网络首发时间: 2015-09-28 10:37
某含金银褐铁矿预处理工艺对氰化浸出的影响
广州有色金属研究院广东省稀土开发及应用重点实验室
中南大学冶金与环境学院
摘 要:
研究了某含金银褐铁矿的工艺矿物学,该矿主要矿物为褐铁矿,铁、铜、锌、铅、锰元素主要以氧化物形式均匀分布在褐铁矿中。针对该矿物特性,本研究采用氧化焙烧-浸出工艺对该矿进行预处理,研究了焙烧条件、浸出条件对该矿中铁、铜、锌、铅、锰元素浸出的影响;通过实验最佳预处理工艺条件为:在温度650℃,保温2 h下焙烧,将焙烧渣在室温下,采用浓度1.5 mol·L-1的硫酸溶液、液固比4∶1、浸出4 h下浸出,铁、铜的浸出率分别为:4.16%,42.26%,较好地选择性除铜;将氧化焙烧-酸浸预处理后的矿物与未处理矿物和氧化焙烧-碱性浸出预处理进行氰化浸出试验对比,银浸出率分别为42.61%,7.10%,13.50%,氧化焙烧-酸浸出预处理后银回收率提高了35%;同时可以回收铜、铁等有价元素。
关键词:
中图分类号: TF80
作者简介:刘志强(1973-),男,湖北赤壁人,硕士研究生,教授级高级工程师,研究方向:有色冶金;E-mail:lzqgd168@126.com;;邱显扬,教授级高级工程师;电话:020-37238521;E-mail:qiuxygz@163.com;
收稿日期:2014-11-25
基金:国家科技部“973计划”项目(2012CB724200)资助;
Cyanidation Leaching Influenced by Pretreatment of Au-Ag-Bearing Limonite
Liu zhiqiang Huang Qingyuan Zhu Wei Li Wei Qiu Xiangyang
Guangdong Province Key Laboratory of Rare Earth Development and Application,Guangzhou Research Institute of Non-Ferrous Metals
School of Metallurgy and Environment,Central South University
Abstract:
