网络首发时间: 2017-04-05 17:08
白光LED用硅基氮 (氧) 化物荧光粉的研究进展
中南大学化学化工学院
北京有色金属研究总院稀土材料国家工程研究中心有研稀土新材料股份有限公司
摘 要:
硅基氮 (氧) 化物荧光粉因其具有结构特性多样化、发光效率高、热稳定性和化学稳定性好等优点, 在白光LED领域有着广阔的应用前景。自20世纪末以来, 多种基质结构的硅基氮 (氧) 化物荧光粉陆续被发现和报道。本文综述了近年来硅基氮 (氧) 化物荧光粉的基质体系和发光性能, 分析总结了硅基氮 (氧) 化物荧光粉的制备方法及发光性能改进的研究新进展。最后, 展望了硅基氮 (氧) 化物荧光粉的研究发展方向, 指出 (Ca, Sr) AlSiN3:Eu2+红色荧光粉需进一步提高发光效率, La3Si6N11:Ce3+黄色荧光粉需进一步完善发光性能与制备工艺、晶体结构间的相互影响规律, 而β-Sialon:Eu2+绿色荧光粉需深入研究激活剂Eu2+的有效溶入机制, 提高其发光性能和发光效率。此外, 开发更多具有更优异性能的新型硅基氮 (氧) 化物荧光粉, 探索工艺条件和缓、成本低廉、适于工业化量产的简易的制备技术、装备和路线, 也是氮 (氧) 化物荧光粉研制需继续努力的方向。
关键词:
中图分类号: TN104.3;TN312.8
作者简介:赵春雷 (1975-) , 男, 黑龙江齐齐哈尔人, 硕士, 教授;研究方向:稀土发光材料;E-mail:zhaochl@vip.163.com;;叶红齐, 教授;电话:0731-88876605;E-mail:yeslab@csu.edu.cn;
收稿日期:2016-09-08
基金:国家重点研发计划项目 (2016YFB0400600, 2016YFB0400605);国家自然科学基金项目 (51502020);2015年工业转型升级强基工程项目资助;
Research Progress in Silicon-Based (Oxy) Nitride Phosphors for Phosphor-Converted White LED
Zhao Chunlei Hu Yunsheng Chen Kai Xu Huibing Shao Lengleng Ye Hongqi
College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Central South University
National Engineering Research Center for Rare Earth Materials, General Research Institute For Nonferrous Metals, Grirem Advanced Materials Co., Ltd.
Abstract:
The silicon-based (oxy) nitride phosphors were considered as promising candidate materials for phosphor-converted white LED owing to their structure characteristics persification, high luminous efficiency, high thermal stability and chemical stability.Since the end of last century, a variety of host structure of silicon-based (oxy) nitride phosphors have been found and reported.Here different kinds of silicon-based (oxy) nitride phosphor host systems and their luminescence properties were reviewed.The latest research progress in the improvement of the preparation methods and luminescence properties of silicon-based (oxy) nitride phosphors were intensively summarized