氧化铝表面粗糙度对熔融铅润湿性及表面张力的影响
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2021年第8期
论文作者:齐振 廖亮 王容岳 张岩岗 袁章福
文章页码:2511 - 2521
关键词:表面粗糙度;润湿;表面自由能;表面张力;氧化铝
Key words:surface roughness; wetting; surface free energy; surface tension; alumina
摘 要:表面粗糙度是高温下的液态金属/陶瓷润湿性的重要影响因素。在923~1123 K的温度范围内研究氧化铝表面粗糙度对铅液滴接触角、接触直径、液滴高度、表面张力的影响。在冷却后使用SEM观察铅/基底界面的微观结构。通过使用几何平均法计算氧化铝基板的表面自由能进而解释铅液滴润湿行为的机理。结果表明,在铅液滴/氧化铝陶瓷系统中,表面粗糙度从0.092 μm增加至2.23 μm,表面自由能逐渐由13.356 mJ/m2增加至39.998 mJ/m2,铅滴的接触直径由9.111 mm减小到7.19 mm,铅降高度由3.41 mm增加到3.85 mm,接触角由113.05°增加到137.15°。此外,发现铅填满了氧化铝的表面凹陷并且没有明显变化,实验证明铅液滴在氧化铝基板上的润湿与Wenzel状态一致。
Abstract: Surface roughness is an important factor that affects the wetting of molten metal on ceramics. The effect of surface roughness of the alumina substrate on the contact angle, contact diameter, drop height and surface tension of molten lead was investigated in the temperature range of 923-1123 K. The microstructure of the lead/substrate interface was observed by SEM. The surface free energy of alumina substrates was calculated by the geometrical average method. When the surface roughness of the substrate increased from 0.092 to 2.23 μm, the surface free energy increased gradually, ranging from 13.356 to 39.998 mJ/m2. The contact diameter of lead droplets decreased from 9.111 to 7.19 mm. The lead drop height increased from 3.41 to 3.85 mm. The contact angle increased from 113.05° to 137.15°. Moreover, the surface depression of the alumina substrate was filled with lead, and no obvious change was observed. The results demonstrated that the wetting of lead drop on alumina substrates was consistent with the Wenzel state.
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 31(2021) 2511-2521
Zhen QI, Liang LIAO, Rong-yue WANG, Yan-gang ZHANG, Zhang-fu YUAN
Collaborative Innovation Center of Steel Technology, University of Science and Technology Beijing, Beijing 100083, China
Received 15 August 2020; accepted 26 March 2021
Abstract: Surface roughness is an important factor that affects the wetting of molten metal on ceramics. The effect of surface roughness of the alumina substrate on the contact angle, contact diameter, drop height and surface tension of molten lead was investigated in the temperature range of 923-1123 K. The microstructure of the lead/substrate interface was observed by SEM. The surface free energy of alumina substrates was calculated by the geometrical average method. When the surface roughness of the substrate increased from 0.092 to 2.23 μm, the surface free energy increased gradually, ranging from 13.356 to 39.998 mJ/m2. The contact diameter of lead droplets decreased from 9.111 to 7.19 mm. The lead drop height increased from 3.41 to 3.85 mm. The contact angle increased from 113.05° to 137.15°. Moreover, the surface depression of the alumina substrate was filled with lead, and no obvious change was observed. The results demonstrated that the wetting of lead drop on alumina substrates was consistent with the Wenzel state.
Key words: surface roughness; wetting; surface free energy; surface tension; alumina
1 Introduction
At high temperature, wettability (wetting and surface tension) of molten metal on a solid surface is an important parameter in various materials processing technologies, such as hot-dip metallic coating, welding and metal/ceramic composites processing [1-6].
The solid surface roughness has a considerable effect on the wettability of molten metal. At present, the research on the influence of roughness on wettability mainly focuses on the non-reactive wetting system at room temperature. The major wetting liquids are water, ethanol, glycerol and silicone oil [7-9]. Studies on high-temperature wetting systems are mostly focused on wetting phenomenon of a smooth substrate, such as the effect of the solid or liquid phase composition, interface reaction and experimental condition. For instance, MA et al [10] investigated the wetting between molten tin and CuFeNiCoCr high-entropy alloy substrate at 573-973 K. The wetting process was divided into three stages. The first stage occurred in the temperature range of 573-673 K. Wetting between molten tin and substrate was poor due to the oxidation of the substrate surface. In the second stage, the oxidation film was dissolved by the reaction between molten tin and the copper-rich phase in the substrate, which improved the wetting at 673-723 K. The third stage temperature was 723-973 K, and tin atoms pass through the copper-rich phase to initiate various chemical reactions, resulting in a further decrease in contact angle. CONG et al [11] reported the effect of interfacial reaction on the wettability of Al and Al-Si alloy/SiC system. With temperature increasing, the wettability between molten Al and SiC was initially affected by SiO2 on the SiC surface. Subsequently, the contact angle was further reduced due to the interfacial reaction of molten Al and SiC. Adding enough Si to molten Al can inhibit the interfacial reaction and maintain good wettability. The authors believed that the rough interface formed by the interface reaction hindered the movement of the triple line. The addition of Si prevented the reaction from damaging the interface. However, the mechanism of how surface roughness affects wetting has been not studied yet, although being mentioned in many studies. The surface roughness of the substrate should have great influence on the wetting of melts at high temperature. Therefore, it is an important subject to study the influence of surface roughness on the wettability of molten metals at high temperature [12-16].
