磁悬浮平台的解耦模糊PID控制
胡汉辉1, 2,谭 青1
(1. 中南大学 机电工程学院,湖南 长沙,410083;
2. 湖南工业职业技术学院 电气工程系,湖南 长沙,410082)
摘 要:
摘 要:介绍差动式磁悬浮平台的结构与工作原理,建立磁悬浮平台的数学模型。采用输入输出空间变量变换实现平台3自由度的解耦,研究磁悬浮平台的模糊PID控制。该控制方法根据不同的偏差E、偏差变化率EC对PID参数Kp,Ki和Kd进行自校正,给出了Kp,Ki和Kd的模糊规则表。实验结果表明:平台的阶跃响应超调量很小,约为6%,上升时间约为0.1 s,稳态误差约为2%;当平台被迫向下偏移0.2 mm时,系统仍能快速回到平衡位置且稳定悬浮,系统具有很好的刚度阻尼特性和鲁棒性。
关键词:
中图分类号:TM273.1 文献标识码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2009)04-0963-06
Decoupling fuzzy PID control for magnetic suspended table
HU Han-hui1, 2, TAN Qing1
(1. School of Mechanical and Electrical Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
2. Department of Electrical Engineering, Hunan Industry Polytechnic, Changsha 410082, China)
Abstract: The working principle and structure of differential magnetic suspension were introduced, and the mathematical model of magnetic table was built up. The input and output space variables were used to transform achieve 3 degrees of freedom of decoupling. The fuzzy PID control plan of magnetic table was proposed and PID parameters, Kp, Ki and Kd, were accomplished self-tuning. According to different deviation E and deviation rate of change EC, and fuzzy regular table of Kp, Ki and Kd were determined. The results show that the system overshoot of step response is very small (about 6%), the rising time is about 0.1 s, and the static error is about 2%. When the platform is deviated 0.2 mm down, the system still can fast return to the balance position and suspend stably, which shows that the system has very good stiffness and damping characteristics and robustness.
Key words: fuzzy control; PID control; magnetic suspension; decoupling control
与机械轴承、气浮支承、液体轴承等支承方式不同,磁悬浮支承技术是利用电磁力的作用使被支承物体与定子之间处于无接触悬浮状态,具有无污染、易维护、高速度、高刚度、高定位精度和长寿命等优点。磁悬浮平台的控制是磁悬浮平台的核心技术,控制器性能不仅决定了磁悬浮能否实现,而且还直接影响到平台的定位精度和承载能力等关键指标,所以,在整个磁悬浮平台设计中,控制器的设计及优化显得尤为重要[1]。磁悬浮控制必须满足系统的快速性、稳定性、鲁棒性等要求。电磁型磁悬浮平台的控制方案[2-5]大体可分为线性控制和非线性控制2类。线性控制以悬浮系统在工作点处的线性化模型为基础,以PID控制[6]和状态反馈控制[7]为代表。非线性控制包括模糊控 制[8]、滑模变结构控制[9]等。苏义鑫等[10-11]提出的模糊控制方案综合了线性控制和模糊控制的优点,但是控制参数的整定仍然是以系统在工作点处的线性特性来进行的,而磁悬浮平台是一个非线性多输入输出系统,各自由度之间存在耦合,因此,本文作者对磁悬浮平台进行解耦线性化,然后,采用模糊PID方法对该平台进行控制,通过计算机仿真[12]和实验,取得了非常好的控制效果。
