AlCuFe共晶合金的显微组织和力学性能
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2020年第12期
论文作者:Sevda ENGIN
文章页码:3183 - 3194
关键词:定向凝固;铝合金;显微组织;抗拉强度;硬度
Key words:directional solidification; aluminum alloy; microstructure; tensile strength; hardness
摘 要:制备特殊用途的AlCuFe合金,评估生长速率变化导致的结果,因为材料生长速率不同而引起的共晶间距(显微组织)的变化会影响其力学、电和热性能。为了研究AlCuFe合金的显微组织,在恒定的温度梯度(G=8.50 K/mm)和5种不同的生长速率(V=8.25, 16.60, 41.65, 90.05, 164.80 μm/s)下,通过定向凝固法制备共晶成分的Al-32.5%Cu-0.5%Fe(质量分数)合金。得到生长速率对共晶间距影响,并通过对显微组织变化的回归分析及Hall-Petch关系得出显微硬度和极限拉伸强度。结果表明,尽管生长速率增加约20倍,但共晶间距却减少约5个数量级,而生长速率和显微组织变化导致的力学性能变化约为1.5个数量级。
Abstract: In the production of AlCuFe alloy for a special application, the growth rate was changed and the results were evaluated. Changes in the eutectic spacing (microstructure) of a material due to the growth rate are known to affect its mechanical, electrical and thermal properties. To evaluate its microstructure, the eutectic composition of Al-32.5wt.%Cu-0.5wt.%Fe was prepared and directional solidification experiments were conducted using a Bridgman-type furnace at a constant temperature gradient (G=8.50 K/mm) and five growth rates (V=8.25, 16.60, 41.65, 90.05, 164.80 μm/s). The effect of the growth rate on the eutectic spacing was then determined, and the resulting microhardness and ultimate tensile strength were obtained based on the change in the microstructure by regression analysis and Hall-Petch correlations. Despite the fact that the growth rate increased by approximately twenty times, the eutectic spacing decreased by a factor of approximately 5, and these changes in the growth rate and microstructure caused the mechanical properties to change by a factor of approximately 1.5.
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 30(2020) 3183-3194
Sevda ENGIN
Department of Energy Systems Engineering, Faculty of Technology, Kütahya Dumluplnar University, Kütahya, Turkey
Received 10 January 2020; accepted 19 October 2020
Abstract: In the production of AlCuFe alloy for a special application, the growth rate was changed and the results were evaluated. Changes in the eutectic spacing (microstructure) of a material due to the growth rate are known to affect its mechanical, electrical and thermal properties. To evaluate its microstructure, the eutectic composition of Al-32.5wt.%Cu-0.5wt.%Fe was prepared and directional solidification experiments were conducted using a Bridgman-type furnace at a constant temperature gradient (G=8.50 K/mm) and five growth rates (V=8.25, 16.60, 41.65, 90.05, 164.80 μm/s). The effect of the growth rate on the eutectic spacing was then determined, and the resulting microhardness and ultimate tensile strength were obtained based on the change in the microstructure by regression analysis and Hall-Petch correlations. Despite the fact that the growth rate increased by approximately twenty times, the eutectic spacing decreased by a factor of approximately 5, and these changes in the growth rate and microstructure caused the mechanical properties to change by a factor of approximately 1.5.
Key words: directional solidification; aluminum alloy; microstructure; tensile strength; hardness
1 Introduction
The elements that constitute an alloy material and the microstructure are the focuses of material science and engineering research and represent a strategic connection between the processing and performance of the material [1,2]. To minimize the number of microstructural errors that may occur during material processing and obtain materials with high performance, it is critical to consider their microstructures. Using scientific data regarding microstructures and the results of simulations and theoretical models, we can estimate the characteristics and performances of materials being developed. With the help of appropriate databases, time and cost savings are achieved by determining the microstructural conditions necessary for specific applications and performances [3].
Issues that affect the microstructure of a material include the process of solidification and whether the material is compound produced [3]. Solidification is the process by which the composition of the material (Co), temperature gradient (G), and growth rate (V) can be independently controlled. Based on these solidification parameters (Co, G and V), the micro- structural values of materials (e.g., eutectic distance, distance between the lamellae or lamellar distance, and distance between the dendrites) will vary, as will their mechanical, electrical, and thermal characteristics [4]. When examining alloys, the growth rate of the alloys during solidification is a more effective indicator than the temperature gradient [5-7]. Therefore, in this study, we investigated the changes in growth rates.
To determine the effect of the solidification parameters on the microstructures of the materials, researchers have and continue to conduct various experimental studies. In most of these studies, to enable independent control of the temperature gradient and the growth rate, Bridgman-type solidification furnaces were used [2,4-17]. The Bridgman-type solidification is a reliable method in which changes in the mechanical characteristics of alloys can be observed by controlling the solidification process at different temperature gradients and growth rates in samples prepared with the desired compositions for use in metallic alloys, especially in the automotive and aircraft industries.
In recent years, due to their corrosion resistance, low density, electrical and thermal conductivity, and easy formability, aluminum and aluminum alloys of eutectic and near-eutectic compositions have been widely employed in the industrial casting, soldering, and welding processes [18,19]. Despite the advantages of using aluminum and aluminum alloys in industrial applications, they also have problems such as low strength and unstable mechanical characteristics. To improve these properties, it is essential to trace the relationships that link the solidification parameters with the eutectic microstructure. Previous research on eutectic growth has enabled the establishment of experimental relationships [20-26]. To overcome the abovementioned problems, we conducted controlled linear solidification experiments on the AlCuFe alloy at a constant temperature gradient and five different growth rates. To clearly determine the dependence of the mechanical characteristics of the AlCuFe alloy on the solidification conditions, a eutectic composition was desired. In this study, the goal was to investigate the change in the mechanical properties of the AlCuFe eutectic alloy with combinations of two or more solid phases initiated simultaneously from the melted alloy [27] to achieve optimized features. The eutectic compositions in the theoretical models were used to evaluate the results obtained in the experiments. In addition to the eutectic composition, microstructures also constitutes another study subject [28,29].