and discussed.At last, the research and development trend in white LED of silicon-based (oxy) nitride phosphors were pointed out. (Ca, Sr) AlSiN3: Eu2+ red phosphors need to be further improved in the luminous efficiency.La3Si6N11:Ce3+ yellow phosphors need to be further studied on the interactional relationship of the luminescent properties with the synthesis technologies and the crystal structures.β-Sialon: Eu2+ green phosphors need to be in-depth investigated on the effective introduction mechanism of the activator Eu2+ into the β-Sialon host and the improvement of luminescent properties and luminous efficiency, and so on.In addition, the development of more new silicon-based (oxy) nitride phosphors with more excellent properties, and the exploration of simple synthesis technologies, equipments and processes with moderate condition, low cost and suitable for industrialized production are also directions for the development of silicon-based (oxy) nitride phosphors.
Keyword:
silicon-based nitride; silicon-based oxynitride; phosphor; white LED;
Received: 2016-09-08
白光LED是一种全固态光源, 具有效率高、能耗低、无污染、寿命长、体积小、响应快、工作电压低及安全性好等优点, 被誉为是继白炽灯、荧光灯、高压气体放电灯之后的21世纪新光源。自从1997年日亚化学公司生产出第一支商用白光LED以来, 白光LED的研究与应用得到了蓬勃发展[1]。目前, 最成熟、市场应用最广泛的白光LED技术是采用荧光粉涂覆半导体芯片的方法获得白光, 应用的荧光粉也已经从最早期的单一的黄色荧光粉拓展到了黄色/绿色荧光粉与红色荧光粉的组合, 因为后者不仅可以获得更高的显色指数, 而且色温可调范围也广, 获得的白光LED光色质量更佳。所涉及的实用型荧光粉除了一直沿用至今的石榴石型铝酸盐荧光粉, 还有碱土金属硅酸盐荧光粉、硅基氮 (氧) 化物荧光粉、氟化物荧光粉等。
硅基氮 (氧) 化物荧光粉是20世纪末才发展起来的一类新型荧光粉体系, 虽然发展时间不长, 但因其具有发光效率高、光谱可调范围宽、热淬灭特性和物理化学稳定性优异等优点, 迅速在白光LED上得到了广泛应用, 并掀起了业界的研究热潮[2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14]。本文希望通过梳理硅基氮 (氧) 化物荧光粉近年来的研究进展, 对硅基氮 (氧) 化物荧光粉的进一步研究的思路和方向提供参考。
1 硅基氮 (氧) 化物荧光粉晶体结构
硅基氮 (氧) 化物荧光粉的晶体结构是由 (Si, Al) X4 (X=O/N, Si可以被Al部分取代) 共角四面体形成的高凝聚三维网络结构, 金属离子在晶格中位于网络的通道区域或间隙位置[5]。在这种网络结构中, (Si, Al) ∶X的比值通常不小于1∶2。由于N原子有3对孤对电子, 它比O原子的共价性更强, 拥有更多的成键可能。在硅基氮 (氧) 化物荧光粉的晶体结构中, 根据N原子联结的Si原子数量, N原子可以分别与2个、3个、4个Si原子联结;同时, (Si, Al) X4四面体通过共角、共边等形成更多复杂的结构, 并给其他金属离子提供了占据空间;而且, 在硅基氮 (氧) 化物的结构中, 大部分氧原子与氮原子在四面体中可以互相随机取代, 这进一步导致了它结构性能的多样化[15]。
