
Conversion of polyaluminocarbosilane(PACS) to Si-Al-C-(O) fibers:
evolutions and effect of oxygen
ZHENG Chun-man(郑春满), LI Xiao-dong(李效东), YU Yu-xi(余煜玺), ZHAO Da-fang(赵大方)
State Key Laboratory of New Ceramic Fibers and Composites,
School of Aerospace and Materials Engineering, National University of Defense Technology, Changsha 410073, China
Received 6 July 2005; accepted 22 November 2005
Abstract: The evolvement of oxygen from polyaluminocarbosilane(PACS) to Si-Al-C-(O) fibers and its effect on properties were investigated by element analysis, solid-state 27Al nuclear magnetic resonance(NMR), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy(FT-IR), thermo-gravimetric analyses(TGA), scanning electron microscope(SEM) and X-ray diffraction(XRD). Element analysis of PACS precursor polymer gives an empirical formula of SiC2.1H11.1O0.12Al0.024. 27Al NMR spectra mass gain shows that the oxygen of cured PACS fibers comes from aluminum aletylacetanate (Al(AcAc)3) and the curing process. Oxygen content can be regarded as a constant mass during the pyrolysis process. During the sintering process of Si-Al-C-O fibers into Si-Al-C fibers, oxygen and carbon decreases with the release of a small amount of CO and/or SiO. Oxygen has a positive effect on the ceramic yield while has a negative effect on the crystallization of Si-Al-C-O fibers. It has great influence on mechanical properties of Si-Al-C-O and excellent tensile strength is usually obtained at the oxygen content of 8%-10%. The Si-Al-C-(O) fibers have excellent thermal stability and creep resistance.
Key words: polyaluminocarbosilane; PACS; SiC fibers; Si-Al-C-(O) fibers; evolutions; properties
1 Introduction
Silicon carbide(SiC) fibers, which have high tensile strength, high elastic modulus and good thermal stability, are one of the best candidates of the reinforcements available for continuous-fiber-reinforced ceramic-matrix composites(CMCs)[1]. SiC fibers derived from polymer pyrolysis have the spectral advantages of the flexibility, fine-diameter form over those from CVD. Since Yajima’s synthesis of polycarbosilane(PCS) as precursor[2, 3], polymer-derived SiC fibers have been extensively studied. Generally, the SiC fibers are produced by synthesis, melt spinning, curing and pyrolysis. During the process, curing is an essential step because the fibers would lose most mass and could hardly retain its cylindrical shape during the subsequent pyrolysis if curing is absent. PCS fibers are heat-treated in air to render the green fibers crosslinked and infusible. Therefore, one problem of these fibers is that thermo-mechanical stability is good only below 1 200 ℃. The major mechanism of the thermal degradation of SiC fibers have been reported to be the oxidation of silicon and carbon to form volatile CO and SiO products, which eventually develops a porous microstructure in fibers[4, 5].
Recently, several attempts have been made with the object of improving the mechanical properties and thermal stability of these fibers. One of the methods is that SiC fibers including hetero-elements of Ti, Zr, Al, B, etc, which were prepared through the physical and chemical modification of precursor[6]. For example, Ishikawa et al[7] have already prepared the high temperature resistance SiC fibers containing Al using polyaluminocarbosilane(PACS), which was synthesized from PCS and aluminum aletylacetanate (Al(AcAc)3).
In this paper, PACS was synthesized by the reaction of polysilocarbonsilane(PSCS) with Al(AcAc)3 which is different from Ishikawa is; the evolvement of oxygen during preparation of Si-Al-C-(O) fibers, the effect on the properties, the thermal stability and creep resistance of Si-Al-C-(O) fibers were investigated through element analysis, solid-state 27Al NMR, FT-IR, mass gain, SEM and XRD.
