铸态Mg-6Zn-2Er合金的室温拉伸失效机制
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2013年第11期
论文作者:刘 轲 王庆峰 杜文博 李淑波 王朝辉
文章页码:3193 - 3199
Key words:Mg alloy; Mg-Zn-Er alloy; microstructure; mechanical properties; W-phase; crack; plastic deformation
摘 要:在室温条件下进行了铸态Mg-6Zn-2Er合金的室温拉伸试验。结果表明,该合金的断裂伸长率为5.6%。粗大的第二相,特别是粗大的Mg3Zn3Er2 相(W相)是合金失效断裂的主要原因。这表明W相不能有效地实现应力的传递,导致自身内部有裂纹产生。比较可知,合金的基体与第二相间的界面比较稳定,没有裂纹产生。因此,合金第二相的尺寸、分布、形貌和类型显著地影响合金的塑性变形行为。
Abstract: Tensile test of the as-cast Mg-6Zn-2Er alloy was conducted at room temperature. The results indicate that the alloy is inclined to failure when the strain reaches 5.6%. The coarse secondary phases are responsible for the failure, especially for the Mg3Zn3Er2 phase (W-phase). It is indicated that the existence of the W-phase activates the stress concentrations due to the incapacity of W-phase for the load transfer, which results in the void at the inner of the W-phase. In comparison, the interface between the matrix and the secondary phase is stable. In conclusion, the characters of the secondary phases with respect to size, distribution, morphology and type, play an important role in the plastic deformation behavior of the alloy.
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 23(2013) 3193-3199
Ke LIU, Qing-feng WANG, Wen-bo DU, Shu-bo LI, Zhao-hui WANG
School of Materials Science and Engineering, Beijing University of Technology, Beijing 100124, China
Received 8 October 2012; accepted 30 January 2013
Abstract: Tensile test of the as-cast Mg-6Zn-2Er alloy was conducted at room temperature. The results indicate that the alloy is inclined to failure when the strain reaches 5.6%. The coarse secondary phases are responsible for the failure, especially for the Mg3Zn3Er2 phase (W-phase). It is indicated that the existence of the W-phase activates the stress concentrations due to the incapacity of W-phase for the load transfer, which results in the void at the inner of the W-phase. In comparison, the interface between the matrix and the secondary phase is stable. In conclusion, the characters of the secondary phases with respect to size, distribution, morphology and type, play an important role in the plastic deformation behavior of the alloy.
Key words: Mg alloy; Mg-Zn-Er alloy; microstructure; mechanical properties; W-phase; crack; plastic deformation
1 Introduction
Magnesium alloys regarded as a light-weight structure material have received a great attention because of their good capabilities, such as high specific strength, good damping capacity and recycle. Importantly, the magnesium resource is abundant, which can meet the needs in aircraft, railway and automotive industries in future. One of the most important magnesium alloys is Mg-Zn binary alloy which is cheap and progressive. Unfortunately, the alloy has inferior mechanical properties so that it is not used as a structure material directly. In order to improve the mechanical properties of the Mg-Zn binary alloys, alloying with other elements is customarily adopted [1-6]. The rare earth (RE) is often added to the Mg-Zn-based alloys in order to improve the tensile properties, plastic formability and creep resistance [7-10]. As expected, the addition of RE obviously improves the mechanical properties of the Mg-Zn alloys resulting from precipitation hardening, refinement of microstructures and solid solution strengthening [11,12].
It is well known that three kinds of ternary phases were observed in Mg-Zn-RE (RE stands for Y or Gd, etc) alloys, i.e. Mg3Zn6RE phase (I-phase), Mg3Zn3RE2 phase (W-phase) and Mg12ZnRE phase (LPSO structure) [13,14]. Both of the I-phase and the LPSO structure play an important role in improving the mechanical properties, except for the W-phase [15-21]. It was reported that the yield tensile strength of the Mg-Zn-Y-Zr alloys ranged from 150 to 450 MPa at room temperature depending on the content of the I-phase [22]. However, the W-phase which leads to a large fall in mechanical properties usually precipitates together with the I-phase during solidification [10,23-25]. Although lots of works concentrating on effects of I-phase on mechanical properties and on how to design an alloy mainly containing the I-phase without the W-phase have been done, few works on an interface between matrix and secondary phases (I-phase or W-phase) during plastic deformation at room temperature have been referred. Therefore, it is important to investigate the transformation of the interfaces and the secondary phases in order to find the failure mechanisms of the alloy containing both of the I-phase and the W-phase.
