Cu-Al金属间化合物的形成与生长及其对电镀Cu/Al层状复合材料电性能的影响
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2016年第12期
论文作者:张健 王斌昊 陈国宏 王若民 缪春辉 郑治祥 汤文明
文章页码:3283 - 3291
关键词:Cu-Al金属间化合物;层状复合材料;电镀;界面反应;生长动力学;电阻率
Key words:Cu-Al intermetallics; laminar composite; electroplating; interfacial reaction; growth kinetics; electrical resistivity
摘 要:采用纯Al片表面浸Zn后再电镀厚Cu层的方法制备Cu/Al层状复合材料。在473~673 K温度范围内对该复合材料进行退火,研究退火过程中Cu/Al界面扩散与反应、界面金属间化合物 (IMCs) 层的长大动力学以及Cu/Al层状复合材料电阻率。结果表明,经过473 K、360 h的退火处理,未观察到Cu-Al IMCs层,显示Zn中间层能有效抑制Cu/Al界面扩散。可是,当复合材料经573 K及以上温度退火时,Zn层中的Zn原子主要向Cu中扩散,从Al侧到Cu侧形成CuAl2/CuAl/Cu9Al4三层结构的反应产物。IMC层遵循扩散控制的生长动力学,Cu/Al复合材料的电阻率随退火温度及时间的增加而增大。
Abstract: Cu/Al laminar composite was prepared by dipping Zn layer and then electroplating Cu thick layer on pure Al sheet. During annealing the Cu/Al composites at temperature from 473 to 673 K, the Cu/Al interfacial diffusion and reaction and its kinetics and also the electrical resistivity of the composites were studied. The results show that no Cu-Al IMC layer is observable as the composites are annealed at 473 K for time till 360 h, indicating that the Zn intermediate layer can effectively suppress the Cu/Al interfacial diffusion. However, as the composites are annealed at 573 K and above, Zn atoms in the Zn layer dissolve into the Cu layer. Tri-layered reaction product of CuAl2/CuAl/Cu9Al4 then forms from the Al side to the Cu side. The IMC layer follows the diffusion-controlled growth kinetics. Electrical resistivity of the Cu/Al composites increases with the increase of the annealing temperature and time.
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 26(2016) 3283-3291
Jian ZHANG1, Bin-hao WANG1, Guo-hong CHEN2, Ruo-min WANG2, Chun-hui MIAO2, Zhi-xiang ZHENG1, Wen-ming TANG1
1. School of Materials Science and Engineering, Hefei University of Technology, Hefei 230009, China;
2. Anhui Institute of Electric Power Science, State Grid, Hefei 230601, China
Received 12 December 2015; accepted 11 April 2016
Abstract: Cu/Al laminar composite was prepared by dipping Zn layer and then electroplating Cu thick layer on pure Al sheet. During annealing the Cu/Al composites at temperature from 473 to 673 K, the Cu/Al interfacial diffusion and reaction and its kinetics and also the electrical resistivity of the composites were studied. The results show that no Cu-Al IMC layer is observable as the composites are annealed at 473 K for time till 360 h, indicating that the Zn intermediate layer can effectively suppress the Cu/Al interfacial diffusion. However, as the composites are annealed at 573 K and above, Zn atoms in the Zn layer dissolve into the Cu layer. Tri-layered reaction product of CuAl2/CuAl/Cu9Al4 then forms from the Al side to the Cu side. The IMC layer follows the diffusion-controlled growth kinetics. Electrical resistivity of the Cu/Al composites increases with the increase of the annealing temperature and time.
Key words: Cu-Al intermetallics; laminar composite; electroplating; interfacial reaction; growth kinetics; electrical resistivity
1 Introduction
Cu/Al laminar composite plates are developed to fulfill joining between the transformer copper output electrodes and the aluminum conductor in a high voltage transformer substation. At present, the composite plates are mainly prepared by various welding processes, e.g., explosive welding, cold roll welding, friction welding and ultrasonic welding. These techniques are usually used for producing the flat Cu and Al plates; however, they are not suitable for fabricating the Cu/Al composite plates with complicated shapes, such as arc-circle or curved surfaces.
