烧结温度对生物医用纳米Ti-15Mo合金组织和摩擦学性能的影响
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2019年第11期
论文作者:Mamoun FELLAH Naouel HEZIL Dekhil LEILA Mohammed ABDUL SAMAD Ridha DJELLABI Stephania KOSMAN Alex MONTAGNE Alain IOST Aleksei OBROSOV Sabine WEISS
文章页码:2310 - 2320
关键词:Ti-15Mo;磨损;摩擦行为;纳米摩擦;烧结;生物医用
Key words:Ti-15Mo; wear; tribological behaviour; nanotribology; sintering; biomedical applications
摘 要:研究烧结温度(1073~1373 K)对具有纳米结构的球磨β型Ti-15Mo 合金结构和摩擦学性能的影响。通过多种技术对试样进行表征,如X射线衍射分析(XRD)、电子扫描电镜(SEM)和球-盘式往复摩擦试验机等;采用不同载荷(2、8 和16 N)进行磨损试验。结果表明,随着烧结温度的升高,合金的平均孔径和晶粒尺寸不断减小,在1373 K时分别达到最低值:4 nm和29 nm,1373 K烧结样品的相对密度高达97.0%。此外,烧结温度越高,试样的相对密度越大、硬度越高、弹性模量越高;1373 K烧结试样由于其较低的闭孔率导致摩擦因数和磨损率也较低。
Abstract: The effect of sintering temperature (1073-1373 K) on the structural and tribological properties of nanostructured ball- milled β-type Ti-15Mo samples was investigated. The prepared samples were characterized using various apperatus such as X-ray diffractometer, scanning electron microscope (SEM) and ball-on-plate type oscillating tribometer. Wear tests were conducted under different applied loads (2, 8 and 16 N). Structural results showed that the mean pore and crystallite size continuously decreased with increasing sintering temperature to reach the lowest values of 4 nm and 29 nm at 1373 K, respectively. The relative density of the sintered sample at 1373 K was as high as 97.0%. Moreover, a higher sintering temperature resulted in higher relative density, greater hardness and elastic modulus of the sample. It was observed that both the friction coefficient and wear rate were lower in the sample sintered at 1373 K which was attributed to the closed porosity.
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 29(2019) 2310-2320
Mamoun FELLAH1,2, Naouel HEZIL3, Dekhil LEILA4, Mohammed ABDUL SAMAD5, Ridha DJELLABI6, Stephania KOSMAN7, Alex MONTAGNE7, Alain IOST7, Aleksei OBROSOV8, Sabine WEISS8
1. Mechanical Engineering Department, ABBES Laghrour-University, Khenchela, P. O. 1252, 40004, Algeria;
2. Tribology and Materials Group, Laboratory of Foundry, Badji Mokhtar University, Annaba, B. O., 12 CP 23000, Algeria;
3. Mater Sciences Department, ABBES Laghrour-University, Khenchela, P. O. 1252, 40004, Algeria;
4. Laboratoire de Mise en forme des Materiaux Metalliques (LMF2M), Universite Badji—Mokhtar, B. P. 12, 23000 Annaba, Algeria;
5. Mechanical Engineering Department, King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals, Box 1180, Dhahran 31261, KSA;
6. Department of Environmental Engineering, College of Chemistry and Environmental Engineering, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen 518055, China;
7. Arts et Metiers ParisTech, MSMP, 8, Boulevard Louis XIV, 59046 Lille Cedex, France;
8. Department of Physical Metallurgy and Materials Technology, Brandenburg Technical University, 03046 Cottbus, Germany
Received 18 January 2019; accepted 23 September 2019
Abstract: The effect of sintering temperature (1073-1373 K) on the structural and tribological properties of nanostructured ball- milled β-type Ti-15Mo samples was investigated. The prepared samples were characterized using various apperatus such as X-ray diffractometer, scanning electron microscope (SEM) and ball-on-plate type oscillating tribometer. Wear tests were conducted under different applied loads (2, 8 and 16 N). Structural results showed that the mean pore and crystallite size continuously decreased with increasing sintering temperature to reach the lowest values of 4 nm and 29 nm at 1373 K, respectively. The relative density of the sintered sample at 1373 K was as high as 97.0%. Moreover, a higher sintering temperature resulted in higher relative density, greater hardness and elastic modulus of the sample. It was observed that both the friction coefficient and wear rate were lower in the sample sintered at 1373 K which was attributed to the closed porosity.
Key words: Ti-15Mo; wear; tribological behaviour; nanotribology; sintering; biomedical applications
1 Introduction
Cobalt-chromium alloys, stainless steel, and titanium alloys are the most important biomaterial alloys with better performance for biomedical applications [1,2]. However, among these biomaterials, titanium alloys are usually employed in the area of orthopaedics, due to their low density, good corrosion resistance, high capacity to attach to tissue and bone, biocompatibility, high hardness and low elastic modulus (50-10 GPa) as compared to stainless steel (200 GPa) or cobalt alloys (235 GPa) [3], making them a good choice as a biomaterial for orthopaedic applications especially for total hip prosthesis use [1,2].
For this application, low elastic modulus is desired to reduce the stress-shielding phenomenon that occurs at the bone-implant interface. This phenomenon is associated with bone atrophy, which is the weakness at the interface between host tissue and implant, eventually leading to a premature rejection of the implant [2].
Nowadays, most of the studies on metallic biomaterials for load-bearing implants have focused on the β-Ti alloys due to their high specific strength, excellent corrosion resistance and good biocompatibility. Non-toxic β-stabilizers such as Mo, Sn, Ta, Nb and Zr are mainly used as alloying elements to achieve new β-type titanium alloys with low elastic modulus [3], including Ti-15Mo (wt.%), Ti-11.5Mo-6Zr-2Fe (wt.%), Ti-24Nb-4Zr-7.8Sn (wt.%) and Ti-36Nb-2Ta-3Zr (wt.%) [4]. Among the alloying elements, niobium is considered to have a good resistance against corrosion and an excellent biocompatibility [5,6]. While the use of molybdenum is rather debatable [7], some researchers have employed molybdenum as an alloying element for titanium alloys such as Ti-Mo-Zr-Fe, Ti-Mo-Ta and Ti-Mo [8-10]. It is well known that the high temperature β-phase Ti has a bcc structure, while the α-phase has a hexagonal compact (hc)-structure which provides β-alloys with a higher wear resistance. The addition of molybdenum gives β-stabilizing properties to titanium alloys. Hence, it is favourable to produce β-alloys with molybdenum as compared to other alloying elements such as Ta, Zr or Nb [11-13]. It has been reported that the elastic modulus, hardness and phase compositions vary for Ti-Mo samples as a function of Mo content [14-16]. The mechanical properties of β-type Ti-Mo alloys depend directly on the processing routes and the alloying elements [17-20]. Therefore, it is necessary to conduct a comprehensive study that will allow rapid characterization and production of an alloy with a variable composition [19,20].
