文章编号:1004-0609(2013)S1-s0722-04
高温反应烧结制备Ti-45Al-10Nb合金
李学问,孙宏飞,张 鹏,房文斌
(哈尔滨工业大学 材料科学与工程学院,哈尔滨 150001)
摘 要:
采用Ti、Al、Nb三种元素粉末为原料,通过机械球磨和真空热压烧结方法,制备全致密的Ti-45Al-10Nb合金。研究球磨粉末形貌,烧结所得坯料的显微组织及成分分布。结果表明:机械球磨有效地细化与复合Ti、Al和Nb三种单质粉末,球磨后的粉末经1 350 ℃、2 h、50 MPa烧结得到密度为4.3 g/cm3的烧结块体,其组织为双态类型。在烧结坯中,三种元素分布均匀。
关键词:
Nb-TiAl合金;元素粉末;真空热压;反应烧结;显微组织;
中图分类号:TG146.2 文献标志码:A
Fabrication of Ti-45Al-10Nb alloy with reaction sintering
LI Xue-wen, SUN Hong-fei, ZHANG Peng, FANG Wen-bin
(School of Materials Science and Engineering, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin 150001, China)
Abstract: A full dense Ti-45Al-10Nb alloy was synthesized by mechanical milling and vacuum hot pressing method with three elements: Ti, Al and Nb. The morphology of milled powders, the microstructure and the distribution of major elements of the sintered specimen were studied. The results show that Ti, Al and Nb powders are refined and well-distributed through mechanical milling. Fully dense compacts are conducted using the milled powders at 1 350 ℃ under the load of 50 MPa for 2 h. The density of the sintered alloy is measured to be 4.3 g/cm3. Elements Ti, Al and Nb distribute evenly the sintered alloy.
Key words: Nb-TiAl alloys; elemental powders; vacuum hot pressing; reaction sintering; microstructure
TiAl金属间化合物具有密度小,室温比强度和比刚度高、高温抗氧化性及力学性能性能优异等特点,在航空航天领域非常具有应用潜力而受到广泛关注[1-4]。研究表明:高Nb-TiAl合金具有更优异的高温性能,能使TiAl的使用温度提高60~100 ℃,被认为是最有应用潜力的新一代高温轻质结构材料[5-7],通常高Nb-TiAl合金的成分为Ti-(45~46)Al-(5~9)Nb-(C,B, Y)(摩尔分数,%)。然而,随着大量高熔点Nb元素的加入,且金属间化合物本身的低室温塑性及较差的铸造性能使高Nb-TiAl合金的加工及成形难度进一步提高[8-9]。采用粉末冶金方法进行净近成形是一种理想的加工技术[10-11],而采用元素粉末冶金工艺能在低成本的基础上实现高Nb-TiAl合金的合成与制备,且可以实现细化晶粒和优化显微组织的作用,因此该工艺引起广泛关注[12-13]。北京科技大学林均品等[14]在高Nb-TiAl合金方面做了开创性工作,德国GKSS[15]利用粉末冶金法对高Nb-TiAl合金板材进行大量研究工作。本文作者采用元素粉末冶金法,通过机械球磨和高温反应烧结工艺制备Ti-45Al-10Nb合金。探讨了经10 h高能球磨后Ti、Al和Nb三种元素粉的演变情况,同时,对其烧结后的组织及元素的扩散进行分析。
