DOI:10.19476/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2019.10.12
SPS烧结温度对NiTi/表面多孔Ti梯度合金组织和性能的影响
邓 霞1, 2,何远怀1, 2,焦美琪1, 2,张玉勤1, 2, 3,蒋业华1, 2
(1. 昆明理工大学 材料科学与工程学院,昆明 650093;
2. 金属先进凝固成形及装备技术国家地方联合工程实验室,昆明 650093;
3. 云南省钛材应用产品工程技术研究中心,楚雄 651209)
摘 要:利用放电等离子烧结技术制备NiTi/表面多孔Ti梯度合金,研究不同烧结温度对梯度合金微观组织、表面孔隙特征、力学性能及体外生物活性的影响及机理。结果表明:随着烧结温度的升高,梯度合金组织由NiTi、α-Ti、Ni、Ti2Ni、Ni3Ti混合相逐渐转变为单一NiTi和α-Ti相,内外层界面形成良好冶金结合,表面孔隙率和平均孔径呈缓慢减小趋势;同时抗压强度值快速增大而弹性模量值变化不大;1000 ℃制备的梯度合金不仅具有良好的表面孔隙特征(孔隙率35.8%、平均孔径423 μm)、较高的抗压强度(632 MPa)、较低的弹性模量(9 GPa)及优异的超弹性行为(超弹性恢复应变>4%),而且体外生物活性显著提高。
关键词:NiTi梯度合金;烧结温度;微观组织;力学性能;体外生物活性
文章编号:1004-0609(2019)-10-2312-09 中图分类号:TB331 文献标志码:A
近等原子比的NiTi合金不仅具有较高的强度、较低的弹性模量、良好的抗腐蚀性和生物相容性,而且具有优异的形状记忆性能和超弹性,因而在牙科、骨科、介入治疗、心内科、耳鼻喉科以及妇科等医学领域中得到了广泛应用[1-3]。但是在临床应用中发现,NiTi合金的弹性模量(55 GPa左右)与人骨弹性模量(3~20 GPa)相比仍然存在不匹配现象,植入人体后容易在骨组织-植入物界面处产生应力-屏蔽效应,导致材料松动或断裂[4];同时由于合金属于生物惰性材料,与人体组织之间难以形成骨性结合,会降低植入体的使用寿命。相关研究表明[5-8],钛合金多孔化处理可使其弹性模量显著降低,且多孔结构可以促进骨组织向内生长和血管化,生物活性明显提高,容易形成稳定的生物固定(骨整合)[9-13];然而多孔化也会导致合金的强度显著下降,无法在人体高承载部位使用,限制了其应用范围。针对以上问题,本文设计了NiTi/表面多孔Ti梯度合金,中间为块体合金,周围为多孔层。中间基体NiTi合金保障材料优异的力学性能、耐蚀性能和生物相容性,表面多孔Ti层可以为材料提供良好的生物活性,这种形式为改善和解决NiTi合金在临床应用中存在的问题提供新的途径。
放电等离子烧结(Spark plasma sintering,SPS)技术具有烧结温度低、升降温速度快(100 ℃/min 以上)、烧结时间短、可以产生温度梯度等独特优势[14],不仅能实现梯度合金的一次成形,而且可以获得良好的界面结合。因此,在前期获得SPS技术制备NiTi/表面多孔梯度NiTi、NiTi-HA材料的基础上[14-15],本文采用SPS技术制备了NiTi/表面多孔Ti梯度合金,研究了不同烧结温度对梯度合金微观组织、表面孔隙特征、力学性能及体外生物活性的影响及机理。
1 实验
