Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 24(2014) 1645-1652
Effect of cooling rate on solidification parameters and microstructure of Al-7Si-0.3Mg-0.15Fe alloy
Rui CHEN, Yu-feng SHI, Qing-yan XU, Bai-cheng LIU
Key Laboratory for Advanced Materials Processing Technology of Ministry of Education, School of Materials Science and Engineering, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China
Received 18 June 2013; accepted 8 September 2013
Abstract: The effects of cooling rate on the solidification parameters and microstructure of Al-7Si-0.3Mg-0.15Fe alloy during solidification process were studied. To obtain different cooling rates, the step casting with five different thicknesses was used and the cooling rates and solidification parameters were determined by computer-aided thermal analysis method. The results show that at higher cooling rates, the primary α(Al) dendrite nucleation temperature, eutectic reaction temperature and solidus temperature shift to lower temperatures. Besides, with increasing cooling rate from 0.19 °C/s up to 6.25 °C/s, the secondary dendritic arm spacing decreases from 68 μm to 20 μm, and the primary dendritic volume fraction declines by approximately 5%. In addition, it reduces the length of Fe-bearing phase from 28 μm to 18 μm with a better uniform distribution. It is also found that high cooling rates make for modifying eutectic silicon into fibrous branched morphology, and decreasing block or lamella shape eutectic silicon.
Key words: aluminium alloys; cooling rate; thermal analysis; solidification parameters; microstructure
1 Introduction
With good combination of castability, corrosion resistance, high specific strength, especially in heat treated conditions, Al-Si-Mg casting alloys have achieved widespread usage in automotive and aerospace industries. These alloys offer the ability to cast complex, thin-walled components by sand or permanent mould casting, due to the excellent fluidity. Actually, superior mechanical properties are required in most cases. Since the mechanical properties of these casting aluminium alloys are strongly influenced by the local microstructural features that form during solidification, such as grain size, secondary/dendritic arm spacing, eutectic silicon, intermetallic compounds and shrinkage, a lot of efforts have been made to refine the microstructural features of the castings [1-3]. Adding chemical modifiers to melt is a common way to refine the microstructure and many studies have been done on it [1,4,5]. Strontium acts as one kind of efficient modifier and a small amount of addition into melt can change the coarse plate-like eutectic silicon into fine and fibrous form. Cooling rate can influence the temperature gradient and solidification rate, and is one of the most important variables which affect microstructure and mechanical properties of castings [2,6,7]. At higher cooling rates, more dendrites with small size will be formed [8], resulting in lower and more uniform distribution of shrinkage porosity due to extended mass feeding. Besides, a high cooling rate makes for refining eutectic silicon phase which greatly affects mechanical properties [9]. Furthermore, the influence of cooling rate on intermetallic phases has rarely been studied because of the small amount. Thermal analysis technique which involves the monitoring of the temperature during solidification, is a conventional method in investigating cooling rates, and from the temperature-time curves recorded we can acquire numerous useful information, such as phase transformation and characteristic temperature parameters, solidification latent heat release, and solid fraction variation [10].
The work aims at studying the effects of cooling rate on the solidification parameters, and the microstructures of Al-7Si-0.3Mg-0.15Fe alloys modified with Sr, including primary dendrites, eutectic silicon particles and Fe-bearing phases, for the subsequent study on the relationship between microstructures and mechanical properties.
2 Experimental
2.1 Materials and thermal analysis
The geometry of the casting with 5 steps, is shown in Fig. 1. The step casting was presented in a range of thicknesses changing from 4 to 30 mm. This configuration allowed to acquire a range of solidification rates and consequently resulted in different microstructures in the casting. The present study was performed on the alloy with a chemical composition of Al-7Si-0.3Mg-0.15Fe (mass fraction, %). Prior to pouring, the melting temperature was maintained at 720-740 °C and degassed with pure and dry argon injected into the melt for 8-10 min. After the dross was removed from the melt surface, strontium modifier was added into the melt using Al-10Sr master alloy and uniformly agitated. The modified melt was poured at (730±5) °C into the sand mould. In order to record the cooling curves, one K-type thermocouple covered with stainless steel sheath was inserted into each step and the positions of thermocouples were indicated by the circles in Fig.1. These thermocouples were attached to a data acquisition system and a computer, recording the time-temperature data. In order to ensure statistical accuracy, the thermal analysis experiments were repeated three times for each step.
