文章编号:1004-0609(2016)-03-0551-09
700~750 ℃GH2984合金的蠕变变形机制
严靖博1,谷月峰1,高义民2,孙 飞3,赵新宝1,党莹樱1,杨 珍1,尹宏飞1, 2
(1. 西安热工研究院有限公司,西安 710032;
2. 西安交通大学 材料科学与工程学院 金属材料强度国家重点实验室,西安 710049;
3. 山东大学 材料科学与工程学院,济南 250061)
摘 要:研究铁镍基高温合金GH2984在700~750 ℃蠕变期间的显微组织演变及其对性能的影响。结果表明:在(700 ℃,300 MPa)蠕变条件下,合金持久寿命仅160 h,变形过程中晶界处的应力集中并促进裂纹的萌生与扩展是造成合金失效的主要原因。应力降至200 MPa时,晶粒旋转导致晶界处应力集中得到释放,抑制裂纹萌生并进而使合金持久寿命明显增长。然而,随着蠕变温度的增加,晶粒在变形过程中伴随出现动态再结晶。这一现象虽然使得合金持久塑性有所增加,但晶粒加工硬化程度较低造成合金持久寿命明显缩短。
关键词:铁镍基高温合金;蠕变;应力集中;动态再结晶
中图分类号:TG135 文献标志码:A
应用实践表明,火电机组锅炉蒸汽参数的提高对于提高发电效率及降低污染物排放均具有显著的改善效果[1-2]。因此,自1998年1月欧洲启动“AD700计划”以来,各国均已开展700 ℃级超超临界火电机组(A-USC)的研发工作[3]。与现有600 ℃级超临界机组(USC)技术相比,新一代锅炉机组要求其关键部件(过热器、再热器等)的选用材料具有(700 ℃,100 MPa)条件下1×105 h以上的服役寿命[4],远超现有的铁素体及奥氏体钢等传统耐热材料的使用性能[5]。为此,欧美等国相继开发出沉淀强化(In740H、Haynes282等)及固溶强化(CCA617、Haynes230等)镍钴基高温合金以满足机组中过热器/再热器等关键部件的服役性能需求[6-7]。然而,上述合金的原料成本较传统材料的相比显著较高,同时较大的流变应力及较高的合金化程度也为其成型、加工与焊接带来极大挑战。
与上述镍钴基合金相比,铁镍基高温合金具有良好的加工性及低廉的原料成本,并已作为高温部件在各个行业获得广泛应用。其中,GH2984合金作为船舰锅炉管材料已有十余年的使用经验,并在600~700℃温度范围内长期服役期间表现出良好的性能及组织稳定性[8]。因此,GH2984合金已作为A-USC机组中过热器/再热器等关键部件的主要候选合金之一而备受关注。为使其满足700 ℃级A-USC锅炉部件服役性能要求,肖璇等[9]通过B、P等元素合金化改善合金晶界,显著提高了其在(700 ℃,350 MPa)条件下蠕变塑性及持久寿命。WANG等[10]通过调整合金中Al与Ti比例获得了更加稳定的组织,抑制了η(Ni3Ti)等有害相在服役期间的形核与生长。然而,过热器/再热器服役过程中内外壁温差、表面腐蚀产物覆盖等诸多因素造成材料实际服役温度往往在700~750 ℃内浮动。研究表明,高温合金在该温度范围内变形机制十分复杂,晶内与晶界变形行为均会对持久寿命产生显著影响。晶内析出相钉扎位错,可以有效提高合金蠕变强度[11],而晶界处强化可以降低应力集中,减少裂纹形成,进一步提高合金持久寿命[12-13]。