网络首发时间: 2016-07-07 16:14
钙钛矿锰氧化物La1.2-xTbxSr1.8Mn2O7 (x=0, 0.05) 的磁熵变和电输运性质研究
包头师范学院内蒙古自治区高等学校磁学与磁性材料重点实验室
摘 要:
采用传统固相反应法制备钙钛矿锰氧化物La1.2-xTbxSr1.8Mn2O7 (x=0, 0.05) 多晶样品, 通过测量样品的磁化强度与温度关系曲线 (MT) 和磁化强度与外加磁场关系曲线 (M-H) 对两样品的磁熵变研究发现:在整个温度测量区间内, x=0和x=0.05两样品在高温部分均表现出顺磁性;随着温度的降低, 两样品分别在245和225 K处发生了二维短程铁磁有序转变 (TC2D) ;在120和70 K处发生了三维长程铁磁有序转变 (TC3D) ;在低温部分, 两样品均表现出团簇自旋玻璃行为。x=0样品在TC3D附近的磁相变为一级相变, x=0.05样品为二级相变, 两样品的磁熵变曲线的对称性良好, 且在外场2 T下两样品在TC3D附近出现的最大磁熵变值分别为:2.17和1.60 J· (kg·K) -1, 因此两样品有利于应用在埃里克森磁制冷循环中。此外, 通过测量零场下电阻率与温度关系曲线 (ρ-T) 对两样品的电输运性质研究发现:x=0样品和x=0.05样品分别在96和93 K处发生了绝缘-金属转变 (TP) , 对TP以上的ρ-T曲线拟合表明, 两样品在高温部分均遵循三维变程跳跃的导电方式, Tb3+离子的掺杂没有改变高温区的导电方式。
关键词:
中图分类号: O611.3
作者简介:武柯含 (1991-) , 女, 河南驻马店人, 硕士研究生, 研究方向:磁学和磁性材料, E-mail:543201748@qq.com;;鲁毅, 教授, 电话:13224855203, E-mail:yilu1958@163.com;
收稿日期:2015-09-25
基金:国家自然科学基金项目 (11164019, 51562032);内蒙古自然科学基金项目 (2011MS0101);内蒙古高校科研重点项目基金项目 (NJZZ11166, NJ10163, NJZY12202);包头重点科技发展项目 (2015Z2011) 资助;
Magnetic Entropy Change and Electrical Transport Properties of Bilayered Perovskite Manganite La1.2-xTbxSr1.8Mn2O7 (x =0, 0. 05)
Wu Kehan Wan Sulei Xu Bao Liu Shaobo Zhao Jianjun Lu Yi
Key Laboratory of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials at Universities of Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, Baotou Normal University
Abstract:
The polycrystalline samples of double-layered perovskite manganite La1.2-xTbxSr1. 8Mn2O7 (x = 0, 0. 05) were prepared by traditional solid state reaction method. The nature of magnetic phase transitions, the magnetic entropy change and possible applications in magnetic refrigeration were explored by measuring and analyzing magnetization curves M (H, T) . In the temperature range measured, the samples with x = 0 and 0. 05 showed paramagnetic behavior at high temperature. At lower temperature, the samples with x = 0 and 0. 05 formed a two-dimensional short-range order at TC2D= 245 and 225 K, and then formed an three-dimensional long-range ferromagnetic order at TC3D= 120 and 70 K, respectively; when at further lower temperature below TC3D, both samples showed cluster spin glass behavior. Near the TC3D, the sample with x = 0 exhibited the characteristic of a first-order transition and gave a maximum magnetic entropy change of 2. 17 J· (kg·K) -1under a 2 T magnetic field, while the sample with x = 0. 05 only displayed a continuous second-order transition and gave maximum magnetic entropy change of 1. 6 J· (kg·K) -1. Therefore, the two samples were beneficial to the application of Erickson magnetic refrigeration cycle. In addition, the electrical transport properties of the samples were investigated by resistivity-temperature (ρ-T) curve. The results showed that the x = 0 sample and the x = 0. 05 sample appeared an insulator-metal transition (TP) at 96 and 93 K, respectively. The fitting to ρ-T curves at temperatures above TPshowed that, the electron conducting mechanism of both samples could be attributed to three-dimensional variable-range hopping in the high temperature range.