The purpose of this study is the investigation of the changes in the eutectic spacing (λ), microhardness (HV), and ultimate tensile strength (σb) of the Al-32.5wt.%Cu-0.5wt.%Fe eutectic alloy based on the rate of solidification. The relationships among the experimental properties were obtained by comparing the linear regression analysis results and Hall–Petch-type correlations obtained from the experiments.
2 Experimental
2.1 Directional solidification and metallography
The number of elements was determined via stoichiometric calculations from the phase diagram of the Al-32.5wt.%Cu-0.5wt.%Fe eutectic alloy. The amounts of the Alfa Aesar aluminum and copper elements of 99.99% in purity and iron elements of 99.97% in purity were determined and weighed by a precision scale and were then placed in turn into a graphite crucible in a vacuum melting furnace. After vacuum melting the aluminum, copper, and iron elements in an oven without oxidation, the mixture was stirred at intervals using a graphite rod to homogenize the alloy. The homogenized alloy was then cast in the casting furnace into 10 cylindrical graphite molds with a height of 200 mm, an inner diameter of 4 mm and an outer diameter of 6.35 mm. In the casting furnace, the molds were completely filled with no air bubbles remaining after casting the melted alloy into the specialized graphite crucibles. The amount of alloy poured into each mold was approximately 7.5 g. The samples were then ready for the controlled solidification experiments.
Each of the prepared graphite crucibles was placed into the Bridgman furnace (Fig. 1) to undergo unidirectionally controlled solidification at a constant temperature gradient (G=8.50 K/mm) at five different growth rates (V=8.25-164.80 μm/s). After a sufficient amount of time (approximately 2 h) had passed to ensure a constant temperature gradient in the sample in the Bridgman furnace, the solidification of each sample was controlled via synchronized motors from the hot to the cold areas, as shown in Fig. 1(b). Details of the Bridgman directional solidification furnace are shown in Fig. 1, and related experimental procedures are described in Refs. [30-35].
After 100-120 mm of controlled solidification was obtained in each sample, they were moved quickly to the cold area independent of the synchronized motor for rapid cooling (quenching). After completing the controlled solidification experiments of each sample, the 10–12 mm part closest to the solid–liquid interface of the sample was cut out using a Struers Minitom cutting device and diamond cutter disc. The cut samples were mounted in epoxy resin. To determine the microstructures of the samples and capture their images microscopically, the samples were prepared using SiC paper and metallographic polishing procedures and a Struers TegraPol-15 device. To enable observation of the sample microstructures, they were etched for 10-15 s by a solution prepared with 5 mL of hydrofluoric acid and 95 mL of water.
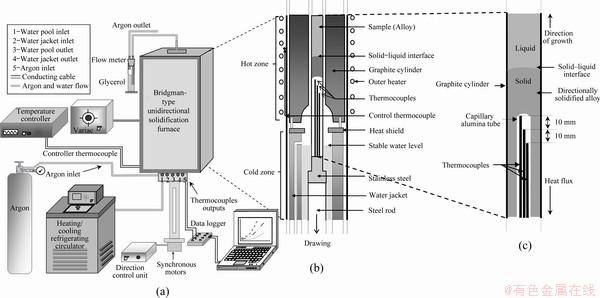
Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of experimental setup (a) details of Bridgman-type directional solidification furnace, hot and cold zones (b), and details of sample (c) [5-7]
2.2 Observation of microstructure and measurement of solidification parameters
Before the start of the sample solidification process in the Bridgman furnace, three K-type thermocouples with 0.25 mm in diameter were placed in the samples, with which the temperature gradients and growth rates were obtained using a data–logger via computer throughout the experiment (Fig. 1(c)). The temperature gradient of the liquid phase (G=ΔT/ΔX) and the solidification speed of the solid–liquid interface (V=ΔX/Δt) were calculated for each sample by determining the ΔT, ΔX and Δt values, i.e., the temperature measured by the thermocouples, the distance between the thermocouples, and the time required by the solid–liquid interfaces to cover the distance between two thermocouples, respectively. Details of the measurements of △T, △X and △t are provided in Refs. [12,30-35].
The microstructures of each of the samples subjected to controlled solidification in the Bridgman furnace were determined using a LEO model scanning electron microscope (SEM) to obtain images of their horizontal and vertical cross sections. To determine each of the phases observed in the samples with eutectic microstructures, as determined by SEM, energy dispersive X-ray (EDX) analyses were performed.
From the images obtained at different magnifications for each sample, the eutectic spacing (λ), which is defined as the total width of the repeated phases in the ordered structures placed side by side, was measured using Image ProPlus software, as shown in Fig. 2. This is known as the linear intercept method. The reliability of the measurements was ensured by repeating the measurement process at least 30 times and taking the average value [36].
2.3 Measurement of microhardness and ultimate tensile strength
One purpose of this study was to determine the effects of the growth rate, which changes the microstructure of the samples, on the mechanical characteristics. To do so, after directional solidification and metallographic investigation of the AlCuFe alloy prepared in a eutectic composition, the microhardness value of each sample was determined using a Future-Tech FM-700 model Vickers hardness measurement device based on a 40-60 μm indentation depth after application of a 500 g load for 10 s. The reliability of the measurement was ensured by repeating this process at least 20 times and taking the average value.