1 实验
实验选用Ti、Al和Nb三种单质元素粉末作为原料,其纯度均达到99.5%,平均粒径小于45 μm。将Ti粉、Al粉和Nb粉按Ti-45Al-10Nb(摩尔分数,%)成分配比。在QM-2SP12行星式球磨机上进行球磨,球磨前先混粉2 h,采取正反转方式,转速为150 r/min。高能球磨时,加入1%(质量分数)的硬脂酸作为过程控制剂,在高纯氩气保护下进行。具体球磨参数为:转速250 r/min,球磨时间10 h,每球磨10 min停20 min。随后,采用真空热压烧结系统对球磨获得的Ti/Al/Nb复合粉末进行高温反应烧结,烧结温度为1 350 ℃,保温时间为2 h,烧结过程中升温速度为5 ℃/min,同时采用分阶段持续加压保压,最终得到尺寸为d60 mm×15 mm的块体材料。
通过OLS3100/SZX16激光共聚焦体视显微镜和FEI Quanta 200FEG扫描电子显微镜(SEM)观察球磨10 h后的粉末及烧结块体材料的形貌组织。另外,采用扫描电子显微镜的能谱仪(EDS)和背散射成像(BSE)定量和定性的分析烧结块体材料的成分分布情况。
2 结果与分析
2.1 Ti-45Al-10Nb复合粉末形貌
为细化并均匀复合三种原始粉末,对按Ti-45Al-10Nb比例配比的复合粉末进行机械高能球磨。图1所示为经10 h高能球磨后的粉末颗粒内部断面及局部放大区域形貌。如图1所示,相对于原始粉末,高能球磨后的Ti、Al和Nb三种元素粉末在机械力作用下,受到磨球的摩擦和撞击等作用产生剧烈的塑性变形,相继发生扁平、破碎和粘合等变化,粉末颗粒总体明显细化,呈不规则分布。同时,部分细小颗粒团聚成较粗大复合粉末颗粒。粒度分析表明,球磨后复合粉末颗粒的平均粒径为13 μm,且三种元素粉末复合均匀,如图1(b)所示。
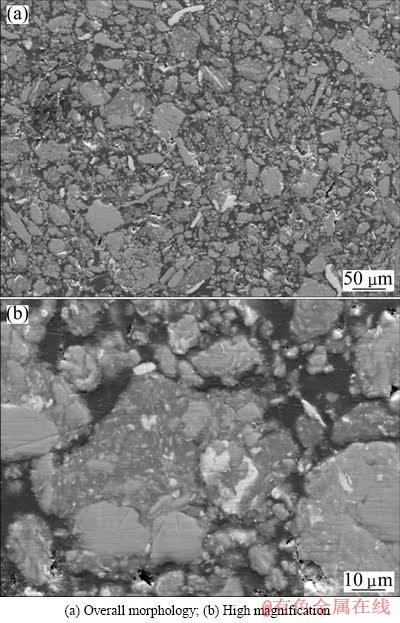
图1 球磨10 h的Ti-45Al-10Nb复合粉末SEM像
Fig.1 SEM images of Ti-45Al-10Nb composite powders after 10 h milling
2.2 Ti-45Al-10Nb复合粉末热分析
对球磨得到的复合粉末进行热分析,图2为Ti-45Al-10Nb复合粉末在1 150~1 500 ℃之间的差热分析(DTA)曲线。在此温度区间内,Ti和Al两种元素反应已经完成,主要发生相转变及部分未完全固溶的Nb元素(或Nb的化合物)的扩散。如图2所示,在此温度区间内,产生两个明显的吸热峰,分析认为第一个吸热峰开始的温度(约1 250 ℃)与发生共析转变温度Teu(α2+γ→α)有关,第二个吸热峰(约1 320 ℃)为α相转变温度Tα。相对于传统低合金化TiAl合金,其发生共析转变温度得到明显提高,分析认为这与高Nb含量的存在有关。Nb元素的加入增加相转变激活能并提高共析转变温度。在1 350~1 500 ℃之间,该阶段的曲线和反应非常复杂。为了得到Nb元素充分扩散的片层组织,选择烧结温度为1 350 ℃。
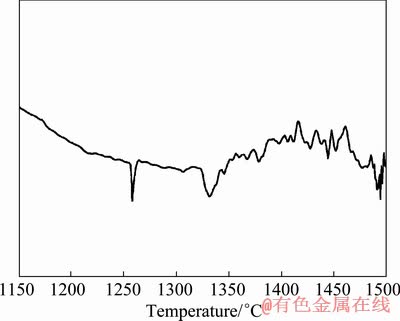
图2 Ti-45Al-10Nb复合粉末的的DTA曲线
Fig.2 DTA curve of Ti-45Al-10Nb composite powder
2.3 烧结块体组织分析
