网络首发时间: 2015-05-13 10:53
真空蒸馏法深度脱除精镉中Tl和In的研究
真空冶金国家工程实验室
省部共建复杂有色金属资源清洁利用国家重点实验室
云南省有色金属真空冶金重点实验室
摘 要:
对真空蒸馏法深度脱除精镉中铊和铟进行了理论分析和实验研究,考察了蒸馏温度对Tl和In脱除效果的影响,并探讨了钢质材料中Fe元素对实验结果的影响。理论分析表明,在真空条件下,Tl和In与Cd均具有分离的可能性,且分离效果较好,即利用真空蒸馏法获得更高纯度的金属Cd是可行的。实验结果表明,随着蒸馏温度的升高,Cd的挥发率呈快速增加趋势,挥发物中的Tl含量增加迅速,Tl的脱除率减小幅度较大,挥发物中In含量增加缓慢且保持在较低水平,In的脱除率减小的幅度较小,挥发物中Fe含量一直保持在较低水平,含量始终保持在1×10~(-8)以下,说明利用钢质材料对提高精Cd纯度不会产生影响;当系统压力为2~5 Pa,蒸馏温度为643 K,保温时间为7 h条件下,精Cd的挥发率为16.21%,挥发产物中Tl含量为2.83×10~(-7),Tl的脱除率为99.76%,In的含量为2.327×10~(-7),In的脱除率为97.97%,可获得纯度为99.9999%的金属Cd。
关键词:
中图分类号: TF819.2
作者简介:闫华龙(1988-),男,河北邯郸人,硕士研究生,研究方向:真空冶金新技术;E-mail:kungong@126.com;;熊恒,副教授;电话:13518758325;E-mail:57160741@qq.com;
收稿日期:2014-06-24
基金:国家自然科学基金青年基金项目(51304096);教育部“创新团队发展计划”项目(IRT1250);云南省复杂有色金属资源清洁利用国家工程实验室开放基金项目(CNMRCUKF1403);云南省科技厅面上自筹项目(2013FZ034)资助;
Intensive Removal of Thallium and Indium from Pure Cadmium by Vacuum Distillation
Yan Hualong Xiong Heng Yang Bin Xu Baoqiang Wang Wei Shu Kai
National Engineering Laboratory for Vacuum Metallurgy
State Key Laboratory of Complex Non-ferrous Metal Resources Clear Utilization
Key Laboratory of Vacuum Metallurgy for Nonferrous Metal of Yunnan Province
Abstract:
The theoretical analysis and the experimental study on intensive removal of Tl and In from pure Cd by vacuum distillation were investigated respectively. Furthermore,the effect of distillation temperature on separating process was analyzed,and the influence of iron in steel materials on experimental result was discussed. According to the theoretical analysis,there was a possibility that Tl and In might be separated from Cd under vacuum conditions with ideal effect,which demonstrated that much purer Cd could be available through vacuum distillation. The experimental result showed that the volatilization rate of Cd had an increase trend as temperature of distillation rose. In content of volatiles increased rapidly,while its removal rate decreased a lot. In content of volatiles increased slowly,as its removal rate decreased a little and was kept at a low level with a rising temperature of distillation. Fe content of volatiles was almost always low,under 1 × 10~(- 8),and the result showed that iron in steel materials did not affect the purification of Cd. When the system pressure was 2 ~ 5 Pa,the distillation temperature was 643 K and the holding time was 7 h,the volatile rate of Cd was16. 21%,the volatile content of Tl was 2. 83 × 10~(- 7),the removal rate reached 99. 76%,In content was 2. 327 × 10~(- 7),the removal rate reached 97. 97%,and the purity of Cd was 99. 9999%.
Keyword:
pure cadmium; vacuum distillation; steel crucible; thallium; indium;
Received: 2014-06-24
镉是一种稀有金属,它没有单独的矿床,一般是铅、锌等重金属冶炼过程中的副产品[1]。Cd的用途十分广泛,常用于配置合金、制造电池、制作原子反应堆的控制棒等[2,3]。近年来,Cd在新型光电功能材料[4]方面的应用使高纯度金属Cd的制备技术受到重视。
Cd常用的提纯方法[5,6,7]有电解精炼法、区域熔炼法、化学处理法、真空蒸馏法等。电解精炼法产出金属纯度较低,需进一步火法精炼;区域熔炼法产量较小;化学处理法[8]流程长且对环境有一定污染;真空冶金国家工程实验室研究利用真空蒸馏法提纯粗金属,获得较好的效果,真空蒸馏法[9,10,11,12,13,14]是在低于大气压力的条件下利用元素间的沸点和蒸气压的差异使主体金属和杂质组分分离,具有提纯纯度较高、消耗少、流程短、对环境无污染等优点。
文献[15]对粗Cd(质量分数为95%~98%)中的主要组分Pb,Tl,Sn,Sb,Zn,As,Fe,Cu和Ni等在真空条件下的挥发行为进行了研究,研究表明,经过一次真空蒸馏,除Zn外其他金属均达到了1#Cd的标准。而利用真空蒸馏法处理精Cd(质量分数为99.99%)尚鲜有人进行过研究,考虑到精Cd中Tl和In的含量占杂质的比例较高,本文研究利用真空蒸馏法深度脱除精Cd中的Tl和In,以获得纯度更高的金属Cd,并得到蒸馏温度对挥发物中Tl和In含量的影响规律。
1 实验
1.1 原料
实验原料来自云南某厂,其化学成分见表1。
由表1可得,精Cd中含量相对较高的杂质金属为Tl,In等,其他含量相对较低,在本文中不予讨论,由于实验采用钢质坩埚和钢质收集器,则需讨论其对实验结果Fe含量的影响。
1.2 可行性分析
判断精Cd中Tl和In能否通过真空蒸馏方法进行分离,可从纯物质饱和蒸气压、分离系数和气液相平衡图等方面进行分析[16]。
表1 精Cd的成分Table 1 Chemical compositions of Cd(10-6,mass fraction) 下载原图

