Evaluation of ecological risk and primary empirical research on heavy metals in polluted soil over Xiaoqinling gold mining region, Shaanxi, China [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2010, 20: 688-694. [10] GUO Wei-hua, LIU Xian-bin, LIU Zhan-guang, LI Guo-feng. Pollution and potential ecological risk evaluation of heavy metals in the sediments around Dongjiang harbor, Tianjin [J]. Procedia Environmental Science, 2010, 2: 729-736. [11] SINGH K P, MOHAN D, SINGH V K, MALIK A. Studies on distribution and fractionation of heavy metals in Gomti river sediments–A tributary of the Ganges, India [J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2005, 312: 14-27. [12] HAKANSON L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control, a sedimentological approach [J]. Water Research, 1980, 14: 975-1001. [13] LI Ren-ying, YANG Hao, ZHOU Zhi-gao, LU Jun-jie, SHAO Xiao-hua, JIN Feng. Fractionation of heavy metals in sediments from Dianchi lake, China [J]. Pedosphere, 2007, 17(2): 265-272. [14] SUNDARAY S K, NAYAK B B, LIN S, BHATT D. Geochemical speciation and risk assessment of heavy metals in the river estuarine sediments—A case study: Mahanadi basin, India [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2011, 186: 1837-1846. [15] AKCAY H, OGUZ A, KARAPIRE C. Study of heavy metal pollution and speciation in Buyak Menderes and Gediz river sediments [J]. Water Research, 2003, 37(4): 813-822. [16] TESSIER A, CAMPBELL P G C, BISSON M. Sequential extraction procedure for the speciation of particulate trace metals [J]. Analytical Chemistry, 1979, 51(7): 844-851. [17] ZHELJAZKOV V D, WARMAN P R. Application of high Cu compost to Swiss chard and basil [J]. The Science of the Total Environment, 2003, 302(1-3): 13-26. [18] AMIR S, HAFIDI M, MERLINA G, REVEL J C. Sequential extraction of heavy metals during composting of sewage sludge [J]. Chemosphere, 2005, 59(6): 801-810. [19] NEMATI K, BAKAR N K A, ABAS M R. Investigation of heavy metals mobility in shrimp aquaculture sludge—Comparison of two sequential extraction procedures [J]. Microchemical Journal, 2009, 91(2): 227-231. [20] JAIN C K. Metal fractionation study on bed sediments of River Yamuna, India [J]. Water Research, 2004, 38: 569-578. [21] PERIN G, GRABOLEDDA L, LUCCHESE M, CIRILLO R, DOTTA L, ZANETTA M L, ORO A A. Heavy metal speciation in the sediments of northern Adriatic Sea—A new approach for environmental toxicity determination [C]//LAKKAS T D. Heavy Metals in the Environment. vol.2, Edinburg. CEP consultants, 1985: 454-456. [22] YANG Zhi-fang, WANG Ying, SHEN Zhen-yao, NIU Jun-feng, TANG Zhen-wu. Distribution and speciation of heavy metals in sediments from the mainstream, tributaries, and lakes of the Yangtze River catchment of Wuhan, China [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2009, 166(2-3): 1186-1194. [23] FERNANDES H M. Heavy metal distribution in sediments and ecological risk assessment: The role of diagenetic processes in reducing metal toxicity in bottom sediments [J]. Environmental Pollution, 1997, 97(3): 317-325. [24] LI Jun, LIU Yun-guo, XU Zhong-jian. Heavy metals speciation and its biological availability in sediment patterns of Changsha- Zhuzhou-Xiangtan section of the Xiangjiang river [J]. Journal of Hunan University of Science & Technology, 2009, 24(1): 116-121. (in Chinese) [25] PERIN G, FABRIS R, MANENTE S, REBELLO WAGENERB A, HAMACHERB C, SCOTTOA S. A five-year study of the heavy-metal pollution of Guanabara Bay sediments (Rio de Janeiro, Brazil) and evaluation of the metal bioavailability by means of geochemical speciation [J]. Water Research, 1997, 31(12): 3017-3028. [26] KWON Y. Ecological risk