超声辅助钎焊Al/Sn接头界面组织演变和力学性能
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2017年第4期
论文作者:郭卫兵 栾天旻 冷雪松 何景山 闫久春
文章页码:962 - 970
关键词:铝合金;锡;超声钎焊;界面组织;力学性能
Key words:aluminum alloy; tin; ultrasonic soldering; interfacial microstructure; mechanical properties
摘 要:低温下钎焊铝合金能够避免母材受热发生软化。研究了使用纯Sn超声钎焊纯Al时,初晶α(Al)对Al/Sn界面显微组织和结合强度的影响。结果表明,在液态Sn中,α(Al)的{111}面的表面能和生长速度最小,因此,析出的初晶α(Al)的形态为{111}面包围的正八面体。超声能够起到提高形核率并细化初晶α(Al)颗粒的作用。在较长的超声和保温时间下,Al/Sn界面会析出大量八面体初晶α(Al)颗粒,使界面呈现出一种起伏不平的形貌,增加了界面实际结合面积和咬合作用。超声作用40 s,保温10 min时界面的结合强度达到63 MPa。
Abstract: Soldering aluminum alloys at low temperature have great potential to avoid softening of base metals. Pure Al was soldered with pure tin assisted by ultrasound. The influence of primary α(Al) on the microstructure of Al/Sn interface and its bonding strength was studied. It is found that the primary α(Al) in liquid tin tends to be octahedron enclosed by Al {111} facet with the lowest surface free energy and growth rate. The ultrasonic action could increase the nucleation rate and refine the particles of primary α(Al). For the longer ultrasonic and holding time, a large amount of the octahedral primary α(Al) particles crystallize at the Al/Sn interface. The bonding interface exhibits the profile of rough dentation, resulting in an increment of bonding interface area and the effect of mechanical occlusion. The bonding strength at interface could reach 63 MPa with ultrasonic time of 40 s and holding time of 10 min.
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 27(2017) 962-970
Wei-bing GUO, Tian-min LUAN, Xue-song LENG, Jing-shan HE, Jiu-chun YAN
State Key Laboratory of Advanced Welding and Joining, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin 150001, China
Received 29 February 2016; accepted 6 May 2016
Abstract: Soldering aluminum alloys at low temperature have great potential to avoid softening of base metals. Pure Al was soldered with pure tin assisted by ultrasound. The influence of primary α(Al) on the microstructure of Al/Sn interface and its bonding strength was studied. It is found that the primary α(Al) in liquid tin tends to be octahedron enclosed by Al {111} facet with the lowest surface free energy and growth rate. The ultrasonic action could increase the nucleation rate and refine the particles of primary α(Al). For the longer ultrasonic and holding time, a large amount of the octahedral primary α(Al) particles crystallize at the Al/Sn interface. The bonding interface exhibits the profile of rough dentation, resulting in an increment of bonding interface area and the effect of mechanical occlusion. The bonding strength at interface could reach 63 MPa with ultrasonic time of 40 s and holding time of 10 min.
Key words: aluminum alloy; tin; ultrasonic soldering; interfacial microstructure; mechanical properties
1 Introduction
Aluminum alloys gain popularity in aerospace and aircraft for their excellent mechanical properties [1,2]. However, high-strength aluminum alloys are extremely sensitive to heat. If they are joined together, softening of the base metals will occur. Zhang and Liu [3] reported coarsening or dissolution of the strengthening precipitates for heated strengthened aluminum alloys in the process of friction stir welding. Longtin et al [4] reported recovery, recrystallization and grain growth for deformation strengthened and ultra-fine grained aluminum alloys when using fusion welding, furnace brazing, and high-temperature soldering. Kim et al [5] found crystallization for the Al-based amorphous alloys at only 190-227 °C. Therefore, soldering aluminum alloys at low temperature is always required for applications in the industries. Sn-based solder with relatively low melting point has great potential for joining aluminum alloys. Faridi et al [6] soldered 2024 Al with Sn-30Pb at temperature of 230 °C. Ding et al [7] applied furnace soldering to join 6061 Al, and the base metal was ultrasonic coated Sn-Pb-Zn alloy before soldering. Nagaoka et al [8] used Sn-Zn hypereutectic solder to join deformation strengthened 1070 Al at 220 °C, and the tensile strength of joint could reach about 150 MPa. Some active Sn-based alloys with Ti element were also used to join aluminum alloys. Gorjan et al [9] soldered A356 aluminum alloys and Al2O3 ceramic with active solder alloy Sn3Ag3Ti assisted by ultrasonic. The interface of Al/solder was strong and joint failed at ceramic/solder interface or through filler metal layer. Wang and TSAI [10] joined anodized 6061 Al with active Sn3.5Ag(0-6%)Ti solder, and the maximum bonding strength reached 22.24 MPa.
