文章编号:1004-0609(2008)S1-0284-06
LiMn2O4/Li4Ti5O12复合材料的制备与电化学性能
何则强1, 2,熊利芝1, 2,吴显明2,陈 上2,黄可龙1
(1. 中南大学 化学化工学院,长沙 410083;
2. 吉首大学 化学化工学院,吉首 416000)
摘 要:
以LiMn2O4、醋酸锂和钛酸四丁酯为原料,乙醇为溶剂,采用原位复合法制备LiMn2O4/Li4Ti5O12复合材料。采用X射线衍射分析、红外光谱、扫描电镜和电化学测试等手段对复合材料进行表征。结果表明,在LiMn2O4/Li4Ti5O12复合材料中晶态的LiMn2O4表面被无定形结构的Li4Ti5O12包覆,但Li4Ti5O12的存在并没有改变LiMn2O4的晶体结构。由于Li4Ti5O12的包覆,LiMn2O4的倍率性能和高温性能都得到显著提高:室温下2.0C放电时20次循环后LiMn2O4/Li4Ti5O12复合材料的可逆容量达到108.4mA?h/g,平均每次循环的容量损失只有0.053%;而55 ℃ 1.0C放电时,经60次循环后LiMn2O4/Li4Ti5O12的放电容量为109.9 mA?h/g,平均每次循环的容量损失为0.036%。
关键词:
中图分类号:TM 912.9 文献标识码:A
Synthesis and electrochemical properties of LiMn2O4/Li4Ti5O12 composite
HE Ze-qiang1, 2, XIONG Li-zhi1, 2, WU Xian-ming2, CHEN Shang2, HUANG Ke-long1
(1. School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
2. College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Jishou University, Jishou 416000, China)
Abstract: LiMn2O4/Li4Ti5O12 composite was synthesized by in-situ composite technique using LiMn2O4, lithium acetate, tetrabutyl titanate as starting materials and was characterized by various electrochemical methods in combination with X-ray diffractometry (XRD), infrared (IR) spectroscopy and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). The results show that the amorphous Li4Ti5O12 is coated on the surface of crystalline LiMn2O4 to form the LiMn2O4/Li4Ti5O12 composite. The structure of LiMn2O4 does not change due to introduction of Li4Ti5O12. Coated with Li4Ti5O12, the rate capability and high temperature cyclability of LiMn2O4 are improved greatly. At room temperature, the discharge capacity of LiMn2O4/Li4Ti5O12 composite is more than 108.4 mA?h/g and the capacity loss per cycle is only 0.053% after cycling 20 times at 2.0C. While at 55 ℃, the discharge capacity of LiMn2O4/Li4Ti5O12 composite is more than 109.9 mA?h/g and the capacity loss per cycle is only 0.036% after cycling 60 times at 1.0C.