复杂多变的结构特性造就了硅基氮 (氧) 化物荧光粉光色性能可调范围广的特性。当植入稀土离子Eu2+或Ce3+等发光中心后, 硅基氮 (氧) 化物网络结构中本身丰富的Si-N键连接方式, 将使得所掺杂稀土离子的能级轨道发生明显改变;而且, 由于氮氮键能 (942 k J·mol-1) 大于氧氧键能 (494k J·mol-1) , 氮-氮键具有较强的共价键性, 会产生强的电子云膨胀效应, 使发光中心 (Eu2+, Ce3+等) 的5d电子的激发态能量降低, 这些稀土离子的5d壳层裸露于外层, 受晶体场的影响显著, 4f-5d能级之间的能量跃迁将随晶体环境的改变而明显变化[3], 从而产生各色各样的光谱发射, 发光范围可以覆盖整个可见光范围, 而且激发光谱涵盖紫外、近紫外和蓝光波段, 能够与紫外LED或者蓝光LED很好的匹配, 满足制作各类高显色白光LED的应用需要[16]。
2 主要的硅基氮 (氧) 化物荧光粉
自20世纪末以来, 多种基质结构的硅基氮 (氧) 化物荧光粉陆续被发现和报道, 根据基质组成中所含元素种类的多少, 可以分为三元系、四元系和多元系硅基氮 (氧) 化物, 其中常见的基质体系主要包括MAl Si N3 (M=Ca, Sr) [17,18,19], MSi N2 (M=Ca, Sr, Ba) [20,21], M2Si5N8 (M=Ca, Sr, Ba) [22], Sr Al Si4N7[25,26], La3Si6N11[27,28,29], MSi2O2N2 (M=Ca, Sr, Ba) [30,31], Ba3Si6O12N2[32,33,34], Sr-Sialon[35,36,37,38], α-Sialon[39,40,41,42,43], β-Sialon[44,45,46,47]等, 与这些基质相匹配的发光中心离子主要是Eu2+和Ce3+。表1列出了文献报道的主要硅基氮 (氧) 化物荧光粉及其发光性能。其中, 已有 (Sr, Ca) Al Si N3:Eu2+, Ca2Si5N8:Eu2+, La3Si6N11:Ce3+及β-Sialon:Eu2+等硅基氮 (氧) 化物荧光粉实现商业化, 为高端白光LED的实现做出了重要贡献。
3 研究进展
3.1 硅基氮 (氧) 化物红色荧光粉
硅基氮 (氧) 化物荧光粉最早的应用是从M2Si5N8:Eu2+ (M=Ca, Sr, Ba) 红色荧光粉开始的, 由于其具有比硫化物体系红粉更为稳定的物理化学性能, 在其批量化制备技术难题被突破后, 便迅速取代硫化物荧光粉应用于高显色白光LED的制作。
表1 报道的主要硅基氮 (氧) 化物荧光粉及其发光性能Table 1 Luminescence properties of some reported silicon-based (oxy) nitride phosphors 下载原图
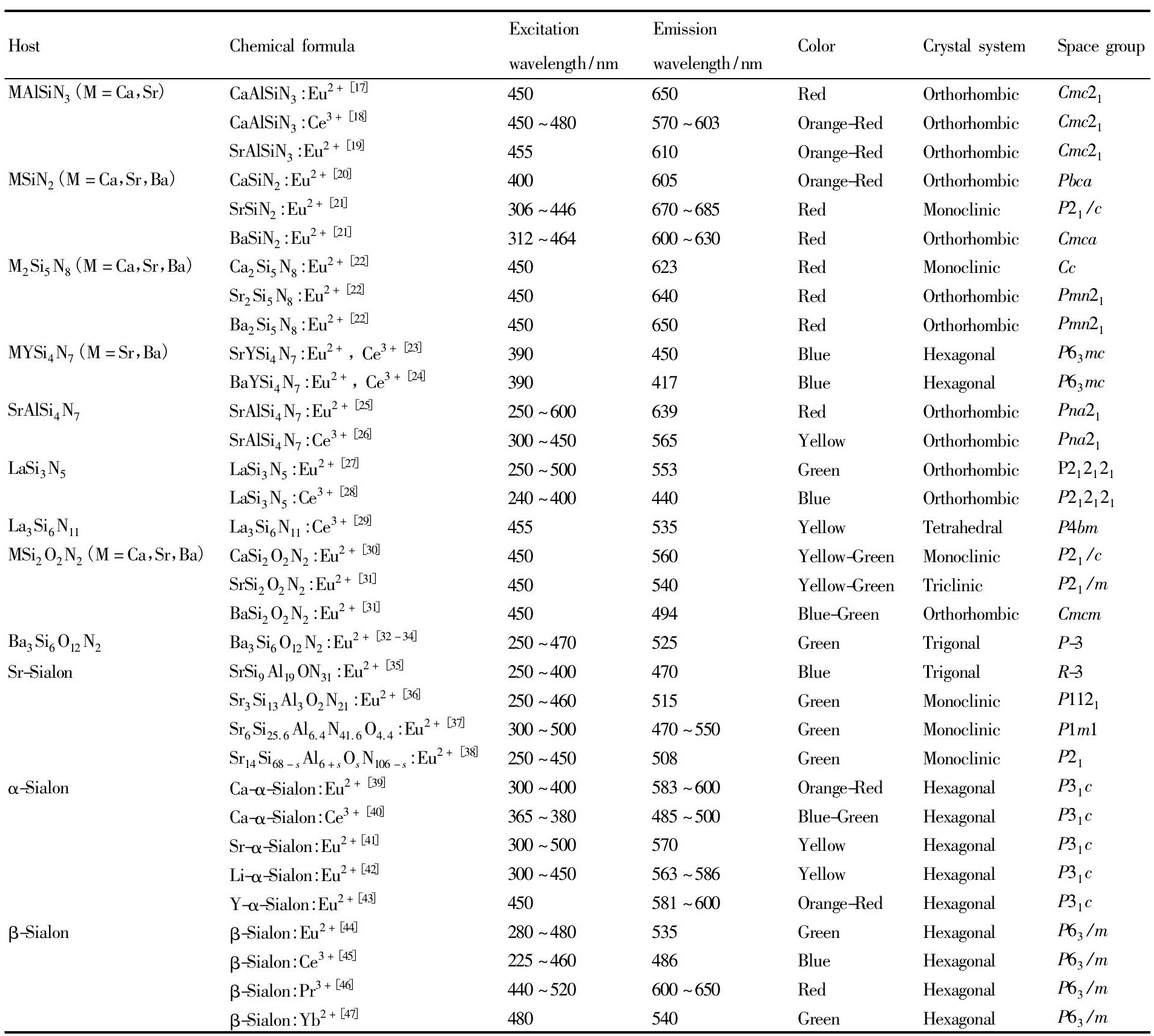
表1 报道的主要硅基氮 (氧) 化物荧光粉及其发光性能Table 1 Luminescence properties of some reported silicon-based (oxy) nitride phosphors
M2Si5N8:Eu2+ (M=Ca, Sr, Ba) 荧光粉是MxSiyNz:Eu2+ (M=Ca, Sr, Ba, z=2/3x+4/3y) 系列荧光粉中的一类[48], 此外还包括MSi N2:Eu2+和M4Si7N12:Eu2+等, 其中以M2Si5N8:Eu2+荧光粉的发光性能最佳。同所有Eu2+离子激活的荧光粉一样, 该系列荧光粉也可通过改变基质中碱土金属 (Ca, Sr, Ba) 种类、含量或者激活剂Eu2+浓度来实现发射光谱的可控调节, 其发射峰值波长的可控调节范围在580~660 nm, 且按Ca, Sr, Ba的顺序红移;另外, Liu课题组研究了Al-O键对SiN键的替换对不同基质体系的M2Si5N8产生不同的光谱移动现象, 并通过阳离子错配理论模型解释了其发光性能的变化规律[49]。研究发现当Eu2+掺杂量保持一致时, 不同碱土金属离子所形成的M2Si5N8:Eu2+晶体结构中Eu2+所处的晶场环境相似, 发射光谱的峰形相似, 但是由于碱土金属离子 (Ca, Sr, Ba) 与N3-进行配位时, 按Ca, Sr, Ba的顺序电负性减小, 因此电子云膨胀效应增强, 导致发射光谱峰值波长红移。