For heat sensitive aluminum alloys, using Sn-based solders can avoid deterioration of mechanical properties of base metals at very low soldering temperature. However, Al and Sn have very weak interaction. The solubility of Al in liquid Sn is only ~1% at 300 °C and will decrease significantly during the process of cooling according to the Al-Sn phase diagram [11]. Al could be hardly dissolved in Sn, which would crystallize from liquid Sn as a phase of primary α(Al) during cooling process. Aluminum has a typically FCC crystal structure, and the lattice parameter a is 0.40495 nm. When primary α(Al) crystallizes from liquid alloys, its anisotropy is not obvious because of the mutual dissolution to other elements. For instance, LIU et al [12] found that the primary α(Al) in hypereutectic Zn-Al alloys has the morphology of quasi-spherical. However, Li et al [13] found that primary α(Al) in Sn is faceted dendrite, which can strengthen the filler metal layer, and explain it as migration of the base metal.
In the present work, pure 1060 Al was chosen as the base metal because it can provide results to which other Al alloys could refer. The morphological evolution and growth mechanism of primary α(Al) in liquid tin were studied from the view of 2D and 3D morphological observation and basic crystal growth theories. 1060 Al was ultrasonically soldered using pure Sn with different ultrasonic and holding time, and the relation between process parameters and interface microstructure, mechanical properties of joints was investigated and discussed.
2 Experimental
The aluminum substrate used in this study is 1060 Al supplied by Dongbei Light Alloys Co. Ltd., the namely chemical composition is shown in Table 1. Tensile strength of base metal is 84.8 MPa, and has no obvious change after soldering thermal cycle. The commercial pure tin (99.9%) was used as a filler metal.
Table 1 Chemical composition of 1060 Al (mass fraction, %)
For the study of morphology evolution and growth mechanism of primary α(Al) in liquid tin, 98 g pure tin was put into an alumina crucible, and the crucible was heated to 300 °C in muffle furnace. Then, 2 g pure Al was added into melted tin with mechanical stirring. The alloys were cooled to room temperature in air.
The schematic of the soldering process was reported in our previous paper [14]. Thickness of base metal is 9 mm, surfaces of substrate and filler metal were mechanically polished with SiC papers, and then ultrasonically cleaned in acetone for 10 min. The soldering temperature was 300 °C, and ultrasonic vibration was applied on the base metal to remove oxide film of substrate and filler metal. The frequency and amplitude of the ultrasonic vibration were 20 kHz and 6.5 μm, respectively. After ultrasonic vibration (UV), a holding time (HT) was kept. Then, samples were removed from the platform and cooled in air. The parameters of soldering processes were donated as “ultrasonic action time + holding time” (UV + HT).
The cross section of the joint was prepared with standard polishing process. Scanning electron microscopy (FEI-Quanta 200F, FEI Helios Nanolab600i) equipped with energy dispersive X-ray spectrometer (EDS) was employed to study the microstructure of primary α(Al) in tin, microstructure of joint, fracture location and morphology of fracture surface, and the SEM/EDS analysis were conducted in standard way. Tensile tests were conducted on a tension testing machine (Instron-5569) to evaluate the mechanical properties of the joints. Three samples for tensile test were cut from the original joints with length of 40 mm and cross-sectional area of 2 mm × 9 mm. The speed of tensile test was 0.5 mm/min.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Microstructure of Sn-2Al alloy
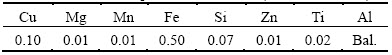
Figure 1 shows the microstructure of the Sn-2Al alloy prepared at 300 °C, it is composed of primary α(Al), β-Sn and Sn-Al eutectic, and primary α(Al) phase is surrounded by β-Sn and Sn-Al eutectic. According to Al-Sn phase diagram, the solubility of Al in pure Sn is about 1% at 300 °C, and would decrease dramatically as temperature drops. Al hardly dissolves Sn at any temperature; Sn-Al eutectic contains 99.4% Sn and 0.6% Al and the eutectic temperature is 228 °C. At the preparing temperature of 300 °C, liquid tin dissolved 1% Al firstly, and became saturated. The primary α(Al) could crystallize at the holding time through the fluctuation in composition and energy, making the liquid alloy sub-saturated. Thus, the rest Al could dissolve into the liquid alloy continuously. In the process of cooling, some primary α(Al) also crystallized because of the decreasing of solubility, and then β-Sn crystallized from liquid alloy, the Al-Sn eutectic phase formed at 228 °C. Table 2 shows the EDS results of all phases in Fig. 1, primary α(Al) contains 98.6% Al and 1.4% Sn. Considering the solubility of Sn in Al and the error of EDS results(error ±1%), the chemical composition of primary α(Al) in Sn-2Al alloy is extremely close to pure Al. β-Sn contains 99.1% Sn and 0.9% Al and Sn-Al eutectic contains 98.8% Sn and 1.2% Al. What’s more, the primary α(Al) phase has morphology of regular facet, which indicates its strong anisotropy in tin.