It is known that electroplating technique is simple and cost-effective. The plating layer has strong bonding with the substrate, and its thickness can be controlled from less than 1 μm to more than 100 μm [1-5]. More importantly, the technique can form a uniform coating on an irregular metal surface for preparing the layered composite with a complicated shape. For example, it is successfully used for producing the Cu-coated Al core conductors.
One key technical barrier on preparing the Cu/Al laminar composites via electroplating is a huge electrode potential difference existing in Cu (0.34 V) and Al (-1.66 V). As the Al plate dipped in the Cu plating aqueous solution, Cu is replaced through a redox reaction between Al and the Cu plating solution. The coated Cu layer is rather poor because of its loose structure and low bonding with the Al plate. In addition, surface oxidation forms an insulation layer on the Al plate to deteriorate its plating ability. In our previous work, a new method was developed to prepare the Cu/Al laminar composite through secondary zinc dipping on the Al plate and sequentially electroplating a Cu layer. The Cu layer can be successfully deposited on the Zn transition layer, because of its much lower electrode potential difference between Cu and Zn (-0.76 V) than that between Cu and Al [6].
The reliability of Cu/Al composites is apparently affected by the Cu/Al interfacial diffusion and reaction. It likely leads to the formation of Cu-Al intermetallics (IMCs). Because these Cu-Al IMCs are more brittle and have higher electrical conductivities than Al and Cu, the service property and lifetime of the Cu/Al composites/ components are therefore degraded, even resulting in early failure of them. And hence, interfacial characteristics of the Cu/Al composites should be paid more attention and completely investigated. Related researches mainly focus on the Cu/Al composites fabricated via welding till now. It has been reported that metallurgical bonding between Cu and Al is achieved by explosion welding [7,8]. In this process, interfacial reaction takes place to form a continuous IMC layer. Shear strengths of cold-pressure welded Cu/Al joints decrease from 0.18 to 0.04 MPa as the IMC layer thickness increases from 2 to 4 μm [9]. During annealing the Cu/1050 Al friction weld joints, an IMC layer of CuAl2, CuAl and Cu9Al4 forms. As the IMC layer thickness increases from 2 to 10 μm, tensile strengths of the joints change from 87 to 40 MPa, meanwhile, electrical resistivities of them considerably increase [10]. During friction stir welding pure copper and 1060 Al, an IMC layer of CuAl2 and Cu9Al4 grows as the rotating speed increases, finally results in failure of the joints along the Cu/Al interfaces based on a brittle-ductile mixed fracture mode [11]. Moreover, tensile strengths of the ultrasonic soldering Cu/Al joints are as low as 35-50 MPa. It also attributes to the IMC interface layer [12].
As the electroplated Cu/Al composites/components service in the high voltage transmission lines, the electrical current heating effect causes temperature rise of them, as a result, the Cu/Al diffusion and reaction, resulting in microstructure and property deterioration of the composites/components. Therefore, researches on the interfacial behavior and thermal stability of the electroplated Cu/Al composites are essentially important. Unfortunately, almost no literature on this issue has been reported so far. In this work, the Cu/Al laminar composites were prepared by electroplating. Interfacial diffusion and reaction, growth kinetics of the Cu-Al IMCs layer and electrical property of the annealed Cu/Al composites were examined. Accordingly, interfacial thermal stability of the electroplated Cu/Al composites was evaluated.
2 Experimental
1060 pure Al with the composition of 0.35% Fe, 0.25% Si, 0.05% Cu, 0.03% Mg, 0.05% Zn, 0.03% Mn, 0.03% Ti, 0.05% V and the balance Al was used in this study. The Al sheets with dimensions of 40 mm × 15 mm × 3 mm were made by line cutting. After being ground and polished, they were unoil-cleaned and alkaline- etched. An alkaline zincate aqueous solution, containing a little Fe, Ni and Cu salts and complexing reagents, was used to deposit about 1 μm Zn layer on the Al sheets through two-step zinc dipping [13,14].