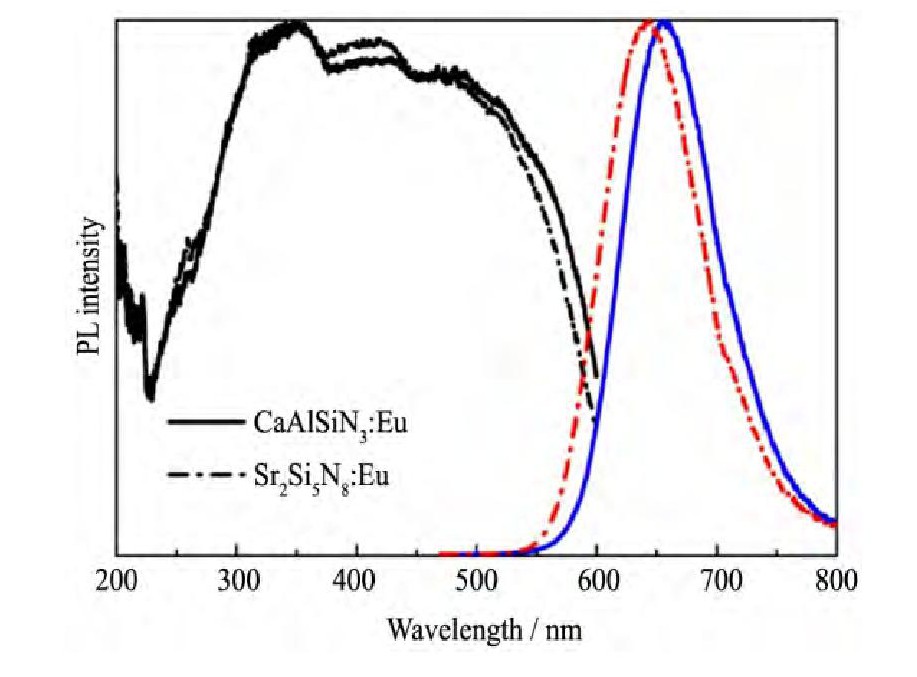
相对于氧化物体系荧光粉, 氮 (氧) 化物荧光粉的合成经常用到氮化硅、氮化铝等具有较大惰性的化合物, 因此往往需要高温、高压的苛刻合成条件。比如M2Si5N8:Eu2+荧光粉, 就是通常以碱土金属氮化物、氮化硅等为原料, 在N2/H2混合气氛下采用气压烧结法合成。为了解决高纯碱土氮化物原料较难获得、成本高昂的问题, Xie等采用碱土金属碳酸盐、氮化硅及氧化铕为原料, 在0.5MPa氮气气氛下1600℃烧结2 h合成M2Si5N8:Eu2+荧光粉, 但产物中含有较多的Sr2Si O4杂相, 影响了目标氮化物红粉的发光性能[50]。Nersisyan等利用Sr X2, Eu X3 (X:F, Cl) 、硅粉、聚四氟乙烯和尿素等原料在氮气气氛中自燃, 合成了Sr2Si5N8:Eu2+红色荧光粉[51], 该方法具有设备简单、工艺过程快速、能耗低等优点, 但反应进程和反应产物的可控性有待提高。M2Si5N8:Eu2+ (M=Ca, Sr, Ba) 荧光粉的物理化学稳定性虽然比硫化物荧光粉要好得多, 然而其发光的温度特性表现的并不尽如人意, M2Si5N8:Eu2+荧光粉在150℃时的发光强度大约只有室温时的85%。2003年, 日本国立材料研究所与三菱化学共同发明出一款150℃时发光强度可达室温时的92%的新型Ca Al Si N3:Eu2+红色荧光粉;而且, 该类荧光粉的激发光谱覆盖250~500 nm波长范围, 通过Sr取代Ca或改变激活剂离子Eu2+的浓度, 其发射峰值波长可在600~690 nm范围可控调节 (图1所示) [17]。但该类荧光粉的合成相比M2Si5N8:Eu2+要更为困难, 其合成需要更大的压强, 如Watanabe等使用Ca S-r Eu Al Si的合金粉在1900℃/190 MPa下焙烧2 h制备了SrxCa1-xAl Si N3:Eu2+ (0.2≤x≤0.8) 荧光粉, 特别地, 当Sr取代Ca时会遇到合成压力增大的问题, 当全部取代时, 形成的将是不稳定的介稳态的Sr Al Si N3, 热力学合成条件十分苛刻, 需要在1900℃-200 MPa下才能合成[52]。
图1 Sr2Si5N8:Eu2+and Ca Al Si N3:Eu2+的激发 (λem=639 nm) 和发射 (λex=450 nm) 光谱Fig.1 Excitation (λem=639 nm) and emission (λex=450 nm) spectra of Sr2Si5N8:Eu2+and Ca Al Si N3:Eu2+[17]
为改善合成条件, 业界研究了合金氮化法、氨化氮化法、超临界合成法等方法, 虽然可以降低合成温度, 但材料的纯度和发光性能难以得到保证, 发光效率仍然较低。
北京有色金属研究总院Liu等从原材料性质、物料扩散、界面反应等方面对 (Ca, Sr) Al Si N3:Eu2+荧光粉的合成进行细致研究, 通过预烧结固化碱土金属、引入低熔点晶化剂强化惰性原料扩散传质等一系列技术手段, 开发出了常压高温制备 (Ca, Sr) Al Si N3:Eu2+氮化物荧光粉的技术, 较好地解决了其高温高压合成的难题[53,54]。
与M2Si5N8:Eu2+荧光粉相比, (Ca, Sr) AlSi N3:Eu2+荧光粉结构中只有1/3的N原子与两个Si原子连接, Al N4四面体和Si N4四面体通过共点连接, 结构更具刚性, 因此其温度特性和耐湿稳定性较M2Si5N8:Eu2+更优良, 在150℃时的发光强度可达室温时发光强度的92%, 高于M2Si5N8:Eu2+的85%[17]。而且, 北京有色金属研究总院Hu等[55]通过高温劣化及耐候性研究发现, 在M2Si5N8和 (Ca, Sr) Al Si N3两种基质中, 激活剂Eu2+离子在后者中的稳定性显著优于前者;也正是由于 (Ca, Sr) Al Si N3:Eu2+相比M2Si5N8:Eu2+的优异性, 使得其成为目前用量最大的LED红色荧光粉。
