激光选区熔化制备Ti-6Al-4V合金的显微组织及在人工模拟唾液中的电化学腐蚀行为
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2021年第1期
论文作者:鞠江 李京京 蒋敏 李梦娅 杨力祥 王开明 杨超 康茂东 王俊
文章页码:167 - 177
关键词:Ti-6Al-4V合金;激光选区熔化;显微组织;电化学腐蚀行为
Key words:Ti-6Al-4V alloy; selective laser melting; microstructure; electrochemical corrosion behavior
摘 要:为了进一步提高植入体的耐腐蚀性,通过激光选区熔化制备Ti-6Al-4V合金。借助扫描电镜、电子背散射、透射电镜、电化学腐蚀试验和接触角试验对其显微组织和在人工模拟唾液中的电化学腐蚀行为进行研究。结果表明:激光选区熔化制备Ti-6Al-4V合金在堆积方向呈现典型的β柱状晶,在扫描方向呈近圆形棋盘状组织,而锻造和锻造+热处理样品呈现典型的等轴晶形貌。在37 °C模拟人工唾液中激光选区熔化制备Ti-6Al-4V合金比锻造和锻造+热处理样品具有更好的耐腐蚀性能,这是由于其具有疏水性、更高的晶界密度和分布均匀的合金元素。
Abstract: Ti-6Al-4V alloy was fabricated via selective laser melting (SLM) to improve its corrosion resistance for implant. The microstructure and electrochemical corrosion behavior were investigated using scanning electron microscopy (SEM), electron backscatter diffraction (EBSD), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), electrochemical test and contact angle test. It can be found that the as-selective laser melted (as-SLMed) Ti-6Al-4V alloys show β columnar microstructure in building direction and nearly circular checkerboard microstructure in scanning direction, while the wrought and wrought+HT samples exhibit equiaxed microstructure. The as-SLMed Ti-6Al-4V alloy exhibits better corrosion resistance than the wrought and wrought+HT samples due to hydrophobicity, high grain boundary density and uniform distribution of alloying elements in simulated artificial saliva at 37 °C.
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 31(2021) 167-177
Jiang JU1,2, Jing-jing LI1,2, Min JIANG1, Meng-ya LI3, Li-xiang YANG1, Kai-ming WANG4, Chao YANG1,2, Mao-dong KANG1,2, Jun WANG1,2
1. Institute of Solidification Science and Technology, School of Materials Science and Engineering, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200240, China;
2. Shanghai Key Laboratory of Advanced High-temperature Materials and Precision Forming, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200240, China;
3. School of Aerospace Engineering, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing 100081, China;
4. State Key Laboratory of Tribology, Department of Mechanical Engineering, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China;
Received 11 March 2020; accepted 28 August 2020
Abstract: Ti-6Al-4V alloy was fabricated via selective laser melting (SLM) to improve its corrosion resistance for implant. The microstructure and electrochemical corrosion behavior were investigated using scanning electron microscopy (SEM), electron backscatter diffraction (EBSD), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), electrochemical test and contact angle test. It can be found that the as-selective laser melted (as-SLMed) Ti-6Al-4V alloys show β columnar microstructure in building direction and nearly circular checkerboard microstructure in scanning direction, while the wrought and wrought+HT samples exhibit equiaxed microstructure. The as-SLMed Ti-6Al-4V alloy exhibits better corrosion resistance than the wrought and wrought+HT samples due to hydrophobicity, high grain boundary density and uniform distribution of alloying elements in simulated artificial saliva at 37 °C.
Key words: Ti-6Al-4V alloy; selective laser melting; microstructure; electrochemical corrosion behavior
1 Introduction
Ti-6Al-4V alloy is widely considered as a promising material in medical fields due to its good workability, excellent biocompatibility, low elastic modulus and high strength, etc [1,2]. However, the undesirable corrosion resistance limits its application in dentistry. APARICIOA et al [3] reported that titanium oxide film broke easily in acid, fluoride and saliva. The complexity of food intake can drastically change pH values of human saliva, which deteriorates the oral environment for teeth [4].
The conventional manufacturing methods, i.e., casting and forging, have many disadvantages such as low utilization rate, long preparation periods and high manufacturing costs. Moreover, it is difficult to fabricate the parts with complex shapes and excellent properties, which limits the application of Ti-6Al-4V alloys in medical fields [5,6]. Many researchers improved the corrosion resistance of the Ti-6Al-4V alloy by surface modification using micro-arc oxidation (MAO) [7], shot peening (SP) [8], plasma electrolytic oxidation (PEO) [9], and laser cladding (LS) [10]. For example, a cortex- like microstructure with irregular vermiform slots on surface of Ti-6Al-4V alloys was fabricated by micro-arc oxidation, which can significantly improve their corrosion resistance [11,12]. However, these methods usually improve the corrosion resistance of Ti-6Al-4V alloys at the cost of a sharp decrease of their strength and modulus. The bonding strength between the coating and substrate is also difficult to guarantee.