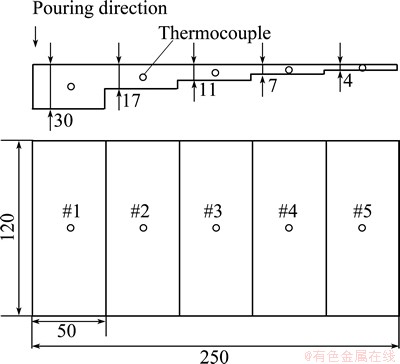
Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of step casting (unit: mm)
2.2 Microstructural analysis
After solidification and removing the thermocouples, each specimen was cut out from the sections where the tips of these thermocouples were located, and were referred to be 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 for convenience. The metallographic specimens were prepared through mechanical grinding and polishing with 2.5 μm and 0.5 μm diamond pastes. Electrolytic etching with the composition of the etch (10 mL HClO4 in volume fraction of 70%), 90 mL anhydrous ethanol) and anodizing for 12-15 s at 0.5 A current (the etching time depends on the size of the section) were performed to reveal the dendritic structure, as well as eutectic silicon morphology. Quantitative microstructural analyses were carried out using an optical microscope (OM) and a scanning electron microscope(SEM) together with energy dispersive spectrometer(EDS). Image analyses were performed on approximately 50 micrographs for each sample to measure the secondary dendritic arm spacing (SDAS), primary dendritic volume fraction and Fe-bearing particle length.
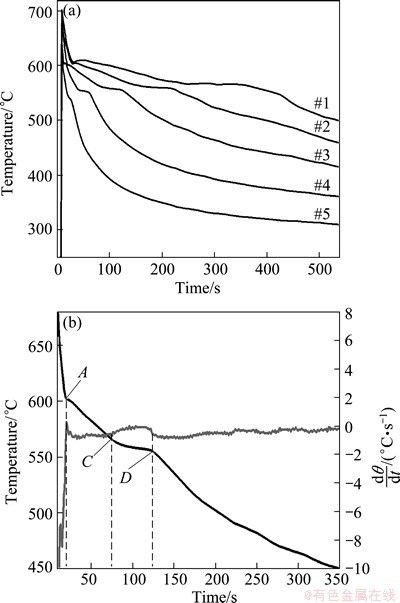
Fig. 2 Cooling curves of different steps (a) and cooling curve #3 (black solid line) with its derivative curve (light gray solid line) (b)
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Solidification behavior analysis
The cooling curves of different steps during solidification (Fig. 2(a)) and the cooling curve #3 with its first order derivative, which indicates the instantaneous cooling rates (dθ/dt) (Fig. 2(b)), are shown in Fig. 2. It can be seen from the cooling curves that the solidification sequence under different cooling rates mainly consists of two obvious phase transformations: firstly, the mass nucleation of aluminium dendrites at point A corresponds the obvious peak in the derivative of the cooling curves; secondly, the main binary (Al+Si) eutectic reaction appears at point C, representing a decline of the cooling rate. If under the condition of equilibrium solidification, more peaks will occur due to the formation of ternary or quaternary eutectic phases, which are difficult to observe from the cooling curves at unequilibrium solidification condition, especially in the case of high cooling conditions [11]. From Fig. 2(a), we can see that there is no thermal arrest time on the cooling curve at point A for #5 step. It is probably that the cooling rate is too high, and the heat release is extremely fast, and the initial step of α(Al) nucleation occurs too fast to be recorded. Some characteristic solidification parameters, such as the mass nucleation temperature of α(Al), θNAl (A point), eutectic temperature of (Al+Si), θNE (C point), solidus temperature, θSOL (D point), and the time for each point, tNAl, tEutectic, tSOL, are measured from the cooling curves, and are listed in Table 1. The average cooling rates are calculated according to the following equation:
