热处理对Nd-Mg-Ni储氢合金结构和性能的影响
北京有色金属研究总院能源材料与技术研究所
摘 要:
采用磁悬浮感应熔炼法制备了Nd-Mg-Ni系储氢合金,重点研究了热处理工艺对合金相组成和电化学性能的影响。采用X射线衍射、扫描电镜和电化学测试系统研究了合金的相结构、显微结构及电化学性能。研究结果表明,Nd0.75Mg0.25Ni2.75Al0.25合金经1173,1273,1373 K退火处理后,随着退火温度的升高,不同相间元素分布更加均匀,Mg元素的浓度差减小,主相Nd2Ni7六方相逐渐增加。电化学P-C-T曲线平台变平缓、平台压降低,电化学容量,倍率性能和荷电保持率有较大提升。对于Nd0.75Mg0.25Ni3.2Al0.1合金,经1373 K,5 h热处理后慢冷较快冷更利于Nd2Ni7相的形成,慢冷试样中Nd2Ni7相可达92.31%,电化学性能更加优异,最大电化学容量为330.1 mA.g-1,循环100周容量保持率为92.2%。
关键词:
中图分类号: TG139.7
作者简介:苑慧萍(1982-),女,辽宁人,博士;研究方向:储氢材料 (E-mail:huiping.yuan1@gmail.com);
收稿日期:2012-12-12
基金:国家科技部863计划(2011AA03A408)资助项目;
Effect of Heat Treatment on Structure and Properties of Nd-Mg-Ni-System Hydrogen Storage Electrode Alloys
Abstract:
The as-cast Nd-Mg-Ni-system hydrogen storage electrode alloy was prepared by vacuum induction levitation melting method.The influence of heat treatment on the phase components and the electrochemical properties was investigated.The XRD,SEM,and electrochemical tests were used to study the