线圈绕Y轴倾斜时多孔介质方腔内空气热磁对流的数值模拟
姜昌伟1,李贺松2,陈冬林1,石尔1,朱先锋1,李茂2
(1. 长沙理工大学 能源与动力工程学院,湖南 长沙,410004;
2. 中南大学 能源科学与工程学院,湖南 长沙,410083)
摘 要:
究圆形载流线圈绕Y轴倾斜时多孔介质方腔内空气热磁对流。采用毕奥-萨伐定律计算磁场强度;对控制方程基本变量采用控制容积法离散,采用SIMPLE算法求解,获得空气热磁对流的流场和温度场以及壁面平均Nusselt数。研究结果表明:线圈倾斜角yeuler和磁场力数γ对多孔介质方腔内空气流场结构与传热性能有重要影响,当γ<100时,努塞尔数Num随着yeuler的变化呈现交替性增大和减小;而当γ>100时,Num随着γ的增加而增大;当yeuler=0°时,方腔上半部区域形成2个大漩涡而下半部区域形成2个小漩涡;当yeuler=±90°时,方腔下半部形成1个垂直大漩涡而顶部形成1个水平小漩涡。
关键词:
中图分类号:TK124 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2012)02-0749-07
Numerical simulation of thermomagnetic convection of air in porous cubic enclosure with coil inclined around Y axis
JIANG Chang-wei1, LI He-song2, CHEN Dong-lin1, SHI Er1, ZHU Xian-feng1, LI Mao2
(1. School of Energy and Power Engineering, Changsha University of Science and Technology, Changsha 410004, China;
2. School of Energy Science and Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China)
Abstract: Thermomagnetic convection of air in a porous cubic enclosure with a electric coil inclined around the Y axis was numerically investigated. Biot-Savart’s Law was used to calculate magnetic field. The governing equations in primitive variables were discretized by the finite-volume method and solved by the SIMPLE algorithm. The flow and temperature fields for the air thermomagnetic convection were presented and the mean Nusselt numbers on the walls was calculated and compared. The results show that the inclination angle of coil yeuler and magnetic force number γ have significant effect on the flow field characteristics and heat transfer performance in a cubic enclosure.When γ<100,Num is increased and decreased alternately with the change of yeuler; Num is increased with the increase of γ when γ>100. When yeuler=0°, two large rolls are generated in the upper part of the cube and two small convection rolls in the opposite direction are generated near the bottom floor. A large vertical roll and a small horizontal roll are generated in the lower and top part of the cube respectively at yeuler=±90°.
Key words: thermomagnetic convection; numerical simulation; porous media; inclined electric coil; magnetic force
