文章编号: 1004-0609(2005)04-0631
微量锑和锡对铝基牺牲阳极材料性能的影响
朱承飞, 徐 峰, 魏无际, 丁 毅, 王 宁
(南京工业大学 材料科学与工程学院, 南京 210009)
摘 要: 熔炼了添加合金元素Sb和Sn的5种Al-Zn-In系牺牲阳极材料, 采用恒电流方法测试了其电化学性能, 采用金相显微镜、 扫描电镜和能谱分析分别观察和分析了阳极材料的显微组织和组成。 结果表明: Sb具有细化晶粒的作用, 但晶界存在较多偏析相, 电流效率偏低; 与Sb相比较, Sn也具有细化晶粒的作用, 电流效率有所提高, 晶界偏析相较少, 但阳极的表面腐蚀溶解不均匀; Sn和Sb的协同作用在于能有效地抑制Si的偏析, 显著提高阳极的电流效率, 使得阳极表面具有良好的腐蚀溶解性。
关键词: 牺牲阳极; 铝合金; 锑; 锡
中图分类号: TG174.41
文献标识码: A
Effect of Sb and Sn on performance of
aluminum sacrificial anode materials
ZHU Cheng-fei, XU Feng, WEI Wu-ji, DING Yi, WANG Ning
(College of Materials Science and Engineering,Nanjing University of Technology, Nanjing 210009, China)
Abstract: Five kinds of Al-Zn-In system sacrificial anode materials with different contents of Sb and Sn were cast. The electrochemical performance was tested with constant current method and microstructures were observed and analyzed by metallography microscope, scanning electron microscope and energy spectrum analysis. The results show that Sb addition can diminish the crystal grain, but the content of segregative phase at crystal boundary increases, and the current efficiency of material is low. Compared with Sb addition, Sn addition can also diminish the crystal grain, the current efficiency increases, the content of segregative phase at crystal boundary reduces, but diffusional corrosion of the anode surface is not uniform. The cooperation of Sb and Sn can prevent Si from segregating effectively and enhance the current efficiency obviously. At the same time, anode materials have preferable surface dissolution characteristics.
Key words: sacrificial anode; aluminum alloy; Sb; Sn