phase structure,microscopic structure,and the electrochemcial properties of the alloys.After heat treatment at 1173,1273,and 1373 K,it was found that the element distribution became uniform and the concentration difference of Mg element in different phases decreased with the increase of the heat treatment temperature.The hexagonal Nd2Ni7-type main-phase content increased.The P-C-T curves became smoothly and the plateau pressure descended.The electrochemical capacity,high rate dischargeability,and the charge retention were improved with the increase of the heat treatment temperature.For Nd0.75Mg0.25Ni3.2Al0.1 hydrogen storage electrode alloy,the slow cooling method after heat treatment at 1373 K for 5 h was in favor of the formation of Nd2Ni7 phase,better than the fast cooling method.The Nd2Ni7 phase content could reach to 92.31%,the maximum discharge capacity was 330.1 mA · g-1,and the charge retainion after 100 cycles was 92.2%.
Keyword:
Received: 2012-12-12
新型稀土镁基储氢合金由于储氢量高,电化学放电容量可达410 m Ah·g-1,较传统AB5型合金提高近30%,同时具有良好的活化性能和高倍率放电性能,近年来被广泛研究,也逐渐被商业化应用。
稀土镁基储氢合金的电化学循环稳定性与其相结构有很大关系
本文以组成为Nd0.75Mg0.25(Ni Al)x(x=3.0,3.3)的储氢合金为研究对象,研究热处理工艺对合金相结构和电化学性能的影响,从而得到具有高丰度A2B7相的Nd-Mg-Ni储氢合金,同时提高储氢合金的综合电化学性能。
1 实验
在氦气气氛保护下,采用磁悬浮感应熔炼方法制备Nd0.75Mg0.25Ni2.75Al0.25和Nd0.75Mg0.25Ni3.2Al0.1储氢电极合金。所用的单质金属纯度均在99.5%以上。为保证合金成分均匀,铸锭翻转重熔3次。将得到的铸态合金再包覆镍片封入充有0.3 MPa氩气的石英管内,在马弗炉中进行热处理。将热处理态的合金机械破碎,研磨并过200目筛,所得合金粉末于电化学性能测试。粒度小于38μm的粉末用于X射线衍射分析。
称取200 mg合金粉与800 mg镍粉均匀混合,在530 MPa压力下冷压成Φ16 mm×1 mm的圆片,用泡沫镍包裹电极片并压型,镍带点焊,作为待测合金电极。电化学性能测试在开口式H型玻璃三电极测试系统中进行,辅助电极为电化学容量远高于待测合金电极的烧结式氢氧化镍(Ni(OH)2/Ni OOH)电极,参比电极为汞-氧化汞(Hg/HgO)电极,电解液为6 mol·L-1的KOH水溶液,测试温度通过恒温水浴保持在25℃。充放电制度为:以60m A·g-1的电流密度充电7 h,静置10 min待电压稳定后,以60 m A·g-1的电流密度放电,截止电压为0.6 V,静置10 min,测试活化性能和容量;以300m A·g-1的电流密度充电80 min,静置10 min电压稳定后,以300 m A·g-1的电流密度放电至0.6 V以测试循环稳定性;以60 m A·g-1的电流密度充电7 h,静置10 min待电压稳定后,分别以300,600,900 m A·g-1的电流密度放电至0.6 V,静置10min,再以60 m A·g-1的电流密度放电至0.6 V,测试电极的倍率性能。合金放氢过程的平衡压-组成-温度(P-C-T)曲线通过电化学方法测定