WANG等[14]发现当时效温度达到750 ℃后,合金中Ni3Al(γ″)长大速度明显加快,对其700 ℃力学性能造成不利影响。ZHONG等[15-16]对GH2984合金在不同温度下的拉伸性能进行测试,结果发现在700 ℃时产生中温脆性严重降低合金塑性,而温度达到750 ℃后出现的再结晶现象对合金强度带则来较大影响,并进一步证实改善晶内强度可使合金750 ℃持久寿命明显提高。由此可见,700~750 ℃范围内温度波动对GH2984合金变形行为影响显著,而对该合金在这一温度范围内变形机制及其对持久性能的影响报道较少。因此,本文作者研究了GH2984合金在不同温度及应力下的蠕变行为,探讨了合金在700~750 ℃温度范围内蠕变变形的组织演变规律及其对合金持久蠕变行为的影响。
1 实验
GH2984合金成分(质量分数)为:33%Fe,19%Cr,2.2%Mo,1.0%Ti,0.4%Al,1.0%Nb,0.06%C,余量为Ni。采用真空熔炼制备合金铸锭并在1200 ℃均匀化处理24 h,随后在1200 ℃轧制为10 mm厚的板材并空冷至室温。沿轧制方向(RD)切取长度70 mm直径9 mm的合金棒材,并将其在1100 ℃固溶处理1 h后空冷,在其进行(750 ℃,8 h)时效处理后以(1 ℃,min)的速度冷至650 ℃,保温16 h后空冷至室温。合金的持久性能试验在Uyama高温持久试验机上进行,试验方法参考国标GB/T 2309-2012《金属材料单轴拉伸蠕变试验方法》,试验参数选择为(700 ℃,300 MPa),(700 ℃,200 MPa)及(750 ℃,150 MPa)。
采用Rigaku RINT-TTR III型高温XRD对经1100 ℃固溶处理1 h后的GH2984合金进行室温及650、700、750 ℃物相检测,其中在高温XRD扫描前先将置于氧化铝垫片上的样品装入炉腔,真空加热至指定温度并保温0.5 h,随后以4 (°)/min的速度对样品表面进行扫描。采用TEOL JSM-6060型扫描电子显微镜(SEM)对合金的持久断口表面形貌进行观察,随后制备持久断口亚表层直切面,并结合TSL OIM 7.0.1-CCD/ADV型电子背散射衍射分析仪(EBSD)对合金晶粒取向演变进行对比分析。采用50%甘油+42%盐酸+8%硝酸的混合溶液对合金直切面样品腐蚀5~10 min,并利用背散射成像技术(BSE)观察变形过程亚表层基体组织结构转变行为。最后在待观测区域切取0.5mm厚的样品并机械研磨至50~100 μm,利用45%醋酸+45%乙二醇单丁醚+10%高氯酸混合溶液在(-10 ℃,30 V)条件下双喷减薄至100nm,并利用Tecnai F20型透射电子显微镜(TEM)分析合金蠕变期间晶粒的显微组织演变规律。
2 实验结果
对热处理态GH2984合金进行EBSD分析,结果如图1所示。合金轧制并热处理后组织均匀,奥氏体平均晶粒尺寸为38 μm。反极图分析结果表明轧制后合金内部大量{112},{110}晶面分别垂直于ND及RD方向垂直于ND方向的晶面指数为{112},而平行于RD方向的晶向指数换算后为<111>,因此,合金轧制后具有{112}<111>板织构特征,并在随后的热处理过程中保留下来(见图1(a))。对合金晶粒内部物相结构进行TEM分析,结果表明合金主要为奥氏体与γ′相构成的双相结构,并在晶界处可观察到少量MC及M23C6型碳化物存在。