In the cylindrical samples that had been directionally solidified at five different growth rates, which measured 4 mm in diameter and 50 mm in length, their ultimate tensile strengths were determined using a Shimatzu universal testing instrument, which applied a tension for 1×10-3 s. The reliability of the measurements was ensured by repeating this process at least three times and taking the average value.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Effect of growth rate on eutectic spacing
As shown in Fig. 3, the microstructure of the Al-32.5wt.%Cu-0.5wt.%Fe eutectic alloy included a regularly ordered matrix Al, white lamellar Al2Cu, and white plate Al7Cu2Fe intermetallic phases. This regular structure indicates that all the phases have low entropy close to the solid-liquid interface, which grows simultaneously via undercooling after nucleation begins. The temperature gradient in the liquid phase near the solid–liquid interface during the process of solidification facilitates the preservation or maintenance of the microstructures in the solid phase.
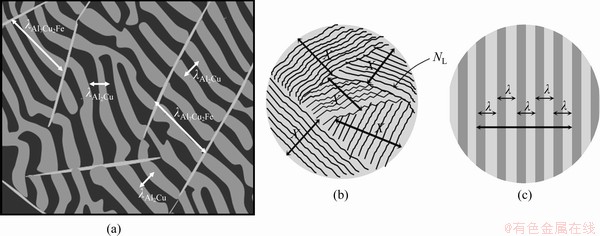
Fig. 2 Measurement of interlamellar spacings for directionally solidified AlCuFe eutectic alloy (a), and schematic views in wide (b) and narrow (c) area (Linear intercept method: λ=X/(NL-1), where X is the total length of lamella and NL the total number of lamella in the area)
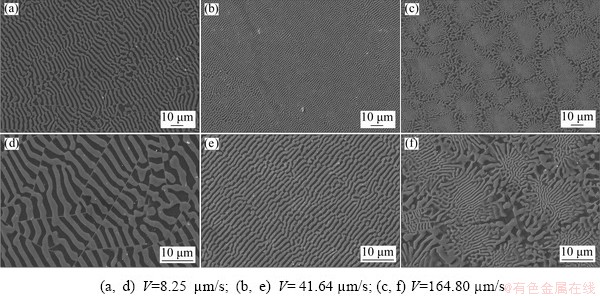
Fig. 3 Typical SEM images of growth morphologies on transverse section of directionally solidified AlCuFe eutectic alloy with different growth rates at constant temperature gradient (G=8.25 K/mm)
The solid solubility of the copper in aluminum is about 5.65% at the eutectic temperature (548 °C). The solid solubility of iron in aluminum is low, approximately 0.03% at the eutectic temperature (655 °C) [37]. According to the EDX results shown in Fig. 4, the components in each phase were identified as the Al2Cu and Al7Cu2Fe intermetallic phases and the Al matrix phase.
The results of the directional solidification experiments, as shown in Fig. 3, reveal that the eutectic spacing (λ) decreased as the growth rate increased, and even the grain boundaries or colonies appeared at high growth rates. In addition, the lamellae became irregular as they thickened around these boundaries.
The eutectic spacing at different growth rates was determined based on the ordered areas in the grains. The highest eutectic spacing values were obtained at the lowest growth rate (V=8.25 μm/s), and the lowest eutectic spacing values were obtained at the highest growth rate (164.80 μm/s).
Using the obtained data, linear regression analysis was performed to fully reveal the relationship between the eutectic spacing and growth rate. As shown in Fig. 5, the relationship between the eutectic spacing and growth rate can be expressed as follows:
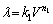 (1)
(1)
where k1 is an equation constant and n1 is the exponential value of the growth rate. The value of n1 must be considered in the results, which is obtained by the logarithmic plot. For alloys that display a regular microstructure based on the Jackson–Hunt theoretical model, this value must be 0.50 [38]. For the AlCuFe eutectic alloy, the values obtained were 0.52 and 0.48, which are very similar to those obtained by the Jackson–Hunt theoretical model.
