DOI: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2016.05.048
脱氮除磷膜生物反应器工艺耦合混凝过程优化
王朝朝1, 2,李思敏1,徐宇峰1,任金柱2,李军2
(1. 河北工程大学 城市建设学院,河北 邯郸,056038;
2. 北京工业大学 建筑工程学院,北京市水质科学与水环境恢复工程重点实验室,北京,100124)
摘要:采用脱氮除磷膜生物反应器(UCT-MBR)工艺处理碳源受限型市政污水,考察氯化铁(FeCl3·6H2O)的投加对UCT-MBR工艺运行效能与膜污染的影响,用傅里叶红外光谱(FT-IR)和能谱(EDX)对膜污染物质进行分析。研究结果表明:氯化铁的投加强化除磷效能,在最优除磷投加浓度运行时(投加浓度为1.8 mmol/L),能够最佳协同生物除磷的作用使得系统总磷(total phosphorus, TP)的去除率达到最高。氯化铁主要是通过增加污泥粒径、降低相对分子质量大于105的溶解性微生物产物(soluble microbial products, SMP)来实现减缓膜污染程度。在最佳污泥可滤性投加浓度运行时(投加浓度为2.6 mmol/L),UCT-MBR工艺的膜污染速率达到最小,但该投加浓度严重地影响污泥的生物活性,降低污泥的硝化与释/吸磷性能,成为制约脱氮除磷效能的主要因素。铁盐的投加没有改变膜污染物质的组分,无机污染对膜污染速率的影响程度比有机污染的小,无机元素协同有机高聚物形成密实滤饼层时存在一定的滞后性。
关键词:膜生物反应器;脱氮除磷;氯化铁;混凝过程;膜污染
中图分类号:X703 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2016)05-1812-11
Optimization of biological nitrogen and phosphorus removal membrane bioreactor process coupling with coagulation process
WANG Zhaozhao1, 2, LI Simin1, XU Yufeng1, REN Jinzhu2, LI Jun2
(1. College of Urban Construction, Hebei University of Engineering, Handan 056038, China;
2. Key Laboratory of Beijing for Water Quality Science and Water Environment Recovery Engineering,
College of Architecture and Civil Engineering, Beijing University of Technology, Beijing 100124, China)
Abstract: A bench-scale biological nitrogen and phosphorus removal membrane bioreactor (UCT-MBR) process was operated to treat carbon-limited municipal wastewater regarding on the influences of ferric chloride (FeCl3·6H2O) addition on the process performance and membrane fouling. FT-IR (Fourier translation infrared spectroscopy, FT-IR) and EDX (energy dispersive X-Ray, EDX) were used to analyze membrane surface foulants. The results show that the phosphorus removal is strengthened with the addition of ferric chloride. The highest removal efficiency of TP (total phosphorus, TP) can be obtained in UCT-MBR process under the condition of the optimal-phosphorus-removal dosing (dosage of 1.8 mmol/L) combined with the biological phosphorus removal process. Membrane fouling is alleviated with the addition of ferric chloride mainly through increasing the sludge particle size and reducing the SMP (soluble microbial products, SMP) fraction concentration with relative molecular mass above 105. The lowest membrane fouling rate in the UCT-MBR process can be obtained under the condition of the optimal-sludge-filterability dosing (dosage of 2.6 mmol/L),
while the optimal-sludge-filterability dosing exhibits a strong influence on sludge bioactivities and reduces the sludge capabilities of nitrification and phosphorus release/uptake, which limits the performance of nitrogen and phosphorus removal. The ferric chloride addition has no effects on their compositions. Moreover, the influence of inorganic fouling on membrane fouling rate is found to be smaller than that of organic fouling. Besides, lag effects are found for inorganic elements combined with biopolymers to form a dense cake layer.
