DOI: 10.11817/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2021-39688
微量Er和Zr对Al-Mg合金再结晶行为和焊接性能的影响
吴 浩,郑志凯,任思蒙,李书磊,赵丕植
(中铝材料应用研究院有限公司,北京102209)
摘 要:本文研究了微量Er和Zr元素对Al-Mg合金再结晶行为及组织演变的影响,同时探讨Er和Zr元素对稳定化态合金的FSW和MIG焊接接头组织和力学性能的影响。结果表明:复合添加Er和Zr元素能够有效抑制Al-Mg-Er-Zr合金冷轧板再结晶和晶粒长大行为,与Al-Mg和Al-Mg-Zr合金相比,其再结晶起始温度和结束温度分别提高至225 ℃和450 ℃,稳定化态板材强度提高30 MPa以上;同时,Er和Zr元素的复合添加能够有效削弱由于焊接热量输入产生的板材形变组织再结晶软化作用,减小热影响区再结晶组织宽度,改善合金焊接接头组织,提高焊接接头性能。Al-Mg-Er-Zr合金的FSW和MIG焊接系数分别提高到85.7%和80%。
关键词:Al-Mg-Er-Zr合金;再结晶行为;焊接性能;显微组织
文章编号:1004-0609(2021)-02-0289-09 中图分类号:TG146.2 文献标志码:A
引文格式:吴 浩, 郑志凯, 任思蒙, 等. 微量Er和Zr对Al-Mg合金再结晶行为和焊接性能的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2021, 31(2): 289-297. DOI: 10.11817/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2021-39688
WU Hao, ZHENG Zhi-kai, REN Si-meng, et al. Effects of Er and Zr micro-additions on recrystallization behavior and welding properties of Al-Mg alloy[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2021, 31(2): 289-297. DOI: 10.11817/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2021-39688
Al-Mg系合金由于具备高比强度、突出的耐蚀性和良好的可焊性,被广泛用于海洋工程及船舶工业等领域[1-2]。作为非热处理强化的变形铝合金,Al-Mg系合金的主要强化方式为固溶强化和形变强化[3-6]。通过增加主合金元素Mg含量可明显提高合金强度,但当Mg含量超过3.5%(质量分数)时,Al-Mg合金长期服役会发生“敏化”而造成合金性能不断衰退,严重影响服役寿命和安全性[7-10]。中高Mg含量的Al-Mg合金需进行合理的稳定化退火,以改善合金耐蚀性,稳定服役性能,但是稳定化退火在一定程度上会造成合金高温回复或再结晶,合金形变强化效应损失,力学性能下降。此外,在Al-Mg合金板材焊接过程中,焊接热量输入同样会引起合金焊接接头热影响区形变组织发生严重回复和再结晶,导致形变组织亚结构强化效应消失,焊接接头性能大幅度下降[11-12]。
研究表明,在铝合金中复合添加稀土元素RE(Sc、Er和Yb)和过渡元素Zr,能析出细小弥散的Al3(RE,Zr) 纳米析出相,除了发挥弥散强化效应外,同时能够抑制形变组织再结晶和晶粒长大行为,有效提高铝合金再结晶温度,稳定合金形变组织,也是潜在扩大Al-Mg合金稳定化工艺窗口的有效途径[13-15]。本文通过在Al-Mg合金中复合添加微量Er和Zr元素,研究Al-Mg-Er-Zr合金冷轧板的再结晶行为及其组织演变规律,并进一步探索Er和Zr元素复合添加对Al-Mg合金的FSW和MIG焊接性能以及焊接热循环对焊接接头组织演变的影响。
