氩弧焊接GH625高温合金的显微组织演变与力学性能
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2016年第1期
论文作者:顾玉丽 陶春虎 魏振伟 刘昌奎
文章页码:100 - 106
关键词:镍基变形高温合金;钨极氩弧焊;显微组织;显微硬度;拉伸性能
Key words:nickel-based wrought superalloy; TIG welding; microstructure; microhardness; tensile property
摘 要:采用钨极氩弧焊接工艺对镍基变形高温合金GH625进行焊接。系统研究焊接接头的显微组织、元素分布、晶界特征和力学性能。结果表明:焊缝组织为奥氏体树枝晶结构,未见明显的热影响区,焊接熔合区的枝晶间区域均匀分布着大量的δ相。与母材相比,焊接熔合区同时具备较高的硬度和较大的晶粒,这可能与焊接熔合区的δ析出相有关。母材较高的强度主要归因于较多的细小晶粒和孪晶界,而焊接接头较低的伸长率可能是由于δ相。
Abstract: The tungsten inert gas welding (TIG) technique was employed to weld the nickel-based wrought superalloy GH625, and the microstructures, element distribution, grain boundary character and mechanical properties of the welded joint were investigated systematically. The results indicated that the welded seam was of austenite dendrite crystal structure and no obvious heat affected zone (HAZ) was observed. A number of precipitated δphases with homogeneous distribution were observed in the interdendritic region of the weld fusion zone. The abnormal phenomenon observed in the weld fusion zone of GH625, i.e., higher hardness and larger grain size compared with the base metal, may be attributed to the precipitated δ phase in the weld fusion zone. The higher tensile strength in the base metal was mainly attributed to the presence of more contents of fine grains and twin boundaries, while the lower elongation in the welded joint was mainly owing to the precipitated δ phase.
Yu-li GU, Chun-hu TAO, Zhen-wei WEI, Chang-kui LIU
Beijing Key Laboratory of Aeronautical Materials Testing and Evaluation, Beijing Institute of Aeronautical Materials, Aviation Industry Corporation of China, Beijing 100095, China
Received 12 January 2015; accepted 15 June 2015
Abstract: The tungsten inert gas welding (TIG) technique was employed to weld the nickel-based wrought superalloy GH625, and the microstructures, element distribution, grain boundary character and mechanical properties of the welded joint were investigated systematically. The results indicated that the welded seam was of austenite dendrite crystal structure and no obvious heat affected zone (HAZ) was observed. A number of precipitated δ phases with homogeneous distribution were observed in the interdendritic region of the weld fusion zone. The abnormal phenomenon observed in the weld fusion zone of GH625, i.e., higher hardness and larger grain size compared with the base metal, may be attributed to the precipitated δ phase in the weld fusion zone. The higher tensile strength in the base metal was mainly attributed to the presence of more contents of fine grains and twin boundaries, while the lower elongation in the welded joint was mainly owing to the precipitated δ phase.
Key words: nickel-based wrought superalloy; TIG welding; microstructure; microhardness; tensile property
1 Introduction
GH625, a nickel-based wrought superalloy with outstanding properties, such as strong tensile strength, excellent fabricability and weldability, is widely used for pipeline parts in gas-turbine engine [1-3]. The GH625 alloyed with Mo and Nb belongs to a solid solution strengthened alloy. However, it has been reported that, the precipitation of the metastable hardening phase of γ′′ occurs at a high temperature, and will transform into orthorhombic δ phase under some specific conditions. If the precipitated γ′′ phase is too much, it will deteriorate the mechanical properties of the resultant GH625 superalloy [4,5].
Fabrication of superalloy components is viable when using tungsten inert gas (TIG) welding [6-8]. GH625 tubes are used extensively in gas turbine engine pipelines, and they are usually exposed at 773 K or above when they are in service. Accordingly, it is essential for the welded structure to possess good mechanical properties, such as strong tensile strength, high creep resistance and outstanding corrosion resistance at room and elevated temperatures. At present, there are few literatures reported about the mechanical properties and relevant microstructures of GH625 weldment. Furthermore, the mechanical property of GH625 weldment may be different from that of the base metal owing to the microstructural evolution during TIG welding, namely the differences in grain size, grain boundary and element distribution as well as the precipitated phases in the weldment. Therefore, it is essential to study the properties and reliability of the welded parts comprehensively, which are always determined by the microstructure of the welded seam. It is necessary to understand whether other undesirable phases will form or not during TIG welding, and whether the corresponding microhardness and elongation of the alloy will obey some laws like other alloys. Having a clearer understanding of underlying factors will optimize the welding technique used for the GH625 superalloy.
