草酸沉淀法制备大颗粒氧化钇工艺研究
包头稀土研究院
稀土冶金及功能材料国家工程研究中心
中国科学院化学研究所
摘 要:
采用草酸沉淀法研究制备了大颗粒氧化钇,并对各制备条件对氧化钇粒度影响进行了分析讨论。同时,结合不同煅烧温度下产物的XRD谱图,对煅烧产物进行物相分析,探讨煅烧过程中产物的晶型转变,并利用SEM观察产物形貌。结果表明:提高酸度、沉淀反应温度、延长陈化时间以及降低加料速度均可以有效增大氧化钇粒度;XRD曲线表明沉淀反应制得前躯体的主要成分为Y2(C2O4)3.10H2O,且当前躯体于400,600,800,1000℃煅烧时,所得产物分别为Y2(C2O4)3.2H2O,YOOH,Y2O3,Y2O3;前躯体形貌与最终的氧化物产品形貌存在一定的相似性,均是由小颗粒形成的团聚体,但颗粒粒度存在较大差异。因此,由实验得出了草酸沉淀法制备大粒度氧化钇的工艺条件,且按此工艺条件制备出粒度大于50μm的氧化钇产品,颗粒分散均匀。此外,本工艺操作简单,产品质量稳定,易于推广,可实现产业化。
关键词:
中图分类号: TQ134.11
作者简介:马莹(1967-),女,河北人,学士,正高级工程师;研究方向:稀土湿法冶金新工艺、新产品,通讯联系人(E-mail:may@rknerc.com);
收稿日期:2010-02-24
基金:内蒙古科技厅创新引导奖励资金项目;
Preparation of Large Particle Yttrium Oxide by Precipitation with Oxalic Acid
Abstract:
The large particle yttrium oxide was prepared using oxalic acid as precipitation agent.The effects of preparation conditions on the particle size of yttrium oxide