1 实验
1.1 实验材料
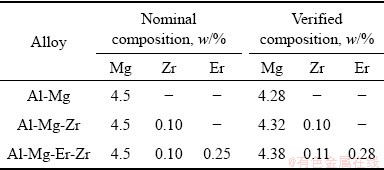
实验共制备三种不同的成分Al-Mg合金,其名义成分与实际成分如表1所示。采用高纯Al锭、高纯Mg锭及Al-6Zr和Al-6Er中间合金等为原材料,经700~760 ℃熔炼铸造成规格为110 mm×110 mm×270 mm的合金铸锭,对铸锭进行(280 ℃, 10 h)+(450 ℃, 24 h) 双级均匀化处理后多道次热轧成6 mm板材,再进行多道次冷轧成2.2 mm的冷轧板,冷轧变形率约为64%。对部分冷轧板材进行(220 ℃, 2 h)的稳定化退火,得到稳定化板材用于FSW和MIG焊接实验。
表1 Al-Mg合金化学成分
Table 1 Chemical compositions of investigated Al-Mg alloys
1.2 实验方法
合金冷轧板进行再结晶退火处理,再结晶退火温度范围为100~550 ℃、温度间隔为25 ℃、退火时间为1 h,水冷至室温,随后进行维氏硬度测试。
焊接实验采用(220 ℃,2 h)稳定化态板材,焊接方向垂直于轧制方向。FSW焊接搅拌头轴肩为双圆环形貌,直径为10 mm,焊接速度为300 mm/min,旋转速度为800 r/min;MIG焊接采用机械焊接,保护气体为氩气,焊丝为5356焊丝,焊接电流为80 A,焊接速度为0.7 m/min。对焊接接头部位进行维氏硬度测试,由焊缝中心向两侧基材方向每隔1 mm取点测试。
对板材再结晶退火试样和焊接接头试样RD/ND面进行阳极覆膜,采用Axio Scope A1光学显微镜进行微观组织观察。采用Fischer HM 2000型显微硬度仪进行维氏硬度测试,载荷为0.98 N,加载时间为10 s。板材拉伸性能采用GB/T 228.1—2010在AG-X Plus-10kN型万能力学试验机上进行测试。
2 实验结果
2.1 合金冷轧板再结晶曲线
图1所示为3种合金冷轧板材的再结晶退火温度和硬度变化曲线。从图1可以看出,随着退火温度的提升,3种合金板材的硬度呈现不断下降趋势。结合图2和3中所示不同退火态金相组织,可以断定板材硬度下降是由变形组织回复和再结晶行为导致。其中Al-Mg合金和Al-Mg-Zr合金板材再结晶起始温度约为200 ℃,Al-Mg-Er-Zr合金板材再结晶起始温度约为225 ℃。

图1 Al-Mg、Al-Mg-Zr和Al-Mg-Er-Zr合金再结晶退火的硬度变化曲线
Fig. 1 Microhardness-annealing curves of Al-Mg, Al-Mg-Zr and Al-Mg-Er-Zr alloys
由图2和3可知,当Al-Mg和Al-Mg-Zr合金冷轧板在250 ℃退火1 h时,硬度降低至80HV左右,合金板材形变组织中存在一定量尺寸相对较小的再结晶晶粒(见图2(a)和(e));当退火温度提高至275 ℃时,合金变形组织中的再结晶晶粒增多,尺寸增大,但其组织依然以回复组织为主,且与Al-Mg合金相比,Al-Mg-Zr合金的再结晶晶粒数量较少,平均晶粒尺寸较小(见图2(b)和(f))。
在300 ℃退火1 h后,Al-Mg和Al-Mg-Zr合金冷轧板形变组织均已完全再结晶,再结晶晶粒细小,硬度值降低至65HV左右。此外,Al-Mg-Zr合金再结晶晶粒的平均尺寸比Al-Mg合金再结晶晶粒略小,两者的平均尺寸分别为27.8 μm和36.4 μm。当进一步提高退火温度至450 ℃时,Al-Mg和Al-Mg-Zr合金再结晶晶粒急剧长大至几百微米,但发现Al-Mg-Zr合金晶粒尺寸出现明显的不均匀长大现象(见图2(d)和(h))。

图2 不同退火温度处理Al-Mg和Al-Mg-Zr合金的金相组织
