文章编号:1004-0609(2017)-01-0089-08
H13钢在铝液中的熔蚀-磨损行为与交互作用机理
肖华强1,陈维平2
(1. 贵州大学 机械工程学院,贵阳 550025;
2. 华南理工大学 国家金属材料近净成形工程技术研究中心,广州 510640)
摘 要:通过对比分析H13钢在高温干摩擦磨损及熔蚀-磨损两种条件下的磨痕形貌、磨损产物及材料流失特征,研究H13钢在铝液中的熔蚀-磨损行为以及腐蚀与磨损的交互作用机理。结果表明:H13钢在铝液中熔蚀-磨损的材料流失量远高于其单纯腐蚀及单纯磨损条件下材料流失量之和。在本实验条件下,熔蚀与磨损的交互作用率均不小于93.9%。对已生成界面金属间化合物为典型腐蚀特征的这一类材料而言,其在铝液中的熔蚀-磨损性能主要由界面金属间化合物的性质、生成速度及其与基体的界面结合情况所决定。
关键词:熔蚀-磨损;金属间化合物;交互作用;铝液
中图分类号:TG172 文献标志码:A
与材料在一般腐蚀性介质(如气体、溶液或颗粒)下的腐蚀-磨损不同,熔蚀-磨损是指材料在高温金属熔体中发生的腐蚀-磨损现象[1-4]。目前,由于高温金属熔体这一腐蚀介质的特殊性,对材料高温熔蚀-磨损行为的研究鲜有报道[5-6]。由于缺乏专用的设备对材料的熔蚀-磨损行为进行测试表征,以及腐蚀界面存在复杂的冶金物理化学反应,有关熔蚀和磨损行为的交互作用机理尚不明确[7-9]。
铝熔体具有极强的腐蚀性,铝工业生产中的一些关键零部件往往因为材料在铝液中的熔蚀-磨损行为而加速破坏,不仅污染铝合金熔体,频繁地更换零部件更大大降低了生产效率,提高了企业成本[10-11]。目前,由于缺乏所需的熔蚀-磨损数据,只能依靠材料在铝液中的腐蚀性能及高温干摩擦磨损性能数据的简单叠加来指导生产,大量使用的仍是高合金的耐磨类模具钢(如H13钢)。ZHU等[12]利用挤压铸造机,将铝熔体高速喷射到试样上,经多次循环后评估试样经循环高速铝熔体冲击后的材料流失情况。尽管Mo基、Ti基和W基试样在动态铝液当中均具有较好的耐腐蚀及冲蚀性能,其材料流失速率大大低于H13钢的,但是上述材料的应用受到成本及成型工艺性的限制。
在前期的工作中,研究了几类常用金属材料在铝液中的腐蚀行为,这些材料在腐蚀界面均生成连续的金属间化合物层[13]。在此基础上,本文作者利用自行研制出的新型环-块式高温熔蚀-磨损测试系统[14-15],对H13钢在铝液中的熔蚀-磨损行为进行研究,并结合高温腐蚀及高温干摩擦磨损数据对其熔蚀及磨损行为的交互作用进行分析,以期得出这一类受铝液浸蚀时以生成界面金属间化合物为典型腐蚀特征的材料在铝液中的熔蚀-磨损机理。
1 实验
实验材料选择常用的商用H13钢和A00纯铝锭,采用氮化硅陶瓷配副。采用静态浸没腐蚀试验来评价材料的耐铝液腐蚀性能,浸蚀实验在一般的井式电阻炉中完成,具体实验过程及结果见文献[13]。材料的高温干摩擦磨损实验及熔蚀-磨损实验均在自行研制的高温熔蚀-磨损测试系统上完成,采用环-块接触型式,H13钢块试样为d 8 mm×10 mm的圆柱。所有试样在进行实验前均用1000号砂纸打磨,然后用丙酮酒精清洗、干燥备用。腐蚀、干摩擦磨损及熔蚀-磨损实验温度均为750 ℃。
摩擦磨损实验的工作载荷分别为5、10、15、20 N,转速为40、60、80、100 r/min,试验时间为30 min。采用失重法来评价材料实验前后的体积损失,对于高温干摩擦磨损须放置对比试样以测定其氧化质量增加,材料的最终磨损质量损失需去除氧化质量增加。对于浸蚀及熔蚀-磨损试样,实验结束后需用10% NaOH(体积分数)浸泡去除腐蚀表面残留的铝,最后用丙酮酒精清洗干燥后称取质量。实验前后,均采用精度为0.1mg的电子天平称取质量,材料的体积磨损量ΔV及磨损速率ω由式(1)和(2)得出:
 (1)
(1)
 (2)
(2)
式中:Δm为磨损质量损失;ρ为试样密度;t为磨损时间;l为滑行距离;N为试验载荷。利用XRD分析磨损表面产物,利用SEM分析磨损表面及磨损界面处的组织形貌。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 熔蚀-磨损行为
