西藏吉瓦地区中冈底斯带岗在岩体晚白垩世的岩浆作用及构造意义
王力圆1, 2,郑有业2,高顺宝1,李伟良1,薛兆龙2
(1. 中国地质大学 地质调查研究院,湖北 武汉,430074;
2. 中国地质大学 资源学院,湖北 武汉,430074)
摘要:总结吉瓦地区岗在岩体的地质特征及成矿意义,为研究其岩石成因及地球动力学背景,对寄主花岗闪长岩和包体的微量元素、稀土元素及同位素等地球化学特征进行分析。研究结果表明:该花岗闪长岩具有高钾、高铝的特征,富集 Rb,Th,K,La和Hf,亏损Ba,Nb,Sr,P和Ti,属于弱过铝质高钾钙碱性系列,具有I型花岗岩的特征。包体与寄主岩经历了岩浆混合作用,二者可能具有不同的岩浆来源,二者稀土和微量元素具有相似的分布样式。从地球化学特征、包体的形态及矿物组合特征均显示出明显的岩浆混合作用趋势。岩浆来自轻稀土元素(LREE)丰度相对较高的壳源物质并可能受到幔源岩浆的混合,寄主岩石与包体相比较,Eu负异常明显。岗在岩体的锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb年龄为(74.8±1.6) Ma,形成于火山弧环境,受到雅鲁藏布特提斯的北向俯冲与班公湖—怒江洋盆南向俯冲消减碰撞双重制约有关。反映了中冈底斯带吉瓦地区从俯冲到碰撞造山并伴随着岩浆活动的中心总体在从南向北发生迁移的过程。岩体发育较多的石英脉,受控于断裂发育,石英脉中含有金矿化,且岩体周围发育砂金矿点,岩体可能为周围的砂金矿点提供了成矿物质,且本身有形成岩浆热液型金矿的潜力。
关键词:中冈底斯;岩浆混合;暗色包体;晚白垩世;吉瓦
中图分类号:P588.121 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2014)08-2740-12
The Upper Cretaceous magmatism from Gangzai pluton in Middle-Gangdese,Jiwa,Tibet and its tectonic significance
WANG Liyuan1, 2, ZHENG Youye2, GAO Shunbao1, LI Weiliang1, XU Zhaolong2
(1. Geological Survey, China University of Geosciences, Wuhan 430074, China;
2. Faculty of Earth Resources, China University of Geosciences, Wuhan 430074, China)
Abstract: The characteristics of the Gangzai pluton geological and metallogenic significance were summarized. In order to study the petrogenesis and geodynamic setting, the major, trace, rare earth elements and isotopes were analyzed. The results indicate that this granodiorite has properties of high-K and high-aluminum. It is in enrichment of Rb, Th, K, La and Hf, and in depletion of Ba, Nb, Sr, P and Ti, and it belongs to weak peraluminous high-K calc-alkaline series, and has properties of I-type granite. The enclaves and the host rock have experienced magma mixing. They may have different magma sources. Their REE and trace elements have similar distribution pattern. The trend of magma mixing is apparently displayed in geochemical properties, enclaves’ form, and mineral association. The