网络首发时间: 2019-01-28 07:00
稀有金属2019年第3期
地浸采铀溶质运移研究进展及展望
李衡 周义朋
东华理工大学水资源与环境工程学院核资源与环境国家重点实验室
摘 要:
地浸采铀相较于传统采铀方法具有低成本、绿色环保、人员需求少等优点, 目前已在全世界采铀行业得到了广泛应用。溶质运移是地浸采铀中研究的关键问题, 了解并掌握地浸采铀中溶质的运移机制, 对于提高铀的浸出效率有着重要意义。首先对地浸采铀溶质运移机制和运移方式的研究进行了综述, 并分别总结了研究溶质运移机制和运移方式对于提高铀浸出效率的意义;其次重点分析了近年来国内外研究人员在地浸采铀反应性溶质运移和多场耦合模型方面相关研究进展, 阐述了地浸溶质运移的复杂性以及研究过程中所面临的挑战。最后综合已有研究, 认为现阶段地浸采铀溶质运移缺少对微观机制、气液固三相反应运移以及尺度转换问题的研究, 且耦合模型也有待进一步完善。对于上述4个问题, 文章有针对性地提出了下一步研究方向的展望建议。
关键词:
地浸采铀 ;溶质运移 ;反应运移 ;运移模型 ;
中图分类号: TD868
作者简介: 李衡 (1993-) , 男, 安徽阜阳人, 硕士研究生, 研究方向:溶浸采铀, E-mail:136909086@qq.com; *周义朋, 副教授;电话:15276358273;E-mail:zyp721@163.com;
收稿日期: 2018-12-16
基金: 国家自然科学基金项目 (41572231); 国家重点基金研究发展计划 (973) 项目 (2015CB453002); 江西省科技计划项目 (20142BFB29004, 20151BBB60093) 资助;
Progress and Prospect of Research on Solute Transport during In-Situ Leaching of Uranium Li Heng Zhou Yipeng
State Key Laboratory of Nuclear Resources and Environment, School of Water Resources & Environmental Engineering, East China University of Technology
Abstract:
Compared with traditional uranium mining methods, in-situ leaching uranium mining has the advantages of low cost, environmental protection and less personnel demand, which has been widely used in the uranium mining industry all over the world. Solute transport is a key problem in the study of in-situ leaching of uranium mining. It is of great significance to improve uranium leaching efficiency to understand and master the transport mechanism of in-situ leaching of uranium mining. Firstly, studies on the transport mechanism and transport mode of solute transport of in-situ leaching uranium mining were reviewed in this paper. And the significance of studying solute transport mechanism and transport mode for improving uranium leaching efficiency were summarized. Secondly, the research progress of reactivity solute transport and multi-field coupling model of in-situ leaching uranium mining were emphatically analyzed by researchers at home and abroad in recent years. The complexity of solute transport and the challenges in the research process were described. At last, based on the existing research, it was found that the solute transport of in-situ leaching of uranium mining lacked the research on microcosmic mechanism, gas-liquid-solid three-phase reaction transport and scale conversion, and the coupling model needed to be further improved at this stage. For the above four questions, the article put forward the prospect of recommendations the next step of research direction.
Keyword:
in-situ leaching uranium mining; solute transport; reactive transport; transport model;
Received: 2018-12-16
地浸采铀是一种在天然埋藏条件下, 通过浸出剂与矿物的化学反应选择性地溶解矿石中的铀, 并提升至地表进行回收的集采、 冶于一体的新型铀矿开采方法
[1 ]
。 20世纪60年代早期美国和前苏联都进行了地浸采铀试验性研究, 并实现工业化应用
[2 ,3 ,4 ,5 ,6 ]
。 地浸采铀不需井巷工程、 生产成本较低、 对地表生态环境破坏小、 能适应于低品位铀矿开采, 已成为国际上一种重要的采铀方法。 据国际原子能机构统计, 2017全世界砂岩型铀矿占总铀矿床的32.4%
[7 ]
, 2015年地浸生产的铀占铀总产量的49%
[8 ]
。 20世纪70年代, 我国开始对地浸采铀工艺进行探索性试验, 于80年代后期掌握了酸法浸出工艺, 进入21世纪后, 我国又先后掌握了碱法和CO2 +O2 的中性浸出工艺, 现在我国已经建立了多座地浸铀矿山
[9 ,10 ,11 ,12 ]
。 近年来在新疆、 内蒙古千吨级产能地浸大基地的建设, 已完成从过去常规粗放开采到地浸绿色开发的转型升级, 目前地浸产能占比达到60%以上
[13 ]
, 预计到2020年地浸将占国内天然铀产能的90%以上
[14 ]
