DOI:10.19476/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2017.10.02
钇含量对MgZn4.5YxZr0.5合金热裂敏感性的影响
冯 羽,毛萍莉,刘 正,王 志,张斯博,王 峰
(沈阳工业大学 材料科学与工程学院,沈阳 110870)
摘要:采用热分析法和铸造热裂试验研究MgZn4.5YxZr0.5(x=0.5,1,2,4,6(质量分数, %))合金的热裂行为。结果表明:MgZn4.5Y1Zr0.5合金的枝晶干涉温度Tcoh最高、在脆弱区域的温度差ΔTc最大、在最后凝固阶段剩余的液相量最少、形成的液膜厚度较薄,补缩程度较低,所能抵御的凝固收缩力最小、裂纹扩展速率最大。这些现象说明MgZn4.5Y1Zr0.5合金具有最高的热裂敏感性。随着Y含量的增加,聚集在晶界处的低熔点相对合金热裂行为的作用以及合金的热裂形成机制均发生变化:当Y含量不超过1%时,低熔点相主要对晶间结合力起破坏作用,合金的热裂形成机制主要是晶间搭桥的断裂;当Y含量超过1%时,低熔点相主要对枝晶分离区起补缩作用,合金的热裂形成机制为晶间搭桥、枝晶分离区域的补缩和液膜共同作用。
关键词:Mg-Zn-Y-Zr系合金;凝固参数;热裂敏感性
文章编号:1004-0609(2017)-10-1970-11 中图分类号:TG146.22 文献标志码:A
镁合金由于具有较高的比强度,比刚度以及优良的铸造性能等优点,已经其成为工程应用中减重材料的首选。然而镁合金化学性质活泼,凝固区间较宽,凝固收缩量大,在凝固成型中极易形成热裂缺陷[1],这成为限制镁合金采用传统铸造法进行生产的瓶颈。前期的研究工作已表明,热裂发生在凝固过程的最后阶段,往往形成于铸件最后凝固的热节处[2-4]。目前,“Constrained Rod Casting”(CRC)铸造热裂试验[5]由于可以比较准确地测量合金发生热裂时的温度、凝固收缩力等,因此该方法被广泛的应用于合金热裂行为的研究。王峰等[6]利用CRC铸造热裂试验研究了Mg-5Al-xCa合金的热裂敏感性,并发现Ca含量为4%,热裂发生时所对应的固相分数最小,合金热裂敏感性最小。ZHOU等[7]利用CRC铸造热裂试验准确地测量出Mg-Zn二元合金发生热裂时的凝固收缩力,并发现凝固收缩应力与裂纹大小存在一一对应的比例关系,即小的裂纹测得大的收缩力,而大的裂纹测得的收缩力就很小。
近年来,具有高强度、高变形等特性的Mg-Zn-Y系镁合金进入了学者们的视线。Zr与Mg具有相近的晶格常数,加入Mg中可作为异质形核的核心,以达到细化组织的目的[8-10]。Y可提高镁合金的共晶温度,在较高的温度下形成稳定的第二相,导致晶界析出行为发生改变[11],这与合金的热裂敏感性密切相关。目前,HUANG等[12-13]和LIU等[14]分别研究当w(Zn)/ w(Y)=0.33~3.33和w(Zn)/w(Y)=0.42~5时Mg-Zn-Y系镁合金的热裂行为,结果发现,不同的w(Zn)/w(Y)比值会影响合金在凝固过程中晶界处形成的第二相的类型和数量,从而影响合金的热裂敏感性。WANG等[2]采用“CRC”研究了Zn含量对Mg-xZn-2Y系合金热裂敏感性的影响,不仅通过显微图像诠释了所研究合金的热裂机理,而且引入收缩力降和凝固收缩力释放率论证了Mg-1.5Zn-2Y 合金具有最大的热裂倾向。
目前研究合金热裂行为的方法主要是微观组织分析和相分析[15-17],很少研究或者讨论合金凝固特性对合金热裂行为的表征。本文作者为了全面地阐述MgZn4.5YxZr0.5(x=0.5,1.0,2.0,4.0,6.0(质量分数,%))系合金的热裂行为,采用热分析法[18]研究了糊状区特性与其热裂敏感性的关系;使用CRC铸造热裂试验测量这些合金发生热裂时的时间、温度以及探究固相分数和凝固收缩力对合金热裂行为的影响;观察断口形貌及断口截面形貌并分析热裂机理。
1 实验
1.1 CRC铸造热裂试验
MgZn4.5YxZr0.5系合金的主要原料为纯镁(99.95%,质量分数)、纯锌(99.7%)、镁-钇中间合金(钇含量25%)、镁-锆中间合金(Zr含量30%)。由于后续分析时需要对铸件的断口以及裂纹截面分别进行SEM显微观察,所以对于每种合金至少做两组CRC试验。为保证两组试验的合金成分一致,先将各成分合金熔炼成金属锭,CRC试验前再将金属锭分割重熔。熔炼金属锭时,采用的是配有Si控温仪的SG-5-10坩埚电阻炉。在熔炼过程中,不断向炉内通入纯N2+0.2%SF6(体积分数)混合而成的保护气体。将预热至100℃以上的纯镁放入不锈钢坩埚中加热。待Si控温仪显示炉内温度为700℃时,将纯锌、镁-钇中间合金、镁-锆中间合金放入同一坩埚中加热。至炉内达到720℃且原料完全熔化时,匀速搅拌熔体3 min并保温20 min,使得合金元素完全溶解和扩散。模具的形状和尺寸示意图如图1(a)所示。约束杆呈圆台状,近浇道端的约束杆直径为12 mm,另一端直径为10 mm。如此设计是为了减少合金与型壁的摩擦,尽可能使铸件自由收缩。浇道与约束杆交界的区域是铸件的热节,也是热裂发生的部位。如图1(b)所示,浇注前在热节圆心的位置插入一根直径为1.5 mm的镍铬-镍硅热电偶。约束杆远浇道端通过一根长120 mm、直径为4 mm的细长钢杆与应力采集器相连接。在开始浇注的同时,镍铬-镍硅热电偶与应力采集器将采集到的模拟信号传送到信号转换模块。信号转换模块再将模拟信号转换成数字信号,并将其传送至计算机中,LabView软件将传送来的信号以图表的形式展现出来。