Selective laser melting (SLM) is one of the advanced additive manufacturing (AM) methods, which can be used to prepare the parts through layer-by-layer controlled by the CAD model [13]. This technique has superior advantages compared with conventional manufacturing methods, such as near net shape, high shaping accuracy, short shaping cycle, and high material utilization and customization [14]. However, the microstructure in scanning direction and built direction show obvious anisotropy [15]. To date, although the mechanical properties of the as-SLMed Ti-6Al-4V alloys were widely concerned [16], rare studies were reported on the corrosion resistance of the as-SLMed Ti-6Al-4V alloys in simulated artificial saliva.
In this work, the SLM parameters were adjusted appropriately compared with those in previous studies [17-19]. Wrought and wrought + heat-treated (HT) Ti-6Al-4V alloys were conducted under the same experimental conditions for a comparative purpose. The microstructure and electrochemical corrosion behaviour of Ti-6Al-4V alloys fabricated using various processes were investigated in simulated artificial saliva. The results can provide basis on the corrosion mechanism of Ti-6Al-4V alloys fabricated using various processes, and give the direction for the process control and optimization of Ti-6Al-4V alloys.
2 Experimental
2.1 Sample preparation
The spherical Ti-6Al-4V powder fabricated by gas atomization method was used in this work. The average particle size of powder was 45 μm, measured using a laser particle size analyzer, as shown in Fig. 1. The Ti-6Al-4V samples were fabricated using an EOS M290 equipment, and the scanning strategy was rotating 60° between layer and layer. The chamber pressure was set to be 0.57 GPa. The Ti-6Al-4V substrate was preheated to 200 °C before printing. The laser power, spot diameter, power thickness and hatching pace were 280 kW, 100 μm, 0.05 mm and 0.06 mm, respectively. The comparative samples were the conventional wrought Ti-6Al-4V alloys and the wrought Ti-6Al-4V alloys heated at 960 °C for 4 h and then water cooling. The samples along built direction and scanning direction were named as XOY and XOZ, respectively.
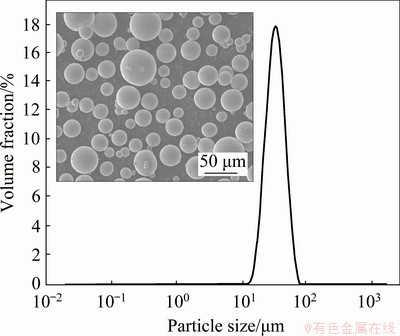
Fig. 1 Morphology and size distribution of Ti-6Al-4V powder
2.2 Electrochemical corrosion test
The electrochemical corrosion tests were conducted in simulated artificial saliva at 37 °C using Gamry electrochemical workstation, a conventional three-electrode cell, as shown in Fig. 2. The Ti-6Al-4V sample, Ag/AgCl and platinum wire were used as working electrode, reference electrode and counter electrode, respectively. The chemical compositions of the simulated artificial saliva (pH=6.8) are given in Table 1. All samples with an exposed area of 1.0 cm2 were prepared using wire cutting, then grinding, polishing, cleaning with alcohol and drying in turn. Firstly, the samples were immersed in simulated artificial saliva for 60 min before testing to stablize the open circuit potential (OCP). Then, the potentiodynamic polarization (Tafel) curves were conducted in the potential range from -2 to 0.5 V at a scan rate of 10 mV/s. Finally, the EIS was conducted using an AC amplitude of 10 mV versus the OCP in the frequency range of 10-2-105 Hz. The relevant values were calculated from fitting the EIS using Zview software.
Table 1 Chemical compositions of simulated artificial saliva

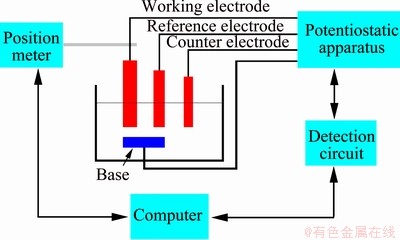
Fig. 2 Typical diagram of three-electrode system
2.3 Characterization
Microstructures were observed using scanning electron microscope (SEM, Mira) and transmission electron microscope (TEM, JEOL JEM2100F). The samples were etched for 60 s with Kroll’s reagent (1 mL HNO3 + 2 mL HF + 97 mL distilled water). Electron back-scattered diffraction (EBSD) was carried out to detect grain orientation and grain size. The hydrophilic and hydrophobic properties of Ti-6Al-4V alloys were detected using contact angle analyzer (DSA100).