热处理后晶粒内部均匀析出约占6.0%体积分数的球状γ′相,其平均直径为23.1 nm(见图1(b))。γ′相主要由Ni与Al,Ti元素构成,其与基体错配度为-0.06%[12],与基体基本保持共格关系。对晶界重位点阵(CSL)观察发现合金中存在较大比例的特殊晶界(∑3、∑9),表明其在变形及热处理等过程中形成大量孪晶(见图1(c))。对合金进行不同温度下的物相组成测试,发现合金在高温具有良好的组织稳定性,在650~750 ℃范围内无新物相生成(见图1(d))。
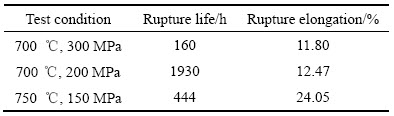
对合金进行3种不同条件的持久性能测试(表1中数据为单次测量结果),结果如表1所示。合金在(700 ℃,200 MPa)条件下其持久断裂时间达1930 h,而增加应力及提高温度会造成材料持久寿命分别降至159 h和444 h。此外,蠕变温度升高至750 ℃后使持久塑性由11.80%增至24.05%,而应力的改变对其影响则不明显。对合金持久断口表面进行比较观察,发现其经(700 ℃,300 MPa)蠕变条件下断裂后表面呈现典型的沿晶断裂特征,表明合金在这一条件下变形时裂纹沿晶界萌生并扩展(见图2(a))。蠕变应力降至200 MPa时,在裂纹萌生区域出现穿晶断裂现象,但随着裂纹扩展,合金单位面积应力增加,最终转变为沿晶断裂为主的裂纹扩展方式(见图2(b))。当蠕变条件为(750 ℃,150 MPa)时,穿晶断裂占较大比例,此时晶界已不再是裂纹扩展的主要途径(见图2(c))。采用TEM对合金蠕变期间微观结构分析,结果在不同条件蠕变后的合金晶粒内部均发现大量位错环,表明在不同温度条件下位错都是以绕过方式通过γ′相(见图3)。
3 分析与讨论
3.1 蠕变过程中微观组织演变
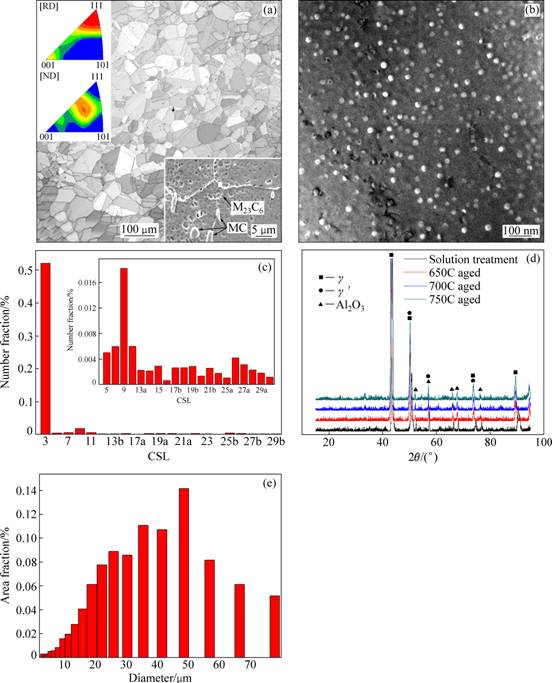
图1 GH2984合金的热处理态组织IQ图、热处理过程中析出的γ′相形貌、热处理态合金CSL晶界分析结果、不同温度下XRD谱及合金晶粒尺寸分析
Fig. 1 IQ map of GH2984 alloy by EBSD analyzing (a); precipitation of γ′ in heat-treated GH2984 alloy (b); CSL analyzing result of heat-treated GH2984 alloy (c), XRD analyzing result of GH2984 alloy at different temperatures (d) and grain size analyzing of alloy (e)
表1 GH2984合金不同条件下持久性能测试结果
Table 1 Creep-rupture results of GH2984 alloy under various test conditions