The process mineralogy investigation and pretreatment of Au-Ag bearing ore were studied. The analysis of process mineralogy showed that the main metallic mineral was limonite,while iron,copper,zinc,lead and manganese were uniformly distributed in the limonite as oxides. Before cyanidation,oxidizing roasting-leaching process( acid and alkaline leaching) was employed as the pretreatment of the ore. Effects of pretreatment parameters on iron,copper and magnesium extraction were investigated. The best results of iron and copper leaching ratio in this work were 4. 16% and 42. 26%,respectively,after the pretreatment of oxidizing roasting( 650 ℃ for 2 h) and acid leaching process( 1. 5 mol·L-1H2SO4,liquid-solid ratio of 4∶ 1,leaching time of 4 h). The silver leaching ratios of cyanidation of the ore before and after pretreatment( oxidizing roasting-acid or alkaline leaching) were 42. 61%,7. 10% and13. 50%,respectively. The result indicated that the recovery of silver had a remarkable 35% increase compared to a direct cyanidation process without the oxidation roasting-acid leaching pretreatment. Moreover,the valuable metals,such as copper,iron and magnesium could also be recovered.
Keyword:
limonite; pretreatment; silver; cyanidation;
Received: 2014-11-25
我国黄金资源分布很广,黄金资源矿床类型较多,多为品位较低的矿床。许多这种金矿中还含有铜元素,铜含量低于0.2%的金矿石一般来说可以直接氰化提金
云南某含金银褐铁矿,原矿金银品位较低,矿石氧化率高,金属矿物以褐铁矿为主,硫化矿物含量甚微,含硫仅为0.11%,并且含铜、锰。目前该类含锰金矿在氰化浸出时,存在银浸出率很低,铜没有回收利用等问题,国内外开展了广泛研究
1实验
1.1原料
矿样为云南某含金银褐铁矿(主要化学成分如表1所示)。实验所用硫酸、氰化钠试剂为市售的工业级试剂。
表1 含金银褐铁矿的主要元素分析结果Table 1 Multi-element analysis results of limonite ore con-taining gold and silver(%,mass fraction) 下载原图
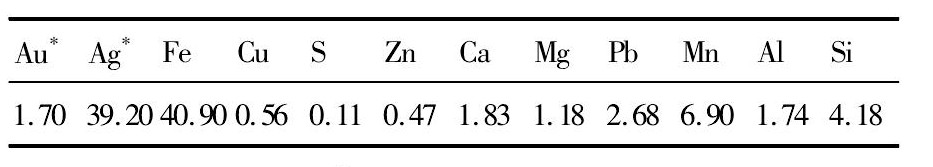
*:Au,Ag unit being 10-6
表1 含金银褐铁矿的主要元素分析结果Table 1 Multi-element analysis results of limonite ore con-taining gold and silver(%,mass fraction)
1.2方法
1.2.1酸浸预处理
将矿石在球磨机中磨到合适粒度后,经过不同温度下煅烧,在可调控温的数显恒温水浴箱中进行酸浸。根据实验条件要求,需控制好搅拌速度、温度等条件。酸浸预处理后,用真空过滤机过滤,液体送化验,渣洗涤干燥后,一部分制样送化验分析,一部分用于测试,其他样进行氰化浸出实验和备用。
1.2.2氰化浸出研究方法
氰化浸出实验在氰化浸出槽中进行。取100 g金矿样品和200 ml水加入氰化浸出槽中,用烧碱调浆到p H为10~11后,加入Na CN,Na CN用量为3 kg·t-1处理矿样,氰化浸出36 h。浸出渣淋洗烘干制样送化验。