X射线衍射在Bruker D8 Advance衍射仪上采集数据,采用Cu Kα射线,功率为2.2 kW,以阶梯扫描方式采样,步长0.02°,每步停留时间1 s,2θ角范围为10°~120°,数据采用TOPAS软件进行相成分及相丰度的分析。采用Hitachi-S4800型场发射扫描电镜观察合金的显微组织及相分布,并通过EDS确定组成相的化学成分,试样采用块状样,镶嵌后表面用砂纸磨平,经金相抛光。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 热处理温度的影响
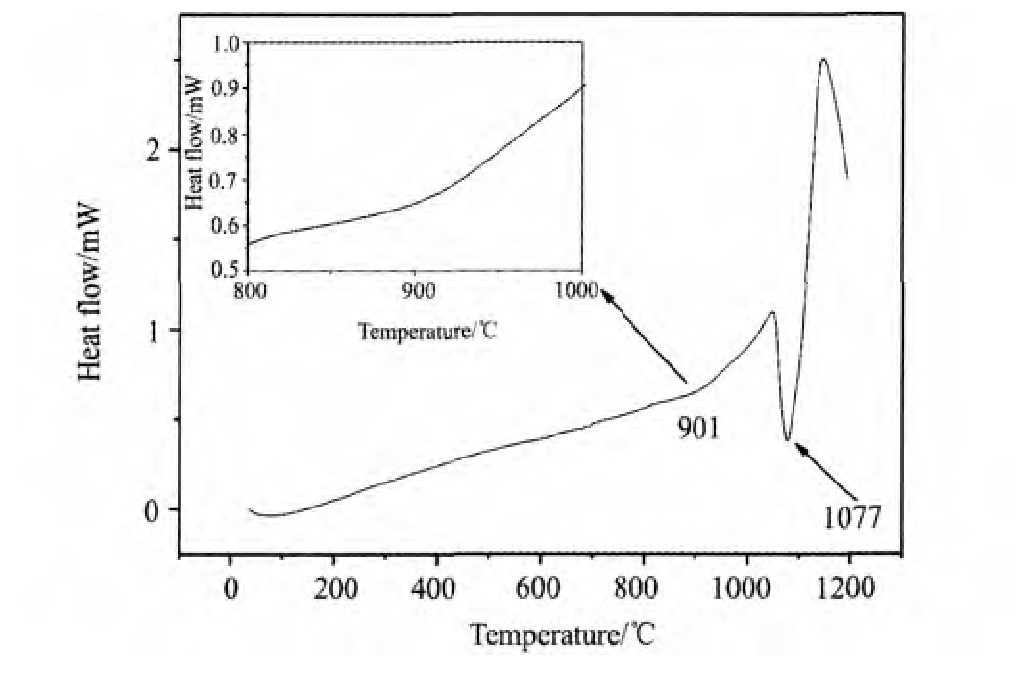
根据DSC差热分析实验,Nd0.75Mg0.25Ni2.75Al0.25铸态合金分别在901和1077℃时出现吸热峰(如图1所示),并参考Nd-Ni二元合金相图,选定的退火温度为1173,1273和1373 K。为了减少Mg元素的挥发热处理时间为5 h,采用随炉冷却方式进行冷却。
图1 Nd0.75Mg0.25Ni2.75Al0.25铸态合金的DSC曲线Fig.1 DSC curves of Nd0.75Mg0.25Ni2.75Al0.25as-cast alloy
2.1.1 显微组织
铸态和不同温度退火态Nd0.75Mg0.25Ni2.75Al0.25合金的SEM照片和各相成分如图2和表1所示。从图中可以看出,成分不同的各组成相在背散射电子图像中体现为明暗变化的不同区域。采用EDS进行成分分析各区域元素组成发现,进行热处理以后,铸态合金中富Nd相消失。随着热处理温度的升高,合金A相与B相中Mg元素含量差逐渐减小,成分更加均匀。
表1 铸态及不同温度退火态Nd0.75Mg0.25Ni2.75Al0.25合金各组成相的成分Table 1Phase constituents of as cast and heat-treated Nd0.75Mg0.25Ni2.75Al0.25electrode alloys 下载原图
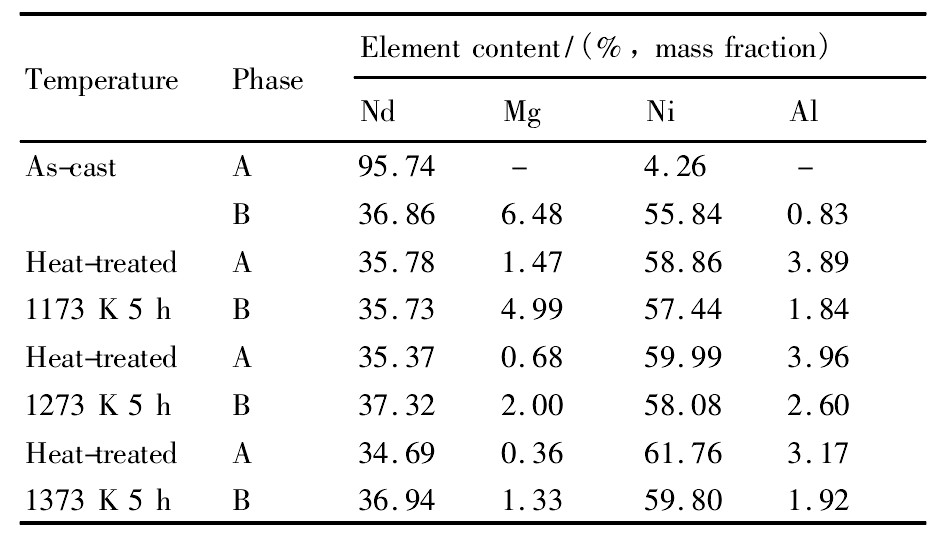