Electroplating Cu layer on the Al sheets was carried out through alkaline Cu plating followed by acidic Cu plating. Ingredients of the alkaline/acidic Cu plating aqueous solutions are available in Refs. [15] and [16]. A DDZ-3 direct current plating power supply was used for Cu plating. The phosphor copper plate was employed as anode, and the anode current density of 1 A/dm2 was chosen to plate the Cu layer in the alkaline aqueous solution at a rate about 12 μm/h. Next, the anode current density of 4 A/dm2 was chosen to deposit the Cu layer in the acidic aqueous solution at a rate about 100 μm/h. The alkaline and acidic Cu plating time was set to be 5 min and 1.4 h, respectively. Evidently, about 140 μm thick Cu layer was formed on the Al sheets (Fig. 1).

Fig. 1 Cross-sectional BSE image showing thick Cu layer plated on Al sheet
An OTF-1200X type tube furnace was used to anneal the Cu/Al composites in temperature range from 473 to 674 K for various time. The annealing process was implemented in H2 protective atmosphere at a heating rate of 10 K/min and a cooling rate of 4 K/min. After the Cu/Al composites annealing at 473 K for 360 h, their interfacial thermal stability was evaluated as servicing in a high-voltage power transmission circumstance (below 423 K in general). Meanwhile, the Cu/Al composites annealed at 573, 623 and 673 K for time range from 3 to 20 min were employed to investigate the formation mechanism and growth kinetics of the IMC layers. The effect of the IMC layer on electrical resistivity of the composites was also studied.
After annealing at 673 K, the Cu/Al laminar composite was peeled off along its interface, phases of the Cu/Al composites on the Al and Cu sides were identified using a Rigaku Rotaflex rotating anode X-ray diffraction (XRD) system, respectively. A diffraction angle of 5° was set. The samples were scanned from 10° to 85° at a rate of 1 (°)/min. Cross-sectional images of the annealed samples were also examined using a Hitachi SU8020 scanning electron microscope (SEM) equipped with an Oxford INCA energy dispersive X-ray (EDX) detector. EDX test was operated at 20 kV with a working distance of 15 mm and a count rate of 3500-4000 count/s. For cross-sectional observation, the samples were cross-sectioned, mounted with epoxy resin, ground with SiC papers in water and then polished with a 0.05 μm Al2O3 particle-water suspension. The measure- ment of electrical resistivity was performed using a SZT-E four-terminal resistance test system.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Annealing treatment
As shown in Fig. 2(a), a bright thin Zn layer situated between the Al and Cu terminals. The Cu and Al sides were separated completely by the Zn layer in the deposited Cu/Al composite plates. Although Zn still enriches at the Cu/Al interface, diffusion of Zn into the plated Cu layer is detectable (Figs. 2(b)-(d)). After the deposited Cu/Al composite was annealed at 473 K for 360 h, the Cu/Al interface was still clear, and no IMC layer was observed (Fig. 3(a)). However, interfacial enrichment of Zn at the Cu/Al interface weakens, mainly due to the diffusion of Zn into the Cu layer. Even so, the interdiffusion between Al and Cu was still prevented (Figs. 3(b)-(d)).
There exists the Al/Zn/Cu interface in the electroplated Cu/Al composite. During annealing, the diffusion of Zn into Cu is much rapider than that of Zn into Al. The explanations are as follows. 1) The plated Cu layer has high-density grain boundaries because of its ultrafine grain size, even on nano scale. Moreover, the electroplated layer is not fully dense in which vacancies and micro-pores exist [5,17,18]. These defects provide rapid paths for diffusion of the Zn atoms into Cu. 2) Although Cu, Al and Zn are all of face-centered cubic structure, atomic radius difference between Cu and Zn (22 pm) is rather less than that between Al and Zn (47 pm), therefore, Zn atoms have a higher solid solubility in Cu than in Al. For example, the solid solubility of Zn in Cu (>30%, mole fraction) is much higher than that of Zn in Al (5%, mole fraction) at 473 K [19]. Therefore, Zn atoms have higher diffusion coefficient and solid solubility in Cu than in Al.

