DOI: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2016.11.018
徐家围子断陷沙河子组致密储层孔径分布定量表征
郭思祺1,肖佃师1, 2,卢双舫1,张鲁川1,谷美维1
(1. 中国石油大学(华东) 非常规油气与新能源研究院,山东 青岛,266580;
2.成都理工大学 油气藏地质与开发工程国家重点实验室,四川 成都,610059)
摘要:以徐家围子断陷沙河子组致密砂砾岩储层为例,联合低温氮气吸附和高压压汞资料标定核磁共振T2谱,实现核磁弛豫时间T2向孔喉半径rc的转换;结合核磁孔径分布曲线和铸体薄片资料,定量评价沙河子组致密储层的微观孔径分布及其影响因素。研究结果表明:核磁孔径分布曲线与低温氮气吸附及压汞的孔径分布曲线基本吻合,弥补前人标定核磁弛豫时间时较小、孔径部分精度较差的不足。沙河子组致密砂砾岩储层孔径主要分布区间为0.01~10 μm,分布曲线多表现为双峰状。孔径主要受压实作用、胶结作用及溶蚀作用影响。随着压实作用的增强,孔隙及喉道变小;胶结物含量的增加进一步降低孔喉连通性;溶蚀作用是致密储层大孔发育的主要因素。
关键词:致密储层;低温氮气吸附;核磁共振;压汞技术;孔径分布
中图分类号:P618.13 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2016)11-3742-10
Quantificational characterization of tight reservoir pore size distribution of Shahezi Formation in Xujiaweizi Fault Depression
GUO Siqi1, XIAO Dianshi1, 2, LU Shuangfang1, ZHANG Luchuan1, GU Meiwei1
(1. Research Institute of Unconventional Oil & Gas and Renewable Energy, China University of Petroleum (East China),
Qingdao 266580, China;
2. State Key Laboratory of Oil & Gas Reservoir Geology and Exploitation,
Chengdu University of Technology, Chengdu 610059, China)
Abstract: Taking tight glutenite reservoir of Shehezi Formation in Xujiaweizi Fault Depression as an example, conversions from nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) T2 to pore throat radius (rc) were realized by cryogenic nitrogen adsorption experiment and mercury injection to calibrate NMR T2, then microscopic pore size distribution and its influence factors were quantitatively evaluated by NMR pore size distribution curves and casting thin sections. The results show that NMR pore size distribution curves are similar to those of nitrogen adsorption and of mercury injection, which remedy the shortages of previous studies that smaller pore sizes