随着能产生高达10 T磁感应强度的超导磁体快速发展,强磁场对以氧气和空气为主的顺磁性流体自然对流的驱动作用机理正成为最近研究的热点。Tagawa等[1]开展了许多磁致顺磁性流体自然对流方面的研究;Carruthers等[2-3]研究了温度梯度和梯度磁场下矩形容器内氧气的热磁对流;Tagawa等[4-8]应用Boussinesq近似的类似方法推导出热磁对流的模型方程,并对磁场作用下腔体内顺磁性流体的传热现象进行了数值模拟和实验研究。杨立军等[9-12]对梯度磁场作用下二维封闭腔体内空气或氧气热磁对流进行了研究,指出梯度磁场可以实现空气或氧气自然对流的强化与控制。Bednarz等[13-16]对由圆形载流线圈产生的磁场作用下方腔内顺磁性流体的自然对流进行了研究,并分析了载流线圈的倾斜角、载流对顺磁性流体传热性能的影响。上述研究都是关于磁场力对自然对流的影响,而目前对磁场力作用下多孔介质自然对流的研究很少。Wang等[17-19]数值模拟了强磁场作用下充满顺磁性或逆性流体的多孔介质方腔内自然对流。强磁场对多孔介质对流换热的影响可应用于强化传热,因此,研究强磁场对多孔介质自然对流的影响具有重要的工程实际应用价值。在此,本文作者对圆形载流线圈绕Y轴倾斜时多孔介质方腔内空气热磁对流进行数值模拟。
1 物理模型
物理模型和坐标系统如图1所示,物理模型包括水平放置的多孔介质方腔和1个产生磁场的圆形载流线圈。充满空气的多孔介质方腔左侧垂直壁面等温加热,右侧垂直壁面等温冷却,其他壁面绝热。载流线圈绕多孔介质方腔放置,其圆心与多孔介质方腔中心位于同一位置且可绕Y轴倾斜。本研究中,多孔介质方腔边长L为0.03 m,线圈半径r为0.05 m。
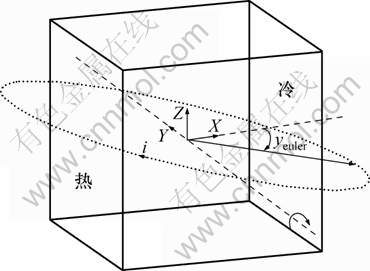
图1 物理模型与坐标系统
Fig.1 Physical model and coordinate system
2 数学模型
2.1 控制方程
对模型进行如下假设:流体为不可压缩牛顿流体;稳态且无相变;多孔介质各向同性;忽略焦耳热、磁场诱导热及热耗散;引入Boussinesq假设处理磁浮升力项。基于上述假设,笛卡尔坐标系下的无因次形式控制方程如下。
连续性方程:
![]() (1)
(1)
动量方程:
![]()
![]() (2)
(2)
![]()
![]() (3)
(3)
![]()
![]() (4)
(4)
能量方程:
![]() (5)
(5)
磁感应强度由毕欧-萨伐定律求解:
![]() (6)
(6)
其中:![]() ;
;![]() ;
;![]() ;
;![]() ;
;![]() ;
;![]() ;
;![]() ;
;![]() ;
;![]() ;
;![]() ;
; ![]() ;
;![]() ;
;![]() ;
;![]() ;
;![]() ;
;![]() ;
;![]() ;μm为真空磁导率,
;μm为真空磁导率,
H×m-1;b为磁感应强度,T;B为无量纲磁感应强度;ρ为空气密度,kg×m-3;p为压力,Pa;μ为空气运动黏度,kg×m-1×s-1;g为重力加速度,m×s-2;K为渗透率,m2;χ0为体积磁化率;T为温度,K;T0=(Th+Tc)/2,K;下标0,h和c分别表示参考值、高温与低温;β为空气体积膨胀系数,K-1;x,y和z为Cartesian坐标系;u,v和w分别为x,y和z方向速度分量,m×s-1;α为空气热扩散率,m×s-1;ν为空气动力黏度,m2×s-1;X,Y和Z为无因次坐标系;U,V和W分别为X,Y和Z方向无因次速度分量;P为无因次压力;θ为无因次温度;Pr为普朗特数;b0为参考磁感应强度,T;i为线圈电流,A;L为方腔边长,m;Ra为Rayleigh数;γ为磁场力数;Da为Darcy数;R为无因次位置矢量;ds为无因次线圈切向矢量。
2.2 边界条件
数学模型的边界条件如下:方腔壁面U=V=W=0;左侧垂直壁面(X=-0.5),θ=0.5;右侧垂直壁面(X=0.5),θ=-0.5;侧部垂直壁面(Y=-0.5,0.5),?θ/?Y=0;顶部和底部壁面(Z=-0.5,0.5),?θ/?Z=0。
2.3 结果描述
总传热性能采用高温壁面平均Nusselt数进行描述:
![]() (7)
(7)
2.4 数值求解
对于上述控制方程与对流传输方程的求解,首先采用基于交错网格系统的控制容积法(Finite volume method,FVM)进行离散,在离散过程中,对流项与扩散项分别采用延迟修正的3阶QUICK差分格式与2阶中心差分格式。每个离散方程都应用逐线迭代的方式求解,在每条迭代线上应用三对角矩阵算法(TDMA)与逐次松弛迭代(SOR)结合的方法进行计算。耦合控制方程的离散方程组采用SIMPLE算法求解。迭代计算收敛准则是对于所求的速度和温度变量,要求前后2步迭代计算结果之差小于5×10-5。