Key words: Li4Ti5O12; LiMn2O4; in-situ composite technique; lithium ion batteries
近几十年来,由于LiMn2O4具有资源丰富、毒性小、易回收,尤其是容易制备、脱锂量大等优点而倍受关注,被认为是最有希望取代LiCoO2的正极材 料[1]。但目前为止,LiMn2O4仍没有取代LiCoO2而应用于锂离子电池,其原因主要有2个:1) LiMn2O4的高温循环性能差[2]。研究发现,导致LiMn2O4的高温循环性能差的因素有Mn的溶解、电解质的分解、充放电循环过程中的结构不稳定、Jahn-Teller 效应等。而这些因素中Mn的溶解被认为是最主要的因素[3]。人们采用阳离子掺杂[4-5]和表面修饰[6-7]等手段部分解决了这个问题。2) LiMn2O4的倍率性能差。由于LiMn2O4的化学扩散系数(10-9~10-12 cm2/s)低[8-10],限制了电极颗粒之间的电流,从而降低了其倍率性能。
因此,如何通过改性提高LiMn2O4的高温性能和倍率性能是当前LiMn2O4研究的重点。考虑到Li4Ti5O12具有以下4个基本特征:1) Li4Ti5O12的化学扩散系数(10-6 cm2/s)[11]比LiMn2O4的大;2) LiMn2O4和Li4Ti5O12都具有尖晶石结构和Fd3m空间群[12-13];3) Li4Ti5O12具有极好的倍率性能[14-16];4) Li4Ti5O12是一种零应变材料,在锂离子嵌入和脱出过程中结构没变化[13]。本文作者采用原位复合法制备LiMn2O4/ Li4Ti5O12复合材料,对其倍率性能和高温性能进行 研究。
1 实验
将12.302 g CH3COOLi·2H2O溶于无水乙醇中,然后缓慢地向其中加入20 mL Ti(C4H9O)4(溶液中Li与Ti的物质的量比为4?5),并不断地搅拌,得到Li4Ti5O12前驱体溶液。然后再加入几滴去离子水并放在干燥箱中100 ℃保持4 h,得到白色或淡黄色的Li4Ti5O12前驱体干凝胶,经研磨后置于马沸炉800 ℃煅烧6 h,得到Li4Ti5O12粉末。
按照n(LiMn2O4)/n(Li4Ti5O12)=19?1向上述Li4Ti5O12前驱体溶液中缓慢加入自制的LiMn2O4,继续搅拌2 h得到均匀的悬浊液。往此悬浊液中加入几滴去离子水并放在干燥箱中100 ℃ 保持4 h,得到黑色前驱体干凝胶。前驱体干凝胶经研磨后置于马弗炉800 ℃煅烧6 h,即可得到黑色的Li4Ti5O12/LiMn2O4复合材料。
采用日本Rigaku型X射线粉末衍射仪对样品进行物相分析(Cu Kα 辐射,40 kV,100 mA,步宽0.02?,扫描速度0.5 (?)/min,扫描范围(2θ)为5?~85?)。采用美国Nicolet公司的傅里叶变换红外谱仪对样品进行红外光谱研究(波长:4 000~400 cm-1;分辨率:0.3 cm-1)。采用JEOL公司的JSM-5600LV Scanning Electron Microscope(SEM)在20 kV下对样品的表面形貌进行观察。
将80%的合成材料、10%的乙炔黑和10%的聚偏氟乙烯(PVDF)溶解在溶剂N-甲基吡咯烷酮(NMP)中形成浆料。将浆料均匀涂在铝箔上,涂层的厚度约为100 μm。将涂好的电极片裁剪成面积为1 cm2的工作电极,在60 ℃下真空干燥12 h备用。测试电池采用常规的扣式电池,以金属锂箔为对电极,1.0 mol/L LiPF6的EC-DMC(体积比为1?1)溶液为电解液,在充满氩气的手套箱中装配而成。所有的电化学测试在电化学综合测试系统上完成。
2 结果与讨论