实验原料为Ni粉(纯度99.7%,平均粒径30 μm)、Ti粉(纯度99.5%,平均粒径25 μm)及NH4HCO3造孔剂(纯度AR,粒径<300 μm)。NiTi/表面多孔Ti梯度合金制备过程:首先按质量比55.07:44.93称取Ni粉与Ti粉,将粉末放入球磨罐中,按球料比3:1加入不锈钢球,再加入无水乙醇并抽真空1 h,在行星式球磨机上以300 r/min速度球磨混粉10 h;球磨后的粉末经40 ℃烘干得到NiTi混合粉末;同时在Ti粉中加入15%(质量分数)的NH4HCO3造孔剂并混合均匀;然后依次将得到的NiTi和Ti-NH4HCO3混合粉末分别装填入模具套筒的内层和外层(见图1),套筒内层尺寸为直径5 mm×140mm、外层尺寸为直径15 mm×140 mm,在压力试验机上整体压制成型;最后将压制成型的坯体装入石墨模具中,在放电等离子烧结设备(SPS-515S,Japan)上进行烧结成形。烧结工艺为:按100 ℃/min的速度升温至所需烧结温度,保温5 min后随炉冷却,系统真空度为2~10 Pa,所用石墨模具为异形模具,以保证烧结过程中坯体不承受烧结系统的轴向压力,从而实现无压烧结,确保表面多孔层的孔隙率,烧结温度分别为850、900、950、1000和1050 ℃。
烧结成形后的梯度合金试样微观结果分析在德国Bruker D8 Advance 型X 射线衍射仪上进行,显微组织和表面孔隙特征(孔隙率、孔径尺寸)利用日本Nikon ECLIPSE MA200金相显微镜及MCV金相分析软件进行观察检测,元素分布分析检测利用荷兰Philips XL30 型扫描电镜(SEM)结合EDS 能谱进行;力学性能测试在日本岛津AG-X万能材料试验机上进行,根据GB/T 7314—2005,将梯度合金按烧结圆柱试样的轴向线切割成标准试样测量其抗压强度、压缩弹性模量及超弹性性能,加载速率为1 mm/min;在37 ℃的模拟人体体液(Hanks'溶液)中进行体外生物活性实验,溶液各成分配比为:去离子水1 L、NaCl 8.00 g、CaCl2 0.14 g、KCl 0.40 g、NaHCO3 0.35 g、MgCl2·H2O 0.1 g、Na2HPO4·12H2O 0.12 g、KH2PO4 0.06 g、MgSO4·7H2O 0.1 g、葡萄糖 1.00 g,实验周期14 d。
2 结果与分析
2.1 烧结温度对梯度合金微观组织与表面孔隙特征的影响
图2所示为纯Ni和Ti金属粉末及球磨后NiTi 混合粉末的XRD谱。从图2可以看出,机械球磨NiTi 混合粉末的衍射峰与原料金属粉末的衍射峰相比变化不大,没有发现化合物相形成,说明球磨过程中金属粉末没有发生合金化反应现象。进一步利用XRD 分析了烧结后梯度合金物相演变,图3所示为NiTi/表面多孔Ti梯度合金在不同烧结温度时的XRD谱。由图3可以看出,当烧结温度为850 ℃时,梯度合金中除了B19′(NiTi)相、B2(NiTi)及α-Ti相外,还存在较多单质Ni、单质Ti及Ni3Ti和Ti2Ni等杂相;随着烧结温度升高,单质Ni、单质Ti及Ni3Ti和Ti2Ni杂相逐渐减少;当烧结温度达到1000 ℃时,单质峰完全消失,梯度合金中主相转变为单一NiTi相和α-Ti相,同时还存在极少量Ni3Ti和Ti2Ni相;烧结温度超过1000 ℃后,合金基体和表面层均出现了熔化现象,梯度结构遭到破坏,故本文不再进行讨论。XRD衍射结果表明,烧结温度的升高促进了梯度合金中NiTi相的形成和转变,中间基体合金逐渐转变为单一NiTi相及少量杂相,表面多孔层主要为α-Ti相。
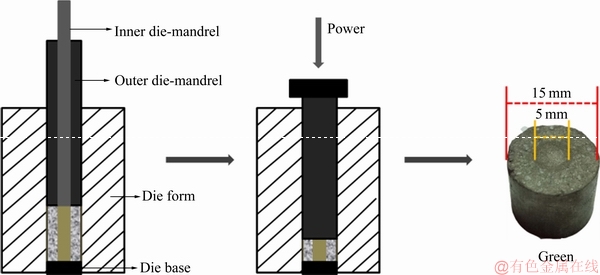
图1 NiTi/表面多孔Ti梯度合金坯体的制备流程图
Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of green bodies fabrication process of NiTi/surface porous Ti gradient alloy
利用金相显微镜观察了梯度合金的中间基体、表面多孔层及界面的形貌,图4所示为不同烧结温度下NiTi/表面多孔Ti梯度合金的光学显微照片。从图4可以看出,烧结温度850 ℃时基体与表面多孔层界面之间存在较多裂纹与缺陷,界面结合较差;当温度升高到900 ℃时,界面结合有所改善但仍然存在微小裂纹;当温度达到950 ℃时,基体与表面多孔层之间的裂纹完全消失且过渡较平滑,界面形成良好的冶金结合;当温度提高到1000 ℃时,基体与表面多孔层界面
仍然是良好的冶金结合,但是在界面处形成了一定宽度的均匀过渡层,且过渡层区域与多孔层和内层的冶金结合良好。进一步利用SEM结合EDS线扫描对界面区域进行了检测分析(见图5),根据检测结果,界面过渡层主要为较多Ti元素和少量Ni元素,厚度约为80 μm,这表明在1000 ℃时,在烧结温度驱动力下,界面处发生了元素的相互扩散反应,形成了Ni和Ti的化合物;中间基体中主要为Ni和Ti元素,表面多孔层主要为Ti元素,基本没有Ni元素的扩散。这说明形成的界面过渡层阻碍了中间基体中Ni元素向表面多孔层的扩散,对材料在使用过程中防止Ni离子的溶出与毒性是极为有利的。另外,通过对中间基体的致密度检测结果表明,850 ℃时,基体致密度为81.9%,致密度较低;随着烧结温度升高,基体致密度提高;当温度为1000 ℃时,基体致密度达到了92.8%,致密度的提高对基体力学性能是非常有利的。综上分析结合XRD结果可知,SPS制备的NiTi/表面多孔Ti梯度合金在烧结温度为1000 ℃时,能够获得较高的致密度、单一NiTi和α-Ti组织、界面结合良好且能防止Ni离子的溶出与毒性,获得了最佳烧结效果。
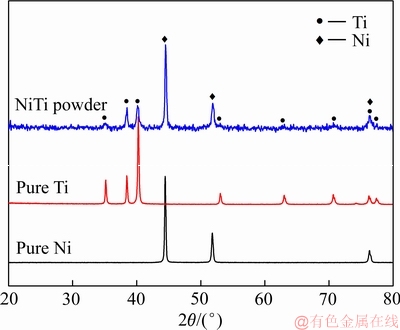
图2 纯Ni和Ti金属粉末及球磨后NiTi 混合粉末的XRD谱
Fig. 2 XRD patterns of pure Ni and Ti powder and NiTi mixed powder after milled
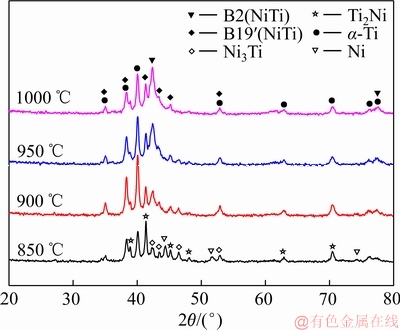
图3 不同烧结温度下NiTi/表面多孔Ti梯度合金的XRD谱
Fig. 3 XRD patterns of NiTi/surface porous Ti gradient alloys at different sintering temperatures
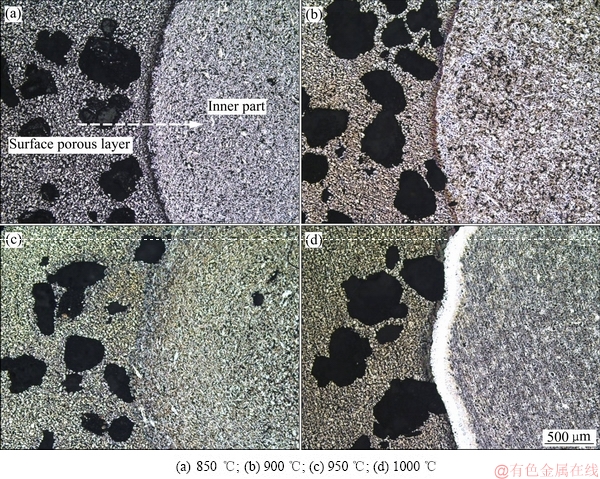
图4 不同烧结温度NiTi/表面多孔Ti梯度合金的光学显微组织形貌
Fig. 4 Optical microscope photographs of NiTi/surface porous Ti gradient alloy at different sintering temperatures
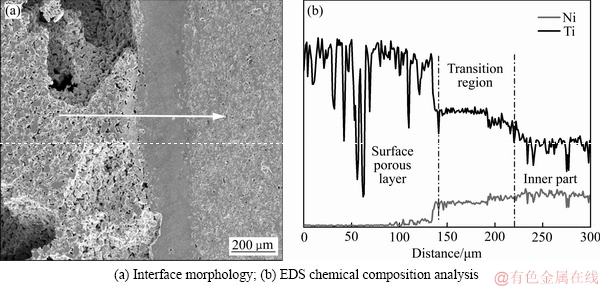
图5 烧结温度为1000 ℃时NiTi/表面多孔Ti梯度合金的界面形貌和EDS线扫描图
Fig. 5 Interface morphology and EDS chemical composition analysis of NiTi/surface porous Ti gradient alloy sintered at 1000 ℃