Fig. 2 Metallographic structures of Al-Mg and Al-Mg-Zr alloy subjected to different annealing temperatures

图3 不同退火温度处理Al-Mg-Er-Zr合金的金相组织
Fig. 3 Metallographic structures of Al-Mg-Er-Zr alloy subjected to different annealing temperatures
与Al-Mg和Al-Mg-Zr合金相比,Al-Mg-Er-Zr合金冷轧板在300 ℃退火1 h后,其硬度约为75HV,明显高于Al-Mg和Al-Mg-Zr合金的硬度;其变形组织发生部分再结晶,但依然以回复组织为主。随着退火温度的升高,Al-Mg-Er-Zr合金组织中再结晶晶粒数量不断增多;当退火温度为450 ℃时(见图3(e)),合金变形组织发生完全再结晶,硬度降至65HV左右;进一步提高退火温度至500 ℃时(见图3(f)),合金再结晶晶粒依然保持均匀细小,平均晶粒尺寸明显低于Al-Mg和Al-Mg-Zr合金的,未出现类似于Al-Mg-Zr合金晶粒组织的不均匀长大现象。
2.2 合金板材焊接性能
三种稳定化态合金板材的FSW焊和MIG焊的焊接接头显微硬度分布如图4所示。从图4可以看出,FSW焊和MIG焊焊接接头的硬度值分布曲线变化趋势基本一致,均以焊缝(WZ)中心为对称轴,两侧呈现近似对称分布。
由图4(a)可以明显看出,Al-Mg、Al-Mg-Zr和Al-Mg-Er-Zr合金焊接接头都存在一个10 mm宽的硬度低值区域,与搅拌头的直径相当,硬度分别约为68HV、70HV和78HV,对应为焊缝区域;沿着远离焊缝方向,硬度不断升高,进入焊接接头热影响区域(HAZ),热影响区宽度4~5 mm。随后硬度达到稳定状态,进入母材区域(BM)。3种合金母材的硬度分别为89HV、93HV和95HV。相比FSW焊,MIG焊接接头变化规律基本相近,但其硬度低值区宽度与热影响区宽度相比略大;Al-Mg、Al-Mg-Zr和Al-Mg-Er-Zr合金焊缝处最低硬度分别为68HV、69HV和72HV,Al-Mg-Er-Zr合金MIG焊缝硬度相比其FSW焊缝硬度损失较大。3种合金母材和焊接接头的力学性能如表2所示。由表2可以明显看出,微量Er和Zr元素的复合添加显著提高了合金的强度和焊接系数,Al-Mg-Er-Zr合金母材的屈服强度和抗拉强度比Al-Mg和Al-Mg-Zr合金的高30 MPa以上,其FSW焊接系数由81.1%提升至85.7%,MIG焊接系数由70.2%提高至80%。Al-Mg-Er-Zr合金强度和焊接系数的提高,这必定归因于微量Er和Zr元素复合添加对合金及其焊接接头组织有显著的改善作用。
2.3 合金焊接接头组织
图5所示为合金焊接接头的金相组织。从图5可以看出,根据焊接热力作用范围,整个合金焊接接头组织分成3个区域(见图5(c)):母材区(BM)、热影响区(HAZ)和热机影响区(TMAZ)。热影响区和热机影响区可分为前进侧(AS)和后退侧(RS)。
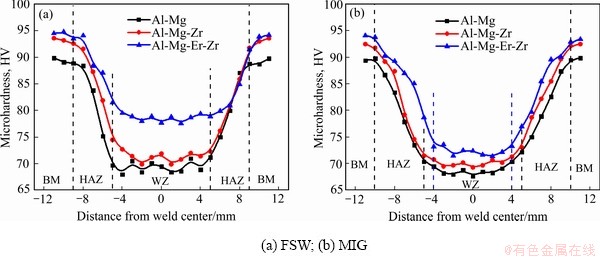
图4 焊接接头显微硬度分布图
Fig. 4 Microhardness distribution of welded joints
表2 合金母材和焊接接头力学性能
Table 2 Mechanical properties of base alloys and theirs welded joints
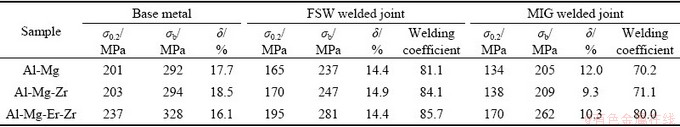

图5 合金的FSW焊接接头金相组织
Fig. 5 Metallographic structures of FSW welded joints of alloy
