添加TiC对激光粒子沉积WC-Co-Cr 和 WC-Ni涂层性能的影响
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2013年第12期
论文作者:B. A. OBADELE P. A. OLUBAMBI O. T. JOHNSON
文章页码:3634 - 3642
关键词:激光熔覆;TiC;WC;腐蚀行为;硬度
Key words:laser particle injection; titanium carbide; tungsten carbide; corrosion behaviour; hardness
摘 要:研究了激光熔覆TiC增强双相不锈钢上WC涂层的机理。分析了激光工艺参数对复合涂层的影响。采用SEM和EDX手段分析了喂料粉末以及复合涂层的形态和微观组织。采用维式硬度计测试了复合涂层的表面硬度,采用动电位曲线法研究了涂层在3.5% NaCl溶液中的耐腐蚀行为。由于激光熔覆处理,在不锈钢表面形成了与基材结合良好的硬陶瓷粒子。添加TiC到WC中得到的复合涂层没有裂缝、孔洞和金属间化合物,没有出现这些对涂层性能不利的缺陷。结果表明,涂层具有较高的显微硬度,且大部分涂层的腐蚀电位变得更负。
Abstract: The mechanisms by which titanium carbide (TiC) improves the properties of tungsten carbide (WC) coatings deposited on duplex stainless steels using laser particle injection technique were investigated. The relationships between laser process parameters and the synthesized composite were studied. The morphologies and microstructures of the feedstock powders and composite coatings were characterized using scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX) techniques. Surface hardness of the composite layers was determined using the Vickers microhardness tester while its corrosion behaviour in 3.5% NaCl solution was investigated by potentiodynamic polarization curve measurement method. As a result of the laser treatment, microstructures characterized by hard ceramic particles with strong bonding to substrate were formed on the surface layer of the steels. The addition of TiC to WC resulted in microstructures free from cracks, pores and intermetallics which could be detrimental to the properties of the composites. High microhardness was observed and most of the coatings shifted the corrosion potential to more noble values with the pseudo-passive curve.
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 23(2013) 3634-3642
B. A. OBADELE, P. A. OLUBAMBI, O. T. JOHNSON
Department of Chemical, Metallurgical and Materials Engineering, Tshwane University of Technology, Private Bag X680, Pretoria, South Africa
Received 7 April 2013; accepted 26 August 2013
Abstract: The mechanisms by which titanium carbide (TiC) improves the properties of tungsten carbide (WC) coatings deposited on duplex stainless steels using laser particle injection technique were investigated. The relationships between laser process parameters and the synthesized composite were studied. The morphologies and microstructures of the feedstock powders and composite coatings were characterized using scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX) techniques. Surface hardness of the composite layers was determined using the Vickers microhardness tester while its corrosion behaviour in 3.5% NaCl solution was investigated by potentiodynamic polarization curve measurement method. As a result of the laser treatment, microstructures characterized by hard ceramic particles with strong bonding to substrate were formed on the surface layer of the steels. The addition of TiC to WC resulted in microstructures free from cracks, pores and intermetallics which could be detrimental to the properties of the composites. High microhardness was observed and most of the coatings shifted the corrosion potential to more noble values with the pseudo-passive curve.
Key words: laser particle injection; titanium carbide; tungsten carbide; corrosion behaviour; hardness
1 Introduction
There has been considerable development in the in situ production of stainless steel matrix composites (SSMMCs) [1-3]. MMCs combine physical, mechanical and metallic properties (ductility and toughness) [4,5] with ceramic characteristics (high strength and modulus) [6,7], leading to greater strength in shear and compression [8,9] and to higher service temperature capabilities [10,11]. The use of MMCs in the aerospace and automotive industries, and other structural applications, has increased over the past 20 years as a result of the availability of relatively inexpensive reinforcements and the development of various processing routes which result in reproducible microstructure and properties [12].