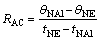 (1)
(1)
The results presented in Table 1 indicate that increasing cooling rate (RAC) causes a decrease in the values at characteristic points. Figure 3 shows the variation trend of the characteristic temperatures θNAl, θEN. It can be observed from Fig. 3(a) that a continuous linear reduction of θNAl from 606 °C to 601 °C when the cooling rate increases from 1.61 to 4.3 °C/s before nucleation, resulting in the increase of nucleation undercooling (θL-θNAl) from 8 to 13 °C. After the formation of α(Al), the melt in the interdendritic areas is enriched in silicon, resulting in the Al-Si eutectic reaction. Variation behavior is seen for the eutectic transformation temperature (θNE) and the undercooling (θE-θNE) shown in Fig. 3(b). It can be seen that the eutectic formation temperature of this alloy significantly decreases with the cooling rate up to 1.75 °C/s, and then becomes more gradual with a further increase in cooling rate. These undercoolings created respectively for α(Al) and eutectic are the driving force of nucleation and growth. JAFARI et al [12] discovered that the θNAl of AZ91D alloy during investment casting decreased linearly with the cooling rates, which is consistent with the results of the present work.
Table 1 Thermal characteristics of cooling curves
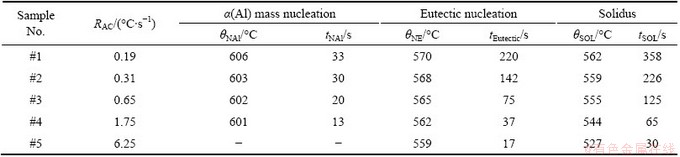
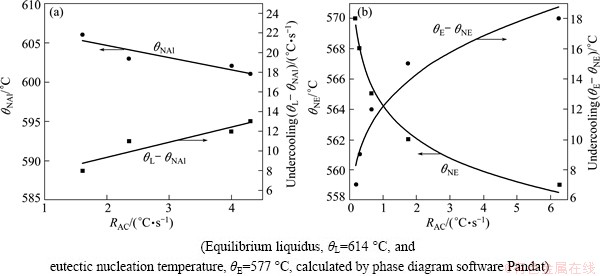
Fig. 3 Effect of cooling rate on α(Al) nucleation temperature (a) and eutectic temperature (b)
A depression of the eutectic temperature with the increasing cooling rate can be explained by coupled area theory. For faceted-nonfaceted Al-Si eutectic alloy, the couple area tends to expand on the side of Si which can be seen in Ref. [13]. At higher cooling rates, the primary α(Al) dendrites solve more Si atoms, with less silicon rejected into the liquid compared with that at low cooling rates. In other words, it needs to shift the eutectic point to a lower temperature to achieve the higher silicon content in liquid.
3.2 Microstructural characterization
The microstructural study of the Al-7Si-0.3Mg- 0.15Fe alloys used in the experiment contains α(Al) dendrites, eutectic silicon, and Fe-bearing intermetallic phases. The main interest to the investigation is the influence of the cooling rate on the microstructural features. The results will be discussed in the following sections.
3.2.1 Primary dendrite
Since castings are characterized in a range of cooling rates, especially for complex ones, the local SDAS values vary significantly in different zones.