在船舶、 海洋平台、 港口码头等海洋工程中, 钢结构的腐蚀情况是很严重的, 牺牲阳极保护是当前广泛采用的钢结构防腐措施之一。 在牺牲阳极材料中, 铝基阳极因其密度小、 电流效率高、 实际电容量大和对钢铁驱动电位适中等优点而得以迅速发展, 并被广泛使用[1, 2]。 但纯铝极易钝化, 在表面生成致密的Al2O3氧化膜, 氧化膜电位较正, 不易溶解, 因此纯铝不宜直接用作牺牲阳极材料。 合金化可阻止铝表面形成连续而致密的氧化膜, 增强其活性。 近40年来, 对铝合金牺牲阳极合金化的研究十分活跃, 相继开发出了许多铝阳极新材料[3-8], 取得了较大的成功。 但还有待进一步深入研究高效铝阳极材料的研制和特殊环境中的铝阳极[9]。 同时关于金属锑对一些金属合金性能的影响已有报道[10], 而有关元素锑以及元素锑和锡对铝阳极性能的影响报道甚少。 本文作者在对Al-Zn-In系阳极研究的基础上, 分别考察了单独添加锑和锡以及同时加入锑和锡对铝阳极性能的影响, 以期开发出高性能的铝合金牺牲阳极, 进一步扩大铝基牺牲阳极的应用范围。 同时初步探讨了铝阳极微观组织与性能的关系。
1 实验
1.1 铝阳极的熔炼
实验用合金元素均为高纯度的单质, 参照文献[11], 按其含量(如表1所示)称取一定质量的金属, 在760℃的电阻坩埚炉内先将铝锭加热熔化, 再加入锌锭熔化, 用C2Cl6除气并扒渣, 最后将用高纯度铝箔包紧的合金元素In、 Sn和Sb压入Al-Zn熔体中, 待完全熔化后, 轻轻搅匀并扒渣, 最后在表面涂有ZnO的铸铁模具中浇注成d16mm×80mm的圆棒, 自然冷却。
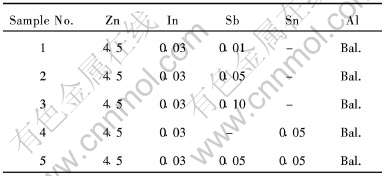
表1 铝基阳极材料的化学成分
Table 1 Chemical compositions of aluminum anode materials(mass fraction, %)
1.2 试样制备
根据国家标准GB4948-2002[12], 用于电流效率测定的圆柱试样尺寸为d16mm×48mm。 试样的一端加工出M3mm×5mm的螺纹孔并引出导线, 用无水乙醇去除油污后干燥称取质量, 阳极工作面积为14cm2, 其余部分用熔融的石蜡涂封以备用。
用于金相观察的圆柱体试样尺寸为d16mm×15mm, 从粗到细用金相砂纸打磨, 然后于抛光机上, 依次经“绒布+W1.0金刚石磨膏+蒸馏水”和“绒布+W0.5金刚石磨膏+蒸馏水”抛光至镜面, 用混合酸[8](1.2mL HF+12.5mL HCl+4.0mL HNO3+500mL H2O)腐刻约60s, 再用丙酮脱水、 吹干备用。
1.3 电化学性能测定
采用恒电流法[12]在室温(25℃)下测定铝阳极的电化学性能, 阴阳极面积比为60∶1。 阴极材料均采用1mm厚的A3钢板, 其规格及形状为d13.5cm×20cm, 工作面积为840cm2。 阳极工作电流密度为1mA/cm2, 实验时间为11d, 实验介质为人工海水, 其化学组成(g/L): NaCl 24.530, Na2SO4 4.090, MgCl2 5.200, CaCl2 1.160, SrCl2 0.025, KCl 0.695, NaHCO3 0.201, KBr 0.101, NaF 0.003, H3BO3 0.027。
实验后去除阳极试样表面的涂封物, 浸入现配的5%HNO3+1%K2Cr2O7(质量分数)混合液中约100min, 除净表面腐蚀产物, 再用蒸馏水清洗干净, 冷风吹干后观察阳极腐蚀后的表面形貌。
1.4 金相分析
金相组织观察采用国产XJZ-1A型金相显微镜, 观察晶粒大小和偏析相数量。 采用日产JSM5900型扫描电镜摄取SEM形貌(制样)照片, 并对偏析相成分采用NORAN VANTAGE能谱分析。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 牺牲阳极电化学性能