1.3分析检测方法
矿石的晶型采用X射线衍射仪(XRD,日本理学D/MAX1200)分析。工艺矿物学采用工艺矿物学参数自动定量分析检测系统(澳大利亚昆士兰大学MLA)进行检测;贵金属含量采用火试金法测定,其他铜等元素含量采用化学法及电感耦合等离子体原子发射光谱法(ICP-AES)测定。用NETZSCH TG209对矿样进行热重(TG)及差热(DSC)分析。
2结果与讨论
2.1含金银褐铁矿的工艺矿物学分析
通过工艺矿物学参数自动定量分析检测系统对矿石进行工艺矿物学分析,分析结果如表2,3,图1所示。从表2可以看出,矿石中金属矿物主要为褐铁矿、铅硬锰矿、硬锰矿、黄铁矿等;非金属矿物主要为方解石、白云石、石英、黑云母、绿泥石等。
表2 含金银褐铁矿中主要金属矿物含量分析结果Table 2 Main metallic mineral contents of limonite ore containing gold and silver(%,mass fraction) 下载原图

表2 含金银褐铁矿中主要金属矿物含量分析结果Table 2 Main metallic mineral contents of limonite ore containing gold and silver(%,mass fraction)
表3 某含金银褐铁矿中主要元素在主要矿物中的分配比例统计Table 3 Allocation proportion of main elements in limonite ore containing gold and silver(%,mass fraction) 下载原图
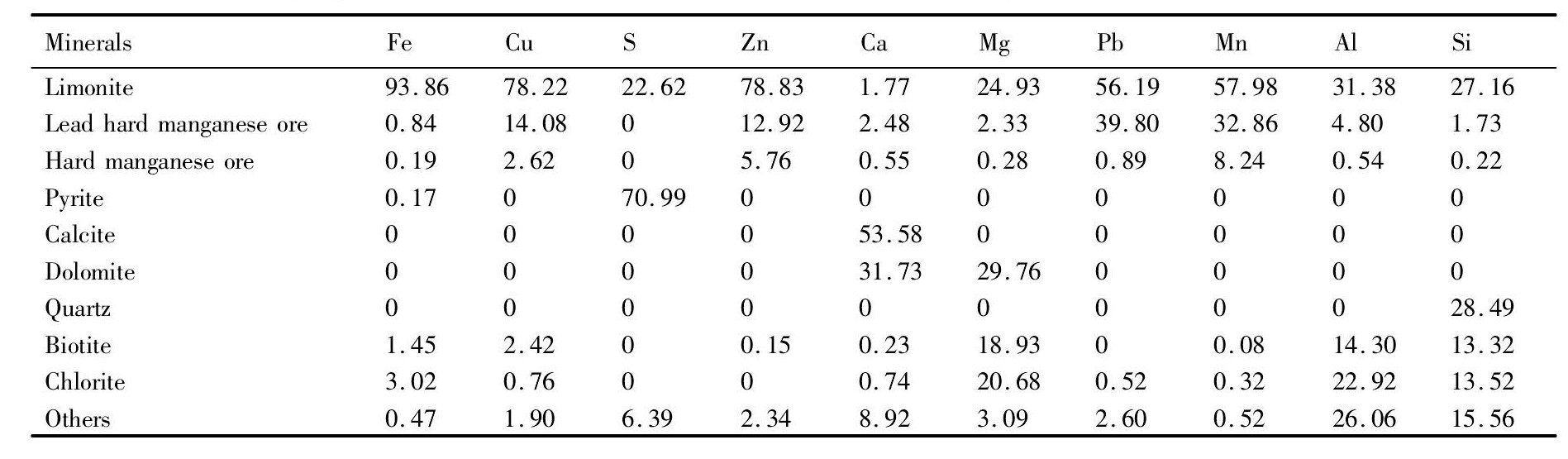
表3 某含金银褐铁矿中主要元素在主要矿物中的分配比例统计Table 3 Allocation proportion of main elements in limonite ore containing gold and silver(%,mass fraction)
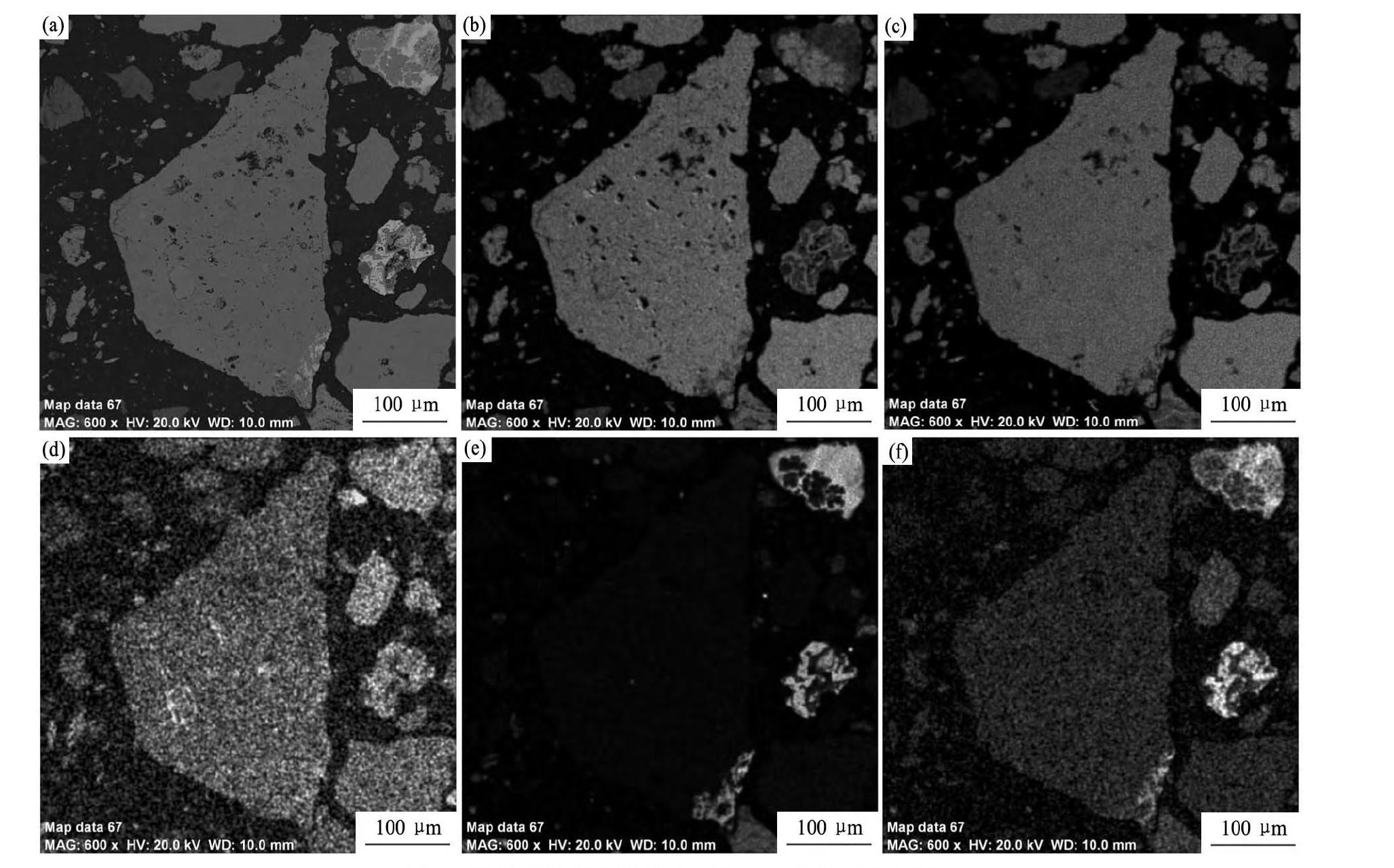
