网络首发时间: 2015-04-07 09:25
铍精矿浸出液中铍的回收工艺试验
南华大学核资源工程学院
湖南水口山有色金属集团有限公司第六冶炼厂
摘 要:
铍是一种稀缺的战略资源,其主要表现在储量少,需求量大。铍矿石浸出液中过多的杂质会给铍的回收带来麻烦,氟是铍浸出液中的有害杂质,氟含量的多少会直接影响铍浸出液中铍的回收率。针对Be O浓度为16.86 g·L-1的铍精矿浸出液进行了回收工艺试验,用NH3·H2O代替Na OH沉淀浸出液中的铍,使得浸出液中的F-能与NH3·H2O生成NH4F。重点分析了氨水对铍的沉淀效率、氢氧化钠用量对氢氧化铍的溶解以及水用量对氢氧化铍水解的影响。结果表明,浸出液中铍回收的最佳工艺条件为:沉淀p H为8.5,碱溶时滤饼中氢氧化钠用量为氧化铍质量的13倍,水解时自来水用量为滤液体积的5倍。铍的总回收率达到了92.82%。同时,降低了沉淀中F的浓度,克服了F对铍精矿浸出液中Be回收的不利影响。
关键词:
中图分类号: TF824
作者简介:王清良(1969-),男,湖南宁乡人,博士,教授,研究方向:化学工艺;电话:13786418292;E-mail:NHWQL@sina.com;
收稿日期:2014-06-04
基金:湖南省科技厅重点项目(2013GK2023)资助;
Recovering Beryllium from Leaching Solution of Beryllium Concentrates
Wang Qingliang Li Zhong Li Qian Hu E'ming Feng Zhigang Cheng Quanhui
School of Nuclear Resource Engineering,University of South China
No.6 Smelting Plant,Hunan Shuikoushan Nonferrous Metals Group Co.,Ltd.
Abstract:
Beryllium is one kind of rare strategic resource. The geological reserve is very low,while the demand is vast. Excessive impurities in leachate of beryllium ore could cause some difficulties for beryllium recovery. Fluoride,as a harmful impurity,directly influences the beryllium recovery in leaching solution. Beryllium recovering experiments were performed by beryllium ore leaching solution with concentration of 16. 86 g·L-1Be O. The precipitation of beryllium was conducted by NH3·H2O instead of Na OH solution,which made F-in the leaching solution react with NH3·H2O to generate NH4 F. The precipitation efficiency of Be O with NH3·H2O was analyzed. The effects of the dosage of Na OH and water on Be OH hydrolysis were also analyzed. The optimal parameters for recovering beryllium from leaching solution were acquired. The results showed that,the optimal p H for precipitation was 8. 5,the optimal consumption of Na OH was 13 times the Be O mass,and the water consumption for hydrolysis was 5 times the amount of filter liquor. The recovery rate of beryllium achieved more than 92. 82%. Meanwhile,the fluoride concentration was decreased in sediments,which overcame the adverse effects of fluoride on Be O recovery from beryllium leachate.