have low precision. The main pore sizes of tight glutenite reservoirs of Shahezi Formation range from 0.01 to 10 μm. Distribution curves are always bimodal. Pore size is mainly affected by compaction, cementation and dissolution. With enhanced compaction, pores and throats become smaller. Increasing cement content reduces connection further, while dissolution is the major factor that tight reservoirs develop megalopores.
Key words: tight reservoirs; cryogenic nitrogen adsorption; nuclear magnetic resonance; mercury injection; pore size distribution
随着常规油气的日益枯竭,资源潜力巨大的非常规油气资源逐步引起广泛的关注及重视,尤其以致密砂岩油气的增长速度最快[1-3]。油气在致密储层中的流动、聚集机理明显不同于常规储层,这主要归因于致密储层中发育微纳米级别的复杂孔喉系统[4]。因此,致密储层成储机理及分级评价的研究,需要精细表征致密储层的微观孔喉结构。储层微观孔隙是指储集岩中孔隙和喉道的几何形状、大小、分布及其连通关系,其是影响储层物性的重要因素[5]。国际纯粹与应用化学协会(IUPAC)命名方法将致密储层孔隙分为3类,孔径小于2 nm的孔隙称为微孔;孔径介于2~50 nm的孔隙称为介孔(或称中孔);孔径大于50 nm的孔隙称为大孔。孔隙结构的表征方法分流体法、射线法和数值模拟法,其中流体法是定量表征孔隙体积及孔径分布的主要方法,包括压汞、低温氮气吸附,射线法包括扫描电镜、核磁共振及中子散射等手段,但各种方法均存在局限性。目前最常用的孔隙结构表征方法为高压压汞法,孔径测量范围受注汞压力限制,不适用于致密储层微孔和介孔的评价。低温氮气吸附可用于表征孔径小于50 nm的微孔及介孔的体积及孔径分布,对大孔部分无法表征。核磁共振对孔隙内流体响应敏感[6],T2谱中包含有关孔喉结构的信息,但测量单位为弛豫时间,需要进行标定,将其转换为孔隙半径。在传统表征技术方法的基础上,多学科、多领域测试手段和方法的有效结合是致密储层孔隙结构表征技术的发展趋势。松辽盆地徐家围子断陷沙河子组SS9H井在2013年获得20.8万m3高产工业气流,展示了沙河子组致密气的良好勘探前景,但沙河子组致密气的勘探与评价工作仍处于起步阶段,亟需对其开展储层微观表征工作,分析孔隙结构及其影响因素,从而明确储层分级评价标准,开展储层综合评价。因此,以松辽盆地北部徐家围子断陷沙河子组致密砂砾岩储层为研究对象,建立一种联合低温氮气吸附和压汞资料标定核磁共振T2谱的方法,定量表征了沙河子组致密储层的孔径分布,并结合薄片、X线衍射分析等研究了其孔径分布的影响因素。
1 研究区地质概况
1.1 区域地质概况
徐家围子断陷为松辽盆地深层的一个低角度单断型箕状断陷,近北北西向展布。该断陷位于松辽盆地东部凹陷区内,可进一步划分为徐西断坳、升平断坳、榆西断坳和徐东斜坡四个次级构造单元[7]。徐家围子地区断陷期地层主要包括白垩系下统的火石岭组、沙河子组和营城组,其中沙河子组地层形成于断陷鼎盛期,构造活动强烈、持续拉张,在深湖-半深湖背景下,发育了扇三角洲、辫状河三角洲及湖底扇等沉积体系。XT1井在沙河子组4 000 m以下地层中获9万m3的工业产能,展示沙河子组致密砂砾岩气良好的勘探潜力。前人研究工作表明,沙河子组气藏具“源储叠置、近源聚集”的特点,油气分布不受构造控制,具备致密砂岩气藏的典型特征,油气甜点区主要受优质储层的控制。因此,开展沙河子组致密储层微观孔隙分布及影响因素的研究,有利于指导该区储层分级评价及优质储层的预测。