Fig. 2 Cross-sectional BSE image (a) and elemental line-scanning spectra for Al (b), Zn (c) and Cu (d) across deposited Cu/Al composite interface
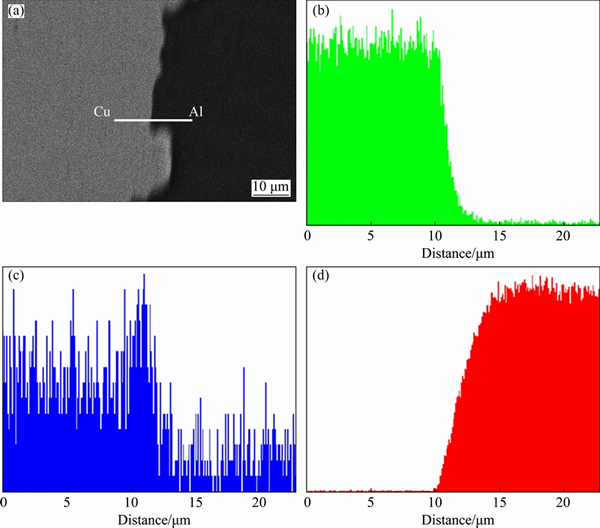
Fig. 3 Cross-sectional BSE image (a) and elemental line-scanning spectra across Cu/Al composite interface annealed at 473 K for 360 h for Cu (b), Zn (c) and Al (d)
According to the Cu-Al binary phase [20], there are five Cu-Al IMCs, i.e., γ2 (Cu9Al4), δ (Cu3Al2), ζ2 (Cu4Al3), η2 (CuAl) and θ (CuAl2) in the Cu-Al binary system. SHISHIDO et al [21] reported that two IMCs of CuAl and CuAl2 formed at the Cu/Al interface after the composites were annealed at 423-473 K in terms of XRD selective area diffraction. UEDONO et al [22] figured out that Cu9Al4 IMC might also form at Cu/Al interface after the composites were annealed at 423-473 K [22]. Accordingly, the IMC reaction products of the annealed Cu/Al composites are likely composed of CuAl, CuAl2 and Cu9Al4.
As mentioned above and in Ref. [23], the Cu-Al IMC layer formed at the Cu/Al interface annealed at 473 K. In this work, after the electroplated Cu/Al composites were annealed at the same temperature, no Cu-Al IMC layer was detected, indicating that the interdiffusion of Cu and Al was effectively restrained by the Zn intermediate layer. The Zn layer deposited on the Al sheet not only makes it happen to plate Cu on the Al sheet, but also acts as the barrier layer to suppress the Cu/Al interfacial diffusion and reaction during annealing the electroplated Cu/Al composites. The thermal stability of the Cu/Al composites is therefore increased.

Fig. 4 Cross-sectional BSE image (a) and EDX spectrum (b) of point A at Cu/Al composite interface annealed at 673 K for 1 min
Table 1 EDX analysis results across Cu/Al composite interface at different positions in Fig. 4(a)

As shown in Fig. 4, after the composite is annealed at 673 K for 1 min, no continuous IMC layer forms at the Cu/Al interface. However, at some locations, e.g., point A in Fig. 4(a), the CuAl2 phase may generate, based on the EDX analysis result in Fig. 4(b). Compositions of the points with a distance interval of 2.5 μm across the Cu/Al interface, as marked in Fig. 4(a), are listed in Table 1. After the composite is annealed at 673 K for 1 min, the Zn content in the original Zn layer (point 4) is just 0.9% (mole fraction) higher than that on the Cu side about 2.5 μm far from the Zn layer (point 3). The reduction of the Zn content in the Zn layer is mainly attributed to Zn atom diffusion from the Zn layer into the Cu layer. It also results in the decrease of the suppression effect of the Zn layer on the Cu/Al interface diffusion. Once the Zn layer at Cu/Al interface is broken, the suppression effect of the Zn layer turns to be weaker and weaker, and eventually disappears. The Cu-Al IMCs begin to nucleate and then grow along the Cu/Al interface, finally form a continuous IMC layer.