Keyword:
perovskite; magnetic entropy change; electrical transport properties;
Received: 2015-09-25
磁制冷是以磁性材料为工质, 利用材料的磁热效应从而达到制冷目的的一种新型制冷技术, 在噪声、效率、寿命、污染等方面优于传统的制冷技术, 因而受到了人们的广泛关注[1,2,3]。双层钙钛矿锰氧化物 (R, A) 3Mn2O7 (R:稀土元素, 如La, Pr, Nd等;A:碱土元素, 如Sr, Ca等) 的结构是由一层 (R/A, O) 盐岩层和两层Mn O6八面体沿着c轴方向交叠堆积而成。这类材料由于其内在的晶格-自旋-轨道-电荷等自由度之间存在关联作用, 因而表现出了丰富的物理现象, 如庞磁电阻效应 (CMR) [4]、磁热效应 (MCE) [5]和电荷有序 (CO) [6]等。通过之前的相关文献发现, 人们已经对钙钛矿锰氧化物的磁熵变方面有所研究, 例如Wang等[7]对La0.6Pr0.1Pb0.3Mn O3样品磁熵变的研究;Zhao等[8]对La1.4Sr1.6-xCaxMn2O7 (0≤x≤1.6) 样品的结构、磁性和磁熵变的研究以及Hamad[9]对Ce0.67Sr0.33Mn O3样品的磁热效应的研究等。除此之外, 人们对Tb3+离子掺杂的钙钛矿锰氧化物的磁熵变方面也进行了研究, 例如:Chen等[10]对 (La1-xTbx) 2/3Ca1/3Mn O3 (x=0~0.2) 系列样品的磁熵变的研究等。然而对Tb3+离子掺杂的La1.2-xTbxSr1.8Mn2O7系列样品的磁熵变的研究至今依然很少。因此, 本文对La1.2-xTbxSr1.8Mn2O7 (x=0, 0.05) 样品的磁熵变和电输运性质进行了研究。
1 实验
采用传统高温固相反应法制备La1.2-xTbxSr1.8Mn2O7 (x=0, 0.05) 多晶样品, 首先, 将纯度为99.9%的La2O3, Sr CO3, Mn CO3和Tb2O3按化学计量比称量, 放入玛瑙研磨钵中混合研磨, 在1000℃下预烧12 h;其次, 将预烧后的粉末再次研磨后在1000℃下预烧12 h;最后, 将两次预烧后的粉末研磨压片, 在1300℃下烧结24 h后得到表面平整光滑的样品。利用振动样品磁强计 (VSM) 测量了样品在0.05 T外加磁场下的磁化强度随温度变化曲线 (M-T) 和不同温度下的磁化强度随外场变化曲线 (M-H) ;利用直流四端法在多功能物性测量系统 (PPMS) 上测量了零场下的电阻率随温度变化曲线 (ρ-T) 。
2 结果与讨论