Due to its importance in the performance of the total hip prosthesis, the problems of friction and wear in these devices have been addressed by many authors [2,8-12]. For this, a wide variety of studies have been reported to enhance wear resistance of metallic biomaterials which may affect corrosion of biomaterials [2,8,9,19]. In the human body, these alloys are exposed to physiological solutions that induce damage material by corrosion. Additionally, the tribological contacts created due to the movement, contribute to the acceleration of the passive film destruction and the material degradation, which is a significant clinical problem [21,22].
Moreover, the benefit of nanocrystalline titanium alloy for improved tribological properties has not been demonstrated unequivocally [23-26]. Therefore, the tribological behaviour of Ti-15Mo sample produced from mechanically milled powders and sintering, need to be investigated [16]. The correlation among composition, sintering temperature, microstructural features, and tribological properties of β-Ti alloys is of primary significance for orthopaedic applications. However, in the case of Ti-15Mo sample biomaterials, this correlation has not been well investigated.
Thus, this work aims to investigate the effect of sintering temperature on the porosity, density, elastic modulus, microhardness, microstructure, lattice parameters, and wear resistance of Ti-15Mo samples and investigate the possibility of using the developed nanostructured Ti-15Mo samples as a biomaterial.
2 Experimental
2.1 Sample preparation
Metal powder (Fig. 1) of Ti and Mo (purity >99.9%, particle size <110 μm) supplied by SIGMA-Aldrich Society, Germany, was used to produce β-type Ti-15Mo sample. The powder was milled for 64.8 ks to obtain uniform properties, based on our previous studies [2,9,13,26] using a high energy ball mill, Fritsch P7. The milled powders were pressed uniaxially at 2.5×108 Pa into circular discs (d=20 mm) by a rigid steel die. Aiming to obtain a high density, the uniaxially- pressed samples were subsequently hot isostatically pressed (HIPed) at 1273 K and at an isostatic pressure of 400 MPa for 1800 s using ASEA-HIP [2,9,13,26,27]. The HIPed samples were then sintered in a vacuum furnace at 4×10-12 MPa for 18 ks at sintering temperatures ranging from 1073 to 1373 K at a heating rate of 5 K/s.
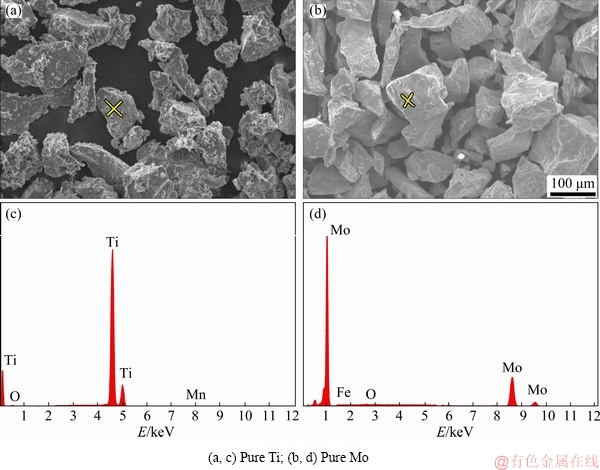
Fig. 1 SEM micrographs (a, b) of as-received powders and their EDS results (c, d)
2.2 Sample characterization
The crystal structures and phase identification of the Ti-15Mo alloy samples were determined by X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis with Cu Kα radiation (λCu=0.15406 nm) operating at 40 kV and 40 mA passing through a nickel filter, using a Bragg-Brentano diffractometer with step size of 0.01 (°)/s. Williamson- Hall equation was used to evaluate the grain size of the sample [26]. Additionally, crystallite size was estimated and was confirmed using XRD analysis via Scherrer’s formula [28].
The lattice parameters were calculated from the low 2θ angles position of their particular diffraction peaks using Bragg’s equation [28,29]. The elastic modulus and Vickers hardness were evaluated under an applied load of 2 N using a universal hardness testing machine (Zwik ZHV2.5) with a Vickers diamond indenter.
HIPed and sintered Ti-15Mo samples were cut into disc specimens (d20 mm × 6 mm) and polished according to ISO 7206–2:2011 standards to a surface roughness Ra of 4.0-6.0 nm. The surface roughness was measured using VEECO-Wyko NT9300 Optical Profiler. The tribological tests were conducted using a ball-on- plate type oscillating tribometer (Tribotester) in accordance with the ASTM G133-95, ISO 7148-1:2012 and ASTMG 99 [25,26] standards under wet conditions using a prepared Hank’s solution, simulating the body fluid (Fig. 2). The chemical composition of Hank’s solution was as follows: NaCl 8 g/L, KCl 0.4 g/L, CaCl2 0.14 g/L, NaHCO3 0.35 g/L, MgSO4·7H2O 0.1 g/L), MgCl2·6H2O 0.1 g/L, MgCl2·6H2O 0.1 g/L, Na2HPO4· 2H2O 0.16 g/L, KH2PO4 0.06 g/L. The tests were carried out under different normal loads of 2, 8 and 16 N at a sliding speed of 10 mm/s with an alumina ball (Al2O3), 6 mm in diameter as a counterface.
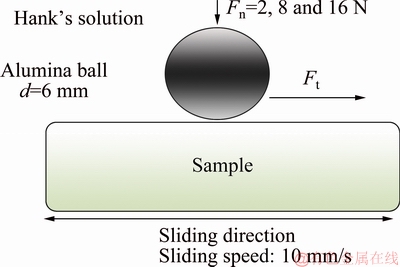
Fig. 2 Pressing of hard bill (counter face) on disks sample
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Structural characterization
The X-ray diffraction spectra of milled and HIPed binary Ti-15Mo samples are presented in Fig. 3. The obtained results show that the phase composition of the Ti-15Mo samples correlates to the sintering temperature. The formation of β phase was observed at all sintering temperatures. Similar results were reported previously by SOCHACKA et al [16], when at least 9 wt.% molybdenum was added to the binary Ti-Mo system. The diffractograms corresponding to the lattice planes for β-bcc phase (220), (110), (101), (110), (004), (022), (110), (221), (011) and (220) were produced in the spectrum [30]. After sintering at 1373 K, most of the peaks disappeared and only the peaks corresponding to (110) and (001) planes were observed. The peaks that corresponded to (211) at 2θ=62.2° and 78.1° disappeared after sintering at a temperature of 1173 K, while peaks corresponding to (101) and (004) planes at 2θ=38.1° and 45.4°, respectively, disappeared at sintering temperature of 1273 K.