1.2 SEM显微观察
采用S-3400N型扫描电镜观察断口试样和裂纹截面试样的微观形貌。其中,裂纹截面试样需打磨抛光,使用腐蚀液(96%无水乙醇+4%硝酸,体积分数)腐蚀后再进行显微观察。
1.3 热分析法
图2所示为双热电偶测试系统示意图。由图2可知,采用双热电偶测试系统[15]来采集测试合金的凝固曲线。使用CRC试验中浇铸出的“T”形杆铸件粗杆部分作为重熔样品,以确保与已进行CRC试验中使用的合金具有相同的化学组成。双热电偶测试实验中,一支电偶采集熔融合金中心部位的温度数据,另一只热电偶采集熔融合金边缘部位的温度数据。为了防止热量从坩埚纵向散失,在坩埚顶部以及底座各安置一块压实的厚石棉板用以隔热。
使用Origin软件分析热电偶采集到的凝固曲线,能够计算出温度对凝固时间的导数dT/dt。通过牛顿基线法[20]可以得到整个凝固过程的固相分数变化率(fs),再结合dT/dt曲线,可以推算出合金凝固过程中的各种温度参数,即合金液相线温度、固相线温度、合金凝固过程中第二相的生成温度、初晶形核的第一特征温度Tn1和第二特征温度Tn2[19-21]。图3所示为求取合金凝固过程中温度参数的方法。以MgZn4.5Y2Zr0.5合金为例,在图3中,1、2、3分别代表形成新相的形成[13]。在热分析中[18],当边缘热电偶dT/dt曲线初次出现拐点时,说明容器边缘合金开始释放初晶形核潜热,Tn1代表此点温度称为初晶形核第一特征温度;当中心热电偶冷却微分曲线出现第一个极大值时,说明容器内部初晶形核潜热释放结束,Tn2代表此点温度称为初晶形核第二特征温度[18]。

图1 热裂模具示意图和热裂检测装置示意图
Fig. 1 Schematic diagrams of mold for hot tearing(a) and hot-tearing detecting device(b)
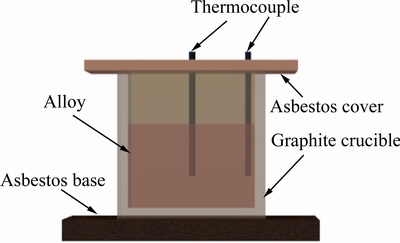
图2 双热电偶测试系统示意图
Fig. 2 Schematic diagram of double-thermocouple tested system
根据牛顿基线法计算固相分数,其方程如下[11]
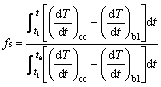 (1)
(1)
式中:下标cc表示冷却曲线(cooling curve);bl表示基线(baseline);t1和ts分别表示凝固开始和凝固结束时所对应的时间。
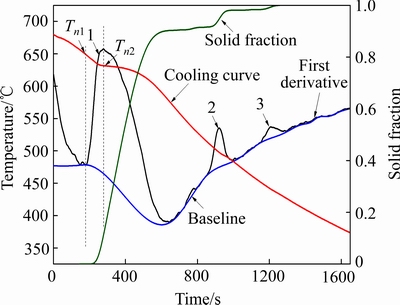
图3 求取合金凝固过程中温度参数的方法
Fig. 3 Determining method for temperature parameters during solidification
RIDDLE等[22]介绍了使用双热电偶法的另一种分析凝固曲线方法,即使用ΔT-t曲线ΔT=Te-Tc。其中,下标e为edge的缩写,代表边缘热电偶;下标c为center的缩写,代表中心热电偶[23-24]。图4所示为Tcoh求取方法的示意图。如图4所示,以MgZn4.5Y0.5Zr0.5合金为例,ΔT-t曲线出现第一个最小值峰时说明枝晶开始接触,其对应的石墨坩埚边缘温度被称为枝晶干涉温度[22-24],Tcoh(下标coh为coherency的缩写,代表枝晶干涉);枝晶干涉温度所对应的固相分数fscoh被定义为枝晶干涉固相分数。
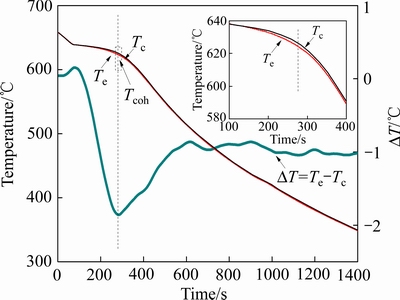
图4 Tcoh求取方法的示意图
Fig. 4 Determining method for Tcoh
2 结果与讨论
2.1 凝固参数对MgZn4.5YxZr0.5系合金热裂敏感性的表征
2.1.1 糊状区特性参数对MgZn4.5YxZr0.5系合金热裂敏感性的表征
