文章编号:1004-0609(2010)S1-s0215-04
Ti-23Al-17Nb合金锻制饼材的组织与性能
程云君,韩积亭,张建伟,梁晓波
(钢铁研究总院 北京100081)
摘 要:
在α2+B2相区制作Ti-23Al-17Nb合金饼材,观察饼材纵断面不同区域的微观组织。对沿径向截取的拉伸试样进行不同固溶温度+850 ℃、16 h、AC时效处理,测试其拉伸性能。对最佳热处理制度处理试样进行不同温度拉伸性能,600 ℃和650 ℃持久性能和650 ℃,100 h热暴露的稳定性等进行测试。结果表明:采用该工艺制作的饼材的组织比自由锻饼材的组织更均匀;经(1 040 ℃,2 h,AC)+(850 ℃,16 h,AC)热处理后,饼材的综合性能良好,可作为航空和航天等领域的备选用材。
关键词:
中图分类号:TG 146 文献标志码:A
Microstructure and properties of Ti-23Al-17Nb alloy forging disk
CHENG Yun-jun, HAN Ji-ting, ZHANG Jian-wei, LIANG Xiao-bo
(Central Iron and Steel Research Institute, Beijing 100081, China)
Abstract: A Ti-23Al-17Nb alloy forging disk was made in α2+B2 phase field. The microstructures of different zones in vertical section disk were observed. The tensile samples cut along the radial direction in the disk were heat treated at different solution temperatures, then aged at 850 ℃, 16 h, AC. The tensile properties were evaluated. Fixed one optimum heat treatment for the samples, the tensile properties at different test temperatures, stress-rupture properties at 600 ℃ and 650 ℃ and thermal stabilities at 650 ℃, 100 h were evaluated. The results show that the microstructure of disk prepared by this forging process is more homogeneous than that of general open forging. The tensile samples with heat treatment of 1 040 ℃, 2 h, AC+850 ℃, 16 h, AC show good combination of strength and ductility. This alloy is good candidate material for aeronautic and astronautic industry.
Key words: Ti-23Al-25Nb alloy; disk; microstructure; property
Ti-23Al-17Nb合金是钢铁研究总院自主研制的一种Ti3Al基金属间化合物合金, 其名义成分为Ti-23Al-17Nb (摩尔分数,%)(简称为Ti-23Al-17Nb合金),因其具有密度低、高温比强度高及抗氧化性能好等特点,在航空航天领域中得到广泛应用[1-2]。随着供货规格类型的不断增加,经常遇到大尺寸规格的棒材和饼材,采用一般的自由锻造方法,对于Ti3Al基合金这类难变形材料,由于变形抗力大,只能进行多火次的拔长或镦粗变形,大尺寸的饼材,在锻后心部往往过热,变形组织不均匀,心部的上下端面处晶粒粗大,晶界明显,性能达不到客户的要求。因此,本文作者参考一些钛合金的饼材制作方法[3-4],首次采用水压机,在两相区进行一火次大变形的镦粗变形方式,制作得到Ti-23Al-17Nb合金饼材, 并对锻后的饼材进行不同固溶温度的热处理工艺试验, 选出一种最佳的热处理工艺,测试热处理后的饼材不同温度的拉伸性能、持久性能和长时稳定性等。
1 实验
实验用合金由真空自耗电弧3次熔炼而成,其化学成分见表1。铸锭首先在B2相区温度经约70%变形量的开坯锻造成约100 mm的方坯,再在(α2+B2)两相区进行3次镦拔,最后在1 250 t水压机上一次压成 d 230×85 mm的饼材,最后一次的变形量大于60%。
对饼材进行了解剖,切取1/4圆饼,做纵向截面的低倍和高倍组织观察,沿径向线切割取d 12 mm×100圆棒进行不同热处理后,再加工成d 5 mm标准试力学拉伸性能试样。用Leica显微图像分析仪和JMS-6480LV扫描电镜进行组织观察。
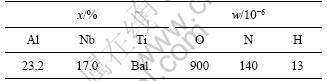
表1 合金的化学成分