It has been extensively researched and established that the incorporation of hard, second-phase particles deliberately added to ferrous matrices using laser melt injection technique can significantly improve certain material properties [13-18]. Among several hard materials that have been studied, WC and TiC have been proven to be excellent reinforcing materials for incorporation into a tough bonding metal matrix. This is due to their high hardness, low density and thermodynamic stability [19,20]. WC belongs to the group of advanced ceramic materials with great industrial importance and is well known as hardfacing material with Co or Ni alloys as binders. Also, WC finds application where wear or corrosion resistant is required [21]. LIU et al [14] studied WCp/Fe steel by laser melt injection technique; the results show that WCp exists in different states in the melt pool. Some particles keep their original block shape, some particles dissolve partially, and the others dissolve completely.
ZHOU et al [22] studied an iron-based WC multi-track coating by laser induction hybrid rapid cladding; the results show that WC particles dissolve completely to form W and C atoms and further precipitate as M12C and M23C6 carbides during rapid solidification. VEREZUB et al [16] investigated in-situ synthesis of a carbide reinforced steel by laser melt injection technology. It was reported that undissolved WC particles were found on top of the coating layer and this was attributed to particles hitting the surface of the melt pool when it is already nearly resolidified and thus the particles cannot dissolve in the melt pool. The decomposition of WC into W2C, C or W as a result of low heat of formation of WC and low affinity of W for C remains a concern. Free C in the melt pool could easily form CO2/CO pores and intermetallic phases such as Co3W3C and Co6W6C with a detrimental effect on the mechanical properties of the coating [23].
Although results on the source of the pores usually conflict whether it was an effect of the physical/ mechanical properties of the material or from an effect purely related to the processing parameters [24]. BUZA et al [25] reported that five different pores could be formed during laser particle injection, surface impurities, shielding gas, powder injection, overheated liquid and exothermic reactions and role of oxide layer on particles. The reasons given are associated with pores formations which are the injection of powder at high velocities where particles could drag air cavities into the liquid and also the presence of thin oxide layer on the metal powders. ANANDA et al [26] studied the structure- property correlation on laser surface alloyed AISI 304 stainless steel with WC+Ni+NiCr. It was reported that the processing parameters in this scanning speed resulted in the formation of microcracks and porosities as well as the area fraction of these defects.
The possible addition of TiC to WC for the purpose of pores and crack elimination has not been studied as far as available literatures are concerned. HUANG et al [27] studied the effect of aluminium addition on 316 austenitic stainless steel reinforced. It was reported that there was a reduction of gas porosity in the clad layer. This was attributed to the higher affinity of aluminium for oxygen (the heat of formation of Al2O3 at 1500 K is -1196.58 kJ/ mol and -369.26 kJ/mol for CO2) than carbon.
On the other hand, Ti/TiC is one of the most stable carbides in iron at high temperatures, and it does not form any ternary phases [28]. TiC is widely used as reinforced phase of composite materials [29]. Addition of TiC to reinforcing steel matrix composites has been an advantage to composition and microstructural modification which could have an impact on a wide range of properties [30]. LAROUDIE et al [31] studied the incorporation of C, TiC and SiC powders on 316L stainless steel. Some large clusters of TiC are distributed within the composite while faceted crystals of TiC are uniformly distributed within the composite. VEREZUB et al [32] investigated the performance of a cutting tool reinforced with Ti and WC produced by in situ laser melt injection technique. The results obtained show that the microstructure of the melted layer seems to be homogeneous and this is attributed to the high velocity of Maranon convection of the laser melted pool.
Owing to the problem of pores and crack formation associated with WC and Ti particles, attempt has been made to investigate the possibility of adding TiC to WC to reduce or eliminate pores and crack defects associated with WC composite coatings on stainless steels and its effects on some coatings properties.
2 Experimental
2.1 Materials
UNS S32205 duplex stainless steel (DSS) specimens were cut to dimensions of 98 mm × 48 mm× 10 mm. The elemental composition is shown in Table 1. Pure WC-9Co-4Cr, WC-10Ni and TiC powders supplied by Weartech (pty) Ltd, South Africa, were used as reinforced carbides (Fig. 1). The mixing ratio of powder, mixing method, mixer, speed and time used were reported in Ref. [33].