As shown in Fig. 5, the Al side sample mainly consists of two IMCs of CuAl and CuAl2, except the Al matrix, and the Cu side sample mainly consists of four IMCs of Cu9Al4, CuAl2, CuAl and CuZn2, except the Cu matrix. Among these IMCs, Cu9Al4, CuAl2 and CuAl are the Cu/Al interfacial reaction products, and CuZn2 precipitates at the Cu/Zn interface. The Cu-Al IMCs form the tri-layered structure, i.e., Cu9Al4, CuAl2 and CuAl, from the Cu terminal to the Al terminal.

Fig. 5 XRD patterns across Cu/Al composite interface annealed at 673 K for 20 min
3.2 Interfacial reaction mechanism
As shown in Table 2 [24], the thermodynamic stability sequence of the Cu-Al IMCs at 673 K is Cu9Al4>CuAl2>CuAl. However, in fact, CuAl2 is preferentially formed, during annealing the Cu/Al couples. This indicates that the Cu/Al interface reaction depends on not only the thermodynamic driving force, but also the atom diffusion and its kinetics.
Table 2 Standard Gibbs free energies of formation of Cu-Al IMCs [24]

It is well known that the diffusion coefficient D is described as
 (1)
(1)
where D0 is the pre-exponential factor, Q is the activation energy, R is the mole gas constant, and T is the annealing temperature. Based on the diffusion data in Table 3 [25], the diffusion coefficient of Cu atoms in Al at 673 K is calculated by

 (m2/s) (2)
(m2/s) (2)
That of Al atoms in Cu is

 (m2/s) (3)
(m2/s) (3)
Apparently, the former is about four times larger than the latter. Therefore, Cu and Al interdiffusion across the Cu/Al interface can be approximately regarded as the Cu atom diffusion into Al. Because of the non-equilibrium diffusion of Al and Cu in the Cu-Al binary system [23], Kirkendall voids are formed on the Cu side adjacent to the Cu/IMCs interface (Fig. 6). Of course, the formation and growth of these Kirkendall voids inevitably result in mechanical and electrical property degradation of the electroplated Cu/Al composites.
Table 3 Pre-exponential factor D0 and activation energy Q for solid state diffusion in Cu-Al binary system [25]


Fig. 6 Cross-sectional BSE image showing IMC layer in Cu/Al composite annealed at 673 K for 20 min
In the initial stage of the Cu/Al interfacial reaction, the diffusion of Zn atoms into the Cu and Al sides results in the reduction of the Zn content at the Cu/Al interface. Correspondingly, the suppression effect of the Zn layer on the Cu/Al interfacial diffusion lowers. The Cu atoms therefore diffuse into the Al side across the Cu/Al interface, and react with the Al atoms to form CuAl2:
[Cu]+2Al=CuAl2 (4)
where the symbol [Cu] denotes a Cu atom diffused into the Al matrix. CuAl2 then grows along the Cu/Al interface and gradually forms a continuous CuAl2 layer. As shown in Table 2, the CuAl2/Cu interface is unstable, thermodynamically, the Cu9Al4 layer then generates between the Cu layer and the CuAl2 layer through the reaction as follows:
7Cu+2CuAl2=Cu9Al4 (5)
This reaction occurs via the diffusion of Cu atoms from the Cu layer to the Cu/CuAl2 interface. Once a continuous Cu9Al4 layer is formed, the Cu atom diffusion should be restrained, leading to the formation of the CuAl layer, as described in Eq. (6):
[Cu]+CuAl2=2CuAl (6)
To sum up, during annealing the electroplated Cu/Al composites, the tri-layered reaction products of Cu9Al4/CuAl/CuAl2 are formed from the Cu side to the Al side. Among them, the CuAl layer is the thinnest.