1.2 储层特征
1.2.1 储层岩石学特征与物性
通过对研究区64块致密砂砾岩样品的薄片鉴定可知:沙河子组岩石类型主要为长石质岩屑砂岩和岩屑长石砂岩(图1(a))。岩屑质量分数最高,达42.53%,以岩浆岩岩屑为主,变质岩屑及沉积岩屑不发育;长石次之,为25.64%;石英质量分数为17.56%。填隙物质量分数平均值为14.24%,主要以泥质杂基及碳酸盐为主。
统计44口井645个物性测试数据,沙河子组致密储层的孔隙度分布在0.3%~11.3%,平均值为4.18%,其中小于6%的样品点占73.5%(图1(b));渗透率分布范围为(0.001~11.2)×10-3 μm2,平均值为0.26×10-3 μm2,其中小于0.1×10-3 μm2的样品点占71%(图1(c))。孔隙度与渗透率间无明显正相关性,表明该区致密储层的孔喉结构较为复杂。
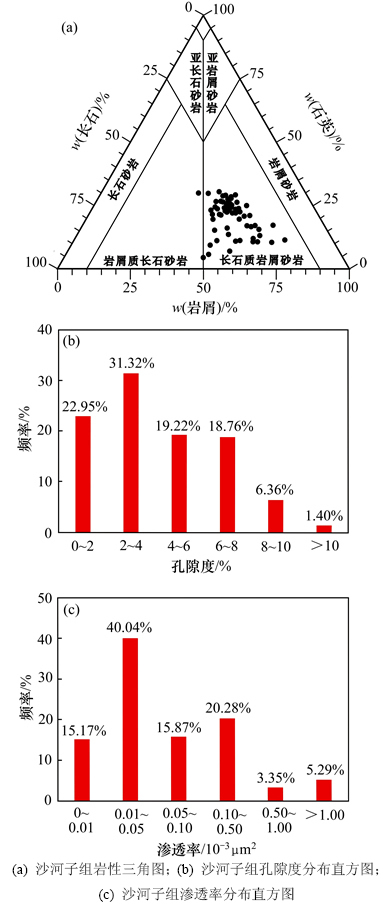
图1 沙河子组岩性三角图及物性分布直方图
Fig. 1 Lithologic triangle diagram and physical property distribution histograms of Shahezi Formation
1.2.2 储集空间类型
储层物性是孔隙结构的宏观反映,物性的差别主要受微观孔隙结构的控制[8]。利用偏光显微镜对铸体薄片进行观察,发现沙河子组储层孔隙类型主要为粒间溶孔及长石、岩屑等颗粒的粒内溶孔,发育少量微裂缝,原生粒间孔不甚发育。
经历了强压实及胶结作用后,沙河子组致密储层中原生粒间孔规模较小或基本被碳酸盐等胶结物充填,粒间孔所占比例较小,薄膜状发育的绿泥石是残余粒间孔保存的主要原因(图2(a)),因其在埋藏过程中的持续生长增强了储层的抗压实能力,并阻止石英次生加大[9-10]。溶蚀孔隙是沙河子组普遍发育的孔隙类型,有效改善了沙河子组储层的物性,是沙河子组获得高产气流的关键。溶蚀孔可分为粒间溶孔和粒内溶孔,碳酸盐胶结物的溶蚀是沙河子组粒间溶孔形成的主要原因(图2(b)),长石和岩屑中不稳定组分被溶蚀后形成粒内溶孔(图2(c)和(d))。沙河子组黏土矿物以伊利石和绿泥石为主,这些矿物晶体间存在大量的晶间孔[11],是沙河子组致密气的另一较发育的孔隙类型(图2(e))。微裂缝多由压实作用造成的钢性颗粒破裂而形成,主要发育在砂质砾岩及砾岩中(图2(f))。微裂缝对致密储层孔隙度贡献较小,但明显改善了储层的渗透性,可以为有机酸等流体的运移提供良好通道,利于储层内溶蚀孔的形成。
2 孔隙表征方法对比
表征储层孔隙结构,深入揭示油气储层的内部结构,对油气田的勘探和开发具有重要意义。压汞技术是目前定量研究岩石孔隙结构最主要的方法之一,压汞曲线的形态可以反映岩石孔隙大小及分布。核磁共振T2谱在油层物理上的含义为岩石的孔隙大小分布,即不同大小孔隙的体积占总孔隙体积的比例。通过分析T2分布,能够确定油水分布状态,估算储集层的孔隙度、渗透率和饱和度等常规物性参数,快速无损地显示岩石内部结构。前人大量研究表明,核磁共振T2谱分布与压汞所获得的孔径分布曲线之间存在密切的相关性,二者都能反映岩石的孔隙结构,可以用高压压汞进行核磁共振T2谱的标定[12-17]。但由于致密储层孔喉窄小,孔隙连通性差,导致最大进汞饱和度低,进汞饱和度多低于60%,表明高压压汞只能反映出一部分较大的孔隙空间,当孔喉半径小于50 nm时,T2分布曲线与毛管压力曲线分布形态出现较大差异[15-17],不能精细表征致密储层中的微孔及介孔。低温N2吸附受样品的限制,大孔被破坏,只对中低孔有效。因此,多种实验方法的有效结合是致密储层孔隙结构表征技术的发展趋势。
联合多种方法可以表征出不同范围内孔隙的分布,能全面反映孔径分布,但各种方法在重叠部分通常会表现出矛盾。核磁共振易受岩石中的顺磁物质影响使测得的孔径偏小,由X线衍射全岩定量分析得知研究区内黄铁矿和菱铁矿的质量分数平均值分别为0.04%和0.71%,对核磁共振T2谱的影响可以忽略不计。相对于高压压汞和低温氮气吸附,核磁共振反映的孔隙结构相对全面,可以识别孔径大于 10 nm的孔隙,但是测量单位为弛豫时间,需要对其进行转换。因此,可以结合低温N2吸附和压汞资料,来标定核磁共振T2谱。