1 工作原理
差动式磁悬浮平台的结构与工作原理如图1所示,导轨固定,悬浮部件依靠与其装配成一体的垂直方向的4对“U”型电磁铁励磁线圈与导轨耦合作用而悬浮,当线圈通电后在每对“U”型电磁铁中产生磁场,该磁场感应导轨使之对平台产生向上的磁吸力,当垂直方向4对磁吸力与悬浮部件的重力平衡时,悬浮部件便悬浮于空中。
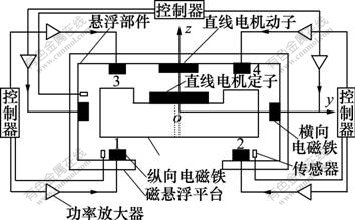
图1 磁悬浮平台结构及工作原理图
Fig.1 Diagram of magnetic structure and working principle
导轨侧面的2对电磁铁,可以提供悬浮部件所需的大小恒定的导向磁力,以保障步进时的运动呈直线。调节水平方向电磁铁通电电流,可改变各自的间隙,提高导向精度。
2 磁悬浮平台建模
2.1 电磁力计算
磁悬浮平台一般采用差动激磁,在这种差动工作方式下,平台的受力为上、下磁铁吸力之差:

2.2 电磁绕组回路电压方程
假设1对差动连接的电磁铁如图2所示,上、下线圈的线圈匝数一样。
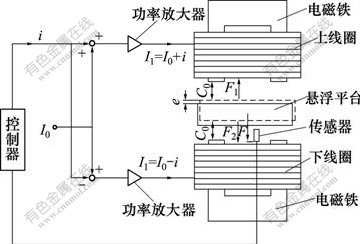
图2 差动方式电磁铁
Fig.2 Differential way electromagnet
对于上线圈,其电压方程为:

2.3 解耦控制分析
对于电磁铁,根据磁路定理,有:
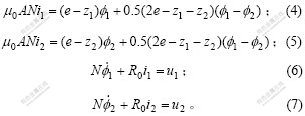
将式(4)和(5)中的i1和i2分别代入式(6)和(7)并略去高次项,得到磁通的变化率的线性近似为:
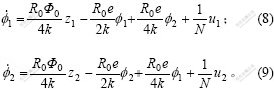
在平衡位置下磁通为![]() ,磁极处的电磁力分别为:
,磁极处的电磁力分别为:
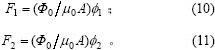
消去磁通,得到2个电磁铁关于力的微分方程为:
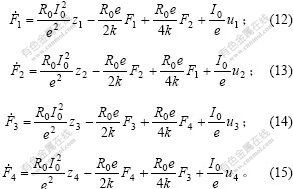
式(12)~(15)是4个电压与力的关系,即将电流控制变为电压控制,没有电流控制所隐含的纯微分环节,避免了控制系统对噪声的过分敏感。
采用如下坐标变换和输入变换:
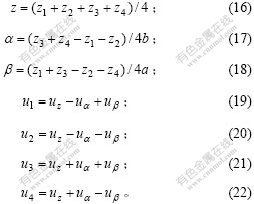
磁悬浮平台经变换和化简可得到3个解耦[13-17]的传递函数:

由式(23)~(25) 3个传递函数,便可以设计3个单输入单输出的控制器。
3 模糊PID控制器设计
3.1 确定系统的输入输出变量
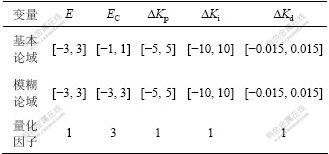
磁悬浮系统控制的目的是使轴承悬浮在某一期望值,因此,选择模糊控制器的输入变量为轴承的位置偏差E和偏差变化率EC,输出量为PID参数的修正量?Kp、?Ki和?Kd。定义E,EC,?Kp,?Ki和?Kd模糊量的模糊子集均为{NB, NM, NS, ZO, PS, PM, PB}。其中:NB, NM, NS, ZO, PS, PM, PB分别表示负大、负中、负小、零、正小、正中和正大。根据论域的覆盖程度和灵敏度、稳定性与鲁棒性原则,各模糊子集均选用三角形隶属函数。它们的变量、基本论域、模糊论域及量化因子如表1所示。
表1 模糊PID参数表
Table 1 Fuzzy PID parameters table
根据PID参数的作用以及在不同的偏差变化下对PID参数的要求,得到针对?Kp,?Ki和?Kd 3个参数模糊子集的模糊控制表(表2)。
表2 ?Kp,?Ki和?Kd模糊子集的模糊规则表
Table 2 Fuzzy rule table of subset of ?Kp, ?Ki, ?Kd
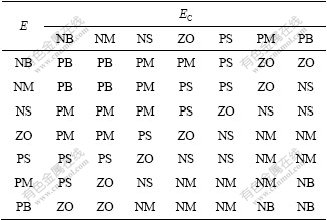
注:?Kp, ?Ki和?Kd的模糊子集均为{NB NM NS ZO PS PM PB}.