In this work, the contact angle, contact diameter and droplet height of liquid lead were systematically measured on alumina substrates with different surface roughnesses at temperatures ranging from 923 to 1123 K. The measurement results and the micrographs of the liquid-solid interface indicated that the wettability of lead drop on alumina substrates were consistent with the Wenzel state. The mechanism of roughness on wetting behavior was proposed based on the Wenzel equation. The effect of roughness on surface tension was also studied.
2 Experimental
2.1 Surface roughness measurement
The alumina substrate used in the experiment was from General Research Institute for Nonferrous Metals. The alumina substrate was processed into four sets of sheets with different roughnesses and the same size 20 mm × 20 mm × 2 mm. At first, it was cleaned in acid solution by using an ultrasonic cleaner for 3-5 min, then followed by acetone, absolute ethanol and deionized water for 20 min. After that, the substrates were placed in a drying cabinet to remove water. The 3D morphology and roughness parameters (Ra, the centerline average, is the arithmetic mean of the height of each point on the contour over the measured length, and r represents the ratio of actual surface area to projected surface area) were measured by confocal laser scanning microscope (CLSM).
2.2 Surface free energy measurement
In a gas-liquid-solid system, when the three- phase interface is in equilibrium condition, the state obeys the following equation [17]:
σsv–σsl=σlvcos θ (1)
where σsl is the solid-liquid interfacial tension, σlv is the surface tension of the liquid, σsv is the surface free energy of the solid, and θ is the contact angle.
Work of adhesion (Wa) between solid surface and liquid can be described as [18]
Wa=σlv+σsv–σsl (2)
Wa=σlv(1+cos θ) (3)
FOWKES [19] proposed that surface energy of any liquid or solid was the sum of dispersive σd and polar σp component as
σ=σd+σp (4)
OWENS and WENDT [20] gave a geometric mean method to calculate Wa:
σlv(1+cos θ)=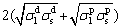 (5)
(5)
where 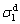 and
and 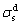 represent liquid and solid dispersion components, and
represent liquid and solid dispersion components, and 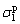 and
and 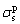 represent liquid and solid polar components, respectively.
represent liquid and solid polar components, respectively.
The surface free energy of alumina substrates can be calculated by the above-mentioned method. Firstly, the contact angles of deionized water and glycerol (analytical grade) on the alumina substrate were measured by the sessile drop method. The measuring equipment consisted of a CCD camera, an automatic syringe and a computer analysis system. The accuracy was ±0.1 μL. Then, the surface free energy of the alumina substrate was calculated by Eq. (5). Surface tension data of deionized water and glycerol were from Refs. [21,22]. The measurement was carried out at room temperature and repeated four times.
2.3 Wetting measurements of lead drop
Wettability of liquid lead on the alumina substrates with different roughnesses was measured by the sessile drop method. Details of the experimental apparatus and procedure can be referred to our previous work [23,24]. The apparatus consisted of a furnace, a photographic equipment, a digitizer and a computer analysis system. A quartz tube was sealed with a quartz cap (inner diameter 30 mm; outer diameter 34 mm; length 560 mm) as a heating chamber. The tip of the thermocouple between quartz pipes was directly placed under the alumina substrate and lead drop. The temperature error was negligible. Ar-5%H2 functioned as a protective gas.
A lead block (purity, 99.99%) was cut into a cylinder (d5.5 mm × 5.5 mm). The polishing cloth was used to remove the oxide surface. The lead sample was later cleaned with acetone by using an ultrasonic cleaner for 20 min, then rinsed with deionized water and dried. The lead cylindrical sample set on a horizontal alumina substrate was put into the quartz tube of the furnace through a quartz support. The quartz tube was sealed and evacuated to 10-3 Pa, then filled with Ar-5%H2 and evacuated again. After repeated three times, the tube was heated and the gas flow rate was maintained at 0.2 L/min. Once reaching the target temperature, photographs of the molten lead drop were taken every 3 min and the corresponding time was recorded. After the prepared sample was cooled, the interface was microscopically characterized.