图1所示为LiMn2O4(a)和LiMn2O4/Li4Ti5O12(b)的X射线衍射谱。从图1中可以明显看到LiMn2O4的特征衍射峰,但看不到Li4Ti5O12的特征衍射峰,这可能是因为在复合材料中Li4Ti5O12处于无定形态的缘故。Li4Ti5O12的存在并没有改变LiMn2O4的晶体结构。由布拉格方程可以计算得到LiMn2O4和LiMn2O4/ Li4Ti5O12的晶格常数分别为0.823 7 nm和0.823 6 nm,即:二者的晶格常数并没有明显变化,说明Li4Ti5O12并没有进入到LiMn2O4的晶格,而是包覆在其表面。
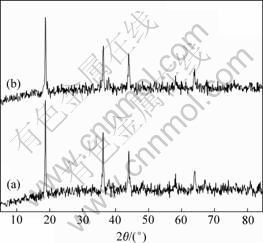
图1 LiMn2O4(a)和LiMn2O4/Li4Ti5O12(b)的X射线衍射谱
Fig.1 XRD patterns of LiMn2O4(a) and LiMn2O4/Li4Ti5O12(b)
图2所示为LiMn2O4 (a) 和LiMn2O4/Li4Ti5O12 (b)的红外光谱图。从图2可知,复合材料的红外光谱与LiMn2O4的特征吸收峰基本一致,这说明Li4Ti5O12的包覆并没有改变LiMn2O4的晶体结构。图2中3 200~ 3 600 cm-1和1 600 cm-1处的吸收峰是因为样品吸收空气中的水分引起的;2 300~2 500 cm-1处的吸收峰是空气中CO2的吸收峰;而出现在400~1 200 cm-1的吸收峰则对应着样品中的金属-氧的吸收峰。
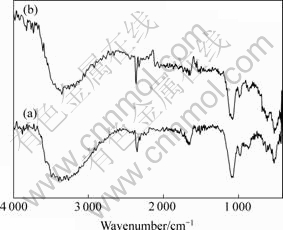
图2 LiMn2O4(a)和LiMn2O4/Li4Ti5O12(b)的红外光谱
Fig.2 IR spectra of LiMn2O4(a) and LiMn2O4/Li4Ti5O12(b)
图3所示为LiMn2O4(a)和LiMn2O4/Li4Ti5O12(b)的扫描电镜照片。从图3可以看到,包覆Li4Ti5O12前尖晶石LiMn2O4微粒棱角分明,是典型的立方结构,颗粒大小分布均匀,晶粒大小为0.5 ?m左右,晶体没有明显的结块。表面包覆Li4Ti5O12后的尖晶石LiMn2O4的晶体颗粒较包覆前的样品大,表面圆滑,颗粒大小分布不均匀,而且出现了团聚现象。大颗粒表面出现的小颗粒,是包覆层上的Li4Ti5O12微粒。
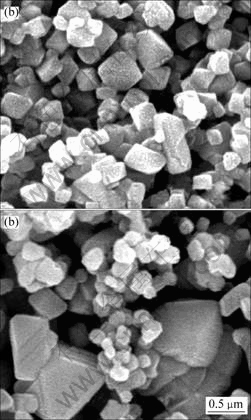
图3 LiMn2O4(a)和LiMn2O4/Li4Ti5O12(b)的扫描电镜图
Fig.3 SEM images of LiMn2O4(a) and LiMn2O4/Li4Ti5O12(b)
图4所示为LiMn2O4(a)和LiMn2O4/Li4Ti5O12(b)的首次放电曲线。从图4可以看到,包覆Li4Ti5O12前后LiMn2O4的首次放电曲线形状基本相同。但由于包覆Li4Ti5O12,LiMn2O4的放电平台电压有所下降,而放电容量也有所降低,LiMn2O4和LiMn2O4/Li4Ti5O12复合材料的放电容量分别达到122.2 mA/g和119.3 mA/g。
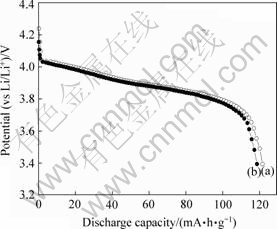
图4 LiMn2O4(a)和LiMn2O4/Li4Ti5O12(b)的首次放电曲线(电流倍率为0.1C)
Fig.4 Initial discharge capacity of LiMn2O4(a) and LiMn2O4/Li4Ti5O12(b) at 0.1C
图5所示为LiMn2O4 (a) 、LiMn2O4/Li4Ti5O12 (b)和LiMn2O4与Li4Ti5O12机械混合物(c)的循环性能曲线(电流倍率为0.1C)。由图5可见,循环100次后,0.1C放电时LiMn2O4的放电容量从122.2 mA?h/g下降到118.3 mA?h/g,平均每次循环的容量损失为0.032%;相同条件下,LiMn2O4与Li4Ti5O12机械混合物的放电容量从119.5 mA?h/g下降到116.2 mA?h/g,平均每次循环的容量损失为0.028%,而LiMn2O4/Li4Ti5O12复合材料的放电容量从119.3 mA?h/g下降到117.1 mA?h/g,平均每次循环的容量损失为0.018%。可见,在LiMn2O4材料中加入Li4Ti5O12后,其循环性能有所改善;而在LiMn2O4表面包覆Li4Ti5O12比LiMn2O4与Li4Ti5O12机械混合更能提高LiMn2O4的循环性能。