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Microstructure
Figure 3 presents the morphologies of Ti-6Al-4V samples fabricated using different processes. From Fig. 3(a), the microstructure of wrought sample is composed of the α phase and the stick-bone-shaped β phase with the length of 1-4 μm. The stick-bone-shaped β phase distributes along the grain boundary, which has been reported in previous study [20]. After heat treatment, the stick-bone-shaped β phase at the grain boundary disappears and the primary equiaxial α phase and secondary fine acicular α phase can be clearly observed [21]. The quenching at temperature lower than the α+β/β phase transition point induces some α phases to dissolve into the β matrix. The α phase remains in the matrix during sequent water cooling. It is very difficult for β phase to transform into α equilibrium phase by diffusion, only forming the supersaturated solid solution (α martensite) through the collective migration of atoms in β phase [22]. From Figs. 3(c-f), the microstructure of the as-SLMed Ti-6Al-4V alloy shows distinct anisotropy. The typical columnar prior β grains passing through several layers are generated due to temperature gradient along the building direction, which is mainly dominated by the formation of the martensite α/α′ needle-shaped phases due to the high cooling rate. WANG et al [23] reported that the width of the columnar prior β grains is related with the laser spot size. The scanning strategy of a 60° rotation of each layer results in a formation of suborbicular chessboard patterns in XOY sample, as shown in Fig. 3(f).
The TEM examinations are conducted to clarify the microstructures of the XOZ and XOY samples, as shown in Fig. 4. From the bright field micrographs in Figs. 4(a, b, e, f), it is clear that the α/α′ phase in XOZ and XOY samples has a hexagonal close-packed (hcp) structure according the selected area diffraction (SAD) patterns of A and B zones with plate-like and twin morphology. Meanwhile, the β phase with cubic (bcc) structure is also determined corresponding to the SADs in Figs. 4(d, h).
3.2 Electrochemical corrosion property
The electrode potential at the metal- electrolyte interface can be used to estimate the tendency of metal corrosion [24]. Figure 5 depicts the OCP (open circuit potential) curves for the Ti-6Al-4V samples fabricated by different processes immersed into simulated artificial saliva at 37 °C. The OCP values of the as-received samples gradually stabilize with an increase of immersion time, which demonstrates that the electrochemical process is mainly controlled by the anodic reaction, and a protective oxide film begins to grow on the electrode surface [25]. The OCP values of wrought, wrought+HT, XOZ and XOY samples gradually approach a constant of about -0.05, -0.01, 0.035 and 0.052 V, respectively. In general, the alloy has better corrosion resistance at higher OCP value. Therefore, it can be determined that the as-SLMed Ti-6Al-4V alloys (XOY and XOZ samples) have better corrosion resistance than the wrought and wrought+HT Ti-6Al-4V alloys. Furthermore, it can be seen that the corrosion resistance of the XOY sample is larger than that of the XOZ sample. which is mainly related to the density of grain boundary [26].

Fig. 3 Phase morphologies of Ti-6Al-4V samples fabricated by different processing
Figure 6 shows potentiodynamic polarization (Tafel) curves of the Ti-6Al-4V samples fabricated by different processes. The corresponding values of corrosion potential (φcorr), corrosion current density (Jcorr) and polarization resistance (Rp) for tested samples were calculated by Chi 760E software, and the results are listed in Table 2. Among them, the φcorr value and the Jcorr value can describe the tendency to corrode and the corrosion rate. As seen from Fig. 6, the XOZ and XOY samples show obviously passivated behaviour in the corrosion potential range from -450 to 150 mV in simulated artificial saliva, which demonstrates that the formed passive film can work as a protective film to inhibit the corrosion of Ti-6Al-4V alloy. What is more, the as-SLMed Ti-6Al-4V sample shows broader corrosion potential range (△φ2) for the passive film compared with that of wrought and wrought+HT samples (△φ1) [27,28]. Moreover, the more stable and protective passive film can be formed on the surface of metal when the the Jcorr is lower [29]. As shown in Table 2, the XOY sample presents lower Jcorr value of (1.75±0.04)×10-3 mA/cm2 than XOZ ((1.98±0.05)×10-3 mA/cm2), wrought ((2.08±0.06)× 10-3 mA/cm2) and wrought+HT samples ((2.56± 0.05)×10-3 mA/cm2). The XOY sample also exhibits the highest Rp value of (2.78±0.05)×104 Ω, while the φcorr value is in the order of XOY>XOZ> wrought>wrought+HT. The corrosion potential for as-SLMed Ti-6Al-4V samples is shifted to be more positive, and the corresponding Jcorr value decreases compared with that of wrought sample. According to the Faraday’s law, the corrosion rate can be calculated using the following equation [30,31]:
Pi=22.85Jcorr (1)
It can be seen that the corrosion rate is positively correlated with the Jcorr, which suggests that the XOY sample displays the lowest corrosion rate, and the most corrosion resistance in simulated artificial saliva.