2.4 Surface tension measurement of lead drop
A software developed by a laboratory staff was used to measure the surface tension of drops. The method and principle are shown in Fig. 1. Firstly, the droplet photos were processed by boundary extraction and domain segmentation to obtain the basic contour points of drop un (n=1, 2, …, n). Secondly, according to the symmetry of the drop contour, the binary image was scanned line by line. The intersection point of the central axis of the image and the first line of the contour was the coordinate origin O. O1 and O2 were the centers of the two curvature circles passing through point p, and R1 and R2 were two radii of curvature. The Young-Laplace equation [25] based on the coordinates of the liquid surface pixels was established:
△P=σlv(1/R1+1/R2) (6)
where △P is the differential pressure of the liquid surface, in the case of no other outside force except gravity, and △P can be expressed as
△P=△P0+ρgz1 (7)
where △P0 is the differential pressure on the selected reference plane, ρ is the density of liquid, g is the acceleration of gravity, and z1 is the vertical height of point p from the reference plane.
When p is at the origin, R1=R2=R0, and then,
△P0=2σlv/R0 (8)
Equation (6) can be expressed as
σlv(1/R1+sinΦ/x1)=2σlv/R0+ρgz1 (9)
And because ds1=R1dΦ, Eq. (9) is expressed as
dΦ/ds1=2/R0+ρgz1/σlv-sin Φ/x1 (10)
Equation (10) is the Laplace curve v=v(s1) obtained by calculation, and the objective function (E) is defined as
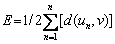 (11)
(11)
where d(un, v) is the normal distance between un and the arc v. The purpose of fitting the contour is to find the arc v that minimizes E and the correct origin of coordinates [25]. Physical parameters of drop are determined by the optimal fitting point. Density ρ=11.4–0.00124T required for calculating the surface tension is derived from the report by KASHEZHEV et al [26].
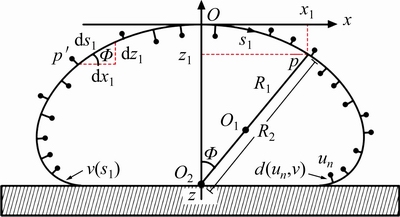
Fig. 1 Theoretical model of surface tension measure- ment with sessile drop method
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Surface roughness of alumina substrate
Figure 2 shows the confocal laser scanning microscope (CLSM) analysis of the alumina substrates with different surface roughnesses. Figures 2(a) to (d) are the 1# to 4# alumina substrates, respectively. The column on the left is the micrograph and the column on the right is the corresponding 3D morphology. The mean values of roughness parameters Ra and r are shown in the figure, which increase gradually from 1# to 4#. Different colors represent different heights in 3D morphology. The more concentrated the colors are, the rougher the surface should be. Among the substrates, 1# substrate is well-polished with a rather smooth surface (Ra=0.092 μm). The surface roughnesses of 2# to 4# substrates increase gradually, and Ra range is 0.834-2.23 μm.
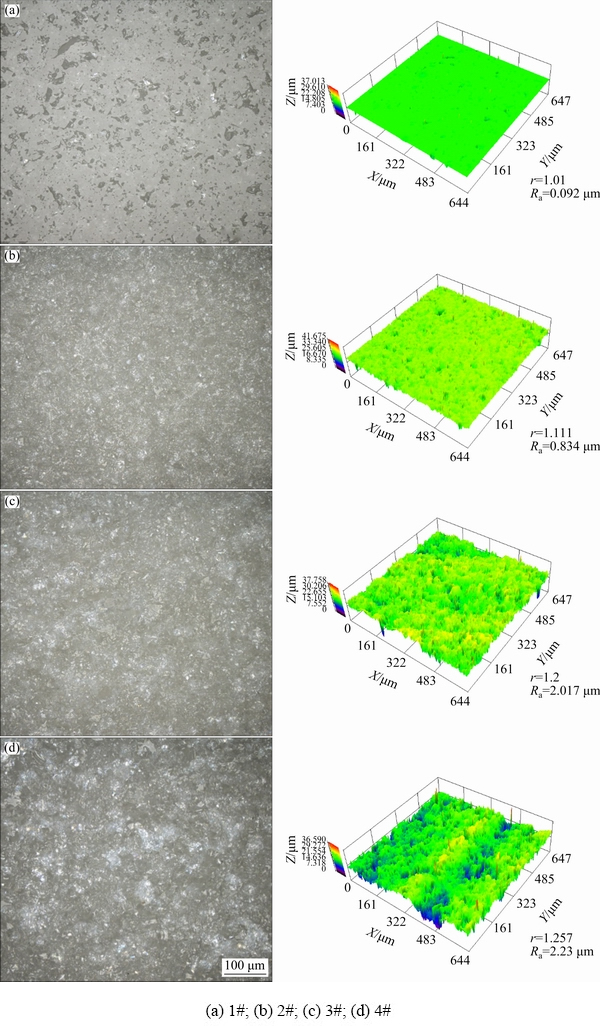
Fig. 2 CLSM analysis for different alumina substrates surface
3.2 Wetting of lead drop on alumina substrate with different roughnesses

Fig. 3 Changes for contact angle of lead drop on alumina substrate with different roughnesses at various temperatures (a), and wetting morphologies at 2700, 3900, 5100, 6300 and 7500 s with different roughnesses (b)