In our laboratory, both of the I-phase and the W-phase have been found in the Mg-Zn-Er alloys with Zr-free. On the basis of our previous work, we chose an alloy with a nominal composition of Mg-6Zn-2Er as a studied alloy. In this work, more attention was paid to investigate the interface between the matrix and the secondary phases (I-phase and W-phase) together with the characteristic of the I-phase and W-phase during the tensile test by transmission electron microscopy.
2 Experimental
The Mg-6Zn-2Er alloys were produced from high-purity Mg (99.5%), high-purity Zn (>99.9%) and Mg-20Er (mass fraction, %) master alloy in an electric resistance furnace at about 750 °C under a protective atmosphere. At about 720 °C, the melting in a graphite crucible was poured into an iron mold with dimensions of 40 mm×100 mm×150 mm. Specimens for the tensile test were made into dog bone-like with size of 5 mm in gauge diameter and 25 mm in gauge length. Tensile test was conducted on a uniaxial tensile testing machine at a speed of 1 mm/min.
Phase analysis was conducted by X-ray diffractometry (XRD). The microstructures of the alloy were observed on an optical microscope (OM), scanning electron microscope (SEM) equipped with an energy dispersive spectroscope (EDS) and transmission electron microscope (TEM) with selected area electron diffraction (SAED) pattern and EDS. Specimens for TEM observation, including the specimen cut from the cast alloy directly and the specimen cut near the fracture of the tensile test specimen, were prepared by argon ion milling technique.
3 Results
3.1 Microstructure
Figure 1 shows the XRD pattern of the Mg-6Zn-2Er alloy. It is suggested that the alloy is mainly composed of α-Mg solid solution together with the I-phase and the W-phase. The RE elements have a similar character that adding them to Mg-Zn alloys leads to the formation of the I-phase and the W-phase. Both the I-phase and the W-phase were observed in the Mg-Zn-Y, Mg-Zn-Gd and Mg-Zn-Er series alloys. The mass ratio of Zn to RE influences the formation of these ternary phases [9,11,26]. XU et al [24] reported that the formation of the I-phase and the W-phase was closely related with the mass ratio of Zn to Y. When the mass ratio ranged from 1.1% to 4.8%, both of the I-phase and W-phase precipitated together. According to the previous researches [9,10], the phase compositions of the Mg-6Zn-2Er mainly are composed of the I-phase and W-phase, which agrees well with the XRD results.
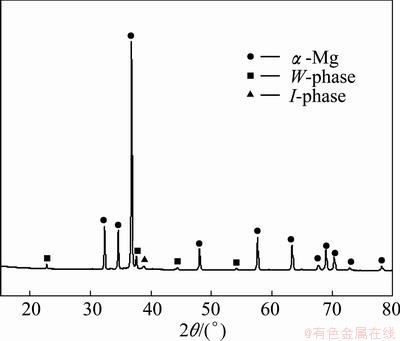
Fig. 1 XRD pattern of as-cast Mg-6Zn-2Er alloy
Figure 2 shows the microstructure of the Mg-6Zn-2Er alloy. The alloy is composed of dendrites of the α-Mg matrix and lots of eutectics coexisting with some tiny particles in the matrix, as shown in Figs. 2(a) and (b). The SEM images suggest that the eutectics in island morphology distribute along the boundaries consecutively. In addition, some of the particles with a globose morphology are found both at boundaries and in matrix, as shown in Figs. 2(c) and (d).
Figure 3 shows the SEM image of the Mg-6Zn-2Er alloy and the EDS results of the secondary phases. Figure 3(a) indicates that three areas labeled as A, B and C, respectively, were tested by EDS. Figure 3(b) shows the EDS result of the area A. It is indicated that the composition of the spherical particles within the matrix is Mg-34.67%Zn-5.96%Er (mole fraction). Its Zn-to-Er mass ratio is closed to that of the I-phase. Moreover, as seen in Figs. 3(c) and (d), the EDS results of the areas B and C indicate that the compositions of the compounds tagged with areas B and C are Mg-24.88%Zn-11.28%Er and Mg-6.78%Zn-2.96%Er, respectively, and the Zn-to-Er mass ratio is adjacent to that of the W-phase. Therefore, we found that the W-phase mainly locates at dendrite boundary, and is considered the dominating secondary phase in the alloy. However, the content of the I-phase is smaller compared with the W-phase.