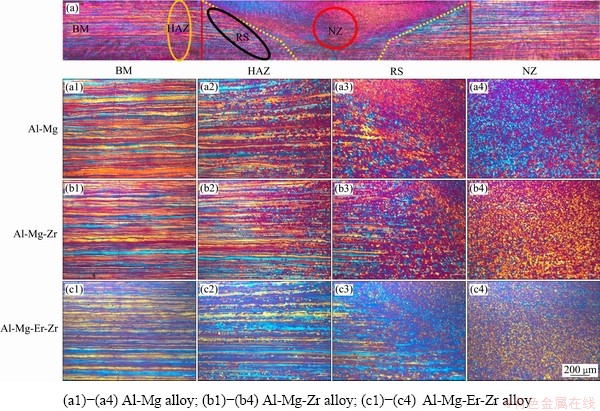
图6 合金的FSW焊接接头不同位置处金相组织
Fig. 6 Metallographic structures of FSW welded joints of alloy
图6所示为合金焊接接头不同位置处的金相组织。从合金母材区域到焊核区域(NZ),其晶粒组织状态分别为板条状回复组织、部分再结晶组织和细晶粒组织。Al-Mg、Al-Mg-Zr和Al-Mg-Er-Zr合金焊接接头的母材组织差别不大,主要为回复组织(见图6(a1)~(c1));但热影响区组织存在一定差异,由于焊接热量的影响,Al-Mg和Al-Mg-Zr合金的热影响区开始出现再结晶晶粒处距离焊缝较远,分别为2.1 mm和1.6 mm,而Al-Mg-Er-Zr合金由于具有较高抗再结晶性能,开始出现再结晶晶粒处距离焊缝较近,约为0.91 mm,绝大部分热影响区以回复组织为主。在后退侧的热机影响区TMAZ-RS(见图6(a3)~(c3)),Al-Mg和Al-Mg-Zr合金组织基本已完全再结晶,尤其是Al-Mg合金的平均晶粒尺寸较大,约为30 μm。在焊核心区NZ(见图6(a4)~(c4)),3种合金的晶粒组织均为细小的等轴晶粒,其中Al-Mg-Er-Zr合金晶粒最为细小,平均晶粒尺寸约为4 μm,低于Al-Mg和Al-Mg-Zr合金的(约为5~7 μm)。

图7 合金的MIG焊接接头金相组织
Fig. 7 Metallographic structures of MIG welded joints of alloy

图8 合金的MIG焊接接头不同位置处的金相组织
Fig. 8 Metallographic structures of MIG welded joints of alloy
图7所示为3种合金板材MIG焊接接头金相组织。整个焊接接头组织特征可以分为焊缝区(WZ)、熔合区(FZ)和热影响区(HAZ)三大部分,其不同位置处的高倍组织如图8所示。与FSW焊接不同,MIG焊接属于熔化焊,其焊缝位置呈现典型的铸造凝固态组织特征,但焊缝中心焊核区(NZ)依然存在差异(见图8(a4)、(b4)和(c4)),其中Al-Mg合金和Al-Mg-Zr合金主要为等轴的枝状晶组织,Al-Mg合金枝状晶组织最为明显,而相比之下,Al-Mg-Er-Zr合金的枝状晶组织有所改善。由图8(a3)、(b3)和(c3)可知,焊接接头的熔合区(FZ)由熔合线分成两部分不同的组织特征:靠近焊缝一侧,由于焊接热量由焊缝向热影响区传输,此区域组织呈现典型的柱状晶粒组织;靠近母材一侧,属于典型的固液交界的半熔化区,与焊核区(NZ)相比,其柱状晶粒组织不明显,为较小的胞状组织特征。
由图8可知,Al-Mg、Al-Mg-Zr和Al-Mg-Er-Zr这3种合金MIG焊接接头的热影响区(HAZ)组织特征差异与FSW焊接接头的基本相似,即热影响区组织的再结晶程度不同,主要是由于Er、Zr元素的加入,对抑制形变组织再结晶发挥着重要的作用。由图8(a2)、(b2)和(c2)可知,Al-Mg和Al-Mg-Zr合金热影响区组织为等轴的再结晶晶粒,且Al-Mg合金的再结晶晶粒尺寸比Al-Mg-Zr合金的要大,分别为45 μm和37 μm。而Al-Mg-Er-Zr合金对应区域组织依然以回复组织为主,伴有少量细小的再结晶晶粒。距焊缝更远的热影响区HAZ-1(见图8(a1)、(b1)和(c1)),Al-Mg合金对应区域组织依然以再结晶组织为主,在靠近母材侧存在未完成再结晶的断续板条状晶粒(见图8(a1)),Al-Mg-Zr合金对应区域组织主要以回复组织为主,仅在靠近焊缝侧出现少许细小再结晶晶粒;而Al-Mg-Er-Zr合金对应区域组织为纤维状的回复组织,没有发现再结晶晶粒存在。由图7可知,Al-Mg、Al-Mg-Zr和Al-Mg-Er-Zr这3种合金焊接接头热影响区再结晶晶粒区域宽度分别为3.26、3.03和0.91 mm。