magma is from crust-derived material which is in enrichment of LREEs, and may be mixed with mantle-derived magma. Compared to enclaves, the host rock has an apparent negative anomaly of Eu. The LA-ICP-MS U-Pb zircon dating of Gangzai pluton shows an age of (74.8±1.6) Ma. It is formed under volcanic-arc environment, and has relationship with the double constraints of the collision of northward subduction of Yarlung Zangbo Tethys and southward subduction of Bangong Nujiang. It is reflected that the center of Jiwa area’s transition is from subduction to collision with magmatism, and moves from south to north in overall. Quartz veins are widely developed in this pluton, and are controlled by faults. Gold mineralization can be found in these veins, and develops into alluvial gold ore occurrences around pluton. The pluton may serve the metallogenic materials for these ore occurrences, and has the capacity of forming magmatic hydrothermal type gold deposit.
Key words: Middle-Gangdese; magma mixing; mafic micro-granular enclaves; the Upper Cretaceous; Jiwa
冈底斯带岩浆发育,以中酸性为主的岩浆活动强烈而复杂,该区的中酸性岩浆活动是青藏高原岩浆活动的缩影,是班公湖—怒江和雅鲁藏布2个特提斯演化的共同作用域。冈底斯花岗岩主要形成于早侏罗世—中新世,从北向南分为3个带,其中中带位于狮泉河—永珠—嘉黎—迫龙藏布断裂带(YNS)以南和麦拉—洛巴堆—米拉山断裂(MLMF) 以北,相当于隆格尔—念青唐古拉复合古岛弧带,根据目前的研究成果,该岩带可划分为3个岩区(亚带),即措勤—申扎岩区、羊八井—旁多岩区和朗那—念青唐古拉—工布江达岩区。花岗岩的时代主要有三叠纪—早侏罗世(227~195.3 Ma)、晚侏罗世—白垩纪(178~65 Ma) 和古近纪—中新世(62~13.6 Ma)3个阶段[1-5]。其中Wen等[6]认为晚白垩纪和早第三纪是冈底斯岩浆活动的 2 个主要阶段,并认为 50~45 Ma 是岩浆最剧烈活动阶段。大多学者认为冈底斯的中生代岩浆岩形成于安第斯型造山过程中[7-10],由于中带大部分位于冈底斯山脉腹地,工作条件艰苦,与冈底斯带南部和北部相比,研究程度要低很多。但该带本身的构造意义和成矿潜力不亚于冈底斯南带和北带。本文作者在1:5万区域地质调查的基础上发现:出露在隆格尔—念青唐古拉带北侧的岗在岩体周边的地方存在较多的金矿点,显示出了该岩体在成矿作用方面的重要意义,因此,对其进行了详细地野外填图和剖面测制,并以此为基础,利用系统的岩石学及地球化学数据来探讨中冈底斯晚白垩世岩浆作用、成因及其构造意义。
1 地质背景
岗在岩体位于尼玛县吉瓦乡南部(图1),属于班公湖—怒江结合带与雅鲁藏布江结合带之间的措勤—申扎岛弧[11],岩体面积较小,约8 km2,呈岩株产出,为花岗岩类,岩性主体为花岗闪长岩,其中含有较多的闪长质暗色包体(MME)。岗在岩体呈近东西向延伸的椭圆形,基本与区域构造线方向一致,并与早白垩世火山岩(区域地质资料为上新世乌郁群(N2wy),最新锆石测年为125 Ma,未发表资料)呈侵入接触关系。
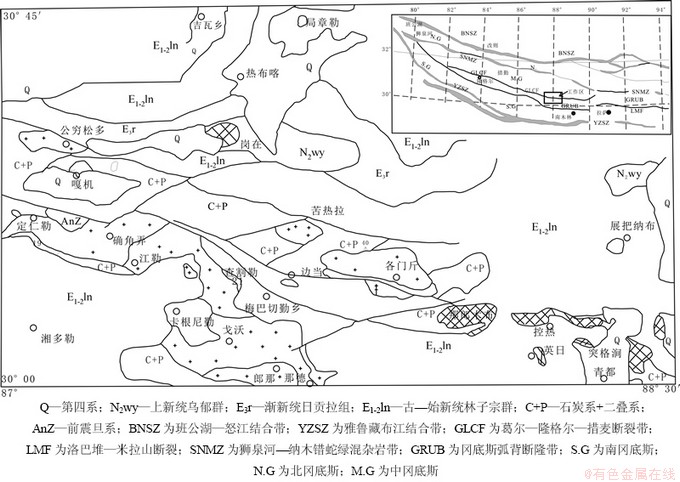