2.1.1 摩擦曲线
图1分别为相同参数下(750 ℃、10 N、60 r/min)H13钢干摩擦磨损和在Al液中熔蚀-磨损的摩擦因数曲线。由图1可以看出,在干摩擦磨损条件下,其稳定摩擦因数约为1.08,而在铝液中,熔蚀-磨损的稳定摩擦因数约为0.79。这说明在Al液当中熔蚀-磨损时,Al熔体具有一定的润滑效果,因此,熔蚀-磨损的摩擦因数较小,而且在进入稳定状态后熔蚀-磨损的摩擦曲线相对也要平稳一些。同时,两种条件下摩擦曲线均存在一定幅度的“振荡”,这说明干摩擦时试样表面的氧化层和Al液当中熔蚀-磨损时磨损面上的金属间化合物层的表面均是粗糙不平的。此外,可以看出,在干摩擦磨损时,摩擦曲线在初始的上升期是非常平滑的,而在铝液当中,熔蚀-磨损时摩擦曲线在接触时有个极大值,此后缓慢下降,几分钟后,又逐渐增大最后稳定下来。这主要是由于在干摩擦磨损条件下,在接触磨损之前,试样表面即已形成了氧化层,而在熔蚀-磨损时,磨损表面金属间化合物层的形成有一个过程。当摩擦副进入铝液之后,由于接触温差,可能在其表面形成一薄层的Al膜,当施加载荷进行磨损时,由于这一层Al膜的破坏出现了一个较大的接触摩擦力。此后,摩擦副进入一个磨合过程,摩擦因数缓慢下降。随着磨损过程的进行,试样表面开始形成金属间化合物层,并同时存在金属间化合物的不断开裂、破碎及剥落,导致摩擦因数的上升。最后,当试样表面的金属间化合物层的生成及破坏过程进入一个稳定阶段后,材料的摩擦因数就稳定下来。

图1 H13钢在干摩擦磨损及熔蚀-磨损下的摩擦曲线
Fig. 1 Wear (a) and corrosion-wear (b) curves of H13 steel under different conditions
2.1.2 磨损量及磨损速率
图2所示分别为H13钢在750 ℃下干摩擦磨损时,材料的体积损失及磨损速率随转速及载荷的变化。由图2可以看出,随着转速及载荷的上升,材料的体积损失都逐渐增大,但是材料流失量非常小,其体积损失量约在0.1~0.4 mm3/h,这表明H13钢在该温度下的磨损量非常小。从磨损速率来看,在较小载荷下由于磨损表面的氧化膜主要以塑性变形为主,尚未发生大面积的开裂剥落,因此其磨损速率较小[5];随着载荷及转速的增大,材料的磨损速率逐渐增加。

图2 H13钢在干摩擦磨损条件下转速和载荷磨损量与磨损速率的影响
Fig. 2 Effects of velocity (a) and load (b) on volume loss and wear rate of H13 under wear condition
图3所示分别为H13钢在750 ℃Al液当中熔蚀-磨损时材料的体积损失及磨损速率随转速及载荷的变化。由图3可以看出,材料在Al液当中熔蚀-磨损时,其体积损失随着转速及载荷的增加而增加。其在750 ℃的Al液当中,材料的熔蚀-磨损体积损失要比其在750 ℃下干摩擦磨损的体积损失高出3个数量级。从磨损速率来看,当转速从40 r/min 逐渐上升到80 r/min 时,材料的磨损速率逐渐增加,而当转速为100 r/min 时,其磨损速率出现了下降。这说明随着转速的增大,材料表面腐蚀产物的破坏行为具有明显的转变。从图3(b)中可以看出,随着载荷的增大,材料的磨损速率逐渐减小。由此可见,在不同载荷作用下,材料表面的破坏型式并没有发生明显变化,材料体积损失增加的并不明显,因此,其磨损速率呈逐渐下降的趋势。
2.2 磨损表面形貌
2.2.1 氧化磨损及熔蚀-磨损形貌对比
图4所示分别为相同参数下(750 ℃、10 N、60 r/min)H13钢干摩擦磨损和在Al液中熔蚀-磨损的后磨损表面的SEM像。由图4可看出,750 ℃下,H13钢的干摩擦磨损为典型的氧化磨损,主要存在氧化膜的塑性流动、变形、起皱及至破裂、剥落等过程。其磨损失效行为主要由氧化膜的软化及破坏两个因素主导[16-18],这印证了前述分析中材料磨损速率随着载荷和转速的变化。从图4(a)可以看出,在材料的磨损表面上存在明显的氧化膜的塑性变形以及起皱破裂,材料的磨损失效形式主要为粘着磨损和磨粒磨损。与干摩擦磨损后的磨痕形貌不同,熔蚀-磨损后磨痕表面整体比较平整,但是从高倍显微形貌可以看出(见图4(b)),磨损面上的产物凹凸不平,同时存在大量的裂纹。这说明在熔蚀-磨损过程中,磨损表面生成的金属间化合物存在明显的开裂及剥落。从磨损形貌来看,无论是氧化磨损还是熔蚀-磨损,磨损表面氧化层或者金属间化合物层的性质及其与基体界面结合情况的都对磨损过程至关重要,腐蚀产物的生成及破坏主导着整个磨损进程。