。
铀的原地浸出是一个典型的溶质运移问题
[15 ]
, 铀迁移过程涉及氧化-还原、 溶解-沉淀、 络合-离解、 吸附-解吸等复杂水文地球化学作用
[16 ]
, 因而呈溶解-迁移-沉积-再溶解的“滚动式”迁移。 复杂的地下水动力场和水文地球化学作用控制着溶质运移的速度、 强度和状态, 而溶质的运移及其浓度的变化则揭示地浸体系的水动力特征和水文地球化学过程
[17 ,18 ]
。 研究地浸过程中溶质的运移特征和组分的变化, 对于了解和掌握地浸溶质的运移规律、 矿层的酸化氧化进程以及发生的水岩作用都具有很重要的意义, 并以此对工艺参数进行有针对性的调整和优化, 以达到提高生产效率的目的
[19 ,20 ]
。 大量试验性研究和地浸生产实践为开展地浸采铀溶质运移研究提供了理想的条件, 并取得了丰富的成果。 本文将从地浸溶质运移机制、 运移方式、 反应性溶质运移以及溶质运移多场耦合模型4个方面介绍其近些年来的研究进展, 并提出了现阶段有待解决的问题和展望建议。
1 地浸溶质运移机制的研究
柱浸和管浸试验 (又称渗滤浸出试验) , 是研究溶质运移重要的室内试验方法
[21 ]
, 目前有关浸铀溶质运移机制的研究也主要基于这些方法。 地浸溶浸液是在饱水的含水层中运动, 有学者认为水平一维流管状模拟试验比垂向柱浸试验更接近地浸条件
[22 ]
。 高柏等
[18 ,23 ]
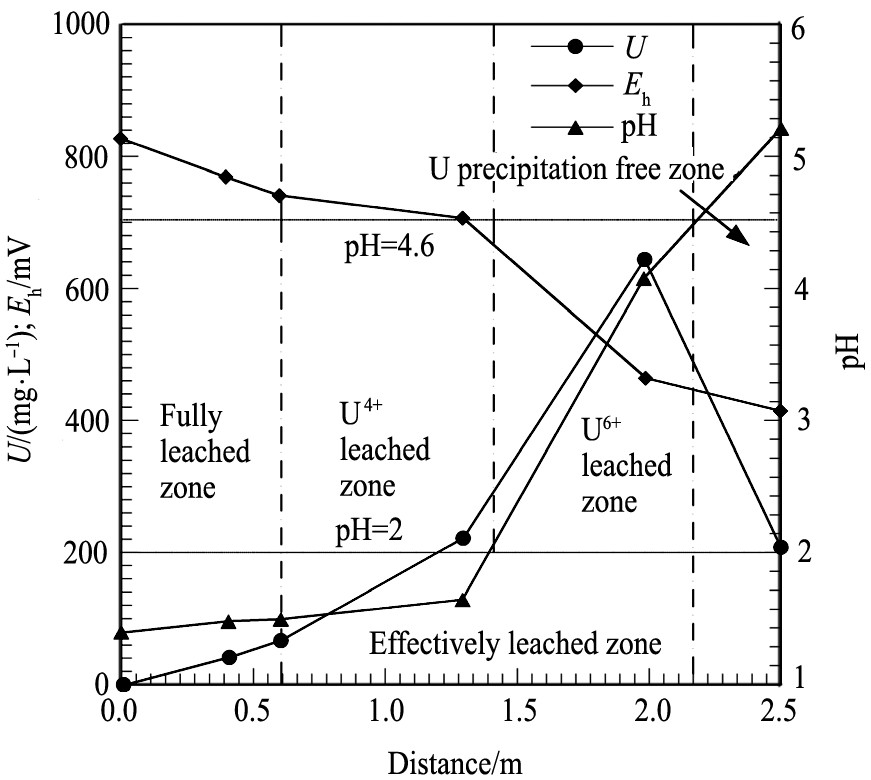
利用管浸试验对酸法地浸中铀的迁移规律进行了研究, 结果表明铀在迁移过程中经历了溶解-沉淀-再溶解的多次旋回。 铀的迁移路径如图1所示, 可划分出充分浸出带、 有效浸出带、 铀沉降带和未浸出带, 每个带都随浸出时间的变化向出液端顺序推移, 浸出结束时整个迁移路径都变为充分浸出带。 而后, 史维浚等
[24 ]
引入溶质迁移面的概念, 探讨了地浸过程溶质的运移机制和发生的水文地球化学作用, 将浸出体系细分为六个带: 铀未浸出带、 六价铀浸出带、 六价铀沉淀带、 次生六价铀化合物溶解带、 四价铀溶解带以及铀完全浸出带, 并指出pH=2.0和E h =700 mV是与铀的浸出运移关系密切的最重要的、 关键性的两个特征性迁移面。 上述研究均基于酸法的地浸工艺, 对于其研究成果是否适用于碱法和CO2 +O2 中性浸出工艺, 还有待探讨。
在碱法地浸试验中, 邢拥国等
[25 ]
将浸出过程分为矿层预氧化、 CO2 +O2 中性浸出及CO2 +O2 +NH4 HCO3 浸出3个阶段, 并指出HCO- 3 是控制溶质 (铀) 运移的关键因素, 且最佳HCO- 3 质量浓度为800 mg·L-1 。 张青林和丁德馨
[26 ]
在CO2 +O2 中性柱浸试验中指出CO2 和O2 对pH和E h 的调节作用对于维持溶质的运移效率至关重要, 其中较高E h 保证了铀元素处于溶解状态, 适当的pH不仅可以保证铀酰离子与HCO- 3 和CO
3
2
-
的有效络合使之浸出, 而且将pH控制在6.6以下还可以有效抑制溶质在运移过程中方解石和白云石的生成。
有关地浸溶质运移机制的研究可以对铀的浸出率、 E h , pH以及各种溶质浓度随时间的变化趋势进行模拟预测。 通过分析氧化剂和浸出剂的消耗量、 浸出液中各种溶质的浓度、 溶浸液的E h 和pH等对铀运移效率的影响, 确定采用何种地浸工艺开发特定铀矿山的可行性及合理的工艺参数。
图1 迁移路径与浸出带关系 (t=64 h)
Fig.1 Relationships between leached zone and migration-path (t =64 h)
[18]
2 溶质迁移方式的研究
溶质在地下水系统中的迁移方式主要有分子扩散迁移、 对流迁移和机械弥散迁移
[27 ]
。 地浸采铀水岩体系也不例外。
分子扩散迁移是基于布朗运动的一种现象, 其在地层中进行得很缓慢, 迁移的距离也是有限的。 徐存东
[28 ]
认为在研究大水体的水环境问题分子扩散可以不考虑, 因为其量级远小于其他因素引起的溶质迁移量级。 周锡堂等
[16 ]
通过研究地浸采铀元素的迁移与沉淀, 认为地浸采铀过程中一个开采单元浸出周期一般仅几年, 时间很短, 因此分子扩散对溶液中元素的迁移所引起的作用不大, 一般可以忽略。 但刘正邦等
[29 ]
通过研究地浸溶质运移的特性, 指出死端孔隙矿石有效浸出主要依赖于分子扩散迁移。 尹升华和吴爱祥
[27 ]
通过分析微生物浸出过程溶质运移及其影响因素, 认为分子扩散迁移是微生物浸出的一个重要过程, 反应物到达浸出反应界面和生成物离开反应界面进入地下液流均需通过分子扩散迁移才能实现。
溶质随水流一起迁移的运动称为对流迁移, 这通常是引起溶质迁移的主要方式, 在铀矿地浸过程中铀酰离子就是依靠井场抽注所形成的对流场进行迁移, 进而从含矿含水层运移到地面。 谢廷婷等
[30 ,31 ]
研究了地浸采铀对流弥散场特征, 认为提高井场流量, 可以增强井场抽注井间的水力交换, 从而加快溶质运移速度, 提高浸出效率。 李兵等
[32 ]
通过分析钻孔抽注液量增大对浸出液铀浓度的影响, 发现注液量的增加有助于提高浸出液铀浓度, 并指出对流迁移是地浸采铀时溶质的主要迁移方式。
溶浸液通过多孔介质流动时, 其流速的分布较为复杂且不均一, 这与孔隙的大小形态和连通情况有关。 由于溶浸液流速不均匀造成的物质运移现象称为机械弥散。 地浸结束后, 含矿含水层中地下水流动系统从较强的抽注流场逐渐恢复至弱的天然流场, 这时溶质在地下水系统中的运移以机械弥散迁移为主
[33 ]
, 而基于机械弥散的溶质迁移是当前涉及地浸采铀所产生的环境问题方面研究的热点
[34 ,35 ,36 ,37 ]
。
溶质在多孔介质中运移时, 以上3种运移方式均同时出现, 各种迁移方式所占比例主要与流速有关。 3种迁移方式在地浸体系中所起作用的大小可以用Peclet数来判别
[38 ]
:
Ρ
e
=
v
d
D
d
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
(
1
)
式中, v 为实际平均流速, m·s-1 ; d 为多孔介质的某种特征长度 (如多孔介质的平均粒径等) , m; D d 为分子扩散系数, m2 ·s-1 。
在一定的地下水流动系统中, D d 基本近似于常数。 含水介质一定后, d 也近似于常数。 则Pe 与v 可以近似成正比。 若v 很小时, Pe 也很小, 溶质以分子扩散迁移为主; 若v 很大时, Pe 也很大, 溶质则以对流迁移为主, 相对来说分子扩散迁移占比很小。 Perkins和Johnston
[39 ]
认为, 当Pe <2×10-2 , 溶质的分子扩散迁移占优; 当Pe >5时, 对流迁移占优; 当2×10-2 <Pe <5时, 机械弥散迁移和分子扩散迁移均起作用。
3 反应性溶质运移的研究
溶质在含矿含水层中的运移性质会受到各种化学反应的影响
[40 ]
, 如氧化-还原、 络合-离解、 溶解-沉淀、 吸附-解吸以及酸碱反应等作用。 因此, 研究地浸采铀反应性溶质运移, 对揭示溶质运移规律是非常有意义的。
砂岩中铀矿物主要以四价形式存在, 不能与含碳酸盐的溶剂或酸性溶剂直接作用, 浸出前应预先被氧化成六价铀, 再利用含矿含水层中的SO
4
2
-
, HCO- 3 和CO