La1.2-xTbxSr1.8Mn2O7 (x=0, 0.05) 多晶样品在外场0.05 T下的磁化强度随温度变化曲线 (M-T) 如图1所示, 其中包括零场冷却曲线 (ZFC) 及带场冷却曲线 (FC) , 测量温区为15~320 K。从图1中可以看出, 在高温部分, 磁化强度趋于零, 样品表现出顺磁性;随着温度的降低, 结合图1 (a) 和 (b) 的插图中 (d M/d T-T曲线) 可以看出, 两样品均发生了两次铁磁转变, 转变点a, b点分别对应三维长程铁磁有序转变温度 (TC3D) 及二维短程铁磁有序转变温度 (TC2D) [11], 其中a1和a2分别为120和70 K, b1和b2分别为245和225 K;在低温部分, 由于反铁磁相和铁磁相的竞争作用, 使得两样品的ZFC曲线和FC曲线都出现了明显的分裂, 表现出了团簇自旋玻璃行为[12]。
图1 0.05 T磁场下La1.2-xTbxSr1.8Mn2O7 (x=0, 0.05) 样品的M-T曲线Fig.1 M-T curves of sample La1.2-xTbxSr1.8Mn2O7 (x=0, 0.05) in a 0.05 T field (d M/d T-T curve shown in inset)
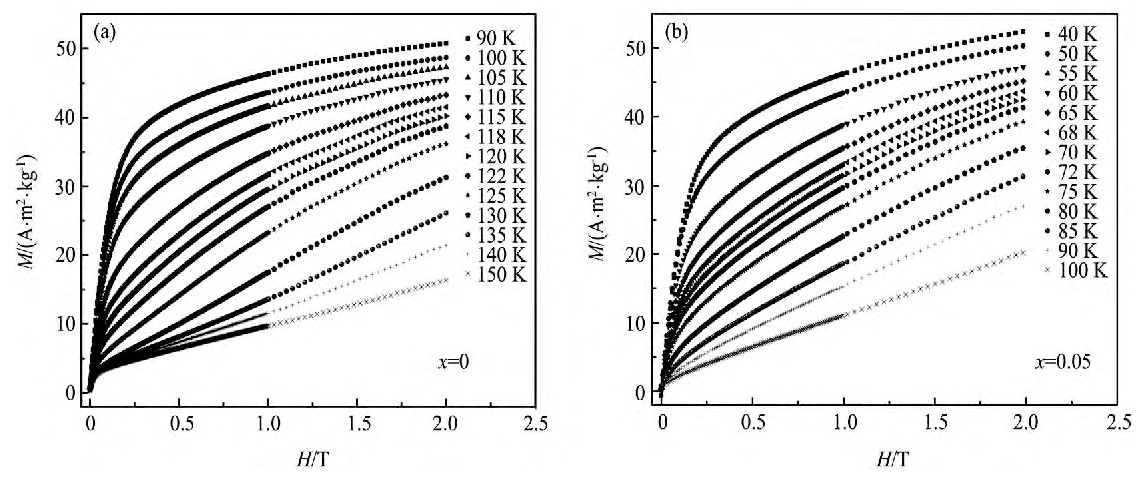
La1.2-xTbxSr1.8Mn2O7 (x=0, 0.05) 多晶样品在不同温度下磁化强度随外加磁场的变化曲线 (M-H) 如图2中 (a) 和 (b) 所示。从图2可以看出, 在测量温区内, 随着温度的升高, 两样品的磁化强度均逐渐变小, 且M-H曲线由趋于饱和变为趋于线性, 这说明两样品由铁磁有序变为顺磁无序, 这是由于分子热运动所致[13]。
La1.2-xTbxSr1.8Mn2O7 (x=0, 0.05) 多晶样品的Arrott曲线 (H/M-M2) 如图3中 (a) 和 (b) 所示。从图3 (a) 插图中可以看出, x=0样品的Arrott曲线在135~150 K温度范围内存在斜率为负的曲线, 而x=0.05样品的Arrott曲线在测量温区内始终未出现负斜率或拐点, 根据Banerjee法则[14], 当x=0时, 样品为一级相变;当x=0.05时, 样品为二级相变。这与La2/3-xEuxCa1/3-ySryMn O3 (x=0~0.4) 系列样品[15]和La0.65Nd0.05Ca0.3Mn0.9B0.1O3 (B=Mn, Cr, Fe) 系列样品[16]中的现象一致。这种由一级相变转变为二级相变的原因可能是小半径的Tb3+离子的掺杂使得A位平均离子半径减小从而产生晶格畸变, 使得自旋-晶格耦合作用降低和双交换作用减弱所致[15,17]。