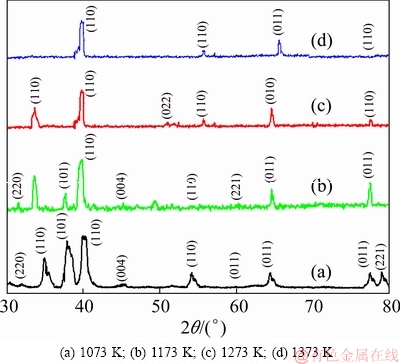
Fig. 3 X-ray diffraction patterns of Ti-15Mo samples sintered at different temperatures
The average crystallite size, as shown in Fig. 4, slowly decreased with increasing sintering temperature, which was also accompanied by an increase in the average strain ε [31]. The crystallite size of HIPed samples sintered at 1073 K was 36 nm, afterwards, it was reduced to 31 nm at 1273 K and it reached the lowest value of 29.4 nm for samples sintered at 1373 K. Similar dependency was reported by WU et al [32]. The mean internal strain values increased from 0.15% to 0.75% with an increase in the sintering temperature from 1073 to 1373 K. The above observations and results can be attributed to the refinement of particle size, up to the nanosized scale followed by an increase in the micro strains induced at the internal level.
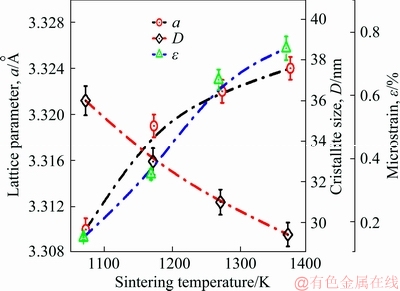
Fig. 4 Evolution of lattice parameters a, average crystallite size D, and internal microstrain ε of sintered Ti-15Mo samples
The β-phase lattice parameter was extracted from 2θ position of their particular diffraction β-bcc peaks (110). This peak represents the strongest diffraction peak for β-phase and it provides appropriate measurements of the lattice parameter for all the sintering temperatures.
As shown in Fig. 4, the lattice parameter a increases with increasing sintering temperature, from 3.313 to 3.324 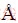 at a sintering temperature of 1073 K and 1373 K, respectively. It is important to mention that only the β-phase was observed with an extension of 1.7% in cell volume. This expansion is translated on XRD patterns (Fig. 3) by a shift of the peaks to smaller 2θ angles [33]. However, heat treatment temperature can cause peak expansion which is an indication of fine crystallite size [34]. The variation of lattice parameter a of Ti-15Mo samples corresponds to the bcc structure as previously reported elsewhere [35-37].
at a sintering temperature of 1073 K and 1373 K, respectively. It is important to mention that only the β-phase was observed with an extension of 1.7% in cell volume. This expansion is translated on XRD patterns (Fig. 3) by a shift of the peaks to smaller 2θ angles [33]. However, heat treatment temperature can cause peak expansion which is an indication of fine crystallite size [34]. The variation of lattice parameter a of Ti-15Mo samples corresponds to the bcc structure as previously reported elsewhere [35-37].
3.2 Samples porosity
Figure 5 shows the pore size distribution of binary Ti-15Mo samples. It was found that with increasing the sintering temperature, the pore size increased gradually and is distributed irregularly. It mainly consists of (1) pores of several nanometer size, which presumably resulted from the volume reduction, occurring during the sintering process, and (2) pores of size of dozen nanometers. Increasing the sintering temperature promotes a decrease in the size of the porosity. At 1073 and 1173 K, the sintered samples had a 70% of porosity more than 70 nm and 30% of porosity less than 70 nm, while the samples sintered at 1273 and 1373 K had a 95% of porosity less than 70 nm which is promising for biomedical applications [38].
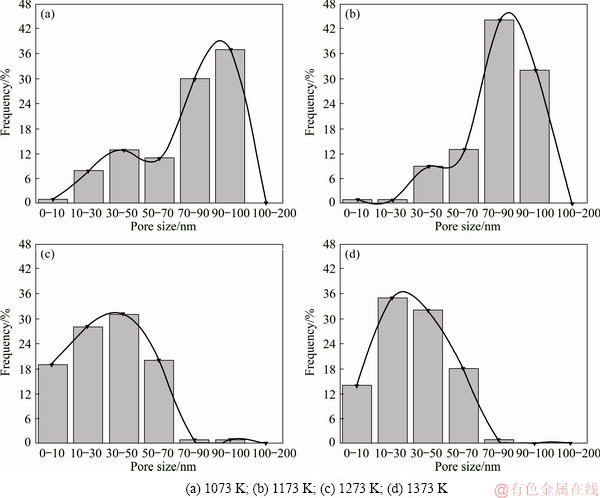
Fig. 5 Pore size distribution of Ti-15Mo samples sintered at different temperatures
In addition, as shown in Fig. 6, the porosity decreased from 0.13% to 0.12%, 0.07% and 0.05%, and the mean porosity size reduced from 45 to 41, 39 and 29 nm, at sintering temperatures of 1073, 1173, 1273 and 1373 K, respectively.
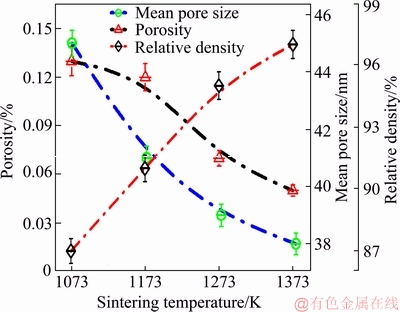
Fig. 6 Evolution of porosity, mean pore size and relative density of sintered Ti-15Mo samples
It has been reported that porous structures can facilitate the growth of cells while also providing nutrient transportation and body fluid pathways which is useful for osseointergeation of the implant, growth and bone regeneration [39,40]. This is beneficial for the growth of the bone and results in stiffness reduction which helps the prevention of stress-shielding phenomenon, which is common in implants and often leads to implantation failure. Finally, it could be concluded that the porous Ti-15Mo samples sintered at different temperatures exhibited a suitable porous structure for bone implantation.