Figure 4 shows the metallographical microstructure of samples 1-5. It can be seen that the microstructure consists of a primary α(Al) (light area), and mixture of eutectic and intermetallics (black area). The scale of microstructure of different step areas with different cooling rates was analyzed by measuring the SDAS which exerts a marked influence on the mechanical properties of casting alloys. Numerous solidification studies have been developed with a view to characterize SDAS under experimental circumstances. In Al-Si casting alloys, SDAS is usually expressed as a function of local solidification time (tSL=tEutectic-tNAl) [14], or average cooling rate RAC according to
SDAS=ASi(tSL)n (2)
or
SDAS=K(RAC)-c (3)
where ASi is a constant for a fixed composition alloy which inversely changes with the silicon content (ASi=15.3, 14.0, 12.8, and 11.5 for 3.8%, 5.7%, 7.5% and 9.7%, respectively) [15]; n and c are the exponents; K is a constant. Based on Ref. [16], the values of n and c range from 0.3 to 0.5, which are related to the calculation method of cooling rates. Figure 5 gives the plots of SDAS versus cooling rate and local solidification time both with a good coefficient of determination R2=0.98, proving the reliability of these two empirical formula in predicting SDAS. This fitting formula is quite in agreement with the results as reported in Ref. [17] that SDAS in A356/A357 alloys fits well the empirical equation SDAS=39.4R-0.317, where R represents the mean cooling rate of primary α(Al) dendrite during solidification.
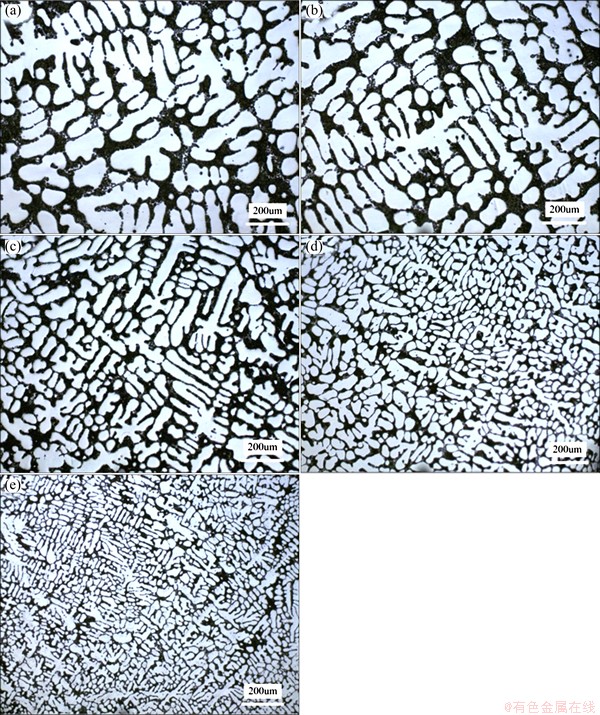

Fig. 4 Optical microstructures of sample 1 (a), sample 2 (b), sample 3 (c), sample 4 (d), sample 5 (e) with different cooling rates
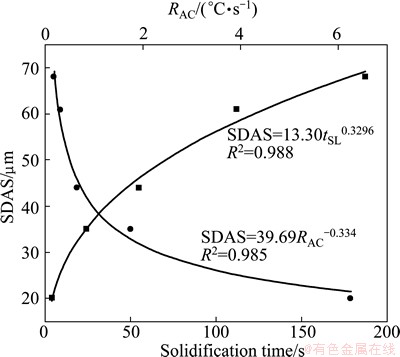
Fig. 5 Effect of cooling rate and solidification time on SDAS
SDAS strongly depends on the cooling rate. According to the analysis of the cooling curves, the increasing cooling rate will increase the undercooling, resulting in more α(Al) grains nucleated, and making for the refinement of microstructure. Due to the different radii of secondary dendritic arms during the growth process, the composition nearby the dendritic surface varies from place to place, and diffuses from the high solubility area (coarse secondary dendritic arms area) to the low-solubility area (fine secondary dendritic arms area), resulting in dissolution of the fine dendritic arms and coarsening of coarse dendritic arms. When the cooling rate increases, there is not enough time for this process, thus refining SDAS.