糊状区特性参数在一定程度上可以定量地表征合金的热裂敏感性[21]。图5显示了通过双热电偶法测得的MgZn4.5YxZr0.5系合金糊状区的几个重要参数,初晶形核的两个特征温度Tn1和Tn2,枝晶干涉点温度Tcoh和枝晶干涉固相分数fscoh。Tn1在Y含量为1%时达到峰值,随着Y含量的增加,呈下降趋势;Tn2则是从Y含量为0.5%就逐渐降低。两个特征温度差(Tn1-Tn2)可以体现初晶形核过程滞留的时间,从而说明释放热量的大小。MgZn4.5YxZr0.5系合金的两个特征温度差(Tn1-Tn2)差异不大,均在10 ℃左右,说明所研究合金在初晶形核过程中释放的热量没有太大差距,不过由于MgZn4.5Y1Zr0.5合金的Tn1为最大,Tn2也较大。所以该合金在凝固过程中形核开始和结束的温度较高,可能会促使枝晶臂较早接触,从而提高枝晶干涉温度。
凝固开始时,合金中有大量的液相存在,各枝晶之间没有机会搭接形成连续的骨架结构。此阶段为整体补缩(Mass feeding)阶段,液相可以自由流动,不会发生热裂[21]。随着温度下降,游离枝晶逐渐长大。根据凝固收缩补偿理论[25-26],当凝固温度达到合金的枝晶干涉温度Tcoh时,枝晶臂开始互相搭接成网络结构。补缩机制开始由整体补缩机制转变为枝晶间补缩机 制[14]。当枝晶连接成网络结构时液相被分割成若干个小熔池,使得液相的流动受到严重阻碍,此时若铸件中某一部分由于凝固收缩而需要液态补缩时,由于液态流动受阻而在此处会形成热裂。因此枝晶干涉温度越高,说明枝晶越发达,即使此时固相分数不高(液相分数相对较高),但由于液相流动受阻而使合金具有较高的热裂敏感性。从图5可以发现,当Y含量为0.5%时,枝晶搭接温度较高,Tcoh在626.1 ℃左右,而枝晶搭接时固相分数比较低,fscoh在0.46。当Y含量为1%时,Tcoh达到所研究合金中的最高值628.5 ℃,而fscoh为最低值0.42。较高的Tcoh(较低的fscoh)表明该合金中的枝晶在液相较多的时候就完成互相碰撞,合金的枝晶间补缩过程会较早开始,增加了补缩的难度,提高了热裂出现的几率[20]。而后随着Y含量分别增加至2%和4%时,Tcoh分别降低至624.4 ℃和617.3 ℃,fscoh分别升高至0.60及0.62。当Y含量增大到6%时,MgZn4.5Y6Zr0.5合金具有最低的Tcoh以及最高的fscoh,分别为611.5 ℃及0.64。较低的枝晶搭接温度说明合金在凝固过程中能进行充分的补缩,因此其热裂敏感性较相对较低。根据以上分析可知,双热电偶所测得枝晶搭接温度Tcoh可以间接的预测合金的热裂敏感性,即合金的枝晶搭接温度越高,其热裂敏感性越高。因此对于本论文所研究的MgZn4.5YxZr0.5系合金来说,根据其枝晶搭接温度Tcoh所预测的热裂敏感性由大到小的顺序为MgZn4.5Y1Zr0.5、MgZn4.5Y0.5Zr0.5、MgZn4.5Y2Zr0.5、MgZn4.5Y4Zr0.5、MgZn4.5Y6Zr0.5,这与前期对MgZn4.5YxZr0.5系合金热裂敏感性的测试结果一致[27]。
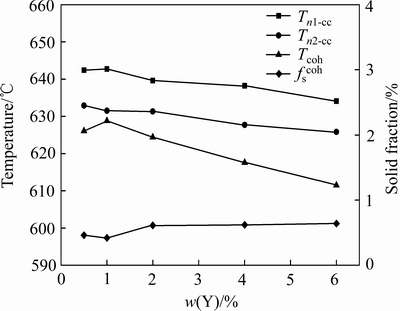
图5 MgZn4.5YxZr0.5系合金的糊状区参数
Fig. 5 Mushy zone parameters of MgZn4.5YxZr0.5 alloys
2.1.2 脆弱区域温度范围对MgZn4.5YxZr0.5系合金热裂敏感性的表征
根据合金凝固过程中的强度理论[19],合金在凝固的最后阶段时强度较低,热裂纹容易在凝固收缩应力的作用下沿晶粒的晶界延伸而形成,断裂性质呈脆性断裂。PUMPHREY等[28]将固相分数为90%~99%的区域定义为“脆弱区域”,该范围对应的温度被定义为ΔTc。在此区域,合金中充斥着大量形成的枝晶,极少量的残余液相无法填补由于凝固收缩应力造成的枝晶分离,裂纹源会迅速扩展形成体积较大的宏观裂纹。所以,脆弱区域的温度范围ΔTc越大,形成热裂的几率也会随之增加[29]。图6所示为MgZn4.5YxZr0.5系合金在脆弱区域中固相分数与ΔTc之间的关系。可以发现,MgZn4.5Y0.5Zr0.5和MgZn4.5Y1Zr0.5的ΔTc值较大并且差异较小,分别为176.9和177.8 ℃。大的温度跨度将产生大的凝固收缩应力[12],意味着这两种合金的热裂倾向较大。随着Y含量的增加,ΔTc值逐渐降低,MgZn4.5Y2Zr0.5和MgZn4.5Y4Zr0.5的ΔTc值分别为143.2和69.4 ℃。MgZn4.5Y6Zr0.5的ΔTc值最低,为35.0 ℃,说明该合金在枝晶分离阶段中脆弱区域的范围最小,即能够获得很大的补偿量,同时凝固收缩力跨度最小,使得热裂敏感程度显著降低。MgZn4.5YxZr0.5系合金脆弱区域的比较结果如表1所列。根据合金脆弱区域ΔTc的分析结果可知,MgZn4.5YxZr0.5系合金的热裂敏感性由大到小的顺序为MgZn4.5Y1Zr0.5、MgZn4.5Y0.5Zr0.5、MgZn4.5Y2Zr0.5、MgZn4.5Y4Zr0.5、MgZn4.5Y6Zr0.5,与上述糊状区特性参数预测结果一致。说明合金糊状区特性参数为预测合金热裂敏感性的一种可靠的试验方法。
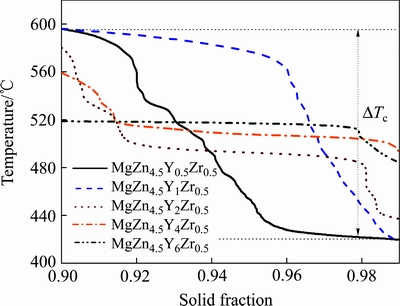