图1 研究区岩浆岩分布图(据卢书炜等[8])
Fig. 1 Distribution of magmatic rocks in the study area
岩体内部发育花岗细晶岩脉(图2(a)),大致北西南东向展布,延长一般为150~300 m。岩体内构造破碎带较发育,穿插多条石英脉,受控于2组近垂直的断层。石英脉中具有明显的金矿化。
2 岩石学及矿物学特征
包体与寄主岩之间的接触关系以截然接触为主(图2(b)和(c)),包体边缘清晰,界线两侧未见冷凝边和烘烤边,说明包体形成过程中,2个端员之间存在热学状态的差异[12]。暗色微粒包体通常呈卵圆形或椭球形,直径一般为5~15 cm,细粒结构,块状构造。色率较深,岩体中部分还可见到少量的淡色包体(图2(d))。岩石包体中斜长石占40%~60%(质量分数,下同),钾长石占15%~20%,角闪石约10%,黑云母约10%,部分样品中出现少量的辉石1%~3%和石英10%~15%。斜长石半自形板状为主,杂乱分布,较轻微绢云母化、高岭土化,局部绿帘石化、绿泥石化,部分隐约见环带,局部被钾长石蚕蚀状;钾长石它形粒状,零散填隙状分布,表面较干净,轻微交代斜长石;角闪石半自形—近半自形柱状、粒状为主,少量它形柱、粒状,杂乱分布,显(褐)绿色,多褪色为淡绿色、少见蓝绿色,局部绿泥石化、褐铁矿化等;黑云母叶片状,杂乱状分布,绿泥石化、褐铁矿化等呈假象(图2(g)和(h))。岩体内见少量围岩捕虏晶,成分主为斜长石,粒径为1.0~3.0 mm,绢云母化、褐铁矿化等。
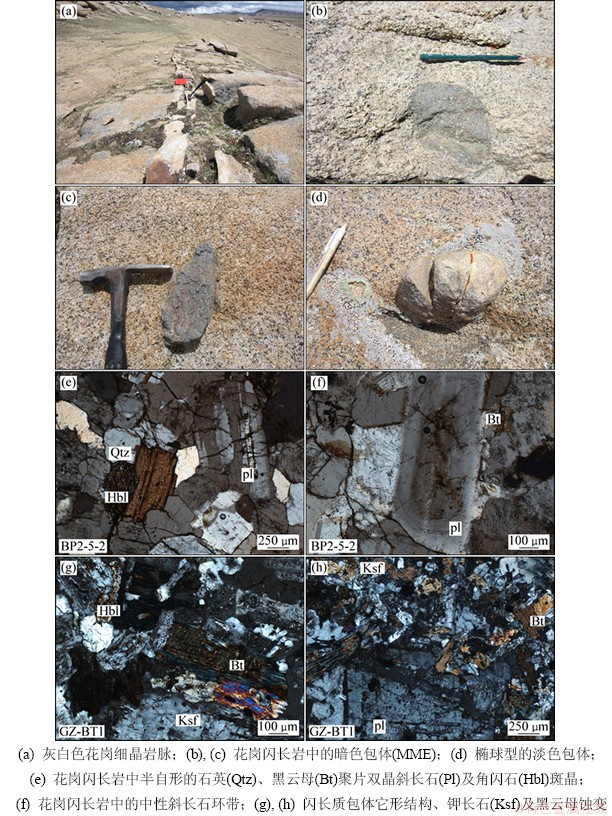

图2 岗在岩体典型野外与显微照片
Fig. 2 Photographs of magmatic rocks in Gangzai region
岗在岩体以灰白色—淡红色花岗闪长岩为主,其次为二长花岗岩,岩体内见少量被褐铁矿等充填的裂隙。整体为中粗粒状为主,块状构造,花岗结构,斑晶为斜长石、钾长石、石英、黑云母、角闪石组成(图2(e))。斜长石以中长石—更长石为主,含量可达55%,半自形板状,双晶较清晰,可见聚片双晶和卡钠复合双晶,杂乱分布,轻微绢云母化、高岭土化等,多具环带构造(图2(f));有的次生矿物沿斜长石核心及环带分布,局部被钾长石蚕蚀状交代可见蠕虫、交代净边结构。钾长石它形粒状,零散填隙状分布,具高岭土化,轻微交代斜长石。石英它形粒状,零散填隙状分布,具波状、带状消光,少见与钾长石似文象交生状。黑云母叶片状,零散分布,少量与角闪石一起呈堆状聚集分布,少见绿泥石化。角闪石半自形—近半自形柱状、粒状,少量它形柱粒状,零散分布,分布状况同黑云母,局部绿泥石化、褐铁矿化。显(褐)绿色,少见褪色为淡绿色。岩内见少量被褐铁矿等充填的裂纹,部分褐铁矿沿晶间分布。
3 地球化学特征
通过实测岩体剖面和野外填图,选取4件包体和6件寄主岩样品进行岩石地球化学分析,其中主量元素、稀土微量元素均在武汉岩矿综合测试中心完成,主量元素主要采用X线荧光光谱(XRF)分析,稀土微量元素采用电感耦合等离子体发射光谱仪(ICP-AES) 分析,分析结果见表1。花岗闪长岩SiO2质量分数介于 66.6%~69.2%,平均为67.6%,暗色包体SiO2质量分数为56.3%~59.6%,平均为57.7%。寄主岩全碱含量较高,花岗闪长岩K2O+Na2O质量分数为6.6%~7.5%,暗色包体中为6.3%~6.7%,在全碱—硅分类图解中(图3)[13],花岗岩类样品全部落入花岗闪长岩区,暗色包体主要集中在闪长岩与二长岩的界限上。
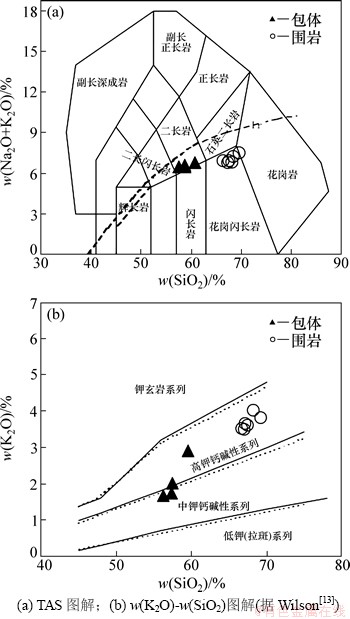
图3 岗在岩体岩石类型和系列划分图解
Fig. 3 Classification and series diagrams of rocks in Gangzai
在SiO2-K2O图解中,包体属于中钾钙碱性系列,寄主岩属于高钾钙碱性系列。包体与寄主岩MgO含量差别较大,包体MgO含量为3.8%~4.6%,平均为4.06%,w(Mg2+)/w(Mg2++Fe2+)介于50%~54%;寄主岩MgO含量为1.27%~1.95%,平均为1.27%,w(Mg2+)/ w(Mg2++Fe2+)介于44%~49%。包体与寄主岩二者MgO含量差别较多,一般认为下地壳岩石部分熔融形成的熔体,其w(Mg2+)/w(Mg2++Fe2+)小于50%,而地幔橄榄岩部分熔融的熔体具有较高的Mg含量[14]。