Table 1 Nominal composition of UNS S32205 stainless steels (mass fraction, %)

2.2 Preparation of laser coatings
Prior to laser coating, the substrates were sandblasted to influence absorptivity of the laser beam radiation [34]. Laser particle injection technique was carried out using a 4400 W Rofin Sinar continuous wave Nd:YAG laser with a wavelength of 1.064 μm equipped with a fibre optic beam delivery system. The powders were fed laterally using a commercial powder feeder instrument equipped with a flow balance to control the powder feed rate. During the laser processing, laser power of 1500 W, scanning speed of 0.0067 m/s and beam diameter of 3 mm were selected to create a melt pool on the surface of the substrate and simultaneously reinforced carbides were injected into the melt pool just behind the laser beam creating 5 multiple tracks overlapping at 50%, shielded with argon gas flowing at 4 L/min. The powders were injected at 2 g/min. Table 2 summarizes the parameters of the specimens.
2.3 Characterization of laser coatings
Specimens for microstructural analyses were grinded and polished to 1 μm diamond suspension. A Phillips (XL30 SERIES) scanning electron microscope (SEM) equipped with a field emission gun was used to assess the microstructure of the polished samples. A qualitative elemental composition was conducted by EDS.

Fig. 1 SEM images of WC-9Co-4Cr (a), WC-10Ni (b) and TiC (c)
Table 2 Laser processing parameters

Specimens for X-ray diffraction (XRD) were cut to dimensions and the coated surface was exposed to the incident rays. XRD scanning was carried out on a PW1710 Philips diffractometer, using monochromatic Cu Kα radiation at 40 kV and 20 mA. Diffractograms were collected over a range of 2θ between 10° and 90° at the step size of 0.02°.
2.4 Microhardness measurement of composites
The hardness of the coating layers was measured using an EmcoTEST DURASCAN microhardness tester equipped with ecos workflow ultra modern software. A load of 0.98 N (100 g) at a dwelling time of 15 s was applied to all the specimens. The microhardness profile was produced through the depth of the coated zone, heat affected zone and to the matrix.
2.5 Electrochemical polarization measurements
Specimens for electrochemical analysis were cut to dimensions of 7 mm×5 mm and prepared according to ASTM G1–03(2011) [35]. The corrosion behaviour of the specimens was studied in 3.5% NaCl environment. Electrochemical measurements were conducted by the potentiodynamic polarization technique according to ASTM G5-94(2011)e1 [36]. All electrochemical measurements were carried out at room temperature (25±1) °C using an Autolab Potentiostat (PGSTAT20 computer controlled) with the general purpose electrochemical software (GPES) version 4.9. Before potentiodynamic cyclic polarization was taken, the specimens were immersed in the electrolytes for suitable time to stabilize at the open circuit potential (OCP). Potentiodynamic polarization curves were measured at a scanning rate of 2 mV/S starting from -1.0 V (with respect to the OCP) to about 1.2 V.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Microstructural characterization of laser reinforced S32205 DSS with WC
The microstructures of the WC coatings are presented in Figs. 2-4 at different magnifications. Figure 2 shows the SEM images of specimen E (S32205 DSS+ WC-9Co-4Cr) laser particle injected coatings. The WC particles were homogeneously distributed in the matrix of the steel due to high wettability of WC in the melt pool. One can see the presence of cracks and pores from Fig. 2(a). This is due to formation or entrapment of gases as a result of dissolution of WC to W and C. The formation of cracks can also be attributed to a high degree of thermal mismatch between the coated layer and the substrate, which increases the thermal stress, thus the propensity for cracking. This is evident from SEM images in Figs. 2, 3 and 4 as cracks propagate from the substrate to the coated zone. Gas pores formed can also be attributed to the interaction of residual carbon present in the WC particles and in the melt pool with dissolved atmospheric oxygen trapped during melt injection [37]. The cracks propagate from the pores to the interface of the coatings and matrix. According to ANANDA et al [26] the volume expansion as a result of dissolution of WC particles and formation of dendrites (Figs. 2(b) and (d)), the difference in coefficient of thermal expansion and large cooling rate could lead to development of compressive residual stresses in the alloyed zone. A microstructure with alternating layers was observed in Fig. 2(c), which is associated with thermal behaviour of laser processing with multiple overlap tracks. The first track deposited fine WC particles in Co matrix [21] forming a free dendrite growth in the matrix. Dendritic growth pattern formation is characterized by a complex interplay of heat/solute diffusion processes and interface curvature effects that are all occurring on different length scales. In free dendritic growth, the latent heat and the solute are both rejected into a uniformly undercooled liquid surrounding the growing dendrite [38]. As the dendrite propagated, the crystalline solid grew and rejected its excess solute, which flew away from the interface by chemical diffusion through the surrounding melt or solution. According to GLICKSMAN and LUPULESCU [39], the latent heat flew away from the dendritic interface by transport processes such as thermal conduction and convection. When the second track of WC particles with 50% overlap was injected, some part of the first track was remelted and a fine cooperative equiaxial dendrite formed (Fig. 2(d)), reducing the WC particles to submicron size. The increase in W contents from the second track deposition resulted in the equiaxial dendrite [40] and as more WC dissolved in the melt pool, the undercooling resulted in precipitation of WC as equiaxial dendrite and seemed to represent a form of M3C (Fe3W3C) carbide as reported by RIABKINA- FISHERMAN et al [19] and LIU et al [14].