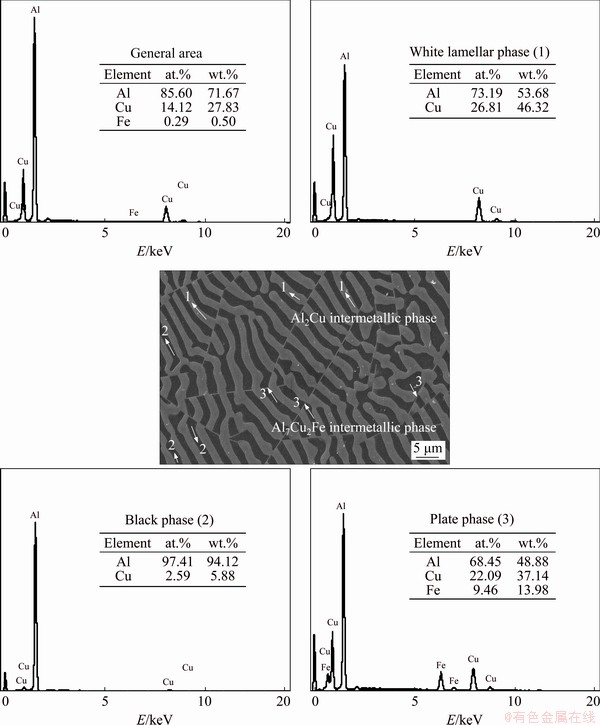
Fig. 4 Chemical composition analysis of AlCuFe eutectic alloy by using SEM and EDX (The black phase is Al, white lamellar phase is Al2Cu, and plate phase is Al7Cu2Fe intermetallics)
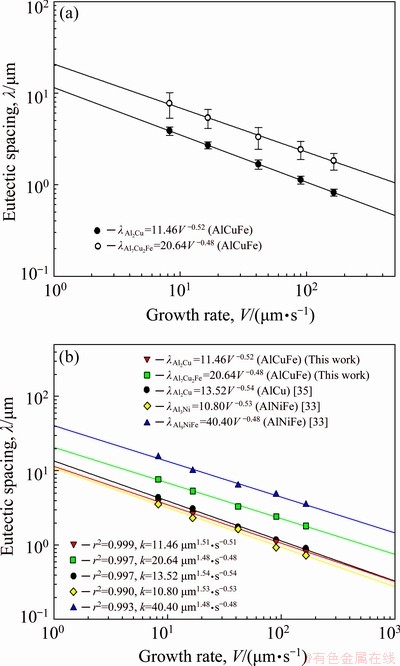
Fig. 5 Variation of eutectic spacing as function of growth rate at constant temperature gradient (G=8.50 K/mm) for ternary AlCuFe eutectic alloys (a) and comparison with ternary AlNiFe and binary AlCu eutectic alloys (b)
The obtained n1 values (0.52 and 0.48) for the AlCuFe eutectic alloy are in good agreement with 0.53 obtained by ENGIN and BüYüK [35] for binary AlCu, 0.53-0.48 obtained by ENGIN et al [33] for ternary AlNiFe, and 0.49, 0.50 and 0.49 obtained by BOYüK et al [39] for the ternary AlCuAg eutectic alloy.
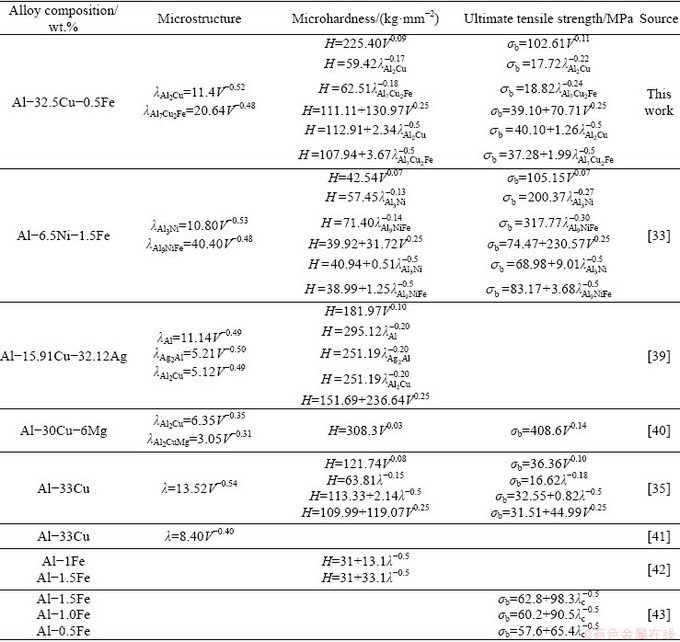
However, the n1 values of 0.52 and 0.48 obtained in this study differ significantly from those (0.35 and 0.31) obtained by KAYGISIZ and MARASLI [40] for the ternary AlCuMg alloy. This is because the 0.50 value was determined for regular eutectic structures, and is not applicable to dendritic microstructures or irregular eutectic structures. When an alloy is not prepared in a eutectic composition, the resulting dendritic microstructures may deviate from those of the theoretical model. Table 1 gives the results of similar previous experiments [33,35,39-43].
The eutectic structures occurred in the Al2Cu lamellar phases between the Al7Cu2Fe plate phases at the lowest growth rate (V=8.25 m/s and G=8.50 K/mm) in the direction of heat flow along the entire sample.
Expansion of the growth rate ranges used in this study could result in unconventional morphologies, including degenerate eutectic, limited, and even amorphous structures [28,29]. Therefore, we used growth rates in the range of 8.25-164.80 μm/s at a constant temperature gradient of 8.50 K/mm to clearly reveal the microstructure formation and its effect on the mechanical properties. In addition, for the AlCuFe eutectic alloy, the growth rate that causes a change in the microstructure has been determined and synchronous motors at fixed speeds are preferred for accurate comparison with similar eutectic alloys. The criterion that determines the constant temperature gradient for the AlCuFe eutectic alloy is the temperature at which the hot zone of the Bridgman furnace is kept constant. We selected the temperature at which the AlCuFe eutectic alloy is completely melted, at which a controlled linear solidification of approximately 10 cm is obtained.
When the growth rate is increased, the Al7Cu2Fe plate phases shorten, and the Al2Cu lamella phases become more prevalent (see Fig. 3(d)). In this study, colonies were observed in the microstructures obtained at the highest growth rate (V=164.80 m/s and G=8.50 K/mm), as shown Fig. 3(f). These microstructures are mainly composed of lamellar phases at the center of the colonies with coarse eutectics at the boundary. DREVET et al [44] referred to this as a micro- structural defect explained by the transient nature of the solidification process, which requires a continuous increase in eutectic density via a nucleation mechanism. In this state, deviations of the chemical balance at the solid–liquid interface have been found to lead to unstable growth conditions [27,44-46].
Table 1 Comparison of values of microstructure, microhardness and ultimate tensile strength for directionally solidified AlCuFe eutectic alloys at constant temperature gradient
Al2Cu lamellar and Al7Cu2Fe plate phases simultaneously grew in the Al matrix using the Bridgman-type linear solidification technique and were distributed uniformly throughout the material (see Fig. 3). Colonies in the AlCuFe eutectic alloy began to form at a growth rate of <90 m/s (see Figs. 3(e, f)). Coarse eutectic phases were observed at the colony boundaries, which may partially benefit the ductility, but the resulting finer colonies may be involved in the distribution of shear stress, which affects the mechanical properties.