表1 铸态及不同温度退火态Nd0.75Mg0.25Ni2.75Al0.25合金各组成相的成分Table 1Phase constituents of as cast and heat-treated Nd0.75Mg0.25Ni2.75Al0.25electrode alloys
图2 铸态及不同温度退火态Nd0.75Mg0.25Ni2.75Al0.25合金的相分布Fig.2 Phase distribution of Nd0.75Mg0.25Ni2.75Al0.25alloys
(a)As-cast;(b)Heat-treated at 1173 K;(c)Heat-treated at 1273 K;(d)Heat-treated at 1373 K
表2 铸态及不同温度退火态Nd0.75Mg0.25Ni2.75Al0.25合金的Rietveld分析结果Table 2 Structure parameters of as-cast and heat-treated Nd0.75Mg0.25Ni2.75Al0.25electrode alloys 下载原图
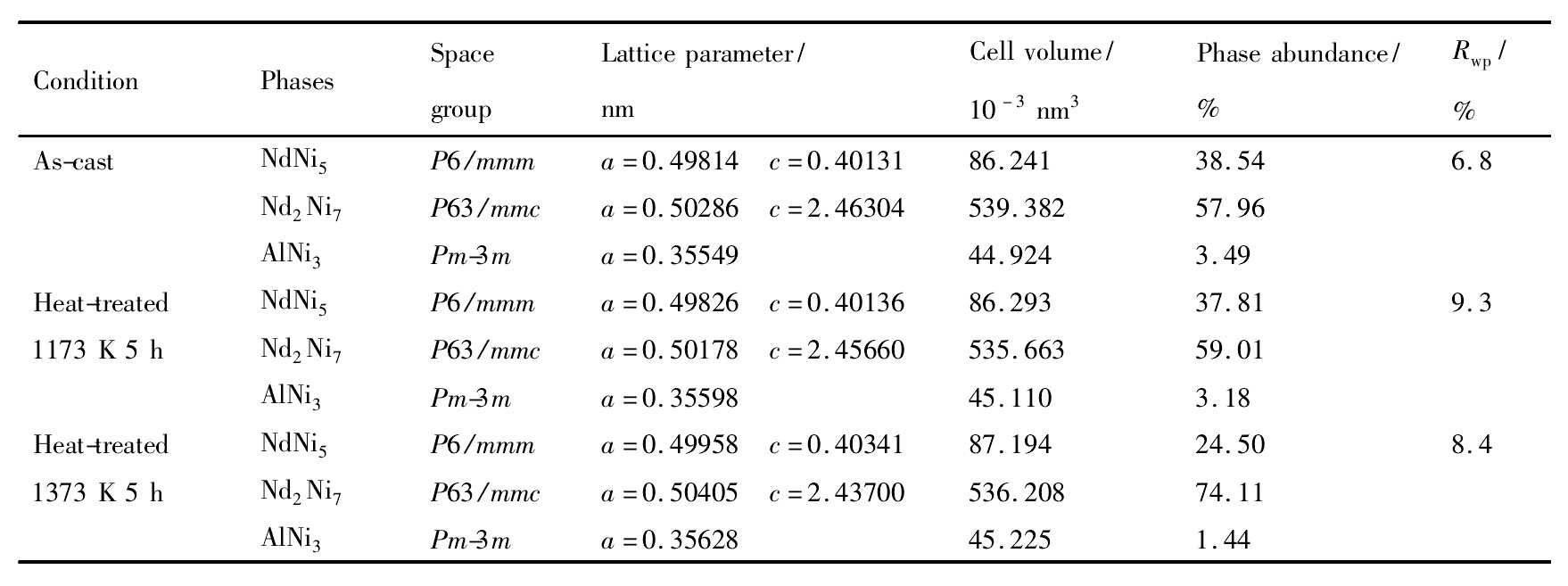
表2 铸态及不同温度退火态Nd0.75Mg0.25Ni2.75Al0.25合金的Rietveld分析结果Table 2 Structure parameters of as-cast and heat-treated Nd0.75Mg0.25Ni2.75Al0.25electrode alloys
2.1.2 相结构分析
为了确定热处理条件对合金物相的影响,对不同温度退火处理的合金试样做了Rietveld分析得到相组成、含量及晶胞体积。从表2中可以看到,热处理使合金内各相发生明显变化,铸态、1173和1373 K退火处理的储氢合金试样为多相结构,主相均为Nd2Ni7型六方相,空间群为P63/mmc,此外还包括NdNi5型六方相和Al Ni3型菱方相。比较各相含量发现,随着热处理温度的升高,Nd2Ni7相逐渐增加,经1373 K,5 h退火处理后,Nd2Ni7型六方相含量从铸态时的57.96%增加到74.11%,NdNi5和Al Ni3相均明显减少。DSC差热分析结果表明,合金分别在901和1077℃时出现吸热峰,结合相结构分析推断,1077℃时的吸热峰可能对应NdNi5到Nd2Ni7的相转变。而901℃时较小的吸热峰,可能与少量不稳定相的转变有关。