This paper focuses on the wetting behavior of lead drops on alumina substrates with different roughnesses. Figure 3(a) shows the distribution of the contact angle of lead drop on alumina substrates with different Ra and the heating curve of the furnace, and Fig. 3(b) shows the wetting patterns at different time under four roughnesses. The start time is the moment when the temperature reaches the melting point of lead. From 923 to 1123 K, constant temperature is maintained at 50 K for 15 min at intervals. During the insulation process, photos are taken every 3 min. At the same temperature, fluctuation of contact angle is caused by measurement error, the maximum of which is 1.5°. Besides, the simulation of morphology of lead drop on alumina substrate with Ra=2.017 μm is shown in Fig. 3. As can be seen, the contact angle of lead drop increases with the increase of substrate surface roughness. At 973 K, the difference of the average contact angle of lead drop between Ra=0.092 μm and Ra=0.834 μm is 16.4°, and Ra increases from 0.834 to 2.017 μm, while the average contact angle only increases by 4.5°. When Ra=2.017 μm and Ra=2.23 μm, the roughness is almost the same and thus a little change in contact angle can be observed. Wetting behavior of lead drop on different substrates confirms that surface roughness is a pivotal factor. The change in contact angle of lead drop is consistent with the WENZEL equation [27].
cos θw=rcos θy (12)
where θw is the actual contact angle, θy is the ideal contact angle, and r is shown in Fig. 2. According to Eq. (12), when the contact angle is greater than 90°, the contact angle increases as the surface roughness increases.
Figure 4 shows the temperature dependence of contact diameter and droplet height of lead drop on alumina substrates with different roughnesses. As can be seen, with the increase of roughness, the contact diameter increases and the droplet height decreases. Because the surface tension of lead drop decreases with the increase of temperature, which promotes the motion of lead drop triple line on alumina substrates. At the same temperature, as the Ra increases, the contact angle, contact diameter, and droplet height show the same degree of change. Moreover, in Figs. 3 and 4, at 6000 s, the values associated with Ra=2.017 μm and Ra=2.230 μm demonstrate that the changes of contact angle, contact diameter, and droplet height are synchronal.
In order to confirm the above analysis based on the microscopic view, representative samples are cross-sectioned through the center of the lead drop. SEM was used to observe the microstructure of the lead/alumina interface. As shown in Figs. 5(a) and (b), in all cases, lead is in close contact with alumina substrates and is full of the surface depression of alumina substrates, which is consistent with Wenzel state. The micrograph provides proof to support the above-mentioned analysis. The surface of Ra=0.092 μm alumina substrate is smooth, the contact line between lead and substrate is relatively smooth. The surface of Ra=2.23 μm alumina substrate is rough, and the two-phase contact line fluctuates greatly. The EDS results (Figs. 5(c-f)) show that the interface between lead and alumina is clear, there are no diffusion and no new phase formation during wetting, which is regarded as a non-reactive wetting [28].