3
2
-
与之络合浸出, 因此将四价铀氧化为六价铀是保证铀元素进入地下水流进行运移的前提。 苏学斌等
[41 ]
评价了新疆某铀矿床使用氧气预氧化矿层的可行性, 其室内搅拌浸出和柱浸试验获得了约40%的浸出率, 后期采用CO2 + O2 强化浸出, 取得了近60%的浸出率。 焦学然等
[42 ]
对地浸所使用的氧化剂过氧化氢氧化性能进行研究, 结果表明: 当加入溶解氧总量为600 mg·L-1 时, 铀浸出效果较好, 铀浸出率大于71.33%。 周义朋等
[43 ]
探讨了酸性含Fe3+ 溶液作用下铀的溶解迁移特征, 结果表明: 在Fe3+ 的氧化作用下, 铀自矿石向溶液中迁移在10 h内达到平衡, 且最佳浓度为2 g·L-1 。
溶质在运移过程中的沉淀作用会引起矿层的化学堵塞, 这极大影响了生产效率。 李坡等
[44 ]
在分析某铀矿床酸法地浸过程中酸耗高、 浸出液铀浓度低时, 认为如果浸出液的pH长期维持在2.5左右, 会导致溶质在运移过程中生成铁、 铝氢氧化物的沉淀, 进而堵塞矿层。 Liu等
[45 ]
研究了碱法地浸中影响碳酸钙溶解沉淀的3个重要因素: Ca2+ , HCO- 3 和pH, 结果表明: 3个因素相互之间呈反相关关系, 限制溶浸液的钙离子浓度、 pH、 碳酸氢根含量在其边界值以内, 确保碳酸钙不发生沉淀的前提下, 尽可能地提高浸铀效率。 从表1可以看出铀浓度与碳酸氢根浓度呈明显的正相关关系, 因此在地浸过程中可以将碳酸氢根浓度适当提高。 许根福
[46 ]
在分析CO2 +O2 中性地浸主要工艺参数及化学沉淀堵塞问题时, 指出水温的升高、 pH值的升高和水中CO2 含量的降低均会促使碳酸盐沉淀生成。
地浸过程生成的铁、 铝、 铀氢氧化物沉淀和碳酸钙沉淀, 不仅堵塞溶质运移的通道, 而且它们对六价铀的吸附作用同样会制约铀的运移效率。 如Bi等
[47 ]
及Johnson和Tutn
[48 ]
的研究表明氢氧化铁沉淀对六价铀的吸附作用会减缓铀的迁移速率从而影响铀的浸出。 Ma等
[49 ]
和Dangelmayr等
[50 ]
的研究则证明了方解石的分布和钙离子的浓度对铀的吸附和反应运移有着重要影响。
砂岩型铀矿中存在较多的粘土矿物, 这些粘土矿物具有很强的吸附能力, 会对地浸过程中铀酰离子的运移产生重要影响。 如修晓茜和张玉燕
[51 ]
在比较不同粘土矿物对铀元素的吸附容量试验中表明, 蒙脱石对铀酰离子的吸附率最大, 其次是伊利石和高岭石。 Nair等
[52 ]
通过柱试验研究了SiO2 , Al2 O3 , TiO2 和FeOOH矿物的吸附作用对铀酰离子的迁移影响, 得出上述矿物对铀酰离子的吸附效力顺序为FeOOH>TiO2 >Al2 O3 >SiO2 。 此外, 硅元素在矿物岩石中大量存在, 其对铀的吸附也不容忽视。 为此, 徐辉等
[53 ]
曾单独探讨过衍生硅胶 (主要成分为SiO2 ) 对铀的吸附性能, 结果表明: 衍生硅胶对铀的吸附与溶液的pH密切相关, 而固液比、 离子强度对吸附效果影响不大, 吸附过程符合Langmuir等温吸附模型和准二级吸附动力学模型。
表1 碳酸钙析出的条件以及相应的铀浓度
Table 1 Calcium carbonate precipitation conditions and corresponding uranium concentration
[45 ]
Experiment
pH
Ca2+ -1 )
HCO- 3 -1 )
U -1 )
6.66
356
1060
95
6.66
138
1200
108
6.90
120
1700
120
6.90
240
850
84
6.90
210
975
93
6.94
258
760
78
酸法地浸之前不仅要对矿层预氧化, 同时也要对矿层进行酸化, 以此避免溶质在运移过程中铁、 铝氢氧化物沉淀的生成。 黄群英等
[19 ,20 ]
分析了某砂岩型铀矿酸法地浸溶质运移与酸化进程的关系, 结果表明: 注液SO
4
2
-
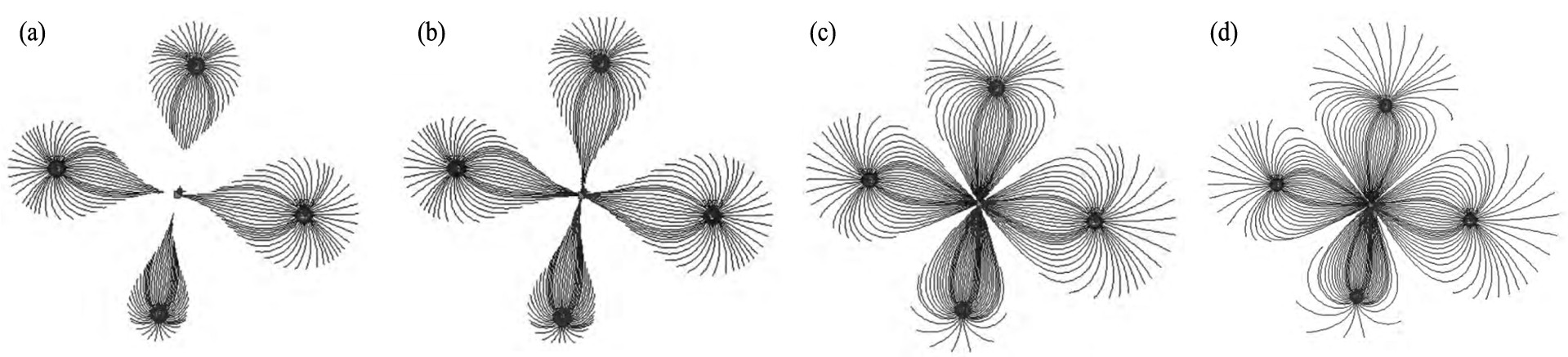
最快8 d抵达抽液孔, 40 d形成由注液控制的稳定对流场; H+ 最快21 d抵达抽液孔, 66 d实现地浸体系H+ 补给与消耗趋于平衡, 稳定的酸性环境逐渐形成; Fe2+ , Fe3+ 与H+ 的运移保持同步, Fe3+ 因水解和还原作用, 在地浸酸化过程中呈溶解-沉淀-再溶解的滚动运移, 并被部分还原为Fe2+ 。 图2展示了酸浸初期溶液渗流随时间的变化趋势, 以“四注一抽”单元井场为例。
地浸采铀是一个水化学场与水动力场耦合的复杂水岩相互作用过程, 地下对流场与溶质组分的变化存在十分密切的关系。 溶质在含矿含水层中的运移不仅会受到对流、 弥散、 扩散等物理作用的影响, 还受到各种化学反应的影响。 因此, 研究地浸溶液注入矿层后的反应运移, 对于工艺参数的针对性调整具有重要意义。
4 溶质运移多场耦合模型的研究
地浸采铀溶质运移涉及许多因素与过程的耦合和反馈作用, 主要有溶浸剂的流动、 浸出液组分的扩散、 水岩相互作用以及作为源汇项处理的各种化学反应与衰变等引起的岩石变形作用、 孔隙度与渗透率的动力演化等
[54 ]
。 传统的溶质运移模型只考虑了对流弥散作用, 未能系统地考虑多种耦合作用的影响。 近年来国内外学者对这一典型的溶质运移进行了有针对性模拟研究, 建立了不同复杂程度的耦合模型, 如对流弥散+吸附, 对流弥散+化学反应, 对流弥散+应力场等。
图2 不同时间溶浸液渗流迹线图
Fig.2 Pathlines of leaching solution flow at different time
[20]
(a) 6th day; (b) 7th day; (c) 40th day; (d) 66th day
国内早期的地浸溶质运移模拟与传统溶质运移模拟无异, 只包含对流弥散作用, 其结果大多只是定性反映溶质的运移特征, 主要存在模拟精度不够高, 与实际情况存在较大偏差, 实用性不强等问题
[55 ,56 ,57 ]
。
固体岩石矿物对溶质的吸附作用是溶质运移过程中一个不可忽略的因素。 Greskwiak等
[58 ]
模拟了非开采条件下的六价铀在不同水化学条件下的多速率非平衡吸附反应运移。 焦友军等
[59 ]
利用PHT3D
[60 ]
模拟比较了六价铀吸附反应运移表面络合模型、 线性吸附等温线模型及Langmuir吸附等温线模型, 结果表明: 表面络合模型更接近实际中多变水化学条件下的吸附。 Li和Zhou
[61 ]
研究了地浸采铀溶质运移的特性, 并通过分析对流、 分子扩散、 机械分散和吸附等作用对溶质的运移和分布的影响, 推导出溶质运移过程中对流-扩散-吸附反应的基本方程。 Johnson等
[62 ]
利用柱试验和广义综合表面络合模型确定了拟建地浸采场铀的吸附参数, 并用以指导后续的生产工作。
地浸过程中包含了各种化学反应, 实际上地浸整个过程都是基于多孔介质中的反应性流体循环, 如何将这些化学反应耦合到地浸溶质运移模型中, 一直是国内外学者研究的热点问题。 Schmidt
[63 ]
为了模拟碱法地浸现场操作条件以及优化井场设计, 建立了一个较为复杂地浸耦合模型, 该模型耦合了溶质运移模型、 氧化速率模型和水动力模型3个部分。 Bommer和Schechter