3 分析与讨论
合金冷轧板再结晶退火研究结果表明,与Al-Mg和Al-Mg-Zr合金相比,复合添加微量Er和Zr元素的Al-Mg-Er-Zr合金能够有效抑制合金形变组织再结晶和晶粒长大行为,提升合金的再结晶温度,同时能有效改善和细化合金的晶粒组织,提升合金性能。而单一添加微量Zr元素的Al-Mg-Zr合金,虽然在一定程度上能够有效抑制形变组织再结晶行为,但效果并不明显,此外还会造成再结晶晶粒不均匀长大现象,这主要归因于合金中Zr元素的不均匀分布。在凝固过程中,Zr元素在Al液中发生包晶反应,大量Zr元素会偏析富集于晶粒内部造成晶界区域出现贫Zr区,导致Al3Zr相不均匀析出;而沿晶界贫Zr区会出现无析出带,最终导致抑制形变组织再结晶和晶粒长大行为的抗力大小及分布不均匀[16-18]。
对于Al-Mg-Er-Zr合金,由于微量Er和Zr元素复合添加,在凝固过程中,Er元素在Al中液发生共晶反应,Er会富集在近晶界区域,提供充足的溶质原子析出,为晶界附近的贫Zr区Al3Zr相析出提高大量异质形核点,使得合金晶内和晶界析出相弥散均匀分布,改善了合金抑制再结晶和晶粒长大行为的抗力及分布,避免了合金再结晶晶粒不均匀长大[15];同时,与Al-Mg和Al-Mg-Zr合金相比,由于微量Er和Zr元素复合添加,Al-Mg-Er-Zr合金屈服强度和抗拉强度均提高了30 MPa以上。
通过对合金焊接性能和组织研究发现,无论是FSW焊接还是MIG焊接,焊缝区域都是整个焊接接头最薄弱的部位,焊接接头拉伸试样断裂位置均在薄弱的焊缝区域。对于FSW焊接来说,虽然焊缝区域的晶粒组织得到了明显细化,但焊缝以外的热影响区以及母材组织以回复组织为主,其提供的形变强化效应远高于焊缝的细晶强化效应,对应的焊接接头硬度分布曲线中焊缝区域硬度值最低(见图4);同理,MIG焊接接头焊缝区均为粗大铸造枝晶组织,合金形变强化效应完全消失,焊缝区强化机制主要为Mg元素的固溶强化,与热影响区和母材的形变强化等相比,焊缝就成为整个焊接接头最薄弱的部位而最先断裂。
同时,3种合金的焊接工艺相同,焊接过程热输入相同,造成热影响区内再结晶程度的差异原因在于合金中纳米弥散相的作用。Al-Mg合金热影响区的组织再结晶程度最为严重;Al-Mg-Zr合金由于Zr元素的添加,合金中存在Al3Zr纳米粒子,在一定程度上能够抑制热影响区再结晶行为的扩展,再结晶区的宽度与Al-Mg合金相比要窄一些;而对于Al-Mg-Er-Zr合金,由于微量Er和Zr元素的复合添加,形成大量均匀分布的Al3(Er,Zr)纳米粒子,显著减小了热影响区范围,削弱了焊接热量输入产生的再结晶软化作用,保证了形变组织的亚结构强化效应,提高了焊接接头的力学性能。可见,微量Er和Zr元素的复合添加,能够有效抑制Al-Mg合金形变组织的再结晶行为,显著改善合金的焊接接头组织,提高合金焊接性能。
4 结论
1) 微量Er和Zr元素复合添加,有效抑制Al-Mg-Er-Zr合金再结晶和晶粒长大行为,分别将合金再结晶起始温度和结束温度提高至225 ℃和450 ℃。
2) 与Al-Mg和Al-Mg-Zr合金相比,Al-Mg-Er-Zr合金的FSW和MIG焊接系数分别提高至85.7%和80%。
3) 微量Er和Zr元素复合添加,能明显改善Al-Mg-Er-Zr合金焊接接头组织,减小热影响区再结晶组织宽度,提高焊接接头性能。
REFERENCES
[1] TOROS S, OZTURK F, KACAR I. Review of warm forming of aluminum-magnesium alloys[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2008, 207(1): 1-12.
