添加剂在四氯化钛气相氧化过程中的作用机制
锦州钛业有限公司
摘 要:
以气态四氯化钛为前躯体,水蒸气、三氯化铝和氯化钾为添加剂,采用高温气相氧化法制备出金红石型二氧化钛超细粉。通过热力学计算、X射线衍射(XRD)、粒度分析、扫描电镜联用X射线光电子能谱(SEM-EDX)等方法研究了水蒸气、三氯化铝和氯化钾在气相反应过程中的作用机制及二氧化钛粒子的形成过程。结果表明,水蒸气起到了成核剂的作用,它与四氯化钛及三氯化铝反应生成的相应氧化物提供了气相反应所需的晶核;三氯化铝作为晶型转化剂的同时,在改善二氧化钛表面状态等方面起到了重要作用;氯化钾是一种离子剂,它的加入提高了二氧化钛粉体的分散性,获得了均匀的粒度分布,细化了晶粒,改变了粉体的消色力。随着氯化钾加入量的逐渐提高,二氧化钛的消色力随之增加,当氯化钾的加入量在(100~120)×10-6时,消色力达到125%。研究同时表明,气相反应中二氧化钛微粒的形成过程可以分为:非均相成核—表面作用与晶型转化—颗粒长大与静电作用等基元步骤。
关键词:
中图分类号: TQ134.11
作者简介:吕滨(1982-),男,辽宁沈阳人,硕士;研究方向:微纳米材料;于学成(E-mail:yuxc@jzthj.com);
收稿日期:2012-03-23
基金:国家自然科学基金资助项目(50672014);
Mechanism of Additives in Vapor Phase Oxidation Process of Titanium Tetrachloride
Abstract:
Ultrafine rutile titanium dioxide powders were synthesized by a vapor oxidation process using titanium tetrachloride as a precursor and water vapor,aluminum trichloride,potassium chloride as additives.The mechanism of water,aluminum trichloride and potassium chloride in vapor phase oxidation process,and the formation course of titanium dioxide were analyzed by thermodynamic calculation,X-ray powder diffraction(XRD),particle size measurement and scanning electron microscopy with X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy(SEM-EDX).Water vapor could be called a nucleant agent here.It provided the crystal nucleus via reaction with titanium tetrachloride and aluminum trichloride.Aluminum trichloride also played an important role in phase transformation and surface shape of titanium dioxide.The adding potassium chloride adjusted the tinting strength of titanium dioxide for improving its dispersed property and particle size distribution size as an ionizing agent.The tinting strength of titanium dioxide increased with adding amount of potassium chloride.When the amount of potassium chloride was(100~120)×10-6 based on titanium dioxide,the tinting strength of titanium dioxide reached 125%.The formation course of titanium dioxide in vapor oxidation process included heterogeneous nucleation,surface action,phase transformation,grain growth,electrostatic interaction,etc.