图1 褐铁矿物的背散射电子像及元素的面分布图Fig.1 SEM image(a)of limonite and EDX elemental scanning of O(b),Fe(c),Cu(d),Mn(e),Pb(f)
含金银褐铁矿中主要元素在主要矿物中的分配比例统计如表3所示。从表3可以看出,金矿中铜、锌、铅、锰元素主要分布在褐铁矿中,其次分布在铅硬锰矿中;金矿中硫元素主要分布在黄铁矿中。从褐铁矿面扫描图(图1)可以看出,铁、铜、氧元素在褐铁矿中均匀分布,锰和铅元素则相对集中在铅硬锰矿、硬锰矿中,且铁、铜、锌、铅、锰元素主要以氧化物形式存在。因此,可以考虑采用酸浸预处理工艺将金矿中的铜、锌、锰等元素浸出。
2.2焙烧条件对浸出的影响
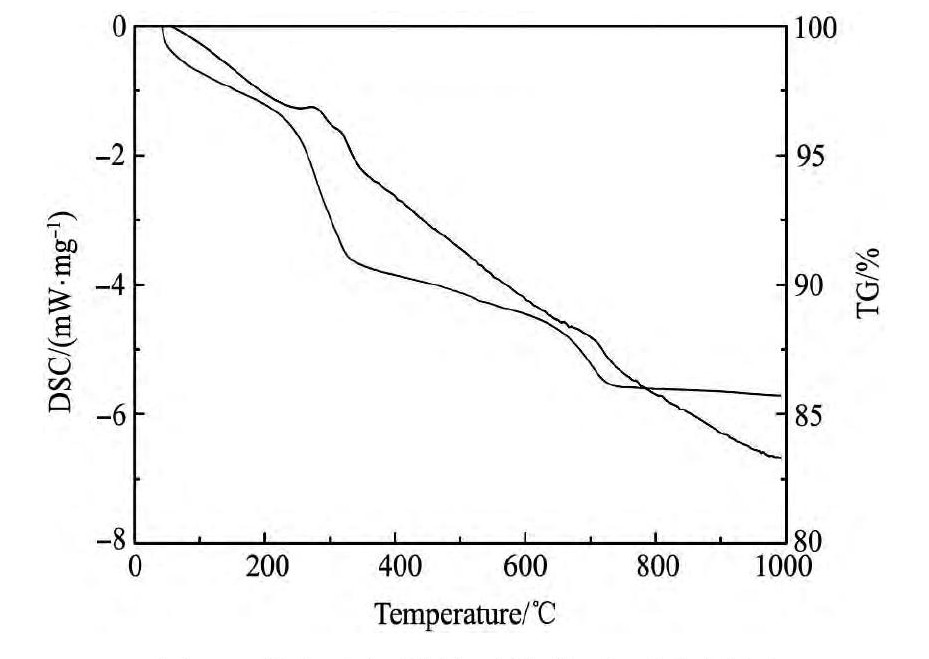
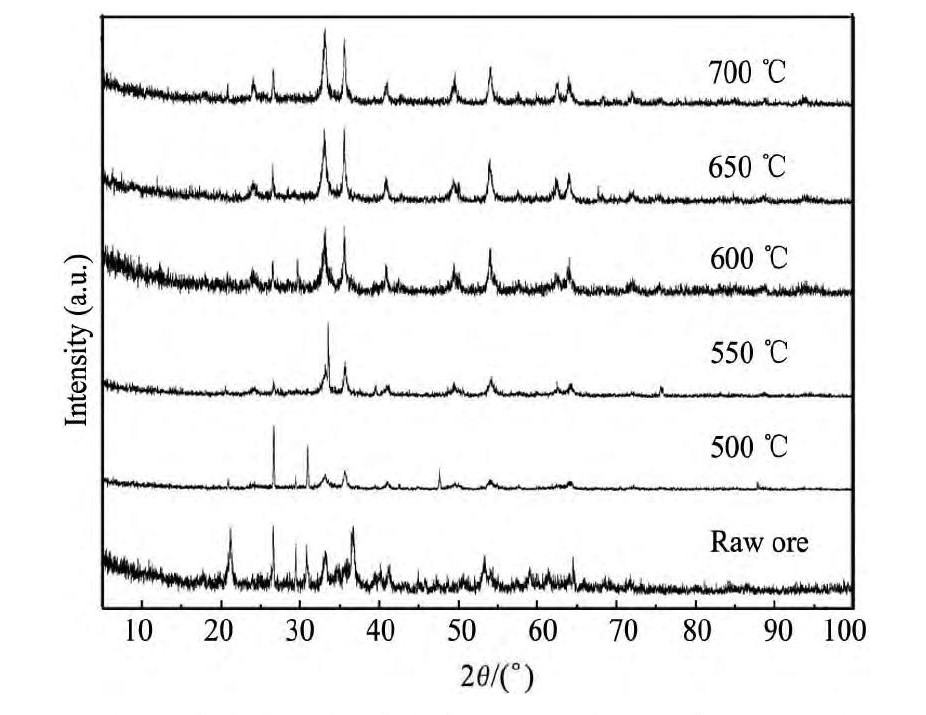
本研究矿物主要以褐铁矿为主,褐铁矿是主要的铁矿物之一,以含水氧化铁为主要成分,化学分子为Fe O(OH)·n H2O。由于褐铁矿比较容易被酸溶解,在采用酸浸直接浸铜、锌、铅、锰时,褐铁矿会大量溶解,造成酸的消耗过大,同时加大浸出液中铜、锌、铅、锰的回收难度和成本。不同铁矿物的酸溶解性不同,本研究采用焙烧改变褐铁矿中铁物相变化,在提高铜、锌、铅、锰浸出率的情况下,尽量减少铁的浸出。将该含金银褐铁矿进行差热-失重分析,从热重分析图(图2)可以看出,该矿在375℃前失重约9.5%,主要失重在280~320℃之间,在该区间存在两个明显的放热峰,主要为褐铁矿脱除结合水;在700℃左右有一个放热峰,并失重4.5%左右。将该含金银褐铁矿分别在500,550,600,650,700℃下煅烧,将原矿与焙烧渣进行XRD分析(图3),从图3可以看出在500℃时该矿物相就已经发生了转变,褐铁矿特征峰开始消失,在550℃时可以明显看到赤铁矿物相的特征峰,600℃以后褐铁矿全部转化为赤铁矿物相。因此,根据热重和XRD分析,如果将该含金银褐铁矿转化为赤铁矿,焙烧温度应在600℃以上。将650℃下焙烧得到的焙烧渣,采用工艺矿物学参数自动定量分析检测系统进行分析,发现焙烧渣中没有褐铁矿和黄铁矿矿物,只有赤铁矿,说明焙烧可以将褐铁矿和黄铁矿全部转化为赤铁矿。
图2 某含金银褐铁矿差热-失重分析图Fig.2 DSC-TG analysis of limonite ore containing gold and silver