The relative density of binary Ti-15Mo sample (Fig. 6) increased with sintering temperature. Samples sintered at 1373 K showed higher density (97%) than the samples sintered at 1073, 1173 and 1273 K that exhibited density values of 87%, 91% and 95%, respectively.
3.3 Microhardness and elastic modulus
The microhardness HV0.02 gradually increased with increasing sintering temperature (Fig. 7). The highest values of 315 and 307 HV0.02 were achieved for samples sintered at 1373 and 1273 K, respectively, while the lowest values of 275 and 296 HV0.02, were measured for samples sintered at 1073 and 1173 K, respectively.
The values of elastic modulus of 75, 80, 92 and 95 GPa were found for samples sintered at 1073, 1173, 1273 and 1373 K, respectively. As mentioned previously, samples sintered at 1073 K (75 GPa) and 1173 K (80 GPa) exhibited low density and high porosity. High values were attributed to a closed porosity and high compact density, which influenced the values of elastic modulus (Fig. 7). It is also to be noted that the closed porosity in the samples as a result of the milling and the HIPed process resulted in the high compact density which in turn led to a significant improvement in the microhardness.
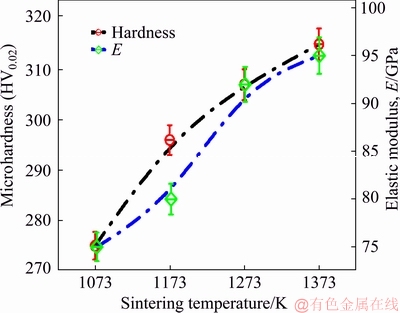
Fig. 7 Hardness and elastic modulus of sintered Ti-15Mo samples
3.4 Friction coefficient
The variation of friction coefficient of nanosized Ti-15Mo samples is displayed in Figs. 8 and 9. As it can be seen from Fig. 8, all samples showed a similar frictional behaviour. At an advanced stage, the friction coefficient achieved a steady state maybe due to the smoothening out of the tracks [2,3,7,19]. Within the first few sliding metres, the specimens sintered at 1073 and 1173 K had higher friction coefficient with considerable fluctuations as compared to that of the specimens sintered at 1273 and 1373 K. In addition, with increasing elastic modulus and hardness as a function of sintering temperature, the contact area decreased resulting in a reduction of the friction coefficient.

Fig. 8 Evolution of friction coefficients of sintered Ti-15Mo samples versus sliding distance at applied load of 8 N
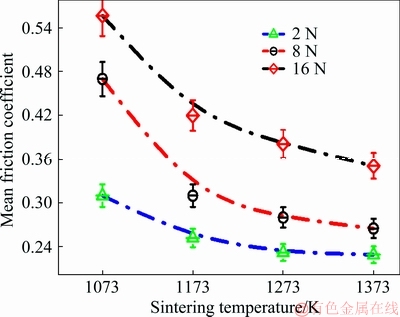
Fig. 9 Mean friction coefficients of sintered Ti-15Mo samples under different applied loads
The average mean values of the friction coefficient throughout the test, as shown in Fig. 9 ranged 0.31-0.56, 0.25-0.42, 0.23-0.38 and 023-0.35 for samples sintered at 1073, 1173, 1273 and 1373 K, respectively. According to this result, the friction resistance improved with increasing sintering temperature due to the closed porosity and grain size refinement. However, considering the implants applications, all tested Ti-15Mo samples, may be the ultimate choice for orthopeadic implants, with relatively low elastic modulus and without toxic alloying elements and low friction coefficient as reported by GEETHA et al [3].
3.5 Wear volume and wear rate
As indicated in Fig. 10(a), the wear volume of the sintered Ti-15Mo decreased with increasing of sintering temperature. The wear volume varied from 17.76×107 to 46×107, from 14.08×107 to 43×107, from 11.87×107 to 37×107 and from 9.23×107 to 34×107 μm3 for samples sintered at 1073, 1173, 1273 and 1373 K, respectively. Furthermore, the wear rate of sintered Ti-15Mo decreased with increasing sintering temperature (Fig. 10(b)). The specific wear rate ranged from 7.565×10-3 to 20.09×10-3, from 6.23×10-3 to 17.95×10-3, from 4.13×10-3 to 14.50×10-3, and from 2.14×10-3 to 11.90×10-3 μm3/(N·μm) for samples sintered at 1073, 1173, 1273 and 1373 K, respectively. On the other hand, the calculated wear rates of the counterface alumina ball were (4.44-16.90)×10-3 and (4.33- 13.450)×10-3 μm3/(N·μm), in the case of samples sintered at 1273 and 1373 K, respectively.
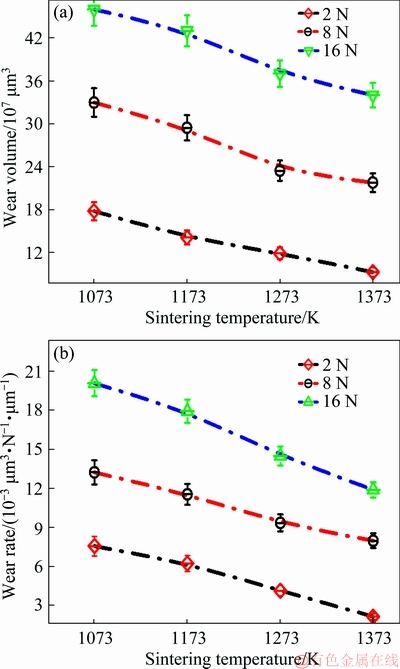
Fig. 10 Evolution of wear volume (a) and wear rate (b) of sintered Ti-15Mo samples under different applied normal loads
The above results suggest that the sliding friction and wear behavior of Ti-15Mo samples not only depend on the sintering temperature, but also depend on the microstructure, and the experimental paramaters such as applied load, sliding speed, testing environment, and friction couple.
As shown in Figs. 8-10, the specimens sintered at 1373 K exhibited a high wear resistance and good tribological properties. This behaviour of sintered binary Ti-15Mo samples (especially those sintered at 1373 K) can be attributed to the enhanced mechanical properties due to closed porosity and grain size refinnement.