Keyword:
vapor phase oxidation; titanium dioxide; rutile; chloride route; tinting strength;
Received: 2012-03-23
TiO2被认为是目前世界上性能最好的白色颜料, 广泛应用于涂料、 塑料、 建材、 造纸、 印刷、 油墨、 化纤、 橡胶、 玻璃、 陶瓷、 环保、 日化、 电子、 照明、 医疗、 卫生、 包装等行业
TiO2的工业生产工艺主要有氯化法和硫酸法两种。 氯化法较硫酸法优势明显: 工艺流程短、 自动化程度高、 优质环保, 是钛白工业发展的趋势和方向。 但是由于氯化工艺的相对复杂和发达国家对该技术的封锁, 致使国内的研究比较落后。 作为氯化钛白的核心技术——气相氧化法中许多科学技术问题诸如: KCl, AlCl3和水蒸气的反应机制及其用量与氧化工艺的关系、 氧化产物最佳冷却方式、 高性能氧化反应装置的设计等均有待深入研究。
国内对气相反应过程中添加剂作用机制的观点有所不同。 一些学者认为
关于TiCl4气相氧化法制备二氧化钛的工艺
1 实 验
1.1制备过程
在四氯化钛预热器内将TiCl4预热至500 ℃, 并使TiCl4发生相变(由液态变为气态); 在氧气预热器内将O2预热至900 ℃。
将预热后的O2通入自制高速气流结合岩盐除疤式氧化反应器内, 利用甲苯燃烧放出的热量将热氧二次预热, 同时通入预热后的TiCl4气体使之发生气相氧化反应。 反应物TiCl4∶O2约为4∶5, 反应区温度约为1800 ℃, 绝压0.44 MPa。 再加入2.6%(占TiO2的量)的气态AlCl3(由Al粉与Cl2反应制得)和不同浓度的KCl溶液, KCl溶液流量用计量泵控制, 通过喷枪加入至氧化反应器中的氧气预热室(以氮气为载气)。 气相反应结束后生成的TiO2经冷却、 袋滤器收料制得。
1.2粉体的表征
采用XRD衍射仪(XD-610)测定TiO2的晶型, 通过XRD分析软件测试金红石型TiO2的晶型转化率; 利用 SEM(SSX-550Q)观察粉体的形貌, 然后用EDX分析粉体中铝元素含量; 以日本WinRoof图像分析软件统计SEM图片中TiO2颗粒的粒度; 通过粒度分析仪(Mastersizer 1000)测定TiO2的粒度分布; 采用GB 5211.16标准, 以蓝浆作展色剂, 用比色法测定TiO2的消色力。
2 结果与讨论