were discussed.Meanwhile,the component and crystalline transition of the calcination product at various calcination temperatures were analyzed by XRD,and the SEM image was also observed.The results showed that the particle size of yttrium oxide could be increased effectively by improving acidity,precipitation temperature,prolonging aging time,and decreasing feeding speed.The XRD patterns showed that the main component of the precursor was Y2(C2O4)3·10H2O,and when the precursor was calcinated at 400,600,800 and 1000 ℃,the products were Y2(C2O4)3·2H2O,YOOH,Y2O3 and Y2O3.There were some similar appearances between the precursor and the final product,which were formed by little particles,but the particle size was quite different from each other.Accordingly,the best preparation conditions were acquired using oxalic acid as precipitation agent,and the size of yttrium oxide was larger than 50 μm by the process.Moreover,the yttrium oxide particles were dispersed uniformly.Otherwise,the method was prone to spread and industrialization because the method was very easy,and the quality of the product was stable.
Keyword:
yttrium oxide;oxalic acid;precipitation;rare earths;
Received: 2010-02-24
我国稀土资源丰富, 具有储量大、 品种齐全, 分布广等特点。 近年来, 随着新材料技术的不断发展, 稀土化合物的应用已由冶金、 化工、 陶瓷等传统领域拓展到永磁、 储氢、 发光等高技术领域; 并由对其化学性质的开发应用发展为对其粒径、 比表面、 比重、 晶体形貌等物性指标的研究, 例如一些树脂填充材料、 喷涂材料都要求氧化物粒度达到10 μm以上
1 实 验
1.1 样品制备
将氧化钇(99.9%)用硝酸溶解配制成一定浓度的硝酸钇溶液, 过滤后待用。 将固体草酸用去离子水加热溶解制成一定浓度的草酸溶液, 并利用HNO3调节酸度, 最后置于恒温水浴槽内, 以250 r·min-1的速度搅拌。 将硝酸钇溶液以一定的速度滴加到草酸溶液中至沉淀完全。 将前躯物恒温陈化一定时间, 过滤, 洗涤, 煅烧制得大颗粒Y2O3。
1.2 分析与表征
制得的Y2O3用Coulter公司生产的L32型激光粒度仪测定颗粒的粒度分布; 用S-3400扫描电子显微镜分析颗粒的形貌, 用BT-1000型粉体综合测试仪测试粉体的分散性; 用PW1700 X射线衍射仪分析颗粒的晶型和物相。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 沉淀过程中不同反应条件对Y2O3颗粒粒度的影响