TEM observation was carried out to confirm the existence of the W-phase and I-phase of alloy. Figure 4 exhibits the W-phase and corresponding SAED pattern of alloy. The coarse W-phase mainly locates at boundary continuously which leads to inferior mechanical properties greatly. Figure 5 shows the I-phase and its corresponding SAED pattern and EDS result. Two types of the I-phase were observed. One with the composition of Mg-62.32%Zn-11.36%Er located at boundary is in large size, and the SAED pattern suggests that it has two-fold symmetry, as shown in Figs. 5(a) and (d); the other is a spherical particle which has its own two-fold symmetry. As suggested above, the distribution and morphology of the I-phase are different from those of the W-phase.
3.2 Mechanical property
Tensile test was carried out at room temperature. The UTS and YTS of the Mg-6Zn-2Er alloy are about 198 and 110 MPa, respectively. Compared with the as-cast Mg-6Zn alloy, the UTS and YTS are approximately improved by 28 MPa and 47 MPa, respectively. However, the elongation of the Mg-6Zn-2Er alloy is lower than that of the Mg-6Zn alloy. The elongation of the Mg-6Zn-2Er alloy is 5.6%, and that of the as-cast Mg-6Zn alloy is 6.4%. The addition of 2.0% Er to the Mg-6Zn alloy leads to a precipitation of Mg-Zn-Er ternary phases, especially the W-phase. As a result, the Mg-6Zn-2Er alloy is inclined to failure early during the tensile test.
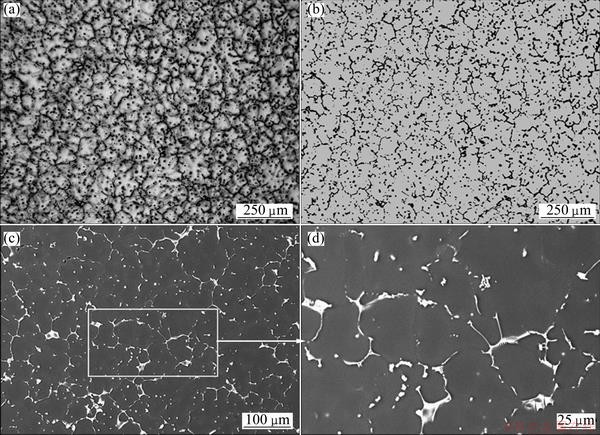
Fig. 2 OM images with bright field (a) and dark field (b) and SEM images (c, d) of as-cast Mg-6Zn-2Er alloy
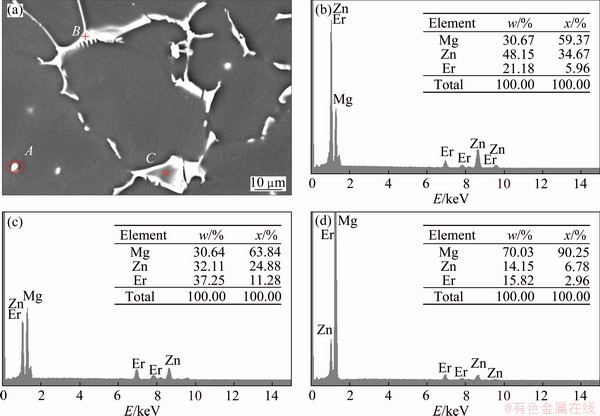
Fig. 3 SEM image (a) of Mg-6Zn-2Er alloy and corresponding EDS results of points A (b), B (c) and C (d) in Fig. (a), respectively
3.3 Failure mechanism
Figure 6 shows SEM images of the typical fracture surface of the Mg-6Zn-2Er alloy after tensile test. Figure 6(a) displays the intergranular fracture surface at lower magnification, which includes a few of lacerated ridges, lots of cleave planes and some cracks. It is considered to be a typical quasi-cleavage fracture mode. However, it is found that the secondary phase is crushed under the effect of the stress during deformation.