Fig. 1 Microstructure of Sn-2Al alloy
Table 2 Chemical composition of phases in Fig. 1
3.2 Morphology evolution of primary α(Al) in Sn
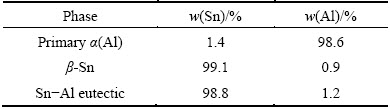
Generally speaking, the primary α(Al) does not show strong anisotropy, and always has a non-faceted interface in contact with liquid alloys. Nevertheless, the morphologies of α(Al) in Sn are similar to those of some intermetallic compounds with strong anisotropy and FCC structure. Song et al [15] found that TiC grain had strong faceting tendency and grew as an octahedral morphology. The primary Mg2Si in Al-Mg2Si alloys also tended to form faceted octahedron in the study of Li et al [16]. So, it is seems that the solidification of α(Al) in Sn is abnormal behavior, as a matter of fact, it also follows the basic theories for crystal growth. Bruno et al [17] reported that crystals would like to exhibit an equilibrium shape with minimum total free energy, and Hamilton et al [18] found that they always crystallize with facets to reduce energy. The primary α(Al) is surrounded by liquid tin during crystallizing, the very weak interaction of Al and Sn makes Al {111} face still having the lowest surface free energy, so the equilibrium shape of α(Al) would be that with {111} face exposed as surfaces.

Fig. 2 Typical 2D morphologies at different growth stages of primary α(Al)
Figure 2 shows the typical 2D morphologies at the different growth stages of primary α(Al). After the liquid Sn is saturated with the dissolved Al, the primary α(Al) will crystallize. Due to the fluctuation in composition and energy, the α(Al) forms spherical crystal nucleus (Fig. 2(a)). When the spherical nucleus grows to a larger size, it will show obvious anisotropy and turn to octahedron after equilibrium of dissolution and crystallization. Anisotropy crystal has preferential growth direction, the small octahedron shows faster growth rate along [011] and [001] directions, gradually forming six axes (Figs. 2(b) and (c)), moreover, with new octahedrons at the end of them (Fig. 2(d)). The new octahedrons continue to grow along their new [011] and [001] directions faster, and adjacent branches would join with each other, forming a new bigger octahedron with symmetric hollows in the center (Fig. 2(e)), the hollows may get smaller or disappear with the growth proceeding, finally, the primary α(Al) could develop to enormous dendrite, as shown in Fig. 2(f).
3.3 Growth mechanism of primary α(Al) in Sn
Li et al [16] reported that the final morphology of a crystal is determined by its own structure (thermodynamics factors) and the crystal growth conditions (kinetic factors). Thermodynamics factors decide the most stable equilibrium shape of crystal, whereas kinetic factors influence the morphology evolution and final shape.
Crystal would like to expose its faces with lower surface energy. Liu et al [19] reported that the closed-packed faces have lower surface energy. Since Al and Sn have very limited mutual solubility, the front interface of crystallization is close to solid pure Al/ liquid pure Sn, different faces of aluminum have unequal surface energy, and therefore, Al shows strong anisotropy in the environment of liquid tin. Smith and Banerjea [20] found that the surface energy ranking of aluminum crystal faces runs as γ{110}>γ{100}> γ{111}. Nie et al [21] reported the Gibbs-Wullf theorem, which illustrated that there exists a definitive positive correlation between the growth rate of a facet and its specific surface energy. That is, the crystallographic face with lower surface energy has lower growth rate. During growth process of crystallization, crystallographic planes with higher specific surface energy will grow faster and disappear gradually. For aluminum, growth rate of different faces runs as {110}>{100}>{111}. Moreover, as close-packed face, {111} plane has the maximum interplanar spacing, and Al atoms would be harder to be adsorbed on the {111} faces compared with {011} and {001} faces. Thus, {011} and {001} faces will shrink gradually with higher growth rate, forming the edges and vertices of octahedron. {111} faces will be reserved as the final surface. Therefore, the primary α(Al) in the equilibrium state exhibits an octahedron crystal enclosed by {111} facets.