Fig. 4 TEM micrographs for XOZ (a, b) and XOY (e, f) samples and corresponding selected area diffraction patterns of α/α′ phase (c, g) and β phase (d, h)

Fig. 5 Open circuit potential as function of time for Ti-6Al-4V samples fabricated by different processes immersed into simulated artificial saliva

Fig. 6 Tafel curves for Ti-6Al-4V samples fabricated by different processes immersed into simulated artificial saliva at 37 °C
Table 2 Fitting parameters of Tafel measurements of Ti-6Al-4V samples fabricated by different processes in simulated artificial saliva at 37 °C

The electrochemical impedance spectroscopy was carried out to investigate more details about the corrosion behavior of tested samples. Figure 7(a) shows the Nyquist plots of Ti-6Al-4V samples manufactured by various processes in the simulated artificial saliva at 37 °C. As shown in Fig. 7(a), all the Nyquist plots present the incomplete capacitive resistance arcs. It is clear that the curvature radius of the XOY sample is larger than that of the XOZ sample, wrought and wrought+HT samples. This suggests that the charge-transfer resistance of XOY sample is the highest, as shown in Table 3. The charge-transfer resistance of the XOY sample is (1.61±0.05)×106 Ω·cm2 which is 1.19, 1.71 and 3.91 times that of the XOZ sample, wrought and wrought+HT samples, respectively. This also suggests that the XOY sample displays better corrosion resistance.

Fig. 7 EIS results in form of Nyquist curve (a) and equivalent circuit used for impedance spectra analysis (b) for Ti-6Al-4V samples fabricated by different processes immersed in simulated artificial saliva at 37 °C
Table 3 Resistances obtained by EIS spectra fitting

Figure 7(b) shows the equivalent circuit for fitting the EIS data. The model consists of resistances for the solution (Rs), porous layer (Rpor), and charge-transfer resistance (Rct), CPE1 corresponding to the capacitance of the outer surface and the double-layer capacitance (Cdl). The passive film formed on the surface of metal can determine the corrosion behavior, and the protectiveness of the passive film is related to its chemical compositions and the crystallography of the surface oxide film [32]. It is reported that the Ti-rich oxide film is formed through a continuous reaction in pure Ti [32]:
Ti+H2O=TiO+2H++2e (2)
2TiO+H2O=Ti2O3+2H++2e (3)
Ti2O3+H2O=2TiO2+2H++2e (4)
For dual-phase Ti-6Al-4V alloy, the β phase is rich in V, while the α phase is rich in Al [33]. LONG and BACK [34] found that the Al oxides are often embedded in the Ti matrix. However, there inevitably exist some defects and pores in the test samples and the formed oxide film. The pore resistance of alloy is the important parameter, which reflects the resistance of corrosive species through pores, cracks and pinholes in the alloy and oxide film. The simulated artificial saliva can permeate into the substrate of the Ti-6Al-4V alloy through the defects and pores. It is noted that the contributions of the oxide film and Ti-6Al-4V substrate to the electrochemical results should also be taken into account. The electrolyte Rs is related to the ohmic distribution between the working and reference. The Rct is associated with the electro- chemical reaction at the interface of Ti-6Al-4V alloy and simulated artificial saliva. The CPE1 can be used to describe the capacitive properties of the Ti-6Al-4V alloy, and the Cdl can be used to describe the capacitance characteristics of double layers formed at the interface of Ti-6Al-4V alloy and simulated artificial saliva. From Table 3, it can be seen that the XOY sample has the Rp value of (9.62±0.07)×104 Ω·cm2, which is higher than that of wrought sample ((2.87±0.06)×104 Ω·cm2) and wrought+HT sample ((0.92±0.02)×104 Ω·cm2). According to the above analysis, the XOY sample has excellent corrosion resistance.