采用排水法测得经1 350 ℃、2 h真空热压烧结后,烧结块体材料的密度约为4.3 g/cm3,接近全致密状态。对烧结坯的组织进行分析,结果如图3所示。从图3(a)可以看出,高温反应烧结后的坯料基体组织由白色和灰色两相组成,其分别为α2-Ti3Al和γ-TiAl相,以γ-TiAl相为主,其次为α2-Ti3Al。在两相基体上细小的灰色颗粒弥散的分布在基体之上,成分分析表明其成分接近Ti2Al,分析认为该灰色颗粒为烧结过程中生成的B2相。同时可以看出部分区域存在少量黑色颗粒,其主要为Al的氧化物,这是由于在球磨制粉及反应烧结过程中有少量氧气存在,反应烧结时活性高的Al极易与O2发生反应,生成氧化物。从图中还可以看出,在此烧结条件下,Nb元素已充分扩散,完全固溶在TiAl基体中,烧结组织存在少量亮区,该区域为Nb元素高固溶区域。金相组织如图3(b)所示,该烧结坯为双态组织,晶粒细小,晶粒尺寸在20 μm左右,烧结组织中存在大量孪晶。该烧结温度处于Tα相转变温度以上,而在此温度下未能生成全片层组织,这主要与高含量的Nb元素的存在有关,Nb元素扩散较慢,致使相的转变需要更长时间。在此温度及保温时间条件下,得到组织及成分分布较均匀的烧结块体材料。
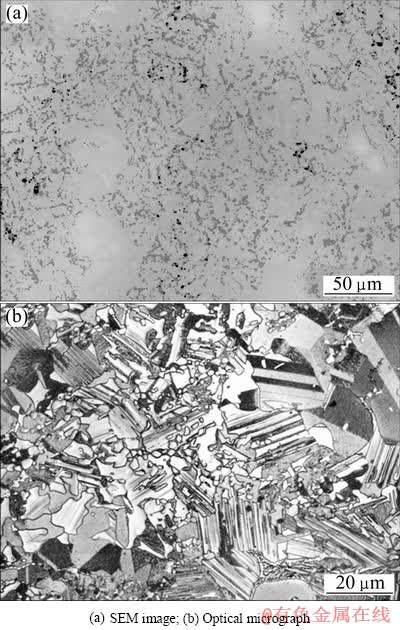

图3 反应烧结Ti-45Al-10Nb块体微观组织形貌
Fig.3 Microstructures of sintered Ti-45Al-10Nb alloy
2.4 元素分布
采用元素线扫描分析烧结坯中三种主要元素分布的均匀性。结果如图4所示,Nb元素的摩尔分数在10%左右,且上下波动幅度较小,说明Nb元素均匀的分布于烧结块体中。而Ti和Al两种元素的摩尔分数在45%上下波动,变化幅度较大,这与烧结中形成不同相有关。总体而言,烧结块体中三种元素含量接近烧结前复合粉末中元素比例。
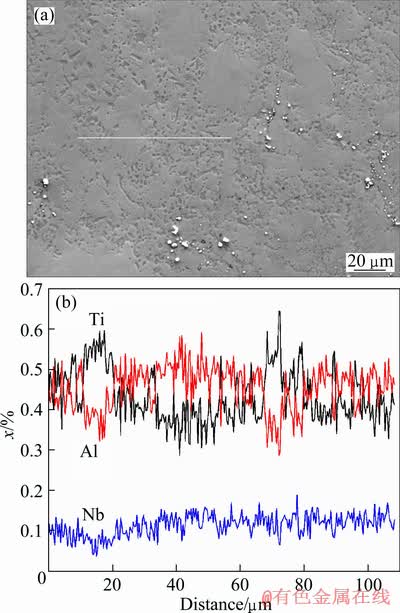
图4 Ti-45Al-10Nb合金的SEM形貌及元素线扫描曲线
Fig.4 SEM image (a) and elemental line scanning curves (b) of sintered Ti-45Al-10Nb alloy
3 结论
1) 经10 h高能球磨后的复合粉末,Ti、Al和Nb三种元素粉得到充分细化与复合,复合粉末平均粒径为13 μm。
2) 反应烧结后的烧结坯主要由γ-TiAl和α2-Ti3Al两相组成,细小的B2相组织弥散分布于基体组织组织中,基体组织为双态类型。
3) 烧结坯中三种元素分布均匀,成分接近原始比例,Nb元素充分扩散,无明显偏析存在。
REFERENCES
[1] WU X H. Review of alloy and process development of TiAl alloys[J]. Intermetallics, 2006, 14(10-11): 1114-1122.
[2] 王 刚, 徐 磊, 崔玉友, 杨 锐. 粉末冶金TiAl基合金高温变形行为及其本构模型[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2010, 20(S1): s269-s273.
WANG Gang, XU Lei, CUI Yu-you, YANG Rui .High temperature deformation behavior of powder metallurgy TiAl alloy and its constitutive model[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2010, 20(S1): s269-s273.
[3] DIMIDUK D M. Gamma titanium aluminide alloys-as assessment within the competition of aerospace structural materials[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 1999, 263: 281-288.