3.2 硅基氮 (氧) 化物黄色荧光粉
随着硅基氮 (氧) 化物荧光粉的陆续被开发, 具有优异光色性能的发黄光的氮 (氧) 化物荧光粉也被开发出来。开发高性能的硅基氮 (氧) 化物黄色荧光粉的另外一个关键意义在于, 其应用可以突破日亚化学“蓝光LED芯片+YAG:Ce3+黄色荧光粉”形成白光LED的核心专利, 因而自被发现以来也得到了行业的持续关注。在目前所研究的硅基氮 (氧) 化物发黄色光的材料体系中, 研究热点主要集中在Ca-α-Sialon:Eu2+和La3Si6N11:Ce3+两大体系荧光粉。
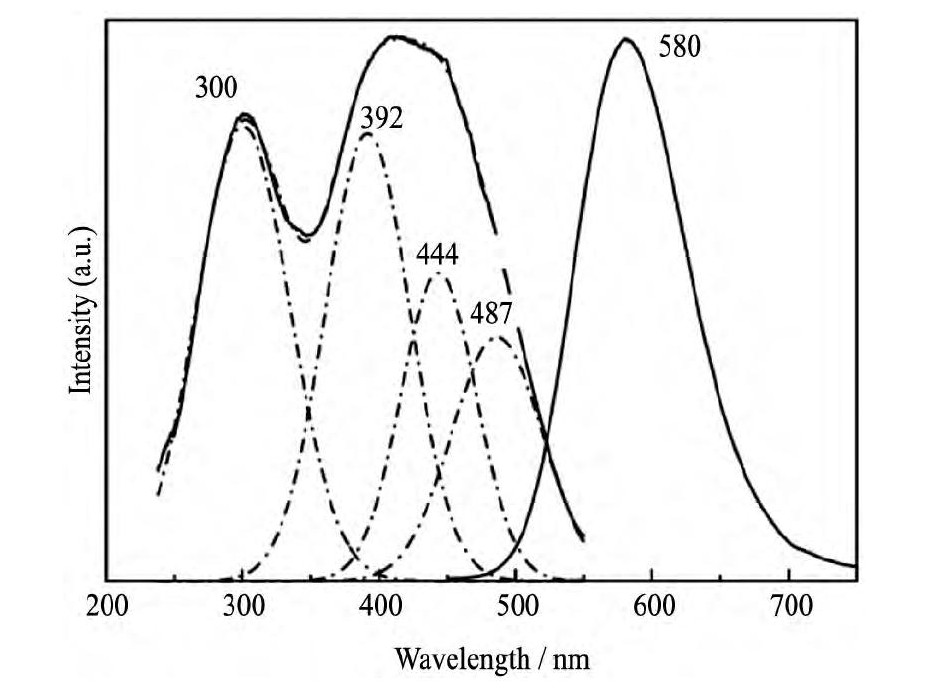
Ca-α-Sialon:Eu2+ (MexSi12- (m+n) Alm+nOnN16-n, 其中:Me为金属元素, 通常为Li, Mg, Ca, Y和部分镧系元素) 是研究较早的氮氧化物黄粉。2004年, Xie等通过固相反应法制备出Ca-α-Sialon:Eu2+, 该体系荧光粉在460 nm蓝光激发下可以发射峰值波长为570~610 nm的黄-橙光 (图2所示) , 与蓝光LED芯片组合后可以获得色温在1900~3300 K范围内可调的白光LED, 也就是说, 采用该一种荧光粉匹配蓝光LED即可实现暖白光[39];而传统的YAG:Ce3+黄色荧光粉在460 nm激发下的发射峰值波长为540~580 nm, 光谱可调范围相对较窄, 更蓝移, 因而制出来的白光LED色温偏高, 例如4000~8000 K的高色温。Xie等的研究还发现, 通过采用Y3+取代Ca-α-Sialon:Eu2+中的Ca2+以及调控Al-O键和Al-N键的取代数量, 能够有效调节荧光粉的晶格参数从而实现光谱裁剪[56]。
制备方面, Ca-α-Sialon:Eu2+荧光粉通常需要在N2气氛下1700℃以上的高温进行烧结才能合成。Liu等[57]研究了微波烧结法制备Ca-α-Sialon:Eu2+荧光粉, 合成温度显著降低, 合成的荧光粉的发光强度和外量子效率也与气压烧结法相当。Chung等[58]采用碳热还原氮化法在1550℃下制备了Ca-α-Sialon:Eu2+荧光粉, 荧光粉的发光性能也可以达到高温固相反应法的水平, 同时避免使用不稳定的金属氮化物原料。此外, 研究者们还研究了Ca-α-Sialon:Eu2+荧光粉的燃烧合成法[59]、喷雾热解法[60]和机械力化学活化法[61]等制备技术, 但是均存在光效不高、热稳定较差等问题, 影响了该系列荧光粉在白光LED封装中的推广应用。
图2 Ca-α-Sialon:Eu2+ (m=2, n=1, Eu=7.5%) 的激发 (λem=580 nm) 和发射 (λex=460 nm) 光谱Fig.2Excitation (λem=580 nm) and emission (λex=460nm) spectra of Ca-α-Sialon:Eu2+[39]
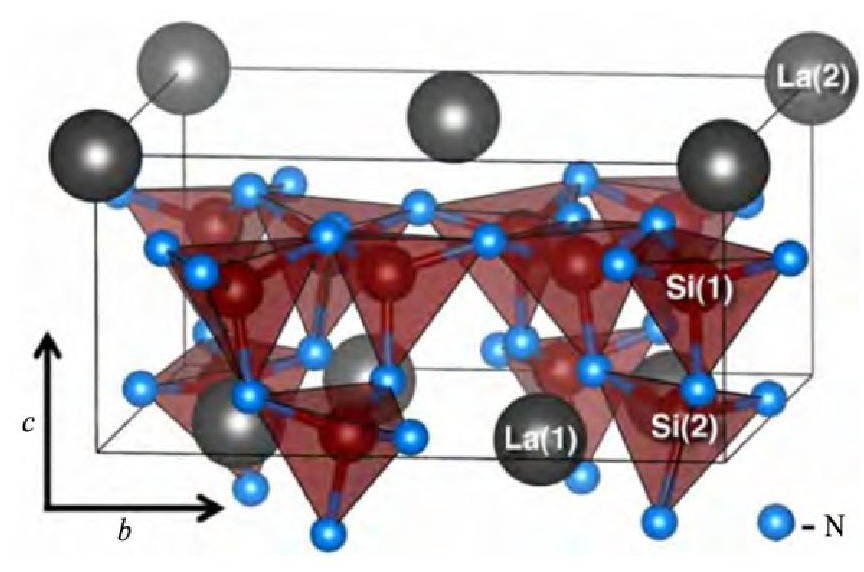
和Eu2+相似, Ce3+的发光受晶体场和电子云膨胀效应的影响很大, 当周围的晶体场和共价性较强时, Ce3+的5d激发态可处于很低的能级位置, 实现高效黄光发射, La3Si6N11:Ce3+就是一类典型的Ce3+激活的氮化物黄色荧光粉。2009年, 三菱化学Kijima等[29]首先报道了La3Si6N11:Ce3+的发光性能, 如图3所示, 该荧光粉能被460 nm蓝光有效激发, 发射出峰值波长位于530~600 nm的宽带黄光, 半高宽较传统的YAG:Ce3+还要宽, 达到110 nm。George等[62]详细研究了La3Si6N11:Ce3+中发光中心Ce3+的浓度与局部占位结构之间的关系, 发现La在晶格中存在La (1) 和La (2) 两种位置, 这使得当Ce3+离子取代La3+时, 也存在Ce (1) 和Ce (2) 两种发光中心位置, 当Ce3+掺杂浓度低 (<5%) 时, Ce3+更倾向于占据La (2) 格位;掺杂浓度高 (>5%) 时, Ce3+更倾向于占据La (1) 格位, 其原因是La (2) -N键长 (0.116 nm) 与CeN键长 (0.1143 nm) 更为接近 (图4所示) 。制备方面, Suehiro等[63]研究发现, 在La3Si6N11:Ce3+中La3+的位置中引入Ca2+, 可以降低合成温度, 抑制La Si3N5相的形成, 并且能够较为有效的改善荧光粉的发光亮度及热稳定性。