根据热力学经典理论, 磁熵变|ΔSM|由外加磁场从0到H0的变化中产生, 其理论公式如下:
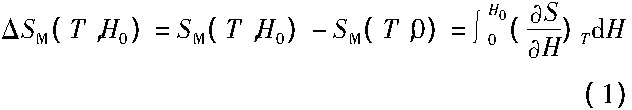
根据麦克斯韦方程:

将式 (1) 变为如下形式:

再对式 (3) 做数值近似, 可以得到:
图2 La1.2-xTbxSr1.8Mn2O7 (x=0, 0.05) 样品在不同温度下的M-H曲线Fig.2 M-H curves of sample La1.2-xTbxSr1.8Mn2O7 (x=0, 0.05)
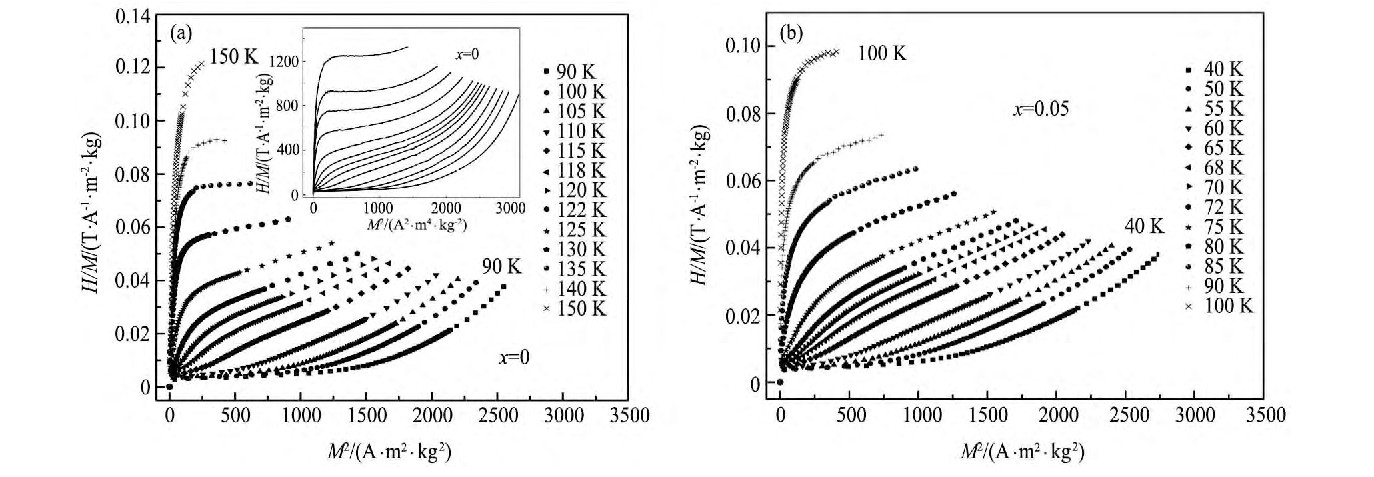
图3 La1.2-xTbxSr1.8Mn2O7 (x=0, 0.05) 样品在2 T外场下的Arrott曲线, (a) 中插图为x=0样品在5 T外场下的Arrott曲线Fig.3 Arrott curves of sample La1.2-xTbxSr1.8Mn2O7 (x=0, 0.05) , Arrott curves of sample La1.2Sr1.8Mn2O7in a 5 T field being shown in inset

式 (4) 中Mi和Mi+1分别表示在外加磁场为Hi时, 温度Ti和Ti+1处相对应的磁化强度值, 将实验测得的M-H曲线数据带入式 (4) 中, 即可得到La1.2-xTbxSr1.8Mn2O7 (x=0, 0.05) 多晶样品在不同外加磁场下的磁熵变值, 如图4 (a, b) 所示。
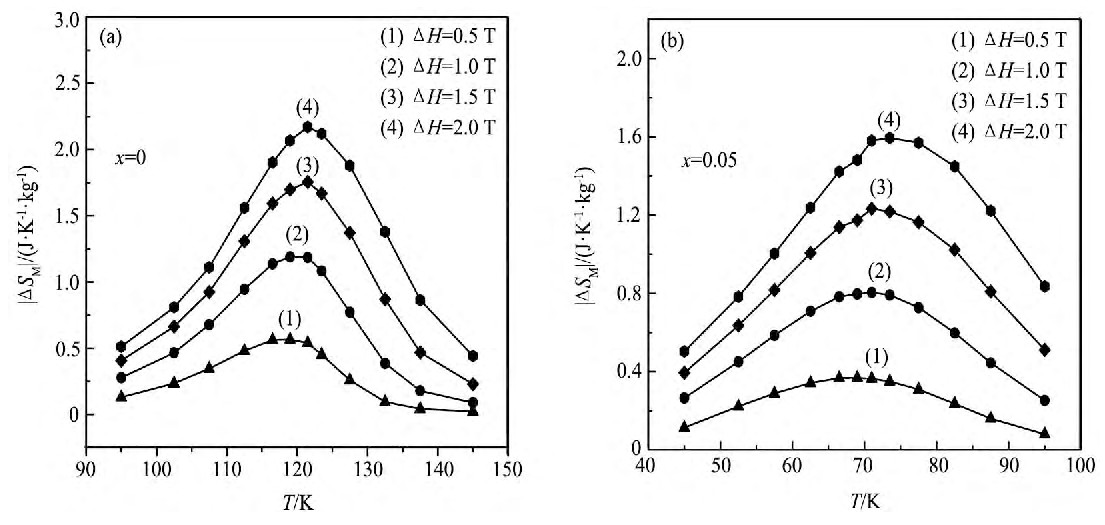
从图4中可以看出, 两样品均在TC3D附近出现了磁熵变最大值, 且磁熵变值随外场的增大而增大, 这是由于外场的增大使得系统内磁有序度增大, 且在磁有序过程中TC3D附近存在的强自旋-晶格耦合导致的[1,18]。从图4中 (a) 和 (b) 还可以看出, x=0.05样品的TC3D和磁熵变相比x=0样品大大降低, 而磁熵变温区却大幅变宽, 这些现象均符合磁相变由一级相变转为二级相变的特征[15,19], 与图3中的现象一致。此外, 从图4中可以看出, 两样品的磁熵变曲线的对称性良好, 在外加磁场2 T下x=0样品和x=0.05样品的最大磁熵变值分别为2.12和1.60 J· (kg·K) -1, 这表明该材料有利于应用在埃里克森磁制冷循环中[3,8,20]。