在计算之前,必须对数学模型、代码的可靠性及准确性进行考核。计算Ra=105和Da=10-3时多孔介质方腔自然对流,考核3种网格形式,即长×宽×高分别为30×30×30,40×40×40和50×50×50,对这3种网格计算所得的Num相对偏差小于3%,因此,综合考虑计算精度和收敛速度,采用40×40×40网格。
3 结果分析与讨论
3.1 磁场力数γ的影响
图2所示为垂直横截面Y=0.5,yeuler=0°,Ra=105和Da=10-3时,磁场力数γ对方腔内磁力与重力合力矢量、温度分布、速度矢量的影响,其中左、右侧壁面分别为高、低温壁面。当无磁场作用即γ=0时,方腔内空气对流为纯重力自然对流,空气沿左侧高温壁面上升而沿右侧低温壁面下降,整个方腔内空气流动形成一个顺时针漩涡。当施加磁场时,由于顺磁性流体空气的磁化率与温度成反比,因此,磁场力抑制左侧高温空气的流动(相对于高温和低磁化率时的平均温度,空气受到抑制);另一方面,靠近右侧壁面的空气处于低温状态,具有较高的磁化率,比平均温度下的空气更容易受到磁力吸引。靠近左侧的高温空气受磁力抑制往下运动,而靠近右侧的低温空气受磁力吸引而往上运动,并且磁浮升力与腔体水平中间平面呈现基本对称分布。当γ=10时,由于重力浮升力远远大于磁力,因此,高温空气沿左侧壁面上升,低温空气沿右侧壁面下降,整个方腔空气流动形成1个呈顺时针的漩涡;当γ=50时,磁浮升力变大,在方腔下半部分,磁浮升力方向与重力方向相反,高温流体受到磁浮升力抑制,沿左侧高温壁面向下运动流向低温壁面,低温流体受磁浮升力吸引沿着低温壁面向上运动,因此,在方腔下半区域流体流动形成1个呈逆时针的小漩涡;而在方腔上半部分,磁浮升力方向与重力浮升力方向相同,它们两者共同作用使空气沿着高温壁面上升,而沿低温壁面下降;当γ大于100时,磁力变得很大,此时,磁浮升力远大于重力浮升力,流体的流动规律与纯磁对流类似,热空气在靠近左侧高温壁面的磁浮升力驱动下沿着高温壁面从方腔水平中间平面分别向顶部和底部绝热壁面流动,然后流向右侧冷壁。当空气靠近右侧冷壁后,由于磁力强吸引力的作用,冷空气分别向下和向上流动到中间线圈平面,最后形成2个基本相互对称的漩涡。
3.2 线圈倾斜角yeuler的影响
图3所示为Ra=105,γ=25,Da=10-3,倾斜角yeuler分别为0°,±30°,±60°和±90°时的计算结果。图中从左侧到右侧分别为磁力与重力合力矢量、温度等温面和速度流线。每个图中,方腔左侧壁面等温加热,右侧壁面等温冷却,其他壁面绝热。
由图3可见:当线圈位于水平位置即yeuler=0°时,在方腔上半部重力和磁力方向几乎完全相同,所以,可以产生更大的合力和加速度;而在方腔下半部,重力与磁力方向几乎完全相反,因此,产生的合力和加速度减少。热空气在靠近左侧高温壁面的磁浮升力驱动下,沿着高温壁面从线圈平面下部分别向顶部和底部绝热壁面流动,然后流向右侧冷壁;当空气靠近右侧冷壁后,由于磁力强吸引力的作用,冷空气分别向下和向上流动到中间线圈平面下部,因此,在腔体上半区域生成了2个大漩涡,而靠近腔体底部地板则生成2个方向相反的小漩涡。
当yeuler=±90°时,靠近方腔热壁面尤其在腔体下半部区域,磁浮升力和重力浮升力方向都向上,驱动热空气沿着热壁面向上运动,这在腔体下半部形成1个大漩涡;在腔体上半部,大约在Z=0.25处大多数热空气被挤出方腔中心,从侧壁来的冷空气进来补充,从而形成1个水平的小漩涡。
当yeuler=60°时,靠近冷壁面的冷空气沿着冷壁面向下运动,并且冷空气受磁场力吸引被吸引至线圈处而不能抵达热壁面,结果在方腔下部区域靠近冷壁面处形成1个大漩涡;另一方面,由于重力浮升力的作用,热空气趋向于沿着热壁向上运动,然而,热空气受到磁力的抑制不能沿着热壁向上运动,削弱了方腔内自然对流,造成Num较小。

图2 磁场力变化时的合力矢量、温度分布、速度矢量
Fig.2 Resultant force vector, Isothermal surface and velocity vector at different magnetic forces
当yeuler=-60°时,靠近热壁底部的磁浮升力绝大多数与重力浮升力方向一致,热空气流向顶部平面,然后到达冷壁面,最后回流到热壁面,此时,方腔内传热性能出现局部最大值。

图3 线圈绕Y轴倾斜时的计算结果
Fig.3 Computed results with a coil inclined around Y axis
研究中还发现,当γ越小,重力浮升力越大于磁浮升力时,流动结构和等温面分布越与纯重力自然对流相似;当γ非常大,磁浮升力远大于重力浮升力时,重力浮升力可以忽略,此时,矢量力合力、流动结构和等温面分布几乎与纯磁对流时完全一样。