[2] HAN B, HUANG J, ZHU Y, et al. Strain rate dependence of properties of cryomilled bimodal 5083 Al alloys[J]. Acta Materialia, 2006, 54(11): 3015-3024.
[3] HUSKINS E, CAO B, RAMESH K. Strengthening mechanisms in an Al-Mg alloy[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2010, 527(6): 1292-1298.
[4] RYEN  , HOLMEDAL B, NIJS O, et al. Strengthening mechanisms in solid solution aluminum alloys[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2006, 37(6): 1999-2006.
, HOLMEDAL B, NIJS O, et al. Strengthening mechanisms in solid solution aluminum alloys[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2006, 37(6): 1999-2006.
[5] KENDIG K, MIRACLE D. Strengthening mechanisms of an Al-Mg-Sc-Zr alloy[J]. Acta Materialia, 2002, 50(16): 4165-4175.
[6] ZOLOTOREVSKY N Y, SOLONIN A, CHURYUMOV A Y, et al. Study of work hardening of quenched and naturally aged Al-Mg and Al-Cu alloys[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2009, 502(1/2): 111-117.
[7] HENRY HOLROYD N, SCAMANS G M. Environmental degradation of marine aluminum alloys: Past, present, and future[J]. Corrosion, 2015, 72(2): 136-143.
[8] KRAMER L, PHILLIPPI M, TACK W, et al. Locally reversing sensitization in 5xxx aluminum plate[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 2012, 21(6): 1025-1029.
[9] CRANE C B, KELLY R G, GANGLOFF R P. Crack chemistry control of intergranular stress corrosion cracking in sensitized Al-Mg[J]. Corrosion, 2015, 72(2): 242-263.
[10] GUPTA R, ZHANG R, DAVIES C, et al. Influence of Mg content on the sensitization and corrosion of Al-xMg (-Mn) alloys[J]. Corrosion, 2013, 69(11): 1081-1088.