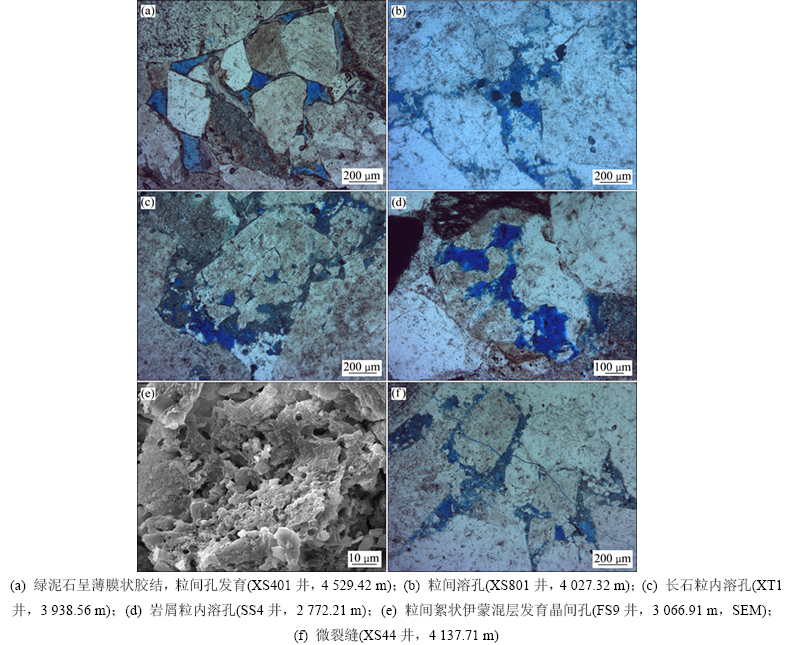
图2 徐家围子断陷沙河子组储层储集间类型
Fig. 2 Reservoir space types of Shahezi Formation in Xujiaweizi Fault Depression
3 基于核磁标定的孔隙表征方法
3.1 基本原理
当饱和油水的样品置于均匀分布的静磁场中时,流体中的氢核(1H)会被磁场极化,表现出磁化矢量。此时对样品施加一定频率的射频场便可产生核磁共振现象。撤掉射频场,可以接收到一个幅度随时间以指数函数衰减的信号。可以用纵向弛豫时间T1和横向弛豫时间T2来描述核磁共振信号衰减的快慢。由于T2测量速度快,多采用T2来测量核磁共振信号的衰减。氢核因做横向弛豫运动与孔隙壁发生碰撞,造成能量损失。孔隙半径越小,碰撞越频繁,氢核能量损失越快,弛豫时间越短,因此孔隙半径与氢核弛豫率呈反比关系[18-20],即:
 (1)
(1)
式中:T2为孔道内流体的核磁共振T2弛豫时间,ms;ρ为岩石的横向表面弛豫率,是表征岩石性质的参数,μm/ms;s/v为孔隙的比表面积,μm-1。
从式(1)可以看出:弛豫时间T2和孔隙比表面积有关,而比表面积受孔隙形状及大小影响。假设孔隙是由理想的球体或柱状管道组成,孔隙半径与喉道呈正比[21-22],则式(1)可改写为
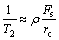 (2)
(2)
式中:Fs为形状因子,球形孔隙Fs=3,柱状喉道Fs=2;rc为孔喉半径,μm。
从式(2)可以看出T2与rc成正比,引入横向弛豫时间与孔喉半径的转换系数C,单位为μm/ms,式(2)可进一步改写为
 (3)
(3)
根据式(3)可以实现核磁横向弛豫时间T2向孔喉半径rc的转换,从而得到核磁孔隙分布,对储层的孔隙结构进行表征。
3.2 实验步骤
本文联合低温氮气吸附及压汞资料得到复合累计孔隙度曲线,用其标定C,实现核磁弛豫时间与孔隙半径的转换。具体实验步骤如下:
1) 将低温氮气吸附和压汞实验结果转变为孔隙度分量。通过压汞资料可以得到不同毛管压力下的进汞饱和度增量ΔSHg,ΔSHg乘以岩石总孔隙度便可得到不同毛管压力所对应的孔隙度分量,根据毛管压力计算出相应的孔喉半径,得到不同孔隙半径对应的孔隙度分量;通过氮气吸附可以得到不同孔隙半径(<100 nm)下单位质量岩石的吸附体积,将孔隙体积乘以岩石骨架密度即得到不同孔隙半径对应的孔隙度分量;根据上述处理,即可得到压汞与氮气吸附不同级别孔径的孔隙体积分数分布(图3(a))。
2) 确定孔隙累计分布。图3(a)中氮气吸附、压汞孔径分布曲线在0.01~0.1 μm处有重叠部分,在重叠部分选择一个符合曲线整体走势的点,该点对应的孔喉半径记为ra。图3(a)中根据曲线的整体走势,在考虑高压压汞和氮气吸附实验精度的前提下,选取二者孔径分布曲线纵坐标差值最小的点,即ra选取为0.053 μm。以ra为界,保留氮气吸附中孔径小于ra的孔喉部分与压汞中孔径大于等于ra的孔喉部分,将保留部分的孔隙度累加即可得到总孔隙度,Φt=5.121%;将保留下来的不同孔径的孔隙度分量除以Φt得到其所占比例,绘制不同孔喉半径下孔隙比例累计分布曲线(图3(b))。
3) 确定最佳标定系数C。将核磁共振T2谱曲线转变为孔隙比例累计曲线,假定不同C值,根据式(3)可将T2弛豫时间转变为孔喉半径,得到不同孔喉半径的孔隙比例累计曲线。对比核磁得到的孔隙比例累计曲线与N2吸附和压汞得到的累计曲线,进行误差计算,找到误差最小时所对应的C,该C即为最佳的转换系数。误差计算公式为
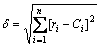 (4)
(4)
式中:ri 为压汞和N2吸附复合累计曲线中的孔喉半径,μm;Ci为T2谱在一定C下换算得到孔隙半径,μm;n为压汞和N2吸附复合累计曲线中孔喉半径分布点数。