Fig. 4 Changes for contact diameter (a) and droplet height (b) of lead drop on alumina substrate with different roughnesses at various temperatures
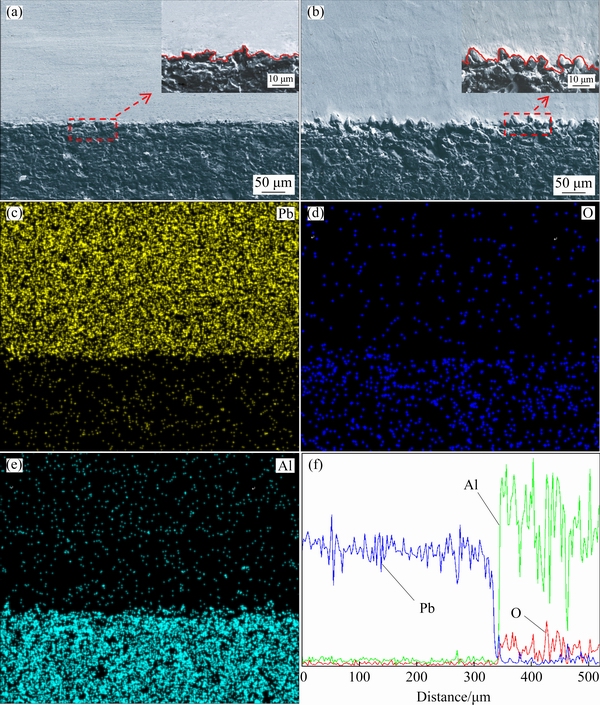
Fig. 5 SEM images (a, b) of interface between lead and alumina substrate, corresponding element distribution maps (c-e) in (a), and linear scanning analysis (f)
3.3 Surface free energy of alumina substrate with different roughnesses
Figure 6 shows the schematic diagram of the wetting mechanism of lead drop on alumina substrates with different roughnesses. From the thermodynamic perspective, when the lead drop reaches the alumina surface, a new liquid-solid interface is created and the same area of the gas-solid interface will be replaced. However, the interface energy of the liquid-solid interface is much larger than that of the gas-solid interface. To minimize the energy of the system, the liquid-solid interface area should be as small as possible. This is why lead drop does not wet the alumina substrate. As shown in Fig. 6(a), in the case that substrate surface is very smooth, after the drop reaches the substrate surface, the triple line moves under the action of the surface tension, and the contact diameter increases while the droplet height decreases. Then, the triple line reaches a steady state quickly. At this time, the contact angle and system energy remain constant. After the substrate surface is roughened, the actual surface area of the substrate increases (Fig. 2) and the surface energy of the substrate increases. After the drop reaches the surface of the rough substrate, if the contact diameter is the same, the liquid-solid interface actual contact area is larger than that of the smooth substrate. And the rough substrate has higher surface energy, so the system energy becomes larger. To minimize the energy of the system, the liquid-solid interface area should be reduced [27]. On the other hand, there are many bumps and pits on the surface of the rough substrate, which hind the triple line movement of lead to pinning [29,30]. Therefore, the contact diameter of lead drop decreases with the increase of surface roughness, and the droplet height and contact angle increase.
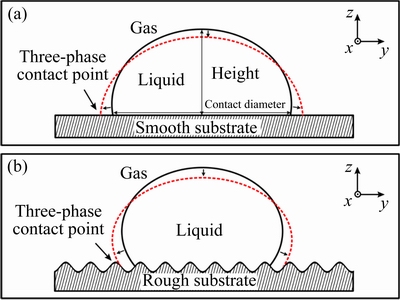
Fig. 6 Wetting of drop on smooth substrate (a) and on rough substrate (b)
To explain the wetting process of liquid lead on the alumina substrates with different surface roughnesses, the surface free energy of substrates was measured and the relationship between surface roughness and surface free energy was analyzed. Figure 7(a) shows the contact angle on alumina substrates with different roughnesses of both deionized water and glycerol. These two liquids would reach a steady state after 10 min. The contact angles of both liquids decrease with the increase of roughness, which is contrary to the trend of contact angle in Fig. 3. However, it also conforms to the theory of Wenzel equation. When the contact angle is less than 90°, the contact angle decreases as the surface roughness increases.
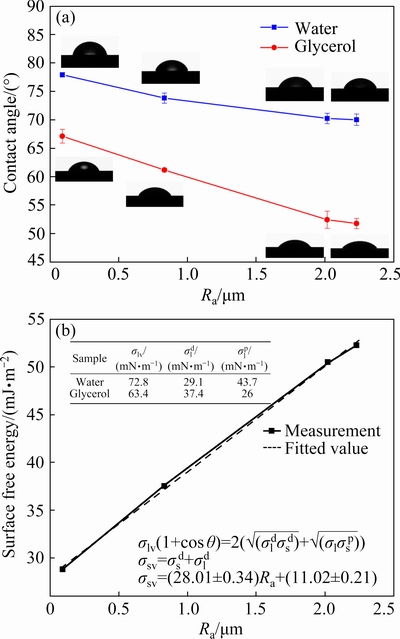
Fig. 7 Contact angle of deionized water and glycerol on alumina substrate of different roughnesses with maximum error of ±2% (a), and relationship between surface free energy and Ra of alumina substrate (b)
The data of surface tension for deionized water and glycerol are shown in Fig. 7(b). The surface free energy of the alumina substrate is calculated by the above geometric means method (Eq. (6)). The surface free energy increases in a positive trend with Ra and the relation equation between them is shown in Fig. 7(b). This result can be explained by thermodynamic, because the surface free energy is defined as the increased free energy per unit area, as
dG=σdA (13)
where G is the surface free energy, and A is the surface area. According to Fig. 2, the surface roughness parameters Ra and r increase simultaneously, which means that the actual surface area of the alumina substrate increases, resulting in surface energy growth.