Key words: membrane bioreactor; nitrogen and phosphorus removal; ferric chloride; coagulation process; membrane fouling
目前城市污水排放标准中对营养元素的要求日益严格,而城市污水中的碳源受限问题成为制约脱氮除磷工艺去除效能的瓶颈。在实际污水处理厂的运行中,往往以保证生物脱氮为前提,采用同步强化生物除磷并辅助化学除磷的方式使处理水质以达到污水排放的一级A指标[1-2]。膜生物反应器(membrane bioreactor,MBR)强化生物脱氮除磷工艺在处理低碳比城市污水时也常耦合混凝过程来达到污水排放指标。这是由于从除磷的效能来讲化学混凝除磷较生物除磷具有较高的稳定性和较快的启动性,此外化学混凝剂的投加可以改变污泥的一些理化特性,比如减小污泥比阻,增大污泥粒径等,从而可以降低膜生物反应器的膜污染速率[3]。SONG等[4]在优化膜生物反应器过滤过程中发现:化学混凝剂的投加可以提高除磷效能并同步改善污泥的可滤性。张岳[5]在研究缺氧/好氧膜生物反应器时发现:在其试验最优氯化铁混凝剂的投加浓度下(40 mg/L),能够最大程度地降低膜污染因子的含量,同时可以最大程度地提高磷的去除率;并且在一定程度上激发了脱氢酶的活性,进一步提高了生物脱氮的效能。然而也有学者在研究中发现,投加铁盐混凝剂虽能够在一定程度上提高除磷效率,但过量的铁盐会使得生物铁结构变得密实,加大了膜污染负荷,降低了膜组件的渗透性[6]。GUO 等[7]也在考查铁盐混凝剂对MBR工艺运行特性的影响时发现:铁盐的投加降低了污泥的活性,在一定程度上了抑制了活性污泥的硝化作用,从而降低了总氮(total nitrogen,TN)的去除率。因此,化学混凝剂的优化投加浓度对于膜生物反应器内污泥的脱氮除磷的生物特性以及抑制膜污染的理化特性具有重要的意义。本文作者以同步脱氮除磷膜生物反应器(university of cape town membrane bioreactor,UCT-MBR)工艺处理碳源受限型废水为研究对象,采用氯化铁(FeCl3·6H2O)作为化学除磷的混凝剂,采用短期运行试验确定除磷最佳与污泥可滤性最佳的投加浓度,并以长期运行试验来考察这2种投加浓度对脱氮除磷效能及膜污染的影响,同步考察反应器内活性污泥生物、理化特性的变化,探究铁盐混凝剂抑制膜污染机制,以便为UCT-MBR工艺处理碳源受限型废水提供强化除磷耦合膜污染抑制的混凝优化控制策略。
1 试验材料与方法
1.1 试验装置与工艺流程
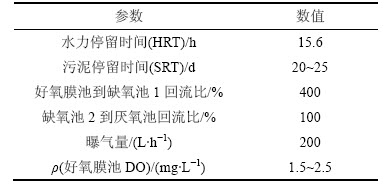
UCT-MBR工艺反应器装置如图1所示。装置各矩形反应池由有机玻璃构成,总有效体积V为28 L,V厌氧池:V缺氧池-1:V缺氧池-2:V好氧膜池为1:1:1:2。该装置由可编程逻辑控制器(programmable logic controller,PLC)系统控制,采用恒通量过滤间歇抽吸方式进行产水,膜通量保持在20 L/(m2·h),抽吸周期为10 min,9 min抽吸,停1 min。通过液位计对厌氧池液位的监控,控制进水泵1的启停,跨膜压差数值通过记录仪在线存储。污水依次经过厌氧池、缺氧池1、缺氧池2、好氧池膜池,最后通过产水泵实现出水。为保持污泥处于悬浮状态,在厌氧池、缺氧池1和缺氧池2配备搅拌桨。好氧膜池采用穿孔曝气,孔径为5 mm,通过空气压缩机对其进行鼓风,一方面是为形成气水剪切流,减缓污泥在膜组件上的沉积;另一方面是为保证好氧池微生物自身需要和降解有机物的生化需氧曝气量。膜组件为一片氯化聚乙烯的平板微滤膜(Kubota公司制造),膜孔径为0.4 μm,膜面积为0.1 m2。反应器温度通过加热棒控制在20 ℃左右,通过便携式WTW Multi 340i检测仪对好氧膜池的溶解氧(dissolved oxygen,DO)进行监控。根据混凝的要求增加了一个加药泵的控制点,以实现对混凝剂投加浓度的控制(本试验阶段,以氯化铁为混凝剂,投加流量控制在2 L/d)。试验期间的其他运行参数如表1所示。
1.2 污泥的接种与驯化及进出水特性
试验的接种污泥取自邯郸某污水处理厂氧化沟工艺的二沉池回流污泥,具有良好的脱氮性能。好氧膜池的污泥(mixed liquor suspended solids, MLSS)质量浓度为5 000 mg/L左右,厌氧池、缺氧池1、缺氧池2和好氧池的污泥量占总反应器污泥总量的14%,19%,20%和47%。在长期运行阶段下定期地取好氧池的污泥测定比好氧速率(Ko)、比硝化速率(Kn)、比释磷速率(Kana)及比好氧吸磷速率(Kaer)[8],mg/(g·h)。
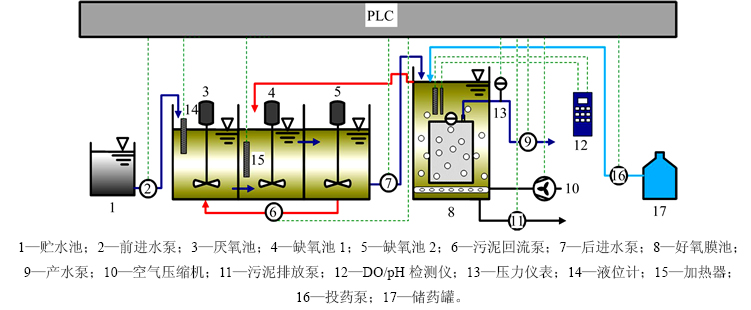
图1 UCT-MBR耦合混凝工艺流程图
Fig. 1 Flow diagram of UCT-MBR coupled with coagulation process
表1 试验运行条件
Table 1 Operational conditions during experiment
试验用水为合成废水,通过稀释城市污水并投加CH3COOH,NH4Cl及KH2PO4达到所需的水质指标。短期运行阶段与长期运行阶段所用进水为同一配水方案,具体的进水水质特征如表2所示。采用此进水水质对污泥驯化1月,之后根据试验方案开展相关的研究工作。
1.3 分析项目及测定方法
1.3.1 化学需氧量(CODcr),NH4+-N,TN,TP,MLSS和挥发性污泥(MLVSS)质量浓度的测定
采用水和废水监测分析方法(4版)中的标准方法[9]测定CODcr,NH4+-N,TN,TP和MLSS质量浓度,污泥粒径采用马尔文粒径仪测定(Worcestershire, UK),pH用便携式WTW Multi 340i检测仪测定;污泥上清液的Zeta电位使用马尔文Zeta电位分析仪(Nano-Z,UK)中测定,每个样品测定3次后取平均值。
表2 试验运行阶段进水水质特性
Table 2 Influent characteristics during operational phases