3.6 Wear scars morphology
Figure 11 illustrates SEM micrographs of worn surface on sintered Ti-15Mo samples, after 1600 cycles of sliding. For specimens sintered at 1073 and 1173 K, abrasion was the main wear mechanism, while at sintering temperatures of 1273 and 1373 K, adhesion was found to be the main wear mechanism.
For sample sintered at 1073 K (Fig. 11(a)), the wear traks consisted of deep grooves produced by plowing or micro cutting from hard asperities or due to the adherent transfer deposits on the counterface. All tested spicemens presented a similair wear mechanism. Irregular areas and a non-homogeneous wear suggestively caused by the movement of abrasive debris particles from the inside to the sides of wear track were detected in the case of the alumina ball counter face [25,26]. In particular, this phenomenon was predominantly observed for sample sintered at 1373 K.
For the samples sintered at 1273 K, it was difficult to identify the friction mechanism. The wear did not follow a conventional outline as in the case of 1073 and 1173 K. Samples sintered at 1273 K (Fig. 11(c)), displayed parallel grooves running along the sliding direction which were covered by wear debris.
The samlple sintered at 1273 K performed as a repellant to the failure mechanisms of traditional sliding wear, resulting in small areas of wear that are isolated and irregularly shaped [41]. Noise and vibration were not apparent.
Samples sintered at 1373 K displayed the lowest wear, as shown in Fig. 9. The low friction coefficient (0.23-0.35) (Fig. 9), high density and microhardness (Fig. 7) are the most important parameters that lead to high wear resistance. The morphology of wear scars showed detachment of the particles. Nevertheless, there was no significant difference in wear morphology of samples sintered at 1273 and 1373 K. In most cases, samples sintered at 1373 K exhibited good wear performance. In addition, the worn surfaces were protected by compressed wear debris forming a smooth transfer film, showing very few marks on the samples, as can be seen from Figs. 11(c, d).
An increase in the friction coefficient or a decrease in wear resistance can cause implant loosening [42]. Wear also affects corrosion as follows: (1) passive film removal by tribological action [42], (2) work hardening and higher surface energy production [42,43], and (3) roughness increase which results in a greater surface area exposed to the corrosive medium and an increase in pit stability [43]. Moreover, the generated wear debris can cause a destructive inflammation to the bone supporting the implant [42].
The wear on the alumina counterface ball, as visually inspected, was greater than the wear of the samples sintered at 1273 and 1373 K, signifying the good wear resistance of these samples, which may be attributed to the better compaction of the transfer layer [44,45]. At the same time, the extent of coverage of the transfer layer also increased, resulting in reducing friction and wear rate, which has been confirmed in earlier studies [46,47].
Figure 12 presents SEM micrographs of samples sintered at 1373 K tested at different normal loads of 2, 8 and 16 N, respectively. A moderately rough wear track was observed (Figs. 12(a, a′)). There were small cracks indicating a mild fracture for the samples tested at 8 N (Figs. 12(b, b′)). A significant surface damage with deformed appearance was observed for sample tested at 16 N (Figs. 12(c, c′)). At higher applied loads, a significant build-up of material around the wear track and some fine particles were also observed.
It is important to point out that the microstructure, grain size and porosity of sintered samples have a significant influence on the hardness, elatic modulus, friction and wear volume of the binary Ti-15Mo sample [35-37]. As expected, in the present study, the binary Ti-15Mo sample with the smallest grain size showed the lowest wear rate which was obtained for the samples sintered at 1373 K leading to its closed porosity and higher density as compared to the un-sintered samples and samples sintered at lower temperatures.
3.7 Wear debris morphology
Samples sintered at 1073 and 1273 K displayed larger chip-like metallic and fine wear particles (Figs. 13(a, b)). Similar features were observed for sample sintered at 1373 K, but the particle size was much smaller. Some larger agglomerates of debris particles generated from the transfer layer could also be observed (Fig. 13(c)). Wear debris were suggestively generated by metal transfer, delamination mechanism, or by the asperities ploughing [48].
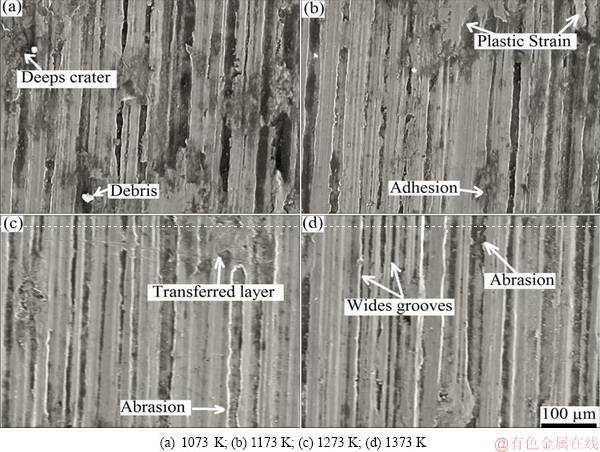

Fig. 11 SEM micrographs of worn surface on Ti-15Mo samples sintered at different temperatures (tested at 8 N)
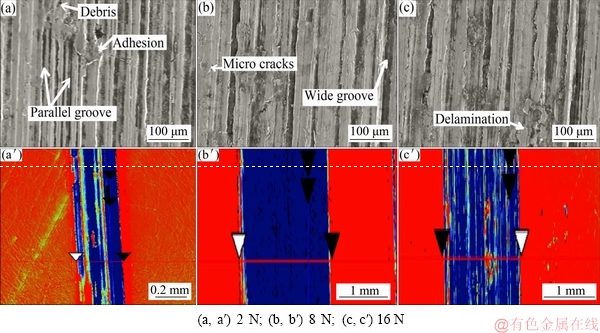
Fig. 12 SEM micrographs of Ti-15Mo sample sintered at 1373 K tested under different applied loads
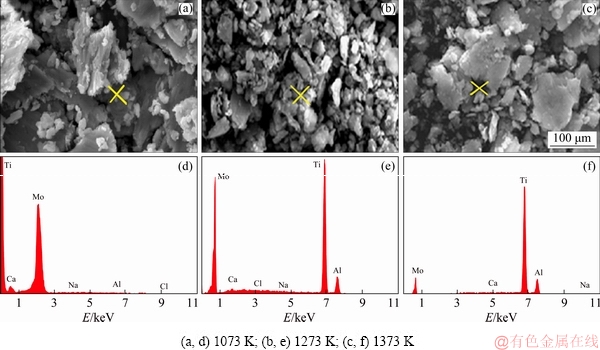
Fig. 13 SEM morphologies (a-c) and corresponding EDS results (d-f) of wear debris of Ti-15Mo samples sintered at different temperatures tested under 8 N
A poor wear resistance of many biomaterials results in debris generation which is harmful for the human body as they may be soluble in blood or particulate debris accumulation, leading to serious inflammatory reactions, allergies or osteolysis, carcinogenetic response and toxicity which can considerably shorten its life-span [49,50]. For example, non-compatible metallic ions like V, Al, Co, Cr, Ni and Fe lead to toxic reactions with adverse effects such as damage of protein, lipids or DNA (with increased Fe content); alteration of sugar levels in the blood (with increased Cr content); toxicity reactions after 4-5 years (with increased Ni or Co content) [51,52]. Therefore, it is of great significance to study the wear behavior of biomaterials.