图3(c)中,假定C取5,15和50,绘制不同C值下孔隙比例累计曲线,通过与N2和压汞累计曲线相比,当C为15时,二者误差最小,两条孔隙比例累积曲线形态趋于一致,确定最佳标定系数C为15。
4) 根据优选出的C,实现核磁共振曲线由T2弛豫时间向孔喉半径rc的转换,得到致密储层中全尺度不同孔径的孔隙体积分布(图3(d))。
3.3 实验精度分析
将核磁转换后的孔径分布与高压压汞及低温N2吸附的结果进行叠合(图4),以检验核磁标定结果的精度。由图4可知:标定后的核磁共振T2谱曲线与低温N2吸附及压汞获得的孔径分布基本一致,两者孔径分布范围基本重合,且孔径的峰值区间也基本一致,这说明标定后的核磁曲线能有效反映致密储层的孔径分布。
核磁共振T2谱曲线与压汞及低温N2吸附表征孔径并不完全重合,主要因为3种方法的测量原理不同。高压压汞通过测量不同压力下的进汞量来反映喉道半径及其相连的孔隙体积,核磁共振测量氢核在孔隙中的弛豫时间来表征不同半径的孔隙,因此对于与小喉道相连的大孔部分,在高压压汞中出现的位置较核磁T2谱滞后,即高压压汞在大孔径部分(>50 nm)表征值要小于核磁共振的表征值,而在较小孔径部分(<50 nm)表征值则大于核磁共振的表征值。低温N2吸附需要粉碎样品,通过气体吸附和脱附原理来表征微孔和介孔的孔径分布,对于孔径小于10 nm的孔隙,核磁横向弛豫时间变得很小,核磁测量值明显低于低温N2吸附结果,而对于孔径为10~50 nm的孔隙,由于粉碎样品破坏岩石中部分孔隙,低温N2吸附结果近似或稍小于核磁共振的表征值。综合上述分析,核磁共振在表征孔径大于10 nm的孔隙部分的精度较高,能全面表征出致密储层不同级别孔隙的分布。
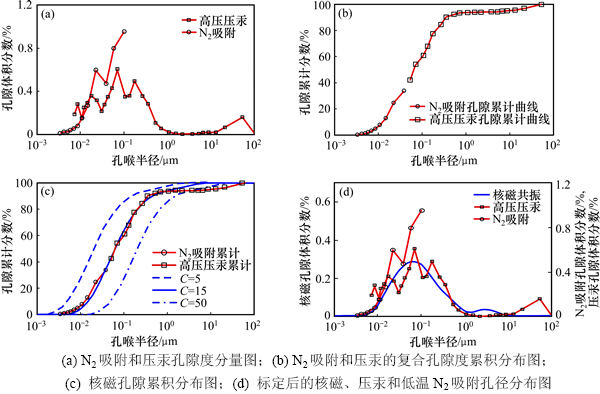
图3 联合压汞、N2吸附标定核磁共振T2谱流程图
Fig. 3 Flow chart of NMR T2 calibration by jointing nitrogen adsorption and mercury injection
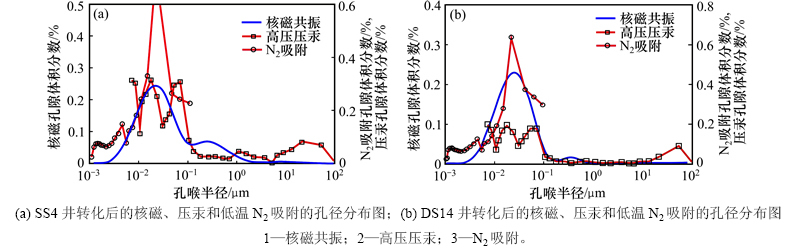
图4 转化后的核磁、压汞和低温N2吸附的孔径分布图
Fig. 4 Pore size distribution of converted NMR, nitrogen adsorption and mercury injection
4 沙河子组致密储层孔径分布及其影响因素
4.1 孔径分布特征
为研究沙河子组致密砂砾岩储层的孔径分布,选取16块砂砾岩样品分别开展核磁共振、高压压汞及低温N2吸附实验,利用本文中标定方法对核磁共振T2谱进行标定,进而分析沙河子组储层的孔径分布及影响因素。致密砂砾岩储层孔径分布范围为0.002~100 μm(图5(a)),孔径分布表现为双峰状,大孔部分峰值集中在2~10 μm,小孔部分峰值集中在10~100 nm。整体上孔径几何均值集中在50~150 nm,孔径大于1 μm的孔隙所占比例小于20%,表明沙河子组致密储层孔喉半径窄小,以纳米级孔隙为主(图5(b))。
4.2 孔径分布的影响因素
4.2.1 黏土矿物质量分数对孔径的影响
国内外研究表明:在沉积及成岩条件相同的情况下,黏土矿物质量分数越高,储层的孔隙度和渗透率越低,储层物性越差[23]。黏土矿物作为填隙物或胶结物充填粒间孔隙,缩小孔喉半径、降低孔喉连通性,使孔隙度及渗透率降低。沙河子组致密储层中黏土质量分数为2%~43%,其中大于10%的样品占77%;黏土矿物质量分数与孔径几何均值呈明显负相关,随黏土矿物质量分数的增加,孔隙半径明显降低,这表明高黏土含量是控制该区致密储层物性差、孔喉半径窄小的一个重要原因(图6(a))。
沙河子组致密储层中黏土矿物以伊利石、伊蒙混层和绿泥石为主,其中伊利石对孔喉半径的影响最大,其含量与孔径表现出极强的负相关性(图6(b))。研究发现:工区内伊利石多呈片丝状、片絮状,由生长点向孔隙空间内伸展,极大地缩小了孔喉半径(图6(c))。同时,在伊蒙混层向伊利石转化过程中,将产生额外的硅元素(图6(d)),这些硅质通常以石英次生加大或自形微晶的方式沉淀,减小孔径、甚至阻塞喉道,使孔隙结构变得更加复杂[24]。