对合金断口切面进行观察,发现合金在(700 ℃,300 MPa)蠕变断裂后,断口亚表层晶界处形成大量二次裂纹(见图4(a))。平行于合金变形方向的晶粒取向以(111)为主,表明变形后合金具有<111>//RD丝织构。由于持久样品的取样方向(或变形方向)与轧制方向一致,因此,表明变形后晶粒取向与原始组织({112}<111>板织构)相比并无明显改变。当应力降至200MPa或温度升至750 ℃后,均导致新的<001>//RD丝织构在亚表层处产生,表明在较低的应力或较高的温度条件下,合金的变形过程会伴随着晶粒位向发生改变。合金在(700 ℃,200 MPa)条件下持久断裂后,亚表层晶界裂纹数量显著减少,且其尺寸明显较小(见图4(b))。由图4(c)可以看到少量穿晶二次裂纹,进一步证实了合金在这一条件下部分裂纹沿晶内扩展现象。对于(750 ℃,150 MPa)持久样品,断口表面与拉伸应力轴呈接近45°角,在亚表层晶界形成大量蠕变孔洞,同时在拉伸样品边缘发现较大尺寸的二次裂纹(见图4(c))。

图2 GH2984合金在不同条件下蠕变的持久断口表面形貌
Fig. 2 Fracture surface morphology of GH2984 after crept under different conditons
3.2 应力对合金蠕变断裂行为的影响
为明确晶粒取向改变对合金蠕变性能的影响,通过分析断口亚表层晶粒的施密特因子(Schmid)及其分布研究蠕变过程中晶粒变形行为,结果如图5所示。由图5可知,合金在700 ℃蠕变过程中二次裂纹主要萌生于具有低Schmid因子的晶粒(LSG)界面处,并沿晶界扩展形成楔形裂纹。合金经过(700 ℃,300 MPa)蠕变期间亚表层的LSG变形协调困难,导致在其晶界处产生应力集中,并在达到临界值后形成楔形裂纹。肖璇等[9]也证实GH2984合金在(700 ℃,350 MPa)蠕变条件下,晶界处会形成应力集中并最终造成楔形裂纹萌生与扩展。然而,随着应力降至200 MPa,在远离断口处(距断口1500 μm以上)LSG减少,同时该区域二次裂纹密度明显降低。
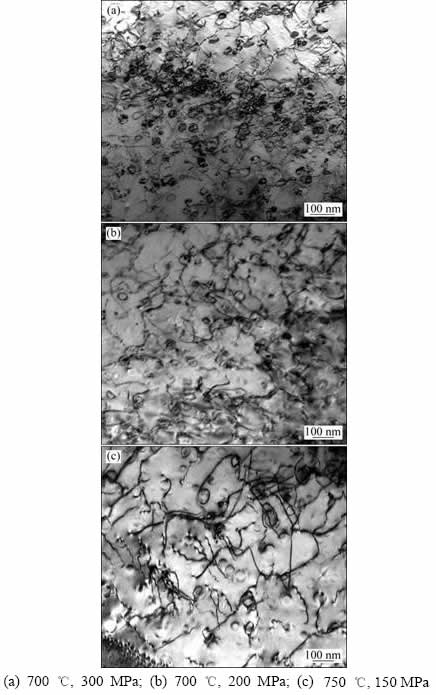
图3 GH2984合金在不同条件下蠕变的显微组织
Fig. 3 Microstructures of GH2984 after crept under different conditions
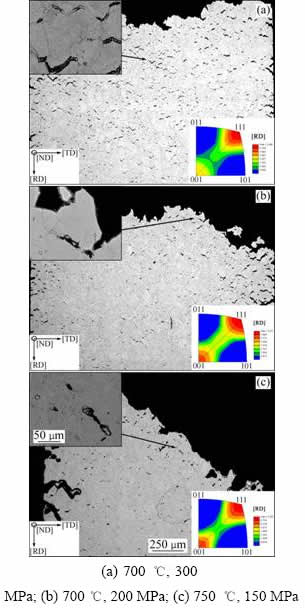
图4 GH2984合金在不同条件下蠕变后的持久断口亚表层切面组织形貌
Fig. 4 Sub-surface cross section microstructure of GH2984 alloy after creep at under different conditions
综上所述可知,合金经过(700 ℃,300 MPa)蠕变断裂后与其变形前在RD方向的晶粒取向一致。而合金在(700 ℃,200 MPa)条件下断裂后,新的<001>//RD丝织构产生于断口亚表层1500~2000 μm处,而在断口附近(距断口700~1200 μm)并未发现晶粒取向的改变(见图6)。ZHANG等[12]研究认为,面心立方晶体在具有{001}取向时变形过程中消耗的应变能力最小。因此,晶粒向<001>丝织构转变将使其变形更加容易,从而使合金在蠕变过程中消耗的应变能降至最低。可见合金在(700 ℃,200 MPa)变形条件下部分区域晶粒在应力作用下由<111>向<001>转动,使得晶粒获得较好的变形协调能力并促使晶界处应力集中得到释放,进而抑制了蠕变过程中裂纹在该区域的萌生与扩展。此外,在低应力蠕变过程中,晶界处碳化物充分析出,进一步阻碍了裂纹的萌生与扩展[13]。而在断口附近区域,晶粒的变形协调使得裂纹数量与(700 ℃,300 MPa)蠕变断裂后相比明显减少,但当应变达到临界值后裂纹仍将在LSG界面形核并扩展[18]。