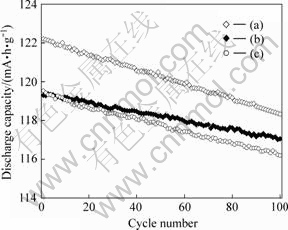
图5 LiMn2O4(a)、LiMn2O4/Li4Ti5O12(b)和LiMn2O4与Li4Ti5O12机械混和物(c)的循环性能曲线(电流倍率为0.1C)
Fig.5 Cycling performances of LiMn2O4(a), LiMn2O4/ Li4Ti5O12(b) and mixture of LiMn2O4 and Li4Ti5O12 at 0.1C
表1所列为不同电流倍率下LiMn2O4/Li4Ti5O12复合材料、LiMn2O4以及LiMn2O4与Li4Ti5O12机械混合物循环性能的比较。从表1可以看到,LiMn2O4/ Li4Ti5O12复合材料和LiMn2O4与Li4Ti5O12机械混合物的可逆比容量略低于LiMn2O4的可逆比容量,这是因为,包覆Li4Ti5O12后,电极中活性物质LiMn2O4的相对含量减少了。随着放电倍率的增大,由于极化作用增大,3种材料的容量都在降低。从20次循环后的容量损失来看,LiMn2O4/Li4Ti5O12复合材料在不同倍率下放电时平均每次循环的容量损失明显低于LiMn2O4和LiMn2O4与Li4Ti5O12机械混合物,如2.0C放电时20次循环后LiMn2O4的可逆容量为108.3 mA?h/g,平均每次循环的容量损失为0.108%;LiMn2O4与Li4Ti5O12机械混合物的可逆容量为106.9 mA?h/g,平均每次循环的容量损失为0.094%;而相同条件 下,Li4Ti5O12/ LiMn2O4复合材料的可逆容量达到 108.4 mA?h/g,平均每次循环的容量损失只有0.053%。可见,包覆Li4Ti5O12后,LiMn2O4的倍率性能大大提高。这是因为,LiMn2O4的化学扩散系数低,限制了大电流倍率时电极材料颗粒之间通过的电流,导致其较差的高倍率性能。但表面包覆Li4Ti5O12后,由于Li4Ti5O12微粒的存在,缩短了锂离子在电极和电解质溶液间扩散距离[17],提高了其扩散速度,从而改善了其倍率性能。同时,由于LiMn2O4具有良好的电催化活性,加速了电极表面的固体电解质界面膜(SEI膜)的形成,从而增加了电极与电解质之间的接触电阻[2],而包覆Li4Ti5O12后,SEI膜的形成受到抑制,接触电阻降低,扩散系数增大。从表1中也可以看到,表面包覆Li4Ti5O12得到的复合材料比LiMn2O4与Li4Ti5O12机械混合物具有更优良的倍率性能,这可能是由于表面包覆材料比机械混合物粒子间混合更加均匀,颗粒间的电接触更好,导致充放电循环过程中电化学极化减少的缘故。
表1 不同电流倍率下LiMn2O4/Li4Ti5O12复合材料和LiMn2O4以及LiMn2O4与Li4Ti5O12机械混合物循环性能的比较
Table 1 Comparison of cycling performance for LiMn2O4/Li4Ti5O12 composite, LiMn2O4 and mixture of LiMn2O4 and Li4Ti5O12 at various current rates
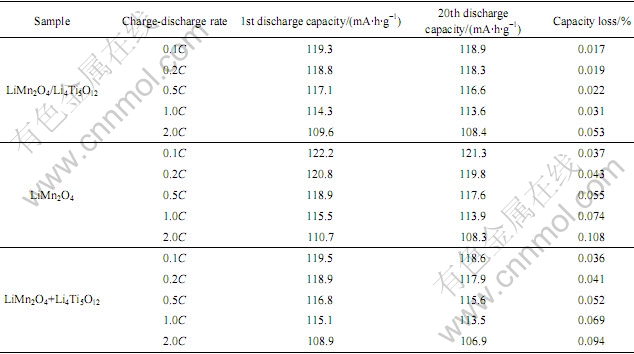