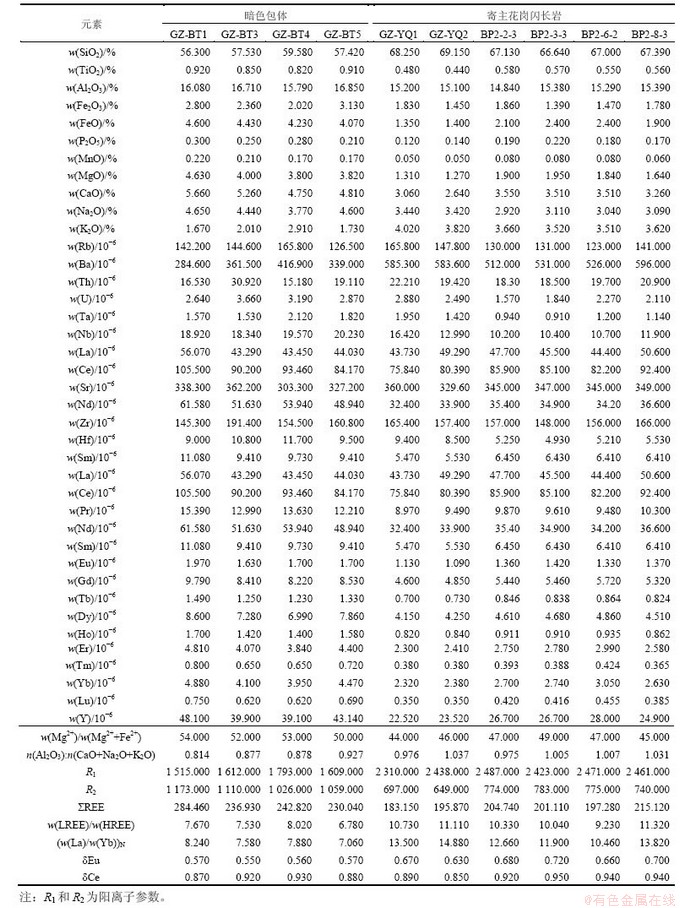
包体的稀土元素总含量大于花岗闪长岩的稀土元素总含量,花岗闪长岩的稀土元素总含量最高为215.12×10-6,最低为183.15×10-6,暗色包体的稀土元素总含量最高为284.46×10-6,最低为230.04×10-6。
两者稀土元素分配曲线显示良好的一致性,轻稀土元素(LREE)相对富集、重稀土元素(HREE)相对亏损,均具有明显 Eu 负异常(图4) [15-16],其寄主岩石w(LREE)/w(HREE)平均为10.46,(w(La)/w(Yb))N介于 10.46~14.88,平均为12.87;暗色包体w(LREE)/ w(HREE)平均为8.14,(w(La)/w(Yb))N介于7.06~13.5,平均为8.85,总体反映二者可能具有不同的岩浆源区,且具有 LREE 丰度相对较高的壳源物质参与岩浆作用的特点。
表1 西藏中冈底斯岗在岩体全岩地球化学成分(质量分数)
Table 1 Rock major, and trace element of magmatic rocks in Gangzi region of Mid-Gangdese, Tibet
原始地幔标准化的微量元素显示出花岗闪长岩和暗色包体具有相似的蛛网分布样式。两者均高场强元素 Nb,Ta,Zr,Hf和Ti 相对亏损;Rb,K,Th和U 相对富集。Ba 相对于 Rb 和 Th 亏损。大离子元素富集和高场强元素亏损。
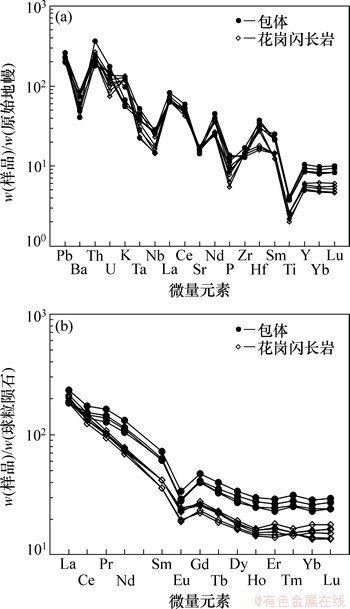
图4 岗在岩体稀土元素球粒陨石标准化配分曲线图(a)和微量元素原始地幔标准化配分曲线图(b)(球粒陨石据见Boynton[15];原始地幔数据见Sun and McDonough [16])
Fig. 4 Chondrite-normalized REE (a) and primitive-mantle-normalized trace element patterns (b) for magmatic rocks in Gangzai
4 同位素年代学特征
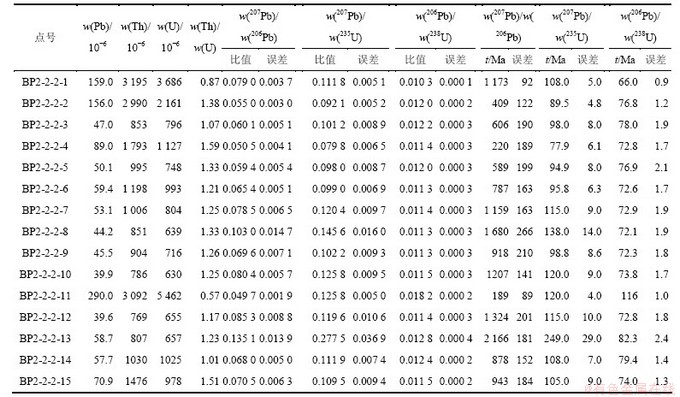
在详细野外工作的基础上,对岗在岩体花岗闪长岩LA-ICP-MS锆石采用U-Pb 测年龄。测试工作在中国地质大学(武汉) 地过程与矿产资源国家重点实验室完成,详细的仪器操作条件、测试方式和数据处理方法见文献[17]。花岗岩样品中锆石多数长柱状少部分短柱状,自形到半自形晶形,颗粒长 100~200 μm,长宽比介于 1:1~2:1;锆石韵律环带构造发育,w(Th)/w(U)范围为0.71~2.0,且样品中锆石振荡环带清晰,属于生长韵律为典型的岩浆成因锆石(图5(a)),花岗闪长岩样品( BP2-2-2)中共15个测点(表2),其中12个测点w(206Pb)/w(238U)年龄分布在71.50~79.56 Ma之间,取得的 12 个分析点的w(206Pb)/w(238U)加权平均年龄为(74.8±1.6) Ma,加权平均方差(MSWD)为2.5,另外1颗锆石显示w(206Pb)/w(238U)年龄分别为 116.0 Ma推测可能为岩浆上升或就位过程中捕获早白垩火山岩的锆石,卢书炜等[18]在岗在岩体中获得黑云母Ar-Ar 年龄为(73.99±1.11) Ma,与本文测得年龄接近,可以确定岗在岩体的成岩年龄(74.8±1.6) Ma为晚白垩晚期。
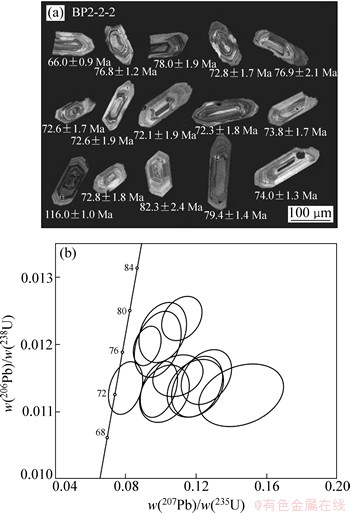
图5 岗在岩体锆石阴极发光(CL)图像(a)和U-Pb年龄谐和图(b)
Fig. 5 Cathodoluminescence (CL) images of representative zircon (a) and concordia diagrams (b) for zircons from magmatic rocks in Gangzai
表2 西藏岗在岩体锆石LA-ICP-MS U Pb分析结果
Table 2 Zircon U-Pb dating of of the magmatic rocks in Gangzai, Tibet
5 讨论
5.1 岩石成因