在人工海水介质中, 实验测得5种牺牲阳极的电化学性能(见表2), 并观察其表面形貌, 结果如图1所示。 添加不同含量Sb的试样1~3, 阳极电流效率值变化不大, 但阳极表面溶解状况较好, 且在实验过程中其表面不粘附腐蚀产物。 从图1可看出, 实验后的试样表面腐蚀较均匀, 仅有极少的阳极表面未被完全腐蚀。 与添加了合金元素Sb的阳极试样相比, 添加合金元素Sn的阳极试样4的电流效率有所提高, 这说明合金元素Sn的加入有助于电流效率的提高, 但阳极表面出现明显局部选择性溶解现象, 且其表面生成难以脱落的白色棉絮状腐蚀产物, 阻止了阳极的进一步活化溶解。 但试样4的腐蚀不均匀, 甚至有些表面有很大的面积仍未溶解, 还保持着实验前加工过的痕迹。 这可能是由于在溶解过程中, 白色絮状腐蚀产物覆盖在阳极表面, 阻止了阳极进一步溶解所致。 试样5则同时添加了合金元素Sb和Sn, 使电流效率显著提高, 在实验过程中不黏附腐蚀产物, 实验后发现其表面腐蚀较为均匀, 表面腐蚀坑也很均匀。 由此可见, Sb和Sn的同时加入, 使阳极材料具有较高的电流效率和均匀的表面腐蚀溶解的优点。
表2 铝阳极的电化学性能
Table 2 Electrochemical properties of aluminum anodes

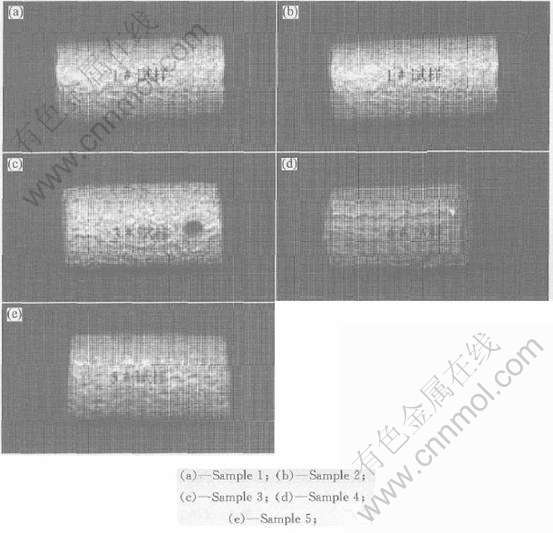
图1 铝阳极的形貌
Fig.1 Photographs of aluminum anodes for samples
2.2 金相分析
2.2.1 试样晶粒尺寸及第二相数量
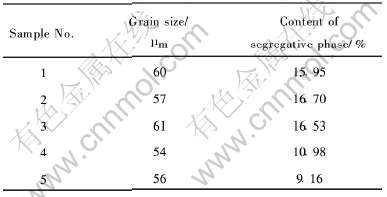
在金相显微镜下观察试样的晶粒大小及第二相含量, 结果如表3所列。 由表3可见, 1~ 5号试样的晶粒平均尺寸相差不大, 但第二相含量有所差别。 在文献[13]中, 添加稀土元素(RE)可使Al-Zn-In系牺牲阳极材料的平均晶粒尺寸细化至60μm, 可见Sb和Sn对铝基合金晶粒同样具有细化作用。 试样4、 5与试样1~ 3相比, 添加不同含量的Sb元素, 第二相含量变化不大; 而加入Sn元素时, 第二相含量明显减少。 这初步说明Sn 的加入抑制了第二相的偏析, 而Sb对第二相的析出抑制作用不明显。 结合所测得试样的电流效率数据(见表2)可认为, 在阳极晶粒尺寸相差不大的情况下, 阳极第二相含量越少, 电流效率就越高, 文献[6]对铝阳极组织与电流效率关系研究得出的结论与此相同。
表3 铝阳极晶粒尺寸和第二相含量
Table 3 Grain size and contentof segregative phase of samples
试样3和5阳极表面形貌的SEM像如图2所示。 由图2可看出, 大小不一的点大多为气孔和混合酸腐刻后留下的活性点小孔, 图中深色长条状是处于晶界的偏析相[13]。 对比图2(a)和(b)可发现, 试样3的第二相含量明显多于试样5的, 这与金相显微镜下观察到的结果相一致。
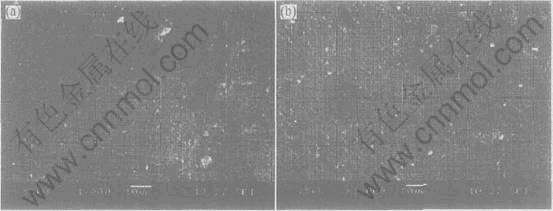
图2 铝阳极的SEM像
Fig.2 SEM images of aluminum anodes
2.2.2 牺牲阳极偏析相的成分分析
为了进一步分析偏析相, 对腐蚀前的阳极试样1、 4和5进行了SEM观察和偏析相成分能谱分析, 图3~5所示分别为阳极试样1、 4和5的SEM形貌和偏析相的能谱图。
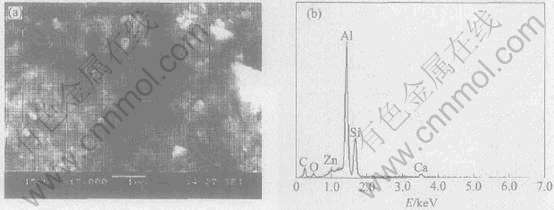
图3 试样1的SEM像和第二相的能谱图
Fig.3 SEM image of aluminum anode(a) and EDS spectra of segregative phase(b) for Sample 1
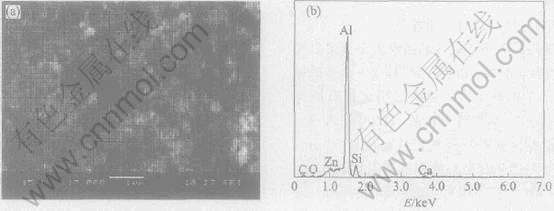
图4 试样4的SEM像和第二相的能谱图
Fig.4 SEM image of aluminum anode(a) and EDS spectra of segregative phase(b) for Sample 4
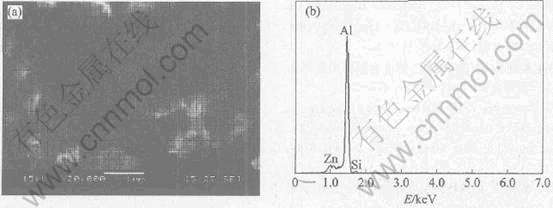
图5 试样5的SEM像和第二相的能谱图
Fig.5 SEM image of aluminum anode(a) and EDS spectra of segregative phase(b) for Sample 5