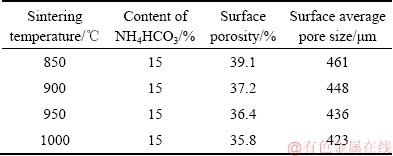
进一步利用金相显微镜及MCV金相分析软件对梯度合金表面孔隙特征(孔隙率、孔径尺寸)进行了观察分析,图6所示为不同烧结温度下NiTi/表面多孔Ti梯度合金表面多孔层的金相照片及MCV金相分析图,表1所列为计算获得的表面层孔隙率与孔径尺寸的数据。从图中可以看出,随着烧结温度的升高,表面层孔隙的分布逐渐均匀,孔的形状与圆整度改善,大孔周围分布着较多小尺寸微孔,且孔与孔之间相互连通。根据表1可知,表面多孔层的孔隙率随着烧结温度的升高呈现出缓慢下降的趋势,由39.1%下降到了35.8%,平均孔径由461 μm下降到423 μm,总体变化不大,说明烧结温度对梯度合金表面多孔层孔隙率和平均孔径的影响较小。相关研究表明[9-13],多孔结构有利于骨组织长入且孔隙率范围在30%~90%、孔径范围在100~500 μm的多孔材料适合骨细胞生长。所制备NiTi/表面多孔Ti梯度合金的表面孔隙率和孔径范围能够满足上述要求,对改善合金生物活性是有利的。
表1 不同温度NiTi/表面多孔Ti梯度合金表面孔隙率及平均孔径
Table 1 Average pore size and porosity of surface of NiTi/surface porous Ti gradient alloy sintered at different temperatures
2.2 烧结温度对梯度合金力学性能与超弹性行为的影响
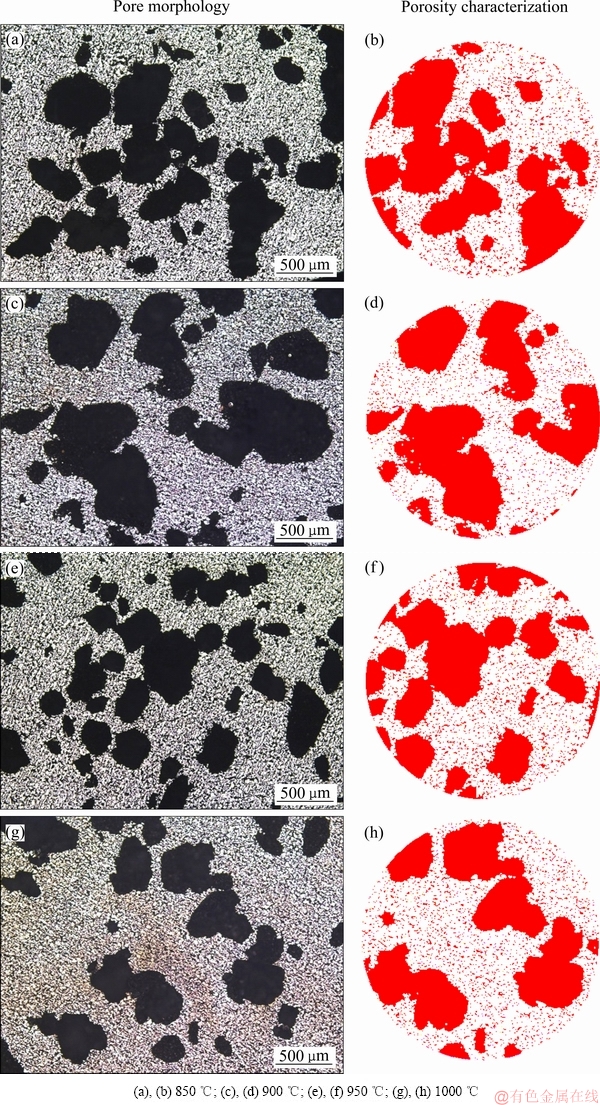
图6 NiTi/表面多孔Ti梯度合金在不同烧结温度时多孔层的孔隙形貌及孔隙率表征图
Fig. 6 Pore morphologies and porosity characterization of porous layer of NiTi/surface porous Ti gradient alloy at different sintering temperatures
图7所示为不同烧结温度下NiTi/表面多孔Ti梯度合金的室温力学性能。从图7可知,烧结温度为850、900、950和1000 ℃时,梯度合金的抗压强度值分别为179.8、267.5、431.6和632.0 MPa;压缩弹性模量分别为3.5、5.9、7.5和9.0 GPa。可以看出,随着烧结温度的升高,梯度合金的抗压强度呈明显增大趋势,而压缩弹性模量则呈缓慢增大趋势,但变化不明显。上述规律主要与梯度合金的组织演变、界面结合、表面孔隙特征及基体合金致密度密切关联。根据前面分析结果,在较低烧结温度时,合金中存在较多Ti、Ni、Ti2Ni、Ni3Ti杂质相,界面处存在较多裂纹和缺陷,基体与多孔层结合较差,同时基体合金致密度也较低,导致梯度合金抗压强度较低;随着烧结温度升高,梯度合金中杂质相减少,组织演变为主要由NiTi相为主及少量Ti2Ni、Ni3Ti相组成,界面逐渐形成了稳定的冶金结合,基体合金致密度也逐渐提高,因而梯度合金抗压强度呈明显增大趋势。而对于压缩弹性模量,由于表面多孔层的存在,导致梯度合金在压缩过程中应力得到大量释放,弹性模量较块体合金显著下降而与多孔合金接近;由于烧结温度对合金表面多孔层孔隙率和平均孔径影响较小,因而弹性模量变化不明显。综上可知,1000 ℃烧结的NiTi/表面多孔Ti梯度合金的抗压强度达到632.0 MPa,远高于多孔NiTi合金的而与块体合金的接近;压缩弹性模量值为9.0 GPa,远低于块体NiTi合金的,而与多孔合金的接近,且与人骨弹性模量(皮质骨3~20 GPa,松质骨0.05~0.5 GPa)[16]非常匹配,具有优异的力学相容性。