图3 H13钢在熔蚀-磨损条件下转速和载荷对磨损量与磨损速率
Fig. 3 Effects of velocity (a) and load (b) on volume loss and wear rate of H13 under corrosion-wear condition
2.2.2 不同转速下熔蚀-磨损表面形貌

图4 干摩擦磨损及熔蚀-磨损后磨痕表面的SEM像
Fig. 4 SEM images of wear surfaces under wear (a) and corrosion-wear (b)

图5 不同载荷和转速下H13铜的熔蚀-磨损形貌
Fig. 5 SEM images of corrosion-wear surfaces under different loads and velocities
图5所示为不同转速下H13钢在750 ℃Al液当中熔蚀-磨损的磨损表面形貌,其中右上角为相对应的局部放大照片。如图5(a)和(b)所示,在较低转速下进行熔蚀-磨损时(40~60 r/min),磨损面整体比较平整,但是从高倍显微形貌可以看出,磨损面上的产物凹凸不平,同时存在大量的裂纹。当转速增大到80 r/min时,磨损表面上存在突出整个磨损面但尚未剥落的块状中间化合物,同时还能观察到中间化合物层成块脱落后的痕迹,而磨损表面的微观结构疏松且更为粗糙。可见,随着转速的上升,熔蚀-磨损表面的中间化合物层开始破裂并剥落,整个磨损表面在微观上越来越粗糙,从而导致摩擦因数逐渐上升。当转速增大到100 r/min时,材料的熔蚀-磨损表面形貌与其他转速有明显区别,其磨损表面主要由表面平整光滑但是明显开裂的中间化合物层所覆盖,从高倍形貌中可以看出,这一表面金属间化合物层细小且致密;同时,这一表层金属间化合物破裂成块脱落后使下层基体重新暴露于铝液当中,其表面凸凹不平且存在大量的小坑和明显的裂纹。说明随着转速的增加,材料破坏型式发生了明显的变化。这主要是由于当摩擦速度较低时,材料磨损面上的腐蚀产物疏松、碎裂、逐渐分层剥落,剥落后的表面仍为疏松粗糙的腐蚀产物层;而当摩擦速度增大到100 r/min时,由于摩擦放热量加大,磨损表面的腐蚀产物可能首先存在一个塑性流动致密的过程,此后再逐渐开裂并整体从基体上剥落下来。
2.2.3 不同载荷下熔蚀-磨损表面形貌
图6所示为样品不同载荷下熔蚀-磨损的表面形貌SEM像。由图6可以看出,在不同载荷下其熔蚀-磨损表面没有明显的差异。从低倍形貌上看其熔蚀-磨损表面都比较平整,从显微形貌上看随着载荷增加,表面金属间化合物层开裂、破碎,使磨损表面更为粗糙。当载荷低时,腐蚀产物表面存在凹坑和裂纹,但是表面还是相对平整(见图6(a));随着载荷上升,表面腐蚀产物开始破碎,载荷越大腐蚀产物表面就越粗糙。
2.3 磨痕表面产物分析
从磨损行为和磨痕形貌分析可以看出,磨损表面的腐蚀产物(氧化膜、金属间化合物)对材料的摩擦行为至关重要,这其中包括产物的性质、生成速率以及其与基体材料的相容性等因素,腐蚀产物的生成及破坏主导着整个磨损进程。图7所示为不同条件下磨痕产物的XRD谱。由图7可以看出,在高温干摩擦磨损时其表面主要形成Fe2O3,而在熔蚀-磨损时主要生成的是Fe2Al5金属间化合物。另外从两个图谱中可以看出,Fe2Al5与Fe基体的峰强比远大于Fe2O3与Fe基体的峰强比,这表明熔蚀-磨损时生成的腐蚀产物显然比高温氧化磨损时生成的氧化物要更多。根据前期对H13钢在铝液当中腐蚀行为的研究[13],H13钢受铝液侵蚀时,其腐蚀界面上的Fe2Al5层以舌状向基体内部生长,其内部存在裂纹以及由互扩散系数差异所形成的孔洞,这些缺陷削弱了Fe2Al5层与H13基体的结合。此外,由于Fe2Al5金属间化合物非常脆,在压力作用下很容易发生开裂破碎,这从熔蚀-磨损的磨痕表面形貌当中可以观察到。因此,在熔蚀-磨损过程中,材料的流失主要是以磨损面上Fe2Al5层的不断破坏剥落为主,Fe2Al5层的生成及破坏的过程正是基体材料受熔蚀与磨损交互作用的综合体现。