2 Experimental
2.1 Samples and sample preparation
PACS was synthesized from PSCS supplied by our laboratory, and Al(AcAc)3 at normal pressure. Its average molecular number was about 1 700 and the melting point was (177±3) ℃. The PACS was melted in nitrogen and spun into fibers composed of 200 continuous filaments with a multi-holes spinning machine[8]. The green fibers were then cured in air oven at a certain heating rate from room temperature to 160-220 ℃ and the holding time was varied to obtain different curing degrees (namely, to obtain different oxygen content). The cured fibers were heated in nitrogen atmosphere at 1 300 ℃ and Si-Al-C-O fibers was obtained. The Si-Al-C fibers was obtained by sintering of Si-Al-C-O fibers at 1 800 ℃ in argon.
2.2 Methods of characterization
Mass gain was measured by weighing PACS fibers before curing and after curing at room temperature. Silicon, aluminum, carbon and oxygen were determined by chemical analysis. Si and Al (by a gravimetric method dissolving with sodium carbonate and sodium peroxide), C (by a combustion volumetric method) and O (by a nitrogen/oxygen analyzer TC-436, LECO, USA). FT-IR spectra were obtained over the range of 4 000 to 400 cm-1 using a Nexus 670 Fourier transform infrared spectrophotometer. KBr discs were used, prepared by compressing a finely ground mixture of about 5 mg of the sample and 300 mg of KBr powder. The morphology of the Si-Al-C-(O) fibers was observed by scanning electron microscope (SEM, JSM-20, JEOL). TGA curves of PACS fibers were obtained with a high temperature NETZSCH STA 449C Thermo-gravimetric analyses at a heating rate of 10 ℃/min. X-ray diffraction measurements were performed by a SiemensD-500 diffractometer (Germany) using nickel filtered copper Kα radiation. The tensile strength of Si-Al-C-(O) fibers was measured using a tensile testing machine (Model-YG-002, Taicang) with a gauge length of 25 mm and a crosshead speed of 2 mm/min at room temperature. Si-Al-C-(O) fibers and Nicalon fibers were treated at high temperature in air in order to characterize their thermal stability.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Source of oxygen
From elemental analysis, the composition of the PACS precursor was Si, 42%; C, 37.51%; H, 16.6% (by difference); O, 2.9%; and Al, 0.99%, giving the empirical formula SiC2.1H11.1O0.12Al0.024. The mole ratio of carbon to silicon in the PACS precursor is about 2∶1. Fig.1 shows the 27Al solid NMR of PACS precursor. It indicates that aluminum and oxygen exists in the form of coordination bond in the PACS precursor and the oxygen mainly comes from Al(AcAc)3. Because of the sensitivity of the PACS precursor to oxygen and moisture,absorption of oxygen or moisture could lead to the higher expected oxygen content.
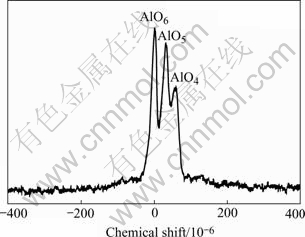
Fig.1 27Al Solid NMR of PACS precursor
FT-IR of PACS fibers and cured PACS fibers heat-treated at different conditions are shown in Fig.2. The intensity of the absorption peak at 2 100 cm-1 of cured PACS fibers is evidently reduced compared with that of non-cured PACS fibers the intensity of that peak at 1 250 cm-1 is very similar. This reduction intensity at 2 100 cm-1 is considered to be the reaction of PACS fibers with oxygen that Si-O-Si bonds are formed [9, 10].
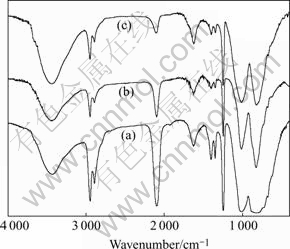
Fig.2 FT-IR of PACS fibers(a), cured PACS fibers heat-treated at 160 ℃ for 2 h(b) and cured PACS fibers heat-treated at 190 ℃ for 6 h in air(c)
Fig.3 shows the relationships between oxygen content and mass gain of cured PACS fibers. The oxygen content of cured PACS fibers is proportional to mass gain, but mass gain percentage of the cured PACS fibers is not equal to oxygen content. The point of contact is about 2.81%, and it approaches to 2.9% that is acquired from elemental analysis.