2.1.3 P-C-T曲线
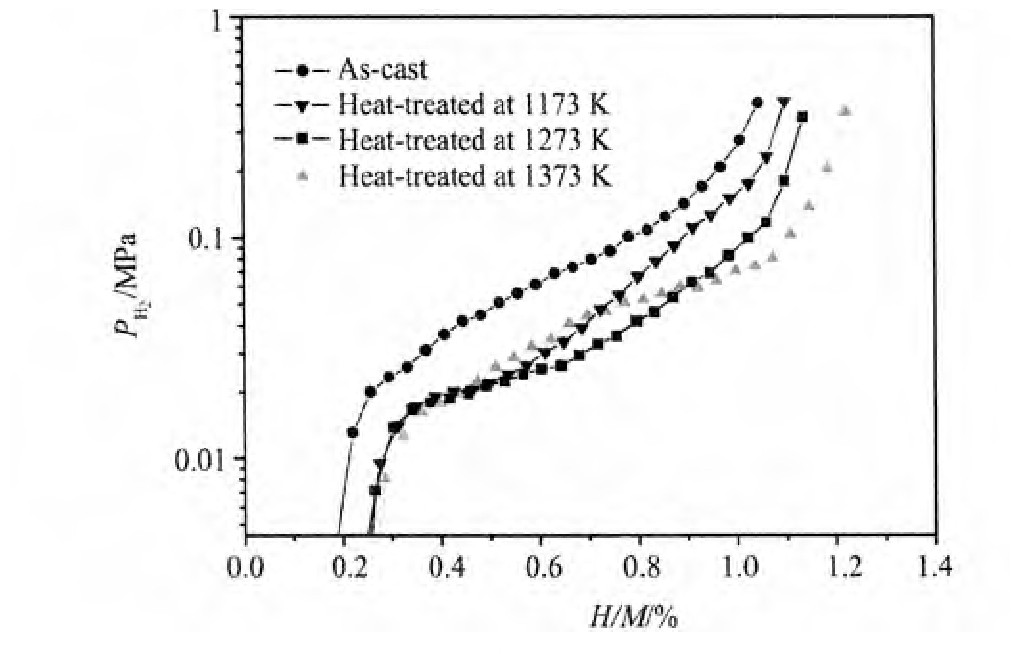
铸态及不同温度退火处理的Nd0.75Mg0.25Ni2.75Al0.25合金放氢过程的电化学P-C-T曲线如图3所示,从图中可以看到,合金的P-C-T曲线均出现单一放氢平台。随着热处理温度的升高,放氢平台越来越平坦并且逐渐变宽,合金的储氢量从铸态时的1.04%增加到1373 K,5 h退火处理后的1.22%,与铸态合金相比,平台压降低了0.02 MPa。
图3 铸态及不同温度退火态Nd0.75Mg0.25Ni2.75Al0.25合金P-C-T曲线Fig.3P-C-T isotherms curves of as-cast and heat-treated Nd0.75Mg0.25Ni2.75Al0.25electrode alloys
2.1.4 电化学性能
合金的显微组织形貌、均匀性和相组成的变化同样影响合金的电化学性能。铸态及不同温度退火处理的Nd0.75Mg0.25Ni2.75Al0.25合金电极在298 K时的活化性能、最大放电容量、倍率放电性能、荷电保持率如图4,5,6所示。从图中可以看到,合金经1~2次充放电循环达到最大放电容量,具有较好的活化性能。随着热处理温度的升高,合金电极最大放电容量从铸态合金时的277.6 m Ah·g-1增加到1373 K,5 h退火处理后的325 m Ah·g-1。结构分析结果表明,1373 K热处理后,Nd2Ni7相含量最多,Nd Ni5相含量减少,因此相应合金电极的最大放电容量增加。
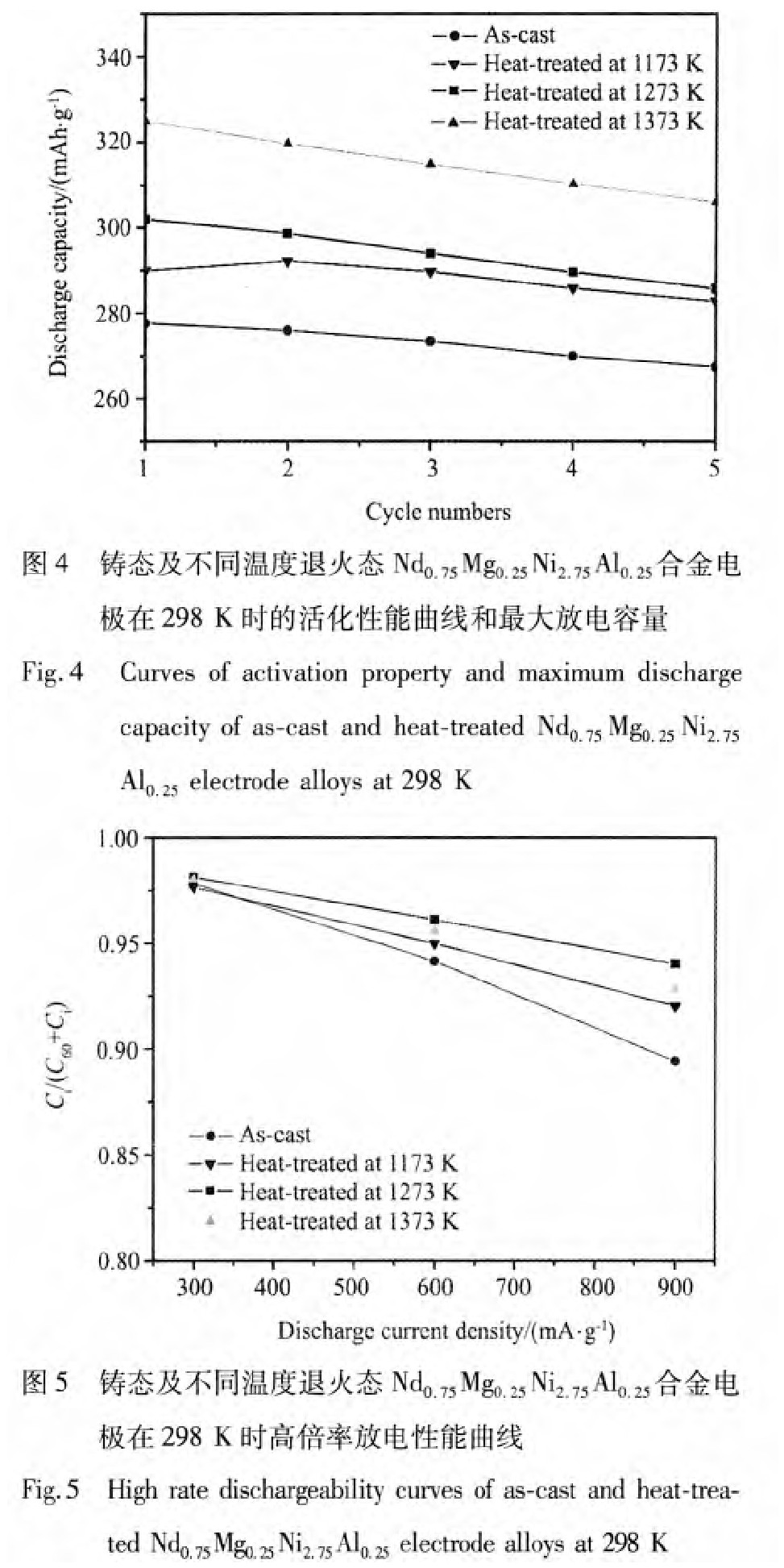
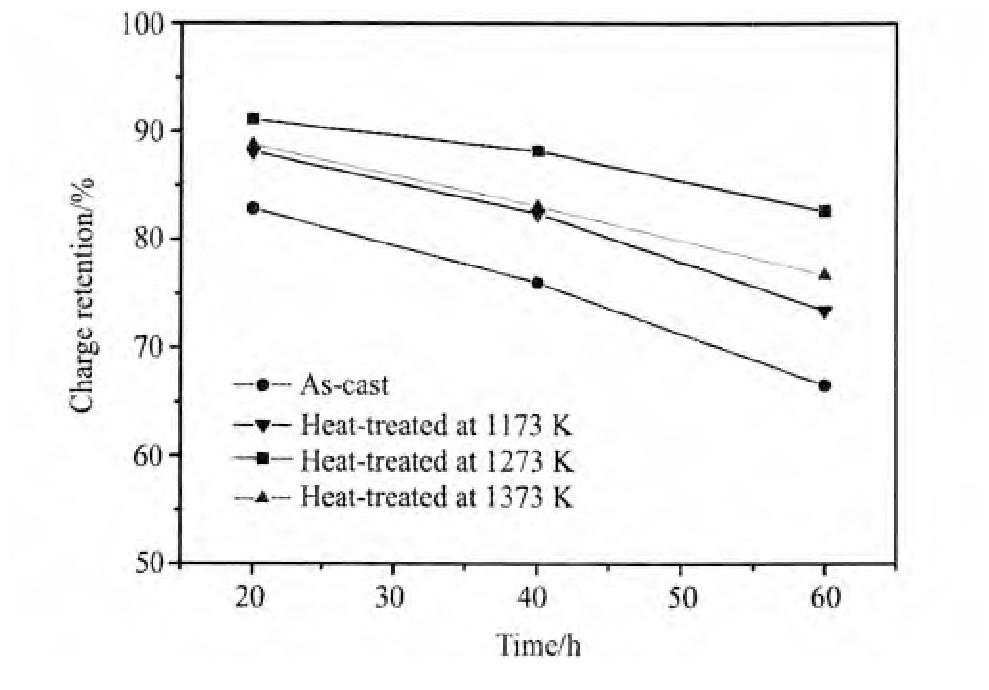
比较铸态及不同温度退火处理态的Nd0.75Mg0.25Ni2.75Al0.25合金电极在298 K时的高倍率放电性能,对于同一合金样品,随着放电电流密度的增加,扩散至合金表面的氢原子来不及参加电子转移放氢而直接复合为氢气脱附,导致放电容量下降,合金电极的高倍率放电性能降低。随着热处理温度的升高,合金电极的高倍率放电性能呈先升高后降低的趋势。