Fig. 4 TEM image and corresponding SAED pattern ( ) of Mg-6Zn-2Er alloy
) of Mg-6Zn-2Er alloy
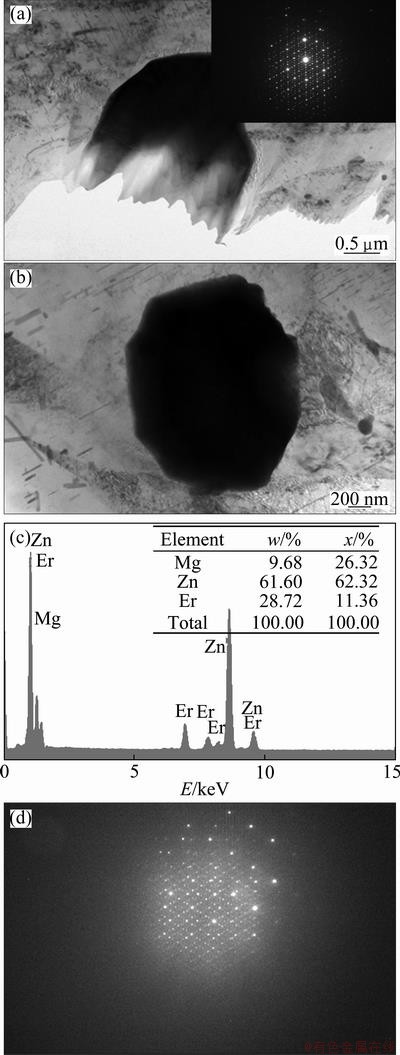
Fig. 5 TEM image of I-phase located at boundary and corresponding SAED pattern with two-fold symmetry (a), I-phase observed in matrix with spherical morphology (b), corresponding EDS result of I-phase (c) and corresponding SAED pattern of spherical I-phase with two-fold symmetry (d)
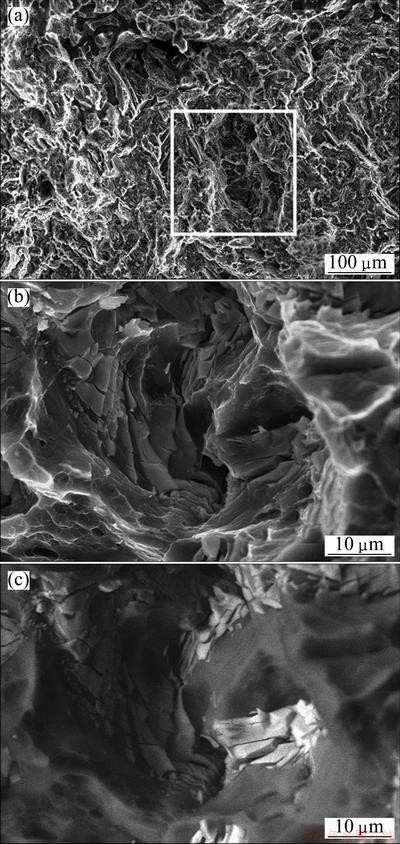
Fig. 6 SEM images of typical fracture surfaces of Mg-6Zn-2Er alloy at low magnification (a) and at high magnification obtained by SE (b) and BSE (c), respectively
Figure 7 shows the TEM images of the W-phase obtained from the specimen after tensile test. Some cracks go across the W-phase and extend to the matrix. However, no obvious crack is found at the interface between the W-phase and the matrix. This indicates that the W-phase itself is easier to crack, but the interface between the matrix and the W-phase is stable during deformation at room temperature.
Figure 8 shows the TEM images of the I-phase obtained from the specimen after tensile test. The broken I-phase with a rectangular morphology was observed in the fractured alloy. This rectangular I-phase was destroyed during deformation, and a tiny crack was also detected. However, the interface between the I-phase and the matrix is stable and no crackle is found. On all accounts, the cracks may be raised from the inner of the coarse secondary phases, and the interface of the matrix/secondary phases is stable.