图3 某含金银褐铁矿在不同煅烧温下的XRD图Fig.3 XRD patterns of limonite ore containing gold and silver at different roasting temperatures
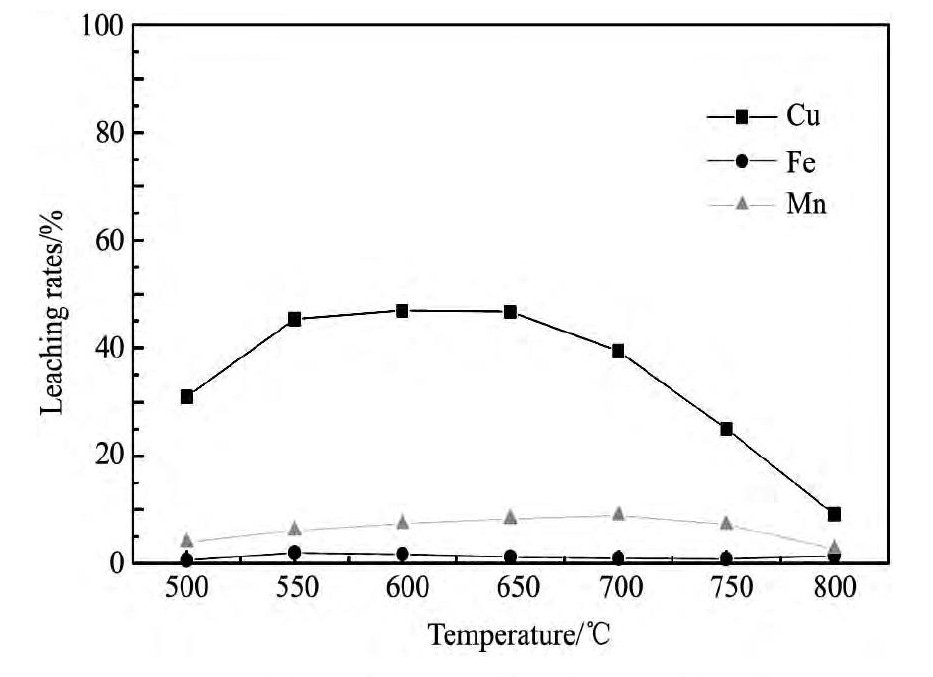
将该含金银褐铁矿分别在500,550,600,650,700℃下煅烧2 h后,将焙烧渣在硫酸浓度1.5 mol·L-1,液固比4∶1,浸出时间4 h,室温搅拌,搅拌速度约300 r·min-1的浸出条件下进行酸浸,浸出结果如图4所示,从图4可以看出,铜浸出率在650℃以前随温度变化不大,高于650℃后浸出率明显下降;铁浸出率随着焙烧温度提高,逐渐降低,主要原因是随着焙烧温度升高,褐铁矿逐步转化成赤铁矿,赤铁矿比较难溶;实验数据表明:在焙烧温度为650℃左右时,铜的浸出率最高、铁的浸出率最低。
2.3浸出条件对浸出的影响
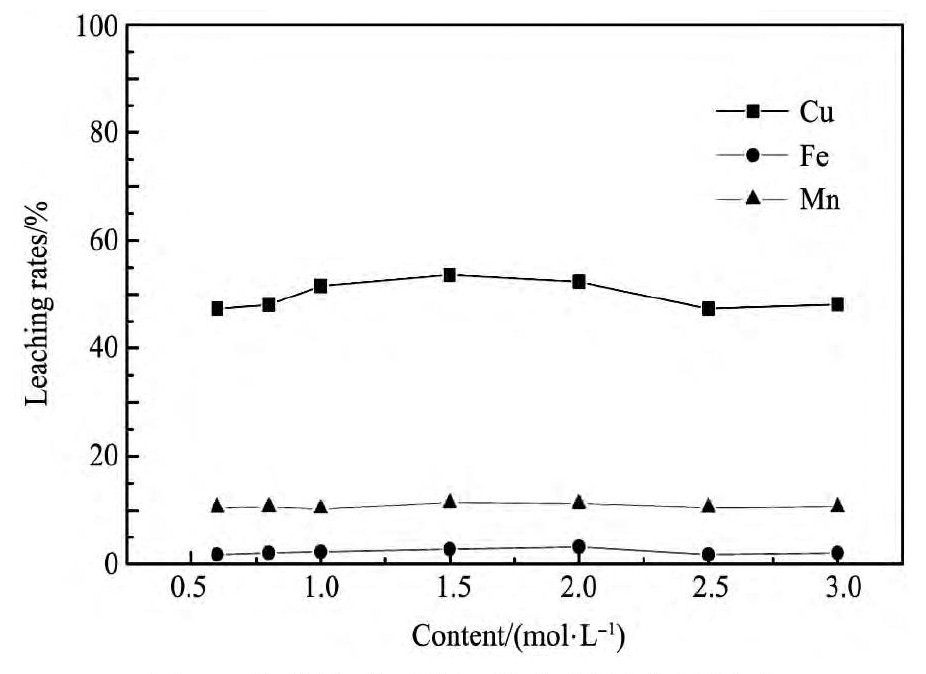
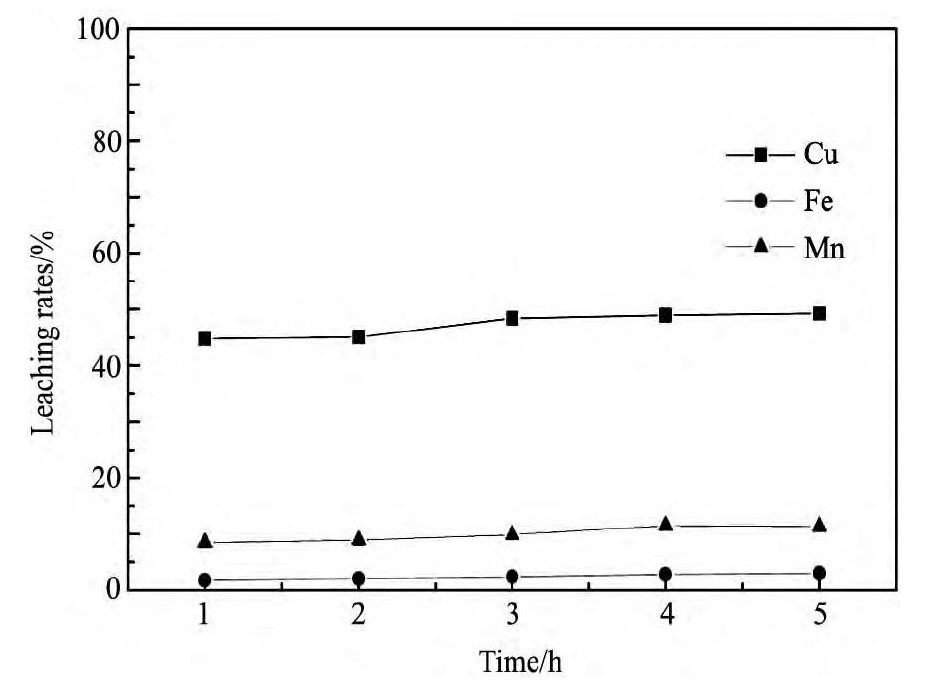
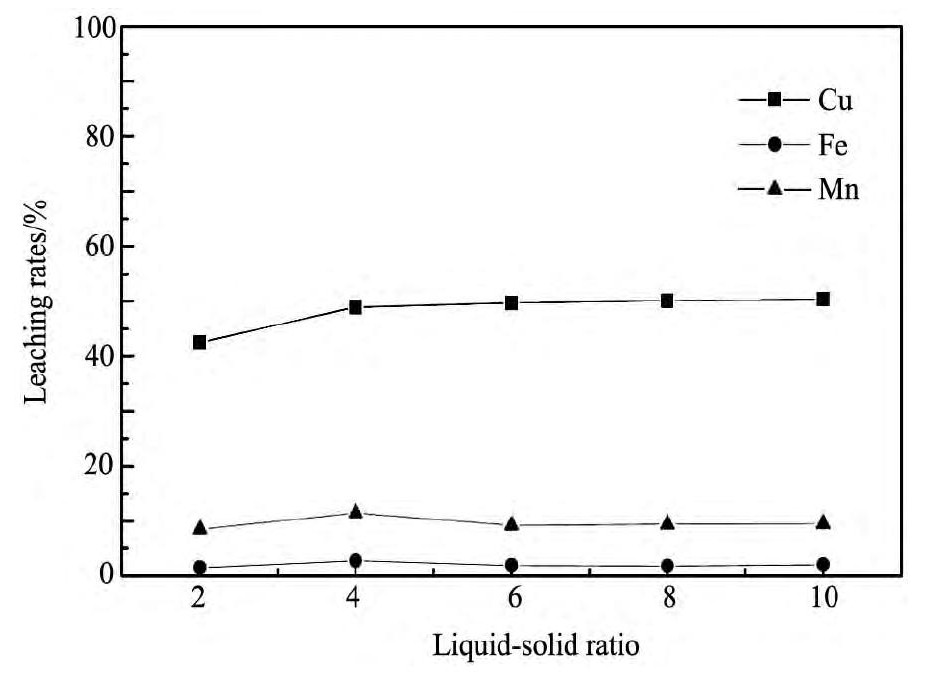
将650℃焙烧渣在不同硫酸浓度下,液固比4∶1,浸出时间4 h,室温搅拌,搅拌速度约300 r·min-1的浸出条件下进行酸浸。从图5可以看出,当硫酸浓度低于1.5 mol·L-1时,随着硫酸浓度的增加,铜、锰的浸出率也增加;但铜、锰的浸出率在硫酸浓度高于1.5 mol·L-1后逐渐减小;因此,考虑浸出率和经济成本,采用硫酸浓度1.5 mol·L-1的硫酸溶液为最佳浸出酸度。将650℃焙烧渣在1.5mol·L-1硫酸浓度下,液固比4∶1,室温搅拌,搅拌速度约300 r·min-1,不同浸出时间的浸出条件下进行酸浸。从图6可以看出,随着浸出时间的增加铜、铁、锰浸出率逐步增加,但在4 h以后,铜、铁、锰浸出率变化不明显;因此,浸出时间4 h为最佳浸出时间。将650℃焙烧渣在1.5 mol·L-1硫酸浓度下,浸出时间4 h,室温搅拌,搅拌速度约300 r·min-1,不同液固比的浸出条件下进行酸浸。从图7可以看出,随着液固比的增加,铜的浸出率增加;在液固比大于4后,铜的浸出率变化不大,而铁、锰的浸出率减少;因此,为了提高铜、锰浸出率及考虑经济成本,最佳浸出液固比为4∶1。