图7 烧结温度对NiTi/表面多孔Ti梯度合金抗压强度和压缩弹性模量的影响
Fig. 7 Effects of sintering temperatures on compressive strength and elastic modulus of NiTi/surface porous Ti graded alloys
多种生物材料(如骨骼、骨胶质等)都有大于2%的可恢复应变[17-18],因此选取1000 ℃烧结的NiTi/表面多孔Ti梯度合金进行了循环加载-卸载的压缩测试,以探讨其超弹性性能。图8所示为该梯度合金在预应变4%条件下的不同循环次数加载-卸载的应力-应变曲线。从图8可以看出,第一次循环开始时,试样的残余应变量为0.87%,超弹性回复应变为3.13%,循环曲线不封闭,其回复率为78%。随着循环加载次数的增多,循环曲线逐渐转向闭合,试样第二次循环至第六次的残余应变分别为0.62%、0.35%、0.28%、 0.22% 和0.15%,相应的超弹性回复应变为3.38%、3.65%、3.72%、3.78%和3.85%。在接下来的循环过程中材料表现出了完全的超弹性,回复率100%并趋于稳定,这是由于在循环的过程中产生了位错场导致局部内应力场的产生,这种内引力场促进奥氏体到马氏体的相变,使其超弹性得到改善。当达到第19次循环加载时,由于材料存在一定数量的孔隙,经过多次循环加载后,局部孔隙开始发生变形并产生裂纹,回复率开始下降,在第25次循环后更为明显,出现锯齿状平台,最终在第28次循环时发生断裂。本文制备的NiTi/表面多孔Ti梯度合金的超弹性回复应变大于4%且加载-卸载循环次数为28次,实验结果表明,该材料具有优异的超弹性性能,其植入人体后抗疲劳性能良好。

图8 NiTi/表面多孔Ti梯度合金在预应变4%下多次加载-卸载的应力-应变曲线
Fig. 8 Multiple loading-unloading stress-strain curves of NiTi/surface porous Ti graded alloy at pre-strain 4%
2.3 梯度合金的体外生物活性
图9所示为致密纯Ti、NiTi合金及NiTi/表面多孔Ti梯度合金在模拟人体体液Hanks'溶液中浸泡14 d后类骨磷灰石的沉积情况。从致密纯Ti(见图9(a))和致密NiTi合金(见图9(b))的浸泡结果可以观察到,仅极少量的沉积物沉积在材料表面的孔洞中;而在NiTi /表面多孔Ti梯度合金表面(见图9(c))可观察到有一定厚度的沉积物沉积在表面多孔层的孔洞处,且形成了一层均匀连续的涂层,通过EDS 分析可知沉积物中含有大量Ca、P、O元素且成分比例接近羟基磷灰石含量,可推测该沉积物为类骨磷灰石。多孔材料有利于营养物质运输和交换,孔内凹陷粗糙处有利于形核生长,因此类骨磷灰石优先沉积在孔洞处。从上述结果可知,与致密块体合金相比,所制备的梯度合金较短时间内能够在表面多孔层形成较多的类骨磷灰石涂层,具有优良的诱导成骨性能,从而显著提高了NiTi合金的生物活性,有利于新骨的长入且植入体与组织之间产生良好的骨性结合。
综上所述,利用SPS技术在1000 ℃烧结制备的NiTi/表面多孔Ti梯度合金不仅具有良好的界面结合且能防止Ni离子的溶出与毒性、适宜的表面孔隙率与平均孔径、优异的力学性能及超弹性,而且还具有良好的生物活性,作为人体内植入物材料显示了良好的应用前景。
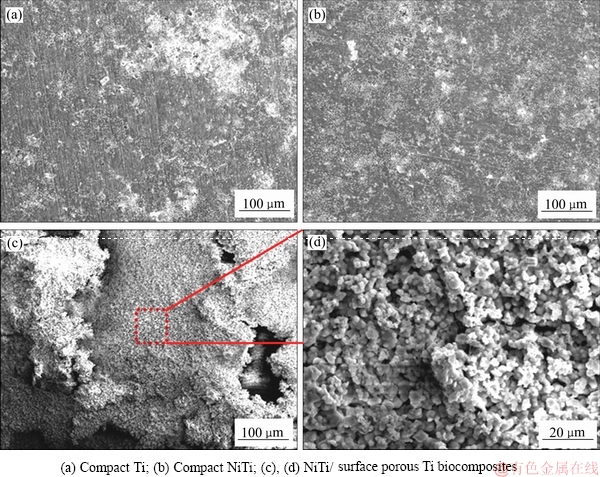