图6 MgZn4.5YxZr0.5系合金在脆弱区域中固相分数与ΔTc之间的关系
Fig. 6 Relationship between solid fraction and ΔTc for MgZn4.5YxZr0.5 alloys in vulnerable region
表1 MgZn4.5YxZr0.5系合金脆弱区域温度范围
Table 1 Temperature range of vulnerable region for MgZn4.5YxZr0.5 alloys
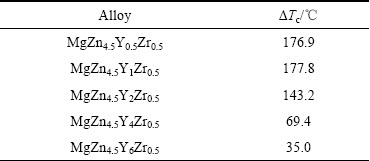
2.1.3 最后凝固阶段剩余液相量对MgZn4.5YxZr0.5系合金热裂敏感性的表征
根据合金凝固过程中的液膜理论[30],当合金凝固到固相线附近时,在枝晶周围的液相会形成液膜覆盖在已凝固的枝晶上。在枝晶形成的初期,其周围的液膜厚度较厚;但是随着凝固的进行,液膜逐渐变薄。当合金在非平衡条件下凝固时,由于发生成分偏析而使低熔点相偏聚于晶界周围,从而使固相线下移,降低了凝固温度,增加了液膜存在的时间。同时在凝固过程中,在凝固收缩应力的作用下,相互接触的枝晶和枝晶周围的液膜发生分离。如果凝固收缩应力足够大使得枝晶间的距离超过一定值后,破坏了液膜作用在枝晶间的结合力从而造成液膜开裂形成晶间裂纹,即热裂。如果凝固后期液膜较薄,液膜与枝晶间的结合力和/或液膜强度不足以抵抗迫使枝晶与液膜分离或液膜被拉断的收缩应力,那么该合金的热裂敏感性就很大。相反地,如果低熔点相的含量不仅能够形成液膜,并且液膜的厚度足够大时,那么由于液膜作用在枝晶间的结合力远远大于凝固收缩应力,即使枝晶在收缩应力作用下枝晶间的间距增大但是仍不足以破坏枝晶间的结合力,那么该合金的热裂敏感性就大大降低。黄张洪等[12]将Mg-Zn-Y合金凝固过程中最后一个新相相变温度到固相线温度作为最后凝固阶段进行研究。在此阶段形成低熔点相。低熔点相偏聚在晶界处,不仅能够形成一定厚度的液膜,并且能对枝晶分离区域回填,增加了枝晶间的结合力,提高了凝固收缩抗力[7]。凝固最后阶段剩余液相分数越高,反应生成的低熔点相越多,液膜分布越连续,对枝晶分离的补缩效果越明显,合金的热裂敏感性也越小[28]。本实验中采用同样的分析方法,即采用凝固过程中最后一个相析出温度到固相线的温度作为凝固的最后阶段的温度范围进行分析。通过图4的分析方法,可以确定MgZn4.5YxZr0.5合金的最后凝固阶段温度范围,从而求取剩余液相量。MgZn4.5YxZr0.5合金的最后凝固阶段温度范围的分析结果表2所列。从表2中可以发现,MgZn4.5Y1Zr0.5合金在最后凝固阶段的剩余液相量最低,仅为0.7%。之后,最后凝固阶段的剩余液相量随着Y含量增加而增加。当Y含量达到6%时,最后凝固阶段的剩余液相量高达24%。这说明近固相线时,MgZn4.5Y1Zr0.5合金中可以对枝晶分离的回填的残余液相最少,补缩最不充分,从而导致该合金较高的热裂敏感性。从最后凝固阶段液相量的多少也可分析出MgZn4.5YxZr0.5系合金的热裂敏感性由大到小的顺序为MgZn4.5Y1Zr0.5、MgZn4.5Y0.5Zr0.5、MgZn4.5Y2Zr0.5、MgZn4.5Y4Zr0.5、MgZn4.5Y6Zr0.5,该分析结果与上述两种分析方法完全一致。
表2 MgZn4.5YxZr0.5系合金最后凝固阶段的剩余液相量
Table 2 Amount of residual liquid in last stage of solidification for MgZn4.5YxZr0.5 alloys
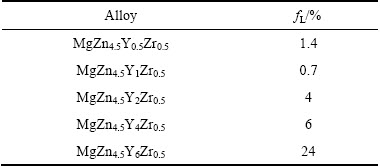
2.2 裂纹宏观图像对MgZn4.5YxZr0.5系合金热裂敏感性的表征
图7所示为通过热裂检测系统(见图1)得到的MgZn4.5YxZr0.5系合金热裂纹的宏观图片。通过“T”形杆热节处的开裂情况,可以判断合金的热裂倾向。对于MgZn4.5Y0.5Zr0.5和MgZn4.5Y1Zr0.5合金,“T”形杆热节处处完全断裂,说明这两种合金的热裂敏感性较高。当Y含量为2%时,虽然形成热裂纹的深度和宽度均较大,但并未完全断裂,说明热裂倾向降低。随着Y含量为4%时,热裂纹的深度和宽度均减小。当Y含量为6%时,在粗杆与细杆交界处仅能看到细小的裂纹,说明该合金的热裂敏感性最低。
2.3 MgZn4.5YxZr0.5系合金热裂纹萌生和扩展情况