[11] RODRIGUES D M, MENEZE L F, LOUREIRO A. The influence of the HAZ softening on the mechanical behaviour of welded joints containing cracks in the weld metal[J]. Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 2004, 71(13): 2053-2064.
[12] 靳佳霖, 徐国富, 李 耀, 等. 焊丝成分对 6082-T6 铝合金焊接接头组织和性能的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2020, 30(1): 1-8.
JIN Jia-lin, XU Guo-fu, LI Yao, et al. Effect of welding wire composition on microstructure and properties of 6082-T6 aluminum alloy welded joints[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2020, 30(1): 1-8.
[13] DING Yu-sheng, GAO Kun-yuan, GUO Shan-shan, et al. The recrystallization behavior of Al-Mg-0.4Mn-0.15Zr-xSc (x=0.04-0.10 wt%) alloys[J]. Materials Characterization, 2019, 147: 262-270.
[14] WU Hao, WEN Sheng-ping, HUANG Hui, et al. A study of precipitation strengthening and recrystallization behavior in dilute Al-Er-Hf-Zr alloys[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2015, 639: 307-313.
[15] WU Hao, WEN Sheng-ping, HUANG Hui, et al. Effects of homogenization on precipitation of Al3(Er,Zr) particles and recrystallization behavior in a new type Al-Zn-Mg-Er-Zr alloy[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2017, 689: 313-322.
[16] ROBSON J D, PRANGNELL P B. Dispersoid precipitation and process modelling in zirconium containing commercial aluminium alloys[J]. Acta Materialia, 2001, 49: 599-613.
[17] WEN Sheng-ping, WANG Wei, ZHAO Wang-hui, et al. Precipitation hardening and recrystallization behavior of Al-Mg-Er-Zr alloys[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2016, 687: 143-151.
[18] GUO Z Y, ZHAO G, CHEN X G. Effects of two-step homogenization on precipitation behavior of Al3Zr dispersoids and recrystallization resistance in 7150 aluminum alloy[J]. Materials Characterization, 2015, 102: 122-130.
Effects of Er and Zr micro-additions on recrystallization behavior and welding properties of Al-Mg alloy
WU Hao, ZHENG Zhi-kai, REN Si-meng, LI Shu-lei, ZHAO Pi-zhi
(Chinalco Materials Application Research Institute Co., Ltd., Beijing 102209, China)
Abstract: The effects of Er and Zr micro-additions on the recrystallization behavior and microstructure evolution of Al-Mg alloy were researched, and meanwhile, the microstructure and mechanical properties of the FSW and MIG welding joints were also analyzed. The results show that the recrystallization and grain growth behavior of Al-Mg-Er-Zr alloy can be inhibited effectively by microalloying with Er and Zr. Compared with Al-Mg and Al-Mg-Zr alloys, the recrystallization start temperature and end temperature of Al-Mg-Er-Zr alloy increase to 225 ℃ and 450 ℃, respectively, and the yield strength and tensile strength increase by more than 30 MPa. Moreover, the recrystallization softening effect of the deformed microstructure, due to the welding temperature field and welding heat input, can be weaken by microalloying with Er and Zr, the width of recrystallization zone in HAZ is reduced, the microstructure and properties of welded joints are improved. The FSW and MIG welding coefficients of Al-Mg-Er-Zr alloy increase to 85.7% and 80%, respectively.
Key words: Al-Mg-Er-Zr alloy; recrystallization behavior; welding properties; microstructure
Foundation item: Project(Z191100004619005) supported by Beijing Municipal Science and Technology Commission, China
Received date: 2020-01-20; Accepted date: 2020-12-24
Corresponding author: WU Hao; Tel: +86-18810613057; E-mail: wuhao2469@126.com
(编辑 龙怀中)
基金项目:北京市能源与材料应用领域技术协同创新项目(Z191100004619005)
收稿日期:2020-01-20;修订日期:2020-12-24
通信作者:吴 浩,博士;电话:18810613057;E-mail:wuhao2469@126.com