3.2 模糊推理及解模糊化
根据前面的模糊规则,对于输入偏差E和偏差变化率EC,经过推理可以得出相应的输出。首先,求出输出变量的隶属度,如对应于?Kp的第1条模糊规则的隶属度为:
![]()
以此类推,可以求得输出量?Kp在不同偏差和偏差变化下的所有模糊规则调整的隶属度。在某一采样时刻,根据偏差和偏差变化的测量值,采用重心法(也即为加权平均法)可以求得此时?Kp为:
 同理,可得到?Ki和?Kd的隶属度。根据上面推导的公式计算出的输出值是增量,所以,还要进行调整。PID参数的调整算法为:
同理,可得到?Ki和?Kd的隶属度。根据上面推导的公式计算出的输出值是增量,所以,还要进行调整。PID参数的调整算法为:
4 实验及分析
图3所示为轴向控制的磁悬浮转子系统的数字控制框图。整个系统包括磁悬浮平台、DSP数字控制器、功放电路、传感器、PC机等装置组成。
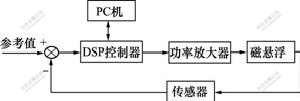
图3 磁悬浮平台系统的数字控制框图
Fig.3 Diagram of digital control of magnetic table system
磁悬浮平台参数为:平台质量1.24 kg,上偏置电流1.1 A,下偏置电流0.9 A,线圈匝数400,气隙2 mm,位移刚度50 768 N/m,电流刚度100.53 N/A。
系统中功率放大器采用电压-电流型功率放大器,其放大倍数为344 mA/V;位移传感器采用电涡流传感器,灵敏度为8 V/mm,其放大倍数为8 000。
图4和图5所示分别为模糊PID控制下磁悬浮平台的阶跃响应和停止时位移波形。从图4和5可以看出,系统阶跃响应超调量很小,约为6%,上升时间约为0.1 s,稳态误差约为2%。
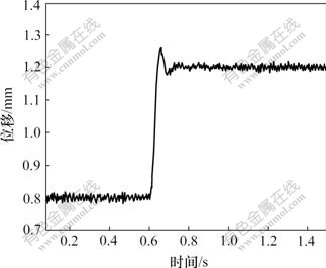
图4 平台起浮时的位移波形
Fig.4 Displacement graph of suspended system

图5 平台停止时的位移波形
Fig.5 Displacement graph of ceased system
图6和图7分别为模糊PID控制和常规PID控制下系统的冲击响应。可见,当系统受到外力冲击时,磁悬浮平台系统被迫向下偏移0.2 mm,但依然能够回到平衡位置且稳定悬浮,这说明系统的刚度阻尼特性好,稳定性好。
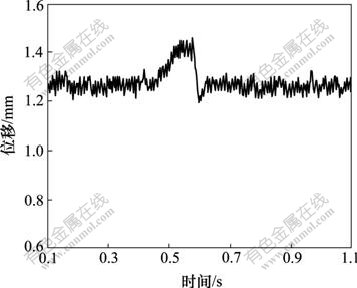
图6 模糊PID控制下的冲击响应
Fig.6 Impact response using fuzzy PID controller
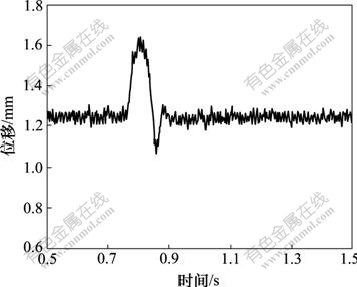
图7 PID控制下的冲击响应
Fig.7 Impact response using PID controller
通过对比模糊PID控制和常规PID控制时系统的冲击响应可知,模糊PID控制器具有更强的鲁棒性和抗干扰能力。
5 结 论
a. 磁悬浮平台控制中3个自由度之间的耦合,可通过输入输出空间中的坐标变换予以消除。
b. 通过分析监测E和EC,根据模糊控制原理对PID 3个参数进行在线修改。
c. 与传统的PID控制方法比较,基于模糊自整定PID控制的磁悬浮平台系统阶跃响应超调量为6%,上升时间为0.1 s,稳态误差为2%。当平台被迫向下偏移0.2 mm时,系统仍能快速回到平衡位置且稳定悬浮,系统对外加干扰具有很强的稳定性,有很好的起浮性能和平稳的停止性能。
参考文献:
[1] Lin C S, Lay Y L, Chen P W, et al. The laser displacement measurement with feedback control in a magnetic levitation and suspension system[J]. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2000, 190(1/2): 25-34.
[2] Stephen C, Paschall II. Design, fabrication, and control of a single actuator magnetic levitation system[D]. Texas: Department of Mechanical Engineering, Texas A&M University, 2002.