In this work, the microstructures of the welded seam and the base metal were characterized by optical microscopy, scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and electron back-scattered diffraction (EBSD). Element contents in all the crucial zones across the weld fusion line were examined by electron probe micro analysis- wavelength dispersive X-ray spectroscopy technique (EPMA-EDS). Microhardness was also measured along the weld cross section. The tensile properties of GH625 superalloy before and after welding at room temperature and 772 K were examined.The main purpose of this work is to reveal the correlation between the microstructure features and the mechanical properties of the welded joint, and to evaluate the reliability of the welded joint.
2 Experimental
The chemical composition of GH625 is as follows: Cr 22.5, Fe 0.2, Mo 8.32, Nb 3.44, C 0.055, Mn 0.002, Al 0.24, Ti 0.20, Co 0.035 and Ni-balance (mass fraction, %). TIG welds were placed on areas perpendicular to the rolling direction of the GH625 tubes with the dimensions of 50 mm in diameter and 2.5 mm in wall thickness. The filler used was GH625 wire with a diameter of 2 mm. The welding groove angle is 45°. Both single weld and butt welding were carried out in this work. The welding parameters were as follows: welding current 94-96 A, welding voltage 12.7 V and welding speed 1.3 mm/s. After welding, the tubes were compressed into a plate to perform tensile testing. Because the tubes were through cold drawing forming, pressing deformation process has little impact on the tensile strength of the material. A post-weld annealing treatment in a vacuum environment was applied to GH625 weld at 900 °C for 2 h to remove the residual stress resulting from the welding and straightening deformation.
The microstructure of the welded joint was observed firstly by an optical microscope and a SEM in order to analyze the welding quality. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) was employed to observe and characterize the precipitated phase in the weld fusion zone. The detailed element distribution across the weld fusion line was characterized by EPMA-WDS so as to further analyze the chemical difference between the weld fusion zone and the base metal. The grain orientation and distribution character were studied by means of EBSD technique. The samples for EBSD were prepared by sectioning, grinding and electrolytic polishing. The EBSD tests were operated at 30 kV, with the specimen tilted by 70° and a scanning step of 0.8 μm.
In order to study the mechanical properties, both microhardness and tensile tests were carried out. The microhardness test was performed on the transverse cross section using the microhardness tester with 300 mg load at an interval of 0.2 mm. The tensile system was under displacement control and the applied load and elongation were measured.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Microstructure characterization
Figure 1 shows the microstructural variations of the as-welded GH625 plate in distinct locations. Figure 1(a) displays the entire weld cross-section image of the plate. It clearly reveals that the welded joint is in good condition and no macroscopic defects are observed in the joint. The width of the welded seam is approximately 6 mm. It can also be observed that the welded seam is a casting microstructure, and the crystallization direction of grains is almost vertical to the weld fusion line, with grains growing into the welding pool. The grain sizes in the center of welded seam are the largest, which indicates that the center of welded seam is the slowest to cool.
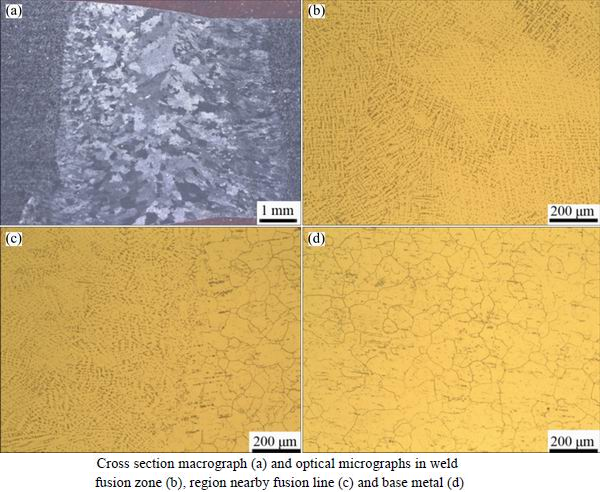
Fig. 1 Microstructures of as-welded GH625 plate in distinct locations
The microstructure of the welded seam is comprised of austenite dendrite crystal, as seen in Fig. 1(b). The grain size and morphology near the fusion line are similar to those far away from the welded seam in the base metal, and no obvious heat affected zone (HAZ) is observed, as shown in Figs. 1(c) and (d), respectively.