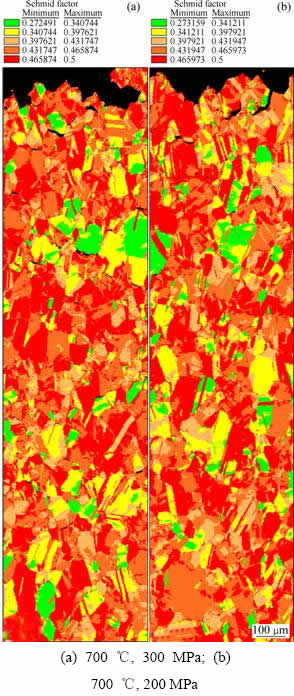
图5 GH2984合金经过不同条件下持久断裂后亚表层晶粒施密特因子分布
Fig. 5 Grain schmid factor distribution in GH2984 alloy after crept under different conditions
3.3 温度对合金蠕变断裂行为的影响
对合金的晶粒尺寸比较发现,合金在(750 ℃,150 MPa)蠕变断裂后亚表层(500~2000 μm范围内)形成大量细小晶粒,且其晶粒尺寸均低于3 μm(见图7(a))。

图6 GH2984合金在不同条件下断裂后700~1200 μm处及1500~2000 μm处晶粒EBSD分析结果
Fig. 6 EBSD analyzing results of grain orientation at 700-1200 μm (a) and 1500-2000 μm (b) from fracture surface after alloy crept at (700 ℃, 300 MPa), and grain orientation at 700-1200 μm (c) and 1500-2000 μm (d) from fracture surface after alloy crept at (700 ℃, 200 MPa)
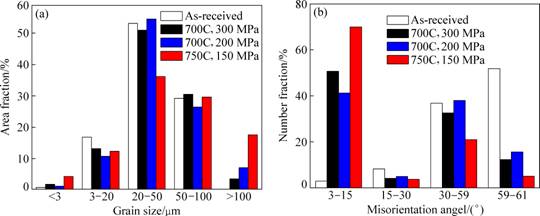
图7 GH2984合金在不同条件下蠕变前后的晶粒尺寸与晶界错配角度分析结果
Fig. 7 Grain size (a) and grain boundary (b) misorientation angel of GH2984 alloy before and after creep at different conditions
对合金晶界错配度的分析发现,750 ℃变形后具有60°角的晶界数量显著降低,表明蠕变过程中孪晶大量消失(见图7(b))。此外,由图7(b)可以看出,蠕变后具有低错配角的晶界数量增加最明显。由上述结果分析可知,合金在(750 ℃,150 MPa)蠕变期间出现动态再结晶(DRX)[19-20]。ZHONG等[15]在对GH2984合金拉伸断口的观察中也发现,合金变形温度由700 ℃上升至750 ℃后,再结晶现象对合金失效机制产生重要影响。