The transition from a cellular to plate-like structure in each alloy system occurs at different growth rates. For example, for the AlCu eutectic alloy, the transition growth rate from a lamellar to platelet structure was determined to occur at <40 μm/s, whereas for the AlCuFe alloy it occurred at <90 μm/s (Fig. 3) [35]. This clearly shows that the Fe element delays transition of the microstructure morphology. The physical and chemical properties of the element (e.g., density, atomic dimensions, and binding properties with other elements) contribute to the change in the microstructural transition growth rate of the alloy [28,29].
3.2 Effect of growth rate on microhardness and ultimate tensile strength
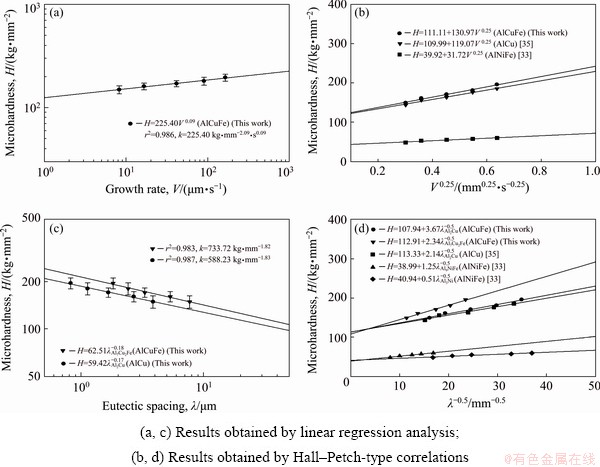
Fig. 6 Variation of microhardness as function of growth rate (a, b) and eutectic spacing (c, d) for directionally solidified AlCuFe eutectic alloy at constant temperature gradient, and comparison with previous similar experimental results
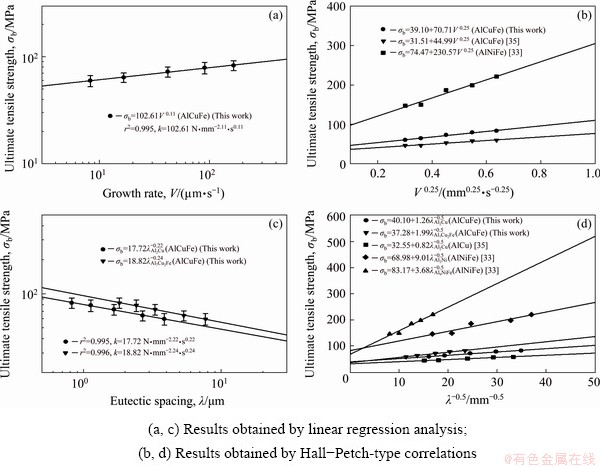
Fig. 7 Variation of ultimate tensile strength as function of growth rate (a, b) and eutectic spacing (c, d) for directionally solidified AlCuFe eutectic alloy at constant temperature gradient, and comparison with previous similar experimental results
Figures 6 and 7 reveal that the microhardness and ultimate tensile strength both increased as the growth rate increased. The relationship between the microhardness of the eutectic structures and the growth rate may be expressed as follows:
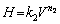 (2)
(2)
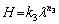 (3)
(3)
The relationship between the ultimate tensile strength and the eutectic spacing and growth rate parameters may be expressed as follows:
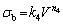 (4)
(4)
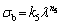 (5)
(5)
where k2, k3, k4 and k5 are the equation constants, while n2, n3, n4, and n5 are the exponential values of growth rate and eutectic spacing, respectively.
An exponential value of 0.09 was obtained by linear regression analysis and used to determine the relationship between microhardness and growth rate, whereas values of 0.17 and 0.18 were obtained by regression analysis and used to determine the relationship between microhardness and eutectic spacing. As given in Table 1, in work by other researchers, the values obtained by linear regression analysis and used to express the relationship between growth rate and microhardness have ranged from 0.03 to 0.10 [33,35,39,40]. The exponential value of 0.09 obtained in this study for the growth rate, as shown in Fig. 6, is in agreement with the values reported for similar studies. The values obtained by linear regression analysis to express the relationship between eutectic spacing and microhardness have ranged from 0.13 to 0.20 [33,35,39]. The exponential values of 0.17 and 0.18 obtained in this study for eutectic spacing, as shown in Fig. 6, are in agreement with those reported for similar studies. As is evident from these results, despite using approximately the same growth rate, the values obtained in different studies differed because the eutectic spacing changed with the composition (eutectic, hypoeutectic, or hyper- eutectic) and characteristics (lamellar, rod-like, cellular, or flake-like) of the alloy.
The results obtained for ultimate tensile strength were similar to those obtained for micro- hardness. In Fig. 7, it is clear that the ultimate tensile strength increased with increases in the growth rate. The obtained exponential value of 0.11, based on the linear regression analysis, was used to determine the relationship between ultimate tensile strength and growth rate. However, the values of 0.22 and 0.24 obtained based on the regression analysis were used to determine the relationship between the ultimate tensile strength and eutectic spacing. From the values given in Table 1, we know that the values obtained by linear regression analysis, which express the relationship between the growth rate and ultimate tensile strength, have ranged from 0.07 to 0.14 [33,35,40]. In this study, the exponential value obtained for the growth rate was 0.11, as shown in Fig. 7, which is in agreement with the values reported by similar studies. Similarly, the values obtained by linear regression analysis to express the relationship between the eutectic spacing and microhardness have ranged from 0.18 to 0.30 [33,35,40]. The exponential values of 0.22 and 0.24 obtained in this study for eutectic spacing, as shown in Fig. 7, are in agreement with those reported by similar studies.