1.3.2 跨膜压差与膜污染阻力
采用数据记录仪在线采集跨膜压差(pTM)数据,并采用下式进行温度(T)校正:
 (1)
(1)
在每一个阶段试验结束时,根据达西公式计算出各部分污染阻力:
 (2)
(2)
其中:μ为透过液动力学黏度,Pa·s;J为产水通量,L/(m2·h);Rt,Rf,Rc,Rp和Rm分别为总阻力、污染阻力、滤饼层阻力、膜孔堵塞阻力和膜固有阻力,1011 m-1。
将膜组件取出反应器,用海绵将膜表面的滤饼层轻微擦去,然后放在清水中在一定压力下进行过滤,并测定出水通量,根据式(2)计算得出Rf,其与Rm的差值为Rp;Rt与Rf的差值为Rc。随后将膜组件浸泡在0.5%的次氯酸钠溶液中,使其渗透性恢复到95%以上,进入下一个试验阶段。
1.3.3 胞外聚合物(EPS)与SMP的萃取与表征
EPS与SMP萃取:EPS的萃取采用离子交换树脂法,取50 mL好氧膜池的活性污泥,在12 000 r/min下离心15 min,然后收集上清液经过0.45 μm微滤膜后测定糖与蛋白质,分别记为 SMPc和SMPP,取其加和作为SMP,mg/L;将离心浓缩的污泥,用缓冲液(缓冲液由2 mmol/L Na3PO4,4 mmol/L Na2HPO4,9 mmol/L NaCl和1 mmol/L KCl组成)补充到原来的体积。根据单位MLVSS质量加70 g的比例将强酸型Na+树脂(粒径为0.3~0.7 mm)和污泥缓冲液加入到锥形瓶中,并使用磁力搅拌器将其控制在800 r/min下搅拌2 h;搅拌结束之后,使用离心机在12000 r/min下离心15 min,取其上清液通过0.45 μm微滤膜,测定过滤液中的糖(硫酸蒽酮法)和蛋白质(考马斯亮蓝法),分别记为 EPSc和EPSP,单位MLSS质量下糖和蛋白质的质量加和作为EPS的质量分数[10],mg/g;采用切割相对分子质量分别为103,104和105的超滤膜(Millipore公司, 美国)对EPS和SMP的相对分子质量进行分级。
1.3.4 红外光谱(FT-IR)和能谱(EDX)分析
每个运行阶段完成后,将膜表面的污染物质收集并进行真空烘干,将粉末状的污染物质按照质量比1:10加入溴化钾进行压片,然后采用傅里叶红外光谱仪(FT-IR 6700,Nicolet公司)进行透射扫描,扫描范围为400~4 000 cm-1;采用X线能谱仪(EDAX Inc.,美国)对污染膜表面的污染物进行扫描分析。2种分析方法的数据采集之后均采用 origin 8.0软件进行处理。
1.3.5 修正污染指数的测定
修正污染指数(modified fouling index,MFI)。在室温条件下,首先取污泥混合液的样品,分为2个部分,一部分直接采用Amicon 8200搅拌杯(美国Millpore公司,膜片使用切割相对分子质量为3×105的再生纤维素膜片,如图2所示)进行恒压(30 kPa)搅拌过滤。
 (3)
(3)
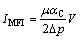 (4)
(4)
式中:t为过滤时间,s;V为单位过滤面积上的过滤体积,m;Rm为膜固有阻力,m-1;μ为透过液动力学黏度,Pa·s;Δp为膜两侧压差,Pa; 为单位面积上的污泥层过滤阻力,L-2。IMFI为恒定压力下t/V与V线性拟合的斜率,该指标的大小表示污泥混合液过滤性质的优劣,较大的IMFI反映污泥混合液过滤性质较差,膜的污染速率越高。
为单位面积上的污泥层过滤阻力,L-2。IMFI为恒定压力下t/V与V线性拟合的斜率,该指标的大小表示污泥混合液过滤性质的优劣,较大的IMFI反映污泥混合液过滤性质较差,膜的污染速率越高。