岩石的类型和岩浆岩形成的地球动力学过程密切相关,岩相学上没有发现堇青石、白云母和石榴子石等传统上作为S型花岗岩判别标志的富铝矿物,本文样品中的暗色包体和花岗闪长岩铝饱和指数(即n(Al2O3):n(CaO+Na2O+K2O),n为物质的量)均小于1.1(表1),由此可以判断岗在岩体花岗闪长岩属于I型[19]。结合实验结果表明,以P2O5,Th和Rb等元素判断花岗岩类别较为可靠。在准铝质或弱过铝质花岗岩浆中,磷灰石的溶解度很低,并且会随着温度的降低和岩浆分异演化SiO2的增加而降低[20];I型和A型花岗岩的P2O5与SiO2呈负相关性,而S型花岗岩的P2O5随着SiO2质量分数增加呈增高或基本不变的趋势[21]。岗在岩体P2O5质量分数为0.12%~0.22%,随着SiO2质量分数增加而降低,Th-Rb图解中(图6)也显示了同样的I型花岗岩趋势。
5.2 包体与寄主花岗闪长岩成因关系
花岗岩中微粒包体的成因复杂多样,不同类型微粒包体的特征和成因,对于理解花岗质岩浆的起源和演化具有十分重要的意义,目前对于暗色包体的来源主要有不同认识:一是认为暗色包体来自岩浆,即包体由混入花岗岩浆中的中基性岩浆固结而成[22-23];二是认为暗色包体来自岩石,即包体是岩石部分熔融产生的富铁镁残余熔渣[24-25];三是认为暗色包体来自靠近寄主岩浆的围岩捕掳体、源区残留体[26]或者同生堆晶岩[27]。
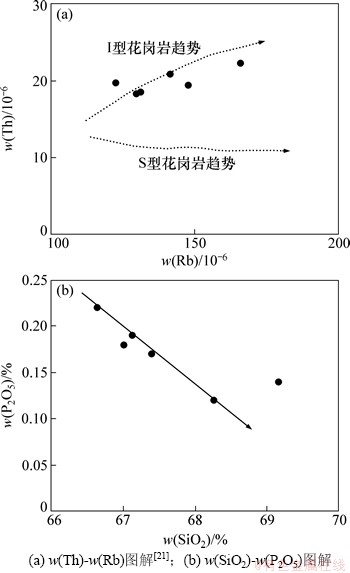
图6 岗在花岗闪长岩岩石类型判别图解
Fig. 6 Discrimination diagrams of granodiorite type
通过包体与寄主花岗闪长岩化学成分的对比可以看出:包体总是比相应的寄主岩富CaO,Fe2O3,FeO,MnO,MgO,TiO2和P2O5,贫K2O,而Al2O3相对持平,包体和寄主岩的主要氧化物质量比之间表现出良好的协变关系,暗示它们在成因上可能存在密切的联系,包体与寄主岩之间很可能发生过岩浆混合作用[28]。包体质量分数比寄主岩的V,Ni和Co质量分数均高,w(Rb)/w(Sr)为0.39~0.55,高于原始地幔值[29]。w(La)/w(Nb)及w(Ba)/w(Nb)分别为2.18~2.96和15.04~21.3,较之原始地幔、洋脊玄武岩及洋岛玄武岩的相应值[30]均偏高,表明其应为幔源基性岩浆经改造的产物,即极可能为由基性岩浆经演化或与酸性岩浆混合产生的过渡岩浆结晶形成。
熔融实验研究表明:陆壳熔融通常富钠[31-33],不能熔融形成具高钾钙碱性特征的花岗质岩浆,Panino等[33]根据陆壳岩石熔融结果提出高钾钙碱性花岗岩通常是壳幔混合的结果。寄主花岗闪长岩为 I 型,属于高钾钙碱性系列,也显示了壳幔岩浆混合起源的特征。
包体的稀土总量、轻重稀土的含量都比寄主花岗闪长岩的高,主要归因于角闪石、单斜辉石和磷灰石等稀土元素的载体矿物含量较多,表明其不是寄主岩浆早期结晶分异产物的堆积体,因为REE为强不相容元素,若闪长质包体是花岗质岩浆结晶分异的产物,则其REE含量应该较寄主花岗岩的低,蛛网图曲线形态整体相似,表明它们在微量元素上发生过交换。岩石样品随着SiO2质量分数的增高,Al2O3,CaO,Fe2O3T,MgO,TiO2 和 P2O5的质量分数呈良好线性关系(图7),包体内出现部分角闪石矿物,暗示其高温基性岩浆侵入到温度相对较低的酸性岩浆房后受到淬冷作用而快速降温冷却的结果[34]。包体形态较规则呈等轴状,表明包体岩浆曾以液态球滴状存在于寄主岩浆中[35],这些特征均是岩浆混合作用区分于岩浆分离结晶作用的一个重要标志。
结合宏观和微观特征来看,花岗岩中含有花岗质的浅色包体和细晶岩脉。镜下可见针状的磷灰石,代表着岩浆快速冷凝结晶的产物,这些特征提供了经典的岩浆混合成因证据[36-37]。在反映岩浆演化方式的TFeO-MgO图解(图8)中,从暗色包体到花岗闪长岩岩浆混合的趋势也非常明显。
5.3 岩浆作用及地球动力学背景
冈底斯中新生代中酸性岩浆活动发育,一般认为是北部班公湖—怒江和南部雅鲁藏布两个特提斯演化的记录[1,38],最新结论认为新特提斯洋大致在晚三叠世或更早的时间打开,同时形成班公湖一怒江洋(北支)及雅鲁藏布洋(南支)[39]。大致于早一中侏罗世之交扩张到最大规模,然后开始消减缩小。北支班公湖一怒江洋大致在早白垩世末(100 Ma左右)完全闭合,完成了拉萨地块与羌塘地块的碰撞拼合,南支雅鲁藏布洋闭合较晚.在白垩纪/古近纪之交印度大陆开始与拉萨地块碰撞[40]。一般认为中部和南部岩浆岩带则集中体现了雅鲁藏布特提斯时空演化的完整经历[41-42],岗在岩体属于中冈底斯,岗在岩体花岗闪长岩成岩年龄在(74.3±1.7) Ma,地球化学特征显示属于高钾钙碱性岩石。岗在岩体构造环境图解[43-44]如图9所示。从图9(a)可知,构造环境投点落在板块碰撞前消减的活动板块边缘,从图9(b)可见:构造环境投点落在火山弧花岗岩范围内。