通过Origin软件对图1(b)收集到的数据进行处理,可以得到凝固收缩力和温度对时间的函数曲线图(见图8)。细线是凝固收缩力曲线,粗线是冷却曲线。凝固收缩力曲线在凝固的初始阶段值为零。这是由于合金在凝固开始时,所形成的固相相对较少,合金的强度还没有建立起来[19]。随着凝固的继续,凝固收缩力开始急剧增加。当凝固收缩力曲线突然出现下降,此时表示凝固组织中出现裂纹,应力开始松弛[2-4]。图8(a)和图8(b)的凝固收缩力曲线产生多次突然下降,说明MgZn4.5Y0.5Zr0.5和MgZn4.5Y1Zr0.5合金在凝固过程中晶间结合力总是无法抵御凝固收缩力,从而出现了多次裂纹。图8(c)中也出现应力松弛的情况有所减少,意味着合金的热裂敏感性有所降低。图8(c)中的凝固收缩力曲线上的虚框内出现了一个平台,说明在此过程中凝固的补缩与枝晶的分离处于一个相互平稳的过程,此时在试样的表面不会有裂纹产生[7]。图8(d)和图8(e)中的凝固收缩力曲线更为平滑,起伏情况较少,说明MgZn4.5Y4Zr0.5和MgZn4.5Y6Zr0.5合金的晶间结合力显著提高,降低了合金的热裂敏感性。
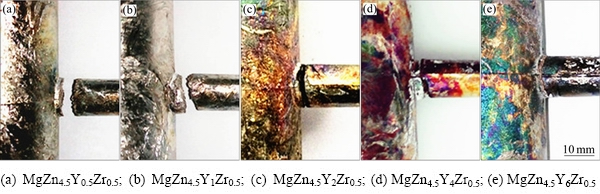
图7 MgZn4.5YxZr0.5系合金热裂纹照片
Fig. 7 Macroscopic hot-tearing photos for MgZn4.5YxZr0.5 alloys
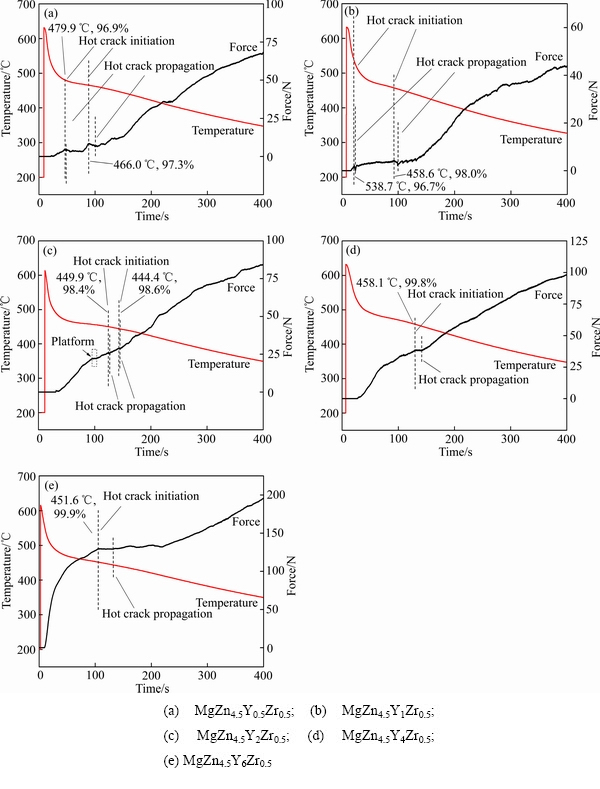
图8 凝固收缩力和温度对时间的函数曲线示意图
Fig. 8 Contraction force and temperature as a function of time for MgZn4.5YxZr0.5 alloys
从图8中可以获得关于MgZn4.5YXZr0.5合金热裂萌生和扩展时的信息。表3对其进行汇总,包括热裂萌生时的温度、固相分数、凝固收缩力、裂纹扩展过程中力的下降量、裂纹扩展时间以及裂纹扩展速率。在表3中,Ti是热裂萌生时的温度;fs-i是裂纹萌生时的固相分数;Fi是热裂萌生时的凝固收缩力;Fr是在裂纹扩展过程中凝固收缩力的跨度;tp是裂纹扩展时间;vp裂纹扩展速率。ZHOU等[7]认为热裂的萌生与扩展与凝固收缩力有相互对应的关系,由此采用凝固收缩力对时间的变化率来表示裂纹的扩展速率,其单位为N/s。对于MgZn4.5Y0.5Zr0.5和MgZn4.5Y1Zr0.5合金,由于枝晶干涉温度较高,枝晶在较高的温度下彼此搭接,从而阻碍残余液相的补缩,最终导致这两种合金在还有一定液相存在时(较低的固相分数)便产生宏观热裂纹。随着凝固收缩应力的增加,依旧无法建立有效的强度来提高晶间结合力,导致了裂纹源会以较快的速度扩展成体积较大的热裂纹并催生二次甚至多次热裂在近凝固结束时萌生和扩展,以至于完全断裂。这说明了MgZn4.5Y0.5Zr0.5和MgZn4.5Y1Zr0.5合金具有较高的热裂敏感性。当Y含量大于等于2%时,在凝固收缩力较低时,并没有形成宏观裂纹。直到凝固收缩力较高时,热裂才开始萌生。而且萌生时的凝固收缩力随着Y含量的增加也逐渐增加,由26.21 N提高至129.57 N。MgZn4.5Y2Zr0.5合金的“T”形杆热节处虽然有二次热裂出现,但“T”形杆热节处并未完全断裂,而MgZn4.5Y4Zr0.5和MgZn4.5Y6Zr0.5合金没有出现二次热裂的现象。随着w(Zn)/w(Y)的降低,产生宏观裂纹时应力释放逐渐降低,微裂纹扩展速度趋于缓慢,这表明合金的晶间结合力逐渐增加,能够有效地抵御裂纹源的扩展,说明合金的抗热裂性能显著提高。
2.4 MgZn4.5YxZr0.5系合金热裂形成机理
图9所示为MgZn4.5YxZr0.5系合金裂纹截面SEM像。从图9可以看出,裂纹的初始位置都是从表面开始的,内部的枝晶在凝固收缩应力作用下发生分离,分离方向与裂纹扩展方向垂直。图9(a)和图9(b)所示分别为MgZn4.5Y0.5Zr0.5合金和MgZn4.5Y1Zr0.5合金裂纹截面的形貌。由于此时的Y含量较低,形成的低熔点相较少,以至于无法在晶界处构成连续的补缩通道。在凝固末期,由于液相分数较低并且补缩通道不顺畅,分离的枝晶得不到残余液相的补缩,从而增大了合金的热裂倾向性。然而,裂纹没有连接成片或者贯通于整个铸件,这是由于在枝晶分离的同时两个相邻的晶粒间形成了对热裂纹的萌生及扩展形成阻碍作用的桥接[31-32]。图9(c)、图9(d)和图9(e)所示分别为MgZn4.5Y2Zr0.5合金、MgZn4.5Y4Zr0.5合金以及MgZn4.5Y6Zr0.5合金的裂纹截面的SEM像。从图中可发现,裂纹在收缩应力作用下发生分离,并沿着晶界发生扩展。然而随着Y含量的增加,晶界处聚集的低熔点相的量也逐渐增加,逐渐形成共晶网络,构成连续的补缩通道,残余液相流动时受到的阻碍逐渐降低,其补缩能力得到很大程度的提升。残余液相的回填可以使分离枝晶重新愈合,阻碍裂纹的扩展以及减少已经开裂的裂纹体积,从而逐渐降低了合金的热裂倾向性。
图10所示为MgZn4.5YxZr0.5合金热裂纹区域的断口形貌。由图10可以看出,晶粒表面覆盖一层薄膜,这是由低熔点相形成的[14]。在凝固收缩力的作用下,晶粒向相反的方向运动,液膜随着晶粒持续被拉伸。
表3 MgZn4.5YxZr0.5系合金热裂萌生和扩展的情况