表4 焙烧渣中主要金属矿物含量分析结果Table 4 Main metallic mineral contents of roasting slag(%,mass fraction) 下载原图

表4 焙烧渣中主要金属矿物含量分析结果Table 4 Main metallic mineral contents of roasting slag(%,mass fraction)
图4 焙烧温度对铜、铁和锰浸出的影响Fig.4 Effect of roasting temperature on leaching rates of cop-per,iron and manganese
图5 硫酸浓度对铜、铁和锰浸出的影响Fig.5 Effect of sulfuric acid concentration on leaching rates of copper,iron and manganese
通过优化氧化焙烧-硫酸浸出预处理工艺条件,将350 g褐铁矿在温度650℃,保温2 h下焙烧,将焙烧渣在室温下,采用浓度1.5 mol·L-1的硫酸溶液、液固比4∶1,浸出4 h,将浸出渣洗涤后烘干得到310.9 g渣;经分析铜含量0.26%,浸出率为42.26%;铁含量44.03%,铁收率为95.84%。
将150 g褐铁矿经过650℃焙烧2 h后,采用氨水浓度为4 mol·L-1、氯化铵浓度为4 mol·L-1的混合浸出剂600 ml,在室温下搅拌浸出4 h,搅速约300 r·min-1。浸出试验结果如表5所示。
图6 浸出时间对铜、铁浸出的影响Fig.6Effect of leaching time on leaching rates of copper and iron
图7 浸出液固比对铜、铁和锰浸出的影响Fig.7 Effect of liquid-solid ratio on leaching copper,iron and manganese
试验结果表明:在氧化焙烧-碱性浸出试验中,铜浸出率只有14.80%,低于氧化焙烧-酸浸试验。
2.4不同预处理条件对氰化浸出的影响