亏损高场强元素P和Ti一般与俯冲有关,朱第成等[5]在区域上总结了冈底斯弧背断隆带(105~135 Ma)、中冈底斯(95~145 Ma)的形成时间,认为冈底斯弧背断隆带和中冈底斯自早侏罗世以来除了受到俯冲作用的影响外,还受到了自东向西逐步扩展的碰撞作用的影响,具有从岛弧向碰撞过渡的背景。结合本区南侧的公穷松多—郎那酸性花岗岩带岩体侵位时间从晚侏罗世晚期开始,连续至晚白垩世早期结束,时间跨度为85~141 Ma,岗在—青都中酸性花岗岩带岩体侵位时间从晚白垩世晚期开始至始新世末期结束时间为39~73 Ma[18]。冈底斯中段东侧的崩纳藏布、甲岗雪山两大岩体的K-Ar同位素年龄为114.67~58.75 Ma [45],大部分位于同碰撞环境内,其次为后碰撞环境。联系到时空上冈底斯—念青唐古拉北侧的纳木错—申扎—措勤—革吉地区形成的巨大的东西向延伸的陆源岩浆弧带,并有钙碱性火山岩套[2-5]与中酸性侵入岩带相配套,本研究认为燕山晚期的岗在岩体受到雅鲁藏布特提斯的北向俯冲与班公湖—怒江洋盆南向俯冲消减碰撞双重制约有关。总体反映出冈底斯中部岩带以燕山晚期—喜马拉雅早期岩浆活动产物为主,具有2个岩浆高峰期,岩浆岩在区域表现为从南往北年龄有变新的趋势并且通过岩体的规模可反映出岩浆活动的中心总体在从南向北发生迁移的过程。
5.4 成矿意义
岗在岩体与火山岩围岩呈侵入接触关系,且沿岩体河流下游发现了多个砂金矿点,通过水系沉积物测量异常浓集中心基本处于岩体与地层及接触部位。异常元素相对简单,主要为Au和Mo,其次为W,Hg,Au。Au和Mo元素丰度高,具有三级浓度分带,通过对岗在岩体的1:1万地质填图及土壤剖面测量工作,本区岩体受控与1条北西向大断裂和一系列次级断裂,在地表圈定了10个石英脉破碎带,破碎带靠近断层发育,一般延长为体长200~500 m,宽20~60 m。根据石英脉分布可知,总体呈北西向,部分呈北东向,受断裂控制。对破碎带中的石英脉化学简分析含金量达4~6 g/t,测区还见到多条花岗细晶岩脉,大部分较破碎,为中粗粒结构,重结晶比较明显,部分含有大颗粒自形的石英颗粒,表面有褐铁矿化,岩体边部早白垩酸性火山岩较发育,与岩体接触部位及岩体内部均可见到硅化现象,有利于形成岩浆热液型金矿,且很可能对下游的砂金矿点提供了成矿物质。
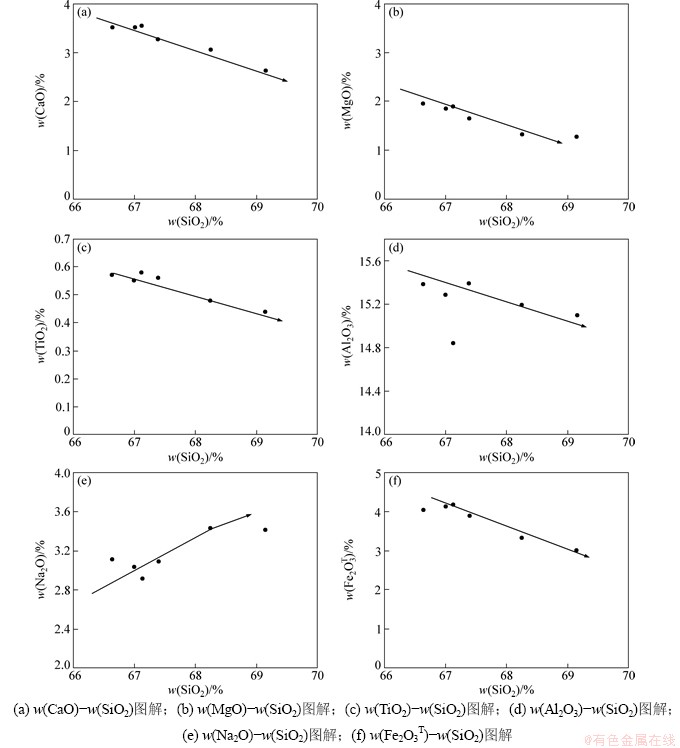
图7 岗在岩体哈克图解
Fig. 7 Harker diagram of magmatic rocks in Gangzai
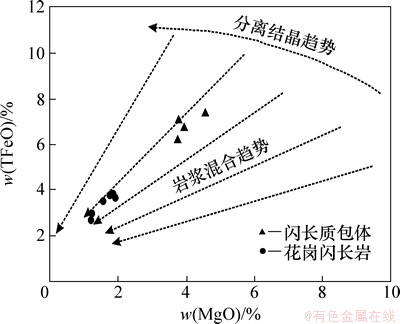
图8 岗在岩浆混合趋势图w(TFeO)-w(MgO)图解
Fig. 8 Magma mixing trend diagrams of magmatic rocks in Gangzai
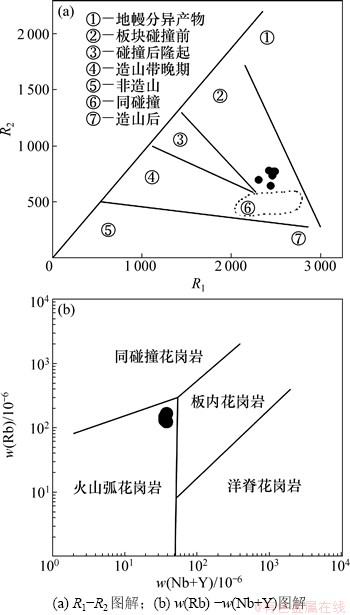
图9 岗在岩体构造环境图解 ((a)据Batcher[43](b)据Peace[44])
Fig. 9 Discrimination diagram of tectonic setting of R1-R2 and Rb-(Nb+Y)
6 结论
(1) 岗在岩体的岩石学、地球化学及年代学特征显示出明显的岩浆混合趋势,花岗闪长岩为I型花岗岩,属于高钾钙碱性系列岩石,包体属于中钾钙碱性系列岩石,二者均富集富K和Rb大离子亲石元素,而亏损 Nb,Ti和P等不活泼的高场强元素及放射性元素Th。二者为具有成因联系的亲源性,包体可能为由基性岩浆经演化或与酸性岩浆混合产生的过渡岩浆结晶形成,且受温压影响以及寄主岩浆的同化混染发生不同组分的相互扩散。
(2) 中冈底斯带岗在岩体岩浆活动时间为74 Ma左右,结合整个区域岩浆特点,具有从南往北年龄变新的趋势,反映了从俯冲到碰撞造山并伴随着岩浆活动的中心总体在从南向北发生迁移的过程。
(3) 岗在岩体很可能产出于欧亚板块与印度板块俯冲碰撞前的火山弧环境,受到雅鲁藏布特提斯的北向俯冲与班公湖—怒江洋盆南向俯冲消减碰撞双重制约有关。
(4) 岗在岩体的含金石英脉受控于断裂发育,可能为周围的砂金矿点提供了成矿物质,且本身有形成岩浆热液型金矿的潜力。
参考文献:
[1] 潘桂棠, 莫宣学, 侯增谦, 等. 冈底斯造山带的时空结构及演化[J]. 岩石学报, 2006, 22(3): 521-533.