[64 ]
对这方面也进行一定的研究工作, 并且对矿物的选择性氧化和影响地浸反应速率的因素进行了探讨。 Liddell和Bautista
[65 ,66 ,67 ]
在使用NH4 HCO3 - (NH4 ) 2 CO3 -H2 O2 溶液进行碱法地浸时, 通过使用部分均衡模型, 模拟了孔隙度、 溶质浓度和矿物间的转换变化, 其模拟结果强调了溶质运移和矿物反应耦合的重要性。 阙为民
[68 ]
建立的地浸采铀地球化学动力学模型耦合了溶质运移模型、 水动力模型和反应动力学模型, 并运用其分析井场流线的特征和评价矿床的水文地质条件。 Regnault等
[69 ]
建立了某地浸铀矿山的三维反应运移模型, 并以此量化地浸的关键过程, 优化矿石溶解速率和试剂的使用。 连国玺等
[70 ]
将GMS
[71 ]
与PHREEQC
[72 ]
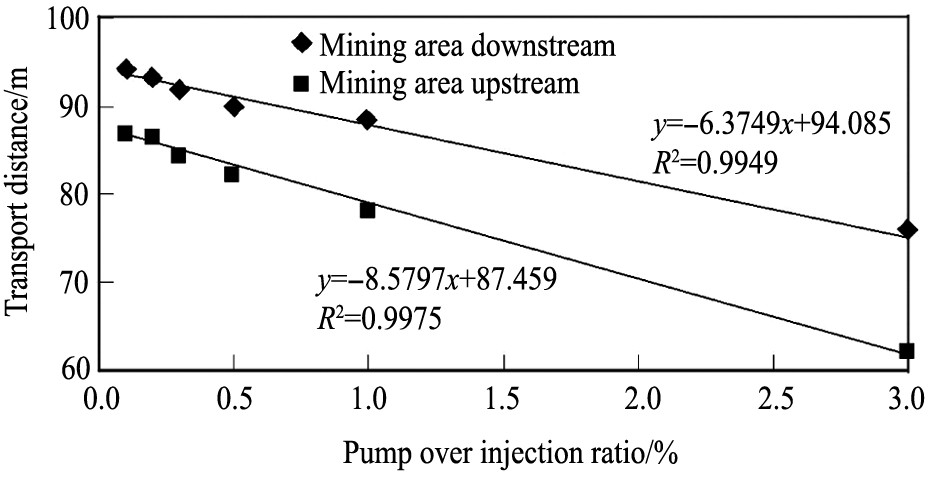
软件耦合对铀元素迁移扩散距离及浓度分布等进行模拟和分析, 其中GMS模拟溶质的对流弥散迁移, PHREEQ则模拟迁移过程中的化学反应, 结果表明: 在0.1%~3.0%的抽注比之间, 铀元素向上、 下游迁移的距离与抽注比大小呈显著的线性关系 (图3) 。
随着溶质的反应性运移, 采区的应力场会发生一定程度的改变, 如沉淀溶解作用会影响到岩石的渗透性, 使水动力条件发生变化。 谭凯旋等
[73 ,74 ]
[54 ]
又在此基础上进一步研究, 并建立了一个地浸采铀多因素、 多过程耦合的综合动力学反应运移模型, 对某地浸采区酸化、 生产、 溶浸末期各阶段的演化进行了模拟, 其结果较好地反映地浸的实际生产状况。 Bonnaud等
[75 ]
利用反应性运移代码HYTEC
[76 ]
模拟了地浸过程中由于注入高密度酸性溶液与矿层水的密度差所引起的溶质向含矿含水层底部进行的密度驱动运移, 并定量化描述了与密度驱动运移相关的铀和酸的损失部分。 最近, Simon等
[77 ]
创造性的将CHESS代码
[78 ]
和HYTEC代码耦合建立了室内柱浸试验动力学反应运移模型, 该模型耦合了水文地球化学模型与水动力模型, 并考虑了由于水文地球化学反应而导致溶浸体系孔隙度和渗透率的变化, 突破传统模型的局限。
图3 铀迁移距离与抽大于注比例的关系
Fig.3 Relation between uranium migration distance and pump over injection ratio
[70]
地浸采铀溶质运移是溶质运移研究领域一个较为复杂问题, 其面临着两个重要挑战: 强烈的化学反应和快速的地下水流, 这极大提高了对于该过程的建模与模拟难度。 因此, 建立多场耦合的综合动力学模型研究地浸溶质运移对于本领域的发展将具有推动作用。
5 存在的问题与展望建议
综上所述, 目前对地浸溶质运移的研究虽然取得了较大进展, 但仍有以下4个问题有待解决: (1) 就尺度而言, 大多数学者的研究均是基于宏观试验的结果, 缺少微观方面的研究; (2) 考虑到地浸溶质运移的复杂性, 其运移模型还有待进一步完善; (3) 气体的存在是地浸溶质运移中一个不可忽略的重要因素, 现阶段很少有学者考虑了气、 液、 固三相反应溶质运移; (4) 地浸溶质运移中尺度转换问题和研究方法的单一也是当前所面临的重要挑战。 因此, 研究地浸溶质运移仍需要进一步加强以下几个方面:
1. 地浸溶质运移的微观研究。 砂岩型铀矿的微观结构、 孔隙的连通情况、 颗粒表面电场以及其孔隙中溶浸液离子之间相互作用对溶质的运移都会产生重要影响
[79 ]
。 目前, 受到试验条件所限, 在孔隙度准确测定、 颗粒表面电场测定、 粒子微观特征观测等方面存在一定的技术困难, 因此需要在观测方法和技术上进行突破。 因此, 笔者认为在微观方面, 应基于砂岩型铀矿的微观结构和理化性质, 开展对各种水岩相互作用机制的研究; 近年来基于计算流体力学 (CFD) 方法、 晶格玻尔兹曼 (LB) 方法和光滑粒子流体动力学 (SPH) 方法的孔隙尺度直接建模以及双尺度介质 (包含微米和亚微米尺度的孔隙度) 建模方法的提出和发展
[80 ,81 ,82 ,83 ]
, 为研究微观状态下渗流模拟提供了途径。 由于微观研究对观测精度要求较高, 因此要注重对新技术的应用, 如纳米级孔隙度的FIB-SEM成像
[84 ,85 ]
、 纳米级孔隙度的小角中子散射 (SANS)
[86 ]
等。
2. 地浸溶质运移耦合模型的进一步研究。 在溶质运移理论模拟研究方面, 现阶段大多数学者对溶质的运移规律的描述只是在水动力弥散方程上进行了拓展; 将另一流体模式与定解条件下溶质运移方程耦合, 即组成了地浸采区溶质运移模型的控制方程。 但是该理论没有考虑各种反应因素对溶质运移的影响, 地浸采铀过程与流体在岩石孔隙中的流体动力学、 溶质迁移、 各种溶质相互反应的化学动力学和水岩相互作用密切相关, 是孔隙岩石中流体流动-反应的耦合过程。 因此, 运用该理论来模拟地浸过程显然是不太合适的。 由于种种原因, 国内这方面的研究工作起步较晚, 虽然也取得了一些研究成果, 但仍与国外有较大差距。 考虑到地浸采铀溶质运移的复杂性, 笔者认为多因素、 多过程相互影响耦合的综合动力学模型仍是未来的一个研究方向。
3. 气、 液、 固三相反应溶质运移的研究。 目前发生于固、 液两相之间溶质的运移、 吸附和反应是地浸溶质运移研究的主要内容, 而气、 液、 固三相在溶质运移研究中常被忽略。 地浸采铀时, 随着溶浸液的注入含矿含水层中的气体会急剧增高, 如酸法浸出过程中酸性溶液与碳酸盐反应生成的CO2 , 过氧化氢分解产生的O2 , 碱法和CO2 +O2 中性浸出注入含矿含水层中的CO2 和O2 等。 其中CO2 +O2 中性地浸则完全是由气体参与浸出, 因此研究气、 液、 固三相反应溶质运移对于CO2 +O2 中性浸出工艺的提升显得尤为重要。 近年来, 国内外曾对CO2 地质封存过程中的“CO2 -地层水-岩石矿物”相互作用进行过一系列的研究, 结果表明这种复杂的作用不仅能够大大改变流体的化学成分和特性, 也能影响元素迁移转化过程以及引起基岩物理性质如渗透率和孔隙度的改变
[87 ,88 ,89 ,90 ]
。 与这一“CO2 -地层水-岩石矿物”相互作用体系相比, 高压CO2 +O2 地浸采铀的过程中的“CO2 +O2 -地层水-岩石矿物”体系有相似之处, 但因O2 引入了较强的氧化还原反应, 而使得矿物溶解沉淀、 次生矿物的形成和元素的迁移转化变得更为复杂。 因此, 笔者认为开展对CO2 +O2 地浸采铀过程中的“气体-流体-矿物”三相反应室内试验、 地球化学模拟以及野外现场试验, 对地浸开采技术研究和创新有着十分重要的意义。
4. 尺度转换问题和多方法综合运用的研究。 地浸过程中的多相、 多尺度流和溶质的反应性运移是一个复杂的非线性体系
[54 ,91 ]
。 目前对溶质运移的研究方式多集中在单一方法上, 这对于研究地浸溶质运移如此复杂的过程显然存在一定的局限性。 另外, 受到尺度效应的影响, 室内试验的结果与野外现场试验的实际值往往相差很大。 因此, 笔者建议多方法结合的方式研究地浸溶质的运移过程, 如可以从微观尺度的研究入手, 为实验室条件下的宏观尺度研究提供理论基础, 以此开展大尺度的野外现场试验, 并在此过程辅以数值模拟的手段加以验证和预测, 提高描述溶质运移过程的精确程度, 减小由于尺度转换而带来偏差。 此外, 由于不同的砂岩型铀矿其地质、 水文地质和水文地球化学条件也各尽不同, 因此建议在研究地浸采铀溶质运移过程时应注重定量化的描述, 得出不同铀矿山的生产工艺参数, 以此做到开发一矿, 研究一矿, 成功一矿。