Fig. 2 SEM images of WC-9Co-4Cr reinforced UNS S32205 DSS at different magnifications
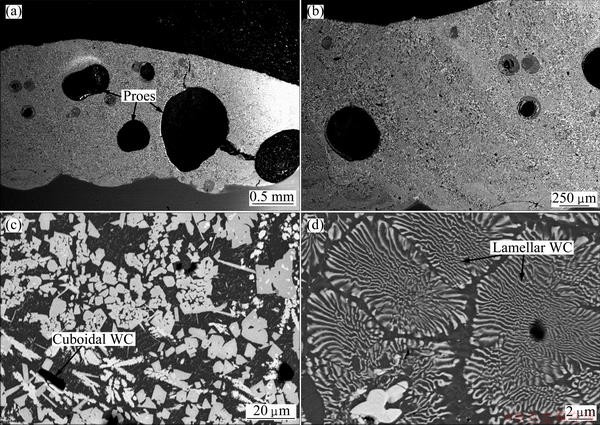

Fig. 3 SEM images of WC-10Ni reinforced UNS S32205 DSS at different magnifications

Fig. 4 SEM images of WC-9Co-4Cr+WC-10Ni reinforced UNS S32205 DSS at different magnifications
Figure 3 shows the SEM images of specimen F. A uniform distribution of fine WC particles with cuboidal, needle-like, dendritic and lamellar morphologies throughout the matrix can be observed, which indicates a precipitation reaction from the liquid phase. The formation of lamellar morphology is noticeable also in Fig. 4 and can be attributed to the presence of Ni in the powder. As it could be seen, the cracks formed propagate through the pores to the surface of the coating. Most of the pores are found at the middle and bottom of coated zone. Figure 4 shows both low and high SEM images of specimen G. It can be seen that the admixed powder has effects on the size, number and distribution of pores in the matrix. Large pores and cracks can be seen close to the interface of the coating/ matrix while small pores could be found close to the top and middle zone of the coating. This can be attributed to the large volume of carbides and intermetallics present which could prevent the escape of trapped CO2 gas coupled with high solidification rate of the melt pool. Cracks could be seen propagating parallel to the direction of laser scan and closer to the interface of coating and matrix and also running through the pores found at the bottom.
3.2 Effect of TiC addition on elimination of pores and cracks
Microstructures of specimens H and I (WC-9Co- 4Cr+TiC and WC-10Ni+TiC) are shown in Figs. 5 and 6. The addition of TiC to WC particles using the same laser processing parameters (laser power of 1500 W and scanning speed of 0.0067 m/s) changed dramatically the microstructures compared with Figs. 2, 3 and 4. Pores and cracks associated with single WC coatings have been reduced/completely eliminated. This could be due to the presence of TiC added to the WC particles. The presence of TiC particles could reduce air cavities being dragged into the melt pool during injection of the particles which did not have enough time to escape due to high solidification rate [17]. As reported by OBADELE et al [33], the agglomeration in the feedstock powder could also improve the uniform distribution of the carbides in the melt pool and these could also lead to reduction/elimination of pores and crack formation in the melt pool. A similar work was conducted by HUANG et al [27] who reported that aluminium powders were added to WC/Ni to eliminate pores formed.