Fig. 7 Average thicknesses of IMC layers vs square root of time as Cu/Al composites annealed at different temperatures
3.3 Growth kinetics of the IMC layer
As mentioned above, three IMC sub-layers gradually form and grow in the electroplated Cu/Al composites via the dominating diffusion of Cu atoms. To investigate the growth kinetics of these IMC layers, the electroplated Cu/Al composites were annealed at temperatures from 573 to 673 K for time till 20 min, respectively. The average thicknesses of CuAl2, Cu9Al4 and CuAl changing with annealing time are plotted in Fig. 7. The linear relationship of the IMC layer thickness with square root of the annealing time can be described as follows:
d=Kt1/2+d0 (7)
where d is the IMC layer thickness, K is the reaction rate constant, t is the annealing time, and d0 is a constant. The linear relationship indicates the diffusion-controlled growth kinetics of the IMC layer. And thus, K can be described as the Arrhenius-type equation:
 (8)
(8)
where K0 is the pre-exponential factor, Q is the growth activation energy, R is the mole gas constant, and T is the annealing temperature. Napierian logarithms of K (ln K) of each IMC layer vs reciprocal of T (1/T) were plotted in Fig. 8. The pre-exponential factors and activation energies were determined to be 3.84×10-11 m2/s and 25.47 kJ/mol for CuAl2, 1.87×10-10 m2/s and 34.16 kJ/mol for Cu9Al4, and 2.62×10-10 m2/s and 36.91 kJ/mol for CuAl, respectively. The growth activation energy of CuAl is the highest among them, indicating that during annealing the electroplated Cu/Al composites, growth of the CuAl layer is confronted with the largest barrier than the others. Furthermore, the growth activation energies of these Cu-Al IMC layers are all smaller than those reported previously. For example, as reported in Ref. [26], the growth activation energies are 97.5 kJ/mol for CuAl2 and 107.85 kJ/mol for Cu9Al4 of the cold-rolled Cu/Al composites. The difference may result from that there are more defects, e.g., vacancies, pores and grain boundaries, in the electroplated Cu layer. The Cu atom diffusion is therefore accelerated to promote the formation and growth of the Cu-Al IMCs in the electroplated Cu/Al composites.

Fig. 8 Plots of K vs T for IMC layers as Cu/Al composites annealed at different temperatures
3.4 Electrical resistivity
As shown in Fig. 9, the electrical resistivities of the Cu/Al composites increase during the annealing process, resulting from the formation and growth of the Cu-Al IMC layer, because the IMC layer has much higher electrical resistivity, compared with those of Cu and Al (the electrical resistivities of Cu, Al, Cu9Al4, CuAl2 and CuAl are 1.75×10-8, 2.83×10-8, 8.0×10-8, 14.2×10-8 and 11.4×10-8 Ω·m, respectively) [10,27]. LEE et al [10] found that the electrical resistivities of the Cu/Al composites increased from 45×10-8 to 85×10-8 Ω·m, as the IMC layer thicknesses changed from 21 to 107.5 μm [10]. In this work, the electrical resistivity of the as-deposited Cu/Al composite was tested to be 2.9×10-8 Ω·m; however, it is increased to 23.3×10-8 Ω·m, companying with the formation of the 12 μm thick Cu-Al IMC layer, as the Cu/Al composite was annealed at 673 K for 20 min.

Fig. 9 Relationships between electrical resistivity of Cu/Al composites with annealing temperature and time
4 Conclusions
1) The Cu/Al laminar composites were prepared by two-step dipping Zn and then electroplating Cu on pure Al sheets. The Cu/Al interfacial reaction and its kinetics during annealing and its effect on the electric properties of the composites were examined.
2) In the electroplated Cu/Al composite, the Zn layer distributes between the electroplated Cu layer and the Al sheet. It has an effect on suppressing the Cu/Al interfacial diffusion and reaction. After the composite was annealed at 473 K for 360 h, the Zn layer still existed at the Cu/Al interface, and no Cu-Al IMC layer was detected.
3) During annealing the Cu/Al composites at 573 K and above, the Zn layer dissolves into the Cu layer, its suppression effect on the Cu/Al interfacial diffusion is gradually lost. The Cu atoms diffuse into the Al sheet to form CuAl2, then Cu9Al4 and CuAl. And thus, the tri-layered reaction products of Cu9Al4/CuAl/CuAl2 (from the Cu side to the Al side) are finally formed.