3.4 Surface tension of lead drop
Figure 8 shows the surface tension measurements of lead drops on four different roughness alumina substrates. The measured results are compared with previous data reported after 1999. In Fig. 8, the surface tension measurements of the four groups of lead drops are within the range of previous research results, and the surface tension decreases as the substrate roughness increases. The surface tension of lead drop on Ra=0.092 μm substrates is close to that measured in most literatures, which indicates that the surface tension of lead on smooth alumina substrate is the most accurate. Substrates with rough surfaces may be used in individual literature, resulting in low surface tension measurements of lead drop. Accordingly, surface roughness has a considerable influence on the measurement of liquid surface tension. However, at present, most people calculate the liquid surface tension based on the Young-Laplace equation (Eq. (3)) which does not consider the impact of surface roughness. Therefore, in order to ensure the accuracy of the liquid surface tension measurement, the substrate should be selected as smooth as possible.
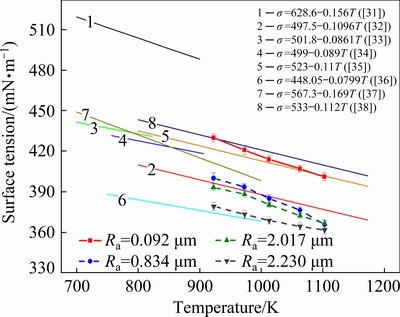
Fig. 8 Temperature dependence of surface tension of lead and roughness dependence of surface tension of lead from experimental data
3.5 Oxygen partial pressure
It has also been proved that oxide film on the molten metal surface affects the authenticity of contact angle and surface tension [39,40]. The purpose of the following calculation is to analyze whether oxygen partial pressure in the furnace is sufficient to cause oxidation reaction on the molten lead surface.
2Pb(l)+O2(g)=2PbO(s) (14)
△GΘ=-425090+179.08 T=
-RTln(1/PO2,sat), T=601-1151 K (15)
where R is the universal gas constant, the activity values of Pb and PbO are both set as unity, and PO2,sat (the saturated oxygen partial pressure) is the equilibrium oxygen partial pressure of Pb/PbO system.
Oxygen partial pressure in Ar-5%H2 atmosphere can be calculated as follows [21]:
2H2(g)+O2(g)=2H2O(g) (16)
△GΘ=-492880+19.62T=
-RTln[(PH2O/PH2)2(1/PO2)] (17)
PO2,sat calculated from thermodynamic data and PO2 in Ar-5%H2 atmosphere are shown in Fig. 9. PO2 in Ar-5%H2 atmosphere is much smaller than PO2,sat in the temperature ranging from 923 to 1123 K, which shows that H2 in atmosphere inhibited the oxidation reaction of molten lead surface. It proves that the wettability data measured in current work are accurate and reliable.
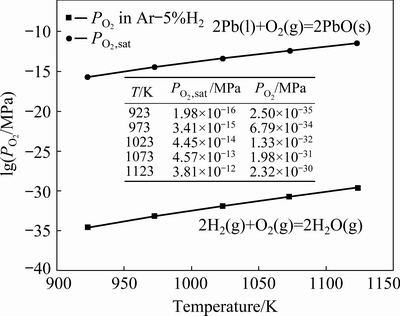
Fig. 9 Oxygen partial pressure in Ar-5%H2 atmosphere and equilibrium oxygen partial pressure of Pb/PbO system
4 Conclusions
(1) With the increase of surface roughness, the actual surface area of alumina substrate increases, resulting in the increase in surface free energy of alumina substrate. The initial energy equilibrium state of the lead drop/alumina substrate system is interrupted. In order to reduce the system energy, the area of solid-liquid interface decreases. Therefore, the contact diameter decreases, the contact angle and the droplet height increase. The change of contact angle conforms to the Wenzel equation.
(2) Lead is tightly bound and does not react with alumina substrates. The surface depression of the alumina substrate is filled with lead. Wettability of lead on the alumina substrates is consistent with the Wenzel state.
(3) The surface tension of lead decreases with the increase of surface roughness of alumina substrate. The smooth substrate is conducive to the accuracy of surface tension.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful for the financial supports from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51974022, U1738101), and Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, China (No. FRF-MP-20-17).
References
[1] WU Mao, HE Xin-bo, DIN Rafi-ud, REN Shu-bin, QIN Ming-li, QU Xuan-hui. Effect of various Ni plating layers and aging on microstructure and shear strength of Sn-2.5Ag-2.0Ni solder joint [J]. Surface & Coatings Technology, 2009, 203: 3011-3018.
[2] ZOU Xiao-dong, ZHAO Da-peng, SUN Jin-cheng, WANG Cong, MATSUURA H. An integrated study on the evolution of inclusions in EH36 shipbuilding steel with Mg addition: From casting to welding [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 2018, 49: 481-489.
[3] DAI Xiu, CAO Yu, SHI Xiao-wei, WANG Xin-long. The PLA/ZIF‐8 nanocomposite membranes: The diameter and surface roughness adjustment by ZIF-8 nanoparticles, high wettability, improved mechanical property, and efficient oil/water separation [J]. Advanced Materials Interfaces, 2016, 3: 1600725.