The sizes of wear debris collected from samples sintered at 1373 K were small and mostly grainy-shaped. However, large flaky-type debris was collected for samples sintered at 1173 K. The oxide layer initially formed may have been removed by the abrasive effect in the form of small particles. The EDS analysis showed peaks of elements such as Ti and Mo belonging to the sintered samples, peaks of Na, Ca and Cl elements coming from simulated body fluid solution, while peaks of Al come from counter face of alumina ball.
It could be concluded that the structural analysis, mechanical properties and tribological properties of the investigated samples at different sintering temperatures showed enhanced properties as compared to wrought Ti-15Mo sample for surgical implant application in accordance with the ASTM F 2006-8 standard for this alloy [53].
4 Conclusions
(1) Sintering of milled and HIPed binary Ti-15Mo samples at 1373 K significantly enhanced the elastic modulus, microhardness, tribological properies due to the high relative density, closed porosity and grain size refinement.
(2) At 1373 K, the binary Ti-15Mo samples showed the lowest friction coefficient and wear rate as compared to samples sintered at lower sintering temperature (1073 and 1173 K).
(3) The closed porosity, the increased relative density and sintering temperature played a significant role in controlling the wear rate.
(4) The higher wear resistance of samples sintered at 1373 K was atributed to their ennhanced structural and mechanical properties.
(5) The pre-dominant frictional and wear mechanisms of sintered binary Ti-15Mo samples were found to be delamination defect, abrasion and adhesion.
References
[1] SONG Jie, WANG Li-ming, ZHANG Xiao-ning, SUN Xiao-gang, JIANG Hong, FAN Zhi-guo, XIE Chao-ying, WU M H. Effects of second phases on mechanical properties and martensitic transformations of ECAPed TiNi and Ti-Mo based shape memory alloys [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2012, 22: 1839-1848.
[2] FELLAH M, LABAIZ M, ASSALA O, DEKHIL L, IOST A. Tribological behavior of AISI 316L stainless steel for biomedical applications [J]. Tribology-Materials, Surfaces & Interfaces, 2013, 7(3): 135-149.
[3] GEETHA M, SINGH A K, ASOKAMANI R, GOGIA A K. Ti based biomaterials, the ultimate choice for orthopaedic implants—A review [J]. Progress in Materials Science, 2009, 54(3): 397-425.
[4] ZHANG Ling-bo, WANG Ke-zheng, XU Li-juan, XIAO Shu-long, CHEN Yu-yong. Effect of Nb addition on microstructure, mechanical properties and castability of β type Ti-Mo alloys [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2015, 25: 2214-2220.
[5] HE Tan, HU Rui, ZHANG Tie-bang, LI Jin-shan. Effect of Nb content on solidification characteristics and microsegregation in cast Ti-48Al-xNb alloys [J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica (English Letters), 2016, 29(8): 714-721.
[6] YANG Dong-hua, GUO Zhi-meng, SHAO Hui-ping, LIU Xiao-ting, JI Ye. Mechanical properties of porous Ti-Mo and Ti-Nb alloys for biomedical application by gel casting [J]. Procedia Engineering, 2012, 36: 160-167.
[7] EISENBARTH E, VELTEN D, MüLLER M, THULL R, BREME J. Biocompatibility of beta-stabilizing elements of titanium alloys [J]. Biomaterials, 2004, 25: 5705-5713.
[8] XU Li-juan, XIAO Shu-long, TIAN Jing, CHEN Yu-yong. Microstructure, mechanical properties and dry wear resistance of β-type Ti-15Mo-xNb alloys for biomedical applications [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2013, 23: 692-698.
[9] FELLAH M, HEZIL N, ABDUL SAMAD M, TOUHAMI M Z, MONTAGNE A, IOST A, MEJIAS A, KOSSMAN S. The effect of milling time on structural, friction and wear behavior of hot isostatically pressed Ti–Ni alloys for orthopedic applications [C]// TMS 2019 148th Annual Meeting & Exhibition Supplemental Proceedings. The Minerals, Metals & Materials Series. Springer, Cham, 2019.
[10] JUNIOR M, SEVERINO J R, NOGUERA R A, de ARAUJO R O, DONATO T A G, ARANA-CHAVEZ V E, CLARO A P R A, MORAES J C S, BUZALAF M A R, GRANDINI C R. Preparation and characterization of Ti-15Mo alloy used as biomaterial [J]. Materials Research, 2011, 14: 107-112.
[11] LIN Dan-Jae, CHUANG Cheng-Chung, LIN Jiin-Huey Chern, LEE Jing-Wei, JU Chien-Ping, YIN Hsiang-Shu. Bone formation at the surface of low modulus Ti-7.5Mo implants in rabbit femur [J]. Biomaterials, 2007, 28: 2582-2589.
[12] YAO Qiang, SUN Jian, XING Hui, GUO Wen-yuan. Influence of Nb and Mo contents on phase stability and elastic property of β-type Ti-X alloys [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2007, 17: 1417-1421.
[13] HEZIL N, FELLAH M. Synthesis, structural and mechanical properties of nanobioceramic (α-Al2O3) [J]. Journal of the Australian Ceramic Society, 2019, https://doi.org/10.1007/s41779-019-00333- 7.
[14] ZHOU Ying-long, LUO Dong-mei. Microstructure and mechanical properties of Ti-Mo alloys cold rolled and heat treated [J]. Materials Characterization, 2011, 62(10): 931-937.