Table 3 Information about the initiation and propagation of hot tearing for MgZn4.5YxZr0.5 alloys
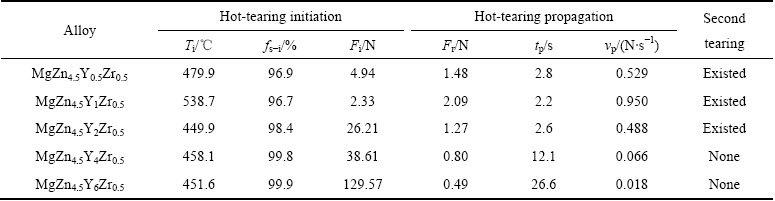
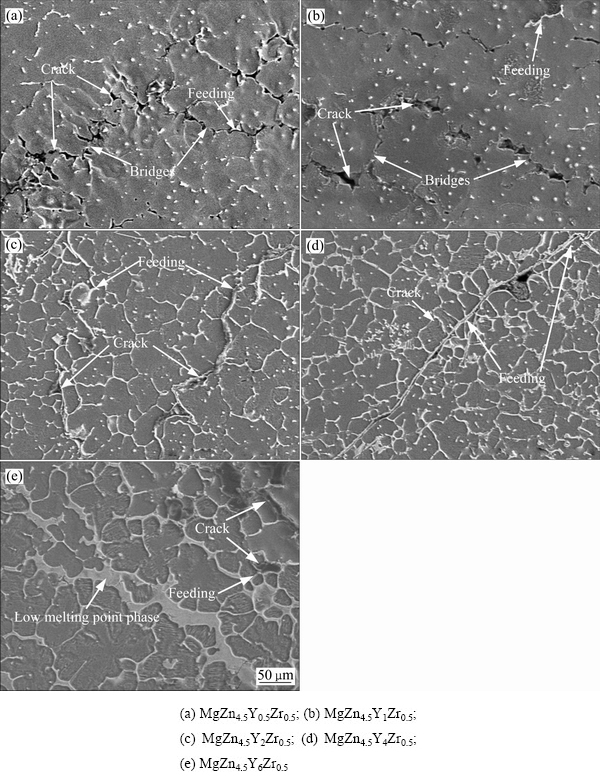
图9 MgZn4.5YxZr0.5系合金裂纹截面形貌
Fig. 9 Section of fracture morphologies of MgZn4.5YxZr0.5 alloys
根据液膜理论[30],热裂的形成取决于液膜厚度和收缩凝固力的大小。液膜厚度影响液膜的强度。由于MgZn4.5Y0.5Zr0.5 和MgZn4.5Y1Zr0.5合金在最后凝固阶段的剩余液相量较低,所以留下的液膜也较少,导致液膜厚度较薄、褶皱较少。所以液膜无法拉伸较长的距离使得破裂的现象较多,从而提高了热裂倾向。而且由于液膜强度较低,抵御凝固收缩力拉扯的能力较差,所以在较低的凝固收缩力时,液膜就会破裂而且扩展迅速,从而形成体积较大的宏观裂纹。从图10(c)中发现,低熔点相明显增多使得褶皱增多,增加了液膜的厚度。在凝固收缩力的作用下,液膜拉伸的长度也有所提高,可以观察到相邻晶粒只是间距变大,并没有完全撕裂的现象。图10(d)和(e)所示分别为MgZn4.5Y4Zr0.5和MgZn4.5Y6Zr0.5合金断口的枝晶分离形貌。从中可以发现,不仅液膜的厚度和拉伸长度有所增加,在撕裂区域中断裂的桥接痕迹也明显增多,说明晶间结合力和抗撕裂性能得到大大提高,从而降低了该合金的热裂敏感性。
综合图9和图10可以发现,当w(Zn)/w(Y)=4.5时,由于非平衡凝固所产生在晶界处的低熔点相能够形成一定厚度的液膜,不过液膜较薄,在较大的凝固收缩应力的作用下很容易被撕裂;而且在晶界处聚集的低熔点相的量不足以形成连续的补缩通道,极大的阻碍了残余液相对分离枝晶的回填。这时的低熔点相对晶间的结合力破坏作用很大,而对分离的枝晶补缩程度却很小,因此造成MgZn4.5Y1Zr0.5合金的热裂倾向性在MgZn4.5YxZr0.5系合金中是最大的。当w(Zn)/ w(Y)=9时,晶界处形成的低熔点低熔点相更少,虽然也无法建立共晶网络,但是少量的低熔点相所产生破坏晶间结合力的能力不如MgZn4.5Y1Zr0.5系合金,所以MgZn4.5Y0.5Zr0.5合金的热裂倾向性逊于MgZn4.5Y1Zr0.5合金。当w(Zn)/w(Y)≥4.5时,较高的枝晶干涉温度和较少的最后凝固阶段剩余液相量使形成的液相补缩和液膜较少,而晶间搭桥对阻碍裂纹扩展的影响更大,所以MgZn4.5Y0.5Zr0.5和MgZn4.5Y1Zr0.5合金热裂形成机理为晶间搭桥的断裂。这两种合金的晶间搭桥较少而且强度较低,使得其对凝固收缩力的抵抗能力较差,热裂敏感性较高。当w(Zn)/w(Y)<4.5时,由于在晶界处富集的低熔点相较多,在晶界处搭建成了连续的共晶网络,补缩通道在更长的时间内保持畅通提供了有力条件,促进了残余液相对枝晶分离的回填。低熔点相由其对晶间结合力的破坏作用逐渐转变为其对晶间由于枝晶分离而产生的收缩的补缩作用。随着Y含量的增加,晶间搭桥数量增多、强度提高,残余液相补缩更为充分,液膜的厚度和强度也显著提高,这使合金的热裂敏感性逐渐降低。因此,MgZn4.5Y2Zr0.5、MgZn4.5Y4Zr0.5和MgZn4.5Y6Zr0.5合金的热裂形成机理为晶间搭桥、枝晶分离区补缩和液膜共同作用。
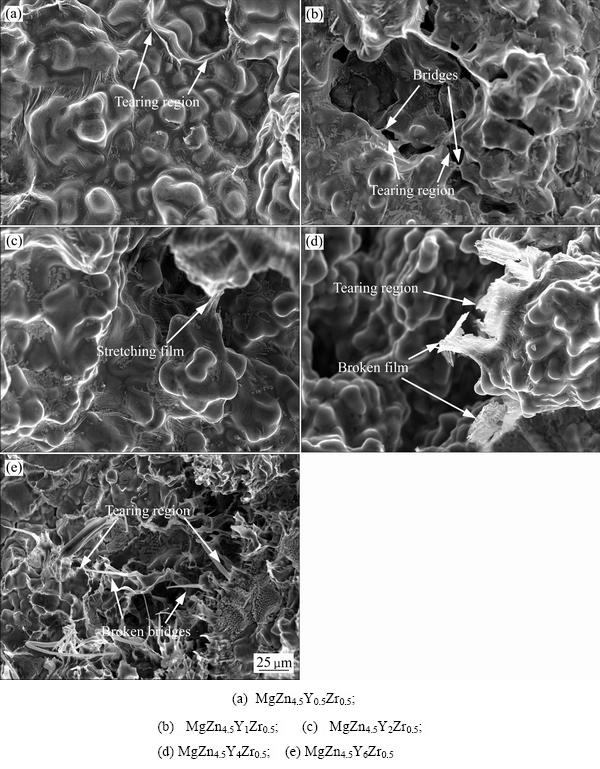
图10 MgZn4.5YxZr0.5合金热裂纹区域的断口形貌
Fig. 10 Fracture morphologies of MgZn4.5YxZr0.5 alloys
3 结论
1) MgZn4.5Y1Zr0.5合金的枝晶干涉温度最高,之后随着Y含量增加,枝晶干涉温度呈下降趋势。MgZn4.5YxZr0.5的枝晶干涉固相分数约为0.42~0.64。其中,MgZn4.5Y1Zr0.5合金的枝晶干涉固相分数最低,MgZn4.5Y6Zr0.5合金最高。
2) MgZn4.5Y1Zr0.5合金在脆弱区域的温度差ΔTc最大、在最后凝固阶段剩余的液相量最少、形成的液膜厚度较薄而且所能抵御的凝固收缩力最小、裂纹扩展速率最大。这些现象说明MgZn4.5Y1Zr0.5合金具有最高的热裂敏感性。
3) 随着Y含量的增加,聚集在晶界处的低熔点相对合金热裂行为的作用以及合金的热裂形成机制均发生了变化:当Y含量不超过1%时,低熔点相主要对晶间结合力起破坏作用,合金的热裂形成机制主要是晶间搭桥的断裂;当Y含量超过1%时,低熔点相主要对枝晶分离区起补缩作用,合金的热裂形成机制为晶间搭桥、枝晶分离区域的补缩和液膜共同作用。
REFERENCES
[1] 王怀国. 镁合金热裂行为研究进展[J]. 材料导报, 2014, 28(10): 84-90.