Based on the morphologies evolution observed and the basic crystal growth theories, the growth patterns of octahedral primary α(Al) in liquid tin are shown in Figs. 3(a)-(f). At the initial stage, Al has isotropic growth rate in every direction, forming spherical nucleus. However, the spherical nucleus does not have the lowest surface energy, and is in a state of metastable. It could be dissolved into liquid tin again, or continue to grow. When the nucleus exceeds a critical size, the spherical nucleus would lose its stability, and show different growth rates along different directions. It will turn to small octahedron after equilibrium of dissolution and crystallization. With the further growth, the octahedron grows rapidly along [011] and [001] directions, forming six branches with new octahedrons at the end of them. Subsequently, adjacent branches grow together to form a hollow octahedron. These holes may get smaller or disappear later, forming a perfect octahedron with eight {111} faces. This completes the growth period of octahedron, and the final octahedron may experience several such periods.
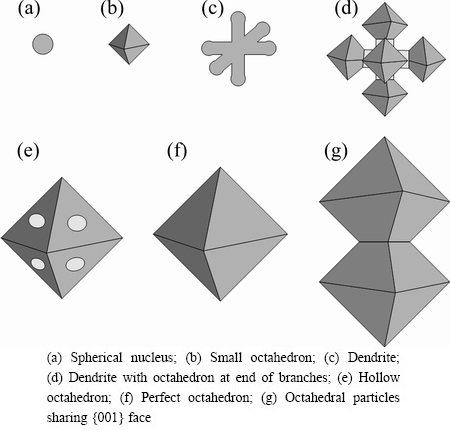
Fig. 3 Schematic of growth pattern of octahedral primary α(Al)
Moreover, the primary α(Al) particles always share their {001} faces with others (Fig. 3(g)). Forming morphology like this can reduce overall surface energy further by removing part of {111} face.
The primary α(Al) prefers to nucleate at the Al substrate when Al was soldered with tin. Figure 4 shows the morphology of fracture surfaces at Al/Sn interface during tensile test. The primary α(Al) with 3D dimension could be observed on the fracture surface in Fig. 4(a). The primary α(Al) exhibits various morphologies: perfect or imperfect octahedron, and dendrite. All of them tend to be enclosed by {111} facet. Figure 4(b) shows the local magnification of area A in Fig. 4(a), which shows a near-perfect octahedron with eight {111} facets. From different cutting angles, various 2D morphologies in polish section are observed, such as perfect or imperfect triangle, quadrangle, diamond, hexagon, small and enormous dendrite. What’s more, some {111} faces with a round hole can be found on the fracture surface in Fig. 4(c).