图6 不同载荷和转速下样品熔蚀-磨损形貌
Fig. 6 SEM images of corrosion-wear surfaces under different loads and velocities
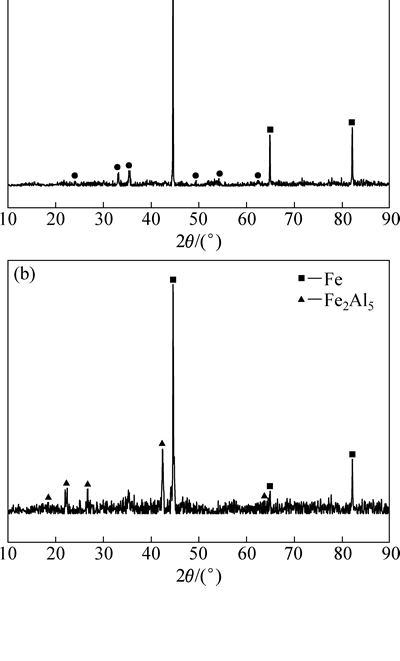
图7 干摩擦磨损及熔蚀-磨损下磨痕产物的XRD谱
Fig. 7 XRD patterns of wear surfaces under different wear (a) and corrosion-wear (b)
2.4 熔蚀-磨损交互作用机理
交互作用是研究材料熔蚀-磨损机理的重点,对于材料在Al液当中熔蚀-磨损行为我们可以利用交互作用率S(也称协同作用率,synergy ratio)来加以表征,定义:
 (3)
(3)
式中:Vtotal为熔蚀-磨损体积损失总量;Vcorr为纯腐蚀体积损失;Vwear为纯磨损体积损失。
图8所示为H13钢在750 ℃Al液当中熔蚀-磨损时的交互作用率,其中各种实验条件下纯腐蚀数据为H13钢在750 ℃下静态腐蚀的体积损失,均为8.02 mm3/h[12]。可以看出,在不同的熔蚀-磨损条件下材料的交互作用率均大于90%。可见,熔蚀-磨损条件下材料的体积损失远高于材料单纯腐蚀与单纯摩擦磨损的体积损失之和。结合图3的相关数据,以(10 N,60 r/min)条件下材料的体积损失为例,H13钢试样在干摩擦磨损时其体积损失仅为0.18 mm3/h,在单纯腐蚀时其体积损失为8.02 mm3/h,而在熔蚀-磨损时其体积损失则高达216.03 mm3/h,该值为前二者之和的26.35倍,其交互作用产生的材料流失占总材料体积损失率高达96.2%。可见,熔蚀-磨损条件下的材料流失主要为腐蚀及磨损这二者的交互作用所产生。
从前面的分析可知,当H13钢在Al液当中进入稳定熔蚀-磨损阶段后,材料的流失主要以磨损面上Fe2Al5层的不断破坏剥落为主,以此来持续地消耗铁基体。磨损过程不停地破坏腐蚀产物,从而使基体重新暴露于铝液当中,促进材料的进一步腐蚀,此外磨损所产生的热效应也能显著加速材料的腐蚀;同时,由于腐蚀产物Fe2Al5比较脆且与基体结合不好,在磨损过程中容易被破碎去除掉,因而能够显著加速材料的磨损。因此,当这一类以生成金属间化合物层为典型腐蚀特征的材料在铝液当中进行熔蚀-磨损时,材料的熔蚀-磨损速率显然是受金属间化合物层的生成及破坏速率所控制。当生成的金属间化合物层致密且与基体结合良好,同时厚度比较小时,材料的熔蚀-磨损性能就相对较好;而当生成较厚的容易破碎剥落的金属间化合物层时,材料在铝液当中的熔蚀-磨损速率将会显著增大。

图8 H13钢在Al液中的熔蚀-磨损交互作用率
Fig. 8 Corrosion-wear synergy ratios of H13 in molten aluminum
3 结论
1) H13钢在Al液中熔蚀-磨损时,材料的流失过程即为Fe2Al5层的不断生成及剥落的过程:磨损能够加速Fe2Al5层生成速度,而Fe2Al5层的存在又加速了试样表面材料的磨损破坏。
2) 熔蚀与磨损二者之间的交互作用极大地加速了材料的流失,交互作用产生的体积损失约占总熔蚀-磨损体积损失的90%以上。
3) 对这一类以生成金属间化合物层为典型腐蚀特征的材料而言,其在铝液当中进行熔蚀-磨损时,材料的熔蚀-磨损速率是由金属间化合物层的生成及破坏速率所控制。
REFERENCES
[1] LIU Yue-ting, MOL J M C, JANSSEN G C A M. Corrosion reduces wet abrasive wear of structural steel[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2015, 107(10): 92-95.