图3 La3Si6N11:Ce3+的激发 (λem=600 nm) 和发射 (λex=450 nm) 光谱以及热稳定性图Fig.3 Excitation (λem=600 nm) and emission (λex=450 nm) spectra and temperature dependency of La3Si6N11:Ce3+[29]
图4 La3Si6N11:Ce3+的晶体结构Fig.4 Crystal structure of La3Si6N11:Ce3+[62]
相比于传统的YAG:Ce3+黄粉, La3Si6N11:Ce3+的发光表现出更好的温度特性。在150℃时, La3Si6N11:Ce3+荧光粉的发光强度仍然保持为常温下的70%, 显著高于YAG:Ce3+ (图3所示) [29]。正是由于这个优势, La3Si6N11:Ce3+黄色荧光粉可适用于较高温度的应用环境[64], 目前, La3Si6N11:Ce3+已开始在大功率白光LED中得到应用。
杜甫、庄卫东等利用高温固相法合成了Ce3+离子激活的La3-xYxSi6N11黄色荧光粉, 并发现, 随着Y3+逐渐取代La3+, 晶体空间群仍保持P4 bm, Y3+以不同比例占据两种格位, 同时发射光谱峰值波长由535 nm红移至552 nm;热淬灭性能随着Y3+掺杂量增加有所降低, 但200℃其发光亮度仍可保持室温时的95%。这些性能表明, La3-xYxSi6N11:Ce3+有望发展成为一款高能量激发用荧光粉。
3.3 硅基氮氧化物绿色荧光粉
硅基氮氧化物绿色荧光粉是获得高显色白光LED的关键材料之一。目前, 见诸报到的硅基氮氧化物绿色荧光粉主要采用Eu2+作为激活剂, 研究的体系主要包括:MSi2O2N2:Eu2+ (M=Ca, Sr, Ba) , Ba3Si6O12N2:Eu2+和β-Sialon:Eu2+等。
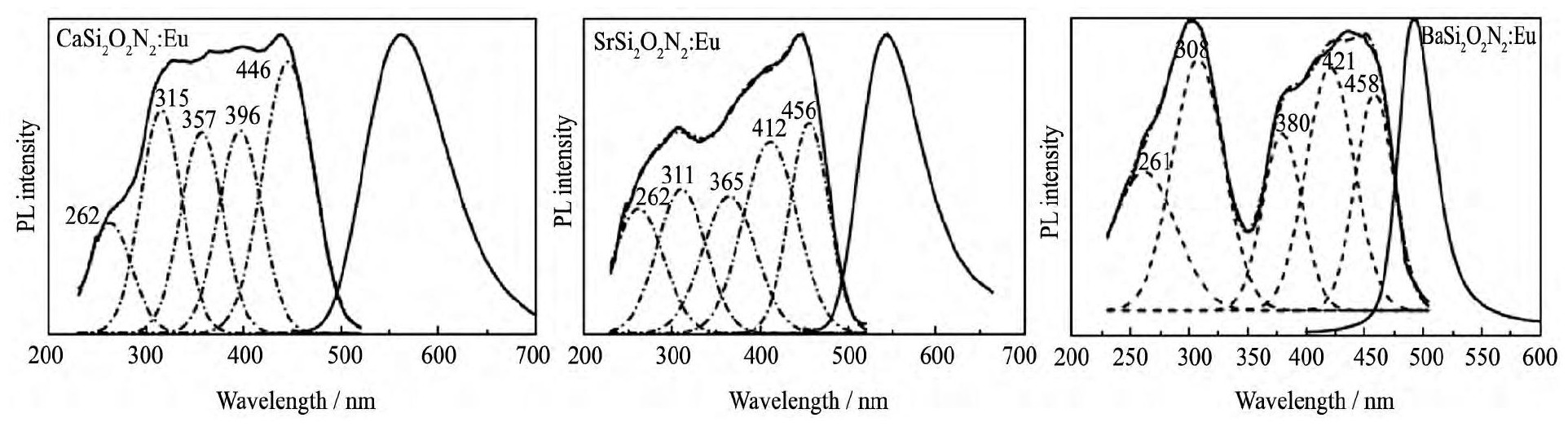
MSi2O2N2:Eu2+ (M=Ca, Sr, Ba) 是最早报道的硅基氮氧化物绿粉体系。它的激发光谱覆盖紫外至蓝光区域, 显示其可以与紫外或蓝光芯片匹配使用, 发射光谱随着基质中碱土金属阳离子的改变有较大区别:Ca Si2O2N2:Eu2+发射峰值波长在550~570 nm的黄绿光, Sr Si2O2N2:Eu2+发射峰值波长为530~550 nm的绿光, Ba Si2O2N2:Eu2+发射峰波长在495~515 nm的蓝绿光, 也就是说, 通过调节碱土金属阳离子的种类和浓度比例, 该体系荧光粉可以实现从蓝绿光至黄绿光的发射 (图5所示) [30,31]。Liu等[65]研究发现, 当在Sr Si2O2N2中共掺Eu2+/Mn2+时, 由于Eu2+和Mn2+之间的能量传递, 荧光粉的激发和发射强度会显著提升。在Ca Si2O2N2:Eu2+中掺入Mg2+, 能够显著改善荧光粉的发光强度与热稳定性, 并且可提高Eu2+的淬灭浓度[66]。
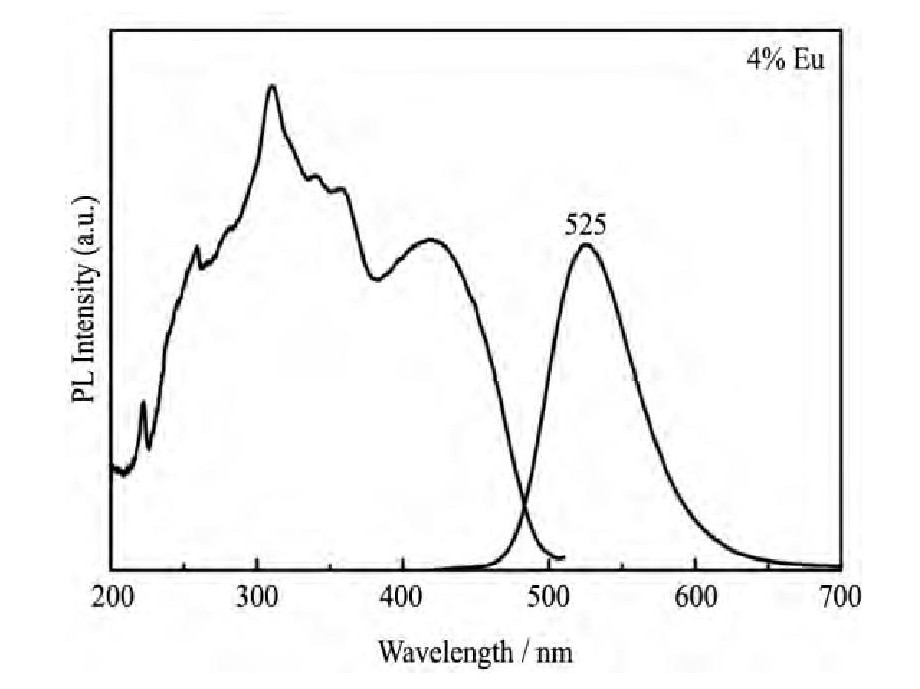
2010年, Braun等[32]采用高温固相法制备出了M3Si6O12N2:Eu2+ (M=Ba, Sr) 绿色荧光粉, Ba3Si6O12N2:Eu2+的激发光谱覆盖250~500 nm, 能被紫外和蓝光有效激发, 发射峰值波长在510~540 nm (图6所示) 。Chen等[33]研究了该类荧光粉的热稳定性, Ba3Si6O12N2:Eu2+在180℃的发光效率为室温下的66%。Li等[34]将Ba3Si6O12N2:Eu2+与Sr2Si5N8:Eu2+红色荧光粉组合, 制备的LED光源显色指数Ra可达88~94[34]。
图5 MSi2O2N2:Eu2+ (M=Ca, Sr, Ba) 的激发和发射光谱Fig.5 Excitation and emission spectra of MSi2O2N2:Eu2+ (M=Ca, Sr, Ba) [30,31]
图6 Ba3Si6O12N2:Eu2+的激发 (λem=527 nm) 和发射 (λex=420 nm) 光谱Fig.6 Excitation (λem=527 nm) and emission (λex=420 nm) spectra of Ba3Si6O12N2:Eu2+[33]