Keyword:
leachate; recovery; beryllium oxide; optimization;
Received: 2014-06-04
铍是一种稀缺的战略资源,其主要表现在储量少,需求量大。世界上主要有美国、日本、独联体、中国、印度等几个少数国家生产铍[1]。而且,世界上铍的需求量在以每年5%~ 6% 的速度增长。铍金属、铍化合物以及铍合金被广泛应用于航空航天、核工业、电子工业中[2]。铍的需求之所以广泛,是因为铍具有其他金属元素无法比拟的优点:铍的化学性质比较稳定,尤其氧化铍不仅密度低,而且有相当高的强度和耐热性。用氧化铍生产出来的陶瓷热传导性最好,陶瓷的强度大、熔点高、不容易变形[3]。在快速发展的半导体材料和集成电路中,氧化铍陶瓷的需求量正在不断增加。水口山六厂作为国内唯一加工铍的企业,其面对日益增加的氧化铍的需求量,每年生产的氧化铍已经不能满足国内的需要,因此铍的地位被重新定义到了一个新的高度。
铍金属产品的生产工艺一般是铍原矿—选矿—铍精矿—预处理—浸出—回收铍的过程[4,5,6,7,8,9]。精矿石加硫酸预处理的主要目的是破坏铍矿石的晶体结构,进而将易溶于酸的Be2 +,Al3 +,Fe2 +,Fe3 +等离子从矿石中分离出来,得到铍的浸出液。由于对Be产品形式和纯度的要求不同,其处理工艺也不尽相同,而且铍矿石浸出液中过多的杂质会给铍的回收带来麻烦,尤其是P,F,Al的分离,P的分离需要特殊的工艺方法[10]。F是铍浸出液中的有害杂质,F含量的多少会直接影响铍浸出液中铍的回收率,这是因为F极易与铝形成稳定的氟铝络合物,影响后续的分离工序[11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19]。在非绿柱石的铍矿中,矿石本身的F含量高,因此,在对非绿柱石的铍矿冶炼中,相应的铍矿浸出液中的F浓度也很高。本文旨在前期大量试验的基础上,克服F对铍浸出液中氧化铍回收率的影响,解决含F铍矿石浸出液中铍回收率不高的问题,并进行了工艺条件优化,为铍矿石浸出液中铍的回收提供借鉴。
1 实验
1. 1 材料
铍矿石浸出液由氧化铍品位为5. 6% 的铍精矿进行加酸保温处理之后浸出得到,浸出液的成分及含量见表1。所用试剂主要有NH3·H2O,Na OH,EDTA,均为分析纯。
混合掩蔽剂溶液: 称取5 g EDTA,5 g酒石酸钾钠于烧杯中,加入30 ml三乙醇胺,加水70 ml搅拌溶解。
铍标准溶液: 称取3. 5410 g硫酸铍(Be SO4·4 H2O) 于烧杯中,加30 ml水,2 ml硫酸,加热溶解,移入1000 ml容量瓶中,用水稀释至刻度,摇匀,此溶液1 ml含500 μg氧化铍。移取2. 00 ml铍标准溶液于500 ml容量瓶中,加50 ml硫酸,用水稀释至刻度,摇匀。此溶液1 ml含2 μg氧化铍。
表1 浸出液成分分析结果Table 1 Composition analysis of leachate ( g·L- 1) 下载原图
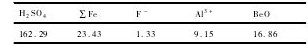
表1 浸出液成分分析结果Table 1 Composition analysis of leachate ( g·L- 1)
0 . 01 mol·L- 1溴化十六烷基三甲铵溶液: 称取3. 64 g CTMAB溶解在100 ml乙醇中,加水至1000 ml。
1. 2 仪器
实验使用仪器设备见表2。
1. 3 方法
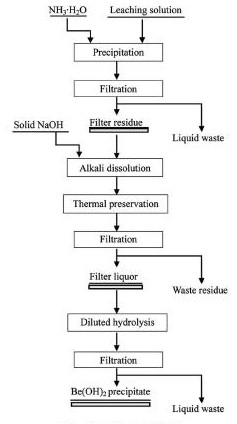