参考文献
[1] IAEA.In situ leach uranium mining:an overview of operations[R].IAEA Nuclear Energy Series NF-T-1.4, Vienna:IAEA, 2016.
[2] Becherkin S G, Bakhurov V G, Lutsenko I K.Underground leaching of uranium from low-grade in situ ores[J].Atomic Energy, 1968, 24 (2) :154.
[3] Gardener J, Richie M I.Leaching of uranium ore in situ[P].US:3309140, 1967.
[4] Underhill D H.In situ leach uranium mining in the U-nited States of America:past, present and future[R].IAEA-TECDOC-720, Vienna:IAEA, 1993.
[5] Mudd G M.Critical review of acid in situ leach uranium mining:1.USA and Australia[J].Environmental Geology, 2001, 41 (3-4) :390.
[6] Mudd G M.Critical review of acid in situ leach uranium mining:2.Soviet Block and Asia[J].Environmental Geology, 2001, 41 (3-4) :404.
[7] IAEA.World distribution of uranium deposits (UDEPO) [R].IAEA-TECDOC-1843, Vienna:IAEA, 2018.
[8] IAEA.Uranium resources as co-and by-products of polymetallic, base, rare earth and precious metal ore deposits[R].IAEA-TECDOC-1849, Vienna:IAEA, 2018.
[9] Que W M, Wang H F, Tian S F, Zhang Z G, Yao Y X.Research status and development of in-situ leaching uranium techniques in China[J].Uranium Mining and Metallurgy, 2005, 24 (3) :113. (阙为民, 王海峰, 田时丰, 张泽贵, 姚益轩.我国地浸采铀研究现状与发展[J].铀矿冶, 2005, 24 (3) :113.)
[10] Su X B, Du Z M.Development and prospect of China uranium in-situ leaching technology[J].China Mining Magazine, 2012, 21 (9) :79. (苏学斌, 杜志明.我国地浸采铀工艺技术发展现状与展望[J].中国矿业, 2012, 21 (9) :79.)
[11] Zhang F F, Su X B, Xing Y G, Su Y R.New progresses on in-situ leaching of uranium deposit[J].China Mining Magazine, 2012, 21 (S1) :9. (张飞凤, 苏学斌, 邢拥国, 苏艳茹.地浸采铀新工艺综述[J].中国矿业, 2012, 21 (S1) :9.)
[12] Wang H F, Xu Y Q, Tang Q S, Ma L C.Mining block leaching rate for in-situ leaching uranium mines in China[J].Journal of East China University of Technology (Natural Science) , 2017, 40 (1) :66. (王海峰, 徐屹群, 汤庆四, 马连春.我国地浸采铀矿山采区浸出率现状分析[J].东华理工大学学报 (自然科学版) , 2017, 40 (1) :66.)
[13] Du Y B.Prospect of technological innovation in China's uranium industry:focusing on uranium forum of China International Mining Conference in 2017:promoting science and technology innovation strategy and international cooperation to build“Four New Systems”[J].China Nuclear Industry, 2017, (11) :28. (杜运斌.中国铀业技术创新展望---聚焦2017中国国际矿业大会铀论坛---推进科技创新战略和国际合作打造“四新体系”[J].中国核工业, 2017, (11) :28.)
[14] Su X B.Efficient green development, promote the construction of uranium mine base[J].China Nuclear Industry, 2016, (11) :16. (苏学斌.高效绿色发展推进铀矿大基地建设[J].中国核工业, 2016, (11) :16.)
[15] Que W M, Tan Y H, Zeng Y J, Wang S D.Geochemical Kinetics and Mass Transport of in-situ Uranium Leaching[M].Beijing:Atomic Energy Press, 2002.191. (阙为民, 谭亚辉, 曾毅君, 王树德.原地浸出采铀反应动力学和物质运移[M].北京:原子能出版社, 2002.191.)
[16] Zhou X T, Que W M, Hu E M, Zhou Q, Su X B.Element migration and sedimentation of in-situ uranium leaching[J].Uranium Mining and Metallurgy, 2000, 19 (2) :78. (周锡堂, 阙为民, 胡鄂明, 周泉, 苏学斌.原地浸出采铀元素的迁移与沉淀[J].铀矿冶, 2000, 19 (2) :78.)