The chemical elements and the phase morphology have a significant effect on the formation and destruction of the passivation film during corrosion process in simulated artificial saliva [35]. All the tested Ti-6Al-4V alloys contain the same chemical elements (Ti, Al and V) and phases (α and β), and easily form Al2O3, V2O5 and TiO2 on the surface [36]. The chemical elements have minimal effect on corrosion resistance of the tested samples. Hence, the difference of corrosion resistance for the tested samples may be mainly related to the phase boundary distribution, the density of passivation film and the uniformity of microstructure. It was reported that if the current density is lower than 0.1 μA/mm2, the higher grain boundary density promotes the formation of oxide film, which can improve the corrosion resistance of the alloy [37,38]. From Fig. 6, the current density does not exceed 0.1 μA/mm2 in all processes. The grain boundary density (denoted by the ratio of total length of grain boundary to total counting point) of the tested samples was calculated by EBSD, as shown in Fig. 8. It can be seen that the grain boundary densities of wrought, wrought+HT, XOZ and XOY samples are 2.99×10-4, 7.99×10-4, 1.35×10-3 and 1.38×10-3 mm-1, respectively, which indicates that as-SLMed samples have better corrosion resistance in simulated artificial saliva. From Fig. 3, the coarse grains in wrought sample can concentrate impurities at grain boundaries, which can reduce the corrosion resistance of the wrought sample [39]. After heat treatment, the grains are obviously refined. A large number of primary equiaxed α grains precipitate in the wrought+HT Ti-6Al-4V alloy. The potential difference is formed between the Al-rich α phase and V-rich β phase, which causes the primary α phase to be corroded first, thus damaging the corrosion resistance [40]. For the XOZ and XOY samples, the pores and cracks are not observed from Fig. 3. CVIJOVIC-ALAHIC et al [41] pointed out that the grain refinement can effectively restrain the aggregation of elements at grain boundary, and the decrease of grain size from 10 to 0.3 μm corresponds to a dilution of segregated element contents by about 1/30. The distributions of Al and V elements in XOZ and XOY samples were detected using the electron probe micro-analyzer (EPMA), as shown in Fig. 9. The ultrafine-grained lamellar α and β phases generated in XOZ and XOY samples reduce the segregation of elements at grain boundaries, which decreases the galvanic influence caused by uneven distribution of alloying elements in various phases. From Figs. 9(b-e), the distribution of Al in XOY sample is more uniform than that in XOZ sample. Hence, the Jcorr value of XOY sample is slightly lower than that in XOZ sample, as listed in Table 2.

Fig. 8 Content of β-Ti and number of crystal boundaries and total length
In addition, WANG and KANEKO [42] found that the corrosion resistance of alloys is also closely related to hydrophobicity and hydrophilia. A hydrophobic surface generally brings about high corrosion resistance in a metal [43]. Therefore, the contact angles of various Ti-6Al-4V samples were tested in simulated artificial saliva and the results are shown in Fig. 10. It can be seen that that the wrought and wrought+HT samples show hydrophilia in simulated artificial saliva. However, the XOZ and XOY samples present hydrophobicity in simulated artificial saliva, exhibiting excellent corrosion resistance.

Fig. 9 EPMA results in different planes of Ti6Al4V alloy
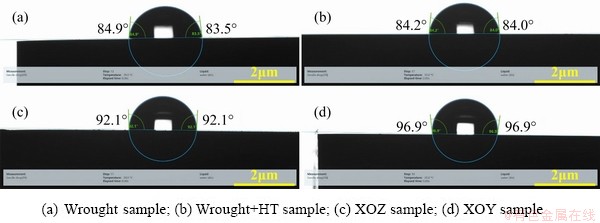
Fig. 10 Hydrophilic and hydrophobic properties of Ti-6Al-4V alloys fabricated by different processes
4 Conclusions
(1) The microstructure of the wrought Ti-6Al-4V alloy is composed of α phase and stick-bone-shaped β phase distributing along grain boundaries. The stick-bone-shaped β phase at the grain boundary disappears, whereas the primary isoaxial α phase and secondary fine acicular phase can be clearly observed after heat treatment.
(2) The as-SLMed Ti-6Al-4V alloys show typical columnar microstructure in the building direction and nearly circular checkerboard microstructure in scanning direction, which are mainly composed of α′ phase with hcp structure and β phase with bcc structure.
(3) The corrosion resistance of as-SLMed Ti-6Al-4V alloys in simulated artificial saliva is better than that of wrought and wrought+HT samples.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful for the financial supports from the National Key R&D Program of China (2017YFB1104100), the New Young Teachers Initiation Plan, China (18X100040027), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51971142), and the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (19Z102060057).