采用TEM对合金断口亚表层组织进行分析,结果发现经过(700 ℃,300 MPa)蠕变断裂后粒内产生大量位错,但并未在晶界附近发现位错塞积或晶界拱出等现象(见图8(a))。这表明合金在该条件下晶粒产生严重加工硬化,但并未达到再结晶所需的变形能临界值。这进一步证实合金在700 ℃时晶界强度相对晶内较弱,在变形过程中首先形成楔形裂纹并导致合金断裂。此时,晶内析出相有效钉扎位错并造成明显的加工硬化,随着应力进一步增加并超过晶界强度时,裂纹在晶界处萌生并扩展。而当变形温度达到750 ℃时,扩散激活能增加使得位错更加容易越过析出相,并在应力较低时便在晶界富集,最终相互反应形成小角度晶界。TEM观察证实大量位错缠结形成小角度晶界,并最终导致亚晶粒形成(见图8(b))。这些亚晶粒与原始态晶粒尺寸相比明显较小,且晶内位错密度较低,表明其在合金变形过程中成为连续动态再结晶形核质点,并可能会在继续变形过程中逐渐转变为具有大角度晶界的再结晶晶粒。这与SAKAI等[21]的研究结论吻合,即Fe-Ni合金等具有较低层错能的合金动态再结晶往往以连续的方式进行,在变形过程中由位错反应形成小角度晶界,并伴随着位错在晶界的不断塞积最终演变为大角度晶界。

图8 合金GH2984合金在700 ℃、300 MPa与750 ℃、150 MPa蠕变断裂后晶界形貌
Fig. 8 Microstructures of grain boundary in alloy after crept at (700 ℃, 300 MPa) (a) and (750 ℃, 150 MPa) (b)
4 结论
1) GH2984合金经轧制及热处理后,平行于轧制方向形成{112}<111>板织构。合金在不同温度下晶内均由奥氏体基体与弥散分布的球状γ′两相结构组成,其中奥氏体平均晶粒尺寸约为38 μm,并在晶粒内部析出体积分数约为6%的球状γ′相,析出相平均直径为23.1 nm。并在晶粒内部发现大量孪晶形成。此外,合金经热处理后。在晶界不连续析出M23C6型碳化物。
2) 合金在(700 ℃,300 MPa)条件下持久寿命仅160 h,持久变形期间亚表层形成大量楔形微裂纹,晶粒内部产生较高密度位错。当蠕变应力降至200 MPa后部分区域在应变能力最小化的驱动下产生晶粒倾转,促进晶界处应力释放并进而抑制了裂纹萌生。在该条件下合金持久寿命增至1930 h,但晶界仍为裂纹扩展的主要途径。
3) 合金在(750 ℃,150 MPa)条件下蠕变时持久寿命仅为444 h,但持久伸长率达到24.05%。蠕变期间晶粒内部孪晶大量消失,同时形成大量亚晶界并进而转变为尺寸细小的再结晶晶粒。可见,700 ℃高应力条件下变形时晶界容易成为裂纹萌生与扩展的主要途径。在较低应力下晶界滑移导致晶粒取向改变,通过协调变形降低了晶界的应力集中并延缓裂纹的萌生。变形温度达到750 ℃时,晶粒强度显著下降,在变形过程中位错缠结并形成大量亚晶界,进而最终转变为细小的再结晶晶粒,提高蠕变塑性的同时降低持久寿命。因此,在700~750 ℃范围内晶粒与晶界的变形行为均将对合金的持久性能产生重要影响,提高蠕变过程中两者的变形协调能力将对条合金持久寿命提高具有良好的改善效果。
REFERENCES
[1] VISWANATHAN R, HENRY J F, TANZOSH J, STANKO G, SHINGLEDECKER J, VITALIS B, PURGERT R. Program on materials technology for ultra-supercritical coal power plants[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 2005, 14(3): 281-292.