[17] Peng D M, Zhang H J, Wang S D.Research of waterrock interaction in in-situ uranium leaching[J].Journal of East China Geological Institute, 2001, 24 (1) :41. (彭丁茂, 张红军, 王树德.原地浸出采铀的水岩作用研究[J].华东地质学学报, 2001, 24 (1) :41.)
[18] Gao B, Sun Z X, Shi W J.An experimental study of migration characteristics and conditions of uranium during the in-situ leaching process[J].Geological Review, 2003, 49 (3) :316. (高柏, 孙占学, 史维浚.地浸过程中铀迁移特征及条件的实验研究[J].地质论评, 2003, 49 (3) :316.)
[19] Huang Q Y.Analysis of solute transportation and acidification process during in-situ acid leaching of sandstone uranium ore[J].Nonferrous Metals (Extractive Metallurgy) , 2015, (6) :50. (黄群英.某砂岩铀矿酸法地浸溶质运移与酸化进程分析[J].有色金属 (冶炼部分) , 2015, (6) :50.)
[20] Huang Q Y, Zhou Y P, Liu K, Chen M F.Relationship between solute transportation and leaching solution flow during early period of acid in-situ leaching at one sandstone-type uranium deposit[J].Nonferrous Metals (Extractive Metallurgy) , 2017, (6) :24. (黄群英, 周义朋, 刘科, 陈梅芳.某砂铀矿地浸单元酸浸初期溶质运移与溶液渗流关系[J].有色金属 (冶炼部分) , 2017, (6) :24.)
[21] Liu X X, Wang L, Xie J P, Liu Y Y.Experimental study on column leach of grade copper oxide[J].Mining and Metallurgical Engineering, 2016, 36 (1) :83. (刘新星, 王龙, 谢建平, 刘媛媛.低品位氧化铜矿柱浸试验研究[J].矿冶工程, 2016, 36 (1) :83.)
[22] Liu J H, Zhou Y P, Liu Y J, Sun Z X, Shi W J, Hu BQ.The new progress of uranium biology in-situ leaching[J].China Mining Magazine, 2012, 21 (S1) :262. (刘金辉, 周义朋, 刘亚洁, 孙占学, 史维浚, 胡宝群.生物地浸采铀研究新进展[J].中国矿业, 2012, 21 (S1) :262.)
[23] Gao B, Shi W J, Wang G H, Sun Z X.Study of migration characteristics of solute (uranium) during in-situ leach process[J].Uranium Geology, 2003, 19 (2) :100. (高柏, 史维浚, 王国华, 孙占学.地浸过程中溶质 (铀) 迁移特征研究[J].铀矿地质, 2003, 19 (2) :100.)
[24] Shi W J, Gao B, Wang G H.Mechanism of solute migration during in-situ leaching sandstone-type uranium deposit[J].Journal of East China Geological Institute, 2004, 27 (1) :24. (史维浚, 高柏, 王国华.砂岩型铀矿地浸过程中的溶质迁移机理[J].东华理工学院学报, 2004, 27 (1) :24.)
[25] Xing Y G, Jiang X H, Huo J D, Liu J H.Alkaline insitu leaching of uranium in high-acid-consumption sandstone-type uranium deposit[J].Hydrometallurgy of China, 36 (6) :467. (邢拥国, 蒋小辉, 霍建党, 刘金辉.某高耗酸砂岩型铀矿床碱法地浸采铀试验研究[J].湿法冶金, 36 (6) :467.)
[26] Zhang Q L, Ding D X.CO2 +O2 column leaching test of sandstone type uranium ore[J].Nonferrous Metals (Extractive Metallurgy) , 2017, (8) :35. (张青林, 丁德馨.某砂岩铀矿石CO2 +O2 柱浸试验[J].有色金属 (冶炼部分) , 2017, (8) :35.)
[27] Yin S H, Wu A X.Study on the solute transportation of bioleaching process its influential factors[J].Mining&Metallurgy, 2008, 17 (1) :21. (尹升华, 吴爱祥.微生物浸出过程溶质迁移及其影响因素研究[J].矿冶, 2008, 17 (1) :21.)
[28] Xu C D.Monitoring and Simulation of Water and Salt Transport in High Lift Irrigation Area[M].Beijing:China Water&Power Press, 2015.30. (徐存东.高扬程灌区水盐运移监测与模拟[M].北京:中国水利水电出版社, 2015.30.)
[29] Liu Z B, Wang H F, Wen Z Q, Ding Y, Jiang Y, Xie TT, Xu G L, Wang G.Study on the characteristics of solution migration and drawing and injection control at well field in-situ leaching uranium[J].Uranium Mining and Metallurgy, 2017, 36 (1) :23. (刘正邦, 王海峰, 闻振乾, 丁叶, 姜岩, 谢廷婷, 胥国龙, 王贵.地浸采铀井场溶液运移特征与抽注液量控制研究[J].铀矿冶, 2017, 36 (1) :23.)
[30] Xie T T, Yao Y X, Gan N, Zhang C, Xu G L, Wen ZQ, Peng Y.Analysis and application of seepage-dispersion field characteristics in-situ leaching uranium (to be continued) [J].Uranium Mining and Metallurgy, 2016, 35 (3) :149. (谢廷婷, 姚益轩, 甘楠, 张翀, 胥国龙, 闻振乾, 彭阳.地浸采铀渗流弥散场特征分析及应用 (待续) [J].铀矿冶, 2016, 35 (3) :149.)
[31] Xie T T, Yao Y X, Gan N, Zhang C, Xu G L, Wen ZQ, Peng Y.Analysis and application of seepage-dispersion field characteristics in-situ leaching uranium (complete) [J].Uranium Mining and Metallurgy, 2016, 35 (4) :229. (谢廷婷, 姚益轩, 甘楠, 张翀, 胥国龙, 闻振乾, 彭阳.地浸采铀渗流弥散场特征分析及应用 (续完) [J].铀矿冶, 2016, 35 (4) :229.)
[32] Li B, Hao Z H, Chen Y.The effect of the pumping and pouring volume rising on the uranium concentration[J].China Mining Magazine, 2016, 25 (S2) :286. (李兵, 郝志华, 陈勇.钻孔抽注液量增大对浸出液铀浓度的影响分析[J].中国矿业, 2016, 25 (S2) :286.)
[33] Zhou Y P, Shen Z L, Sun Z X, Liu J H, He J T.The simulation of leaching solution chemical components transportation during the in-situ leaching uranium mining experiment in a sandstone-type uranium deposit[J].China Mining Magazine, 2012, 21 (S1) :298. (周义朋, 沈照理, 孙占学, 刘金辉, 何江涛.某砂岩型铀矿地浸采铀试验溶浸液化学组分运移模拟[J].中国矿业, 2012, 21 (S1) :298.)
[34] Roshal A, Kuznetsov D.Simulation of propagation of leachate after the ISL mining closure[A].Merkel B J, Hasche-Berger A.Uranium in the Environment[C].Berlin:Springer, 2006.217.
[35] Borch T, Roche N, Johnson T E.Determination of contaminant levels and remediation efficacy in groundwater at a former in situ recovery uranium mine[J].Journal of Environmental Monitoring, 2012, 14 (7) :1814.
[36] He Z, Hu K G, Wang G Q, Feng G W.Numerical simulation of uranium transport in situ leaching uranium mine based on GMS[J].Nuclear Electronics&Detection Technology, 2015, 35 (11) :1106. (何智, 胡凯光, 王国全, 冯光文.基于GMS的某铀矿地下水中铀迁移模拟[J].核电子学与探测技术, 2015, 35 (11) :1106.)
[37] Hu K G, Zhang L, He Z, Yang P D.A simulation research about the natural adsorption of U in the immersion liquid of in-situ leaching uranium depositions based on GMS[J].Mine Engineering, 2017, 5 (3) :23. (胡凯光, 张磊, 何智, 杨盘东.基于GMS某地浸铀矿地浸液中铀的吸附模拟[J].矿山工程, 2017, 5 (3) :23.)