4) During annealing the Cu/Al composites at temperature from 573 to 673 K, the IMC layer growth follows a diffusion-controlled kinetic mechanism. The growth activation energies of CuAl2, CuAl and Cu9Al4 were calculated to be 25.5, 36.91 and 34.16 kJ/mol, respectively.
5) With the increase of the annealing temperature and time, the IMC layer thickness increases, resulting in the enlargement of the electrical resistivity of the Cu/Al composites.
References
[1] TANG W M, HE A Q, LIU Q, IVEY D G. Solid state interfacial reactions in electrodeposited Cu/Sn couples [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2010, 20: 90-96.
[2] ZAMANI M, AMADEH A, LARI S M, BAGHAL. Effect of Co content on electrodeposition mechanism and mechanical properties of electrodeposited Ni-Co alloy [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2016, 26: 484-491.
[3] ZHANG Hai-jun, SUN Jian-feng. Oxidation and hot corrosion of electrodeposited Ni-7Cr-4Al nanocomposite [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2015, 25: 191-198.
[4] HE A Q, LIU Q, IVEY D G. Development of stable, non-cyanide solutions for electroplating Au-Sn alloy films [J]. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics, 2006, 17: 63-70.
[5] TANG W M, HE A Q, LIU Q, IVEY D G. Room temperature interfacial reactions in electrodeposited Au/Sn couples [J]. Acta Materialia, 2008, 56: 5818-5827.
[6] ZHANG Jian, CHEN Guo-hong, WANG Ruo-ming, MIAO Chun-hui, ZHENG Zhi-xiang, TANG Wen-ming. Effect of alkaline etching solution concentration on secondary zinc dipping on pure aluminum surface [J]. Journal of Functional Materials, 2016, 47(5): 5201-5206. (in Chinese)
[7] LYSAK V I, KUZMIN S V. Energy balance during explosive welding [J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2015, 222: 356-364.
[8] ZHANG Nan, WANG Wen-xian, CAO Xiao-qing, WU Jia-qi. The effect of annealing on the interface microstructure and mechanical characteristics of AZ31b/AA6061 composite plates fabricated by explosive welding [J]. Materials and Design, 2015, 65: 1100-1109.
[9] ABBASI M, KARIMI T A, SALEHI M T. Growth rate of intermetallic compounds in Al/Cu bimetal produced by cold roll welding process [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2001, 319: 233-241.
[10] LEE W B, BANG K S, JUNG S B. Effects of intermetallic compound on the electrical and mechanical properties of friction welded Cu/Al bimetallic joints during annealing [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2005, 390: 212-219.
[11] ZHANG Qiu-zheng, GONG Wen-biao, LIU Wei. Microstructure and mechanical properties of dissimilar Al-Cu joints by friction stir welding [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2015, 25: 1779-1786.
[12] WATANABE T, TAKAYAMA H, YAMGISAWA A. Soldering of aluminum alloy 6063 to copper with ultrasonic action [J]. Journal of Japan Institute of Light Metals, 2003, 53: 245-250.
[13] YU Xin-wei, ZHAO Guo-peng, HUANG Xiao-jun, HONG Rong, CHEN Yao, LI Mei-qing, HUANG Xiu-fang. Effect of metal ion zincing of aluminum alloy in cyanide-free zinc dipping solution [J]. Materials Protection, 2005, 38: 26-28. (in Chinese)
[14] LI Ling, YUAN Guo-wei, LIN De-yu. The chemical plating nickel base alloy theory and technology [M]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology Press, 2000. (in Chinese)
[15] KANUNGO M, MISHRA K G, DAS S C. Study on morphology of copper deposited onto aluminium by immersion plating from an oxalate bath containing perchloric acid [J]. Minerals Engineering, 2003, 16: 1383-1386.
[16] ALLAN C, HAMILTON J. Acid sulfate and pyrophosphate copper plating [J]. Plating and Surface Finishing, 1997, 84: 47-53.