图2 搅拌过滤反应器装置示意图
Fig. 2 Schematic diagram of stirred filtration cell installation
1.3.6 试验方案
短期试验方案:以UCT-MBR反应器的连续运行为基础,氯化铁以0.2 mmol/L为投加步阶连续投加到好氧膜池,投加14个步阶(投加浓度由0.2 mmol/L 增加到2.8 mmol/L),每个步阶运行1周,考察混凝除磷率的变化;并同步取好氧膜池污泥进行间歇过滤试验,测定其IMFI以考察污泥的可滤性与污染潜质。长期运行方案:采用UCT-MBR反应器连续运行的方式,对好氧膜池连续投加混凝剂,考察其对工艺脱氮除磷效能以及过滤持续运行的影响。具体的运行阶段如表3所示。
表3 长期运行的不同试验阶段
Table 3 Long-term operational phases of experiment

2 结果与讨论
2.1 短期优化混凝剂投加浓度试验研究
混凝剂的优化投加浓度基于2个方面的考虑:一方面是基于最佳除磷效能的基础上选取最优的投加浓度。若混凝剂投加浓度不足,絮凝剂不能与污水中的磷充分接触反应, 在絮体沉降后,仍有一部分未被絮凝,致使剩余磷含量较高;若投加浓度过量,则絮体间的架桥作用所必须的粒子表面吸附活性点被絮凝剂所包裹,使架桥所需的粒子表面活性点不足,而使得絮凝剂颗粒间的吸附架桥作用变得困难,以致处理效果下降[11]。另一方面是考虑混凝剂对污泥可滤性的影响,适量的混凝剂能够通过吸附电中和作用降低污泥体系内部的排斥力,通过吸附架桥作用增大污泥的粒径,然而混凝剂投加过量将会对污泥体系产生相反的效果。因此,采用MFI的测定方法来确定最优污泥可滤性投加浓度。
由图3(a)可见:在铁盐投加浓度为1.8 mmol/L 时,TP的去除率达到最高,平均为91.5%。由图3(b)可见:IMFI也是随着投加浓度的增加而降低,但是在1.8 mmol/L时并没有出现拐点,而在投加浓度为2.6 mmol/L时出现拐点,这也许是由于铁盐在1.8 mmol/L时用来形成磷酸铁沉淀,而少部分发生水解作用的缘故,而在2.6 mmol/L时能够满足除磷条件下的最优污泥可滤性的投加浓度。由图3(c)可以进一步解释,污泥在投加浓度为1.8 mmol/L时的污泥混合液的Zeta电位为-8 mV左右,而在2.6 mmol/L时接近于中性,可以知道铁盐的投加浓度在2.6 mmol/L时可以基本中和带有负电位的胶体类物质,从而达到最佳絮体聚集并提高污泥可滤性的效果。 因此,采用 1.8 mmol/L作为系统内长期运行的最优除磷投加浓度;采用2.6 mmol/L作为系统内长期运行的最优污泥可滤性投加浓度;并采用2.2 mmol/L 作为综合考查系统长期运行除磷效能与污泥可滤性的优化投加浓度。
2.2 长期运行下有机污染物与营养物的去除效能
2.2.1 COD的去除效能
长期运行下不同阶段UCT-MBR工艺对有机污染物的去除效能如图4所示。在阶段Ⅰ无铁盐投加时,进水ρ(COD)平均在235.9 mg/L,经过缺氧池、好氧池的降解之后膜池上清液质量浓度降低到36.4 mg/L,生化去除率达到84.6%,经过膜过滤之后,ρ(COD)进一步降低到 26.8 mg/L,系统总平均去除率达到了88.3%。到了阶段Ⅱ,铁盐投加后,膜池上清液的ρ(COD)由36.4 mg/L降低约19.2%,稳定在29.8 mg/L。而在阶段Ⅳ膜池上清液的ρ(COD)达到了4个阶段的最低值,约为23.3 mg/L,过膜之后降低到12.6%,总平均去除率提高到94.5%。可以明显地看出混凝剂的投加在一定程度上降低了膜池上清液COD的质量浓度,这是由于铁盐水解产物能够有效、充分地吸附大分子有机物,从而降低了COD的质量浓度[12]。
2.2.2 氮的去除效能
长期运行下不同运行阶段系统内的硝化与反硝化的效果如图5所示。在阶段Ⅰ和阶段Ⅱ时氨氮的去除率分别达到99.0%和99.9%,在最优除磷投加浓度下并没有对生物的硝化与反硝化作用产生影响,TN的去除率分别达到70.0%和69.2%。然而,在阶段Ⅲ和阶段ⅣTN的去除率明显下降,去除率分别降至63.6%和51.6%,同时看到氨氮的去除率降至94.1%和85.9%,表明混凝剂的投加了抑制了活性污泥中硝化菌群的活性,成为制约反硝化的瓶颈。

图3 氯化铁浓度对TP去除磷率,IMFI以及Zeta电位和pH的影响
Fig. 3 Effects of ferric chloride concentrations on TP removal, IMFI, zeta potential and pH

图4 不同运行阶段UCT-MBR工艺对COD的去除效能
Fig. 4 Performance of COD removal in UCT-MBR process during different phases