In addition to the SDAS, a variation in the cooling rate affects the volume fraction of α(Al) dendrites. According to Ref. [18], mechanical properties are related to the amount of dendritic α(Al) phase for Sr-modified Al-Si alloy. For quantitative metallography by image analysis, the volume fraction is equal to the area percent in a random section. After being etched, the eutectic becomes dark and the dendrite is light (Fig. 4), so the software can easily distinguish these two features. The amount of dendritic α(Al) phase of this alloy with varying cooling rates is plotted in Fig. 6. The statistical result suggests that the dendritic quantity decreases with the increasing cooling rates. In other words, the quantity of eutectic and intermetallic phases increases with the increasing cooling rate (in the lower and intermediate cooling range). In Ref. [19], it also demonstrated such relationship between the amount of eutectic and cooling rate experimentally and theoretically for Al-Fe-Si alloys. It is reasonable to believe that the phenomenon is attributed to the decreasing time (tSL=tEutectic-tNAl) for the homogenizing effects of coarsening for α(Al) dendrites when the cooling rate is improved. When cooling rate is below 1.75 °C/s, there is a relatively significant decrease from 61% to 56% in the amount of α(Al), while increasing the cooling rate from 1.75 °C/s to 6.25 °C/s only decreases by less than 1% α(Al) in volume fraction. The reason may be that the amount of dendrites is affected by solidification time, nucleation, growth rate, and the latter two factors produce obvious effects on the amount of dendrites in the high-cooling rate, resulting in slow decline from 1.75 °C/s to 6.25 °C/s.
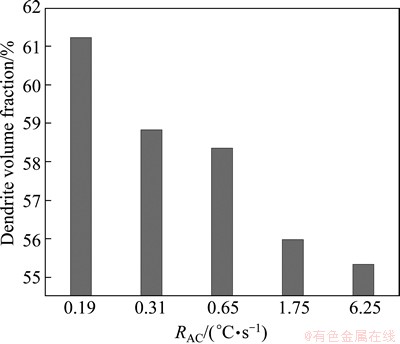
Fig. 6 Variation of dendrite volume fraction with average cooling rate
3.2.2 Silicon particle characterization
Size, morphology and distribution of eutectic silicon are vital microstructural parameters determining mechanical properties of A356 alloy. It is well known that the unmodified eutectic silicon has an undesired plate-like morphology, which is the stress concentrator reducing strength, ductility and fatigue strength. Figure 7 shows the eutectic silicon morphology surrounding dendrites in as-cast state of samples 1, 3 and 5, and Figs. 7(d) shows the typical morphology of the Sr-modified alloy in higher magnification. These SEM images indicate that most of eutectic silicon was changed into fibrous-like morphology after addition of Sr, and show the different degrees of eutectic Si modification under different cooling rates. It can be observed that with the increasing cooling rate, the eutectic silicon size refines, and the branched morphology becomes more apparent. The low cooling rate of sample 1 contains some block or lamella shape eutectic silicon surrounded by dendrites which presents as facet feature and becomes less when the cooling rate reaches 0.65 °C/s. When the cooling rate increased to 6.25oC/s, the block or lamella shape eutectic silicon disappeared and the branched structure of fibrous shape enhanced, weakening eutectic silicon facet characterization. Some studies performed with Sr modified AlSi7Mg alloy revealed that eutectic silicon would change into fibrous when the cooling rate was 9.8 °C/s, and even spicate silicon appeared further, improving the cooling rate [20].
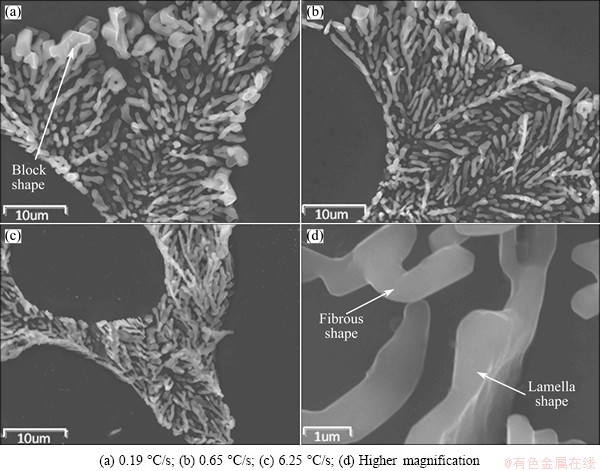
Fig. 7 SEM images morphologies of eutectic silicon at different cooling rates
Many literatures [2,21] about modification treatment have well established that modification of Al-Si eutectic is typically accompanied by a depression of the eutectic temperature. According to the analysis of cooling curves above, the eutectic temperature decreases with the increasing cooling rate, leading to a larger depression of eutectic arrest temperature, and improving the modification effect of Sr on eutectic silicon.