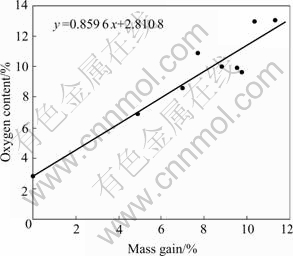
Fig.3 Relationship between oxygen content of cured PACS fibers and mass gain
In a word, the oxygen content of cured PACS fibers includes two parts: one comes from Al(AcAc)3 and another is introduced into PACS fibers during the curing process.
3.2 Evolutions of oxygen
Pyrolysis of cured PACS fibers is a conversion process from organic to inorganic. In the process, hydrogen and methane are evolved, as well as some trace of carbon monoxide[11, 12]. Table 1 lists the chemical composition of cured PACS pyrolyzed to certain temperature, PACS600 means the Si-Al-C-O fibers obtained by pyrolyzing cured PACS fibers at 600 in nitrogen. It can be seen that oxygen of the fibers can be regarded as a constant mass during the pyrolysis.
Table 1 Chemical composition of cured PACS pyrolyzed to certain temperature(mass fraction, %)
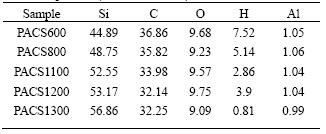
Table 2 lists the evolutions of oxygen and carbon with sintering temperature, Si-Al-C-O 1400 means the Si-Al-C fibers obtained by sintering Si-Al-C-O fibers at 1 400 ℃ in argon. It shows that oxygen and carbon decrease with the increasing sintering temperature and the silicon increases with increasing sintering temperature. It is due to the reaction of carbon and a small amount of silicon with oxygen of Si-Al-C-O fibers to form volatile CO and/or SiO[7].
Table 2 Chemical composition of Si-Al-C-O fibers and sintering product(mass fraction, %)
3.3 Effect of oxygen on properties of Si-Al-C-(O) fibers
TG-DTA shows that the ceramic yield of PACS fibers is 52% and the cured PACS fibers heat-treated at 190 ℃ for 6 h in air is 78%. It shows that the oxygen has a positive effect on the ceramic yield. The relationships of tensile strength of the Si-Al-C-O fibers and mass gain are shown in Fig.4. All fibers with mass gain less than 7%, fuse together on heat treatment at 1 300 ℃ and do not maintain fibers shape. The tensile strength of Si-Al-C-O fibers increases with increasing mass gain, and reaches a maximum value when mass gain is 8 to 10%, and then decreases.
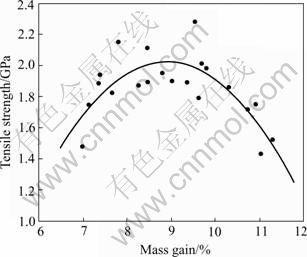
Fig.4 Relationship of tensile strength and mass gain
Fig.5 shows SEM images of Si-Al-C-O fibers surface with different oxygen contents. Figs.5(a) and (c) show a smooth surface and no heterogeneity. In Figs.5(b) and (d), the surface is rough and deposits are observed. The deposits are SiC grains caused by the reaction between SiO gas and C, and the decrease in the mechanical properties of Si-Al-C-O fibers are owing to the surface injured by them[13].
As being pointed out, the strength of SiC fibers is more determined by the microstructure of fibers. Excellent tensile strength could be only obtained for finely crystallized fibers given a fixed composition[14]. So, to reach a better strength, the fibers should be crystallized to a proper size, neither too large nor too small (amorphous). Fig.6 shows the XRD patterns of Si-Al-C-O fibers with different oxygen content. In Figs.6(a) and (b) the diffraction peak (111) of β-SiC is clear, and the separation of the peak (220) and (311) of β-SiC is also clear. However, in Fig.6(c) the diffraction peak (111) and the separation of the peak (220) and (311) of β-SiC are also observable, but they are not clear. These indicate that the crystallization of β-SiC in the Si-Al-C-O fibers is inhibited with increasing of oxygen content.