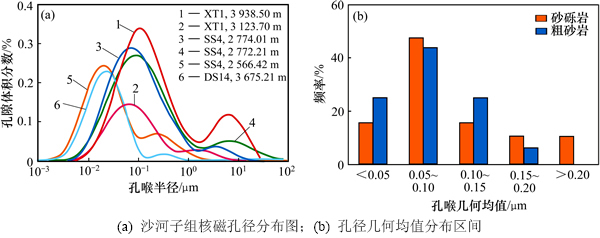
图5 沙河子组孔径分布特征
Fig. 5 Pore size distribution features of Shahezi Formation
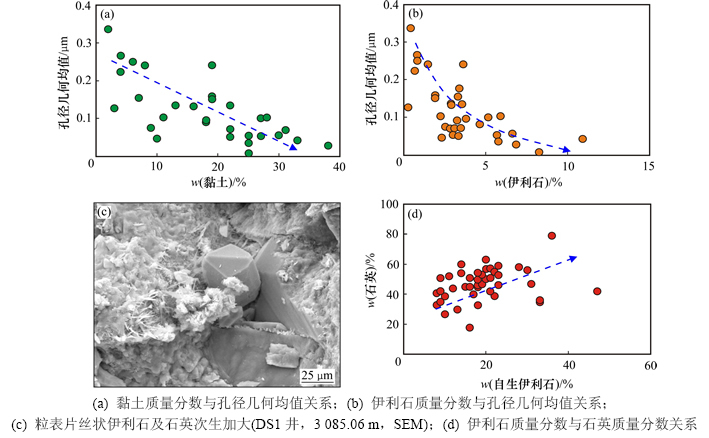
图6 黏土矿物含量对孔径的影响
Fig. 6 Effects of clay minerals content on pore size
4.2.2 成岩作用对孔径的影响
沙河子组普遍发育的破坏性成岩作用有压实作用及胶结作用,建设性成岩作用主要为溶蚀作用。其中压实作用较强,颗粒多呈点-线接触,局部可见凹凸接触。主要发育的胶结作用有3类:碳酸盐胶结、硅质胶结及黏土矿物胶结。溶蚀作用是致密储层物性得以改变的重要途径,长石及岩屑的溶蚀在沙河子组内最为发育。成岩作用对储层物性的影响具有双重性,压实作用和胶结作用使孔隙度降低,而溶蚀作用则增加了孔隙度[25],结合铸体薄片及核磁孔径分布曲线来分析不同成岩作用对孔径的影响。
分析不同压实强度下岩石孔径的变化,铸体薄片显示图7(a)中Ⅰa,Ⅰb,Ⅰc及Ⅰd 4块样品的压实作用依次增强。其中,Ⅰa样品呈基底胶结,碳酸盐胶结物充填粒间孔隙,颗粒多呈点接触,压实作用弱;Ⅰb样品为孔隙胶结,颗粒间多为点-线接触,压实作用较弱;Ⅰc样品为接触胶结,颗粒多呈线接触,压实作用中等;Ⅰd样品呈镶嵌式胶结,云母压弯变形、局部石英发育压裂缝。观察4块样品的核磁孔径分布曲线(图7(a))可知:曲线多具双峰,主峰主要分布在10 nm至1 μm区间上,次峰主要分布区间为1~10 μm。随着压实作用的增强,双峰均表现出总孔隙度减小,主峰孔径变化不大,而次峰孔径降低幅度较大,说明压实作用使大孔部分孔径减小,小孔部分体积变小。
胶结作用是造成储层致密的主控因素。分析不同程度的胶结作用下岩石孔径的变化。通过铸体薄片观察,图7(b)中Ⅱa,Ⅱb,Ⅱc及Ⅱd 4块样品的胶结物含量依次增加,观察核磁孔径分布曲线(图7(b))可知:随着胶结作用的增加,孔隙度及主峰孔喉半径均减小,且大孔的发育明显减弱。当胶结作用较强时(Ⅱd样品),孔隙连通性变差,曲线表现出孤立多峰状分布,说明胶结作用使孔径减小,严重时可堵塞喉道,增加孔隙结构的复杂性。
溶蚀作用是改善致密储层物性的关键。研究区普遍发育的长石及岩屑为次生孔隙的发育提供了必要条件。图7(c)中Ⅲa,Ⅲb,Ⅲc及Ⅲd 4块样品的溶蚀作用依次增强,核磁孔径分布曲线(图7(c))多为双峰,主峰中孔径主要分布区间为0.01~1 μm,次峰中孔径主要分布区间为1~10 μm。随着溶蚀作用的增强,主峰孔隙度增加幅度不大,孔径变化不大,次峰孔隙度及孔径明显增大,说明致密储层中的大孔多为溶蚀孔隙。
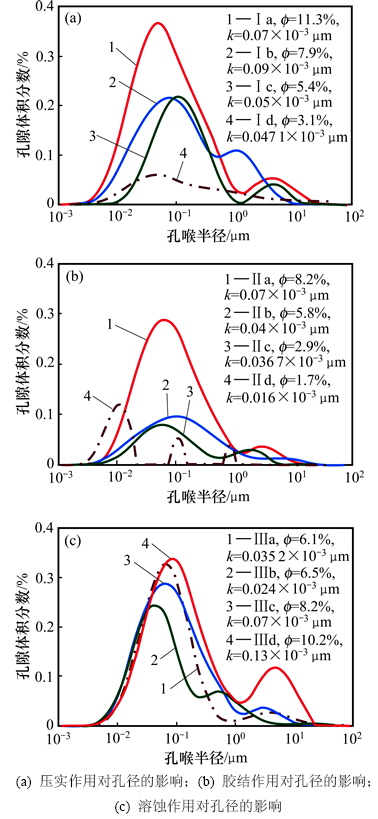
图7 不同成岩作用下的核磁孔径分布曲线
Fig. 7 NMR pore size distribution curves of different diagenesis
5 结论
1) 压汞法、低温N2吸附及核磁共振之间存在内在联系,三者都可反映岩石的孔隙结构。联合低温N2吸附及高压压汞资料标定核磁共振T2谱,将核磁弛豫时间T2向孔喉半径rc转换,可以实现致密储层多尺度孔喉系统的全面表征,表征精度达10 nm。
2) 徐家围子断陷沙河子组致密砂砾岩储层孔径的主要区间为0.01~10 μm,孔径小于1 μm的孔隙占80%以上,表明沙河子组致密储层孔喉半径窄小,以纳米级孔隙为主。
3) 黏土矿物质量分数越高,孔径越小。其中,伊利石对孔径的影响最大。压实作用和溶蚀作用对大孔隙的影响显著。压实作用使大孔部分孔径减小,小孔部分体积变小。溶蚀作用使大孔隙数量明显增加,而对小孔隙影响不大。胶结作用是导致致密储层孔隙结构复杂的关键因素。
参考文献:
[1] 邹才能, 朱如凯, 吴松涛, 等. 常规与非常规油气聚集类型、特征、机理及展望: 以中国致密油和致密气为例[J]. 石油学报, 2012, 33(2): 173-187.