3.2.3 Fe-intermetallics variation
Most of the intermetallic phases are formed at α(Al) interdendrites or the area between eutectic silicon and α(Al) dendrites, which can be seen from Fig. 8. The solidification sequence of A356 alloy mainly contains three reactions if neglecting the formation of Mg2Si phase and the last one reaction is L+Al5FeSi→Al+Si+ π-Al8FeMg3Si6. Since elements Mg and Fe are rejected by the α(Al) solid and eutectic, because of their very low solubility, they segregated at interdendritic and dendritic edge in the remaining liquid, consequently solidified as intermetallic phases. Because of irregular shape, it is difficult to acquire a reliable quantitative measurement of the volume fraction of intermetallic phases. The approach used in the study to quantify the intermetallic characterization is measuring the average length by metallography, which is a useful tool in characterizing the structure changes of intermetallic phases. Approximately 100 intermetallic particles were analyzed for each sample with different cooling rates and the analyzed particles are all the largest three in every metallograph. The average length of intermetallics for cooling rates 0.19, 0.31, 0.65, 1.75, 6.25 °C/s are 28.1, 27.1, 22.9, 19.7, and 18.2 μm, respectively as shown in Fig. 9. It suggests that improving cooling rate can make for refinement of intermetallics. At a higher cooling rate, the grain size and secondary dendritic arm spacing are refined (Fig. 4), resulting in the larger dendritic boundary area per unit volume, thus the remaining liquid areas are thinner and broken-up into a large number of isolated channels, preventing the intermetallics from connection [22]. According to the result of WANG et al [23], the size of Fe-bearing particles can reduce by as much as 50% when the SDAS decreases from 60 μm to 20 μm. Another reason for intermetallics refinement is that when the cooling rate increases, there is fewer time for the intermetallic particles to grow and coarsen, resulting in small and short particles. Therefore, high cooling rates for Sr modified alloys not only refine eutectic silicon, but also the intermetallic phases, which have more significant effects on mechanical properties of cast alloy.
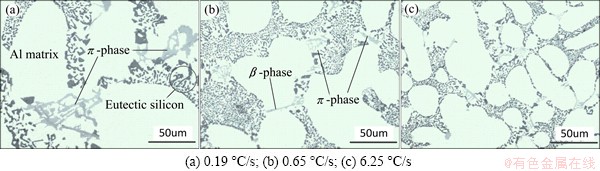
Fig. 8 Size and distribution of Fe-bearing phases at different cooling rates
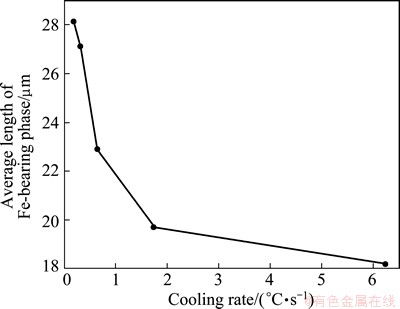
Fig. 9 Average length of Fe-bearing phases at different cooling rates
The possible minor intermetallic phases existing in A356 alloys are π-AlFeMgSi, needle-like β-AlFeSi, and Mg2Si. TAYLOR et al [24] examined the effect of Mg content on the relative volume fraction of the existing minor phases for iron contents of 0.12% in detail. They found that in as-cast state, the π phase absorbed almost all the Mg element and its volume fraction was approximately at level of 1%, independent of Mg content, while β phase and Mg2Si only occupy 0.1% (volume fraction) respectively with a small variation when Mg level was improved. WANG and CACERES [17] could not detect the Mg2Si formation reaction from DTA curves for A356 alloys with Mg contents below 0.6%. Relative study [25] has proved that adding Sr into Al-Si-Mg alloy with a small amount of Fe can change needle-like β-phase into nodular and block shape morphology. In our experiment, there is no Mg2Si phase found and most of the Fe-bearing phases contain elements Al, Si, Mg, Fe after the analysis of EDS and few β phases are found.