图9 不同材料在Hanks’溶液中的类骨磷灰石沉积SEM像
Fig. 9 SEM images of bone-like apatite in different materials in Hanks’ solution
3 结论
1) 利用SPS技术制备了基体为NiTi、表面为多孔Ti的梯度合金。随着烧结温度升高,梯度合金组织由NiTi、α-Ti、Ni、Ti2Ni、Ni3Ti混合相逐渐转变为单一NiTi和α-Ti相,内外层界面形成稳定冶金结合,表面孔隙率和平均孔径呈缓慢减小趋势。
2) SPS制备的NiTi/表面多孔Ti梯度合金具有较高的抗压强度和与人骨匹配的低弹性模量。随着烧结温度的升高,梯度合金抗压强度值呈明显增大趋势(由179.8 MPa提高到632.0 MPa),而弹性模量值变化较小(3.5~9.0 GPa)。
3) 1000 ℃制备的NiTi/表面多孔Ti梯度合金不仅具有良好的表面孔隙特征(孔隙率35.8%、平均孔径423 μm)、较高的抗压强度(632 MPa)、较低的弹性模量(9 GPa)及优异的超弹性行为(超弹性恢复应变>4%),而且体外生物活性显著提高。
REFERENCES
[1] GILL P, MUSARAMTHOTA V, MUNROE N, DATYE A, DUA R, HAIDER W, MCGORON A, ROKICKI R. Surface modification of Ni-Ti alloys for stent application after magnetoelectropolishing[J]. Materials Science and Engineering C, 2015, 50: 37-44.
[2] FOURNIER E, DEVANEY R, PALMER M, KRAMER J, KHAJA R E, FONTE M. Superelastic orthopedic implant coatings[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 2014, 23(7): 2464-2470.
[3] CHEN Q, THOUAS G A. Metallic implant biomaterials[J]. Materials Science and Engineering R, 2015, 87: 1-57.
[4] LIU X, WU S, YEUNG W K, CHAN Y L, HU T, XU Z, LIU X, CHUNG C Y, CHEUNG M C, CHU K. Relationship between osseointegration and superelastic biomechanics in porous NiTi scaffolds[J]. Biomaterials, 2011, 32(2): 330-338.
[5] ABIDI I H, KHALID F A. Sintering and morphology of porous structure in NiTi shape memory alloys for biomedical applications[J]. Advanced Materials Research, 2012, 570: 87-95.
[6] 刘爱辉, 徐吉林. 医用多孔NiTi合金的显微组织、力学性能及耐蚀性[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2014, 43(11): 2763-2767.