图5 不同运行阶段UCT-MBR工艺对NH4+-N和TN的去除效能
Fig. 5 Performance of NH4+-N, TN removal in UCT-MBR process during different phases
污泥浓度、污泥活性及污泥比硝化速率的变化如图6所示。由图6可见:随着铁盐的投加,污泥质量浓度也随之增加,然而w(MLVSS)/w(MLSS)随之降低,具体而言,ρ(MLSS)由4 940 mg/L(阶段Ⅰ)提高到6 630 mg/L(阶段Ⅳ),w(MLVSS)/w(MLSS)则由75%降到40%,可以知道无机铁盐的加入增加了污泥中无机质的组分含量;同样Ko和Kn也分别由3.54和2.82 mg/(g·h)降到0.93和1.09 mg/(g·h),表明在阶段Ⅲ和阶段Ⅳ时铁盐的摄入对系统污泥的硝化活性产生了强烈的抑制作用。由于混凝剂在水中的水解作用,使得系统内的酸度增加(由序批式试验可见,在铁盐的投加浓度为2.6 mmol/L时,混合液的pH降到了5.5); 由于正常的硝化过程中适宜的pH应在6.0~8.0之间,可以知道铁盐水解引起的pH下降成为影响硝化过程的主要因素。可见,在最优污泥可滤性投加浓度下,生物脱氮尤其是生物的硝化作用受到了抑制,从而影响了整体脱氮的效能。
2.2.3 磷的去除效能
不同运行阶段UCT-MBR工艺对TP的去除率效果如图7所示。由图7可见:在阶段Ⅰ时,进水ρ(TP)为6.14 mg/L,出水质量浓度平均为2.97 mg/L,平均去除率仅为51.6%。在阶段Ⅱ运行时,最优除磷投加浓度使得TP的去除率迅速地提高到98.2%,出水ρ(TP)稳定在0.11 mg/L。在阶段Ⅳ可以看到随着混凝剂投加浓度的增加,混凝除磷的效能下降,除磷率降到81.6%,出水质量浓度稳定在1.1 mg/L。在阶段Ⅲ时系统出水ρ(TP)稳定在0.48 mg/L左右,去除率介于阶段Ⅱ和阶段Ⅳ的去除率之间,为92%左右。

图6 不同阶段好氧膜池的污泥浓度、比好氧速率和比硝化速率
Fig. 6 MLSS concentrations, SOUR and SNR of aerobic sludge during different operational phases

图7 不同运行阶段UCT-MBR工艺对磷的去除效能
Fig. 7 Performance of TP removal in UCT-MBR process during different phases
图8所示为不同运行阶段UCT-MBR工艺中聚磷菌的活性。由图8可见:相对于阶段Ⅰ,阶段Ⅱ时的聚磷菌的活性降低的并不明显,膜池污泥的比释磷、吸磷速率分别由3.65和5.37 mg/(g·h)降到3.19和4.70 mg/(g·h)。因此,在最优除磷投加浓度对PAOs的活性影响较小,因此在阶段Ⅱ时能保证混凝除磷与生物除磷的最优协同作用,除磷效能达到最高。而在阶段Ⅳ时,膜池污泥的比释磷、吸磷速率分别降至2.18和3.05 mg/(g·h),在最优污泥可滤性混凝投加浓度下PAOs的活性受到了一定的抑制,其次过量投加,会削弱絮凝剂颗粒之间吸附架桥的作用,导致粒子表面活性点不足,从而降低了混凝剂水解产生的氢氧化物对磷酸根离子的吸附作用,导致在阶段Ⅳ时出水TP质量浓度达到最高。

图8 不同运行阶段UCT-MBR工艺中聚磷菌的活性
Fig. 8 PAOs activities in UCT-MBR process during different operational phases
2.3 长期运行下的膜污染特性与机制
2.3.1 长期运行下的膜污染特性
不同运行阶段的跨膜压差如图9所示。由图9可见:在铁盐的投加阶段,膜污染的速率明显比未投加阶段的低。在最优污泥可滤性投加浓度下,膜污染速率也达到了最低,证明了短期试验对污泥可滤性的评估,并且说明了混凝剂的投加改善了膜组件的渗透性。由表4可以看到:在4个运行阶段下滤饼层的阻力始终是总污染阻力的主要成分(71%~72%)。阶段Ⅱ和阶段Ⅳ在同一运行周期下,pTM, end分别达到36和28 kPa,较未投加混凝剂阶段分别降低了20.0%和37.8%。随着混凝剂投加浓度的增加(阶段Ⅰ到阶段Ⅳ),膜污染阻力的各组分均有所降低,其中滤饼层阻力与膜孔堵塞阻力分别由42.56×1011和13.10×1011 m-1 降低到26.75×1011和6.30×1011 m-1,总阻力也由59.94×1011 m-1 降低到37.3×1011 m-1。
2.3.2 PSD的变化
图10所示为在长期运行下不同铁盐投加浓度下污泥粒径的分布。由图10可见:铁盐的投加能够明显

图9 不同运行阶段UCT-MBR工艺的跨膜压差变化
Fig. 9 TMP evolution in UCT-MBR process during different operational phases
表4 试验运行不同阶段膜污染阻力分布
Table 4 Distributions of membrane filtration resistances during different operational phases