ZOU Caineng, ZHU Rukai, WU Songtao, et al. Types, characteristics, genesis and prospects of conventional and unconventional hydrocarbon accumulations: taking tight oil and tight gas in China as instance[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2012, 33(2): 173-187.
[2] 李建忠, 郭彬程, 郑民, 等. 中国致密砂岩气主要类型、地质特征与资源潜力[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2012, 23(4): 607-615.
LI Jianzhong, GUO Bincheng, ZHENG Min, et al.Main types, geological features and resource potential of tight sandstone gas in China[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2012, 23(4): 607-615.
[3] 戴金星, 倪云燕, 吴小奇. 中国致密砂岩气及在勘探开发上的重要意义[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2012, 39(3): 257-264.
DAI Jinxing, NI Yunyan, WU Xiaoqi. Tight gas in China and its significance in exploration and exploitation[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2012, 39(3): 257-264.
[4] 邹才能, 朱如凯, 白斌. 中国油气储层中纳米孔首次发现及其科学价值[J]. 岩石学报, 2011, 27(6): 1857-1864.
ZOU Caineng, ZHU Rukai, BAI Bin. First discovery of nano-pore throat in oil and gas reservoir in China and its scientific value[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica,2011, 27(6): 1857-1864.
[5] 吴胜和,熊琦华. 油气储层地质学[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 1998: 113-122.
WU Shenghe, XIONG Qihua. Petroleum reservoir geology[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 1998: 113-122.
[6] LUTHI S. Geological well logs: Their use in reservoir modeling[M]. Springer Science & Business Media, 2001: 159-180.
[7] 刘学锋, 钟广法, 王正允, 等. 松辽盆地北部徐家围子断陷构造格局及其成因[J]. 西安石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2006, 21(4): 6-10.
LIU Xuefeng, ZHONG Guangfa, WANG Zhengyun, et al. Tectonic framework of Xujiaweizi Faulat Depression in northern Songliao Basin and its origin[J]. Journal of Xi’an Shiyou University (Natural Science Edition), 2006, 21(4): 6-10.
[8] GALEAZZI S, POINT O, HADDADI N, et al. Regional geology and petroleum systems of the Illizi–Berkine area of the Algerian Saharan Platform: An overview[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2010, 27(1): 143-178.
[9] BERGER A, GIER S, KROIS P. Porosity-preserving chlorite cements in shallow-marine volcaniclastic sandstones: Evidence from Cretaceous sandstones of the Sawan gas field, Pakistan[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2009, 93(5): 595-615.
[10] 黄思静, 谢连文, 张萌, 等. 中国三叠系陆相砂岩中自生绿泥石的形成机制及其与储层孔隙保存的关系[J]. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2004, 31(3): 273-281.
HUANG Sijing, XIE Lianwen, ZHANG Meng, et al. Formation mechanism of authigenic chlorite and relation to preservation of porosity in non-marine Triassic reservoir sandstones, Ordos Basin and Sichuan Basin, China[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology (Science and Technology Edition), 2004, 31(3): 273-281.
[11] 何自新, 贺静. 鄂尔多斯盆地中生界储层图册[M].北京:石油工业出版社, 2004: 107-109.
HE Zixin, HE Jing. Atlas of Mesozoic reservoirs in Ordos Basin[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2004: 107-109.
[12] SLIJKERMAN W F J, HOFMAN J P, LOOYESTIJN W J, et al. A practical approach to obtain primary drainage capillary pressure curves from NMR core and log data[J]. Petrophysics, 2001, 42(4): 334-343.
[13] 何雨丹, 毛志强, 肖立志, 等. 核磁共振T2分布评价岩石孔径分布的改进方法[J]. 地球物理学报, 2005, 48(2): 373-378.
HE Yudan, MAO Zhiqiang, XIAO Lizhi, et al. An improved method of using NMR T2 distribution to evaluate pore size distribution[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2005, 48(2): 373-378.
[14] 王学武, 杨正明, 李海波, 等. 核磁共振研究低渗透储层孔隙结构方法[J]. 西南石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2010, 32(2): 69-72.
WANG Xuewu, YANG Zhengming, LI Haibo, et al. Experimental study on pore structure of low permeability core with NMR soectra[J]. Journal of Southwest Petroleum University (Science and Technology Edition), 2010, 32(2): 69-72.
[15] 运华云, 周灿灿. 利用T2分布进行岩石孔隙结构研究[J]. 测井技术, 2002, 26(1): 18-21.
YUN Huayun, ZHOU Cancan. Researching rock pore structure with T2 distribution[J]. Well Logging Technology, 2002, 26(1): 18-21.
[16] 刘堂宴, 马在田, 傅容珊. 核磁共振谱的岩石孔喉结构分析[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2003, 38(3): 328-333.