3.3 EDS and XRD analysis of MMCs
Figure 7 shows the XRD patterns of WC coatings. High tungsten content was detected in the interdendritic region by EDS and point analysis on the specimens indicates the presence of the W-rich carbides. EDS analysis indicates high peaks of Fe and W which show that WC melt has high wettability in the melt pool [41,42]. XRD result confirmed the rich phase of Fe6W6C peaks (Fig. 7(c)). The dissolution of WC to form free W and C resulted in the formation of Fe6W6C6. LIU et al [14] explained the Fe-W-C phase diagram shown in the following reaction:
M+WC+W→Fe6W6C6 (1)
where M represents the high temperature solvent containing W, C and Fe. Peak of Co was detected by XRD and peaks for the reaction Co with C and W to form the Co6W6C [43].

Fig. 5 SEM images of WC-9Co-4Cr+TiC mixed powders injected into UNS S32205 duplex stainless steel

Fig. 6 SEM images of WC-10Ni+TiC mixed powders injected into UNS S32205 duplex stainless steel

Fig. 7 XRD patterns of UNS S32205 DSS reinforced with WC-9Co-4Cr (a), WC-10Ni (b), WC-9Co-4Cr+WC-10Ni (c), WC-9Co-4Cr+ TiC (d) and WC-10Ni+TiC (e) lased at 1500 W with scanning speed of 0.0067 m/s
3.4 Microhardness profile
The hardness of the composite was measured along the depth from the irradiated surface to the matrix, and the result is shown in Fig. 8. The Vickers hardness (HV) for specimen H ranges from HV0.1 1150 to HV0.1 926 while for specimen I it ranges from HV0.1 1091 to HV0.1 949, while S32205 DSS reinforced with TiC alone, from HV0.1 584 to HV0.1 432. The hardness generally decreases further down to the heat affected zone (HAZ). Addition of WC particles increased the hardness by almost 3 times. The increase in hardness confirms the high wettability of WC in the melt pool and the homogeneous distribution of these carbides in the melt pool [39].
3.5 Electrochemical polarization measurements
Figure 9 shows the potentiodynamic polarization curves for the carbide reinforced steel and the as-received S32205 DSS in 3.5% NaCl solutions at room temperature. It could be seen that the anodic polarization performances of the coatings and the as-received specimen are quite different. They exhibit different anodic polarization performance with the coatings showing more shift towards positive potential. All the coatings (specimens E, F, G, H and I) displayed the pseudo-passive regions in the range of -0.4 V to -0.25 V except for specimen A (as-received) which showed a significant passivation region. Polarisation curves of specimens E and H were very similar, indicating little effect of the TiC addition on a positive shift of the potential. The little effect could also be attributed to the presence of carbides from Co-Cr binder used as there was a significant shift to positive potential for specimen I which also contained the same amount of TiC from -0.590 V (specimen F) to -0.502 V. From Table 3 corrosion current density (Jcorr) and corrosion potential (φcorr) for specimen A were 2.0×10-7 A/cm2 and -87 V respectively, while φcorr for specimens H and I increased significantly to -0.64 and -0.50 V, respectively. For the coatings, the current does not decrease or remains constant with increasing potential, but increases only slightly. Nevertheless, the corrosion resistance depends critically on the laser processing parameters [44].

Fig. 8 Vickers hardness profile from coated surface to matrix of S32205 DSS reinforced with blend of TiC with WC-9Co-4Cr and WC-10Ni

Fig. 9 Potentiodynamic polarization curves of S32205 DSS alone and reinforced WC particles
Table 3 Corrosion data obtained from electrochemical tests at room temperature in 3.5% NaCl solution

4 Conclusions
1) The optimum laser processing parameters for WC+TiC reinforced S32205 DSS is laser power of 1500 W and scanning speed of 0.0067 m/s. Generally, depth of the melt increases with the decrease of beam scanning speed.
2) Phases such as Co6W6C6 and Fe6W6C6 and W2C are confirmed in the WC, which indicates dissolution of the WC particles in the S32205 DSS. Pores and cracks are present as a result of formation of CO/CO2 gas trapped in the melt pool.
3) The addition of TiC to WC produces crack and pore-free stainless steel composites with enhanced effect on the hardness of the matrix. The XRD analysis confirms the presence of only the desirable phases. The microhardness of the composites is significantly improved.