由铍回收工艺流程( 图1) 可以看出,试验主要包括5 个工艺步骤:
( 1) 氨水沉淀。分别取高浓度氧化铍浸出液4份,每份200 ml于500 ml的烧杯中,此浸出液中氧化铍浓度为16. 86 g·L- 1,氧化铍质量为3. 372 g。分别将4 份氧化铍浸出液在磁力加热搅拌器上加热至90 ℃ 以上,用氨水调p H至6. 5,7. 5,8. 5 和9. 0 进行沉淀,并计算氨水消耗量。将得到的沉淀用真空过滤机进行固液分离,再用90 ℃ 以上、1. 5 倍浸出液体积的热水进行洗涤,分析滤液中的氧化铍含量,得出浸出液中氧化铍沉淀的最佳p H值。
( 2) 过滤与洗涤。滤渣用90℃以上的水进行洗涤,热水用量为浸出液体积的1. 5 倍。
( 3) 碱溶。在最佳沉淀p H条件下,制备3 份沉淀,进行洗涤,过滤后得到3 份滤饼,置于500 ml烧杯中,分别加入与原浸出液中氧化铍的质量比为1∶ 10,1∶ 12,1∶ 13 的氢氧化钠。放入自制反应釜中,在密闭125 ℃ 的条件下加热2 h,取出后用真空过滤机进行固液分离,分析滤液中氧化铍的浓度,得出在氧化铍溶解效果最佳时的氢氧化钠用量。
表2 试验用仪器和设备Table 2 Experiment instruments and equipment 下载原图
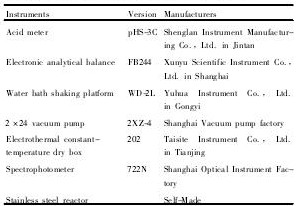
表2 试验用仪器和设备Table 2 Experiment instruments and equipment
图1 铍回收工艺流程图Fig. 1 Process flow diagram of beryllium recovery
( 4) 水解。在前期试验的最佳沉淀p H与最佳碱溶氢氧化钠用量条件下,进行水解试验。选用在最佳条件沉淀、碱溶、过滤之后的滤液4 份,分别按体积比为1∶ 2,1∶ 3,1∶ 4,1∶ 5 加入水,煮沸1. 5 h,考虑到煮沸蒸发造成的溶液体积的变化,在煮沸过程中适当加入自来水,使溶液的体积与原来体积保持一致。氢氧化铍在煮沸条件下不断析出,过滤、洗涤、烘干、称重、分析氧化铍含量,计算氧化铍回收率。
( 5) 最后将氢氧化铍沉淀过滤、烘干、分析铍含量和计算铍的回收率。
2 结果与讨论
2. 1 p H对氨水沉淀的影响
在非绿柱石的铍矿回收氧化铍的工艺中,氟一直是影响氧化铍回收率的最重要因素,以往用氢氧化钠沉淀氧化铍时,溶液中的氟不与氢氧化钠进行反应,使得氟继续和氧化铍伴生在一起,影响氧化铍的回收率[20,21,22,23]。用氨水作为铍精矿浸出液的沉淀剂,不仅起到了沉淀氧化铍的效果,而且实现了氟与铍的分离。反应式如下:
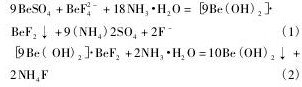
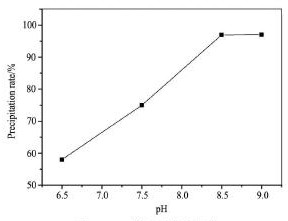
采用4 份氧化铍浸出液( 氧化铍浓度为16. 86g·L- 1) 在磁力加热搅拌器上加热至90 ℃ 以上,分别用氨水调p H至6. 5,7. 5,8. 5 和9. 0 进行沉淀,计算氨水消耗量。然后过滤洗涤,分析浸出液中氧化铍沉淀效果,试验结果见图2。
从图2 可以看出用氨水将p H值调为6. 5,氧化铍的沉淀率为58. 01% ,沉淀率很低,不能满足要求。继续增加氨水的用量,调整p H为7. 5,虽然氧化铍的沉淀率比p H为6. 5 时提高了近20% ,但是沉淀率也只有74. 97% 。当浸出液p H分别调至8. 5 和9. 0 时,氧化铍的沉淀率达到了97. 00% 和97. 06% ,由此可以看出在p H为8. 5 时,氨水消耗量为130 ml,继续增大氨水的用量对氧化铍的沉淀率影响是很小的,考虑到成本以及氨水的消耗,得出沉淀浸出液中氧化铍的最佳p H值为8. 5。