LIU Tangyan, MA Zaitian, FU Rongshan. Analysis of rock pore throat structure with NMR spectra[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 2003, 38(3): 328-333.
[17] 赵彦超, 陈淑慧, 郭振华. 核磁共振方法在致密砂岩储层孔隙结构中的应用: 以鄂尔多斯大牛地气田上古生界石盒子组 3 段为例[J]. 地质科技情报, 2006, 25(1): 109-112.
LIU Yanchao, CHEN Shuhui, GUO Zhenhua. Application of NMR technology to pore structure in tight sandstone: a case from Third Member of Shihezi Formation Upper Paleozoic in Daniudi Gas Field, Ordos Basin[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2006, 25(1): 109-112.
[18] 王为民, 赵刚, 谷长春, 等. 核磁共振岩屑分析技术的实验及应用研究[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2005, 32(1): 56-59.
WANG Weimin, ZHAO Gang, GU Changchun, et al. Experiment and application of NMR technology on cutting[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2005, 32(1): 56-59.
[19] 丁绍卿, 郭和坤, 刘卫, 等. 核磁共振岩样分析技术在储层评价中的应用[J]. 大庆石油地质与开发, 2007, 25(6): 22-23.
DING Shaoqing, GUO Hekun, LIU Wei, et al. Application of NMR rock sample analysis technique in reservoir evaluation[J]. Petroleum Geology and Oilfield Development in Daqing, 2007, 25(6): 22-23.
[20] 高辉. 特低渗透砂岩储层微观孔隙结构与渗流机理研究[D]. 西安: 西北大学地质系, 2009: 87-89.
GAO Hui. Research on micro-pore structure and micro-flow mechanism of ultra low permeability sandstone reservoir[D]. Xi’an: Northwestern University. Department of Geology, 2009: 87-89.
[21] 李天降, 李子丰, 赵彦超, 等. 核磁共振与压汞法的孔隙结构一致性研究[J]. 天然气工业, 2006, 26(10): 57-59.
LI Tianjiang, LI Zifeng, ZHAO Yanchao, et al. Consistency of pore structures between NMR and mercury intrusion method[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2006, 26(10): 57-59.
[22] 赵杰, 姜亦忠, 王伟男, 等. 用核磁共振技术确定岩石孔隙结构的实验研究[J]. 测井技术, 2003, 27(3): 185-188.
ZHAO Jie, JIANG Yizhong, WANG Weinan, et al. Investigation of rock pore structure using NMR technology, Well Logging Technology, 2003, 27(3): 185-188.
[23] 王行信. 泥岩中碎屑高岭石的分布及其在沉积环境研究中的意义[J]. 大庆石油地质与开发, 1983, 2(1): 1-6.
WANG Xingxin. The distribution of clastic kaolinite in mudstone and its significance in the study of sedimentary environment[J]. Petroleum Geology and Oilfield Development in Daqing, 1983, 2(1): 1-6.
[24] 孟万斌, 吕正祥, 冯明石, 等. 致密砂岩自生伊利石的成因及其对相对优质储层发育的影响: 以川西地区须四段储层为例[J]. 石油学报, 2011, 32(5): 783-790.
MENG Wanbin, L Zhengxiang, FENG Mingshi, et al. The origin of authigenic illite in tight sandstones and its effect on the formation of relatively high-quality reservoirs: a case study on sandstones in the 4th member of Xujiahe Formation, western Sichuan Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2011, 32(5): 783-790.
Zhengxiang, FENG Mingshi, et al. The origin of authigenic illite in tight sandstones and its effect on the formation of relatively high-quality reservoirs: a case study on sandstones in the 4th member of Xujiahe Formation, western Sichuan Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2011, 32(5): 783-790.
[25] 库丽曼, 刘树根, 朱平, 等. 成岩作用对致密砂岩储层物性的影响: 以川中地区上三叠统须四段气藏为例[J].天然气工业, 2007, 27(1): 33-36.
KU Liman, LIU Shugen, ZHU Ping, et al. Influence of diagenesis on poroperm characteristics of tight sand reservoirs: taking the gas reservoirs in the 4th member of Xujiahe Formation in the upper Triassic as examples[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2007, 27(1): 33-36.
(编辑 杨幼平)
收稿日期:2015-11-27;修回日期:2016-02-23
基金项目(Foundation item):国家自然科学重点基金资助项目(41330133);国家重点基础研究发展计划(973计划)项目(2014CB239005-001);山东省优秀中青年科学家科研奖励基金资助项目(2014BSE28018);中国石化科技攻关项目(P15028);高校自主创新科研计划项目(15CX05046A,15CX07004A) (Project(41330313) supported by the Key Program of National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project(2014CB239005-001) supported by the National Basic Research Development Program (973 Program) of China; Project(2014BSE28018) supported by Outstanding Young Scientist Research Reward Fund of Shandong Province; Project(P15028) supported by the Research Project Funded by the SINOPEC Corporation; Projects(15CX05046A, 15CX07004A) supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities)
通信作者:卢双舫,教授,博士生导师,从事聚焦于非常规油气地质学和油气地球化学方面研究;E-mail: lushuangfang@qq.com