La1.2-xTbxSr1.8Mn2O7 (x=0, 0.05) 多晶样品在零场下的电阻率及磁电阻随温度变化曲线 (ρ-T) , 以及通过热激活 (lnρ-T) 、小极化子 (ln (ρ/T) -T) 和变程跳跃 (lnρ-T-1/ (n+1) ) 3种模型对ρ-T曲线高温部分的拟合曲线如图5所示。从图5 (a, e) 可以看出, 两样品均发生了一次绝缘-金属转变, 转变温度TP1 (样品1转变温度) 和TP2 (样品2转变温度) 分别为:96和93 K。另外, 对两样品TP以上的ρ-T曲线进行了3种模型拟合, 对比发现两样品在高温区均遵循三维变程跳跃的导电方式, 这说明无序效应在电输运过程中起主导作用, 且Tb3+离子的掺杂并没有改变高温区的导电方式[21]。
3 结论
主要研究了La1.2-xTbxSr1.8Mn2O7 (x=0, 0.05) 多晶样品的磁熵变和电输运性质。通过M-T曲线和M-H曲线分析发现:在15~320 K的整个测量温区内, 在高温部分, 两样品均表现出顺磁性;随温度的降低, x=0样品和x=0.05样品均先后发生了二维短程铁磁有序转变 (TC2D) 和了三维铁磁有序转变 (TC3D) , 两样品的TC2D分别为245和225K, TC3D分别为:120和70 K;在低温部分, 由于两相竞争出现团簇自旋玻璃现象。通过Arrott曲线和|ΔSM|-T曲线分析发现:在TC3D附近, x=0样品的磁相变为一级相变, x=0.05样品为二级相变, 在外场2 T下两样品的最大磁熵变值分别为2.17和1.6 J· (kg·K) -1。对比发现, Tb3+离子掺杂后x=0.05样品的磁相变发生改变、磁熵变和TC3D均降低, 这表明A位离子掺杂后, 双交换作用和自旋-晶格耦合作用均减弱。通过ρ-T曲线分析发现:两样品金属-绝缘转变温度以上的高温部分均遵循三维变程跳跃的导电方式, 说明无序效应在电输运过程中起主导作用。
图4 La1.2-xTbxSr1.8Mn2O7 (x=0, 0.05) 样品在不同磁场下的|ΔSM|-T曲线Fig.4|ΔSM|-T curves of sample La1.2-xTbxSr1.8Mn2O7 (x=0, 0.05) in different magnetic fields

图5 La1.2-xTbxSr1.8Mn2O7 (x=0, 0.05) 样品在零场下的电阻率随温度变化Fig.5 Temperature dependence of resistivity for La1.2-xTbxSr1.8Mn2O7 (x=0, 0.05) samples at field of 0 T (a, e) ρ-T curve; (b, f) lnρ-T curve; (c, g) ln (ρ/T) -T curve; (d, h) lnρ-T-1/ (n+1) curve
参考文献