[2] VISWANATHAN R, PURGERT R, GOODSTINE S, TANZOSH J, STANKO G, SHINGLEDECKER J P, VITALIS B. Program on materials technology for ultrasupercritical coal-fired boilers[C]//GANDY D, SHINGLEDECKER J. Advances in Materials Technology for Fossil Power Plants: Proceedings of the 5th International Conference, Ohio: ASM International, 2008: 05226G.
[3] WRIGHT I G, MAZIASZ P J, ELLIS F V, GIBBONS T B, WOODFORD D A. Materials issues for turbines for operation in ultra-supercritical steam[R]. UT Battelle LLC: Oak Ridge National Laboratory, 2004.
[4] TAKANO S, AOKI Y, KUBUSHIRO K. Development of 700 degree celsius class advanced ultra-supercritical boiler[J]. IHI Engineering Review, 2009, 49: 185-191.
[5] YAN J, GU Y, LU J. On precipitates in Fe-Ni base alloys used for USC boilers[J]. Materials Science and Technology, 2014, 31: 389-399.
[6] VISWANATHANA R, COLEMANA K, RAO U. Materials for ultra-supercritical coal-fired power plant boilers[J]. International Journal of Pressure Vessels and Piping, 2006, 83: 778-783.
[7] YUAN Y, ZHONG Z H, YU Z S, YIN H F, DANG Y Y, ZHAO X B, YANG Z, LU J T, YAN J B, GU Y. Microstructural evolution and compressive deformation of a new Ni-Fe base superalloy after long term thermal exposure at 700 ℃[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2014, 619: 364-369.
[8] 郭建亭, 杜秀魁. 一种性能优异的过热器管材用高温合金GH2984[J]. 金属学报, 2005, 41: 1221-1227.
GUO Jian-ting, DU Xiu-kui. A superheater tube superalloy GH2984 with excellent properties[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2005, 41: 1221-1227.
[9] 肖 旋, 赵海强, 王常帅, 郭永安, 郭建亭, 周兰章. B和P对GH984合金组织和力学性能的影响[J]. 金属学报, 2013, 49: 421-427.
XIAO Xuan, ZHAO Hai-qiang, WANG Chang-shuai, GUO Yong-an, GUO Jian-ting, ZHOU Lan-zhang. Effects of B and P on microstructure and mechanical properties of GH984 alloy[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2013, 49: 421-427.
[10] WANG T T, WANG C S, GUO J T, ZHOU L Z. Stability of microstructure and mechanical properties of GH984G alloy during long-term thermal exposure[J]. Materials Science Forum, 2013, 747/748: 647-653.
[11] 郭建亭, 袁 超, 侯介山. 高温合金的蠕变及疲劳-蠕变-环境交互作用规律和机理[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2011, 21: 487-504.
GUO Jian-ting, YUAN Chao, HOU Jie-shan. Creep and creep-fatigue-environment interaction and mechanisms of superalloys[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2011, 21: 487-504.
[12] 侯介山, 丛培娟, 周兰章, 秦学智, 袁 超, 郭建亭. Hf对抗热腐蚀镍基高温合金微观组织和力学性能的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2011, 21: 945-953.
HOU Jie-shan, CONG Pei-juan, ZHOU Lan-zhang, QIN Xue-zhi, YUAN Chao, GUO Jian-ting. Effect of Hf on microstructure and mechanical behavior of hot corrosion resistant Ni-based superalloys[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2011, 21: 945-953.
[13] 田素贵, 谢 君, 周晓明, 钱本江, 伦建伟, 于丽丽, 汪武祥. 淬火工艺对FGH95合金组织结构与蠕变性能的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2010, 20: 852-858.
TIAN Su-gui, XIE Jun, ZHOU Xiao-ming, QIAN Ben-jiang, LUN Jian-wei, YU Li-li, WANG Wu-xiang. Effects of quenching technics on microstructure and creep properties of FGH95 superalloy[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2010, 20: 852-858.