4 Conclusions
1) Increasing the cooling rate from 0.19 to 6.25 °C/s, the primary α(Al) dendrite nucleation temperature, eutectic reaction temperature and solidus temperature shift to lower temperatures, resulting in a larger undercooling both for α(Al) and eutectic.
2) The secondary dendritic arm spacing is very sensitive to cooling rate and an increase of cooling rate from 0.19 to 6.25 °C/s decreases SDAS from 68 to 20 μm, and the volume fraction of primary dendrites declines by approximately 5%. The eutectic silicon is refined and the branched structure of fibrous shape is enhanced at higher cooling rates. The average length of Fe-bearing phases is 28 μm at 0.19 °C/s while it decreases to 18 μm when the cooling rate arrives 6.25 °C/s, refining both the size and distribution.
References
[1] CESCHINI L, MORRI A, MORRI A. Predictive equations of the tensile properties based on alloy hardness and microstructure for A356 gravity die cast cylinder head [J]. Materials and Design, 2011, 32: 1367-1375.
[2] ZHANG L Y, ZHOU B D, ZHAN Z J. Mechanical properties of cast A356 alloy, solidified at cooling rates enhanced by phase transition of a cooling medium [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2007, 448: 361-365.
[3] HOSCH T, NAPOLITANO R E. The effect of the flake to fiber transition in silicon morphology on the tensile properties of Al-Si eutectic alloys [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2010, 528: 226-232.
[4] LI B, WANG H W, JIE J C. Microstructure evolution and modification mechanism of the ytterbium modified Al-7.5%Si-0.45%Mg alloys [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2011, 509: 3387-3392.
[5] DONG Y, ZHENG R G, LIN X P. Investigation on the modification behavior of A356 alloy with a Sr-Y composite modifier [J]. Journal of Rare Earths, 2013, 31: 204-208.
[6] DOBRZANSKI L A, MANIARA R, SOKOLOWSKI J. Effect of cooling rate on the solidification behavior of AC AlSi7Cu2 alloy [J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2007, 191: 317-320.
[7] HEMANTH J. Effect of cooling rate on dendrite arm spacing (DAS), eutectic cell count (ECC) and ultimate tensile strength (UTS) of austempered chilled ductile iron [J]. Materials and Design, 1999, 21: 1-8.
[8] HOSSEINI A, SHABESTARI S C, GHOLIZADEH R. Study on the effect of cooling rate on the solidification parameters, microstructure, and mechanical properties of LM13 alloy using cooling curve thermal analysisi technique [J]. Materials and Design, 2013, 50: 7-14.
[9] ESKIN D, DU Q, RUVALCABA D. Experimental study of structure formation in binary Al-Cu alloys at different cooling rates [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2005, 404: 1-10.
[10] HERNANDEZ F C R, SOKOLOWSKI J H. Thermal analysis and microscopical characterization of Al-Si hypereutectic alloys [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2006, 419: 180-190.
[11] WANG Q G, DAVIDSON C J. Solidification and precipitation behavior of Al-Si-Mg casting alloys [J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2001, 36: 739-750.
[12] JAFARI H, IDRIS M H, OURDJINI A. In situ melting and solidification assessment of AZ91d granules by computer-aided thermal analysis during investment casting [J]. Materials and Design, 2013, 50: 181-190.
[13] MAKHLOUF M M, GUTHY H V. The aluminum-silicon eutectic reaction: Mechanisms and crystallography [J]. Journal of Light Metals, 2001, 1: 199-218.