The SEM image of the weld fusion zone is shown in Fig. 2. The illustration is an enlarged view of the location arrow pointed. It reveals that a number of precipitated phases appear in the weld fusion zone. The needle-like precipitated phase distributes densely and homogeneously in the interdendritic region. Figure 3 displays the bright-field transmission electron micrograph in weld fusion zone and selective area electron diffraction (SAED) pattern taken from the needle-like precipitate along the [110] zone axis. The SAED pattern consists of distinct diffraction spots, which are corresponding to the orthorhombic structure of δ phase with a=0.574 nm, b=0.422 nm and c=0.454 nm.

Fig. 2 SEM image of weld fusion zone

Fig. 3 Bright-field transmission electron micrograph in weld fusion zone
The existence of δ precipitation, which usually emerges during long-term exposure [9], is not universal in GH625. Therefore, the appearance of δ phase during the welding process was a direct consequence of the prolonged and potentially cumulative exposure to high temperatures during cooling and repeated thermal excursions from adjacent deposition passes [10]. In addition, the chemical segregation between the dendrite arm and the interdendritic region facilitates the formation of the stabilized Nb-rich δ phase, an equilibrium phase of the metastable phase γ′′, which can play an important role in strengthening the alloy. However, it is noted that, when the content of δ phase exceeds some extent, it will have a detrimental effect on the strength and plasticity of the alloy [11].
In order to acquire the element distribution along the weld fusion line, EPMA-WDS line scans were performed and the plots of the variation of the main elements (Al, Cr, Fe, Mn, Mo, Nb and Ni,) as a function of scanning distances across the fusion line are presented in Fig. 4. The location of 1.0 mm in the abscissa represents the weld fusion line, while the left side is in the weld fusion zone, and the right side is in the zone of the base metal. It can be seen that the WDS curves of the elements Cr, Fe, Mo, Nb and Ni in the weld fusion zone fluctuate more greatly than that of the base metal, which shows a relatively gentle WDS curve. From these results, it can be concluded that the precipitated phase only exists in the weld fusion zone whereas there is absence of precipitated phase in the base metal. The contents of the refractory elements, such as Nb and Mo, in the weld fusion zone are obviously more than that in the base metal. Hence, it can be also deduced that the precipitated phase is δ phase and more refractory elements will result in high hardness.
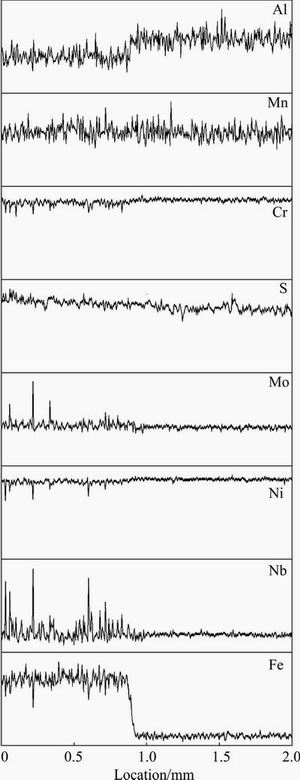
Fig. 4 EPMA-WDS line scan curves across weld fusion line
3.2 Grain and misorientation distribution
In order to investigate the evolution of grain and misorientation after the TIG welding process, EBSD analysis was performed in several distinct zones. Figure 5 presents the inverse pole figure (IPF) in several distinct zones. It can be seen that there is no obvious texture or preferred orientation in the weld seam zone. In comparison with the fusion zone nearby the fusion line, the bigger grains in the weld center zone appear. In these three zones, the grain size of the base metal is the smallest.
Welding is considered as a casting process due to the high temperature gradients and rapid solidification. Among the sizes in the aforementioned three zones, the grain size in the welded seam’s center is the largest. These results indicate that the slowest cooling speed happens in the welded seam’s center. The Hall-Petch relationship can be employed to explain the relationship between the yield stress (σy) and the grain size (d). The formula is shown as [12]where σ0 is the friction stress needed to move individual dislocations, and ky is a constant associated with the stress required to extend dislocation activity into adjacent unyielded grains. According to the above equation, it can be inferred that the yield strength of the base metal should be higher than that of the welded seam zone due to the smaller grains.
σy=σ0+kyd1/2 (1)
As shown in Fig. 6, the appreciable differences in densities of high degree misorientation boundaries are revealed by EBSD for the two zones. It can be seen that the grain boundaries in the weld fusion zone are comprised of random low angle boundaries and high angle boundaries; however, no twin boundaries are found. On the contrary, the fraction of austenite twin boundaries in the base metal is approximately 30%. Therefore, the superior strength and ductility of the base metal listed in Table 1 may be attributed to the presence of high degree of misorientation boundaries. It is reported that the twin boundaries are more resistant to cracks than the random high angle boundaries especially at high temperatures [13,14].