从能谱图可看出, 3种阳极的偏析相中均存在不同含量的杂质元素Si, 这与文献[14]的研究结论相同, 文献[14]称之为Si相。 从图3~5中可看出, 试样1析出物中的杂质元素Si含量最多, 其次是试样4, 最少的是试样5。 由此可见, 单独向阳极中添加Sn能抑制杂质元素Si在晶界的偏析, 而Sb对Si元素的析出抑制作用不明显。 但同时添加元素Sn和Sb时, 二者共同作用能更有效地阻止杂质元素Si的析出。 偏析相中的主要杂质为Si, 偏析相相对于铝基体的为阴极相。 在活化溶解初期, 基体正常溶解; 但随着基体的进一步溶解, 偏析相自行脱落, 从而使基体晶粒周围产生空隙, 有些晶粒还来不及放电就自行脱落, 造成电流效率的损失。 有研究者[15, 16]发现铝阳极在某些条件下出现“粉碎性”腐蚀的原因即在于此, 这同样也是阳极试样1~3的电流效率低于阳极试样4和5的原因。
3 结论
1) 单独添加合金元素Sb具有细化晶粒的作用, 试样表面腐蚀较为均匀, 但因其晶间存在较多偏析相, 致使电流效率偏低。 单独添加Sn元素不仅可以细化晶粒, 而且还可以减少晶间的偏析相, 使得电流效率有所提高。 但由于腐蚀产物粘附在阳极表面, 阻碍了阳极的溶解脱落, 导致材料表面的腐蚀溶解不均匀。
2) 同时添加合金元素Sn、 Sb时, 能有效地抑制Si元素在晶界的偏析, 使阳极材料既具有较高的电流效率, 又具有良好的表面溶解性, 实现了协同改进铝基牺牲阳极材料性能的目的。
REFERENCES
[1] 屈钧娥, 齐公台. 铝合金牺牲阳极材料研究现状[J]. 材料导报, 2001, 11(15): 24-26.
QU Jun-e, QI Gong-tai. Current status of research on aluminum alloy sacrificial anodes[J]. Materials Review, 2001, 11(15): 24-26.
[2] 齐公台, 郭稚弧, 林汉同. 腐蚀防护常用的几种牺牲阳极材料[J]. 材料开发与应用, 2001, 16(1): 36-40.
QI Gong-tai, GUO Zhi-hu, LIN Han-tong, et al. The sacrificial anode materials commonly used in corrosion protection[J]. Materials Exploiture and Application, 2001, 16(1): 36-40.
[3] Shibli S M A, Gireesh V S. Surface activation of aluminium alloy sacrificial anodes by IrO2[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2003, 219(3-4): 203-210.
[4] 刘学庆, 张经磊, 侯保荣. 海洋工程用铝基牺牲阳极发展概况[J]. 海洋科学, 2000, 24(8): 38-41.
LIU Xue-qing, ZHANG Jing-lei, HOU Bao-rong. Development of aluminum based sacrificial anode for marine project[J]. Marine Sciences, 2000, 24(8): 38-41.
[5] 孙鹤建, 火时中. 铟在铝基牺牲阳极溶解过程中的作用[J]. 中国腐蚀与防护学报, 1987, 7(2): 115-220.
SUN He-jian, HUO Shi-zhong. The role of indium in the dissolution of Al-Zn-In anodes[J]. Journal of Chinese Society for Corrosion & Protection, 1987, 7(2): 115-220.