[3] 朱熀秋, 徐龙祥. 径向四自由度主动磁悬浮轴承控制器研究与探讨[J]. 应用科学学报, 2002, 20(1): 55-60.
ZHU Huang-qiu, XU Long-xiang. A study and discussion on a controller for radial four-degree freedom active magnetic bearing[J]. Journal of Applied Sciences, 2002, 20(1): 55-60.
[4] 李群明, 朱 伶, 徐 震. 磁悬浮球的鲁棒控制器设计[J]. 中南大学学报: 自然科学版, 2007, 38(5): 922-927.
LI Qun-ming, ZHU Ling, XU Zhen. Robust controller design of maglev ball system[J]. Journal of Central South University: Science and Technology, 2007, 38(5): 922-927.
[5] Gentili L, Marconi L. Robust nonlinear disturbance suppression of a magnetic levitation system[J]. Automatica, 2003, 39(4): 735-742.
[6] XU Shao-hui, XU Zheng-guo, JIN Neng-qiang, et al. Acceleration sensorless levitation control scheme for the hybrid maglev system[C]//Proc Int Conf on Magnetically levitated System’2004. Shanghai, 2004.
[7] Gurol S, Baldi R, Bever D. Status of the general atomics low speed urban maglev technology development program[C]//The 18th International Conference on Maglev Systems and Linear Drivers. Shanghai, 2004.
[8] WANG Zhang-hai, WANG De-jun. Dynamic characteristics of a rolling mill drive system with backlash in rolling slippage[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2000, 97(1): 69-73.
[9] Yeou K T, Tsih C W. A novel compensation approach for self- sensing maglev system with controlled-PM electromagnets[J]. IEEE Trans on magnets, 1995, 31(6): 4208-4210.
[10] 苏义鑫, 王 娟, 胡业发. 磁悬浮轴承的变参数PID控制[J]. 武汉理工大学学报, 2004, 26(2): 35-37.
SU Yi-xin, WANG Juan, HU Ye-fa. A variable parameter PID controller for the magnetic bearings[J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology, 2004, 26(2): 35-37.
[11] 姚河清, 冯 骏. 基于模糊自整定PID控制的磁悬浮轴承控制器[J]. 河海大学常州分校学报, 2004, 18(1): 46-48.
YAO He-qing, FENG Jun. PID controller of magnetic suspension bearing based on fuzzy self-regulating[J]. Journal of Hohai University Changzhou, 2004, 18(1): 46-48.
[12] 石 玗, 贺 军, 吴明亮. 铝合金脉冲MIG焊熔宽控制系统仿真[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2007, 17(12): 1955-1959.
SHI Yu, HE Jun, WU Ming-liang. Simulation of MIG welding control system for aluminum alloy[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2007, 17(12): 1955-1959.
[13] 李黎川, 丁玉成. 超精密磁悬浮工作台及其解耦控制[J]. 机械工程学报, 2004, 40(9): 84-88.
LI Li-chuan, DING Yu-cheng. High-precision magnetically suspended table and its decoupling control[J]. Chinese Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2004, 40(9): 84-88.
[14] 宋文荣, 张 玲. 进给机构磁悬浮系统的解耦控制分析[J]. 哈尔滨工业大学学报, 2005, 37(3): 325-328.
SONG Wen-rong, Zhang Ling. Decoupling control of a maglev feeding mechanism[J]. Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology, 2005, 37(3): 325-328.
[15] Li L. Compensation of rotor imbalance for precision rotation of planar magnetic bearing rotor[J]. Precision Engineering, 2003, 27(2): 140-150.
[16] 曹建荣, 虞 烈. 感应型磁悬浮电动机的解耦控制[J]. 电工技术学报, 2000, 15(5): 1-5.
CAO Jian-rong, YU Lie. Pecouping control for induction type bearingless motor[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2000, 15(5): 1-5.
[17] Mao J, Tachikawa H, Shimokohbe A. Precision positioning of DC-motor-driven aerostatic slide system[J]. Precision Engineering, 2003, 27(1): 32-41.
收稿日期:2008-11-15;修回日期:2009-02-25
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(50675227)
通信作者:胡汉辉(1971-),男,湖南浏阳人,副教授,从事机械电子控制技术研究;电话:13874899614;E-mail: hhxhn_01@163.com