[14] WANG T, WANG C, SUN W, QIN X, GUO J, ZHOU L. Microstructure evolution and mechanical properties of GH984G alloy with different Ti/Al ratios during long-term thermal exposure[J]. Materials & Design, 2014, 62: 225-232.
[15] ZHONG Z H, GU Y F, YUAN Y, SHI Z. Tensile properties and deformation characteristics of a Ni-Fe-base superalloy for steam boiler applications[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2014, 45: 343-350.
[16] ZHONG Z H, GU, YUAN Y, SHI Z. A new wrought Ni-Fe-base super alloy for advanced ultra-supercritical power plant applications be yond 700 ℃[J]. Materials Letters, 2013, 109: 38-41.
[17] ZHANG J M, ZHANG Y, XU K W. Dependence of stresses and strain energies on grain orientations in FCC metal films[J]. Journal of Crystal Growth, 2005, 285: 427-435.
[18] 张俊善. 材料的高温变形与断裂[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2007: 145.
ZHANG J S. High temperature deformation and fracture of materials[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2007: 145.
[19] DUDOVA N, BELYAKOV A, SAKAI T, KAIBYSHEV R. Dynamic recrystallization mechanisms operating in a Ni-20%Cr alloy under hot-to-warm working[J]. Acta Materialia, 2010, 58: 3624-3632.
[20] BRANGER V, MATHON M H, BAUDIN T, PENELLE R. “In-situ” neutron diffraction study of the cube crystallographic texture development in Fe53%-Ni alloy during recrystallization[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2000, 43: 325-330.
[21] SAKAI T, BELYAKOV A, KAIBYSHEV R, MIURA H, JONAS J J. Dynamic and post-dynamic recrystallization under hot, cold and severe plastic deformation conditions[J]. Progress in Materials Science, 2014, 60: 130-207.
Rupture mechanism of GH2984 crept at temperature between 700-750 ℃
YAN Jing-bo1, GU Yue-feng1, GAO Yi-min2, SUN Fei3, ZHAO Xin-bao1,
DANG Ying-ying1, YANG Zhen1, YIN Hong-fei1, 2
(1. Xi’an Thermal Power Research Institute, Xi’an 710032, China;
2. State Key Laboratory for Mechanical Behavior of Materials,
School of Materials Science and Engineering, Xi’an Jiaotong University, Xi’an 710049, China;
3. School of Materials Science and Engineering, Shandong University, Jinan 250061, China)
Abstract: The microstructure evolution and its effect on the properties of GH2984 alloy between 700 and 750 ℃ were investigated. The results show the rupture life is only about 160 h when the alloy was crept at 700 ℃ and 300 MPa. The stress concentration and consequently crack nucleation and propagation are the main reason for failure of the alloy. When the stress decreases, the stress concentration is released by the grain rotation. It inhibits the crack nucleation and thus extends the alloy rupture life obviously. However, accompanied with the grain deformation proceeding, the dynamic recrystallization occurs when the creep temperature increases. This leads to the increases of the alloy creep ductility, but decreases the alloy rupture life because of the lower work hardening extent.
Key words: Fe-Ni-base superalloy; creep; stress concentration; dynamic recrystallization
Foundation item: Project (51301131) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project (20141613) supported by the State Key Laboratory for Mechanical Behavior of Materials of Xi’an Jiaotong University, China
Received date: 2015-05-06; Accepted date: 2015-12-18
Corresponding author: YAN Jing-bo; Tel: +86-18109266166; E-mail: yf625oscar@163.com
(编辑 龙怀中)
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(51301131);西安交通大学金属材料强度国家重点实验室开放研究项目(20141613)
收稿日期:2015-05-06;修订日期:2015-12-18
通信作者:严靖博,工程师,博士;电话:18109266166;E-mail:yf625oscar@163.com