图4所示为Ra=105和Da=10-3时,Num数随yeuler与γ的变化关系。图中曲线1表示γ=0工况下的Num,此时方腔内对流为纯重力对流,其他5条曲线表示不同磁场强度下重力和磁力耦合对流工况。从图4可以发现:当线圈倾斜角变化时,Num表现出复杂的变化行为,这些工况下计算所得的Num呈现出非对称性;线圈倾斜角yeuler接近于0°时出现Num最大值;另外,当γ=25与50时,Num随着yeuler的变化呈现交替性增大和减小,当磁浮升力和重力浮升力协同较好时,Num比纯重力对流时的大;而当磁浮升力和重力浮升力协同较差时,Num比纯重力对流时的小;当γ>100时,任意线圈倾斜角下Num均随着γ的增加而增大。

图4 Num随yeuler与γ的变化关系
Fig.4 Relationship among Num, yeuler and γ
4 结论
(1) 当线圈水平布置时,随着磁场力的增大,多孔介质方腔垂直横截面Y=0.5上空气流动由1个顺时针漩涡逐渐过渡到2个流动方向相反的漩涡,最后形成2个基本相互对称的漩涡。
(2) 线圈倾斜角yeuler和γ对多孔介质方腔内传热性能有重要影响,当γ<100时,Num随着yeuler的变化呈现交替性增大和减小;而当γ>100时,任意线圈倾斜角下Num均随着γ的增大而增大。
(3) 当yeuler=0°时,方腔内形成4个向前后绝热壁面倾斜的漩涡;当yeuler=±90°时,方腔下半部形成1个大漩涡而上部形成1个水平小漩涡;当yeuler为其他值时,方腔内流动结构变得非常复杂。
参考文献:
[1] Tagawa T, Ozoe H. Convective and diffusive phenomena of air in a vertical cylinder under strong magnetic field[J]. Numerical Heat Transfer Part B, 2002, 41(3): 1-14.
[2] Carruthers J, Wolfe R. Magnetothermal convection in insulation paramagnetic fluids[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 1968, 39(12): 5718-5722.
[3] Braithwaite D, Beaugnon E, Tournier R. Magnetically controlled convection in a paramagnetic fluid[J]. Nature, 1991, 354: 134-136.
[4] Tagawa T, Ujihara A, Ozoe H. Numerical computation for Rayleigh-Benard convection of water in a magnetic field[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2003, 46(21): 4097-4104.
[5] Shigemitsu R, Tagawa T, Ozoe H. Numerical computation for natural convection of air in a cubic enclosure under combination of magnetizing and gravitational forces[J]. Numerical Heat Transfer Part A, 2003, 43(5): 449-463.
[6] Kaneda M, Tagawa T, Ozoe H. Effect of the rayleigh number on the magnetizing force convection in a cube with cusp-shaped magnetic field[J]. Progress in Computational Fluid Dynamics, 2002, 2(2): 72-79.
[7] Akamatsu M, Higano M, Takahashi Y. Numerical prediction on heat transfer phenomenon in paramagnetic field gradient[J]. IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 2004, 14(2): 1674-1681.
[8] Filar P, Fornalid E, Kaneda Y. Three-dimensional numerical computation for magnetic convection of air inside a cylinder heated and cooled isothermally from a side wall[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2005, 48(9): 1858-1867.