Table 1 Chemical composition of alloy
2 结果与讨论
图1所示为1/4圆饼纵向的截面的宏观照片及对应的不同部位的光学金相组织。由宏观照片可见,心部的易变形区有变形流线,中心上下的难变形区未见明显的粗晶区,晶粒基本为模糊晶。各区微观组织为等轴的α2和B2转变组织。α2颗粒大小大多在10 μm以下,其分布随各区域变形程度不同而稍有不同变化,未见粗片和长条的α2相,说明变形比较充分,组织比多火次小变形量的自由锻饼材均匀。
在α2+B2两相区锻造后的Ti3Al基合金,经固溶+时效处理后,可获得双态组织[5-6],此种组织容易兼顾航空部件要求的长时稳定性和短时力学性能相匹配的综合性能。本研究进行了3种不同固溶温度处理的实验,时效温度均为850 ℃,16 h,AC。图2所示为3种处理所对应的金相组织,该组织由B2相基体、α2相颗粒及O相板条构成,3个相因成分差异而在扫描电镜的二次电子图像中分别呈白色、黑色和灰色。组织中较大的黑色α2相颗粒周边均形成了一层较薄的灰色环形边沿,这一形态的O相可能由α2+B2相界形核生成。随固溶温度的增加,α2相颗粒变小,α2量也减少,基体的O相板条变粗。
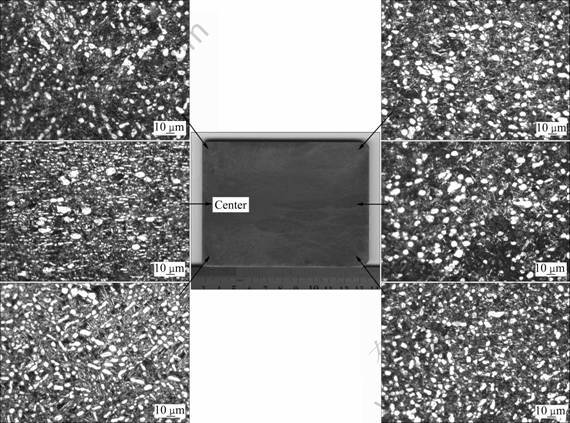
图1 饼材1/4纵断面的宏观组织及箭头所指区域的微观组织
Fig.1 Macrostructure of 1/4 disk vertical section and microstructures of different zones with arrow indicating
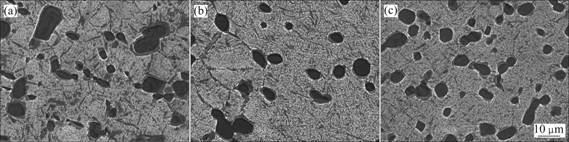
图2 Ti-23Al-17Nb合金饼材经不同固溶温及850 ℃时效后的显微组织
Fig.2 Microstructures of Ti-23Al-17Nb alloy disk solution-treated at different solution temperatures and aged at 850 ℃; (a) 1 020 ℃, 2 h, AC; (b) 1 040 ℃, 2 h, AC; (c) 1 060 ℃, 2 h, AC
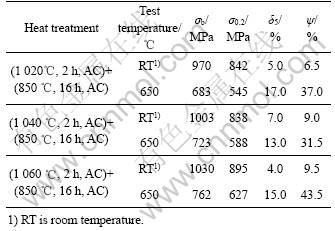
表2所列为3种不同固溶温度下的双态组织拉伸性能。由表2可看出,随固溶温度的升高,合金的拉伸强度有所增加,但室温伸长率以1 040 ℃固溶处理最好。
表2 不同固溶温度下合金的双态组织拉伸性能
Table 2 Tensile properties of alloy with duplex micro- structures under different solution temperatures
选定(1 040 ℃、2 h,AC)+(850 ℃、16 h,AC)处理制度对饼材进行热处理后,做不同温度的拉伸性能测试,其结果如图3所示。由图3可看出,随拉伸实验温度增加,拉伸强度缓慢下降,在600 ℃后下降加快。伸长率(δ5)和断面收缩率(ψ)随温度升高而上升, 在400 ℃以后开始下降,650 ℃时达到最低值, 而后又上升。这一规律是Ti3Al和Ti2AlNb基这类合金常见现象[7-9],有研究者认为这是环境因素的影响,或可能是O相在此温度范围内动态应变时效的结果。
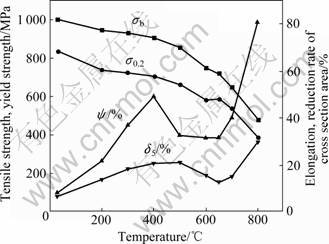
图3 Ti-23Al-17Nb合金饼材的拉伸性能与温度的关系
Fig.3 Relationship between tensile properties and temperature of Ti-23Al-17Nb alloy disk
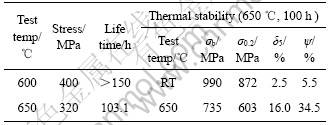
表3所列为饼材的持久和经650 ℃,100 h热暴露后试样再拉伸的性能,其持久性能高于一般高温钛合金的[10],热暴露后的性能在强度上与暴露前相比,变化不大,但室温塑性有所下降,650 ℃的塑性变化不大。
表3 Ti-23Al-17Nb合金饼材的持久和热稳定性能
Table 3 Stress rupture and thermal stability properties for Ti-23Al-17Nb alloy disk
3 结论
1) 采用水压机在α2+B2两相区最后一火次大变形量工艺锻制的Ti-23Al-17Nb合金饼材,其各区的变形组织通过低倍观察无明显清晰晶粒存在,通过高倍观察则无粗片的α2长条,组织优于一般多火次小变形量的自由锻饼材的。
2) 采用以上方式锻制的饼材,经(1 040 ℃,2 h,AC)+(850 ℃,16 h,AC)热处理后,综合性能良好,不同温度的拉伸性能和持久性能优于一般高温钛合金的,应是航空长时间使用和航天领域短时间高温使用的轻质备选材料之一。
REFERENCES
[1] ZONG Zeng-yong, ZOU Dun-xu, LI Shi-qiong. Advance in Ti3Al and TiAl intermetallics research in CISRI[J]. Acta Metallurgical Sinica: English Letters, 1995, 8: 531-541.