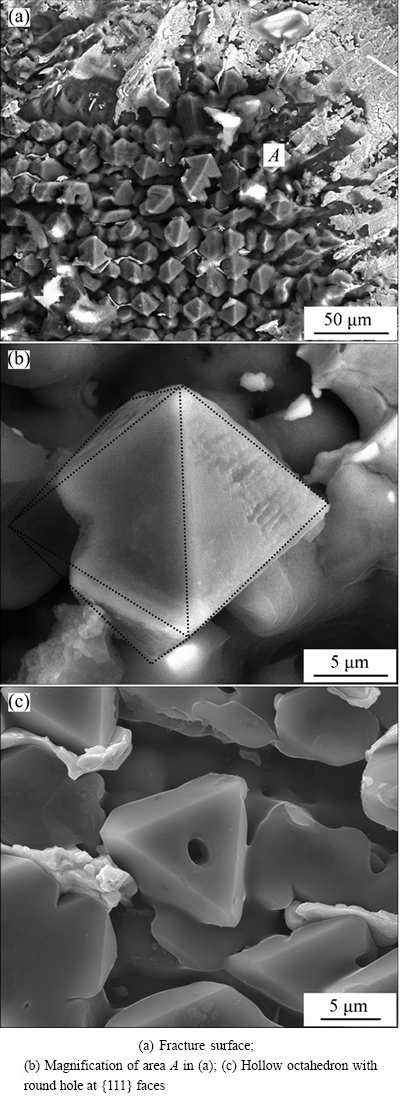
Fig. 4 SEM images of fracture surfaces
3.4 Relationship between soldering parameter and interfacial microstructure
It is found that the primary α(Al) in liquid Sn exhibits various morphologies during soldering. The microstructure of primary α(Al) at Al/Sn interface could be varied by changing ultrasonic and holding time. Figure 5 shows Al/Sn interfacial structures obtained with different ultrasonic and holding time. The interface shown in Fig. 5(a) was obtained with ultrasonic action for 5 s, the interface is straight due to the uniform dissolution of Al in Sn. Moreover, some semi-spherical α(Al) particles grow at the interface (Fig. 5(b)). Then, the duration of ultrasonic action and holding was extended to 10 s + 10 min, and the microstructure of the interface is shown in Fig. 5(c). With the increase of holding time, numerous primary α(Al) particles nucleate and grow at interface. They show different growth rates along different crystallographic directions, and finally turn to octahedron, exposing {111} face. Figure 5(d) shows the interface obtained with the ultrasonic action and holding duration of 40 s + 10 min. A lot of α(Al) particles also crystallize at interface, and they are finer with longer ultrasonic action time. Abramov et al [22] found that the growing crystals can be broken down by hydraulic shock waves resulting from the ultrasonic cavitation effect, and homogeneously distribute as fine solid particles. That is to say, ultrasound can increase the nucleation rate. The duration of ultrasonic action increases, the octahedral primary α(Al) has increment in quantity, and decrease in size. The variation of element distribution is not obvious with changing the ultrasonic and holding time (Figs. 5(e) and (f)).
Figure 6 shows the relationship between the tensile strength of joints and the duration of ultrasonic action and holding. The weakest joint was prepared with 5 s. The tensile strength is as low as 30 MPa. With increasing ultrasonic action and holding time, tensile strength of joints is raised. The tensile strengths of joints prepared with 10 s + 10 min and 20 s + 10 min are 39 and 50 MPa, respectively. What’s more, the strength is double for the joints with 40 s + 10 min, reaching 63 MPa.
Figures 7(a) and (b) show the fracture paths of joints with the duration of ultrasonic action and holding for 5 s and 40 s + 10 min. Fracture of all joints occurs at Al/Sn interface, which also indicates very weak interaction between Al and Sn. The interface obtained by 5 s is straight with few semi-spherical α(Al). The interface obtained by 40 s + 10 min exhibits profile of rough dentation. With a quite long time of dissolution and crystallization, a large amount of octahedral primary α(Al) particles crystallize at interface, resulting in augment of actual bonding area at interface. Besides, the octahedral crystal is larger in middle section, which will increase the effect of mechanical occlusion. Since parameters do not change the element distribution, and microstructures of all joints are similar, the raise of strength should be attributed to the increment of actual bonding area and occlusion effect.