沉淀反应过程中, 反应条件不同会对Y2O3颗粒粒度产生较大影响
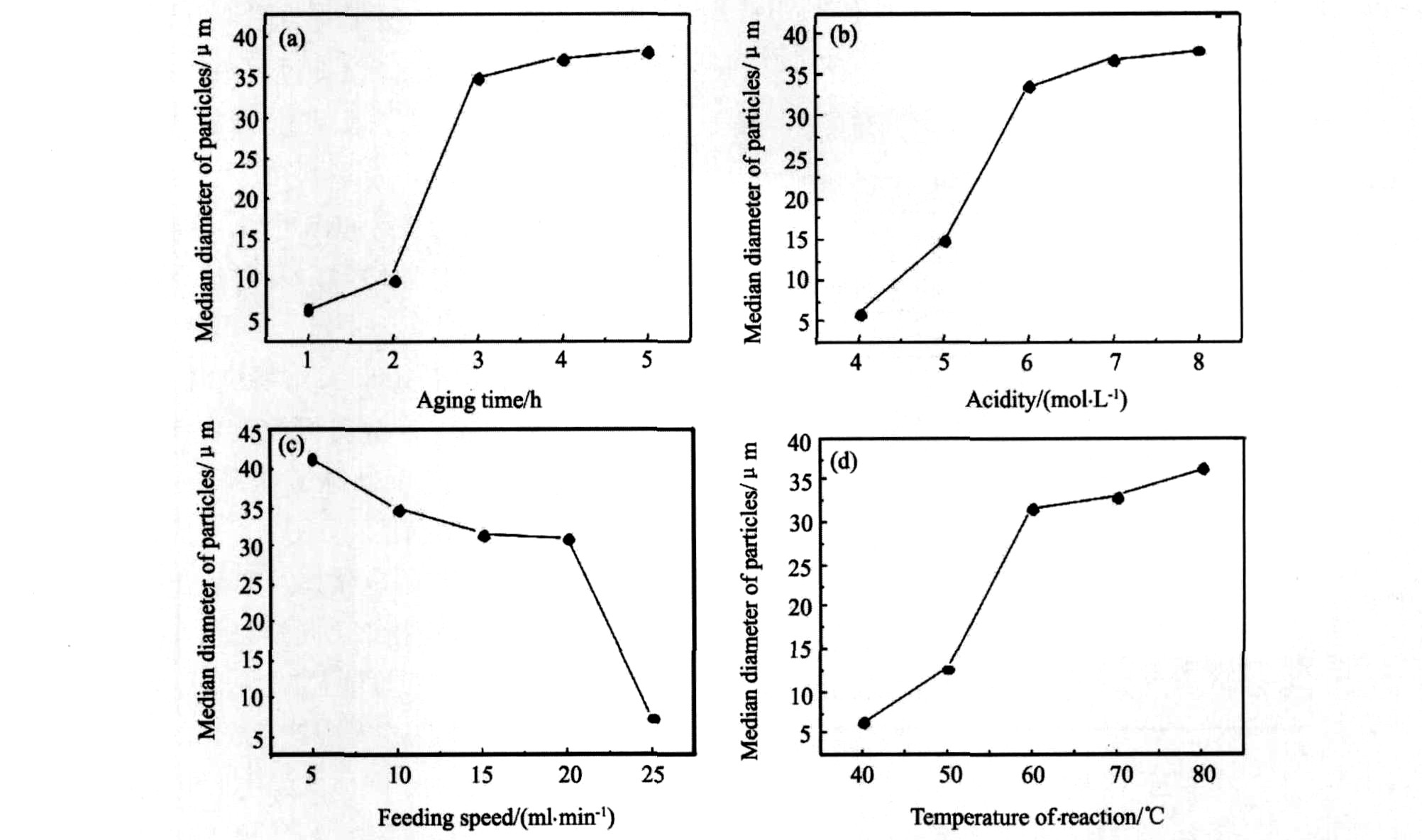
由图1(a)中陈化时间与Y2O3颗粒粒度的关系曲线可以看出, 随陈化时间增加, 颗粒粒度D50增大。 陈化过程中, 沉淀和母液之间存在溶解平衡, 随着陈化时间的延长, 小颗粒不断溶解, 大颗粒逐渐长大, 所以陈化有利于颗粒长大; 图1(b)为酸度与Y2O3粒度的关系曲线, 由图看出, 随酸度增加, D50增大。 由于增加酸度可有效抑制晶核的生成速度, 增加晶核的生长速度, 从而有利于颗粒长大。 但当酸度太高时, 会增加草酸钇的溶解量, 降低最终产物的收率(表1即为不同酸度条件下的产物收率), 所以酸度调节不宜太高; 从图1(c)中加料速度与Y2O3颗粒粒度的关系曲线可看出, 随加料速度增加, Y2O3颗粒粒度逐渐降低。 由于加料速度较小时, 晶粒的生长速度大于成核速度, 有利于颗粒长大, 所以适当降低沉淀过程中的加料速度有利于生成粒度较大的Y2O3颗粒; 图1(d)为沉淀反应温度与Y2O3颗粒粒度的关系曲线。 温度升高时, 沉淀的相对过饱和度增加, 成核速度增大, 粒径减小, 但颗粒间聚合作用能力也相应增加, 最后使得颗粒粒度增大。
图1 沉淀过程中不同反应条件与Y2O3颗粒粒度的关系曲线
Fig.1 Relation curves between different reaction conditions during precipitation and particle size of Y2O3
由上述实验, 选择合适的反应条件, 制备出粒径(D50)大于50 μm的氧化钇。
2.2 不同温度下煅烧产物的XRD物相分析