[38] Shen Z L.Hydrogeochemical Foundation[M].Beijing:Geological Publishing House, 1986.39. (沈照理.水文地球化学基础[M].北京:地质出版社, 1986.39.)
[39] Perkins T K, Johnston O C.A review of diffusion and dispersion in porous media[J].Society of Petroleum Engineers Journal, 1963, 3 (1) :70.
[40] Xie M L, Mayer K U, Claret F, Alt-Epping P, Jacques D, Steefel C, Chiaberge C, Simunek J.Implementation and evaluation of permeability-porosity and tortuosity-porosity relationships linked to mineral dissolution-precipitation[J].Computational Geosciences, 2015, 19 (3) :655.
[41] Su X B, Liu N Z, Ma X L, Han Q T.Condition evaluation of in-situ leaching by natural reagent at a uranium deposit[J].Uranium Mining and Metallurgy, 2007, 26 (4) :174. (苏学斌, 刘乃忠, 马新林, 韩青涛.新疆某铀矿床天然成因试剂地浸条件评价[J].铀矿冶, 2007, 26 (4) :174.)
[42] Jiao X R, Sun Z X, Shi W J.Study of oxidizing property of hydroperoxide in uranium in-situ leaching[J].Nonferrous Metals (Extractive Metallurgy) , 2013, (12) :21. (焦学然, 孙占学, 史维浚.地浸采铀中过氧化氢氧化性能研究[J].有色金属 (冶炼部分) , 2013, (12) :21.)
[43] Zhou Y P, Ji H B, Sun Z X, Liu Y J, Xu L L, Shi WJ, Liu J H.Uranium migration kinetics in acid solution containing ferric iron[J].Acta Geological Sinica, 2016, 90 (12) :3554. (周义朋, 吉宏斌, 孙占学, 刘亚洁, 徐玲玲, 史维浚, 刘金辉.酸性含Fe3+ 溶液作用下铀的溶解迁移特征[J].地质学报, 2016, 90 (12) :3554.)
[44] Li P, Liu G H, Duan B S, Feng G P, Shao Y F, Zhou JY.Analysis on the problems of high acid consumption and low concentration of uranium in a deposit in Xinjiang[J].Uranium Mining and Metallurgy, 2018, 37 (1) :26. (李坡, 刘国宏, 段柏山, 冯国平, 邵勇峰, 周江勇.新疆某矿床酸耗高、浸出液铀浓度低的原因分析[J].铀矿冶, 2018, 37 (1) :26.)
[45] Liu J H, Sun Z X, Shi W J, Zhou Y P.Factors influencing in-situ leaching of uranium mining in a sandstone deposit in Shihongtan, Northwest China[J].Journal of Groundwater Science and Engineering, 2015, 3 (1) :16.
[46] Xu G F.Analysis of the main technological parameters of CO2 +O2in situ leaching uranium and problems by chemical precipitation blocking[J].Uranium Mining and Metallurgy, 2014, 33 (4) :197. (许根福.CO2 +O2 地浸采铀主要工艺参数及化学沉淀堵塞问题分析[J].铀矿冶, 2014, 33 (4) :197.)
[47] Bi Y Q, Hyun S P, Kukkadapu R K, Hayes K F.Oxidative dissolution of UO2 in a simulated groundwater containing synthetic nanocrystalline mackinawite[J].Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2013, 102:175.
[48] Johnson R H, Tutn H.Reactive transport modelling at uranium in situ recovery sites:uncertainties in uranium sorption on iron hydroxides[A].Brown A, Figueroa L, Wolkersdorfer C.Annual International Mine Water Association Conference:Reliable Mine Water Technology[C].Wisconsin:International Mine Water Association, 2013.377.
[49] Ma R, Liu C X, Greskowiak J, Prommer H, Zachara J, Zheng C M.Influence of calcite on uranium (VI) reactive transport in the groundwater-river mixing zone[J].Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 2014, 156:27.
[50] Dangelmayr M A, Reimus P W, Wasserman N L, Punsal J J, Johnson R H, Clay J T, Stone J J.Laboratory column experiments and transport modeling to evaluate retardation of uranium in an aquifer downgradient of a uranium in-situ recovery site[J].Applied Geochemistry, 2017, 80:1.
[51] Xiu X Q, Zhang Y Y.Study on the adsorption of clay minerals on uranium by laboratory experiments[J].Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 2013, 33 (S2) :574. (修晓茜, 张玉燕.粘土矿物对铀元素的吸附实验研究[J].矿物学报, 2013, 33 (S2) :574.)
[52] Nair S, Karimzadeh L, Merkel B J.Sorption of uranyl and arsenate on Si O2, Al2O3, Ti O2 , and Fe OOH[J].Environmental Earth Sciences, 2014, 72 (9) :3507.
[53] Xu H, Han X Y, Liang W, Wang Yu, Wang Y Q, Wang Y.Sorption and separation of Pt, Pd and U from aqueous solution by aminophosphonic acid derivative silica[J].Chinese Journal of Rare Metals, 2018, 42 (2) :113. (徐辉, 韩小元, 梁威, 王煜, 王耀芹, 王毅.氨基膦酸衍生硅胶吸附剂分离铂、钯和铀[J].稀有金属, 2018, 42 (2) :113.)
[54] Zeng S, Tan K X, Sang X, Shi W G.Numerical simulation on multi-field and multi-process coupling dynamics of in-situ leaching of uranium[J].Atomic Energy Science and Technology, 2011, 45 (4) :500. (曾晟, 谭凯旋, 桑潇, 史文革.原地浸出采铀多场多过程耦合动力学数值模拟[J].原子能科学技术, 2011, 45 (4) :500.)
[55] Zhao C H, Li G M, Lei Q F, Ye S D.Application of numerical simulation technology in in-situ leaching uranium mine[J].Geotechnical Investigation&Surveying, 2007, (7) :27. (赵春虎, 李国敏, 雷奇峰, 叶善东.数值模拟技术在地浸采铀矿山中的应用[J].工程勘察, 2007, (7) :27.)
[56] Liu J W, Xu L C, Yang Y.Predicting the migration of uranium in groundwater of a in-situ leaching uranium mine[J].Uranium Mining and Metallurgy, 26 (2) :84. (吕俊文, 徐乐昌, 杨勇.某地浸采铀矿山采区井场地下水中铀迁移预测[J].铀矿冶, 2007, 26 (2) :84.)
[57] Li C G, Tan K X.Modeling the migration of radioactive contaminants in groundwater of in situ leaching uranium mine[J].Journal of University of South China (Science and Technology) , 2011, 25 (3) :25. (李春光, 谭凯旋.地浸采铀地下水中放射性污染物迁移的模拟[J].南华大学学报 (自然科学版) , 2011, 25 (3) :25.)
[58] Greskowiak J, Gwo J, Jacques D, Yin J, Mayer K U.A benchmark for multi-rate surface complexation and 1Ddual-domain multi-component reactive transport of U (VI) [J].Computational Geosciences, 2015, 19 (3) :585.
[59] Jiao Y J, Shi X Q, Wu J C.Comparison of uranium (VI) adsorption models in uranium mill tailings aquifer[J].Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2015, 35 (10) :3193. (焦友军, 施小清, 吴吉春.铀尾矿库渗漏地下含水层中六价铀的几种吸附反应运移模型对比[J].环境科学学报, 2015, 35 (10) :3193.)
[60] Appelo C A J, Rolle M.PHT3D:a reactive multicomponent transport model for saturated porous media[J].Groundwater, 2010, 48 (5) :627.
[61] Li Q C, Zhou J.Research on character of solute transport in in-situ leaching of uranium in sandstone uranium deposit[A].Merhran S A.Design, Manufacturing and Mechatronics:Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Desi[C].Singapore:World Scientific Publishing, 2015.1086.