References
[1] NIINOMI M, NAKAI M, HIEDA J. Development of new metallic alloys for biomedical applications [J]. Acta Biomaterialia, 2012, 8(11): 3888-3903.
[2] PENG He-li, LI Xi-feng, CHEN Xu, JIANG Jun, LUO Jing-feng, XIONG Wei, CHEN Jun. Effect of grain size on high-temperature stress relaxation behavior of fine-grained TC4 titanium alloy [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2020, 30(3): 668-677.
[3] APARICIOA C, GIL F J, FONSECA C, BARBOSA M, PLANELL J A. Corrosion behavior of commercially pure Ti shot blasted with different materials and sizes of shot particles for dental implant applications [J]. Biomaterials,2003, 24(2): 263-275.
[4] ARTHUR L G, ANGELES M A, ANA C, APARECIDA M L, JARDINI A L, de ZAVAGLIA C A, DAMBORENEA J J. Heat treatments effects on functionalization and corrosion behavior of Ti-6Al-4V ELI alloy made by additive manufacturing [J].Journal of Alloys and Compounds,2018, 765(15): 961-968.
[5] BARTOLOMEU F, BUCIUMEANU M, PINTO E, ALVES N, SILVA F S, CARVALHO O, MIRANDA G. Wear behavior of Ti6Al4V alloys processed by selective laser melting, hot pressing and conventional casting [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2017, 27(4): 829-839.
[6] WU Bin-tao, PAN Zeng-xi, LI Si-yuan, CUIURI D, DING Dong-hong, LI Hui-jun. The anisotropic corrosion behaviour of wire arc additive manufactured Ti-6Al-4V alloy in 3.5%NaCl solution [J]. Corrosion Science, 2018, 137(6): 176-183.
[7] GU Yan-hong, CHEN Ling-ling, YUE Wen, CHEN Ping, CHEN Fei, NING Chen-yun. Corrosion behavior and mechanism of MAO coated Ti6Al4V with a grain-fined surface layer [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2016, 664(4): 770-776.
[8] YIN Mei-gui, CAI Zhen-bing, LI Zhen-rong, ZHOU Zhong-rong, WANG Wen-jian, HE Wei-feng. Improving impact wear resistance of Ti-6Al-4V alloy treated by laser shock peening [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2019, 29(7): 1439-1448.
[9] KASEEM M, CHOE H C. Triggering the hydroxyapatite deposition on the surface of PRO-coated Ti-6Al-4V alloy via the dual incorporation of Zn and Mg ions [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2020, 819(5): 153038.
[10] KANYANE L R, ADESINA O S, POPOOLA A P I, FAROTADE G A, MALATJI N. Microstructural evolution and corrosion properties of laser clad Ti-Ni on titanium alloy (Ti6Al4V) [J]. Procedia Manufacturing, 2019, 35(6): 1267-1272.
[11] LIN Xiu-zhou, ZHU Min-hao, ZHENG Jian-feng, LUO Jun, MO Ji-liang. Fretting wear of micro-arc oxidation coating prepared on Ti6Al4V alloy [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2010, 20(4): 537-546.
[12] FAZEL M, SALIMIJAZI H R, GOLOZAR M A, GARSIVAZ JAZI M R. A comparison of corrosion, tribocorrosion and electrochemical impedance properties of pure Ti and Ti6Al4V alloy treated by micro-arc oxidation process [J]. Applied Surface Science, 2015, 324(1): 751-756.
[13] BONNIN ROCA J, VAISHNAV P, FUCHS E R H, MORGAN M G. Policy needed for additive manufacturing [J]. Nature Materials, 2016, 15(8): 815-818.
[14] JU Jiang, ZHOU Yang, WANG Kai-ming, LIU Ya-hui, LI Jing-jing, KANG Mao-dong, WANG Jun. Tribological investigation of additive manufacturing medical Ti6Al4V alloys against Al2O3 ceramic balls in artificial saliva [J]. Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials, 2020, 104(4): 103602.
[15] HERNANDEZ-NAVA E, SMITH C J, DERGUTI F, TAMMAS-WILLIAMS S, LEONARD F, WITHERS P J, TODD I, GOODALL R. The effect of defects on the mechanical response of Ti-6Al-4V cubic lattice structures fabricated by electron beam melting [J]. Acta Materialia, 2016, 108(4): 279-292.
[16] ZHANG Qi, LIANG Zheng-long, CAO Miao, LiU Zi-fan, ZHANG An-feng, LU Bing-heng. Microstructure and mechanical properties of Ti6Al4V alloy prepared by selective laser melting combined with precision forging [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2017, 27(5): 1036-1042.