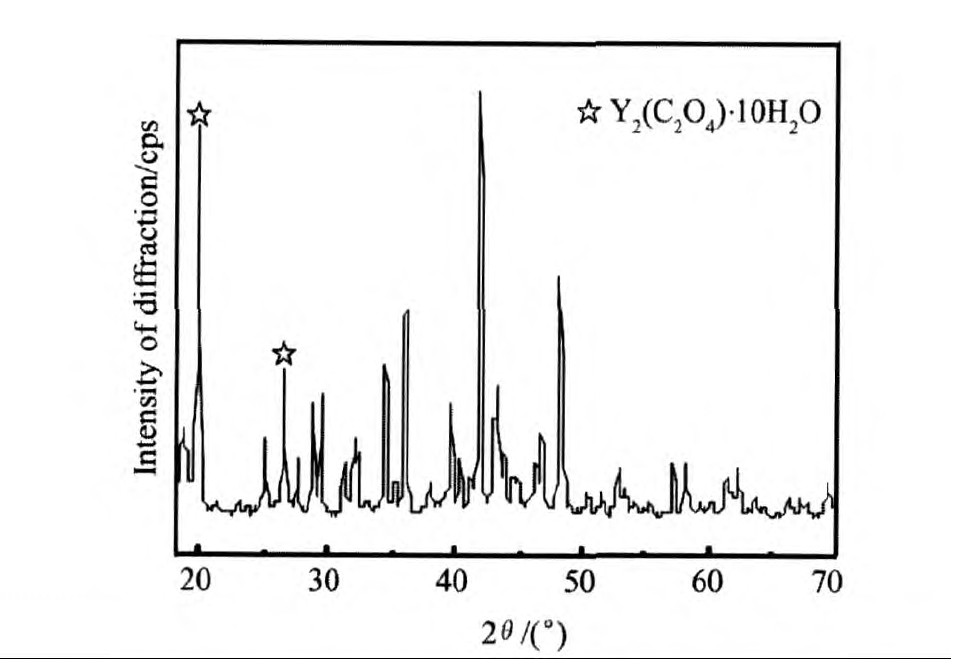
根据实验确定的反应条件, 采用草酸沉淀法制备了大颗粒Y2O3的前驱物, 且前躯物的主要成分为Y2(C2O4)3·10H2O, 其XRD曲线如图2所示。
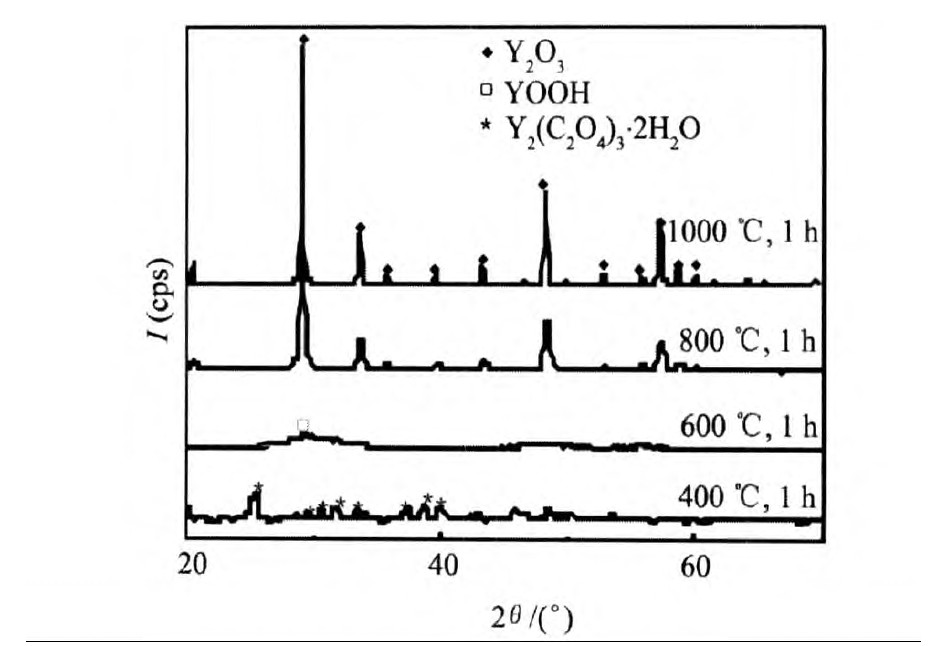
取4份相同质量的前驱物分别在400, 600, 800, 1000 ℃温度下煅烧1 h。 对煅烧后的产物进行物相分析, 结果如图3所示。
从图3中的谱图可以看出, 前驱物在热分解过程中其产物结构发生了转变。 煅烧温度达400 ℃时, 因结晶水的脱除而使前驱物由Y2(C2O4)3·10H2O转变成Y2(C2O4)3·2H2O; 当温度升高到600 ℃左右时, 前驱物中的结晶水已完全脱除, 且产物结构由Y2(C2O4)·2H2O转变为YOOH相; 而当温度达到800 ℃时, 煅烧产物已转变为Y2O3, 但Y2O3的衍射峰与前驱物在1000 ℃下煅烧产物的衍射峰相比较弱, 所以800 ℃时, 相变反应并不完全。 若将前驱物在1000 ℃下煅烧, 其产物的XRD图谱显示出完好的衍射峰, 峰形狭窄, 此时煅烧产物不仅完全转变为Y2O3, 且前驱物中未洗净的杂质离子也已彻底挥发, 因此为得到反应完全且高纯度的Y2O3颗粒, 需将煅烧温度升高到1000 ℃。
表1 不同酸度条件下的产物收率
Table 1 Product yield with diferent acidity
Acidity/M |
4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
Yield/% |
70.6 | 75.3 | 73.4 | 81.5 | 66.2 |
图2 前驱物的XRD曲线Fig.2 XRD pattern of the precursor