WANG Huai-guo. Development of hot tearing in magnesium alloys[J]. Materials Review, 2014, 28(10): 84-90.
[2] WANG Z, LI Y Z, WANG F, HUANG Y D, SONG J F, MAO P L, LIU Z. Hot tearing susceptibility of Mg-xZn-2Y alloys[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2016, 26(12): 3115-3122.
[3] WANG Z, SONG J F, HUANG Y D, SRINIVASAN A, LIU Z, KAINER K U, HORT N. An investigation on hot tearing of Mg-4.5Zn-(0.5Zr) alloys with Y additions[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2015, 46(5): 2108-2118.
[4] WANG Z, LI Y Z, WANG F, SONG J F, LIU Z, MAO P L. Effect of Cu additions on microstructure mechanical properties and hot tearing susceptibility of Mg-6Zn-0.6Zr alloys[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 2016, 25(12): 5530-5539.
[5] NOVIKOV I I, GRUSHKO O E. Hot cracking susceptibility of Al-Cu-Li and Al-Cu-Li-Mn alloys[J]. Materials Science and Technology, 1995, 11(9): 926-932.
[6] 王 峰, 董海阔, 王 志, 毛萍莉, 刘 正. Mg-5Al-xCa的热裂行为[J]. 金属学报, 2017, 53(2): 211-219.
WANG Feng, DONG Hai-kuo, WANG Zhi, MAO Ping-li, LIU Zheng. Hot cracking behavior of Mg-5Al-xCa alloys[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2017, 53(2): 211-219.
[7] ZHOU L, HUANG Y D MAO P L, KAINER K U, LIU Z, HORT N. Influence of composition on hot tearing in binary Mg-Zn alloys[J]. International Journal of Cast Metals Research, 2011,24(3/4): 170-176.
[8] 蔚晓嘉, 刘邱祖, 韩世平. 热处理对Mg-8Gd-2.5Nd-0.5Zr合金组织和力学性能的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2017, 27(1): 82-88.
WEI Xiao-jia, LIU Qiu-zu, HAN Shi-ping. Effects of heat treatment on microstructure and mechanical properties of Mg-8Gd-2.5Nd-0.5Zr alloy[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2017, 27(1): 82-88.
[9] MOKDAD F, CHEN D L. Strain-controlled low cycle fatigue properties of a rare-earth containing ZEK100 magnesium alloy[J]. Materials & Design, 2015, 67: 436-447.
[10] 胡耀波, 杨生伟, 姚青山, 潘复生. 挤压比及Mn含量对Mg-10Gd-6Y-1.6Zn-XMn镁合金组织和性能的影响[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2017, 46(1): 135-142.
HU Yao-bo, YANG Sheng-wei, YAO Qing-shan, PAN Fu-sheng. Effects of extrusion ratio and Mn content on microstructure and properties of Mg-10Gd-6Y-1.6Zn-XMn magnesium alloy[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2017, 46(1): 135-142.
[11] LIU Z, ZHANG S B, MAO P L, WANG F. Effect of Y on hot tearing formation mechanism of Mg-Zn-Y-Zr alloys[J]. Materials Science and Technology, 2014, 30(10): 1214-1222.
[12] 黄张洪, 张 燕, 陈荣石, 韩恩厚. Mg-Zn-Y-Zr合金热裂敏感性的研究[J]. 铸造, 2009, 58(8): 788-792.
HUANG Zhang-hong, ZHANG Yan, CHEN Rong-shi, HAN En-hou. Hot tearing susceptibility of Mg-Zn-Y-Zr alloys[J]. Foundry, 2009, 58(8): 788-792.
[13] HUANG Z H, LIANG S M, CHEN R S, HAN E H. Solidification pathways and constituent phases of Mg-Zn-Y-Zr alloys[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2009, 468(1/2): 170-178.
[14] LIU Z, ZHANG S B, MAO P L, WANG F. Effects of Y on hot tearing susceptibility of Mg-Zn-Y-Zr alloys[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2014, 24(4): 907-914.
[15] 毛萍莉, 秦佳明, 刘 正, 王 志, 杨金龙. EW75镁合金的热裂行为[J]. 材料热处理学报, 2016, 37(6): 55-60.
MAO Ping-li, QIN Jiang-ming, LIU Zheng, WANG Zhi, YANG Jin-long. Hot tearing susceptibility of EW75 magnesium alloy[J]. Transactions of Materials and Heat Treatment, 2016, 37(6): 55-60.
[16] ZHANG X B, SUN J, WANG M L, ZHANG Y J, MA N H, WANG H W. Improvement of yttrium on the hot tearing susceptibility of 6TiB2/Al-5Cu composite[J]. Journal of Rare Earths, 2015, 33(12): 1335-1340.