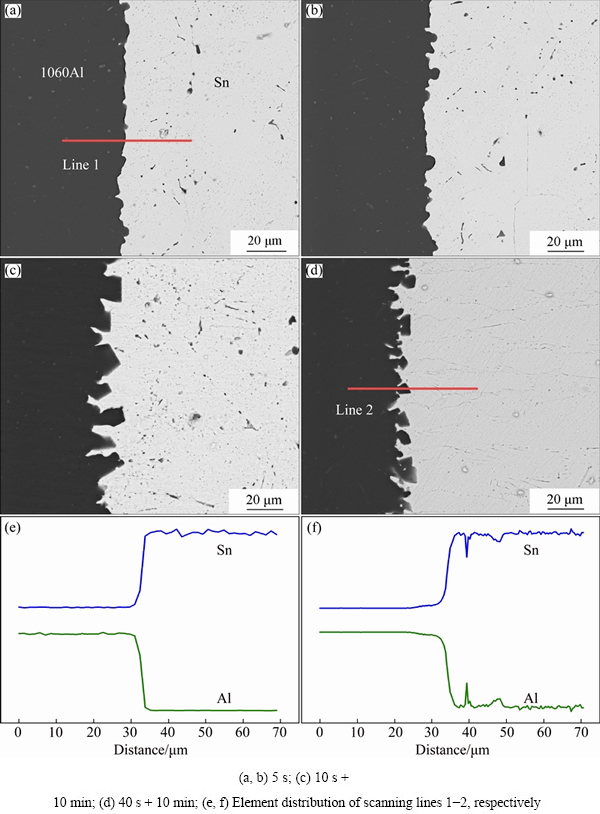
Fig. 5 SEM images of Al/Sn interfaces obtained with different process parameters and corresponding line scans
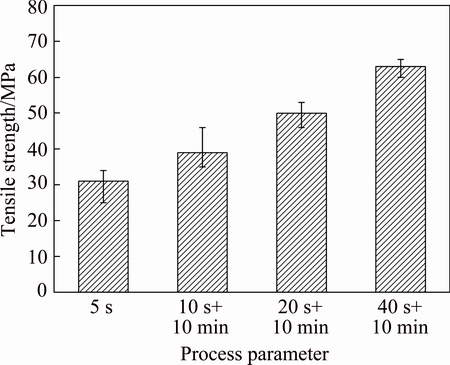
Fig. 6 Tensile strength of joints with different process parameters
Figure 8 shows the fracture surfaces of joints with process of 5 s. Ultrasonic time of 5 s is sufficient to remove the oxide film of Al base metal. Al dissolved in the tin could not crystallize without holding time. There are only several semi-spherical α(Al) particles at the interface. Fracture occurs at Al/Sn interface and the fracture surface is relatively flat.
Figures 9 and 10 show the fracture surfaces of joint with process of 40 s + 10 min, there are a large amount of primary α(Al) particles with equilibrium shape at Al/Sn interfaces. And there are two typical morphologies of α(Al) particles observed from the fracture surface (donated as the morphology of type I and II). Primary α(Al) with the morphology I is shown in Fig. 9(a), and its corresponding outlines on fracture surface of Sn side are shown in Fig. 9(b). This kind of primary α(Al) connects its {001} face to the base metal to reduce its total surface energy further. Primary α(Al) with morphology II is shown in Fig. 10(a), and its corresponding outlines on fracture surface of Sn side are shown in Fig. 10(b). This kind of primary α(Al) shares its {001} face to others.
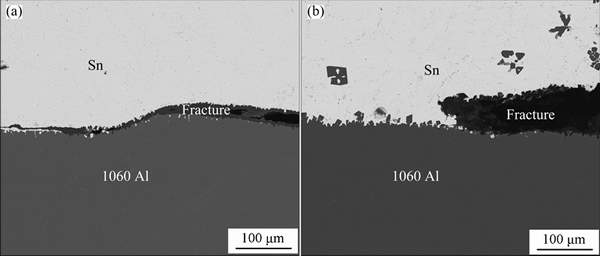
Fig. 7 SEM images showing fracture paths of joints with 5 s (a) and 40 s + 10 min (b)

Fig. 8 SEM images showing fracture surfaces of joints with 5 s
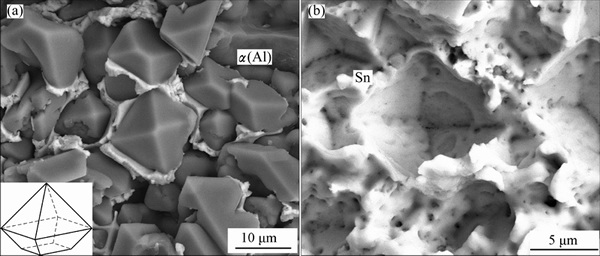
Fig. 9 SEM images of fracture surfaces showing primary α(Al) with morphology of type I on Al side (a) and Sn side (b)
The element distribution at interface does not change with changing of the ultrasonic and holding time, which means that the difference of strength cannot be explained from the reason of metallurgy. The crystal structures of primary α(Al) particles have close relationship with the mechanical behavior. The contribution of equilibrium α(Al) particles to the actual interface area is analyzed as follows: supposing that the shear strength is half of tensile strength, and neglecting the shear factor of inclined plane, the morphology I increases actual interface area by 140%, and the morphology II increases actual interface area by 85%, respectively by rough estimation. About 450 clearly visible α(Al) particles were counted from fracture surface. Particles with morphology I take about 5%, and particles with morphology II take about 95%, respectively. The actual interface area increases by about 140%×5%+85%×95%≈88%. That is, for the joint with 40 s + 10 min, the actual interface area is almost twice of namely area of joint.