增大污泥的粒径。在阶段Ⅰ膜池活性污泥的平均粒径为59.6 μm,在阶段Ⅱ,Ⅲ和Ⅳ阶段时平均粒径增大了17.4%,35.2%和50.3%,混合液粒径在1~10 μm范围的体积分数均比阶段Ⅰ的小。铁盐的水解产生正电荷吸附在絮体颗粒表面,降低絮体表面电荷数量,降低絮体之间的排斥力,并且可以通过吸附架桥作用能够将细小粒径的颗粒进行聚集,形成较大的絮状结构,因此能够降低粒径在1~10 μm范围内的颗粒物,从而改善了污泥的可滤性。而在阶段Ⅰ细小颗粒物的增多,也会较快的富集在膜表面,降低了滤饼层的通透性,提高了滤饼层的阻力占总阻力的比重,与表4的试验结果一致。白琳等[13]发现:通过在膜生物反应器内培养好氧颗粒污泥,增大污泥的粒径,较常规的污泥絮体膜生物反应器,膜污染速率降低约58.9%。因此,通过投加混凝剂的方式增大污泥的粒径,也是实现延缓膜污染的重要手段。

图10 不同运行阶段下膜池污泥粒径的分布
Fig. 10 Particle size distributions of activated sludge in membrane tank during different operational phases
2.3.3 EPS的变化
不同运行阶段下膜池污泥胞外聚合物的相对分子质量分布如图11所示。由图11可见:在运行的4个阶段下,不同氯化铁的投加浓度并没有改变其EPS相对分子质量的分布状态,主要是以相对分子质量大于105和小于103的组分存在,分别占到EPS的49%~52%和23%~27%。不同运行阶段下好氧膜池污泥胞外聚合物中多糖类与蛋白质相对分子质量分布的情况如图12(a)与12(b)所示。由图12(a)和12(b)可以看到:在阶段Ⅱ,Ⅲ和Ⅳ较阶段Ⅰ时w(EPSc)有所增加。在阶段Ⅳ下增长的幅度最大,其中w(EPSc)在相对分子质量大于105和小于103的组分分别由6.0和2.5 mg/g增加到6.5和3.7 mg/g,增加了8.3%和48.0%。ESPp与EPS的分布类似,也主要是由相对分子质量大于105和小于103的组分存在,其中大于105的组分在阶段Ⅳ较阶段Ⅰ提高到33.3%。因此,从整体来看,混凝剂的投加对于促进了EPS的产生,主要是提高了EPSc中大于105组分的比污泥质量浓度。

图11 不同运行阶段膜池污泥胞外聚合物相对分子质量分布
Fig. 11 EPS relative molecular mass fractionation of activated sludge in membrane tank during different operational phases

图12 不同运行阶段膜池污泥胞外聚合物中糖类和蛋白质相对分子质量分级
Fig. 12 EPSc and ESPp relative molecular mass fractionation of activated sludge in membrane tank during different operational phases
大相对分子质量的SMP在絮凝剂的作用下与污泥絮体结合,由液相转移到固相,使得EPS的比污泥质量浓度有所增高;此外铁盐水解释放出来的H+,降低溶液中的pH会促使微生物产生EPS以适应不利的环境。EPS产量的增多对于膜的渗透性不利,较多的EPS产量将会加速膜污染的速率。然而,在该试验阶段可以看到w(EPS)虽然有所增加,但是,膜污染速率并没有增加。这是因为在该试验阶段发现污泥的ρ(SMP)降低以及污泥絮体粒径增加都是降低膜污染的要素,长期运行下跨膜压差的变化是由各个因素的共同作用的结果。纪婧[14]在研究对混合液性质对膜污染的影响时发现,铁盐对膜污染的延缓作用主要是通过降低ρ(SMP),中和污泥表面电荷以及提高污泥表面的疏水性(也是微生物EPS产量增多的结果)实现的。
2.3.4 SMP的变化
SMP的相对分子质量分布对于膜污染的影响很大。ZHANG 等[12]在研究SMP对膜生物反应器膜污染的影响中发现:SMP中大相对分子质量(>105)的组分对于膜污染的影响要大于小相对分子质量组分。大分子有机物能够在膜孔内被直接截留,成为引起膜孔堵塞的主要因素,而小分子有机物能够透过膜孔。在不同运行阶段下膜池污泥的SMP的相对分子质量分布如图13所示。由图13可以看到:在阶段ⅠSMP的分布也主要是以双峰的形式分布,以相对分子质量大于105和小于103的组分分别占52%和23%。随着混凝剂投加,可以看到SMP中大相对分子质量所占的比重有明显降低。具体而言,在阶段Ⅱ、阶段Ⅲ和阶段Ⅳ相对分子质量大于105的组分分别降到19%,13% 和13%,而相对分子质量小于103的组分分别增大到60%,65% 和66%。铁盐通过絮凝作用,将混合液中的胶体与溶解性大分子集聚,与污泥絮体表面相结合,从而降低了在膜池上清液中溶解态中的有机物的含量。WU等[15]在研究中发现:聚铁絮凝剂的投加能够有效地降低上清液中TOC的含量,延缓了膜表面凝胶层的形成,提高了滤饼层通透性。
图14(a)和14(b)所示分别为SMPc与SMPp在铁盐混凝剂投加完之后的变化。由图14(a)和14(b)可见:在阶段ⅠSMPc中主要是以相对分子质量大于105和小于103的组分存在,ρ(SMPc)分别为 6.9和5.5 mg/L。