[4] YU A, KIM M, LEE C, LEE J. Wetting and interfacial reaction characteristics of Sn-1.2Ag-0.5Cu-xIn quaternary solder alloys [J]. Metals and Materials International, 2011, 17(3): 521-526.
[5] CONTRERAS A. Wetting of TiC by Al-Cu alloys and interfacial characterization [J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2007, 311: 159-170.
[6] SHARMA A, SRIVASTAVA A K, LEE K, AHN B. Impact of non-reactive ceria nanoparticles on the wettability and reaction kinetics between lead-free Sn–58Bi and Cu pad [J]. Metals and Materials International, 2019, 25(4): 1027-1038.
[7] XU Peng-yun, COYLE T W, PERSHIN L, MOSTAGHIMI J. Superhydrophobic ceramic coating: Fabrication by solution precursor plasma spray and investigation of wetting behavior [J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2018, 523: 35-44.
[8] LAI Qing-quan, ZHANG Lei, EUSTATHOPOULOS N. Enhanced wetting of dual-phase metallic solids by liquid metals: A new effect of interfacial reaction [J]. Acta Materialia, 2013, 61(11): 4127-4134.
[9] TERRIZA A, ALVAREZ R, BORRAS A, COTRINO J, YUBERO F, GONZALEZ-ELIPE A R. Roughness assessment and wetting behavior of fluorocarbon surfaces [J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2012, 376: 274-282.
[10] MA Guo-feng, LI Zheng-kun, YE Heng, HE Chun-lin, ZHANG Feng, HU Zhuang-qi, Wetting and interface phenomena in the molten Sn/CuFeNiCoCr high-entropy alloy system [J]. Applied Surface Science, 2015, 356: 460-466.
[11] CONG Xiao-shuang, SHEN Ping, WANG Yi, JIANG Qi-chuan. Wetting of polycrystalline SiC by molten Al and Al-Si alloys [J]. Applied Surface Science, 2014, 317: 140-146.
[12] TUNTHAWIROON P, KANLAYASIRI K. Effects of Ag contents in Sn–xAg lead-free solders on microstructure, corrosion behavior and interfacial reaction with Cu substrate [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2019, 29: 1696-1704.
[13] MANDAL S, RAO V, RAY A K. Characterization of the brazed joint interface between Al2O3 and (Ag-Cu-Ti) [J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2004, 39(16): 5587-5590.
[14] VOLCEANOV E, VOLCEANOV A, STOLERIU S. Assessment on mechanical properties controlling of alumina ceramics for harsh service conditions [J]. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2007, 27(2-3): 759-762.
[15] LI Jian-qiang, PAN Wei, YUAN Zhang-fu, CHEN Yun-fa. Titanium metallization of alumina ceramics by molten salt reaction [J]. Applied Surface Science, 2008, 254: 4584-4590.
[16] HUH J, HWANG M, SHIM S, KIM T, KIM J. Effect of Al and Mg contents on wettability and reactivity of molten Zn–Al-Mg alloys on steel sheets covered with MnO and SiO2 layers [J]. Metals and Materials International, 2018, 24: 1241-1248.
[17] WANG Shi-ren, ZHANG Yue, ABIDI N, CABRALES L. Wettability and surface free energy of graphene films [J]. Langmuir, 2009, 25(18): 11078-11081.
[18] STAMMITTI-SCARPONE A, ACOSTA E J. Solid-liquid- liquid wettability and its prediction with surface free energy models [J]. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 2019, 264: 28-46.
[19] FOWKES F M. Attractive forces at interfaces [J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry, 1964, 56(12): 40-52.
[20] OWENS D K, WENDT R C. Estimation of the surface free energy of polymers [J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 1969, 13(8): 1741-1747.
[21] SINGH A K, SINGH J K. Fabrication of durable super- repellent surfaces on cotton fabric with liquids of varying surface tension: Low surface energy and high roughness [J]. Applied Surface Science, 2017, 416: 639-648.
[22] WANG Li-long, Study on adhesion effect of asphalt and mineral based on surface free energy [D]. Xi’an: Chang’an University, 2013: 1-75. (in Chinese)
[23] YUAN Zhang-fu, MUKAI K, HUANG Wen-lai. Surface tension and its temperature coefficient of molten silicon at different oxygen potentials [J]. Langmuir, 2002, 18(6): 2054-2062.
[24] YUAN Zhang-fu, MUKAI K, TAKAGI K, OHTAKA M, HUANG Wen-lai, LIU Qiu-sheng. Surface tension and its temperature coefficient of molten tin determined with the sessile drop method at different oxygen partial pressures [J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2002, 254(2): 338-345.