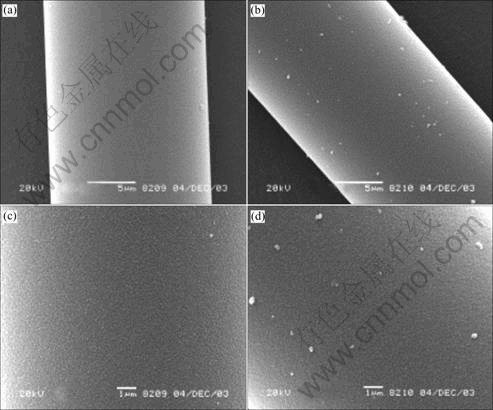
Fig.5 SEM images of Si-Al-C-O fibers surface with oxygen content of 9.94% ((a) and (c)) and 12.97% ((b) and (d))
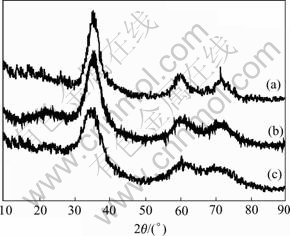
Fig.6 XRD patterns of Si-Al-C-O fibers with oxygen content of 7.97%(a), 9.42%(b) and 12.97%(c)
3.4 Thermal stability and creep resistance Si-Al-C-(O) fibers
The tensile strength of Si-Al-C-(O) and Nicalon at high temperature after thermal exposure test are shown in Fig.7. The tensile strength of all fibers decreased with increasing heat treatment time in a similar way. Nicalon heat-treated at 1 300 ℃ for 10 h in air exhibited low strength, no strength after heat-treated at 1 300 ℃ for 30 h in air. However, Si-Al-C-O and Si-Al-C heat-treated at 1 300 ℃ for 30 h in air showed high tensile strength
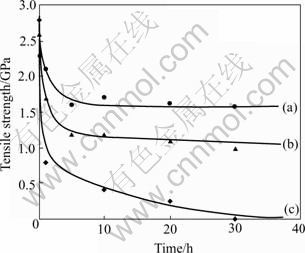
Fig.7 Tensile strength of Si-Al-C(a), Si-Al-C-O fibers(b) and Nicalon after exposure at 1 300 ℃ in air(c)
residue, which was about 50% and 70%.
The creep resistance of ceramic fibers was evaluated by the blending stress relaxation test developed by Morscher et al[15]. In this test, the fiber was wound around a graphite rod with a radius of R0 and heat-treated in Ar for 1 h. Then the stress relaxation ratio, m, was calculated using the remaining radius(R) of the relaxed fiber from the following equation, m=1-R0/R. Therefore, the value of m is between 0 and 1. The closer to 1 the value of m, the more excellent the creep resistance.
Fig.8 shows the creep resistance of Si-Al-C-O and Si-Al-C fibers in comparison with Nicalon, Hi-Nicalon and Tyranno SA for 1 h in argon. As can be seen from Fig.8, Si-Al-C shows a higher value of m than any other fibers. Moreover, in the case of Si-Al-C, the m is about 0.4 even at 1 800 ℃. Tyranno SA also has the excellent creep resistance, but the m is 0 when the temperature is above 1 800 ℃. Si-Al-C-O and Hi-Nicalon have the same creep resistance, which is better than Nicalon.
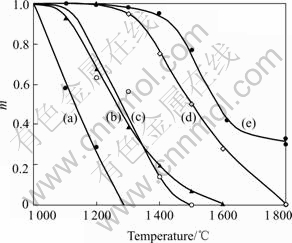
Fig.8 Creep resistance of Si-Al-C-O(c) and Si-Al-C fibers(e) in comparison with Nicalon(a), Hi-Nicalon(b) and Tyranno SA(d) for 1 h in argon
4 Conclusions
1) The empirical formula of PACS precursor polymer is SiC2.1H11.1O0.12Al0.024. 27Al NMR spectra and weight gain shows that the oxygen of cured PACS fibers comes from aluminum aletylacetanate (Al(AcAc)3) and curing process.