图13 不同运行阶段膜池污泥溶解性微生物产物相对分子质量分布
Fig. 13 SMP relative molecular mass fractionation of activated sludge in membrane tank during different operational phases
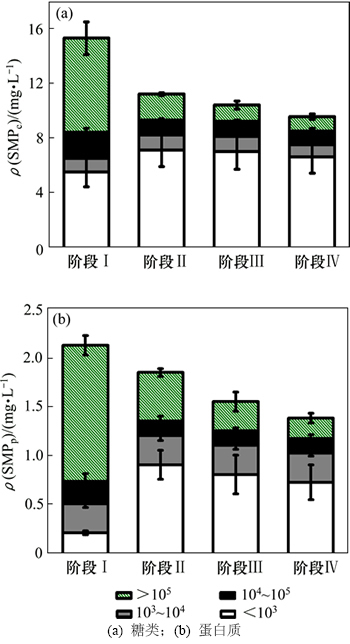
图14 不同运行阶段膜池溶解性微生物产物中糖类和蛋白质相对分子质量分级
Fig. 14 SMPc and SMPp relative molecular mass fractionation of activated sludge in membrane tank during different operational phases
而在阶段Ⅱ,Ⅲ和Ⅳ时主要是以相对分子质量小于103的组分存在,ρ(SMPc)较阶段Ⅰ分别增加到7.1,7.0和6.6 mg/L;SMPc中以相对分子质量大于105存在的多糖类较阶段Ⅰ分别降低72.5%,82.6%和85.2%。SMPp在阶段Ⅰ中相对分子质量的分布与SMPc有所不同,主要是以相对分子质量大于105的多糖类存在。在阶段Ⅱ,Ⅲ和Ⅳ时,SMPp中以相对分子质量大于105组分存在的蛋白类物质较阶段Ⅰ分别降低64.3%,78.6%和85.0%。随着铁盐混凝剂的投加,在SMP组分中大相对分子质量的SMPc与SMPp的去除率也随之增加,到达最优污泥可滤性混凝投加浓度时ρ(SMPc)与ρ(SMPc)也达到最低。
2.3.5 膜污染物质组成的变化
图15所示为不同运行阶段膜污染物质的傅立叶红外光谱。由图15可知:在不同运行阶段膜污染物质的有机组成差别不大,主要是以糖类与蛋白质类二级结构等形式的有机物存在,可以推断不同铁盐投加浓度对于微生物代谢产物的种类并无差别,但其形成的混凝絮体对有机高分子有机物的吸附程度有区别,因此,可以看到在不同运行阶段的膜污染物质的FT-IR图谱在相同的波长下的透过率不同,相应地反映了膜污染物质中有机成分的差别。可以看到FT-IR谱图中透射率由小到大顺序为阶段Ⅰ,Ⅱ,Ⅲ和Ⅳ,即与直接被截留的相对分子质量大于105的SMP质量浓度顺序一致。