PAN Guitang, Mo Xuanxue, HOU Zengqian, et al, 2006. Spatial-temporal framework of the Gangdese Orogenic Belt and its evolution[J].Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2006, 22(3): 521-533.
[2] 莫宣学, 董国臣, 赵志丹, 等. 西藏冈底斯带花岗岩的时空分布特征及地壳生长演化信息[J]. 高校地质学报, 2005, 11(3): 281-290.
MO Xuanxue, DONG Guochen, ZHAO Zhidan, et al. Granitoids and crustal growth in the east-Kunlun Orogenic Belt[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 2005, 11(3): 281-290.
[3] 朱弟成, 莫宣学, 赵志丹, 等. 西藏南部二叠纪和早白垩世构造岩浆作用与特提斯演化新观点[J]. 地学前缘, 2009, 16(2): 1-20.
ZHU Dicheng, MO Xuanxue, ZHAO Zhidan, et al. Permian and Early Cretaceous tectonomagmatism in southern Tibet and Tethyan evolution: New perspective[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2009, 16(2): 1-20.
[4] 朱弟成, 潘桂棠, 莫宣学, 等. 冈底斯中北部晚侏罗世-早白垩世地球动力学环境: 火山岩约束Ⅱ[J]. 岩石学报, 2006, 22(3): 534-546.
ZHU Dicheng, PAN Guitang, MO Xuanxue, et al. Late Jurassic-Early Cretaceous geodynamie setting in middle northern Gangdese: New insights from volcanic rocks[J]. Acta Petrologiea Sinica, 2006, 22(3): 534-546.
[5] 朱弟成, 潘桂棠, 王立全, 等. 西藏冈底斯带中生代岩浆岩的时空分布和相关问题的讨论[J]. 地质通报, 2008, 27(9): 1535-1550.
ZHU Dicheng, PAN Guitang, WANG Liquan, et al. Spatial variations of Mesozoic magmatic rocks in the Gangdise belt, Tibet, China, with a discussion of geodynamic setting-related issues[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2008, 27(9): 1535-1550.
[6] Wen D R, Liu D Y, Chung S L, et al. Zircon SHRIMP U-Pb ages of the Gangdese batholith and implications for Neotethyan subduction in southern Tibet[J]. Chemical Geology, 2008, 252: 191-201.
[7] Chung S L, Chu M F, Zhang Y, et al. Tibetan tectonic evolution inferred from spatial and temporal variations in post-collisional magmatism[J]. Earth Science Reviews, 2005, 68: 173-196.
[8] Wen D R, Chung S L, Song B, et al. Late Cretaceous Gangdese intrusions of adakitic geochemical characteristics, SE Tibet: Petrogenesis and tectonic implications[J]. Lithos, 2008, 105: 1-11.
[9] Ji WQ, Wu F Y, Chung S L, et al. Zircon U-Pb geochronology and Hf isotopic constraints on petrogenesis of the Gangdese batholith, southern Tibet[J]. Chemical Geology, 2009, 262: 229-245.
[10] Zhang Z M, Zhao G C, Santosh M, et al. Late Cretaceous charnockite with adakitic affinities from the Gangdese batholith, southeastern Tibet: Evidence for Neo-Tethyan mid-ocean ridge subduction? [J]. Gondwana Research, 2010, 17: 615-631.
[11] 潘桂棠, 肖庆辉, 陆松年, 等.中国大地构造单元划分[J]. 中国地质, 2009, 36(1): 1-28.
PAN Guitang, XIAO Qinghui, LU Songnian, et al. Subdivision of tectonic units in China[J]. Geology in China, 2009, 36(1): 1-28.
[12] Vernon R H. Interpretation of microstructure of microgranitoid enclaves[C]//Enclaves and Granite Petrology. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 1991: 277-292.
[13] Wilson M. Igneous petrogenesis[M]. London: Allen and Unwin, 1989.
[14] Rapp R P, Shimizu N, Norman M D, et al. Reaction between slab-derived melts and peridotite in the mantle wedge:Experimental constraints at 3.8GPa[J]. Chemical Geology, 1999, 160(4): 335-356.
[15] Boynton W V. Geochemistry of the rare earth elements: Meteorite studies[C]//Henderson P. Rare Earth Element Geochemistry. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 1984.
[16] Sun S S, McDonough W F. Chemical and isotope systematics of oceanic basalts: Implications for mantle composition and processes. Magmatism in Ocean Basins[J]. Spec Publ Geol Soc Lond, 1989, 42: 313-345.
[17] Liu Y S, Hu Z C, Zong K Q, et al. Reappraisement and refinement of zircon U-Pb isotope and trace element analyses by LA-ICP-MS[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2010, 55(15): 1535-1546.
[18] 卢书炜, 张良, 任建德, 等. 青藏高原冈底斯岩浆弧的分带性及其地质意义[J]. 地质通报, 2004, 23(9/10): 1023-1032.
LU Shuwei, ZHANG Ling, REN Jiande, et al. Zonality of the Gangdise magmatic arc on the Qinghai-Tibet plateau and its geological significance[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2004, 23(9/10): 1023-1032.
[19] Chappell B W, While A J R. I- and S-type granites in the Lachlan Fold Belt[J]. Trans Royal Soc Edinburgh: Earth Sci, 1992, 83: 1-26.
[20] Wolf M B, Londou D. Apatite dissolution into peraluminous haplogranitic melts: An experimental study of solubilities and mechanism[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Aeta, 1994, 58: 4127-4145.
[21] 李献华, 李武显, 李正祥. 再论南岭燕山早期花岗岩的成因类型与构造意义[J]. 科学通报, 2007, 52(9): 981-991.