HRD900从铸态时的89.4%升高到1273 K时的94.0%,然后降低到1373 K时的92.8%。合金电极在298 K时的荷电保持率在经过热处理后明显提高,1273 K热处理后合金298 K,60 h荷电保持率为94.1%。合金电化学性能改善的主要原因是合金中Nd2Ni7相含量的增加。
图6 铸态及不同温度退火态Nd0.75Mg0.25Ni2.75Al0.25合金电极在298 K时的荷电保持率Fig.6Charge retention of as-cast and heat-treated Nd0.75Mg0.25Ni2.75Al0.25electrode alloys at 298 K
2.2 冷却速度的影响
在上述实验中,由于合金成分中B侧元素的原子分数偏低,同时Al含量偏高,导致合金中A2B7相仍较少,并存在少量Al Ni3相。进一步改进合金成分,提高B侧元素的原子分数,并降低Al元素的含量,制备了Nd0.75Mg0.25Ni3.2Al0.1合金,在1373 K下采用相同的方法进行热处理,并分别采用急冷和随炉冷却两种冷却方式,研究冷却方式对合金相成分和电化学性能的影响。
从表3中的Rietveld分析结果可以看到,提高x(B)/x(A)比例后,采用相同的方法进行热处理,Al Ni3相消失,Nd2Ni7相比例进一步增加,慢冷样品中Nd2Ni7相含量为92.31%,较快冷样品有所提高。
对慢冷和快冷样品进行了循环寿命的测试,100周充放电循环后慢冷样品的容量保持率为92.2%,较快冷样品83.4%提高了近10%(如图7)。表4中电化学测试结果表明,慢冷处理的Nd0.75Mg0.25Ni3.2Al0.1合金的容量、倍率性能和荷电保持率等电化学性能更好。主要原因为合金中Nd2Ni7相含量增加,Nd Ni5相含量减少。
表3 不同冷却方式热处理的Nd0.75Mg0.25Ni3.2Al0.1合金的Rietveld分析结果Table 3 Structure parameters of fast and slow cooling Nd0.75Mg0.25Ni3.2Al0.1alloys 下载原图
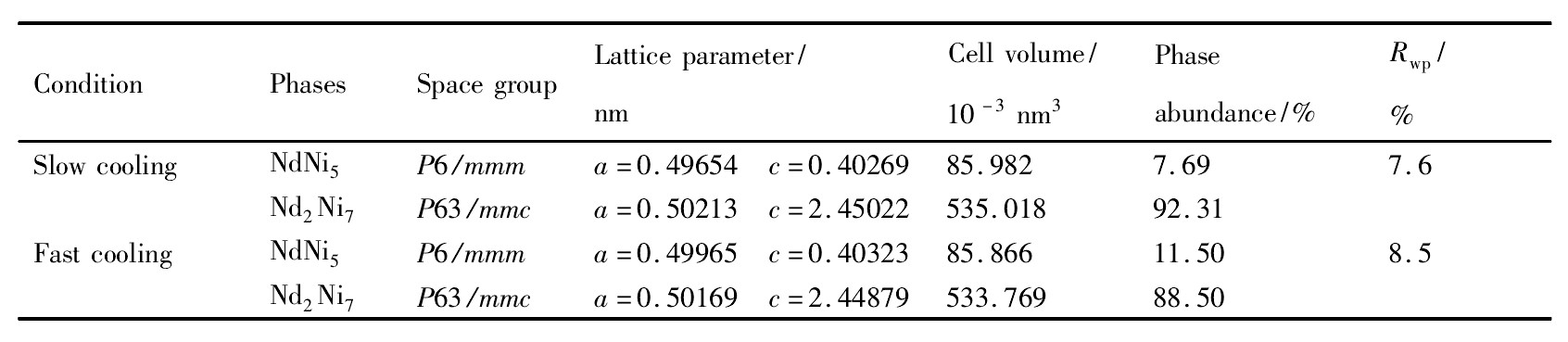