Another type of analysis that defines the relationship between microhardness and the eutectic spacing and growth rate parameters is the Hall-Petch-type correlation, which can be expressed as follows:
H=H0+k6V0.25 (6)
H=H0+k7λ-0.50 (7)
Hall-Petch-type correlations used to indicate the relationship between ultimate tensile strength and the eutectic spacing and growth rate parameters may be expressed as follows:
σb=σb0+k8V0.25 (8)
σb=σb0+k9λ-0.50 (9)
where H0 is the microhardness of the solid phase in balance with the liquid phase at the melting temperature, σb0 is the initial ultimate tensile strength of the solid phase in balance with the liquid phase at the melting temperature, and k6, k7, k8 and k9 are equation constants.
Hall-Petch-type correlations clearly express the relationships among the eutectic spacing, growth rate and microhardness. The values of 111.11, 112.91 and 107.94 kg/mm2 enable us to define the relationships among microhardness, growth rate, and eutectic spacing, respectively, Furthermore, the H0 values for the eutectic spacing and growth rate are similar. In Table 1, we see that the values of 111.11, 112.91 and 107.94 kg/mm2 obtained based on the Hall–Petch-type correlations indicate the initial hardness of the equilibrated solid eutectic phases in equilibrium with the liquid phase of the AlCuFe eutectic alloy at the melting temperature. These values ranged from 31 to 251.19 kg/mm2, which are similar to the values obtained for similar studies [33,35,39].
When we compare the experimental results obtained for the AlCuFe eutectic alloy with those obtained elsewhere [35] for the AlCu eutectic alloy, it is evident that small changes in the amount of alloying elements used in the composition affects the microhardness value (Table 1). The intermetallic phases and arrays that occur may change the microhardness value. A study of the AlCuMg [40] eutectic alloy obtained a colony growth rate >45 μm/s at a constant temperature gradient and microhardness values that were higher than those of the AlCuFe eutectic alloy. The increasing growth rate did not change the eutectic array in the AlCuMg [40] eutectic alloy, although it did decrease the eutectic spacing of the intermetallic phases in the colonies. However, the added Cu element provides a higher ultimate tensile strength than that of the AlFe [42].
The Hall-Petch-type correlations also clearly indicate the relationships among the eutectic spacing, growth rate, and ultimate tensile strength. The values of 39.10, 40.10 and 37.28 MPa enable the relationships among the ultimate tensile strength, growth rate, and eutectic spacing to be defined, respectively, and the σb0 values for the eutectic spacing and growth rate are similar. As shown in Table 1, the values 39.10, 40.10 and 37.28 MPa obtained by the Hall–Petch-type correlations indicate that the initial ultimate tensile strength of the equilibrated solid eutectic phases in equilibrium with liquid in the AlCuFe eutectic alloy at its melting temperature ranged from 31.51 to 83.17 MPa, which agree with those obtained in similar studies [33,35,43].
The chemical composition, growth rate, microstructure, and properties of the material are interrelated with and thus influence each other. When the chemical components of the material are fixed, control of the solidification microstructure has played the main role [47,48]. Generally, a fine microstructure in alloys indicates higher strength, i.e., when the grains are thin, more grains will form in the material. Thus, plastic deformation, which occurs due to external forces, is distributed uniformly and carried by more grains. As a result, the mechanical properties can be fixed by means of the microstructural mechanism.
4 Conclusions
(1) Even though the growth rate increased by approximately 20 times, eutectic spacings of Al2Cu and Al7Cu2Fe phases decreased. This resulted in increased microhardness and ultimate tensile strength of the solidified samples.
(2) Eutectic spacings dependent on growth rate are given by λAl2Cu=11.46V-0.52 and λAl7Cu2Fe= 20.64V-0.48.
(3) Linear regression analyses represent the evolution of experimental microhardness and ultimate tensile strength against the growth rate: H=124.74V0.09,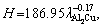 H=214.17
H=214.17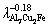 and σb=47.06V0.11,
and σb=47.06V0.11,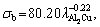
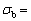
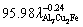 .
.
(4) Hall-Petch-type correlations were shown to represent the evolution of experimental microhardness and ultimate tensile strength against growth rate: H=111.11+130.97V0.25, H=112.91+ 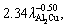
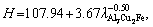 and σb=39.10+ 70.71V0.25,
and σb=39.10+ 70.71V0.25,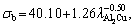 σb=37.28+
σb=37.28+ 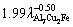 .
.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported financially by the Scientific and Technical Research Council of Turkey (TUBITAK) under Contract No. 112T588. The author is grateful to the Scientific and Technical Research Council of Turkey (TUBITAK) for its financial support.
References
[1] BOETTINGER W J, CORiELL S R, GREER A L, KARMA A, KURZ W, RAPPAZ M, TRiVEDi R. Solidification microstructures: Recent developments, future directions [J]. Acta Materialia, 2000, 48: 43-70.
[2] JONES H. Some effects of solidification kinetics on microstructure formation in aluminium-base alloys [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2005, 413-414: 165-173.
[3] HECHT U, GRANASY L, PUSZTAI T, BOTTGER B, APEL M, WITUSIEWICZ V, RATKE L, de WILDE J, FROYEN L, CAMEL D, DREVET B, FAIVRE G, FRIES S G, LEGENDRE B, REX S. Multiphase solidification in multicomponent alloys [J]. Materials Science and Engineering R:Reports, 2004, 46: 1-49.