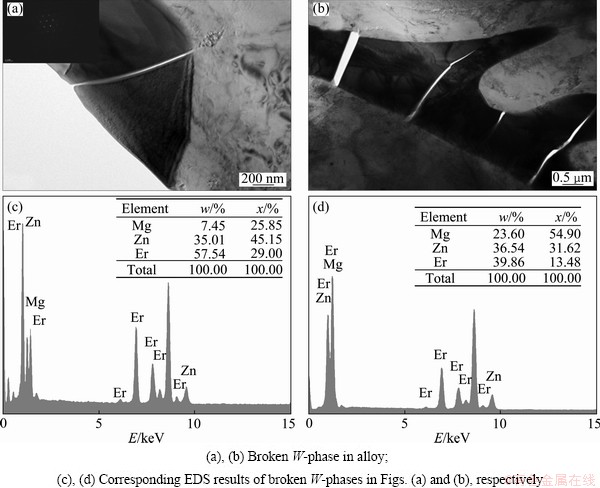
Fig. 7 TEM images and corresponding EDS results of W-phase observed from fractured as-cast Mg-6Zn-2Er alloy after tensile test
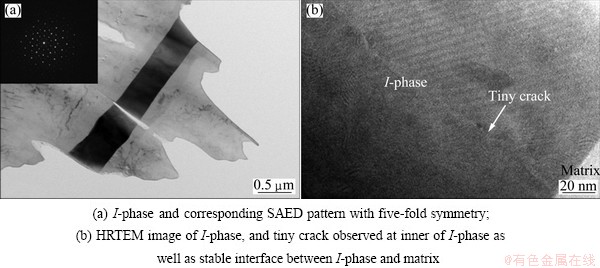
Fig. 8 TEM images and corresponding SAED pattern of I-phase observed from fractured alloy after tensile test
4 Discussion
The factors that influence the plastic failure of the alloy at room temperature mainly include the microstructures of the grains and the secondary phases. Furthermore, the secondary phases usually play a key role in plastic deformation, especially for the intergranular phases. Generally, the dislocations move along the closely packed plane in the matrix during deformation. The long dislocation line is pinned by the mass points or foreign substances, then turns into short dislocation lines and dislocation loops, resulting in dislocation multiplication. Moreover, the dislocations continue motioning until come up against the boundaries. Generally, the existence of the coarse secondary phases which are distributed at boundaries retards the movement of the dislocations and the stress is not enough to activate the dislocations to transfer across the boundaries. As a result, the dislocations are piled up around the coarse secondary phases at the boundaries, which improves the mechanical properties greatly. Although the secondary phases lead to improvement of the mechanical properties, including tensile strength, hardness and creep resistance, the stress concentrations will be introduced at the interface of matrix and secondary phases or at the inner of the secondary phase. If the coarse secondary phases are not apt to harmonize with the plastic deformation, the void nucleation will happen under the stress concentrations.
As stated above, the W-phase is thought as the dominating secondary phase in the alloy. Moreover, most of the W-phases observed in Mg-6Zn-2Er alloy are distributed along the dendrite grain boundaries. The dislocations have not ability to bypass or cut through the big compounds. Furthermore, it was reported that the W-phase with a cubic structure had a noncoherent boundary with matrix [15,27]. As a result, the W-phase does not effectively transfer the load to the matrix via harmonizing with plastic deformation. The stress concentration around the W-phase is introduced by the plastic deformation. In addition, the W-phase is easy to be brittle. Consequently, the W-phase will be broken to release the stress concentration. The void at the inner of the W-phases is considered to be a crack core during deformation at room temperature.
The distribution and morphology of the I-phase in the Mg-6Zn-2Er alloy are different from those of the W-phase, as shown in Fig. 5, which is suggested that the generative mechanism of the I-phase is special. On the whole, the size and content of the I-phase are smaller than those of the W-phase, as shown in Fig. 3. Especially, the I-phase is just like to precipitate as a block or spheroid shape, but the W-phase usually precipitates as an island shape which attracts the stress concentrations greatly and is easy to be broken. It makes sure that the failure of the alloy is attributed to the W-phase. However, as shown in Fig. 8, the I-phase with a long rectangle shape is also broken during deformation. The phenomenon is coincident with the common sense. As reported, the quasicrystal is isotropic and has a special quasiperiodic ordered lattice structure, the structure of which determines that the I-phase is so fragile that it is not appropriate to be used as structural materials directly [28,29].
Furthermore, the interface between the matrix and the secondary phases (including W-phase and I-phase) is well. There is no obvious crack along the interface boundary of the matrix/secondary phase. In other words, the void is easier to form at the inner of the coarse compounds than in the matrix [30]. In conclusion, the crack cores are mainly concentrated at the inner of the secondary phase, especially at the inner of the W-phase. It should be noted that the type, morphology, content, distribution and size of the secondary phases have important effects on the mechanical properties. As suggested in our investigation, if we produce a Mg-6Zn-2Er alloy, in which the main secondary phase has a small size and a sphere shape, the plastic deformation behavior of the alloy will be improved. Moreover, if the Mg-6Zn-2Er alloy mainly includes the I-phase with a special morphology and distributing dispersedly, and mechanical properties of the alloy will be further improved greatly. The type, morphology and distribution of the secondary phase can be controlled by adjusting the solidification process and the heat treatment process.