表3 不同冷却方式热处理的Nd0.75Mg0.25Ni3.2Al0.1合金的Rietveld分析结果Table 3 Structure parameters of fast and slow cooling Nd0.75Mg0.25Ni3.2Al0.1alloys
图7 不同冷却方式热处理的Nd0.75Mg0.25Ni3.2Al0.1合金电极的循环稳定性Fig.7 Cycling stabilities of fast and slow cooling Nd0.75Mg0.25Ni3.2Al0.1alloy electrodes
表4 不同冷却方式热处理Nd0.75Mg0.25Ni3.2Al0.1合金电极的电化学性能Table 4 Electrochemical properties of fast and slow cool-ing Nd0.75Mg0.25Ni3.2Al0.1alloy electrodes 下载原图
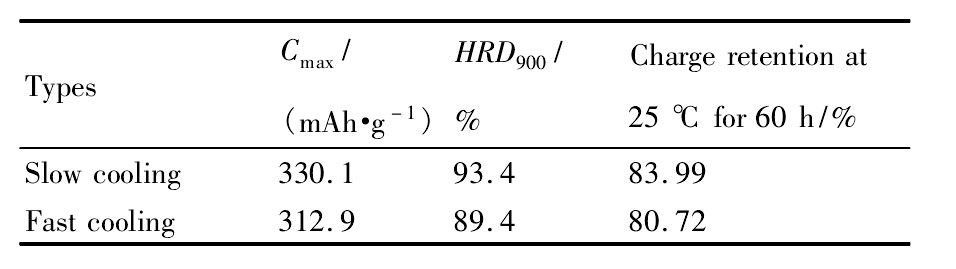
表4 不同冷却方式热处理Nd0.75Mg0.25Ni3.2Al0.1合金电极的电化学性能Table 4 Electrochemical properties of fast and slow cool-ing Nd0.75Mg0.25Ni3.2Al0.1alloy electrodes
3 结论
1.对于Nd0.75Mg0.25Ni2.75Al0.25合金,随着热处理温度的升高,不同相成分分布更加均匀,不同相间Mg元素的浓度差减小。铸态及热处理态的合金为多相结构,主相均为Nd2Ni7六方相,且随着退火处理温度的升高,Nd2Ni7相逐渐增加,1373 K,5 h退火处理后,Nd2Ni7相含量为74.11%。电化学测试结果表明,经过退火处理合金中Nd2Ni7相增加,电化学P-C-T曲线平台变平缓,平台压降低,电化学容量,倍率性能和荷电保持率均有较大提升。
2.对于Nd0.75Mg0.25Ni3.2Al0.1合金,采用相同的热处理温度和处理时间,慢冷较快冷样品,性能更加优异,Nd2Ni7相含量可达92.31%,最大电化学容量为330.1 m A·g-1,循环100周后容量保持率为92.3%,表明退火处理有利于Nd2Ni7相的形成。
参考文献