[2] GUZMAN A M, MARTINEZ D I, GONZALEZ R. Corrosion-erosion wear of refractory bricks in glass furnaces[J]. Engineering Failure Analysis, 2014, 46(11): 188-195.
[3] DEAMLEY P A, MALLIA B. The chemical wear (corrosion-wear) of novel Cr based hard coated 316L austenitic stainless steels in aqueous saline solution[J]. Wear, 2013, 306(1/2): 263-275.
[4] 李 琦, 刘洪喜, 张晓伟, 姚 爽, 张 旭. 铝合金表面激光熔覆NiCrAl/TiC复合涂层的磨损行为和耐蚀性能[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2014, 24(11): 2805-2812.
LI Qi, LIU Hong-xi, ZHANG Xiao-wei, YAO Shuang, ZHANG Xu. Wear behavior and corrosion resistance of NiCrAl/TiC composite coating on aluminum alloy by laser cladding[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2014, 24(11): 2805-2812.
[5] ZHANG Xian-man, CHEN Wei-ping. Review on corrosion-wear resistance performance of materials in molten aluminum and its alloys[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2015, 25(6): 1715-1731.
[6] KIM H J, YOON B H, LEE C H. Sliding wear performance in molten Zn-Al bath of cobalt-based overlayers produced by plasma-transferred arc weld-surfacing[J]. Wear, 2003, 254(5/6): 408-414.
[7] RIBEIRO A M, ALVES A C, ROCHA L A, SILVA F S, TOPTAN F. Synergism between corrosion and wear on CoCrMo Al2O3 biocomposites in a physiological solution[J]. Tribology International, 2015, 91(12): 198-205.
[8] CHEN Jun, WANG Jian-zhang, YAN Feng-yuan, ZHANG Qing, LI Quan-an. Corrosion wear synergistic behavior of Hastelloy C276 alloy in artificial sea water[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2015, 25(2): 661-668.
[9] STACK M M, ABDELRAHMAN G H. Mapping erosion-corrosion of carbon steel in oil-water solutions: effects of velocity and applied potential[J]. Wear, 2012, 274: 401-413.