[62] Johnson R H, Truax R A, Lankford D A, Stone J J.Sorption testing and generalized composite surface complexation models for determining uranium sorption parameters at a proposed in-situ recovery site[J].Mine Water and the Environment, 2016, 35 (4) :1.
[63] Schmidt R D.Geochemical modeling of in-situ leaching in a heterogeneous porous medium[J].Mines, Metallurgy&Exploration, 1987, 4 (2) :89.
[64] Bommer P M, Schechter R S.Mathematical modeling of in-situ uranium leaching[J].Society of Petroleum Engineers Journal, 1979, 19 (6) :393.
[65] Liddell K C, Bautista R G.Simulation of in situ uraninite leaching-part I:a partial equilibrium model of the NH4 HCO3 - (NH4 ) 2 CO3 -H2 O2 leaching system[J].Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 1994, 25 (2) :171.
[66] Liddell K C, Bautista R G.Simulation of in situ uraninite leaching-part II:the effects of ore grade and deposit porosity[J].Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 1995, 26 (4) :687.
[67] Liddell K C, Bautista R G.Simulation of in situ uraninite leaching-part III:the effects of solution concentration[J].Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 1995, 26 (4) :695.
[68] Que W M.Geochemical kinetics and mass transport of in-situ leaching of uranium[J].Uranium Mining and Metallurgy, 2004, 23 (1) :1. (阙为民.原地浸出采铀地球化学动力学模型研究[J].铀矿冶, 2004, 23 (1) :1.)
[69] Regnault O, Lagneau V, Fiet N.3D reactive transport simulations of uranium in situ leaching:forecast and process optimization[A].Merkel B J, Arab A.Uranium-Past and Future Challenges[C].Switzerland:Springer International Publishing, 2015.725.
[70] Lian G X, Li M J, Tang Q S, Sun J, Cao F B, He Z F, Bai X K.Research on influence of relationship of the drawing over injection ratio to the groundwater environment[J].Uranium Mining and Metallurgy, 2017, 36 (2) :144. (连国玺, 李梦姣, 汤庆四, 孙娟, 曹凤波, 何占飞, 柏学凯.某地浸井场抽大于注比例与地下水环境影响关系的研究[J].铀矿冶, 2017, 36 (2) :144.)
[71] Gene W, Castleton K J, Pelton M A.FRAMES-2.0software system:linking to the groundwater modeling system (GMS) RT3D and MT3DMS models[R].PNNL-16758, Washington:US Department of Energy, 2007.
[72] Parkurst D L, Appelo C A J.Description of input and examples for PHREEQC version 3:a computer program for speciation, batch-reaction, one-dimensional transport, and inverse geochemical calculations[R].TM6-A43.Virginia:US Geological Survey, 2013.
[73] Tan K X, Wang Q L, Hu E M, Hu K G, Zhou Q.Multiple processes coupling and reaction front propagation during in-situ leach mining:1.Theoretical analyses[J].Uranium Mining and Metallurgy, 2005, 24 (1) :14. (谭凯旋, 王清良, 胡鄂明, 胡凯光, 周泉.原地溶浸开采中的多过程耦合作用与反应前锋运动:1.理论分析[J].铀矿冶, 2005, 24 (1) :14.)
[74] Tan K X, Wang Q L, Hu E M, Hu K G, Zhou Q.Multiple processes coupling and reaction front propagation during in-situ leach mining:2.numerical simulation[J].Uranium Mining and Metallurgy, 2005, 24 (2) :57. (谭凯旋, 王清良, 胡鄂明, 胡凯光, 周泉.原地溶浸开采中的多过程耦合作用与反应前锋运动:2.数值模拟[J].铀矿冶, 2005, (2) :57.)
[75] Bonnaud E, Lagneau V, Regnault O, Fiet N.Reactive transport simulation applied on uranium ISR:effect of the density-driven flow[A].Merkel B J, Arab A.Uranium-Past and Future Challenges[C].Switzerland:Springer International Publishing, 2015.699.
[76] Lagneau V, Lee J V D.HYTEC results of the MoMas reactive transport benchmark[J].Computational Geosciences, 2010, 14 (3) :435.
[77] Simon R B, Thiry M, Schmitt J M, Lagnegu V, Langlais V, Bélières M.Kinetic reactive transport modelling of column tests for uranium in situ, recovery (ISR) mining[J].Applied Geochemistry, 2014, 51:116.
[78] Lee J V D, Windt D L.CHESS tutorial and cookbook, updated for version 3.0.user’s manual[R].LHM/RD/02/13.Paris:MINES Paris Tech, 2002.
[79] Yin M S, Yu Y, Shao J Y.Reviews of study on solute transport model in leaky aquifer system based on the influence of aquitard[J].Safety and Environmental Engineering, 2016, 23 (3) :10. (尹茂生, 喻月, 邵骏煜.基于弱透水层影响的越流含水层系统溶质运移模型研究综述[J].安全与环境工程, 2016, 23 (3) :10.)
[80] Tartakovsk A M, Redden G, Lichtner P C, Scheibe TD, Meakin P.Mixing-induced precipitation:experimental study and multiscale numerical analysis[J].Water Resources Research, 2008, 44 (6) :2389.
[81] Blunti M J, Bijeljic B, Dong H, Gharbi O, Lglauer S, Mostaghimi P, Paluszny A, Pentland C.Pore-scale imaging and modeling[J].Advances in Water Resources, 2013, 51 (1) :197.
[82] Yoon H, Kang Q J, Valocchi A J.Lattice boltzmannbased approaches for pore-scale reactive transport[J].Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, 2015, 80 (12) :393.
[83] Prodanovic'M, Mehmani A, Sheppard A P.Imagedbased multiscale network modelling of microporosity in carbonates[J].Geological Society London Special Publications, 2015, 406 (1) :95.
[84] Landrot G, Ajo-Franklin J B, Yang L, Cabrini S, Steefel C I.Measurement of accessible reactive surface area in a sandstone, with application to CO2 mineralization[J].Chemical Geology, 2012, 318-319:113.
[85] Noiriel C.Resolving time-dependent evolution of pore scale structure, permeability and reactivity using X-ray microtomography[J].Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, 2015, 80 (8) :247.
[86] Anovitz L M, Cole D R, Jackson A J, Rother G, Littrell K, Allard L F, Pollington A D, Wesolowski D J.Effect of quartz overgrowth precipitation on the multiscale porosity of sandstone:a (U) SANS and imaging analysis[J].Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2015, 158:199.
[87] Kharak Y K, Cole D R, Hovorka S D, Gunter W D, Knauss K G, Freifeld B M.Gas-water-rock interaction in Frio Formation following CO2injection:implications for the storage of greenhouse gases in sedimentary basins[J].Geology, 2006, 34 (7) :577.
[88] Gaus I.Role and impact of CO2 -rock interactions during CO2 storage in sedimentary rocks[J].International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control, 2010, 4 (1) :73.
[89] Wunsch A, Navarre-Sitchler A K, Moore J, Ricko A, Mccray J E.Metal release from limestones at high partial-pressures of CO2 [J].Chemical Geology, 2014, 363:40.
[90] Wang G H, Zhao J, Zhang F J, Tao Y.Interactions of CO2 brine rock in sandstone reservoir[J].Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology) , 2013, 44 (3) :1167. (王广华, 赵静, 张凤君, 陶怡.砂岩储层中CO2 -地层水-岩石的相互作用[J].中南大学学报 (自然科学版) , 2013, 44 (3) :1167.)
[91] Wang Y X, Lin X Y.The Development Strategy of China Discipline:Groundwater Science[M].Beijing:Science Press, 2018.249. (王焰新, 林学钰.中国学科发展战略---地下水科学[M].北京:科学出版社, 2018.249.)