[4] KAYGISIZ Y. Effect of growth velocities on microstructure and mechanical properties of eutectic Al-Si-Mg-Ni-(Fe) alloy [J]. Materials Research Express, 2019, 6(6): 066510.
[5] CADIRLI E, BOYUK U, ENGiN S,KAYA H, MARASLI N, ARI M. Investigation of microhardness and thermo- electrical properties in the Sn-Cu hypereutectic alloy [J]. Journal of Materials Science-Materials in Electronics, 2010, 21(5): 468-474.
[6] LIU G H, Li X Z,ZHANG Y,CHEN R R,SU Y Q, GUO J J, FU H Z, WANG Z D, WANG G D. Effect of growth rate and diameter on microstructure and hardness of directionally solidified Ti-46Al-8Nb alloy [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2014, 24: 4044-4052.
[7] MiN Z X, SHEN J, WANG L S, LiU L. Effect of traveling magnetic field on dendrite growth of Pb-Sn alloy during directional solidification [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2011, 9: 1976-1980.
[8] QU Min, LIU Lin, CUI Yan, LIU Feng-bin. Interfacial morphology evolution in directionally solidified Al-1.5%Cu alloy [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2015, 25: 405-411.
[9] MILLER J D, POLLOCK T M. Stability of dendrite growth during directional solidification in the presence of a non-axial thermal field [J]. Acta Materialia, 2014, 78: 23-36.
[10] LI X, REN Z, FAUTRELLE Y. Effect of a high axial magnetic field on the microstructure in a directionally solidified Al-Al2Cu eutectic alloy [J]. Acta Materialia, 2006, 54: 5349-5360.
[11] WALKER H, SHAN L, LEE J H, TRIVEDI R. Eutectic growth in three dimensions [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2007, 38: 1417-1425.
[12] KAYA H, ENGiN S, BOYüK U, CADIRLI E, MARASLI N. Unidirectional solidification of Zn-rich Zn-Cu hypoperitectic alloy [J]. Journal of Materials Research, 2009, 24(11): 3422-3431.
[13] ENGIN S, BüYüK U, KAYA H, MARASLI N. Directional solidification and physical properties measurements of the zinc-aluminum eutectic alloy [J]. International Journal of Minerals Metallurgy and Materials, 2011, 18: 659-664.
[14] KOCAK Y, ENGIN S, BOYUK U, MARASLI N. The influence of the growth rate on the eutectic spacings, undercoolings and microhardness of directional solidified bismuth-lead eutectic alloy [J]. Current Applied Physics, 2013, 13(3): 587-593.
[15] LIU D, ZHANG H W, LI Y X,CHEN X, LIU Y. Effects of composition and growth rate on the microstructure transformation of beta-rods/lamellae/alpha-rods in directionally solidified Mg-Li alloy [J]. Materials & Design, 2017, 119: 199-207.
[16] WANG J A, WANG J H, SONG Z X. Microstructures and microsegregation of directionally solidified Mg-1.5Gd magnesium alloy with different growth rates [J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2017, 46(1): 12-16.
[17] LI K, XIONG F H, CHEN G Y, ALI W, LU X G, LI C H. Directional solidification of Ti-46Al-8Nb alloy in BaZrO3 coated Al2O3 composite mould [J]. Intermetallics, 2018, 102: 106-113.
[18] STEFANESCU D M, ABBASCHIAN G J, BAYUZICK R J. Solidification processing of eutectic alloys [M]. Warrendale: Metallurgical Society, 1988.
[19] CAMPBELL J. Castings [M]. 2nd ed. Butterworth- Heinemann, 2003.
[20] SILVA B L, GARCIA A, SPINELLI J E. Complex eutectic growth and Bi precipitation in ternary Sn-Bi-Cu and Sn-Bi-Ag alloys [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2017, 691: 600-605.
[21] ELLIOT R. Eutectic solidification [J]. International Metals Reviews,1997, 22: 161-86.
[22] TILLER W A. Liquid metals and solidification [M]. Cleveland: ASM, 1958.
[23] REYES R V, BELLO T S, KAKITANI R, COSTA T A, GARCIA A, CHEUNG N, SPINELLI J E. Tensile properties and related microstructures aspects of hypereutectic Al–Si alloys directionally solidified under different melt superheats and transient heat flow conditions [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2017, 685: 235-243.
[24] KAYA H, CADIRLI E, GüNDüZ M, ULGEN A. Effect of the temperature gradient, growth rate, and the interflake spacing on the microhardness in the directionally solidified Al-Si eutectic alloy [J]. Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 2003, 12: 544-551.
[25] HOSCH T, ENGLAND L G, NAPOLITANO R E. Analysis of the high growth-rate transition in Al-Si eutectic solidification [J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2009, 44: 4892-4899.
[26] KAKITANI R, REYES R V, SPINELLI J E, CHEUNG N, GARCIA A. Relationship between spacing of eutectic colonies and tensile properties of transient directionally solidified Al-Ni eutectic alloy [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2018, 733: 59-68.
[27] KAKITANI R, REYES R V, GARCIA A, SPINELLI J, CHEUNG N. Relationship between spacing of eutectic colonies and tensile properties of transient directionally solidified Al-Ni eutectic alloy [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2018, 733: 59-68.
[28] RAMOS L S, REYES R V, GOMES L F, GARCIA A, SPINELLI J E, SILVA B L. The role of eutectic colonies in the tensile properties of a Sn-Zn eutectic solder alloy [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2020, 776: 138959.