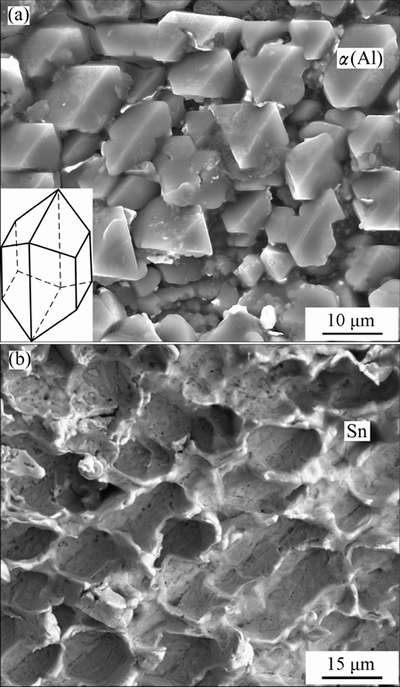
Fig. 10 SEM images of fracture surfaces showing primary α(Al) with morphology of type II on Al side (a) and Sn side (b)
The engineering stress is defined as
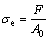 (1)
(1)
where σe is the engineering stress, F is the maximum force and A0 is the original area of joints.
A0 is the same to joints with different interface structures. Aa is donated as actual area of micro interface. For the joints with 5 s, Aa≈A0. For the joints with 40 s + 10 min, Aa≈2A0. Besides, the octahedron is larger in middle section, which will increase the effect of mechanical occlusion during tensile test. Thus, it can be concluded that the native tensile strength obtained at 300 °C is about 30 MPa, and the increment of actual interface area and effect of occlusion would improve the engineering stress. The bonding strength at interface could reach 63 MPa with ultrasonic time of 40 s and holding time of 10 min.
4 Conclusions
1) Morphology evolution and growth mechanism of primary α(Al) in liquid tin are similar to those of some intermetallic compounds with strong anisotropy and FCC structure. For the weak interaction between Al and Sn, the primary α(Al) would like to expose its {111} facet to minimize the total surface free energy in liquid tin. So, the equilibrium shape of primary α(Al) exhibits an octahedron enclosed by {111} facet.
2) The microstructure of primary α(Al) at Al/Sn interface could be varied by changing ultrasonic and holding time during soldering. The primary α(Al) with a structure of octahedron with {111} facets is formed after long holding time, and the ultrasonic action could increase the nucleation rate and refine the particles of primary α(Al). A large amount of octahedral primary α(Al) particles with {111} facet crystallize at the Al/Sn interface after long ultrasonic action and holding time.
3) The octahedral primary α(Al) at interface could increase the actual interface bonding area and effect of mechanical occlusion, and the tensile strength was raised from 30 to 63 MPa with parameters of 40 s + 10 min.
References
[1] CHEN Gang, ZHANG Yu-min, DU Zhi-ming. Mechanical behavior of Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy under tension in semi-solid state [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2016, 26(3): 643-648.
[2] Gholami S, Emadoddin E, Tajally M, BORHANI E. Friction stir processing of 7075 Al alloy and subsequent aging treatment [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2015, 25(9): 2847-2855.
[3] Zhang H, Liu H. Mathematical model and optimization for underwater friction stir welding of a heat-treatable aluminum alloy [J]. Materials & Design, 2013, 45(6): 206-211.
[4] Longtin R, Hack E, Neuenschwander J, Janczak- Rusch j. Benign joining of ultrafine grained aerospace aluminum alloys using nanotechnology [J]. Advanced Materials, 2011, 23(48): 5812-5816.
[5] Kim J H, Park J S, Jeong H T, KIM W T, KIM D H. Fabrication of Misch metal-Al-Ni-Cu-C bulk metallic glass matrix composite by gravitational casting in air atmosphere [J]. Materials Science & Engineering A, 2004, 386: 186-193.
[6] FARIDI H R, DEVLETIAN J H, HUE P L. A new look at flux-free ultrasonic soldering [J]. Welding Journal, 2000, 79(9): 41-45.
[7] Ding M, Zhang P L, Zhang Z Y, YAO S. Direct-soldering 6061 aluminum alloys with ultrasonic coating [J]. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 2010, 17(2): 292-297.
[8] Nagaoka T, Morisada Y, Fukusumi M, Takemoto T. Joint strength of aluminum ultrasonic soldered under liquidus temperature of Sn-Zn hypereutectic solder [J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2009, 209(11): 5054-5059.