图15 不同运行阶段膜污染物质的傅立叶红外光谱
Fig. 15 FT-IR spectra of membrane foulants in different operational phases
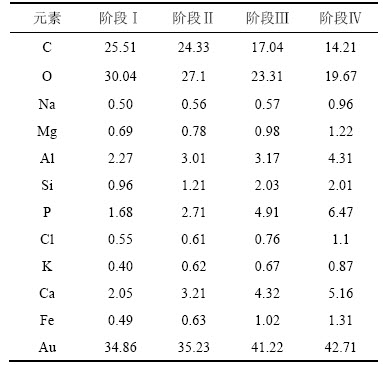
对膜污染物质的元素(表5)分析可知:随着铁盐投加浓度的增加,膜污染中的铁元素与其他无机元素的比例在增加,而有机元素的比重在降低,但是由不同阶段的跨膜压差可知,膜污染速率却在下降。说明在4个阶段中的有机污染对膜污染速率的影响远大于无机污染的影响,并且无机元素在与有机高分子聚合物形成密实滤饼层时是以大相对分子质量有机物在膜表面沉积为前提,因此,无机元素协同有机高聚物形成密实滤饼层时存在一定的滞后性。
表5 不同运行阶段膜表面污染物质中的元素组成(质量分数)
Table 5 Compositions of elements in membrane foulants during different operational phases %
3 结论
1) 氯化铁的投加强化了UCT-MBR工艺在处理碳源受限废水时的除磷效能。在最优除磷投加浓度运行时(投加浓度为1.8 mmol/L),能够最佳协同生物除磷的作用使得系统TP的去除率达到最高(98.2%,出水为0.11 mg/L),并且此投加浓度对污泥的硝化性能影响不大,NH4+-N与TN的去除效能也能够保持在99.9%和69.2%。
2) 氯化铁主要是通过增加污泥粒径、降低大分子有机物浓度来实现减缓膜污染程度。在最佳污泥可滤性投加浓度运行时(投加浓度为2.6 mmol/L),可以使得污泥絮体的排斥作用达到最小,污泥粒径达到最大,并且最大程度地降低相对分子质量大于105 SMP的质量浓度,使得UCT-MBR工艺的膜污染速率达到最小。但是该投加浓度严重地影响了污泥的生物活性,降低了污泥的硝化与释/吸磷性能,成为制约脱氮除磷效能的主要因素。在优化投加浓度运行时,UCT-MBR工艺的运行效能与膜污染速率均处于最优除磷投加浓度与最优污泥可滤性投加浓度之间。
3) 铁盐的投加没有改变膜污染物质的组分,无机污染对膜污染速率的影响程度比有机污染的小,无机元素协同有机高聚物形成密实滤饼层时存在一定的滞后性。
参考文献:
[1] 郝晓地, 衣兰凯, 付昆明. 侧流磷回收强化低碳源污水脱氮除磷效果的模拟与实验研究[J]. 环境工程学报, 2013, 7(1): 231-236.
HAO Xiaodi, YI Lankai, FU Kunming. Modeling and experimental study on enhancing effect of BNR by phosphate recovery in side-stream of anaerobic supernatant[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2013, 7(1): 231-236.
[2] WANG Yuan, TNG K H, WU Hao, et al. Removal of phosphorus from wastewaters using ferrous salts: a pilot scale membrane bioreactor study[J]. Water Research, 2014, 57: 140-150.
[3] 李永明, 唐利, 纪婧, 等. 絮凝剂对MBR活性污泥理化性质的影响研究[J]. 上海交通大学学报(农业科学版), 2010, 28(6): 558-562.
LI Yongming, TANG Li, JI Jing, et al. Impact of flocculants on physical and chemical properties of the activated sludge in MBR[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiaotong University (Agricultural Science), 2010, 28(6): 558-562.
[4] SONG K G, KIM Y, AHN K H. Effect of coagulant addition on membrane fouling and nutrient removal in a submerged membrane bioreactor[J]. Desalination, 2008, 221(1/2/3): 467-474.
[5] 张岳. 投加活性炭和氯化铁对A/O-MBR运行的影响[D]. 天津: 天津大学环境科学与工程学院, 2011: 25-32.
ZHANG Yue. The influence of adding PAC and Fecl3 to the performance of A/O-MBR[D]. Tianjin: Tianjian University. College of Environmental Science and Technology, 2011: 25-32.
[6] 张倩, 王锦, 石晓庆. 投加氯化铁对SMBR 工艺效能及膜污染的影响[J].水处理技术, 2009, 34(11): 79-83.
ZHANG Qian, WANG Jin, SHI Xiaoqing. Effect of coagulant ferric chloride dosage on efficiency and membrane fouling of SMBR[J]. Technology of Water Treatment, 2009, 34(11): 79-83.
[7] GUO W S, NGO H H, VIGNESWARAN S, et al. Effect of different flocculants on short-term performance of submerged membrane bioreactor[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2010, 70(12): 274-279.
[8] 肖景霓. 膜生物反应器强化除磷脱氮性能研究[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学环境学院, 2007: 35-40.
XIAO Jingni. Enhanced simultaneous phosphorus and nitrogen removal in membrane bioreactors[D]. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology. School of Environmental Science and Technology, 2007: 35-40.
[9] 国家环境保护总局. 水和废水监测分析方法[M]. 4版. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 2004: 210-284.
State Environmental Protection Administration of China. National standard methods for water and wastewater quality analysis[M]. 4th ed. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press, 2004: 210-284.
[10] MALAMIS S, ANDREADAKIS A. Fractionation of proteins and carbohydrates of extracellular polymeric substances in a membrane bioreactor system[J]. Bioresour Technol, 2009, 100(13): 3350-3357.
[11] 郑怀礼, 刘克万, 龙腾锐, 等. 聚合氯化铝铁(PAFC)絮凝剂污水除磷的研究[J]. 环境化学, 2005, 24(6): 693-695.
ZHENG Huaili, LIU Kewan, LONG Tengrui, et al. Study on polyalum ferric chloride for phosphorus removal in municipal wastewater treatment[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2005, 24(6): 693-695.
[12] ZHANG H F, SUN B S, ZHAO X H, et al. Effect of ferric chloride on fouling in membrane bioreactor[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2008, 63(2): 341-347.
[13] 白琳, 杨凤林, 王秀, 等. 好氧硝化颗粒污泥膜生物反应器性能和膜污染研究[J]. 环境工程学报, 2009, 3(5): 817-824.
BAI Lin, YANG Fenglin, WANG Xiu, et al. Performance and membrane fouling of aerobic nitrifying granule membrane bioreactor[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2009, 3(5): 817-824.
[14] 纪婧. 絮凝剂对减缓膜-生物反应器膜污染速率的效果和机理研究[D]. 上海: 上海交通大学农业与生物学院, 2009: 62-84.
JI Jing. Study on effect and mechanisms of flocculants on mitigating membrane fouling in membrane bioreactors[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Jiaotong University. School of Agriculture and Biology, 2009: 62-84.
[15] WU J L, HUANG X. Effect of dosing polymeric ferric sulfate on fouling characteristics, mixed liquor properties and performance in a long-term running membrane bioreactor[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2008, 63(1): 45-52.
(编辑 杨幼平)
收稿日期:2015-05-13;修回日期:2015-07-05
基金项目(Foundation item):国家水体污染控制与治理科技重大专项(2012ZX07203003);河北省高等学校科学技术研究项目(QN2015115);(Project(2012ZX07203003) supported by National Water Pollution Control and Treatment Science and Technology Major Project; Project (QN2015115) supported by Colleges and Universities in Hebei Province Science and Technology Research Projects)
通信作者:徐宇峰,讲师,从事污水处理技术与应用;E-mail: jackstarfly@126.com