图6所示为55 ℃时LiMn2O4、LiMn2O4/Li4Ti5O12复合材料以及LiMn2O4与Li4Ti5O12机械混合物的高温循环性能,放电倍率为1.0C。在55 ℃时,LiMn2O4、LiMn2O4/Li4Ti5O12和LiMn2O4与Li4Ti5O12机械混合物的首次放电容量分别为113.1、112.3和112.9 mA?h/g,都比室温时的的稍低(见表1)。经20次循环后,LiMn2O4和LiMn2O4/Li4Ti5O12和LiMn2O4与Li4Ti5O12机械混合物的放电容量分别为111.3,111.5和111.4 mA?h/g,平均每次循环的容量损失为0.080%,0.036和0.066%;经60次循环后,LiMn2O4、LiMn2O4/ Li4Ti5O12和LiMn2O4与LiTi5O12机械混合物的放电容量分别为108.0,109.9和108.8 mA?h/g,平均每次循环的容量损失为0.075%,0.036%和0.061%。可见,由于包覆Li4Ti5O12,LiMn2O4的高温性能显著提高。这是因为,用Li4Ti5O12包覆在LiMn2O4的表面,直接与电解液接触的锰减少了,从而在一定程度上抑制了锰的溶解,改善了尖晶石锂锰氧的循环性能,尤其是改善了其高温性能。
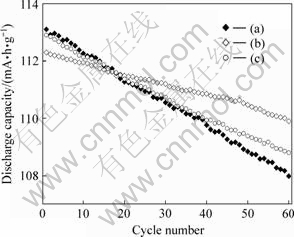
图6 LiMn2O4(a)、LiMn2O4/Li4Ti5O12(b)和LiMn2O4与Li4Ti5O12机械混合物的高温循环性能曲线(电流倍率为1.0C,温度为55 ℃)
Fig.6 High temperature cycling performances of LiMn2O4(a), LiMn2O4/Li4Ti5O12(b) and mixture of LiMn2O4 and Li4Ti5O12(c) at 1.0C and 55 ℃
3 结论
1) 采用原位复合法制备了LiMn2O4/Li4Ti5O12复合材料。在LiMn2O4/Li4Ti5O12复合材料中晶态的LiMn2O4表面被无定形结构的Li4Ti5O12包覆。
2) 由于Li4Ti5O12的包覆,缩短了锂离子在电极和电解质溶液间扩散距离,提高了其扩散速度,从而改善了LiMn2O4的倍率性能。
3) 由于Li4Ti5O12的包覆,电极表面直接与电解液接触的锰减少了,从而在一定程度上抑制了锰的溶解,改善了LiMn2O4的循环性能,尤其是改善了其高温性能。
REFERENCES
[1] GUYOMARD D, TARASCON J M. Li Metal-free rechargeable LiMn2O4/carbon cells: Their understanding and optimization[J]. J Electrochem Soc, 1992, 139(4): 937-948.
[2] AMATUCCI G G, BLYR A, SIGALA C, ALFONSE P, TARASCON J M. Surface treatments of Li1+xMn2-xO4 spinels for improved elevated temperature performance[J]. Solid State Ionics, 1997, 104(1/2): 13-25.
[3] ANTONINI A, BELLITTO C, PASQUALI M, PISTOIA G. Factors affecting the stabilization of Mn spinel capacity upon staring and cycling at high temperatures[J]. J Electrochem Soc, 1998, 145(8): 2726-2732.
[4] WU Xian-ming, CHEN Shang, HE Ze-qiang, MA Ming-you, XIAO Zhuo-bing, LIU Jian-ben. Solution-derived lithium manganese oxide thin films with silver additive and their characterization[J]. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2007, 101(1): 217-222.