LIU Ai-hui, XU Ji-lin. Microstructure, mechanical properties and corrosion resistance of the biomedical porous NiTi alloy[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2014, 43(11): 2763-2767.
[7] LI Y H, CHEN N, CUI H T, WANG F. Fabrication and characterization of porous Ti-10Cu alloy for biomedical application[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2017,723: 967-973.
[8] DUAN B, ZHANG Y, WANG D, ZHAO Y, XIE C. Fabrication and properties of porous NiTi alloy by gel-casting with TiH2 powders[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 2017, 4: 1-8.
[9] 刘 超, 杨海林, 李 婧, 阮建明. 生物医用多孔Nb-Ti合金的孔隙率和力学性能[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2014, 24(3): 752-757.
LIU Chao, YANG Hai-lin, LI Jing, RUAN Jian-ming. Porosity and mechanical properties of biomedical porous Nb-Ti alloy[J]. Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2014, 24(3): 752-757.
[10] LI J, YANG H, WANG H, RUAN J. Low elastic modulus titanium-nickel scaffolds for bone implants[J]. Materials Science and Engineering C, 2014, 34(1): 110-114.
[11] RHALMI S, ODIN M, ASSAD M, TABRIZIAN M, RIVARD C H, YAHIA L H. Soft tissue and in vitro cell response to porous nickel-titanium: A biocompatibility evaluation[J]. Biomedical Materials and Engineering, 1999, 9(3): 151-162.
[12] JIAN Y T, YANG Y, TIAN T, STANFORD C, ZHANG X P, ZHAO K. Effect of pore size and porosity on the biomechanical properties and cytocompatibility of porous NiTi alloys[J]. Plos One, 2015, 10(6): 128-138.