2. 2 碱溶氢氧化钠用量对氧化铍溶解率的影响
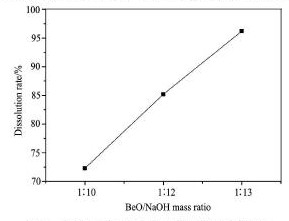
通过试验前分析结果可以得知浸出液中的杂质主要是Al3 +,Fe2 +和Fe3 +,加入氨水调节p H之后生成的主要是Be( OH)2,Fe( OH)2,Fe( OH)3,Al( OH)3。加入氢氧化钠之后,氢氧化铍能与氢氧化钠生成溶于水的铍酸钠,氢氧化铝与氢氧化钠生成溶于水的偏铝酸钠,氢氧化铁不能与氢氧化钠反应。根据上述结果,选用沉淀p H为8. 5,制备3 份沉淀,并洗涤过滤,得到滤饼( 含氧化铍3. 271 g) 。分别加入与原浸出液中氧化铍的质量比为1∶ 10,1∶ 12,1∶ 13 的氢氧化钠用量( 33. 72,40. 47,43. 84g) ,放入密闭反应釜125 ℃ 条件下加热2 h后,抽滤分离,分析氧化铍的溶解率。试验结果见图3。
图2 p H对铍沉淀率的影响Fig. 2 Effect of p H on beryllium precipitation
由图3 结果可以看出,滤饼中氢氧化钠与氧化铍的质量最佳混合比为13∶ 1,此时滤饼中的氧化铍溶解率达到了96. 19% 。
2. 3 水用量对氧化铍水解的影响
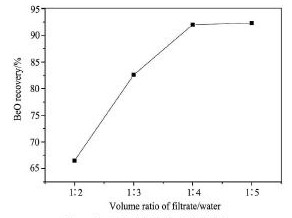
水解的主要目的是实现铍与铝的分离,去除杂质铝,因为铍酸钠在水中能水解成为氢氧化铍,而偏铝酸钠不水解。其反应式为: Na2Be O2+ 2H2O= Be( OH)2↓ + 2Na OH。在氧化铍浸出液的最佳沉淀p H 8. 5、碱溶氢氧化钠最佳用量1∶ 13 条件下,进行水解试验。选用在最佳条件下沉淀、碱溶、过滤之后的滤液4 份,此滤液中氧化铍的含量为3. 146 g,分别按体积比为1∶ 2,1∶ 3,1∶ 4,1∶ 5 加水,氢氧化铍在煮沸条件下不断水解析出,煮沸1. 5 h后,得到氧化铍。试验结果见图4。
由图4 可以看出,水解时滤液与自来水的加入量为1 ∶ 2 和1 ∶ 3 时,氧化铍的回收率均未达到90% 以上,当比例提高至1∶ 4 和1∶ 5 时,氧化铍的回收率均超过了92% ,由于自来水的成本很低,自来水用量的增加不会对成本带来很大的影响,而且滤液与自来水的比例为1∶ 5 时的氧化铍回收率比1∶ 4 时的回收率高出0. 29% 。最后选用滤液与自来水结合的最佳比例为1∶ 5。
图3碱溶氢氧化钠用量对氧化铍溶解率的影响Fig.3 Effect of Na OH on beryllium hydroxide dissolution rate
图4 水用量对氧化铍水解的影响Fig. 4 Effect of water dosage on hydrolysis of beryllium oxide
3 结论
1. 通过试验可以看出,用氨水沉淀铍矿浸出液中氧化铍,不仅达到了比较理想的沉淀效果,最终还实现了铍和氟的分离,降低了氟在浸出液回收中的不利影响。
2. 由以上条件试验结果可知,浸出液中氧化铍回收的最佳工艺条件为: 沉淀p H为8. 5,氨水消耗量为130 ml/3. 372 g Be O; 碱溶时滤饼中氢氧化钠用量为氧化铍质量的13 倍,氢氧化铍滤饼的溶解率达到了96. 19% ; 水解时自来水用量为滤液体积的5 倍,此时氧化铍的总回收率为92. 82% ,满足了工艺要求。
参考文献