assessment of sediment in wastewater discharging area by means of metal speciation [J]. Microchemical Journal, 2001, 70(3): 255-264. [27] LI Yu, WANG Yan-bin, GOU Xin, SU Yi-bing, WANG Gang. Risk assessment of heavy metals in soils and vegetables around non-ferrous metals mining and smelting sites, Baiyin, China [J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2006, 18(6): 1124-1134. [28] BAI Jun-hong, CUI Bao-shao, CHEN Bin, ZHANG Ke-jiang, DENG Wei, GAO Hai-feng, XIAO Rong. Spatial distribution and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments from a typical plateau lake wetland, China [J]. Ecological Modelling, 2011, 222(2): 301-306. [29] ZHOU Jian-min, DANG Zhi, CAI Mei-fang, LIU Cong-qiang. Soil heavy metal pollution around the Dabaoshan mine, Guangdong province, China [J]. Pedosphere, 2007, 17(5): 588-594. [30] SHI G, CHEN Z, BI C, LI Y, TENG J, WANG L, XU S. Comprehensive assessment of toxic metals in urban and suburban street deposited sediments (SDSs) in the biggest metropolitan area of China [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2010, 158: 694-703. 祝慧娜1, 2,袁兴中1, 2,曾光明1, 2,蒋 敏1, 2,梁 婕1, 2, 张 长1, 2,尹 娟3,黄华军1, 2,刘智峰1, 2,江洪炜1, 2 1. 湖南大学 环境科学与工程学院,长沙 410082; 2. 环境生物与控制教育部重点实验室(湖南大学),长沙 410082; 3. 广西财经学院 工商管理系,南宁 530003 摘 要:基于潜在生态风险指数(RI)和风险评价代码(RAC),建立改进的潜在生态风险指数(MRI)。该方法考虑了单个重金属不同形态毒性的不同。以株洲霞湾港底泥为例,研究Cd、Cu、Pb、Zn的污染状况及其形态特征,并分别运用潜在生态风险指数、风险评价代码以及改进的潜在生态风险指数3种方法对霞湾港底泥进行风险评价。实验数据显示,霞湾港底泥的重金属污染严重。根据改进的潜在生态风险指数,重金属生态风险呈现Cd>Pb>Cu>Zn递减的顺序。通过对比得出,改进的生态风险评价综合了潜在生态风险指数和风险评价代码2种方法的优点,评价结果更加可靠,能够为风险管理提供一定的理论依据。 关键词:重金属;化学形态;改进的潜在生态风险指数;底泥;霞湾港 (Edited by YANG Hua) Foundation item: Projects (51039001, 50978087, 51009063, 50808071) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project (SX2010-026) supported by State Council Three Gorges Project Construction Committee Executive Office, China; Project (2009ZX07212-001) supported by Ministry of Environmental Protection of China; Project (BYHGLC-2010-02) supported by Guangzhou Water Authority, China; Project (CX2010B157) supported by Hunan Provincial Innovation Foundation for Postgraduate, China Corresponding author: YUAN Xing-zhong; Tel: +86-731-88821413; E-mail: yxz@hnu.edu.cn DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(11)61343-5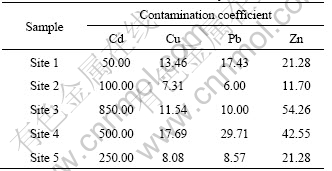
![]() ) of heavy metals were ranked in the order of Zn
) of heavy metals were ranked in the order of Zn![]() values for Zn were below 80, indicating low-moderate risk. The very high risk to environments posed by Cd should give rise to widespread concerns.
values for Zn were below 80, indicating low-moderate risk. The very high risk to environments posed by Cd should give rise to widespread concerns.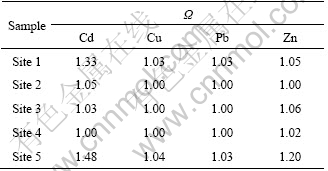
![]() and
and ![]() of each heavy metal
of each heavy metal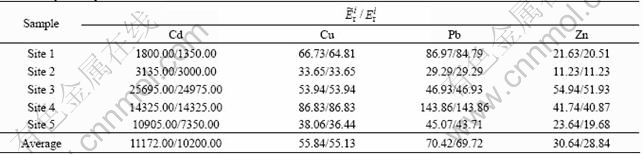
![]() in Table 6. It could be obtained that the element of Cd accounted for most of the total risk, and the percentages arranged from 91.12% to 99.40% with a mean of 97.07%. Pb ranked the second among the heavy metals contributing to the total risk, and the average was 1.38%, which was followed by 1.12% (Cu), 0.43% (Zn). It could be concluded that the high ecological risk was primarily dominated by Cd.
in Table 6. It could be obtained that the element of Cd accounted for most of the total risk, and the percentages arranged from 91.12% to 99.40% with a mean of 97.07%. Pb ranked the second among the heavy metals contributing to the total risk, and the average was 1.38%, which was followed by 1.12% (Cu), 0.43% (Zn). It could be concluded that the high ecological risk was primarily dominated by Cd.基于改进的潜在生态风险指数的
霞湾港底泥重金属生态风险评价