5 Conclusions
The addition of Er improves the strength of the alloy but is harmful to the elongation obviously. The W-phase and I-phase are observed in the Mg-6Zn-2Er alloy. However, it is obviously found that the volume fraction of the W-phase is higher than that of the I-phase. The size, distribution, morphology and noncoherent boundary with matrix of the W-phase decide that the load does not transfer from one matrix to another matrix during plastic deformation at room temperature. As a result, dislocations will be piled up around the W-phase and the stress concentrations occur. Under the stress concentrations, the void will be first present at the inner of the W-phase.
References
[1] BUHA J. The effect of Ba on the microstructure and age hardening of an Mg–Zn alloy [J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2008, 491: 70-79.
[2] ALIZADEH A, MAHMUDI R. Effect of Sb additions on the microstructural stability and mechanical properties of cast Mg-4Zn alloy [J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2010, 527: 5312-5317.
[3] BETTLES C J, GIBSON M A, VENKATESAN K. Enhanced age-hardening behavior in Mg–4 wt.% Zn micro-alloyed with Ca [J]. Scr Mater, 2004, 51: 193-197.
[4] GENG J, GAO X, FANG X Y, NIE J F. Enhanced age-hardening response of Mg-Zn alloys via Co additions [J]. Scr Mater, 2011, 64: 506-509.
[5] LE Qi-chi, ZHANG Zhi-qiang, SHAO Zhi-wen, CUI Jian-zhong, XIE Yi. Microstructures and mechanical properties of Mg-2%Zn-0.4%RE alloys [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2010, 20(S): s352-s356.
[6] MENDIS C L, BAE J H, KIM N J, HONO K. Microstructures and tensile properties of a twin roll cast and heat-treated Mg–2.4Zn– 0.1Ag–0.1Ca–0.1Zr alloy [J]. Scr Mater, 2011, 64: 335-338.
[7] HE S M, PENG L M, ZENG X Q, DING W J, ZHU Y P. Comparison of the microstructure and mechanical properties of a ZK60 alloy with and without 1.3 wt.% gadolinium addition [J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2006, 433: 175-181.
[8] LUO Z P, SONG D Y, ZHANG S Q. Strengthening effects of rare earths on wrought Mg-Zn-Zr-RE alloys [J]. J Alloys Compd, 1995, 230: 109-114.
[9] LI J H, DU W B, LI S B, WANG Z H. Tensile and creep behaviors of Mg–5Zn–2.5Er alloy improved by icosahedral quasicrystal [J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2010, 527: 1255-1259.
[10] LI Han, DU Wen-bo, LI Jian-hui, LI Shu-bo, WANG Zhao-hui. Creep properties and controlled creep mechanism of as-cast Mg-5Zn-2.5Er alloy [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2010, 20(7): 1212-1216.
[11] BAE D H, KIM S H, KIM D H, KIM W T. Deformation behavior of Mg–Zn–Y alloys reinforced by icosahedral quasicrystalline particles [J]. Acta Mater, 2002, 50: 2343-2356.
[12] YANG J, WANG L D, WANG L M, ZHANG H J. Microstructures and mechanical properties of the Mg–4.5Zn–xGd (x=0, 2, 3 and 5) alloys [J]. J Alloys Compd, 2008, 459: 274-280.
[13] LUO Su-qin, TANG Ai-tao, PAN Fu-sheng, SONG Kai, WANG Wei-qing. Effect of mole ratio of Y to Zn on phase constituent of Mg-Zn-Zr-Y alloys [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2011, 21(S): s795-s800.
[14] LUO Z P, ZHANG S Q. Comment on the so-called Z-phase in magnesium alloys containing zinc and rare-earth elements [J]. J Mater Sci Lett, 1993, 12: 1490-1492.
[15] XU D K, LIU L, XU Y B, HAN E H. Effect of microstructure and texture on the mechanical properties of the as-extruded Mg–Zn–Y– Zr alloys [J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2007, 443: 248-256.
[16] HAGIHARA K, KINOSHITA A, SUGINO Y, YAMASAKI, KAWAMURA M, YASUDA H Y, UMAKOSHI Y. Plastic deformation behavior of Mg97Zn1Y2 extruded alloys [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2010, 20(7): 1259-1268.