[25] ROTENBERG Y, BORUVKA L, NEUMANN A W. Determination of surface tension and contact angle from the shapes of axisymmetric fluid interfaces [J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 1983, 93(1): 169-183.
[26] KASHEZHEV A Z, KUTUEV R A, PONEZHEV M K, VSOZAEV V A, KHASANOV A I. Density and surface tension polyterms of lead-based alloys [J]. Bulletin of the Russian Academy of Sciences: Physics, 2012, 76: 791-793.
[27] WENZEL R N. Resistance of solid surfaces to wetting by water [J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry, 1936, 28: 988-994
[28] KUMAR G, PRABHU K N. Review of non-reactive and reactive wetting of liquids on surfaces [J]. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 2007, 133(2): 61-89.
[29] NICOLAS E. Wetting by liquid metals-application in materials processing: The contribution of the Grenoble group [J]. Metals, 2015, 5(1): 350-370.
[30] SHUTTLEWORTH R, BAILEY G L J. The spreading of a liquid over a rough solid [J]. Discussions of the Faraday Society,1948, 3: 16-22.
[31] MIKHAILOV V N, EVTIKHIN V A, LYUBLINSKI I E, VERTKOV A V, CHUMANOV A N. Lithium for fusion reactors and space nuclear power systems of XXI century [M]. Moscow: Energoatomizdat, 1999: 528.
[32] GASIOR W, MOSER Z, PSTRUS J. Density and surface tension of the Pb-Sn liquid alloys [J]. Journal of Phase Equilibria, 2001, 22(1): 20-25.
[33] NOVAKOVIC R, RICCI E, GIURANNO D, GNECCO F. Surface properties of Bi-Pb liquid alloys [J]. Surface Science, 2002, 515(2): 377-389.
[34] TANAKA T, NAKAMOTO M, OGUNI R, LEE J, HARA S. Measurement of the surface tension of liquid Ga, Bi, Sn, In and Pb by the constrained drop method [J]. Materials Research and Advanced Techniques, 2004, 95(9): 818-822.
[35] YUAN Zhang-fu, KE Jia-jun, LI Jing, Surface tension of metals and alloys [M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2006: 30-32. (in Chinese)
[36] PLEVACHUK Y, SKLYARCHUK V, ECKERT S, GERBETH G. Some physical data of the near eutectic liquid lead–bismuth [J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2008, 373(1-3): 335-342.
[37] ALCHAGIROV B B, DYSHEKOVA F F, ARKHESTOV R K. Surface tension of lead–lithium melts [J]. Russian Journal of Physical Chemistry A, 2016, 90(11): 2262-2269.
[38] GANCARZ T, GASIOR W. Density, surface tension, and viscosity of liquid Pb-Sb alloys [J]. Journal of Chemical & Engineering Data, 2019, 63(5): 1471-1479.
[39] YUAN Zhang-fu, MUKAI K, HUANG Wen-lai. Effects of antimony on the surface tension of molten silicon [J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2002, 249(2): 471-475.
[40] YUAN Zhang-fu, FAN Jian-feng, LI Jing, KE Jia-jun, MUKAI K. Surface tension of molten bismuth at different oxygen partial pressure with the sessile drop method [J]. Scandinavian Journal of Metallurgy, 2004, 33(6): 338-346.
齐 振,廖 亮,王容岳,张岩岗,袁章福
北京科技大学 钢铁共性技术协同创新中心,北京 100083
摘 要:表面粗糙度是高温下的液态金属/陶瓷润湿性的重要影响因素。在923~1123 K的温度范围内研究氧化铝表面粗糙度对铅液滴接触角、接触直径、液滴高度、表面张力的影响。在冷却后使用SEM观察铅/基底界面的微观结构。通过使用几何平均法计算氧化铝基板的表面自由能进而解释铅液滴润湿行为的机理。结果表明,在铅液滴/氧化铝陶瓷系统中,表面粗糙度从0.092 μm增加至2.23 μm,表面自由能逐渐由13.356 mJ/m2增加至39.998 mJ/m2,铅滴的接触直径由9.111 mm减小到7.19 mm,铅降高度由3.41 mm增加到3.85 mm,接触角由113.05°增加到137.15°。此外,发现铅填满了氧化铝的表面凹陷并且没有明显变化,实验证明铅液滴在氧化铝基板上的润湿与Wenzel状态一致。
关键词:表面粗糙度;润湿;表面自由能;表面张力;氧化铝
(Edited by Xiang-qun LI)
Corresponding author: Zhang-fu YUAN, Tel: +86-18911786560, E-mail: zfyuan2016@ustb.edu.cn
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(21)65671-6
1003-6326/ 2021 The Nonferrous Metals Society of China. Published by Elsevier Ltd & Science Press
2021 The Nonferrous Metals Society of China. Published by Elsevier Ltd & Science Press