[15] ZHAO Xing-feng, NIINOMI M, NAKAI M, HIEDA J. Beta type Ti-Mo alloys with changeable Young’s modulus for spinal fixation applications [J]. Acta Biomaterialia, 2012, 8(5): 1990-1997.
[16] SOCHACKA P, MIKLASZEWSKI A, JURCZYK M. Development of β-type Ti-x at. % Mo alloys by mechanical alloying and powder metallurgy: Phase evolution and mechanical properties (10≤x≤35) [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2019, 776: 370-378.
[17] GABRIEL S B, PANAINO J V P, SANTOS I D, ARAUJO L S, MEI P R, de ALMEIDA L H, NUNES C A. Characterization of a new beta titanium alloy, Ti-12Mo-3Nb, for biomedical applications [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2012, 536(S): s208-s210.
[18] CHEN Yu-yong, XU Li-juan, LIU Zhi-guang, KONG Fan-tao, CHEN Zi-yong. Microstructure and properties of titanium alloys Ti-Mo for dental use [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2006, 16(S): s824-s828.
[19] FELLAH M, AISSANI L, IOST A, ZAIRI A, MONTAGNE A, MEJIAS A. Wear and friction behavior of two AISI 316L and Ti6Al7Nb in total hip arthrosis [J]. Materiaux & Techniques, 2018, 106(4): 402. https://doi.org/10.1051/mattech/2018051. (in German)
[20] XU Li-juan, XIAO Shu-long, TIAN Jing, CHEN Yu-yong, HUANG Yu-dong. Microstructure and dry wear properties of Ti-Nb alloys for dental prostheses [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2009, 19(S3): s639-s644.
[21] DIOMIDIS N, MISCHLER S, MORE N S, ROY M. Tribo-electrochemical characterization of metallic biomaterials for total joint replacement [J]. Acta Biomaterialia, 2012, 8(2): 852-859.
[22] RUNA M J, MATHEW M T, ROCHA L A. Tribocorrosion response of the Ti6Al4V alloys commonly used in femoral stems [J]. Tribology International, 2013, 68: 85-93.
[23] GENG Guo-sheng, XU Jiu-hua. Surface integrity and fatigue property of a high speed milled titanium alloy [J]. Advanced Materials Research, 2008, 53-54: 305-310.
[24] WANG Xiao-peng, XU Li-juan, CHEN Yu-yong, KEE Do-Woo, XIAO Shu-long, KONG Fan-tao, LIU Zhi-guang. Effect of milling time on microstructure of Ti35Nb2.5Sn/10HA biocomposite fabricated by powder metallurgy and sintering [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2012, 22: 608-612.
[25] FELLAH M, LABAIZ M, ASSALA O, DEKHIL L, IOST A. Friction and wear behavior of Ti-6Al-7Nb biomaterial alloy [J]. Journal of Biomaterial and Nanobiotechnology, 2013, 4(4): 374-384.
[26] FELLAH M, AISSANI L, ABDUL SAMAD M, MONTAGNE A. Effect of replacing vanadium by nobium and iron on the tribological behavior of HIPed titanium alloys [J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica (English Letters), 2017, 30(11): 1089-1099.
[27] FELLAH M, LABAIZ M, ASSALA O, ABDUL SAMAD M, IOST A, SASSANE N. Experimental study of new titanium alloy Ti-6Al-4Fe for biomedical application [C]//Proceeding of ICM'2015. Universite des Frères Mentouri Constantine, Algerie, 2015.
[28] XU Wen-chen, HUANG Kai, WU Shi-feng, ZONG Ying-ying, SHAN De-bin. Influence of Mo content on microstructure and mechanical properties of β-containing TiAl alloy [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2017, 27: 820-828.
[29] IBRAHIM A, ABDEL HAMID Z, ABDEL AAL A. Investigation of nanostructured and conventional alumina-titania coatings prepared by air plasma spray process [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2010, 527: 663-668.
[30] RAZAVI M, RAHIMIPOUR M R, RAJABI-ZAMANI A H. Synthesis of nano crystalline TiC powder from impure Ti chips via mechanical alloying [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2007, 436: 142-145.
[31] KOMIYAMA S, SUTOU Y, OIKAWA K, KOIKE J, WANG M, SAKURAI M. Wear and oxidation behavior of reactive sputtered δ-(Ti, Mo)N films deposited at different nitrogen gas flow rates [J]. Tribology International, 2015, 87: 32-39.
[32] WU Jie, GUO Rui-peng, XU Lei, LU Zheng-guan, CUI Yu-you, YANG Rui. Effect of hot isostatic pressing loading route on microstructure and mechanical properties of powder metallurgy Ti2AlNb alloys [J]. Journal of Materials Science and Technology, 2017, 33(2): 172-178.
[33] GUO Rui-peng, XU Lei, ZONG Bernie Ya-Ping, YANG Rui. Characterization of prealloyed Ti–6Al–4V powders from EIGA and PREP process and mechanical properties of HIPed powder compacts [J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica (English Letters), 2017, 30(8): 735-744.
[34] MARECI D, SUTIMAN D, CAILEAN A, CRETESCU I. Effect of vanadium replacement by zirconium on the electrochemical behavior of Ti6Al4V alloy in ringer’s solution [J]. Environmental Engineering and Management Journal, 2008, 7(6): 701-706.
[35] FLAVIA F C, PETERSON L F, EDERSN L, ALESSANDRA C, RUBENS C. Ti-Mo alloys employed as biomaterials: Effects of composition and aging heat treatment on microstructure and mechanical behavior [J]. Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials, 2014, 32: 31-38.
[36] ZHANG Wei-dong, LIU Yong, WU Hong, SONG Min, ZHANG Tuo-yang, YAO Tian-hang. Elastic modulus of phases in Ti-Mo alloys [J]. Materials Characterization, 2015, 106: 302-307.
[37] OLIVEIRA N T C, ALEIXO G, CARAM R, GUASTALDI A C. Development of Ti-Mo all for biomedical applications: Microstructure and electrochemical characterization [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2007, 452-453: 727-731.
[38] LI Yong-hua, CHEN Rui-bo, QI Guang-xia, WANG Zhong-tang, DENG Zi-yu. Powder sintering of porous Ti-15Mo alloy from TiH2 and Mo powders [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2009, 485: 215-218.