3.3 Mechanical properties
The microhardness distribution was measured at different depths across the weld fusion line, which is illustrated in Fig. 7. The value of 0 in the abscissa represents the weld fusion line, while the left side is the location of the weld fusion zone, and the right side is the location of the base metal. The microhardness variations at different weld depths are very similar, indicating that the mechanical property of the GH625 superalloy is not affected very much by the welding engrgy. The value of hardness nearby the fusion line is close to the mean value of the base metal of HV0.3 238, which also shows that HAZ is absent in the base metal and the alloy can escape the welding heat.
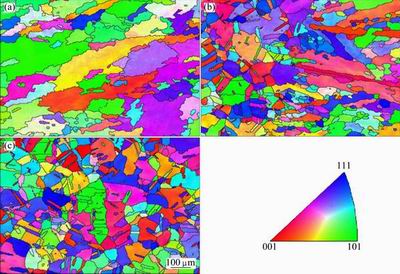
Fig. 5 EBSD IPFs of grain boundary distribution of weld center zone (a), region nearby fusion line (b) and base metal (c)

Fig. 6 Histograms of degrees of grain boundaries of weld center zone (a) and base metal (b)

Fig. 7 Microhardness profile taken horizontally along cross section of weld
The microhardness variation is constant across the weld fusion zone by the large, indicating that the weld metal material is relatively homogeneous and consistent with the aforementioned microstructure to some extent. It can be clearly observed that the microhardness is higher in the weld fusion zone than that in the base metal. The value of microhardness is increased by about HV0.3 30 from the base metal to the weld fusion zone. The hardness variation is not in line with the differences in strength and in grain size for the weld fusion zone and the base metal. Therefore, this type of hardness distribution across the weld fusion line is not only related with strength and grain size, but also correlates with grain boundary, precipitated phases and element distribution within different regions during welding. The change of grain sizes from the base metal to the weld fusion can refer to the EBSD results. The abnormal phenomenon observed in the weld fusion zone, i.e., high hardness with large grain size, may be attributed to the distribution of alloy elements and precipitated phases in the weld fusion zone. From the microstructural observation and the EPMA testing results, it can be concluded that the introduction of more contents of refractory elements Nb and Mo will enhance the strength and facilitate the formation of a number of precipitated phases densely distributed in the weld fusion zone, which results in a high hardness eventually in the weld fusion zone.
The tensile tests of the base metal and the welded joint were carried out at 273 and 773 K, respectively, and the results are shown in Table 1. The tensile strength and elongation of the welded joint are 735 MPa and 35.29% at 273 K, nearly 90% and 68% as high as those of the base metal, respectively. Whereas at 773 K, the tensile strength and elongation of the welded joint are 616 MPa and 27.06%, nearly 92% and 60% as high as those of the base metal, respectively. In general, the strengthening mechanism of superalloy includes solid solution strengthening, grain refine strengthening and precipitate strengthening. From the comparison between the base metal and the welded joint, it can be concluded that the higher strength in the base metal mainly is attributed to more fine grains and twin boundaries, while the lower elongation in the welded joint is mainly owing to the precipitated δ phase, which makes the material more brittle.
The microstructures nearby the tensile fracture surfaces of the welded joint at 273 and 773 K are shown in Fig. 8. Under these two conditions, many cavities were formed after the tensile test. It is noteworthy that all of the cavities exist in the precipitated δ phase, and are prone to form more brittle structures, even though the point is higher strength. It can be concluded that the precipitated δ phase during the welding is detrimental to the performance of the welded part. It is reported that a small amount or small block of the precipitated δ phase existing in superalloy has little influence on the mechanical properties; however, when the δ phase precipitates heavily, it will harm the plasticity of the alloy at room and elevated temperatures. The δ phase also occurs in superalloy using other welding process such as the laser welding [15].
Table 1 Tensile properties of base metal and welded joint at 273 and 773 K
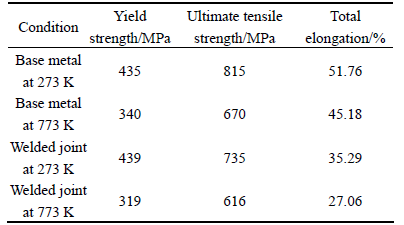

Fig. 8 SEM images nearby fracture surfaces of welded joint at 273 K (a) and 773 K (b)
4 Conclusions
1) The weld seam is of austenite dendrite crystal structure, and the crystallization direction of grains is almost vertical to the weld fusion line and no obvious HAZ is observed there.