将氧化焙烧-酸浸预处理后的矿物与未处理矿物和氧化焙烧-碱性浸出预处理进行氰化浸出试验对比试验研究,具体氰化浸出条件为:液固比2∶1,石灰添加量50000 g·t-1、氰化钠3000 g·t-1,p H=10.0,浸出36 h,转速1398 r·min-1;具体试验结果见表6。结果表明,褐铁金矿经过氧化焙烧-酸浸预处理后与未处理矿物和氧化焙烧-碱性浸出预处理相比,银浸出率分别为42.61%,7.10%,13.50%,氧化焙烧-酸浸出预处理后银回收率提高了35%;但由于氧化焙烧-酸浸预处理后矿物含铜仍有0.26%,还需进一步研究降低铜含量,提高银的浸出率。
表5 碱性浸出试验结果Table 5 Results of alkaline leaching 下载原图

Mineral:size-0.074 mm 86.5%;Mn 3.44%,Cu 0.40%,Fe 40.81%;150 g
表5 碱性浸出试验结果Table 5 Results of alkaline leaching
表6 褐铁精矿预处理后的氰化浸出试验结果Table 6 Results of cyanation after limonite pretreatment 下载原图
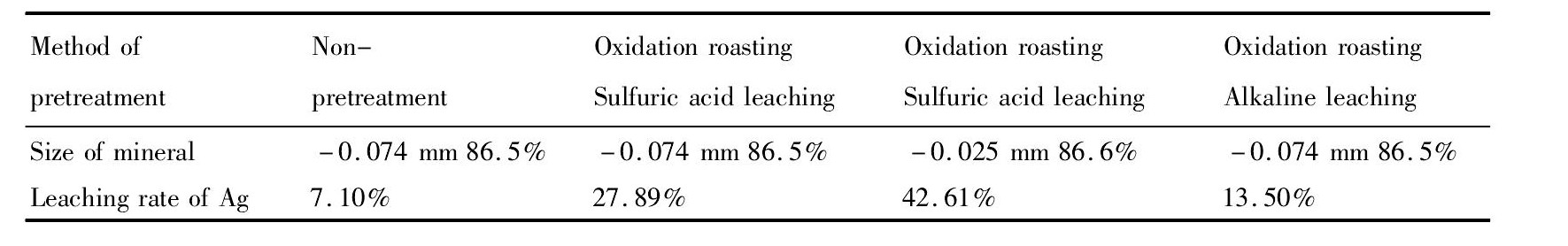
表6 褐铁精矿预处理后的氰化浸出试验结果Table 6 Results of cyanation after limonite pretreatment
3结论
1.某含金银褐铁矿的工艺矿物学研究表明:该矿主要为褐铁矿;铁、铜、锌、铅、锰元素主要呈氧化物形式均匀分布在褐铁矿中。
2.采用焙烧对该矿进行预处理,在温度650℃,保温2 h下焙烧,褐铁矿全部转化为赤铁矿,黄铁矿全部氧化了。
3.采用硫酸对焙烧渣进行了浸出实验研究,通过实验最佳浸出工艺条件为:在室温下,采用浓度1.5 mol·L-1的硫酸溶液、液固比4∶1、浸出4 h下浸出,铁、铜的浸出率分别为:4.16%,42.26%,较好地选择性除铜;铁的品位提高到44.03%,为下一步铁的回收打下了基础。
4.将氧化焙烧-酸浸预处理后的矿物与未处理矿物和氧化焙烧-碱性浸出预处理进行氰化浸出试验对比,银浸出率分别为42.61%,7.10%,13.50%;研究结果表明:通过氧化焙烧-酸浸预处理工艺不仅可以回收铜、铁等有价元素,还可以将银的回收率分别提高35%。
参考文献