4) φcorr of the coated specimens shifts in the noble direction from –0.873 V of the as-received specimen to -0.50 V of the coating with the formation of a pseudo passivation region.
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial assistance from the National Research Foundation (NRF) under the National Nanotechnology Equipment Program (NNEP) (74407). The financial support received from Tshwane University of Technology and the African Laser Centre (ALC) for Babatunde Abiodun Obadele during the course of this study is also acknowledged.
References
[1] WANG F, MEI J, WU X H. Compositionally graded Ti6Al4V+TiC made by direct laser fabrication using powder and wire [J]. Materials and Design, 2007, 28(7): 2040-2046.
[2] DO NASCIMENTO A M,  V, LERARDI M C F, de HOSSON J T H M. Microstructure of reaction zone in WCp/duplex stainless steels matrix composites processing by laser melt injection [J]. Surface & Coatings Technology, 2008, 202(10): 2113-2120.
V, LERARDI M C F, de HOSSON J T H M. Microstructure of reaction zone in WCp/duplex stainless steels matrix composites processing by laser melt injection [J]. Surface & Coatings Technology, 2008, 202(10): 2113-2120.
[3] ATTIA A N. Surface metal matrix composites [J]. Materials and Design, 2001, 22(6): 451-457.
[4] TJONG S C, MA Z Y. Microstructural and mechanical characteristics of in situ metal matrix composites [J]. Materials Science and Engineering R, 2000, 29(3-4): 49-113.
[5] FARID A, GUO S. On the processing, microstructure, mechanical and wear properties of cermet/stainless steel layer composites [J]. Acta Materialia, 2007, 55(4): 1467-1477.
[6] PENG H X, FAN Z, MUDHER D S, EVANS J R G. Microstructures and mechanical properties of engineered short fibre reinforced aluminium matrix composites [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2002, 335(1-2): 207-216.
[7] LEE J, EUH K, OH J C, LEE S. Microstructure and hardness improvement of TiC/stainless steel surface composites fabricated by high-energy electron beam irradiation [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2002, 323(1-2): 251-259.
[8] MOYA J S, LOPEZ-ESTEBAN S, PECHARROMAN C. The challenge of ceramic/metal microcomposites and nanocomposites [J]. Progress in Materials Science, 2007, 52(7): 1017-1090.
[9] CESCHINI L, MINAK G, MORRI A. Tensile and fatigue properties of the AA6061/20 vol.%Al2O3p and AA7005/10 vol.% Al2O3p composites [J]. Composite Science and Technology, 2006, 66(2): 333-342.
[10]  D, MITKOV M. The influence of SiC particles on the compressive properties of metal matrix composites [J]. Materials Characterization, 2001, 47(2): 129-138.
D, MITKOV M. The influence of SiC particles on the compressive properties of metal matrix composites [J]. Materials Characterization, 2001, 47(2): 129-138.
[11] QU X, ZHANG L, WU M, REN S. Review of metal matrix composites with high thermal conductivity for thermal management applications [J]. Progress in Natural Science: Materials International, 2011, 21(3): 189-197.
[12] CHOW T W, KELLY A, OKURA A. Fibre-reinforced metal-matrix composites [J]. Composites, 1985, 16(3): 187-206.
[13] DEGNAN C C, SHIPWAY P H. A comparison of the reciprocating sliding wear behavior of steel based metal matrix composites processed from self-propagating high temperature synthesized Fe-TiC and Fe-TiB2 master alloys [J]. Wear, 2002, 252(9-10): 832-841.
[14] LIU D, LI L, LI F, CHEN Y. WCp/Fe metal matrix composites produced by laser melt injection [J]. Surface & Coatings Technology, 2008, 202(9): 1771-1777.
[15] PEI Y T, OCELIK V, de HOSSON J T H M. SiCp/Ti6Al4V functionally graded materials produced by laser melt injection [J]. Acta Materialia, 2002, 50(8): 2035-2051.
[16] VEREZUB O,  Z, BUZA G, VEREZUB N V, KAPTAY G. In-situ synthesis of a carbide reinforced steel matrix surface nanocomposite by laser melt injection technology and subsequent heat treatment [J]. Surface & Coatings Technology, 2009, 203(20-21): 3049-3057.