TiO2有3种晶型, 即板钛型、 锐钛型和金红石型。 其中板钛型属于斜方晶系且是不稳定的晶型, 而锐钛型和金红石型都属于四方晶系但晶体结构不同
2.1水蒸气和AlCl3蒸气在气相反应中的作用
实验中添加的AlCl3蒸气在反应中起到了晶型转化剂的作用
李晋林等
TiCl4(g)+2H2O(g)→TiO2(s)+4HCl(g) (2)
TiCl4(g)+O2(g)→TiO2(s)+2Cl2(g) (3)
2AlCl3(g)+3H2O(g)→Al2O3(s)+6HCl(g) (4)
表1TiCl4和AlCl3在气相反应中自由能与温度的关系
Table 1Relationships between ΔG and T of vapor phase reaction of TiCl4and AlCl3
Reactions |
ΔG/(kJ·mol-1) |
||||||||
1000 K |
1200 K | 1400 K | 1600 K | 1700 K | 1800 K | 1900 K | 2000 K | 2100 K | |
(2) |
-163.89 | -184.57 | -205.70 | -227.12 | -241.94 | -248.94 | -264.50 | -271.14 | -287.29 |
(3) |
-108.50 | -94.45 | -80.66 | -67.13 | -64.17 | -53.86 | -21.69 | -40.90 | -39.41 |
(4) |
-131.86 | -126.45 | -121.58 | -117.06 | -115.54 | -112.97 | -111.61 | -109.22 | -108.11 |
(5) |
-62.12 | -25.02 | 11.68 | 48.04 | 65.72 | 84.09 | 101.51 | 119.85 | 137.02 |
(2):TiC l4(g)+2H2O(g)→TiO 2(s)+4HCl(g);(3):TiC l4(g)+O2(g)→TiO 2(s)+2Cl2(g);(4):2AlC l3(g)+3H2O(g)→Al2O3(s)+6HCl(g);(5):2AlC l3(g)+3/2O2(g)→Al2O3(s)+3Cl2(g)
2AlCl3(g)+3/2O2(g)→Al2O3(s)+3Cl2(g) (5)