[10] HAMEED A G. The morphology of coating/substrate interface in hot-dip-aluminized steels[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2008, 472(1): 157-165.
[11] YAN M, FAN Z. Review durability of materials in molten aluminum alloys[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2001, 36(2): 285-295.
[12] ZHU Yu-long, SCHWAM D, WALLACE J F, BIRCEANU S. Evaluation of soldering, washout and thermal fatigue resistance of advanced metal materials for aluminum die-casting dies[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2004, 379(1): 420-431.
[13] XIAO Hua-qiang, CHEN Wei-ping, LIU Zhe. Corrosion resistance of 91W-6Ni-3Fe refractory metal, TiAl compound and iron based alloys in molten aluminum[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2012, 22(9): 2320-2326.
[14] 陈维平, 吴 晶, 罗洪峰. 新型高温金属腐蚀-磨损试验机及其应用[J]. 特种铸造及有色合金, 2012, 32(10): 883-885.
CHEN Wei-ping, WU Jing, LUO Hong-feng. A new high temperature test rig for corrosion-wear in molten metal and its application[J]. Special Casting & Nonferrous Alloys, 2012, 32(10): 883-885.
[15] 陈维平, 吴 晶, 罗洪峰. 一种砝码加载环块式腐蚀磨损试验机: 中国, CN101975708B[P]. 2012-05-09.
CHEN Wei-ping, WU Jing, LUO Hong-feng. Weight loading ring-piece type corrosive wear tester: China, CN101975708B[P]. 2012-05-09.
[16] MALECKA J, GRAESIK W, HERNAS A. An investigation on oxidation wear mechanisms of Ti-46Al-7Nb-0.7Cr-0.1Si-0.2Ni intermetallic-based alloys[J]. Corrosion Science, 2010, 52(1): 263-272.
[17] HASAN G, HUSEYIN C. Effect of thermal oxidation on corrosion and corrosion-wear behaviour of a Ti-6Al-4V alloy[J]. Biomaterials, 2004, 25(16): 3325-3333.
[18] CUI X H, WANG S Q, WANG F, CHEN K M. Research on oxidation wear mechanism of the cast steels[J]. Wear, 2008, 265(3): 468-476.
Corrosion-wear behavior and synergy mechanism of H13 tool steel in molten aluminum
XIAO Hua-qiang1, CHEN Wei-ping2
(1. School of Mechanical Engineering, Guizhou University, Guiyang 550025, China;
2. School of Mechanical and Automotive Engineering, South China University of Technology, Guangzhou 510640, China)
Abstract: Through analyzing and comparing the surface morphologies, wear debris and material loss of H13 tool steel both under high temperature dry sliding wear and corrosion-wear in molten aluminum conditions, the corrosion-wear behavior and synergy mechanism between corrosion and wear of H13 tool steel in molten aluminum were investigated. The results show that the material loss of corrosion-wear is much higher than the total material loss of purely corrosion and purely wear. The synergy rate of corrosion-wear is not less than 93.9% in our experiments. For those materials, the typical corroded feature is to generate intermetallic compound layer between the substrate and molten aluminum, the corrosion-wear resistance of material is depended on the formation rate and characterization of intermetallic compound layer, as well as the combination between the substrate and the intermetallic zone.
Key words: corrosion-wear; intermetallics; synergy; molten aluminum
Foundation item: Project(51271080) supported by the National Nature Science Foundation of China; Project(20142053) supported by the Science and Technology Foundation of Guizhou Province, China; Project(2013010) supported by the Opening Project of National Engineering Research Center of Near-Net-Shape Forming for Metallic Materials, South China University of Technology, China; Project (2013[39]) supported by the Scientific Research Foundation of Guizhou University, China
Received date: 2015-11-23; Accepted date: 2016-06-20
Corresponding author: XIAO Hua-qiang; Tel: +86-13984168037; E-mail: xhq-314@163.com
(编辑 王 超)
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(51271080);贵州省科学技术基金资助项目(20142053);国家金属新材料近净成形工程技术研究中心开放基金资助项目(2013010);贵州大学引进人才基金资助项目(2013[39])
收稿日期:2015-11-23;修订日期:2016-06-20
通信作者:肖华强,副教授,博士;电话:13984168037;E-mail: xhq-314@163.com