Z, BUZA G, VEREZUB N V, KAPTAY G. In-situ synthesis of a carbide reinforced steel matrix surface nanocomposite by laser melt injection technology and subsequent heat treatment [J]. Surface & Coatings Technology, 2009, 203(20-21): 3049-3057.
[17] VREELING J A, OCELIK V, de HOSSON J T H M. Ti-6Al-4V strengthened by laser melt injection of WCp particles [J]. Acta Materialia, 2002, 50(19): 4913-4924.
[18] AYERS J D, TUCKER T R. Particulate-TiC-hardened steel surfaces by laser melt injection [J]. Thin Solid Film, 1980, 73(1): 201-207.
[19] RIABKINA-FISHERMAN M, RABKIN E, LEVIN P, FRAGE W, DAREL M P, WEISHEIT A, GALIN R, MORDIKE B L. Laser produced functional graded tungsten carbide coatings on M2 high-speed tool steel [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2001, 302(1): 106-114.
[20] ALA-KLEME S,  P, LIIMATAINEN J, HELLMAN J, HANNULA S P. Abrasive wear properties of tool steel matrix composites in rubber wheel abrasion test and laboratory cone crusher experiments [J]. Wear, 2007, 263(1-6): 180-187.
P, LIIMATAINEN J, HELLMAN J, HANNULA S P. Abrasive wear properties of tool steel matrix composites in rubber wheel abrasion test and laboratory cone crusher experiments [J]. Wear, 2007, 263(1-6): 180-187.
[21] PICAS J A, XIONG Y, PUNSET M, AJDELSZTAJN L, FORN A, SCHOENUNG J M. Microstructure and wear resistance of WC-Co by three consolidation processing techniques [J]. International Journal of Refractory Metals & Hard Materials, 2009, 27(2): 344-349.
[22] ZHOU S, DAI X, ZHENG H. Microstructure and wear resistance of Fe-based WC coating by multi-track overlapping laser induction hybrid rapid cladding [J]. Optics & Laser Technology, 2012, 44(1): 190-197.
[23] LEE C W, HAN J H, YOON J, SHIN M C, KWUN S I. A study on powder mixing for high fracture toughness and wear resistance of WC-Co-Cr coatings sprayed by HVOF [J]. Surface & Coatings Technology, 2010, 204(14): 2223-2229.
[24] WANG L, PRATT P, FELICELLI S D, EL KADIRI H, BERRY J T, WANG P T, HORSTEMEYER M F. Pore formation in laser-assisted powder deposition process [J]. Journal of Manufacturing Science and Engineering, 2009, 131(5): 1-9.
[25] BUZA G, JANO V, SVEDA M, VEREZUB O, KALAZI Z, KAPTAY G, ROOSZ A. On the possible mechanisms of porosity formation during laser melt injection (LMI) technology [J]. Materials Science Forum, 2008, 589: 79-84.
[26] ANANDA S, PITYANA S, MAJUMDAR J D. Structure-property- correlation in laser surface alloyed AISI 304 stainless steel with WC+Ni+NiCr [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2012, 536: 159-169.
[27] HUANG S W, SAMANDIA M, BRANDT M. Evaluation of duplex coatings produced with a pulsed Nd:YAG laser and filtered arc [J]. Surface & Coatings Technology, 2002, 153(1): 31-39.
[28] GUMMESON P U, GUSTAFSON D A. Modern developments in powder metallurgy [C]//Proceedings of the International Powder Metallurgy Conference, Orlando, 1998: 431-441.
[29] TJONG S C, LAU K C. Abrasion wear resistance of stainless-steel composites reinforced with hard TiB2 particles [J]. Composites Science and Technology, 2000, 60(8): 1141-1146.
[30] GOWTAM D S, ZIYAUDDIN M, MOHAPE M, SONTAKKE S S, DESHMUKH V P, SHAH A K. In-situ TiC-reinforced austenitic steel composite by self-propagating high temperature synthesis [J]. International Journal of Self-Propagating High-Temperature Synthesis, 2007, 16(2): 70-78.