[9] 杨立军, 任建勋, 宋耀祖. 不同磁场布置对空气自然对流的影响[J]. 太阳能学报, 2003, 24(3): 413-420.
YANG Li-jun, REN Jian-xun, SONG Yao-zu. Effects of different magnetic field configurations on air natural convection[J]. Acta Energiae Solaris Sinica, 2003, 24(3): 413-420.
[10] 杨立军, 杜小泽,杨勇平.永磁梯度磁场布置方式对空气自然对流换热的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2007, 58(12): 2980-2985.
YANG Li-jun, DU Xiao-ze,YANG Yong-ping. Influences of permanent gradient magnetic field configurations on air natural convection heat transfer[J]. Journal of Chemical Industry and Engineering, 2007, 58(12):2980-2985.
[11] 杨立军, 杜小泽, 刘登瀛. 超导磁体系统产生的磁场作用下的微重力环境[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2006, 26(22): 157-161.
YANG Li-jun, DU Xiao-ze, LIU Deng-ying. Micro-gravity environment generated by superconducting magnet system[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2006, 26(22): 157-161.
[12] 杨立军, 任建勋, 杜小泽. 不同磁致纵向涡形式对空气自然对流的影响[J]. 工程热物理学报, 2006, 27(2): 283-285.
YANG Li-jun, REN Jian-xun, DU Xiao-ze. Influence of different magnetically induced longitudinal vortices on air convection heat transfer[J]. Journal of Engineering Thermophysics, 2006, 27(2): 283-285.
[13] Bednarz T, Tagawa T, Kaneda M. Numerical study of joint magnetisation and gravitational convection of air in a cubic enclosure with an inclined electric coil[J]. Progress in Computational Fluid Dynamics, 2005, 5(4): 261-270.
[14] Bednarz T, Lei C W, John C, et al. Effects of a transverse, horizontal magnetic field on natural convection of a paramagnetic fluid in a cube[J]. International Journal of Thermal Sciences, 2009, 48(2): 26-33.
[15] Bednarz T, Fornalik E, Ozoe H, et al. Influence of a horizontal magnetic field on the natural convection of paramagnetic fluid in a cube heated and cooled from two vertical side walls[J]. International Journal of Thermal Sciences, 2008, 47(8): 668-679.
[16] Kakarantzas S C, Sarris I E, Greco A P. Magnetohydrodynamic natural convection in a vertical cylindrical cavity with sinusoidal upper wall temperature[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2009, 52(1): 250-259.
[17] WANG Qiu-wang, ZENG Ming, HUANG Zi-peng. Numerical investigation of natural convection in an inclined enclosure filled with porous medium under magnetic field[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2007, 50(17): 3684-3689.
[18] ZENG Min, WANG Qiu-wang , Ozoe H. Natural convection of diamagnetic fluid in an enclosure filled with porous medium under magnetic field[J]. Progress in Computational Fluid Dynamics, 2009, 9(2): 77-85.
[19] ZENG Min, WANG Qiu-wang, HUANG Zi-peng. Numerical investigation of natural convection in an enclosure filled with porous medium under magnetic field[J]. Numerical Heat Transfer Part A, 2007, 52(10): 959-971.
收稿日期:2011-02-03;修回日期:2011-04-15
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(51004115)
通信作者:姜昌伟(1973-),男,浙江江山人,博士,副教授,从事传热传质理论及工程应用研究;电话:0731-85258408;E-mail:cw.jiang@163.com
摘要:通过数值分析研究圆形载流线圈绕Y轴倾斜时多孔介质方腔内空气热磁对流。采用毕奥-萨伐定律计算磁场强度;对控制方程基本变量采用控制容积法离散,采用SIMPLE算法求解,获得空气热磁对流的流场和温度场以及壁面平均Nusselt数。研究结果表明:线圈倾斜角yeuler和磁场力数γ对多孔介质方腔内空气流场结构与传热性能有重要影响,当γ<100时,努塞尔数Num随着yeuler的变化呈现交替性增大和减小;而当γ>100时,Num随着γ的增加而增大;当yeuler=0°时,方腔上半部区域形成2个大漩涡而下半部区域形成2个小漩涡;当yeuler=±90°时,方腔下半部形成1个垂直大漩涡而顶部形成1个水平小漩涡。