图3 前驱物在不同温度下煅烧产物的XRD曲线Fig.3 XRD patterns of the products with various calcination temperature
2.3 前驱物及其煅烧产物的颗粒形貌及粒度分布规律
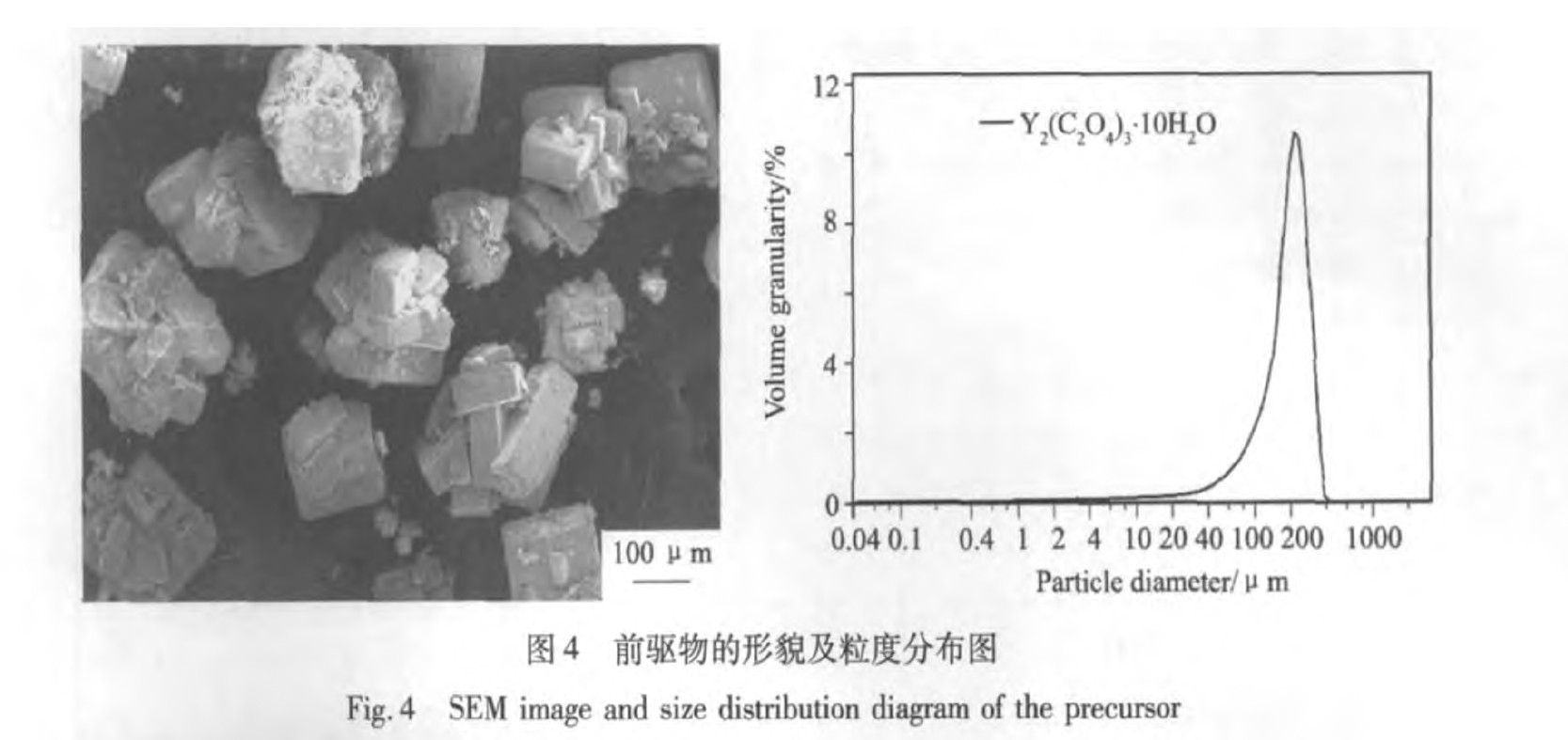
热分解过程中, 前驱物的颗粒形貌将会对最终产物产生一定的影响。 图4为前驱物煅烧前的形貌及粒度分布图。 沉淀过程中, 由于颗粒之间存在一定的团聚力, 反应生成的Y2(C2O4)3·10H2O会不断聚集在一起, 形成大的团聚体。 而由图4中前驱物的粒度分布图可知, 草酸沉淀反应制得的前驱物颗粒分散均匀, D50可达200 μm, 且前驱物中小颗粒较少。
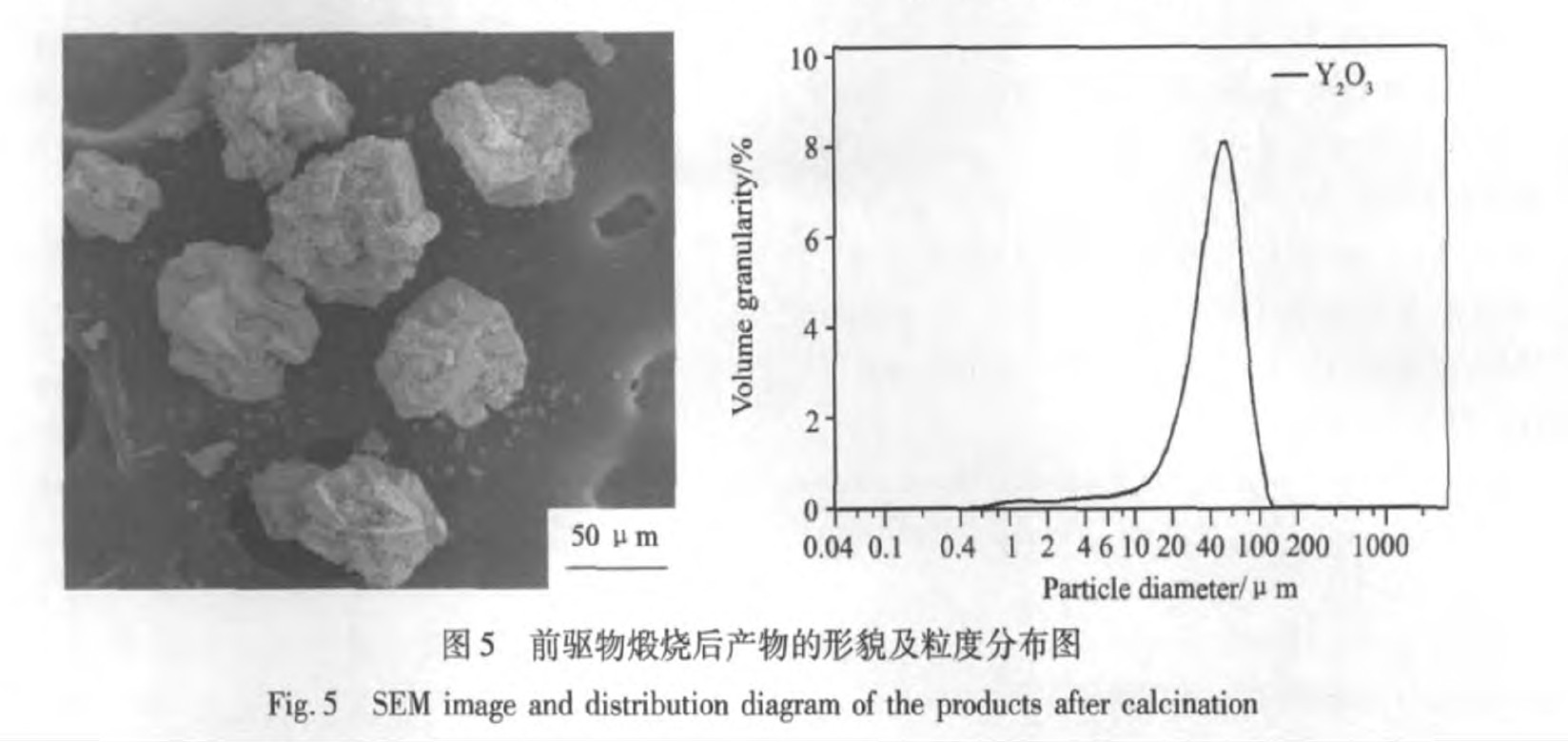
由于前驱物于1000 ℃下煅烧时, 可得到反应完全的氧化物颗粒, 故将沉淀反应制得的前驱物在1000 ℃下煅烧1 h制得Y2O3颗粒, 颗粒形貌及粒度分布如图5所示。
从图5中的扫描电镜图可以看出, Y2O3颗粒形貌与前驱物形貌相似, 同样是由小颗粒形成的团聚体, 但团聚体粒度明显减小, D50大于50 μm。 由于草酸盐热分解过程中产生的气体不断逸出, 使得前躯体形成的中间体或无定形的氧化钇碎化, 粒度减小。 由该法制得的Y2O3颗粒粒度分布比较均匀, 近似于正态分布。
3 结 论
1. 采用草酸盐沉淀法制备大颗粒氧化钇工艺可行, 制得的氧化钇粒径(D50)可达到50 μm以上, 且分散均匀。
2. 草酸沉淀法制备大颗粒氧化钇时, 应选择适宜的条件, 如反应温度、 加料速度、 反应酸度、 陈化温度与时间、 煅烧温度与时间等。
3. 本工艺操作简单, 产品质量稳定, 易于推广, 可实现产业化。
参考文献
注释
1Optimization of PID Control Parameters for Large Diameter Silicon Crystal Growth