[17] LI J L, CHEN R S, MA Y Q, KE W. Hot tearing of sand cast Mg-5% Y-4% RE (WE54) alloy[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica (English Letters), 2013, 26(6): 728-734.
[18] DAHLE A K, ARNBURG L. On the assumption of an additive effect of solute elements in dendrite growth[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 1997, A225: 38-46.
[19] 张斯博. Mg-Zn-Y合金热裂行为测试研究[D]. 沈阳: 沈阳工业大学, 2014.
ZHANG Si-bo. Investigations on testing methods and hot tearing susceptibility of Mg-Zn-Y-Zr alloys[D]. Shenyang: Shenyang University of Technology, 2014.
[20] UPADHYA K G, STEFANESCU D M. Computer-aided cooling curve analysis: Principle and applications in metal casting[J]. Transactions of the American Foundry Society, 1989, 97: 61-66.
[21] 马跃群, 梁松茂, 陈荣石, 韩恩厚. AZ6X镁合金的糊状区特性表征[J]. 金属学报, 2007, 43(3): 254-258.
MA Yue-qun, LIANG Song-mao, CHEN Rong-shi, HAN En-hou. Characterization of mushy zone properties of AZ6X magnesium alloys[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2007, 43(3): 254-258.
[22] SHANKAR S, RIDDLE Y W, MAKHLOUF M M. Nucleation mechanism of the eutectic phases in aluminum-silicon hypoeutectic alloys[J]. Acta Materialia, 2004, 52: 4447-4460.
[23] 黄张洪, 曲恒磊, 富招弟, 孙 丹, 舒 莹, 杨 健, 杨建朝. Zr对Mg-6Zn-2Y合金组织及凝固行为的影响[J]. 金属热处理, 2011, 36(9): 10-12.
HUANG Zhang-hong, QU Heng-lei, FU Zhao-di, SHU Ying, YANG Jiang, YANG Jian-chao. Effect of Zr on microstructure and solidification behavior of Mg-Zn-Y alloys [J]. Heat Treatment of Metals, 2011, 36(9): 10-12.
[24] 黄张洪, 赵 惠, 吕利强, 高文柱. 热分析技术及其应用[J]. 热加工工艺, 2010, 39(7): 19-26.
HUANG Zhang-hong, ZHAO Hui,  Li-qiang, GAO Wen-zhu. Thermal analysis and its application[J]. Hot Working Technology, 2010, 39(7): 19-26.
Li-qiang, GAO Wen-zhu. Thermal analysis and its application[J]. Hot Working Technology, 2010, 39(7): 19-26.
[25] MATHIER V, VERNEDE S, JARRY P, RAPPAZ M. Two-phase modeling of hot tearing in aluminum alloys: applications of a semicoupled method[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2009, 40(4): 943-957.
[26] 丁 浩, 傅恒志, 刘忠元, 陈荣章, 刘伯操, 钟振纲, 唐定中. 凝固收缩补偿与合金的热裂倾向[J]. 金属学报, 1997, 33(9): 921-926.
DING Hao, FU Heng-zhi, LIU Zhong-yuan, CHEN Rong-zhang, LIU Bo-cao, ZHONG Zhen-gang, TANG Ding-zhong. Compensation of solidification contraction and hot cracking tendency of alloys[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 1997, 33(9): 921-926.
[27] FENG Y, MAO P L LIU Z, WANG Z, QIN J M, WANG F. Hot tearing susceptibility of MgZn4.5YxZr0.5 alloys and mechanism[J]. China Foundry, 2016, 13(3): 159-165.
[28] PUMPHREY W I, JENNINGS P H. A consideration of the nature of brittleness and temperature above the solidus in castings and welds in aluminum alloys[J]. Journal Institute of Metals, 1948, 75: 235-256.
[29] HUANG H, FU P H, WANG Y X, PENG L M, JIANG H Y. Effect of pouring and mold temperatures on hot tearing susceptibility of AZ91D and Mg-3Nd-0.2Zn-Zr Mg alloys[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2014, 24 (4): 922-929.
[30] 李庆春. 铸件形成理论基础[M]. 北京: 机械工业出版社, 1982.
LI Qing-chun. The theoretical foundation of casting forming technology[M]. Beijing: China Machine Press, 1982.
[31] CLYNE T W, WOLF M, KURZ W. The effect of melt composition on solidification cracking of steel, with particular reference to continuous casting[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 1982, 13(2): 259-266.
[32] CLYNE T W, DAVIES G J. A quantitative solidification cracking test for castings and an evaluation of cracking in Al-Mg alloys[J]. The Brithish Foundryman, 1975, 68: 238-244.
Effect of yttrium content on hot tearing susceptibility of MgZn4.5YxZr0.5 alloys
FENG Yu, MAO Ping-li, LIU Zheng, WANG Zhi, ZHANG Si-bo, WAMG Feng
(School of Materials Science and Engineering, Shenyang University of Technology, Shenyang 110870, China)
Abstract: Thermal analysis method and constrained rod casting (CRC) were used to study hot tearing behavior of MgZn4.5YxZr0.5 (x=0.5, 1, 2, 4, 6 (mass fraction, %)) alloys. The results show that MgZn4.5Y1Zr0.5 alloy possesses the highest hot tearing susceptibility (HTS) among the tested alloys due to the highest coherency temperature (Tcoh), the largest temperature difference (ΔTc) in vulnerable region, the least residual liquid in last stage of solidification, the lowest anti-contraction force of thinner film, the poorer feeding capability and the highest crack propagation rate. The role of low-melting point phases gathering at grain boundary on the HTS and the main mechanism of hot tearing shift gradually with different Y contents: when Y is not more than 1%, the role is mainly a damaging effect on intergranular binding force and the main mechanism is fracture of intergranular bridges; when Y is more than 1%, the role is mainly an intergranular feeding effect on formed separated dendrites and the main mechanism is the collective effect of intergranular bridges, intergranular feeding and film.
Key words: Mg-Zn-Y-Zr alloy; solidification parameter; hot tearing susceptibility
Foundation item: Projects(51504153, 51571145) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China
Received date: 2016-06-28; Accepted date: 2017-03-24
Corresponding author: MAO Ping-li; Tel: +86-24-25497131; E-mail: pinglimao@yahoo.com
(编辑 龙怀中)
基金项目:国家科学自然基金资助项目(51504153,51571145)
收稿日期:2016-06-28;修订日期:2017-03-24
通信作者:毛萍莉,教授,博士;电话:024-25497131;E-mail: pinglimao@yahoo.com