[5] DOKKO K, HORIKOSHI S, ITOH T, NISHIZAWA M, MOHAMEDI M, UCHIDA I. Microvoltammetry for cathode materials at elevated temperatures: Electrochemical stability of single particles[J]. J Power Sources, 2000, 90(1): 109-115.
[6] GNANARAJ J S, POL V G, GEDANKEN A, AURBACH D. Improving the high-temperature performance of LiMn2O4 spinel electrodes by coating the active mass with MgO via a sonochemical method[J]. Electrochem Comm, 2003, 5(11): 940-945.
[7] LEE S W, KIM K S, MOON H S, KIM H J, CHO B W, CHO W I, JU J B, PARK J W. Electrochemical characteristics of Al2O3-coated lithium manganese spinel as a cathode material for a lithium secondary battery[J]. J Power Sources, 2004, 126(1/2): 150-155.
[8] DEISS E. Spurious chemical diffusion coefficients of Li+ in electrode materials evaluated with GITT[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2005, 50(14): 2927-2932.
[9] WU Xian-ming, HE Ze-qiang, CHEN Shang, MA Ming-you, XIAO Zhuo-bing, LIU Jian-ben. The effect of thickness on the properties of solution-deposited LiMn2O4 thin films[J]. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2007, 105(1): 58-61.
[10] WU Xian-ming, CHEN Shang, HE Ze-qiang. LiMn2O4 thin films derived by rapid thermal annealing and its Li ion diffusion behavior[J]. Rare Metals, 2006, 25: 620-624.
[11] TAKAI S, KAMATA M, FUJINE S, YONEDA K, KANDA K, ESAKA T. Diffusion coefficient measurement of lithium ion in sintered Li1.33Ti1.67O4 by means of neutron radiography[J]. Solid State Ionics, 1999, 123(1/4): 165-172.
[12] MIURA K, YAMADA A, TANAKA M. Electric states of spinel LixMn2O4 as a cathode of the rechargeable battery[J]. Electrochimica Acta,1996, 41(2): 249-256.
[13] OHZUKU T, UEDA A, YAMAMOTO N. Zero-strain insertion material of Li[Li1/3Ti5/3]O4 for rechargeable lithium cells[J]. J Electorchem Soc, 1995, 142(5): 1431-1435.
[14] SINGHAL A, SKANDAN G, AMATUCCI G, BADWAY F, YE N, MANTHIRAM A, YE H, XU J J. Nanostructured electrodes for next generation rechargeable electrochemical devices[J]. J Power Sources, 2004, 129(1): 38-44.
[15] HE Ze-qiang, XIONG Li-zhi, WU Xian-ming, LIU Wen-ping, HUANG Ke-long. Preparation of Li4Ti5O12-polyaniline composite by in-situ polymerization method and its electrochemical properties[C]//International Battery Material Association 2007 Conference (IBA2007), 2007: 197-198.
[16] WU Xian-ming, XIAO Zhuo-bing, HE Ze-qiang, MA Ming-you, LIU Jian-ben, XU Ming-fei. Preparation and characterization of Li4/3Ti5/3O4 thin films by solution deposition[J]. Materials Letters, 2006, 60(1): 422-427.
[17] 刘东强, 吁 霁, 孙玉恒, 何泽珍, 刘兴泉. LiMn2O4表面包覆Li4Ti5O12的制备及倍率特性[J]. 无机化学学报, 2007, 23(1): 41-45.
LIU Dong-qiang, YU Ji, SUN Yu-heng, HE Ze-zhen, LIU Xing-quan. Preparation and rate property of Li4Ti5O12 coated LiMn2O4 for lithium ion battery[J]. Chinese Journal of Inorganic Chemistry, 2007, 23(1): 41-45.
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(20376086);中国博士后科学基金资助项目(2005037700);湖南省自然科学基金资助项目(07JJ3014);湖南省教育厅科研项目(07A058);中南大学博士后科学基金资助项目(2004107)
通讯作者:何则强,副教授,博士;电话:13787930478;E-mail: csuhzq@163.com
(编辑 赵 俊)