[17] YAMASAKI M, ANAN T, YOSHIMOTO S, KAWAMURA Y. Mechanical properties of warm-extruded Mg–Zn–Gd alloy with coherent 14H long periodic stacking ordered structure precipitate [J]. Scr Mater, 2005, 53: 799-803.
[18] HONMA T, OHKUBO T, KAMADO S, HONO H. Effect of Zn additions on the age-hardening of Mg–2.0Gd–1.2Y–0.2Zr alloys [J]. Acta Mater, 2007, 55: 4137-4150.
[19] LIU K, ZHANG J H, SUN W, QIU X, LU H Y, TANG D X, ROKHLIN L L, ELKIN F M, MENG J. Effect of Zn concentration on the microstructures and mechanical properties of extruded Mg-7Y-4Gd-0.4Zr alloys [J]. J Mater Sci, 2009, 44: 74-83.
[20] HOMMA T, KUNITO N, KAMADO S. Fabrication of extraordinary high-strength magnesium alloy by hot extrusion [J]. Scr Mater, 2009, 61: 644-647.
[21] HAGIHARA K, KINOSHITA A, SUGINO Y, YAMASAKI M, KAWAMURA Y, YASUDA H Y. Effect of long-period stacking ordered phase on mechanical properties of Mg97Zn1Y2 extruded alloy [J]. Acta Mater, 2010, 58: 6282-6293.
[22] PARK E S, YI
[23] LEE J Y, KIM D H, LIM H K, KIM D H. Effects of Zn/Y ratio on microstructure and mechanical properties of Mg-Zn-Y alloys [J]. Mater Let, 2005, 59: 3801-3805.
[24] XU D K, LIU L, XU Y B, HAN E H. The influence of element Y on the mechanical properties of the as-extruded Mg–Zn–Y–Zr alloys [J]. J Alloys Compd, 2006, 426: 155-161.
[25] XU D K, TANG W N, LIU L, XU Y B, HAN E H. Effect of W-phase on the mechanical properties of as-cast Mg–Zn–Y–Zr alloys [J]. J Alloys Compd, 2008, 461: 248-252.
[26] LIU Y, YUAN G, LU C, DING W J. Stable icosahedral phase in Mg–Zn–Gd alloy [J]. Scr Mater, 2006, 55: 919-922.
[27] SINGH A, TSAI A P. On the cubic W phase and its relationship to the icosahedral phase in Mg–Zn–Y alloys [J]. Scr Mater, 2003, 49: 143-148.
[28] NAIR K S, MITTAL M S. Rare earths in magnesium alloys [J]. Mater Sci Forum, 1988, 30: 89-104.
[29] PETTERSON G, WESTENGEN H, HOIER R, LOHNE O. Microstructure of a pressure die cast magnesium-4wt.% aluminium alloy modified with rare earth additions [J].Mater Sci Eng A, 1996, 207: 115-120.
[30] SOMEKAWA H, SINGH A, MUKAI T. High fracture toughness of extruded Mg–Zn–Y alloy by the synergistic effect of grain refinement and dispersion of quasicrystalline phase [J]. Scr Mater, 2007, 56: 1091-1094.
刘 轲, 王庆峰,杜文博, 李淑波, 王朝辉
北京工业大学 材料科学与工程学院,北京100124
摘 要:在室温条件下进行了铸态Mg-6Zn-2Er合金的室温拉伸试验。结果表明,该合金的断裂伸长率为5.6%。粗大的第二相,特别是粗大的Mg3Zn3Er2 相(W相)是合金失效断裂的主要原因。这表明W相不能有效地实现应力的传递,导致自身内部有裂纹产生。比较可知,合金的基体与第二相间的界面比较稳定,没有裂纹产生。因此,合金第二相的尺寸、分布、形貌和类型显著地影响合金的塑性变形行为。
关键词:Mg合金;Mg-Zn-Er合金;微观结构;力学性能;W相;裂纹;塑性变形
(Edited by Xiang-qun LI)
Foundation item: Projects (51071004, 51101002) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project (2011BAE22B01-3) supported by the National Science and Technology Supporting Plan during the 12th Five-Year Period, China
Corresponding author: Wen-bo DU; Tel/Fax: +86-10-67392917; E-mail: duwb@bjut.edu.cn
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(13)62852-6