[29] KAKITANI R, GOUVEIA G L, GARCIA A, CHEUNG N, SPINELLI J E. Thermal analysis during solidification of an Al-Cu eutectic alloy: Interrelation of thermal parameters, microstructure and hardness [J]. Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, 2019, 137: 983-996.
[30] ASTA M, BECKERMANN C, KARMA A, KURZ W, NAPOLITANO R, PLAPP M, PURDY G, RAPPAZ M, TRIVEDI R. Solidification microstructures and solid-state parallels: Recent developments, future directions [J]. Acta Materialia, 2009, 57: 941-971.
[31] BERTELLI F, FREITAS E S, CHEUNG N, ARENAS M A, CONDE A, de DAMBORENEA J, GARCIA A. Microstructure, tensile properties and wear resistance correlations on directionally solidified Al-Sn-(Cu; Si) alloys [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2017, 695: 3621-3631.
[32] BERKDEMIR A, GüNDüZ M. Effect of growth rate and Mg content on dendrite tip characteristics of Al-Cu-Mg ternary alloys [J]. Applied Physics A, 2009, 96(4): 873-886.
[33] ENGiN S, BüYüK U, MARASLI N. The effects of microstructure and growth rate on microhardness, ultimate tensile strength, and electrical resistivity for directionally solidified Al-Ni-Fe alloys [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2016, 660: 23-31.
[34] CADIRLI E, BüYüK U, ENGiN S, KAYA H. Effect of silicon content on microstructure, mechanical and electrical properties of the directionally solidified Al-based quaternary alloys [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2017, 694: 471-479.
[35] ENGiN S, BüYüK U. Variations with growth rate of the microstructural, mechanical and electrical properties of directionally solidified the Al-Cu alloy [J]. Journal of Science and Technology Institute, 2018, 8(2): 209-221. (in Turkish)
[36] OURDJINI A, LIU J, ELLIOTT R. Eutectic spacing selection in Al-Cu system [J]. Materials Science and Technology, 1994, 10: 312-318.
[37] MONDOLFO L F. Metallography of aluminum alloys [M]. New York: John Wiley & Sons, Inc, 1943: 77.
[38] JACKSON K A, HUNT J D. Lamellar and rod eutectic growth [J]. Transactions of the Metallurgical Society of AIME,1966, 236: 1129-1142.
[39] BOYüK U, MARASLI N, KAYA H, CADIRLI E, KESLIOGLU K. Directional solidification of Al-Cu-Ag alloy [J]. Applied PhysicsA, 2009, 95: 923-932.
[40] KAYGISIZ Y, MARASLI N. Microstructural, mechanical, and electrical characterization of directionally solidified Al-Cu-Mg eutectic alloy [J]. Physics of Metals and Metallography, 2017, 1184: 389-398.
[41] CADIRLI E, üLGEN A, GüNDüZ M. Directional solidification of the aluminium-copper eutectic alloy [J]. Materials Transactions JIM, 1999, 40(9): 989-996.
[42] SILVA B L, GARCIA A, SPINELLI J E. The effects of microstructure and intermetallic phases of directionally solidified Al-Fe alloys on microhardness [J]. Materials Letters, 2012, 89: 291-295.
[43] GOULART P R, SPINELLI J E, CHEUNG N, GARCIA A. The effects of cell spacing and distribution of intermetallic fibers on the mechanical properties of hypoeutectic Al-Fe alloys [J]. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2010, 119: 272-278.
[44] DREVET B, CAMEL D, DUPUY M, FAVIER J J. Microstructure of the Sn-Cu6Sn5 fibrous eutectic and its modification by segregation [J]. Acta Mater, 1996, 44: 4071-4084.
[45] HAN S H. Stability of a eutectic interface during directional solidification [D]. Iowa State University, 1995: 143.
[46] FARAG M M, TAHA M A. The structure and strength of unidirectionally solidified commertial purity Al-Ni composites [C]//Proceedings of the Conference on In Situ Composites. National Academy of Sciences, Washington, D.C., 1973: 297-307.
[47] SHANG Z. Microstructures and mechanical properties of directionally solidified NiAl-Cr(Mo) alloy under high temperature gradient [D]. Xi’an: Northwestern Polytechnical University, 2015.
[48] REN Q, SU H J, ZHANG J, YAO B, MA W D, LIU L, FU H Z, HUANG T W, GUO M, YANG W C. Solid-liquid interface and growth rate range of Al2O3-based eutectic in situ composites grown by laser floating zone melting [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2016, 662: 634-639.
Sevda ENGIN
Department of Energy Systems Engineering, Faculty of Technology, Kütahya Dumluplnar University, Kütahya, Turkey
摘 要:制备特殊用途的AlCuFe合金,评估生长速率变化导致的结果,因为材料生长速率不同而引起的共晶间距(显微组织)的变化会影响其力学、电和热性能。为了研究AlCuFe合金的显微组织,在恒定的温度梯度(G=8.50 K/mm)和5种不同的生长速率(V=8.25, 16.60, 41.65, 90.05, 164.80 μm/s)下,通过定向凝固法制备共晶成分的Al-32.5%Cu-0.5%Fe(质量分数)合金。得到生长速率对共晶间距影响,并通过对显微组织变化的回归分析及Hall-Petch关系得出显微硬度和极限拉伸强度。结果表明,尽管生长速率增加约20倍,但共晶间距却减少约5个数量级,而生长速率和显微组织变化导致的力学性能变化约为1.5个数量级。
关键词:定向凝固;铝合金;显微组织;抗拉强度;硬度
(Edited by Bing YANG)
Corresponding author: Sevda ENGiN; E-mail: sevda.engin@dpu.edu.tr
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(20)65453-X