[6] 唐和清. 铝合金牺牲阳极的研究与应用[J]. 化工腐蚀与防护, 1992, 18(1): 1-9.
TANG He-qing. Study and application of aluminum alloy sacrificial anode[J]. Corrosion and Protection on Chemical Engineering, 1992, 18(1): 1-9.
[7] Reboul M C, Delatte D C. Activation mechanism for sacrificial Al-Zn-Hg anodes[J]. Materials Perfomance, 1980, 9(5): 35-40.
[8] 孔小东, 朱梅五, 丁振斌, 等. 铝合金牺牲阳极研究进展[J]. 稀有金属, 2003, 27(3): 376-381.
KONG Xiao-dong, ZHU Mei-wu, DING Zhen-bin, et al. Progress in aluminium alloy sacrificial anode[J]. Chinese Journal of Rare Metals, 2003, 27(3): 376-381.
[9] 李 异, 李永广. 铝牺牲阳极在热海泥中的电化学性能 [J]. 材料开发与应用, 2001, 16(3): 19-22.
LI Yi, LI Yong-guang. Electrochemical performance of the Al anodes in sea bed mud at elevated temperature[J]. Materials Exploiture and Application, 2001, 16(3): 19-22.
[10] 杨 忠, 李高宏, 李建平, 等. 锑和稀土对Mg-9%Al-0.4%Zn合金铸态组织与力学性能的影响[J]. 铸造, 2002, 51(11): 690-694.
YANG Zhong, LI Gao-hong, LI Jian-ping, et al. Effect of antimony and rare earth on as-cast microstructure and mechanical properties of Mg-9%Al-0.4%Zn alloy[J]. Foundry, 2002, 51(11): 690-694.
[11] 靳兰芬, 朱有兰. Al-Zn-In-Sn牺牲阳极电化学性能研究[J]. 广东工学院学报, 1994, 11(增刊): 34-39.
JIN Lan-fen, ZHU You-lan. The studies of electrochemical characteristic and its survey technology of the Al-Zn-In-Sn sacrificial anode[J]. Journal of Guangdong Institute of Technology, 1994, 11(S): 34-39.
[12] GB4948-2002. 铝-锌-铟系合金牺牲阳极[S].
GB4948-2002. Sacrificial Anodes of Al-Zn-In System Alloy[S].
[13] 廖海星, 齐公台, 喻克雄, 等. 含稀土高温铝合金牺牲阳极的研究与应用 [J]. 石油化工腐蚀与防护, 2004, 21(4): 19-20.
LIAO Hai-xing, QI Gong-tai, YU Ke-xiong, et al. Research on sacrificing anode of high-temperature Al alloy containing rare earth and application[J]. Corrosion & Protection in Petrochemical Industry, 2004, 21(4): 19-20.
[14] 齐公台, 郭稚弧, 屈钧娥. 合金元素Mg对含RE铝阳极组织与性能的影响[J]. 中国腐蚀与防护学报, 2001, 21(4): 220-224.
QI Gong-tai, GUO Zhi-hu, QU Jun-e. Effect of magnesium on microstructure and perfomance of containing RE aluminum anode[J]. Journal of Chinese Society for Corrosion & Protection, 2001, 21(4): 220-224.
[15] 唐和清, 郑家燊, 魏伯康, 等. HT高温铝合金牺牲阳极的研究[J].华中理工大学学报, 1992,20(4):133.
TANG He-qing, ZHENG Jia-shen, WEI Bo-kang, et al. Research on HT aluminum alloy sacrificial anode[J].Journal of Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 1992, 20(4): 133-139.
[16] 廖海星, 齐公台, 喻克雄. 固溶处理对含RE铝牺牲阳极组织与性能的影响 [J]. 材料热处理学报, 2004, 25(3): 54-57.
LIAO Hai-xing, QI Gong-tai, YU Ke-xiong. Effect of water-quenching on microstructure and electrochemical performance of aluminum anode containing RE[J]. Transactions of Materials and Heat Treatment, 2004, 25(3): 54-57.
收稿日期: 2005-03-08;
修订日期: 2005-04-08
作者简介: 朱承飞(1977-), 男, 讲师, 博士研究生.
通讯作者: 朱承飞, 电话: 025-83587250; 传真: 025-83587251; E-mail: Zhucf@njut.edu.cn
(编辑 李艳红)