[9] Gorjan L, Blugan G, Boretius M, Pierre S D L, Ferraris M, Casalegno V, Rizzo S, Graule T, Kuebler J. Fracture behavior of soldered Al2O3 ceramic to A356 aluminum alloy and resistance of the joint to low temperatures exposure [J]. Materials & Design, 2015, 88: 889-896.
[10] Wang W L, Tsai Y C. Microstructural characterization and mechanical property of active soldering anodized 6061 Al alloy using Sn-3.5Ag-xTi active solders [J]. Materials Characterization, 2012, 68(6): 42-48.
[11] Zhang H, Cui W, He J, YAN J YANG S. Formation and evolution of intermetallic compounds at interfaces of Cu/Al joints by ultrasonic-assisted soldering [J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2015, 223: 1-7.
[12] LIU Yang, LI Hong-ying, JIANG Hao-fan, LU Xiao-chao. Effects of heat treatment on microstructure and mechanical properties of ZA27 alloy [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2013, 23(3): 642-649.
[13] Li Y, Leng X, Cheng S, YAN J. Microstructure design and dissolution behavior between 2024 Al/Sn with the ultrasonic- associated soldering [J]. Materials & Design, 2012, 40: 427-432.
[14] Guo W B, Leng X S, Yan J C, TAN Y M. Ultrasonic soldering aluminum at low temperature [J]. Welding Journal, 2015, 94(6), 189-195.
[15] Song M S, Huang B, Huo Y Q, ZHANG S G, ZHANG M X, HU Q D, LI J G. Growth of TiC octahedron obtained by self- propagating reaction [J]. Journal of Crystal Growth, 2009, 311(2): 378-382.
[16] Li C, Wu Y Y, Li H, LIU X F. Morphological evolution and growth mechanism of primary Mg2Si phase in Al-Mg2Si alloys [J]. Acta Materialia, 2011, 59(3): 1058-1067.
[17] Bruno M, Massaro F R, Pastero L, Costa E, Rubbo M, Prencipe M, Aquilano D. New estimates of the free energy of calcite/water interfaces for evaluating the equilibrium shape and nucleation mechanisms [J]. Crystal Growth & Design, 2013, 13(3): 1170-1179.
[18] Hamilton J C, Siegel D J, Istvan D, Francois L. Why do grain boundaries exhibit finite facet lengths? [J]. Physical Review Letters, 2003, 90(24): 246102-1-4.
[19] Liu G, Chen K, Zhou H, TIAN J, PEREIRA C, FERREIRA J. Fast shape evolution of TiN microcrystals in combustion synthesis [J]. Crystal growth & design, 2006, 6(10): 2404-2411.
[20] Smith J R, Banerjea A. New approach to calculation of total energies of solids with defects: Surface-energy anisotropies [J]. Physical Review Letters, 1987, 59(21): 2451-2454.
[21] Nie J, Wu Y, Li P, LI H, LIU X F. Morphological evolution of TiC from octahedron to cube induced by elemental nickel [J]. Cryst Eng Comm, 2012, 14(6): 2213-2221.
[22] Abramov V, Abramov O, Bulgakov V, Sommer F. Solidification of aluminium alloys under ultrasonic irradiation using water-cooled resonator [J]. Materials Letters, 1998, 37(1): 27-34.
郭卫兵,栾天旻,冷雪松,何景山,闫久春
哈尔滨工业大学 先进焊接与连接国家重点实验室,哈尔滨 150001
摘 要:低温下钎焊铝合金能够避免母材受热发生软化。研究了使用纯Sn超声钎焊纯Al时,初晶α(Al)对Al/Sn界面显微组织和结合强度的影响。结果表明,在液态Sn中,α(Al)的{111}面的表面能和生长速度最小,因此,析出的初晶α(Al)的形态为{111}面包围的正八面体。超声能够起到提高形核率并细化初晶α(Al)颗粒的作用。在较长的超声和保温时间下,Al/Sn界面会析出大量八面体初晶α(Al)颗粒,使界面呈现出一种起伏不平的形貌,增加了界面实际结合面积和咬合作用。超声作用40 s,保温10 min时界面的结合强度达到63 MPa。
关键词:铝合金;锡;超声钎焊;界面组织;力学性能
(Edited by Xiang-qun LI)
Foundation item: Project (51435004) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China
Corresponding author: Jiu-chun YAN; Tel: +86-451-86418695; E-mail: jcyan@hit.edu.cn
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(17)60112-2