[17] KASPEROVICH G, HAUBRICH J, GUSSONE J, REQUENA G. Correlation between porosity and processing parameters in TiAl6V4 produced by selective laser melting [J]. Materials and Design, 2016, 105(9): 160-170.
[18] CAO Sheng, CHU Rui-kai, ZHOU Xi-gen, YANG Kun, JIA Qing-bo, LIM C V S, HUANG Ai-jun, WU Xin-hua. Role of martensite decomposition in tensile properties of selective laser melted Ti-6Al-4V [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2018, 744(5): 357-363.
[19] WALKER K F, LIIU Q, BRANDT M. Evaluation of fatigue crack propagation behaviour in Ti-6Al-4V manufactured by selective laser melting [J]. International Journal of Fatigue, 2017, 104(11): 302-308.
[20] WANG Zhi-yong, LI Pei-feng. Characterisation and constitutive model of tensile properties of selective laser melted Ti-6Al-4V struts for microlattice structures [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2018, 725(5): 350-358.
[21] GU Dong-dong, HAGEDORN Y, MEINERS W, MENG Guang-bin, BATISTA R J S, WISSENBACH K, POPRAWE R. Densification behavior, microstructure evolution, and wear performance of selective laser melting processed commercially pure titanium [J]. Acta Materialia, 2012, 60(9): 3849-3860.
[22] SUPROBO G, PARK N, BAEK E R. Effect of double stage solution treatment on the volume fraction of massive phase (αm) as a new method to obtain a fine lamellar α/β in Ti-6Al-4V alloy [J]. Intermetallics, 2019, 113(10): 106581.
[23] WANG Zhen, XIAO Zhi-yu, TSE Y, HUANG Chuan-shou, ZHANG Wei-wen. Optimization of processing parameters and establishing of a relationship between microstructure and mechanical properties of SLM titanium alloy [J]. Optics and Laser Technology, 2019, 112(4): 159-167.
[24] KHAN M A, WILLIAMS R L, WILLIAMS D F. The corrosion behaviour of Ti-6Al-4V, Ti-6Al-7Nb and Ti-13Nb-13Zr in protein solutions [J]. Biomaterials, 1999, 20(7): 631-637.
[25] BRUCHI S, BERTOLINI R, GHIOTTI A. Coupling machining and heat treatment to enhance the wear behaviour of an additive manufactured Ti6Al4V titanium alloy [J]. Tribology International, 2017, 116(12): 58-68.
[26] FAZEL M, SALIMIJAZI H R, GOLOZAR M A, GARSIVAZ JAZI M R. A comparison of corrosion, tribocorrosion and electrochemical impedance properties of pure Ti and Ti6Al4V alloy treated by micro-arc oxidation process [J]. Applied Surface Science, 2015, 324(1): 751-756.
[27] RAVINDRAN P, FAST L, KORZHAVYI P A, JOHANSSON B. Density functional theory for calculation of elastic properties of orthorhombic crystals: Application to TiSi2 [J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 1998, 84(9): 4891-4904.
[28] YILDIZ F, YETIM A F, ALSARAN A, EFEOGLU I. Wear and corrosion behaviour of various surface treated medical grade titanium alloy in bio-simulated environment [J]. Wear, 2009, 267(5): 695-701.
[29] CHELARIU R, TRINCA L C, MUNTEANU C, BOLAT G, SUTIMAN D, MARECI D. Corrosion behavior of new quaternary ZrNbTiAl alloys in simulated physiological solution using electrochemical techniques and surface analysis methods [J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2017, 248(9): 368-375.
[30] ZHANG Xin, ZHANG Kui, LI Xing-gang, DENG Xia, LI Hong-wei, ZHANG Bao-dong, WANG Chang-shun. Comparative study on corrosion behavior of as-cast and extruded Mg-5Y-7Gd-1Nd-0.5Zr alloy in 5% NaCl aqueous solution [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2012, 22(5): 1018-1027.
[31] YANG Y, KITASHIMA T, HARA T, HARA Y, IWASAKI S. Effect of temperature on oxidation behaviour of Ga-containing near-α Ti alloy [J]. Corrosion Science, 2018, 133(4): 61-67.
[32] TSUTSUMI Y, NISHIMURA D, DOI H, NOMURA N, HANAWA T. Difference in surface reactions between titanium and zirconium in Hank’s solution to elucidate mechanism of calcium phosphate formation on titanium using XPS and cathodic polarization [J]. Materials Science and Engineering C, 2009, 29(5): 1702-1708.