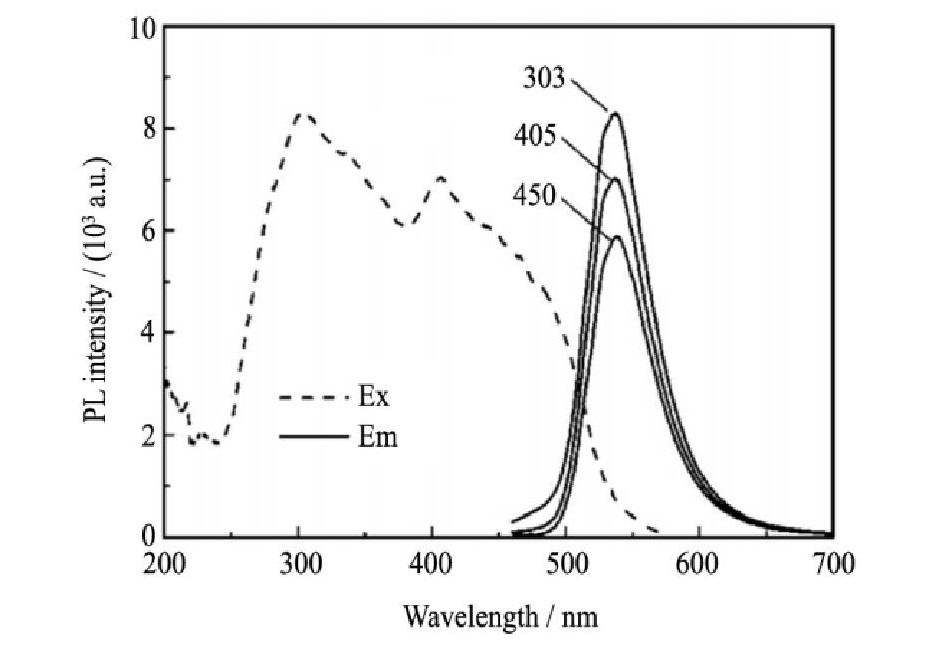
目前研究较多且已经实现产业化的硅基氮氧化物绿粉主要为β-Sialon:Eu2+ (分子式为:Si6-z AlzOzN8-z:Eu2+, 其中0<z≤4.2) , 其结构特征是由Eu溶入β-Sialon陶瓷中形成, 其中Sialon是由Si3N4中的Si-N键被Al-O键置换形成的固溶体。2005年, 日本NIMS和电气化学的Hirosaki等采用高温固相反应法 (1900℃-0.9 MPa-N2) 首次制备合成了β-Sialon:Eu2+绿色荧光粉[67], 颗粒宏观表现为直径0.5μm、长度10μm左右的棒状结构。该类荧光粉可以被紫外到蓝光波段的光有效激发, 发射出峰值波长在525~545 nm的绿光, 半高宽35~45 nm (图7所示) , 色坐标 (0.32, 0.64) , 能够很好地满足液晶显示用绿粉的要求[44,68]。但是, 由于合成温度高达2000℃, 且需要较高的合成压力, 对合成装备的要求非常苛刻, 国内对该系列荧光粉的研究还较少。本课题组采用高温固相法进行β-Sialon:Eu2+的合成研究, 目前已获得了纯相、粒度可控的β-sialon:Eu2+氮氧化物绿色荧光粉, 其在蓝光激发下的发射峰值波长在530~545 nm, 色坐标y值在0.62~0.64。
另外, 为避开苛刻的制备条件, 部分研究者尝试用燃烧合成法[69]、碳热还原氮化法[70]和模板辅助合成法[71]等制备β-Sialon:Eu2+荧光粉, 但是合成步骤较复杂, 且产品纯度不够, 发光性能较差, 不能满足实际应用需要。目前, β-Sialon:Eu2+荧光粉因色纯度高, 发光强度高, 热稳定性好, 已经成为背光源领域不可替代的绿色荧光粉。将β-Sialon:Eu2+和氟化物红粉与蓝光LED芯片相匹配, 可以制得光效为100 lm·W-1, 色域为110%NTSC的封装器件, 能够很好地满足高端液晶显示背光源领域的需求[72]。
图7 β-Sialon:Eu2+的激发 (λem=535 nm) 和发射 (λex=303, 405, 450 nm) 光谱Fig.7Excitation (λem=535 nm) and emission (λex=303, 405, 450 nm) spectra ofβ-Sialon:Eu2+[44]
3.4 硅基氮 (氧) 化物蓝色荧光粉
目前, 白光LED用硅基氮 (氧) 化物蓝色荧光粉的研究较为分散, 主要原因是目前白光LED的实现方式中以蓝光芯片激发为主, 尚不需要蓝色荧光粉与之匹配;但在紫外LED激发三基色荧光粉的方式中, 蓝色荧光粉却是必不可少的, 因而也得到了业界的广泛研究, 硅基氮 (氧) 化物也是其中重要的基质。截至目前, 研究较多的硅基氮 (氧) 化物蓝色荧光粉主要涉及Ca-α-Sialon:Ce3+, LaSi3N5:Ce3+和MYSi4N7:Ce3+ (M=Sr, Ba) 等体系, 均采用Ce3+作为激活剂。
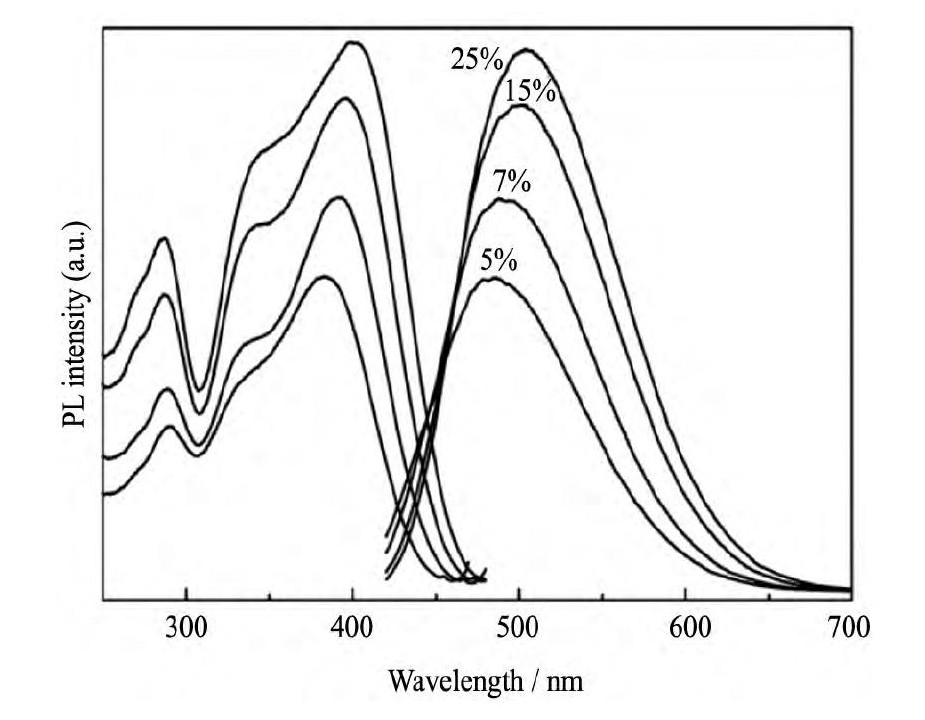
Xie等[40]研究发现, 将Ca-α-Sialon:Eu2+荧光粉中的激活剂Eu2+换成Ce3+, 其在310~420 nm之间具有较强的激发效率, 发射峰值波长位于480~510 nm, 同时考察了不同的Ce3+浓度对Ca-α-Sialon:Ce3+荧光粉发光性能的影响 (图8所示) 。Gan等也研究了Ce3+掺杂量对Ca-α-Sialon:Ce3+发光性能的影响, 发现随着Ce3+离子浓度的增加, 荧光粉的发光强度逐渐增强, 其将原因归因于Ce3+占据Ca2+的不等价取代, 当Ce3+占据Ca2+位置时, 在晶体内部形成大量的电荷缺陷[73]。Li等[74]通过采用Li+取代Ca-α-Sialon:Ce3+中的Ca2+以及改变Al-O键和Al-N键的取代数量, 能够有效调节Ca-α-Sialon:Ce3+固溶体的晶格参数从而实现光谱裁剪。
图8 Ca-α-Sialon:Ce3+ (m=2, n=1) 的激发 (λem=495nm) 和发射 (λex=390 nm) 光谱Fig.8Excitation (λem=495 nm) and emission (λex=390nm) spectra of Ca-α-Sialon:Ce3+[40]