[14] PEDRO R, JOSE E, SPINELLI, WISLEI R. Mechanical properties as a function of microstructure and solidification thermal variables of Al-Si castings [J]. Material Science and Engineering A, 2006, 421: 245-253.
[15] SPINELLI J E, PERES M D, GARCIA A. Thermosolutal convective effects on dendritic array spacings in downward transient directional solidification of Al-Si alloys [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2005, 403: 228-238.
[16] FLENINGS M C. Solidification process [M]. USA: MacGrraw-Hill, 1974.
[17] WANG Q G, CACERES C H. Mg effects on the eutectic structure and tensile properties of Al-Si-Mg alloys [J]. Mater Sci Forum, 1997, 242: 159-164.
[18] LIAO H C, SUN Y, SUN G X. Correlation between mechanical properties and amount of dendritic α-Al phase in as-cast near-eutectic Al-11.6%Si alloys modifies with strontium [J]. Material Science and Engineering A, 2002, 335: 62-66.
[19] DUTTA B, RETTNMAYR M. Effect of cooling rate on the solidification behavior of Al-Fe-Si alloys [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2000, 283: 218-224.
[20] LI Bao. Modification evolution of eutectic silicon AlSi7Mg alloy and micro-mechanism [D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2011. (in Chinese)
[21] KNUUTINEN A, NOGITA K, MCDONALDS S D, DAHLE A K. Modification of Al-Si alloys with Ba, Ca, Y and Yb [J]. Journal of Light Metals, 2001, 1: 229-240.
[22] VERMA A, KUMAR S, GRANT P S. Influence of cooling rate on the Fe intermetallic formation in an AA6063 Al alloy [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2013, 555: 274-282.
[23] WANG Q G, APELIAN D, LADOS D A. Fatigue behavior of A356/A357 aluminum cast alloys. Part II—Effect of microstructural constituents [J]. Journal of Light Metals, 2001, 1: 85-97.
[24] TAYLOR J A, STJOHN D H, BARRES J I, COUPER M J. Influence of Mg content on the microstructure and solid solution chemistry of Al-7%Si-Mg casting alloys during solution treatment [J]. Materials Science Forum, 2000, 277: 331-337.
[25] RODRIGUEZ S H, RAFAEL E, REYES G. On influence of Ti and Sr on microstructure, mechanical properties and quality index of cast eutectic Al-Si-Mg alloy [J]. Materials and Design, 2011, 32: 1865-1871.
冷却速度对Al-7Si-0.3Mg-0.15Fe合金凝固参数和微观组织的影响
陈 瑞,石玉峰,许庆彦,柳百成
清华大学 材料学院,先进成形制造教育部重点实验室,北京 100084
摘 要:研究凝固过程中冷却速度对Al-7Si-0.3Mg-0.15Fe合金凝固参数和组织的影响。为了获得不同的冷却速度,设计了5个不同厚度阶梯的阶梯间。通过计算机辅助热分析法得到冷却速度和凝固参数。结果显示,冷却速度越高,初生α(Al)的形核温度、共晶反应温度以及固相线的温度都越低。当冷却速度由0.19 °C/s 增加到 6.25 °C/s时,二次枝晶臂间距(SDAS)从68 μm下降到20 μm,初生相的体积分数也下降5%。铁相的平均长度由28 μm下降到18 um,并且提高了铁相在基体中的分布均匀性。此外,冷却速度的提高,有利于促进共晶硅向纤维状分支结构的转变,减少了基体中的块状和板状共晶硅。
关键词:铝合金;冷却速度;热分析;凝固参数;微观组织
(Edited by Xiang-qun LI)
Foundation item: Projects (2005CB724105, 2011CB706801) supported by the National Basic Research Program of China; Projects (10477010, 51171089) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Projects (2009ZX04006-041-04, 2011ZX04014-052) supported by the Important National Science &Technology Specific, China
Corresponding author: Qing-yan XU; Tel: +86-10-62795482; E-mail: scjxqy@mail.tsinghua.edu.cn
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(14)63236-2