2) A number of precipitated δ phases distribute densely in the interdendritic region of the weld fusion zone.
3) The abnormal phenomenon observed in the weld fusion zone, i.e., high hardness with large grain size may be attributed to the precipitated phases and the corresponding distribution of alloy elements in the weld fusion zone.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Dr. Y. LIU for providing the welds. In addition, the authors would like to thank Dr. F E. CUI for EBSD tests and Prof. S. J. WU for tensile tests.
References
[1] HENDERSON M B, ARRELL D, LARSSON R. Nickel based superalloy welding practices for industrial gas turbine applications [J]. Science and Technology of Welding and Joining, 2004, 9(1): 13-21.
[2] RAI S K, KUMAR A, SHANKAR V. Characterization of microstructures in Inconel 625 using X-ray diffraction peak broadening and lattice parameter measurements [J]. Scripta Materialia, 2004, 51: 59-63.
[3] CHEN W S, WANG C Y, SHIUE R K. Brazing Inconel 625 using the copper foil [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2013, 44: 5725-5731.
[4] RAJANI ZAREIE H R, AKBARI MOUSAVI S A A. The effect of explosive welding parameters on metallurgical and mechanical interfacial features of Inconel 625/plain carbon steel bimetal plate [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2012, 556: 454-464.
[5] ZHAO Yu-xin. Cold deformation behaviors of GH625 alloy and their effects [J]. Journal of Materials Engineering, 2000, (9): 36-37. (in Chinese)
[6] VELU M, BHAT S. Metallurgical and mechanical examinations of steel-copper joints arc welded using bronze and nickel-base superalloy filler materials [J]. Materials and Design, 2013, 47: 793-809.
[7] OSOBA L O, DING R G, OJO O A. Microstructural analysis of laser weld fusion zone in Haynes 282 superalloy [J]. Materials Characterization, 2012, 65: 93-99.
[8] BONIFAZ E A, RICHARDS N L. Modeling cast In-738 superalloy gas tungsten arc welds [J]. Acta Materialia, 2009, 57: 1785-1794.
[9] SUNDARARAMAN M, KUMAR L, ESWARA PRASAD G. Precipitation of an intermetallic phase with pt2mo-type structure in alloy 625 [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 1999, 30: 41-52.
[10] CLARK D, BACHE M R, WHITTAKER M T. Shaped metal deposition of a nickel alloy for aero engine applications [J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2008, 203: 439-449.
[11] CLARK D, BACHE M R, WHITTAKER M T. Microstructural characterization of a polycrystalline nickel-based superalloy processed via tungsten-inert-gas-shaped metal deposition [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 2010, 41(12): 1346-1353.
[12] OLA O T, OJO O A, CHATURVEDI M C. Laser arc hybrid weld microstructure in nickel based IN738 superalloy [J]. Materials Science and Technology, 2013, 29(4): 426-438.
[13] FONDA R W, WERT J A, PEYNOLDS A P. Friction stir welding of single crystal aluminium [J]. Science and Technology of Welding and Joining, 2007, 12(4): 304-314.
[14] YUN S L, HONG P K, HAI D C. Microscopic examination of an alloy 600/182 weld [J]. Materials Characterization, 2009, 60: 1496-1506.
[15] QU Feng-sheng, LIU Xu-guang, XING Fei, ZHANG Kai-feng. High temperature tensile properties of laser butt-welded plate of Inconel718 superalloy with ultra-fine grains [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2012, 22(10): 2379-2388.
顾玉丽,陶春虎,魏振伟,刘昌奎
中航工业 北京航空材料研究院 航空材料检测与评价北京市重点实验室,北京 100095
摘 要:采用钨极氩弧焊接工艺对镍基变形高温合金GH625进行焊接。系统研究焊接接头的显微组织、元素分布、晶界特征和力学性能。结果表明:焊缝组织为奥氏体树枝晶结构,未见明显的热影响区,焊接熔合区的枝晶间区域均匀分布着大量的δ相。与母材相比,焊接熔合区同时具备较高的硬度和较大的晶粒,这可能与焊接熔合区的δ析出相有关。母材较高的强度主要归因于较多的细小晶粒和孪晶界,而焊接接头较低的伸长率可能是由于δ相。
关键词:镍基变形高温合金;钨极氩弧焊;显微组织;显微硬度;拉伸性能
(Edited by Xiang-qun LI)
Corresponding author: Yu-li GU; Tel:+86-13520869020; E-mail: bluebee4646@163.com
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(16)64094-3