从表1的Ti-Al-H-O-Cl五元素体系自由能与温度的关系可见, (2), (3), (4)式的ΔG值均为负值, 在气相反应中都能生成相应的氧化物; 而(5)式的ΔG值在温度高于1400 ℃以上时均为正值, 故在高温气相反应中(5)式不可能发生。
比较(2), (3), (4)式的ΔG值可知, 反应依次按照(2), (4), (3)进行。 在高温气相过程中, TiCl4蒸气首先按照(2)式与水蒸气反应生成TiO2, 然后AlCl3按照(4)式反应生成Al2O3, 这两种反应产物都是极其微小的, 具有较大的表面能和较高的活性, 提供了反应所需的晶核。 最后, TiCl4按照(3)式发生氧化反应, 生成的TiO2在晶核周围长大。 所以, 称为成核剂的应该是水蒸气, 单一的称AlCl3为成核剂是片面的。
采用EDX测试TiO2微粒中的Al含量。 在靠近其核心区域(非正中心)的Al元素的质量分数约为0.53%(表2), 而在TiO2粒子周围未检测出Al元素的存在。 可见, EDX的分析结果和热力学行为的分析结果是一致的。
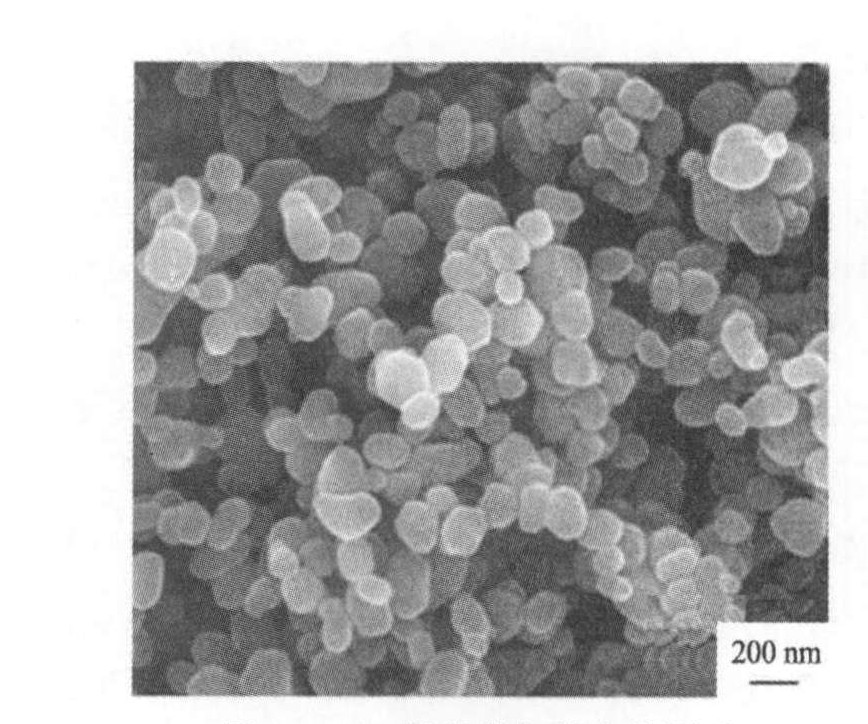
图1为TiO2微粒的SEM图片。 可以看出TiO2近似球状, 这是由于AlCl3的存在改善了TiO2的表面状态, 防止颗粒沿某一晶面定向长大, 使颗粒成球形
表2靠近TiO2核心区域的元素含量
Table 2Content of elements near core area of TiO2
Elements |
Ti | Al | O | Total |
Content/(%, mass fraction) |
59.40 | 0.53 | 40.07 | 100.00 |
图1 TiO2微粒的扫描电镜图片
Fig.1 SEM micrographs of titanium dioxide
所以, 氯化钛白气相反应的实质是: 在高温高速的状态下TiCl4及AlCl3与水蒸气反应生成的氧化物晶核均匀的分散并相互碰撞, AlCl3在改善TiO2的表面状态的同时作为晶型转化剂将TiO2晶核转化为金红石型, 然后TiCl4与O2反应生成的TiO2在此晶核上附聚、 长大, 形成同种晶型的TiO2。
2.2KCl在气相反应中的作用
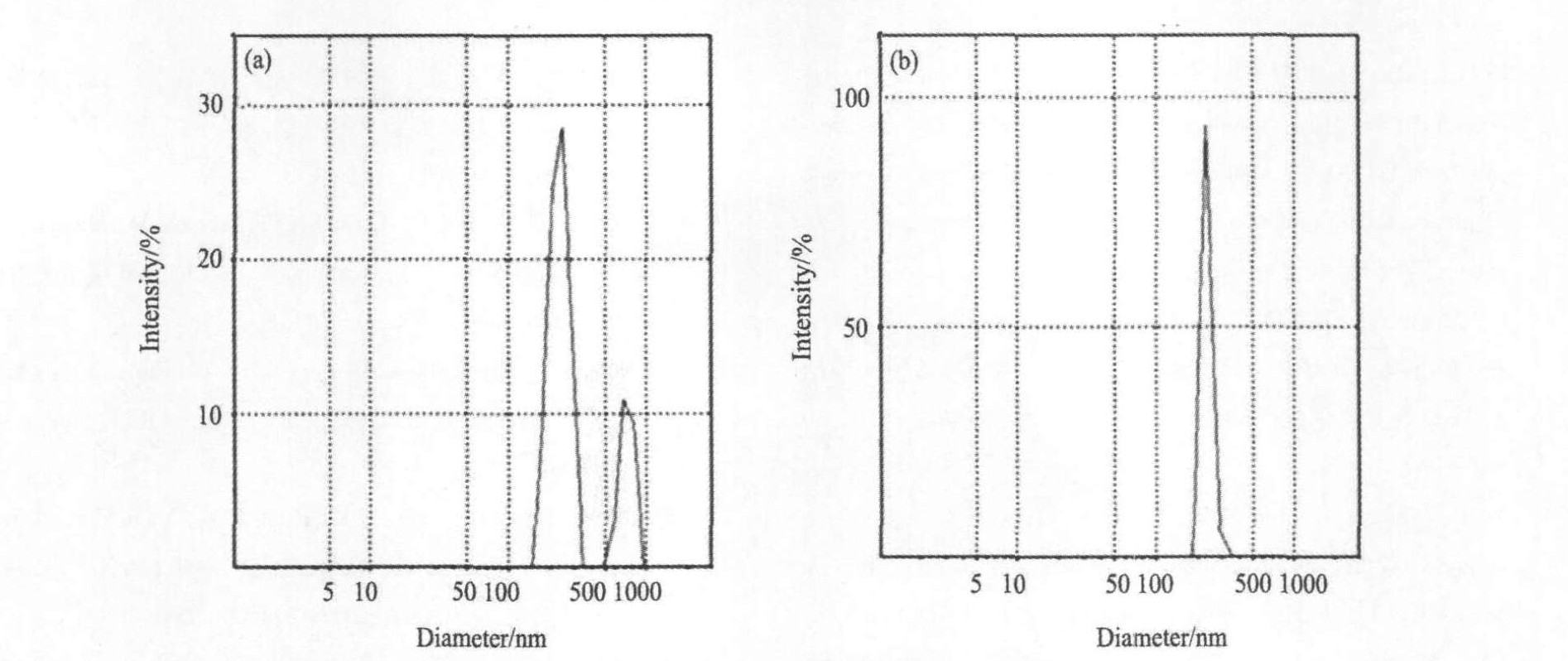