[4] PAUL J D H, LORENZ U, OEHRING M, APPEL F. Up-scaling the size of TiAl components made via ingot metallurgy[J]. Intermetallics, 2013, 32: 318-328.
[5] HUANG Z W, ZHU D G. Thermal stability of Ti-44Al-8Nb-1B alloy[J]. Intermetallics, 2008, 16: 156-167.
[6] Z C LIU, LIN J P, LI S J, CHEN G L. Effects of Nb and Al on the microstructures and mechanical properties of high Nb containing TiAl base alloys[J]. Intermetallics, 2002, 10(7): 653-659.
[7] CHEN G L, XU X J, TENG Z K, WANG Y L, LIN J P. Microsegregation in high Nb containing TiAl alloy ingots beyond laboratory scale[J]. Intermetallics, 2007, 15: 625-631.
[8] LASALMONIE A. Intermetallics: Why is it so difficult to introduce them in gas turbine engines?[J]. Intermetallics, 2006, 14: 1123-1129.
[9] LIU B, LIU Y, ZHANG W, HUANG J S. Hot deformation behavior of TiAl alloys prepared by blended elemental powders[J]. Intermetallics, 2011, 19(2): 154-159.
[10] TAGUCHI K, AYADA M, ISHIRAHA K N, SHINGU P H. Near-net shape processing of TiAl intermetallic compounds via pseudoHIP-SHS route[J]. Intermetallics, 1995, 3(1): 91-98.
[11] 欧阳鸿武, 刘 咏, 贺跃辉, 黄伯云. 粉末冶金TiAl合金排气门的研制[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2002, 12(2): 334-337.
OUYANG Hong-wu, LIU Yong, HE Yue-hui, HUANG Bai-yun. Development of powder metallurgy TiAl-based alloy automotive exhaust valve[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2002, 12(2): 334-337.
[12] 肖代红, 袁铁锤, 贺跃辉, 王守仁. 粉末冶金钛合金的制备与力学性能[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2010, 20(S1): s303-s308.
XIAO Dai-hong, YUAN Tie-chui, HE Yue-hui, WANG Shou-ren. Synthesis and mechanical properties of powder metallurgy titanium alloy [J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2010, 20(S1): s303-s308.
[13] SU Y J, ZHANG D L, KONG F T, CHEN Y Y. Microstructure and mechanical properties of TiAl alloys produced by rapid heating and open die forging of blended elemental powder compacts[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2013, 563: 46-52.
[14] 林均品, 张来启, 宋西平, 叶 丰, 陈国良. 轻质γ-TiAl金属间化合物的研究进展[J]. 中国材料进展, 2010, 29(2): 1-8.
LIN Jun-pin, ZHANC Lai-qi, SONG Xi-ping, YE Feng, CHEN Guo-liang. Status of research and development of light-weight γ-TiAl intermetallic based compounds[J]. Materials China, 2010, 29(2): 1-8.
[15] DAS G, KESTLER H, CLEMENS H, BARTOLOTTA P A. Sheet gamma TiAl: Status and opportunities[J]. JOM, 2004, 56(11): 42-45.
(编辑 王 超)
收稿日期:2013-07-28;修订日期:2013-10-10
通信作者:李学问;Tel:0451-86403365;E-mail:lixuewen2000@163.com
摘 要:采用Ti、Al、Nb三种元素粉末为原料,通过机械球磨和真空热压烧结方法,制备全致密的Ti-45Al-10Nb合金。研究球磨粉末形貌,烧结所得坯料的显微组织及成分分布。结果表明:机械球磨有效地细化与复合Ti、Al和Nb三种单质粉末,球磨后的粉末经1 350 ℃、2 h、50 MPa烧结得到密度为4.3 g/cm3的烧结块体,其组织为双态类型。在烧结坯中,三种元素分布均匀。
[2] 王 刚, 徐 磊, 崔玉友, 杨 锐. 粉末冶金TiAl基合金高温变形行为及其本构模型[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2010, 20(S1): s269-s273.
[11] 欧阳鸿武, 刘 咏, 贺跃辉, 黄伯云. 粉末冶金TiAl合金排气门的研制[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2002, 12(2): 334-337.
[12] 肖代红, 袁铁锤, 贺跃辉, 王守仁. 粉末冶金钛合金的制备与力学性能[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2010, 20(S1): s303-s308.
[14] 林均品, 张来启, 宋西平, 叶 丰, 陈国良. 轻质γ-TiAl金属间化合物的研究进展[J]. 中国材料进展, 2010, 29(2): 1-8.