LI Xianhua, LI Wuxian, LI Zhengxiang. Types of petrogenesis of early Yanshan Period in Nanling area and its tectonic significance[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2007, 52(9): 981-991.
[22] Diego P, Giampiero P. Chaotic dynamics and fractals in magmatic interaction processes: A different approach to the interpretation of mafic microgranular enclaves[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2000, 175: 93-103.
[23] Cole J W, Gamble J A, Burt R M, et al. Mixing and mingling in the evolution of andesite-dacite magmas: Evidence from co-magmatic pluton enclaves, Taupo volcanic zone, New Zealand[J]. Lithos, 2001, 59: 25-46.
[24] Chen G N, Grapes R H, Zhang K. Mesozoic crustal melting and tectonic deformation in SE China[J]. International Geology Review, 2003, 45(10): 948-957.
[25] Garca-Moreno O, Castro A, Corretg L G, et al. Dissolution of tonalitic enclaves in ascending hydrous granitic magmas: An experimental study[J]. Lithos, 2006, 45: 66-78.
[26] Charlier B, Namur O, Toplis M J, et al. Large-scale silicate liquid immiscibility during differentiation of tholeiitic basalt to granite and the origin of the Daly gap[J]. Geology, 2011, 39(10): 907-910.
[27] Dodge F C W, Kistler R W. Some additional observations on inclusions in the granitic rocks of the Sierra Nevada[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1990, 95( B11): 17841-17848.
[28] Langmuir C H. A general mixing equation with application to Icelandic basalt[J]. Earth and Planet Sci Lett, 1978, 37: 380-392.
[29] Hofmann A W. Chemical differentiation of the earth: the relationship between mantle, continental crust, and oceanic crust[J]. Earth and Planet Sci Lett, 1988, 90: 297-314.
[30] Jahn B M, WU F Y, Lo C H, et al. Crustal-mantle interaction induced by deep subduction of the continental crust: Geochemical and Sr-Nd isotope evidence from post-collisonal maficultramafic intrusions of the northern Dabie complex, central China[J]. Chem Geol, 1999, 157(1/2): 119-146.
[31] Rutter J M, Wyllie P. Metlting of vapour-absent tonalite at 10 kbar to simulate dehydration-melting in the deep crust[J]. Nature, 1988, 331: 159-160.
[32] Rapp R P, Watson E B. Dehydration melting of metabasalt mantle recycling[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1995, 36: 891-931.
[33] Panino Douce Alberto E. What do experiments tell us about the relative contributions of crust and mantle to the origin of granitic magmas. Understanding Granites: Integrating New and Classical Techniques[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 1999, 168: 55-75.
[34] 李胜荣, 孙丽, 张华锋. 西藏曲水碰撞花岗岩的混合成因:来自成因矿物学证据[J]. 岩石学报, 2006, 22(4): 884-894.
LI Shengrong, SUN Li, ZHANG Huafeng. Magma mixing genesis of the Qushul collislonal granitoids, Tibet, China: Evidences from gentic mineralogy[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2006, 22(4): 884-894.
[35] 王德滋, 谢磊. 岩浆混合作用: 来自岩石包体的证据[J]. 高校地质学报, 2008, 14(1): 16-21.
WANG Dezi, XIE Lei. Magma mingling: Evidence from Enclaves[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 2008, 14(1): 16-21.
[36] Mo X X, Hou Z Q, Niu Y L, et al. Mantle contributions to crustal thickening during continental collision: Evidence from Cenozoic igneous rocks in southern Tibet[J]. Lithos, 2007, 96: 225-242.
[37] Dider J, Barbarm B. Enclaves and granite petrology[M]. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 1991: 403-413.
[38] 莫宣学, 潘桂堂. 从特提斯到青藏高原形成: 构造-岩浆事件的约束[J]. 地学前缘, 2006, 13(6): 43-51.
MO Xuanxue, PAN Guitang. From the Tethys to the formation of the Qinghai2Tibet Plateau: Constrained by tectono-magmatic events. Earth Science Frontiers, 2006, 13(6): 43-51.
[39] 莫宣学. 岩浆作用与青藏高原演化[J]. 高校地质学报, 2011, 17(3): 351-367.
MO Xuanxue. Magmatism and evolution of the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 2011, 17(3): 351-367.
[40] 莫宣学. 青藏高原地质研究的回顾与展望[J]. 中国地质, 2010, 37(4): 841-853.
MO Xuanxue. A review and prospect of geological researches on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau[J]. Geology in China, 2010, 37(4): 841-853.
[41] MO Xuanxue, NIU Yaoling, DONG Guocheng, et al. Contribution of syncollisional felsic magmatism to continental crust 570 growth: A case study of the Paleogene Linzizong volcanic Succession in southern Tibet[J]. Chemical Geology, 2008, 250(1/2/3/4): 49-67
[42] Zhang Z M, Zhao G C, Santosh M, et al. Late Cretaceous charnockite with adakitic affinities from the Gangdese batholith, southeastern Tibet: Evidence for Neo-Tethyan mid-ocean ridge subduction[J]? Gondwana Research, 2010, 17: 615-631.
[43] Batchelor B, Bowden P. Petrogenetic interpretation of granitoid rock series using multicationic parameters[J]. Chemical Geology, 1985, 48: 43-55.
[44] Pearce J A. Sources and setting of granitic rocks[J]. Episodes, 1996, 19(4): 120-125.
[45] 葛良胜, 邓军, 杨立强, 等, 西藏冈底斯地块中新生代中酸性侵入岩浆活动与构造演化[J]. 地质与资源, 2006, 15(1): 1-10.
GE Liangsheng, DENG Jun, YANG Liqiang, et al. The Meso-Cenozoic acidic-intermediate magmatism and tectonic evolution[J]. Geology and Resources, 2006, 15(1): 1-10.
(编辑 赵俊)
收稿日期: 2013-08-07;修回日期: 2013-11-20
基金项目: 青藏高原矿产调查评价专项项目(1212011121250)
通信作者: 郑有业(1962-),男,河南信阳人,教授,从事基础地质、成矿规律及矿产勘查评价研究;电话:027-67883331;E-mail:zhyouye@163.com