[31] LAROUDIE F, TASSIN C, PONS M. Laser surface alloying of 316L stainless steel: different hardening routes and related microstructures [J]. Journal de Physique IV, 1994, 4: C4-77–C-80.
[32] VEREZUB O,  Z, SYTCHEVA A, KUZSELLA L, BUZA G, VEREZUB N V, FEDOROV A, KAPTAY G. Performance of a cutting tool made of steel matrix surface nano-composite produced by in situ laser melt injection technology[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2011, 211(4): 750-758.
Z, SYTCHEVA A, KUZSELLA L, BUZA G, VEREZUB N V, FEDOROV A, KAPTAY G. Performance of a cutting tool made of steel matrix surface nano-composite produced by in situ laser melt injection technology[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2011, 211(4): 750-758.
[33] OBADELE B A, MASUKU Z H, OLUBAMBI P A. Turbula mixing characteristics of carbide powders and its influence on laser processing of stainless steel composite coatings [J]. Powder Technology, 2012, 230: 169-182.
[34] THAWARI G, SUNDARARARJAN G, JOSHI S V. Laser surface alloying of medium carbon steel with SiC(P) [J]. Thin Solid Films, 2003, 423(1): 41-53.
[35] ASTM G1-03(2011). Stand practice for preparing, cleaning, and evaluating corrosion test specimens [S].
[36] ASTM G5-94(2011)e1. Standard reference test method for making potentiostatic and potentiodynamic anodic polarization measurements [S].
[37] BRANDT M, HUANG S W, SAMANDI M. Deposition of WC/Ni clad layers with a pulsed Nd:YAG laser [J]. Journal of Laser Applications, 2003, 15(1): 31-36.
[38] RAMIREZ J C, BECKERMANN C. Examination of binary alloy free dendritic growth theories with a phase-field model [J]. Acta Materialia, 2005, 53(6): 1721-1736.
[39] GLICKSMAN M E, LUPULESCU A O. Dendritic crystal growth in pure materials [J]. Journal of Crystal Growth, 2004, 264(4): 541-549.
[40] ZHOU S, DAI X. Microstructure evolution of Fe-based WC composite coating prepared by laser induction hybrid rapid cladding [J]. Applied Surface Science, 2010, 256(24): 7395-7399.
[41] KAPTAY G. Modelling interfacial energies in metallic systems [J]. Materials Science Forum, 2005, 473-474: 1-10.
[42] EUSTATHOPOULOS N, NICHOLAS M G, DREVET B. Wettability at high temperatures [M]. Boston: Pergamon Press, 1999: 281-282.
[43] LIU S L, ZHANG X P, GENG G Q. Influence of nano-WC-12Co powder addition in WC-10Co-4Cr AC-HVAF sprayed coatings on wear and erosion behaviour [J]. Wear, 2010, 269(5-6): 362-367.
[44] CONDE A, COLACO R, VILAR R, de DAMBORENEA J. Corrosion behaviour of steels after laser surface melting [J]. Materials and Design, 2000, 21(5): 441-445.
B. A. OBADELE, P. A. OLUBAMBI, O. T. JOHNSON
Department of Chemical, Metallurgical and Materials Engineering, Tshwane University of Technology,
Private Bag X680, Pretoria, South Africa
摘 要:研究了激光熔覆TiC增强双相不锈钢上WC涂层的机理。分析了激光工艺参数对复合涂层的影响。采用SEM和EDX手段分析了喂料粉末以及复合涂层的形态和微观组织。采用维式硬度计测试了复合涂层的表面硬度,采用动电位曲线法研究了涂层在3.5% NaCl溶液中的耐腐蚀行为。由于激光熔覆处理,在不锈钢表面形成了与基材结合良好的硬陶瓷粒子。添加TiC到WC中得到的复合涂层没有裂缝、孔洞和金属间化合物,没有出现这些对涂层性能不利的缺陷。结果表明,涂层具有较高的显微硬度,且大部分涂层的腐蚀电位变得更负。
关键词:激光熔覆;TiC;WC;腐蚀行为;硬度
(Edited by Xiang-qun LI)
Corresponding author: P. A. OLUBAMBI; Tel: +27-12-3823598; E-mail: polubambi@gmail.com; olubambipa@tut.ac.za
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(13)62911-8