2) Oxygen content can be regarded as a constant mass during the pyrolysis process. During the sintering process of Si-Al-C-O fibers into Si-Al-C fibers, oxygen and carbon decrease with the release of a small amount of CO and/or SiO.
3) Oxygen has a positive effect on the ceramic yield and has a negative effect to crystallization of Si-Al-C-O fibers. It has great influence on mechanical properties of Si-Al-C-O and excellent tensile strength is usually obtained at the oxygen content of 8%-10%.
4) The Si-Al-C-(O) fibers have excellent thermal stability and creep resistance.
References
[1] Johnson D W, Evans A G, Goettler R W. Ceramic Fibers and Coatings: Advanced Materials for the Twenty-First Century[M]. Washington D C: National Academy Press, 1998. 1-49.
[2] Yajima S, Hasegawa J, Iimura M. Synthesis of continuous silicon carbide fiber with high tensile strength. and high Young’s modulus[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 1978(13): 2569-2576.
[3] Yajima S, Hayashi J, Omori M, OKAMURA K. Development of SiC fibre with high tensile strength [J]. Nature, 1976, 261: 683-685.
[4] Man T, Hecht N L, Cullum D E M C, HOENIGMAN J R, KIM H M, KATZ A P, LIPSITT H A. Thermal stability of SiC fibers (Nicalon) [J]. Journal of Materials Science, 1984, 19(4): 1191-1201.
[5] Clark T J, Marons R, Stamatoff J B, ROBE J. Thermal degradation of Nicalon SiC fiber [J]. Ceramic Engineering & Science Process, 1985, 6(7-8): 576-578.
[6] Yu Y X, Li X D, Cao F. Advances in the polymer-derived SiC fibers including hetero-element [J]. Journal of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2003, 4: 371-375.(in Chinese)
[7] Iisikawa T, Kohtoku Y, Kumagawa K, YAMAMURA T, NAGASAWA T. High strength alkali-resistant sintered SiC fiber stable to 2 200 ℃ [J]. Nature, 1998, 391: 773-774.
[8] Wang Y D, Feng C X, Song Y C. Study on process of continuous SiC fibers [J]. Aerospace Materials &Technology, 1997(2): 21-25. (in Chinese)
[9] Chu Z Y, Song Y C, Xu Y S, FU Y B. Enhance irradiation cross-liking of polycarbosilane [J]. Journal of Materials Science Letters, 1999, 18(21): 1793-1795.(in Chinese)
[10] Zheng C M, Zhu B, Li X D. Study on thermal-curing of polycarbosilane fibers [J]. Acta Polymerica Sinica, 2004(2): 246-250.(in Chinese)
[11] Ly H Q, Taylor R, Day R J, HEATLEY F. Conversion of polycarbosilane (PCS) to SiC-based ceramic, part Ⅱ pyrolysis and characterization [J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2001, 36: 4045-4057.
[12] Soraru G D, Babonneau F, Mackenzie J D. Structural evolutions from polycarbosilane to SiC ceramic [J]. Journal of Materials Science, 1990, 25: 3886-3893.
[13] Hasegawa Y. New curing method for polycarbosilane with unsaturated hydrocarbons and application to thermally stable SiC fiber [J]. Composite Science & Technology. 1994, 51: 161-166.
[14] Hasegawa Y, Okamura K. Synthesis of continuous silicon carbide fibre. Part 3, pyrolysis process of polycarbosilane and structure of the products [J]. Journal of Materials Science, 1983,18(12): 3633-3648.
[15] Morscher G N, DiCarlo J A, Wagner T. Fiber creep evaluation by stress relaxation measurements [J]. Ceramic Engineering & Science Process, 1991, 12(7-8): 1032-1038.
Foundation item: Project(59972042) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China
Corresponding author: ZHENG Chun-man; Tel: +86-731-4576421; E-mail: zhengchunman@sohu.com; xdli0153@sina.com
(Edited by LONG Huai-zhong)