[2] 李世琼, 张建伟, 程云君, 梁晓波. Ti3Al和Ti2AlNb基金属间化合物结构材料研发现状[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2005, 34(Supple 3): 104-109.
LI Shi-qiong, ZHANG Jian-wei, CHENG Yun-jun, LIANG Xiao-bo. Current status on development of Ti3Al and Ti2AlNb intermetallic structural materials[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2005, 34(Supple 3): 104-109.
[3] 魏寿庸, 王永强, 关少轩, 刘羽寅. TA15钛合金大直径棒材的组织与性能[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2008, 37(Suppl.3): 49-52.
WEI Shou-yong, WANG Yong-qiang, GUAN Shao-xuan, LIU Yu-yin. The microstructure and mechanical properties of TA15 alloy large-sized bar[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2008, 37(Supple 3): 49-52.
[4] 李渭清, 冯永琦, 王鼎春, 何书林, 乔恩利, 雷家峰, 刘羽寅. 镦粗变形工艺对TC18组织和性能的影响[J]. 钛工业进展, 2008, 25(4): 24-26.
LI Wei-qing, FENG Yong-qi, WANG Ding-chun, HE Shu-lin, QIAO En-li, LEI Jia-feng, LIU Yu-yin. Influence of compression deformation process on the microstructure and properties of TC18 alloy[J]. Titanium Industry Progress, 2008, 25(4): 24-26.
[5] 张建伟, 张海深, 张学成, 梁晓波, 程云君, 李世琼. Ti-23Al-17Nb合金双态组织的控制及其对力学性能的影响[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2010, 39(2): 372-376.
ZHANG Jian-wei, ZHANG Hai-shen, ZHANG Xue-cheng, LIANG Xiao-bo, CHENG Yun-jun, LI Shi-qiong. Control of duplex microstructure of Ti-23Al-17Nb alloys and its effect on mechanic properties[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2010, 39(2): 372-376.
[6] 张建伟, 程云君, 梁晓波, 李世琼. (α2+B2+O)三相区温度变形的Ti3Al基板材的组织和性能[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2008, 37(Suppl.3): 561-564.
ZHANG Jian-wei, CHENG Yun-jun, LIANG Xiao-bo, LI Shi-qiong. Study on the microstructure and properties of hot rolling sheets of Ti3Al based alloy processed in (α2+B2+O) phase field[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2008, 37(S3): 561-564.
[7] WARD C H. Microstructure evolution and its effect on tensile and fracture behaviour of Ti-Al-Nb α2 intemetallics[J]. International Materials Review, 1993, 38(2): 79-101.
[8] BANERJEE D, GOGIA A K, NANDY T K, MURALEEDHARAN K, MISHRA R S. The physical metallurgy of Ti3Al based alloys[C]//DARALIA R, LEWANDOWSKI J J, LIU C T, MARTIN P L, MIRACLE D B, NATHALM V. Structural Intermetallics. The Mineral, Metals & Materials Society, 1993: 19-33.
[9] LI Ship-qiong, MAO Yong, ZHANG Jian-wei, LI Jun-tao, CHENG Yun-jun, ZONG Zeng-yong. Effect of microstructure on tensile properties and fracture behavior of intermetallic Ti2AlNb alloys[J]. Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China, 2002, 12(4): 582-586.
[10] 张喜燕, 赵永庆, 白晨光. 钛合金及应用[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2005: 123-153.
ZHANG Xi-yan, ZHAO Yong-qing, BAI Chen-guang. Titanium alloy and its applications[M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2005: 123-153.
(编辑 龙怀中)
通信作者:程云君;电话:010-62181009;E-mail: chengyj100@sina.com