图2(a)表示的是未加KCl制备的TiO2的粒度分布图。 可以看出, TiO2的粒度分布不均匀, 含有约21%的大颗粒TiO2, 平均粒度为269 nm; 图2(b)给出的是加入100×10-6(相对TiO2的质量)的KCl所制备的TiO2的粒度分布图。 可以看出, 颗粒粒度分布窄, 平均粒度为255 nm。
本实验使用的KCl不仅无毒无害、 价格低廉, 而且它的加入不会降低TiO2的白度、 亮度和色调
图2 TiO2的粒度分布 (a) 未加KCl (b) 添加KCl的量为100×10-6
Fig.2 Particle size distribution of titanium dioxide (a) without KCl (b) adding 100×10-6 KCl based on TiO2
2.3KCl与消色力之间的关系
消色力是颜料对光的吸收和散射的结果。 由于TiO2是一种白色颜料, 对光的吸收非常小, 不像有色颜料, 光的吸收起着重要的作用, 因此TiO2的消色力主要取决于它对可见光的散射能力, 散射力越大, 消色力越高。
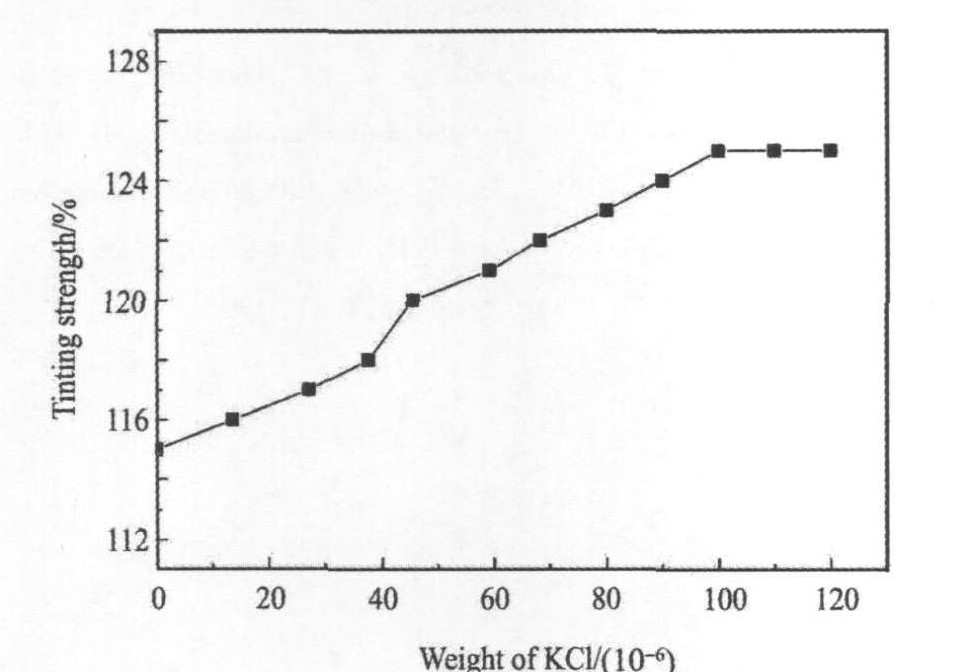
图3给出了KCl的加入量与消色力之间的关系。 可以看出, 不添加KCl的TiO2的消色力较低, 仅为115%。 消色力随着KCl加入量的增加而提高, 当KCl加入量增加至(100~120)×10-6时, 消色力达到较高值125%, 这说明TiO2的消色力受粒度、 粒度分布和分散性的影响较大。 另外, 由于TiO2粒度与消色力成正态分布
图3 KCl加入量与消色力之间的关系
Fig.3 Relationships between tinting strength and additive amount of KCl based on TiO2
综上所述, 本实验中TiO2微粒的形成过程可以分为: 非均相成核—表面作用与晶型转化—颗粒长大与静电作用等基元步骤。
3 结 论
1. 以前提出的气相氧化过程中的成核剂是KCl或AlCl3是不成立的。 热力学计算和EDX分析的结果表明, 作为晶核的应该是与水蒸气反应生成的TiO2和Al2O3, 可称之为成核剂的是水蒸气。
2. AlCl3作为晶型转化剂的同时, 改善了TiO2的表面状态, 使颗粒呈球状。
3. KCl是一种离子剂, 它的加入提高了粉体的分散性, 获得了均匀的粒度分布, 细化了晶粒, 可以调节粉体的消色力。
参考文献