[13] BASSANI P, PANSERI S, RUFFINI A, MONTESI M, GHETTI M, ZANOTTI C, TAMPIERI A, TUISSI A. Porous NiTi shape memory alloys produced by SHS: Microstructure and biocompatibility in comparison with Ti2Ni and TiNi3[J]. Journal of Materials Science Materials in Medicine, 2014 , 25(10): 2277-2287.
[14] 栗 智, 张 磊, 张玉勤, 蒋业华, 周 荣. 表面多孔NiTi-羟基磷灰石/NiTi生物复合材料的制备与性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2017, 34(7): 1540-1546.
LI Zhi, ZHANG Lei, ZHANG Yuqin, JIANG Ye-hua, ZHOU Rong. Fabrication and properties of surface porous NiTi-HA/NiTi biocomposites[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2017, 34(7): 1540-1546.
[15] 栗 智, 张 磊, 孟增东, 何正员, 张玉勤, 蒋业华. SPS制备NiTi表面多孔梯度合金的组织演变与力学性能研究[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2018, 47(1): 371-377.
LI Zhi, ZHANG Lei, MENG Zeng-dong, HE Zheng-yuan, ZHANG Yu-qin, JIANG Ye-hua. Microstructure evolution and mechanical properties of porous surface NiTi gradient alloy prepared by spark plasma sintering[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2018, 47(1): 371-377.
[16] HENCH L. Bioceramics[J]. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 1998, 81(7): 1705-1728.
[17] AYDOG T, BOR S. Superelasticity and compression behavior of porous TiNi alloys produced using Mg spacers[J]. Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials, 2012, 15: 59-69.
[18] GIBSON L J, ASHBY M F. Cellular Solids: Structure and properties[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1997.
Effects of sintering temperatures on microstructure and properties of NiTi/surface porous Ti graded alloy by spark plasma sintering
DENG Xia1, 2, HE Yuan-huai1, 2, JIAO Mei-qi1, 2, ZHANG Yu-qin1, 2, 3, JIANG Ye-hua1, 2
(1. School of Materials Science and Engineering, Kunming University of Science and Technology, Kunming 650093, China;
2. National-local Joint Engineering Laboratory of Metal Advanced Solidification Forming and Equipment Technology, Kunming 650093, China;
3. Engineering Technology Research Center of Titanium Products and Application of Yunnan Province, Chuxiong 651209, China)
Abstract: NiTi/Surface porous Ti gradient alloys were prepared by spark plasma sintering (SPS) technology. The effects and mechanism of different sintering temperatures on the microstructure, surface pore characteristics, mechanical properties and in vitro biological activity of the gradient alloys were investigated. The results show that the gradient alloys are consisted of NiTi, α-Ti, Ni, Ti2Ni, Ni3Ti mixed phase and gradually transforms into NiTi and α-Ti phase with the increase of sintering temperatures. Furthermore, a stable metallurgical bonding on the internal and external interface of the alloys could be observed. Meanwhile, the porosity and average pore size of surface porous layer is in a slowly decreasing trend. As a result, the compressive strength of the alloys increases significantly, but the compressive elastic modulus of the alloys changes less. Gradient alloy sintered at 1000 ℃ not only exhibits good surface pore characteristics (35.8% porosity as well as 423 μm average pore size), higher compressive strength (632 MPa), lower the compressive elastic modulus (9 GPa) and excellent superelastic recovery strain (>4%), but also shows good in vitro biological activity.
Key words: NiTi gradient alloy; sintering temperatures; microstructure; mechanical properties; in vitro biological activity
Foundation item: Project(31660262) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China
Received date: 2018-09-20; Accepted date: 2019-01-05
Corresponding author: ZHANG Yu-qin; Tel: +86-13708861766; E-mail: zyqkust@163.com
(编辑 龙怀中)
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(31660262)
收稿日期:2018-09-20;修订日期:2019-01-05
通信作者:张玉勤,教授,博士;电话:13708861766;E-mail:zyqkust@163.com