2008年, Suehiro等[28]采用高温固相法制备了化学组成为La1-xSi3N5:Cex (x=0.01~0.50) 的蓝色荧光粉, 其发射峰值波长在460~490 nm可调, 在355~380 nm激发下, 外量子效率可达34%~67%。Ibrahim等[76]采用第一性原理计算了LaSi3N5:Ce3+荧光粉的电子结构与带宽, 得知结构中的空位通过N3-/O2-替换实现电价平衡, 计算得到的La Si3N5:Ce3+带宽是4.65 e V[75]。La Si3N5:Ce3+的热稳定性显著高于现有的La-Si-O-N发光材料, 是一种潜在的近紫外激发白光LED用蓝色荧光粉。
Ce3+掺杂的MYSi4N7蓝色荧光粉的发光特性受基质碱土金属阳离子M2+的影响, 其中Sr Y-Si4N7:Ce3+激发光谱有3个宽峰 (分别位于280, 320和340 nm) , 发射光谱覆盖360~570 nm范围, 发射峰值波长位于450 nm附近[23]。Ba YSi4N7:Ce3+激发光谱有4个宽峰 (分别位于285, 297, 318, 338 nm) , 发射峰值波长位于415 nm附近[24]。另外, MYSi4N7体系荧光粉可以通过改变发光中心离子的类型来实现光谱调节, 如在390nm近紫外光激发下, Ba YSi4N7:Eu2+和Sr YSi4N7:Eu2+分别发射绿光和黄光, 发射峰值波长分别为500~530 nm和550~570 nm[77]。
综上, 虽然目前实用型白光LED主要基于蓝光LED芯片开发, 尚无蓝色荧光粉的用武之地;但目前的技术储备也是非常有意义的, 随着紫外LED技术的发展, 未来“紫外LED+三基色荧光粉”将具有非常光明的前景, 这也将使硅基氮 (氧) 化物蓝色荧光粉的研究更趋明朗化和实用化[78]。
4 展望
当前, 白光LED用荧光粉正朝着高稳定性、高光效、高显指等方向发展, 以满足高端照明和显示的要求。硅基氮 (氧) 化物荧光粉以其独特的结构、优异的发光性能和稳定性, 已成为目前白光LED荧光粉研发和推广应用的重点, 正在推动并持续推动高端白光LED的纵深发展。然而, 目前广泛应用的硅基氮 (氧) 化物荧光粉仍然有较大的改善空间, 例如: (Ca, Sr) Al Si N3系列红色荧光粉在经历国内外广大科技工作者的多年耕耘之后, 其结构特点、光谱性能以及合成机制等方面都已基本清晰, 目前产品也已实现大规模商品化并广泛应用。未来, 在持续追求白光LED光源高品质的大背景下, 对该体系荧光粉的研究重点在其量子效率的提升和晶体生长机制的揭示等。本课题组通过研究该体系荧光粉的步控合成机制和发光中心Eu2+离子配位理论模型, 揭示了其晶粒生长取向的影响因素和发光性能的变化规律, 然而突破量子效率的技术瓶颈仍有困难, (Ca, Sr) Al Si N3系列红色荧光粉研发深度还需进一步挖掘。对于La3Si6N11:Ce3+黄色荧光粉, 由于在其主相合成反应的同时存在生成La Si3N5的副反应, 两者的吉布斯自由能差距导致纯相合成困难, 严重影响了荧光粉的发光亮度及稳定性;该类荧光粉未来的研究重点在于, 通过进一步细致研究反应历程, 找到有效抑制或阻止La Si3N5杂相形成的控制手段, 合成高纯的La3Si6N11:Ce3+黄色荧光粉, 提高荧光粉的发光效率和稳定性。而对于β-Sialon:Eu2+绿色荧光粉, 未来应重点研究Eu2+在β-Sialon基质晶格中所处的化学环境与β-Sialon:Eu2+荧光粉发光性能之间的关系, 揭示Eu2+的有效溶入机制, 提高制备过程中Eu2+进入β-Sialon晶格六边形管状通道的含量, 提升β-Sialon:Eu2+荧光粉的发光性能;在研究手段上, 可以考虑利用同步辐射光源或者球差电镜等先进技术深入研究β-Sialon:Eu2+荧光粉的发光特性与发光中心晶格配位环境的关系;在组成与结构上, 可通过元素替代或掺杂等手段, 改善稀土离子周围的晶体场环境, 实现β-Sialon:Eu2+荧光粉量子效率的提高或者发光性能的裁剪设计等。其次, 探索工艺条件缓和、成本低廉、适于工业化量产的简易的制备技术、装备和路线也是氮 (氧) 化物荧光粉研制继续努力的方向。另外, 更多具有更优异性能的新型硅基氮 (氧) 化物荧光粉也亟待开发, 因此, 需要业界的共同努力。
参考文献
[16] Yamamoto H.White LED phosphors:the next step[J].Proc.SPIE, 2010, 7598:759808.