[33] METIKOS-HUKOVIC M, KWOKAL A, PILJAC J. The influence of niobium and vanadium on passivity of titanium-based implants in physiological solution [J]. Biomaterials, 2003, 24(21): 3765-3775.
[34] LONG M, BACK H J. Titanium alloys in total joint replacement—A materials science perspective [J]. Biomaterials, 1998, 19(18): 1621-1639.
[35] ZHOU Ying-long, NIINOMI M, AKAHORI T, FUKUI H, TODA H. Corrosion resistance and biocompatibility of Ti-Ta alloys for biomedical applications [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2005, 398(1-2): 28-36.
[36] FOJTO J, JOSKA L, MALEK J. Corrosion behaviour of porous Ti-39Nb alloy for biomedical applications [J]. Corrosion Science, 2013, 71(6): 78-83.
[37] DAI N W, ZHANG Lai-chang, ZHANG Jun-xi, ZHANG Xin, NI Qing-zhao, CHEN Yang, WU Mao-liang, YANG Chao. Distinction in corrosion resistance of selective laser melted Ti-6Al-4V alloy on different planes [J]. Corrosion Science, 2016, 111(10): 703-710.
[38] LIU L, XU G, WANG A, WU X, WANG R. First-principles investigations on structure stability, elastic properties, anisotropy and Debye temperature of tetragonal LiFeAs and NaFeAs under pressure [J]. Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids, 2017, 104(5): 243-251.
[39] BALOYI N M, POPOOLA A P I, PITYANA S L. Microstructure, hardness and corrosion properties of laser processed Ti6Al4V-based composites [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2015, 25(9): 2912-2923.
[40] DAI Nian-wei, ZHANG Lai-chang, ZHANG Jun-xi, CHEN Qi-meng, WU Mao-liang. Corrosion behavior of selective laser melted Ti-6Al-4V alloy in NaCl solution [J]. Corrosion Science, 2016, 102(1): 484-489.
[41] CVIJOVIC-ALAHIC J, CVIJOVIC Z, MITROVIC S, PANIC V, RAKIN M. Wear and corrosion behaviour of Ti-13Nb-13Zr and Ti-6Al-4V alloys in simulated physiological solution [J]. Corrosion Science, 2011, 53(2): 796-808.
[42] WANG R G, KANEKO J. Hydrophobicity and corrosion resistance of steels coated with PFDS film [J]. Surface Engineering, 2013, 29(4): 255-263.
[43] LIU Yan, YIN Xiao-ming, ZHANG Ji-jia, YU Si-rong, HAN Zhi-wu, REN Lu-quan. A electro-deposition process for fabrication of biomimetic super-hydrophobic surface and its corrosion resistance on magnesium alloy [J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2014, 125(10): 395-403.
鞠 江1,2,李京京1,2,蒋 敏1,李梦娅3,杨力祥1,王开明4,杨 超1,2,康茂东1,2,王 俊1,2
1. 上海交通大学 材料科学与工程学院,凝固科学与技术研究所,上海 200240;
2. 上海交通大学 上海市先进高温材料及其精密成型重点实验室,上海 200240;
3. 北京理工大学 宇航学院,北京 100081;
4. 清华大学 机械工程系 摩擦学国家重点实验室,北京 100084
摘 要:为了进一步提高植入体的耐腐蚀性,通过激光选区熔化制备Ti-6Al-4V合金。借助扫描电镜、电子背散射、透射电镜、电化学腐蚀试验和接触角试验对其显微组织和在人工模拟唾液中的电化学腐蚀行为进行研究。结果表明:激光选区熔化制备Ti-6Al-4V合金在堆积方向呈现典型的β柱状晶,在扫描方向呈近圆形棋盘状组织,而锻造和锻造+热处理样品呈现典型的等轴晶形貌。在37 °C模拟人工唾液中激光选区熔化制备Ti-6Al-4V合金比锻造和锻造+热处理样品具有更好的耐腐蚀性能,这是由于其具有疏水性、更高的晶界密度和分布均匀的合金元素。
关键词:Ti-6Al-4V合金;激光选区熔化;显微组织;电化学腐蚀行为
(Edited by Bing YANG)
Corresponding author: Jun WANG, Tel/Fax: +86-21-54742683, E-mail: junwang@sjtu.edu.cn;
Mao-dong KANG, Tel/Fax: +86-21-54742683, E-mail: kangmd518@sjtu.edu.cn
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(20)65485-1
1003-6326/ 2021 The Nonferrous Metals Society of China. Published by Elsevier B.V. & Science Press
2021 The Nonferrous Metals Society of China. Published by Elsevier B.V. & Science Press