[17] JANG J H, NAM D G, PARK Y H, PARK I M. Effect of solution treatment and artificial aging on microstructure and mechanical properties of Al-Cu alloy [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2013, 23: 631-635.
[18] ONUKI J, KOIIUMI M, ARAKI I. Investigation of the reliability of copper ball bond to aluminum electrodes [J]. IEEE Transactions on Components Hybrids Manufacturing Technology, 1988, 10(4): 550-555.
[19] KIM H J,LEE J Y,PAIK K W, KOH K W,WON J H. Effects of Cu/Al intermetallic compound (IMC) on copper wire and aluminum pad bond ability [J]. IEEE Transactions on Components & Packaging Technologies, 2001, 26: 44-51.
[20] GALE W F, TOTEMIER T C. Smithells metals reference book [M]. 8th ed. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2004.
[21] SHISHIDO I, MATSUO A, TOYOYAMA H, MIZUNO M, ARAKI H. Influence of lattice defects introduced in copper during electroplating on the interlayer reaction to Sn-3.0Ag-0.5Cu lead free solder [J]. Journal of Japan Institute of Light Metals, 2006, 70: 548-553.
[22] UEDONO A, MORI K, ITO K, IMAMIZU K, HACHIYA T. Impact of residual impurities on annealing properties of vacancies in electroplated Cu studied using monoenergetic positron beams [J]. Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 2007, 46: 483-485.
[23] XU Hui, LIU C, SILBERSCHMIDT V V, PRAMANA S S, WHITE T J, ACOFF V L. Behavior of aluminum oxide, intermetallics and voids in Cu-Al wire bonds [J]. Acta Materialia, 2011, 59: 5661-5673.
[24] QING Jing. Cu/Al composite interface combined with thermodynamic/kinetc research [D]. Ganzhou: Jiangxi University of Science & Technology, 2012. (in Chinese)
[25] ZHANG Lian-meng, HUANG Xue-hui, SONG Xiao-lan. Fundamentals of materials science [M]. Wuhan: Wuhan University Technology Press, 2004. (in Chinese)
[26] CHEN C Y, HWANG W S. Effect of annealing on the interfacial structure of aluminum-copper Joints [J]. Materials Transactions, 2007, 48: 1938-1947.
[27] BRAUNOVIC M, ALEKSANDROV N. Intermetallic compounds at aluminum-to-copper electrical interfaces: effect of temperature and electric current [J]. IEEE Transactions on Components Packaging & Manufacturing Technology A, 1994,17: 78-85.
张 健1,王斌昊1,陈国宏2,王若民2,缪春辉2,郑治祥1,汤文明1
1. 合肥工业大学 材料科学与工程学院,合肥 230009;
2. 国家电网安徽省电力公司 电力科学研究院,合肥 230601
摘 要:采用纯Al片表面浸Zn后再电镀厚Cu层的方法制备Cu/Al层状复合材料。在473~673 K温度范围内对该复合材料进行退火,研究退火过程中Cu/Al界面扩散与反应、界面金属间化合物 (IMCs) 层的长大动力学以及Cu/Al层状复合材料电阻率。结果表明,经过473 K、360 h的退火处理,未观察到Cu-Al IMCs层,显示Zn中间层能有效抑制Cu/Al界面扩散。可是,当复合材料经573 K及以上温度退火时,Zn层中的Zn原子主要向Cu中扩散,从Al侧到Cu侧形成CuAl2/CuAl/Cu9Al4三层结构的反应产物。IMC层遵循扩散控制的生长动力学,Cu/Al复合材料的电阻率随退火温度及时间的增加而增大。
关键词:Cu-Al金属间化合物;层状复合材料;电镀;界面反应;生长动力学;电阻率
(Edited by Wei-ping CHEN)
Foundation item: Project (2012QTXM0751) supported by the Scientific and Technological Research Project, State Grid, China
Corresponding author: Wen-ming TANG; Tel/Fax: +86-551-62901362; E-mail: wmtang@hfut.edu.cn
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(16)64462-X