[39] GAO Zhi-fang, LI Qun-yin, HE Fang, HUANG Yuan, WAN Yi-zao. Mechanical modulation and bioactive surface modification of porous Ti-10Mo alloy for bone implants [J]. Materials and Design, 2012, 42: 13-20.
[40] MARECI D, CHELARIU R, BOLAT G, CAILEAN A, GRANCEA V, SUTIMAN D. Electrochemical behaviour of Ti alloys containing Mo and Ta as β-stabilizer elements for dental application [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2013, 23: 3829-3836.
[41] FELLAH M, ASSALA O, LABAIZ M. Comparative study on tribiological behavior of Ti-6Al-7Nb and SS AISI 316L alloys, for Total hip prosthesis [C]//TMS 2014 143rd Annual Meeting & Exhibition Supplemental Proceedings. The Minerals, Metals & Materials Series. Springer, Cham, 2014: 237-246.
[42] ABDURABO HUSSEIN M, ABDUL SAMAD M, AL-AQEELI N. Wear characteristics of metallic biomaterials: A Review [J]. Materials, 2015, 8(5): 2749-2768.
[43] ARSLAN E, TOTIK Y, DEMIRCI S E E, ALSARAN A. Influence of surface roughness on corrosion and tribological behavior of CP-Ti after thermal oxidation treatment [J]. Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 2010, 19: 428-433.
[44] GHADIMI M, SHOKUHFAR A. Effects of mechanical alloying on microstructure and microhardness of nanocrystalline NiTi shape memory alloy [J]. International Journal of Advanced Design and Manufacturing Technology, 2013, 5(5): 25-29.
[45] FELLAH M, AISSANI L, ABDUL SAMAD M, PRAKASAM M, PURNAMA A, MONTAGNE A, IOST A, MEJIAS M. Effect of calcination temperature on friction and wear behavior of α–Alumina (α-Al2O3) for biomedical applications [J]. International Journal of Applied Ceramic Technology, 2019, 16(2): 462-470.
[46] FELLAH M, LABAIZ M, ASSALA O, DEKHIL L, TALEB A, REZAG H, IOST A. Tribological behavior of Ti-6Al-4V and Ti-6Al-7Nb alloys for total hip prosthesis [J]. Advances in Tribology, 2014, 2014: 13. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/451387.
[47] FELLAH M, ABDUL SAMAD M, LABAIZ M, ASSALA O, IOST A. Sliding friction and wear performance of the nano-bioceramic α-Al2O3 prepared by high energy milling [J]. Tribology International, 2015, 91: 151-159.
[48] FELLAH M, AISSANI L, ABDUL SAMAD M, PURNAMA A, DJBAILI H, MONTAGNE A, IOST A, NOUVEAU C. Effect of Zr content on friction and wear behavior of Cr-Zr-N coating system [J]. International Journal of Applied Ceramic Technology, 2018, 15(3): 701-715.
[49] KUNCICKA L, KOCICH R, LOWE T C. Advances in metals and alloys for joint replacement [J]. Progress in Materials Science, 2017, 88: 232-280.
[50] HO W F, JU Chien-Ping, LIN J H Chern. Structure and properties of cast binary Ti-Mo alloys [J]. Biomaterials, 1999, 20: 2115-2122.
[51] ASRI R I M, HARUN W S W, SAMYKANO M, LAH N A C, GHANI S A C, TARLOCHAN F, RAZA M R. Corrosion and surface modification on biocompatible metals: A review [J]. Materials Science and Engineering C, 2017, 77: 1261-1274.
[52] HE Zheng-yuan, ZHANG Lei, SHAN Wen-rui, ZHANG Yu-qin, JIANG Ye-hua, ZHOU Rong, TAN Jun. Characterizations on mechanical properties and in vitro bioactivity of biomedical Ti-Nb-Zr-CPP composites fabricated by spark plasma sintering [J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica (English Letters), 2016, 29(11): 1073-1080.
[53] ASTM. Standard specification for wrought titanium-15 molybdenum alloy for surgical implant application [S]. ASTM F 2066-08. Philadelphia (USA): ASTM, 2008.
Mamoun FELLAH1,2, Naouel HEZIL3, Dekhil LEILA4, Mohammed ABDUL SAMAD5, Ridha DJELLABI6, Stephania KOSMAN7, Alex MONTAGNE7, Alain IOST7, Aleksei OBROSOV8, Sabine WEISS8
1. Mechanical Engineering Department, ABBES Laghrour-University, Khenchela, P. O. 1252, 40004, Algeria;
2. Tribology and Materials Group, Laboratory of Foundry, Badji Mokhtar University, Annaba, B. O., 12 CP 23000, Algeria;
3. Mater Sciences Department, ABBES Laghrour-University, Khenchela, P. O. 1252, 40004, Algeria;
4. Laboratoire de Mise en forme des Materiaux Metalliques (LMF2M), Universite Badji—Mokhtar, B. P. 12, 23000 Annaba, Algeria;
5. Mechanical Engineering Department, King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals, Box 1180, Dhahran 31261, KSA;
6. Department of Environmental Engineering, College of Chemistry and Environmental Engineering, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen 518055, China;
7. Arts et Metiers ParisTech, MSMP, 8, Boulevard Louis XIV, 59046 Lille Cedex, France;
8. Department of Physical Metallurgy and Materials Technology, Brandenburg Technical University, 03046 Cottbus, Germany
摘 要:研究烧结温度(1073~1373 K)对具有纳米结构的球磨β型Ti-15Mo 合金结构和摩擦学性能的影响。通过多种技术对试样进行表征,如X射线衍射分析(XRD)、电子扫描电镜(SEM)和球-盘式往复摩擦试验机等;采用不同载荷(2、8 和16 N)进行磨损试验。结果表明,随着烧结温度的升高,合金的平均孔径和晶粒尺寸不断减小,在1373 K时分别达到最低值:4 nm和29 nm,1373 K烧结样品的相对密度高达97.0%。此外,烧结温度越高,试样的相对密度越大、硬度越高、弹性模量越高;1373 K烧结试样由于其较低的闭孔率导致摩擦因数和磨损率也较低。
关键词:Ti-15Mo;磨损;摩擦行为;纳米摩擦;烧结;生物医用
(Edited by Bing YANG)
Corresponding author: Mamoun FELLAH; Tel: +213-660-348885; E-mail: mamoun.fellah@yahoo.fr
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(19)65137-X