表1 精Cd的成分Table 1 Chemical compositions of Cd(10-6,mass fraction)
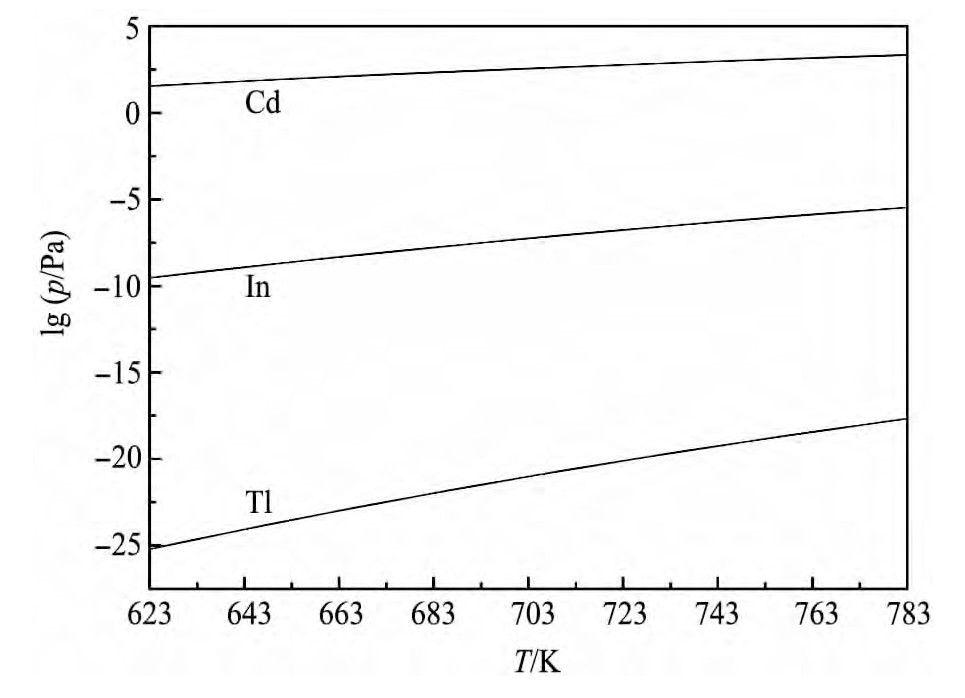
饱和蒸气压分析:由文献[16]中的克劳修斯-克莱普朗方程和数据可计算得各金属饱和蒸气压(p)和温度(T)的关系,如图1所示。
由图1可知,在623~783 K温度范围内,Tl和In与Cd的饱和蒸气压相差较大,具有分离的可能性。
分离系数分析:经过热力学分析,有关学者提出用分离系数来判断两种合金或粗金属组分用蒸馏法分离的可能性[15],对于Cd-A体系有:

式中:β为分离系数,γA和γCd为金属A和金属Cd的活度系数;pA和pCd为金属A和金属镉的饱和蒸气压。当β值远大于或远小于1,则两金属具有分离的可能性;当β接近于1时,则不易分离。
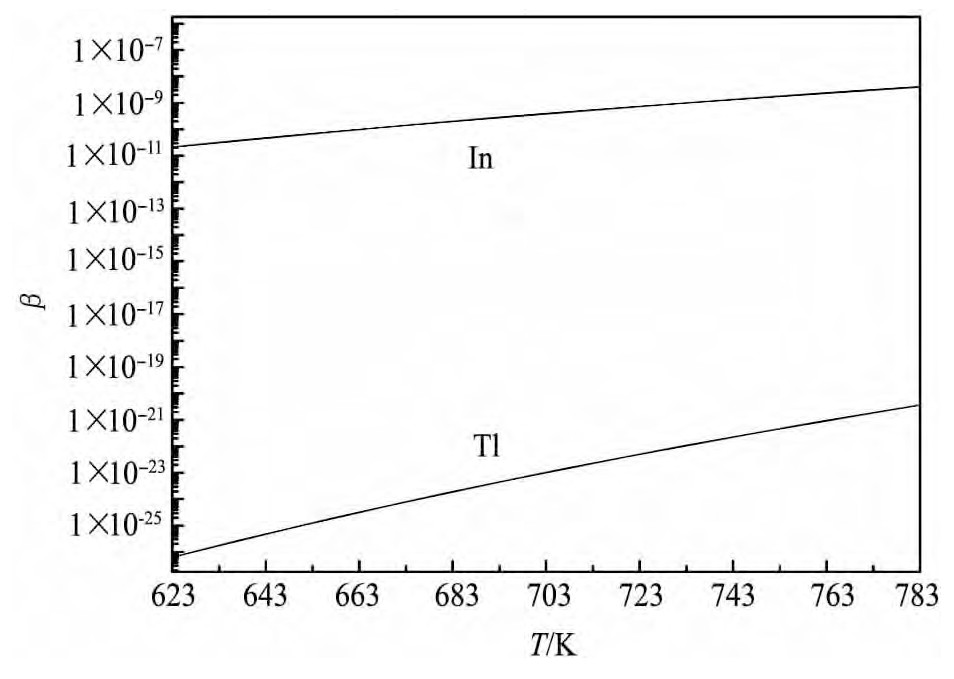
若忽略温度对活度系数的影响,根据文献[16]查得各金属的活度系数,计算可得分离系数与温度关系,如图2所示。
图1 纯金属饱和蒸气压与温度的关系Fig.1 Relationship between vapor pressure of pure metals and temperature
图2 分离系数与温度的关系Fig.2 Relationship between separation coefficients and temperature
由图2可知,在623至783 K温度范围内,Tl和In的分离系数均远小于1,则可说明Cd与Tl和In能进行分离。
气液相平衡图分析:不同温度下,精Cd经一次真空蒸馏,气相中的Tl和In含量可由公式(2)[16]估算得。
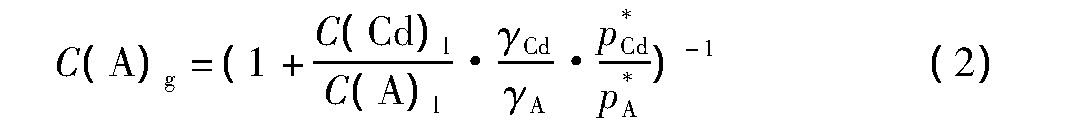
式中:C(A)g和C(A)l分别为组元A在气液相中的摩尔分数,C(Cd)l为Cd在液相中的摩尔分数。
由上式可得理论Cd-Tl以及Cd-In气液相平衡图,如图3所示。
由图3可知,当温度为623~783 K区间内,液相中Tl和In含量均为1×10-7~1×10-3范围内,气相中的Tl和In含量始终保持在一个较低的水平,Tl含量低于1×10-27、In含量低于1×10-14;随着蒸馏温度的升高,气相中Tl和In含量均有逐渐增加的趋势;随着液相中Tl和In含量增加,气相中含量也相应增加。由此可知降低蒸馏温度可减少气相中的Tl和In含量,因此为使镉充分优先挥发进入挥发物,Tl和In在残留物中富集,应控制蒸馏温度为较低水平。
1.3 实验设备与方法
实验采用自制内热式真空炉,其结构分为5个部分:钢质真空室,钢质冷凝器,石墨发热体,控温测温装置,真空抽取与测量装置。采用钢质坩埚进行蒸馏实验。挥发产物采用辉光放电质谱仪(GD-MS)进行分析,此检测方法可检测含量较低的杂质成分。
原料和残留物的质量采用精确度为0.01 g的电子天平进行称量,挥发的质量按式(3)计算:

精Cd的挥发率采用式(4)计算:

元素i的脱除率按式(5)计算:

1.4 步骤
实验前精Cd用低浓度的草酸溶液处理表面,在真空干燥箱中干燥完全,再放入钢质坩埚中,将坩埚置于真空炉内,待系统压力为2~5 Pa时,升温至蒸馏温度,保温一定时间,断电,待温度降到100℃以下,关冷却水,取出冷凝物和残留物,称量后,取样送检测。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 挥发量分析
控制系统压力为2~5 Pa,称取精Cd质量500 g,蒸馏表观面积3000 mm2,蒸馏温度分别为643,663,683,703和723 K,保温时间7 h,考察蒸馏温度对精Cd挥发情况的影响,实验结果如表2所示。
由表2可知,蒸馏温度较低时,精Cd的挥发量和挥发率均较小,但随着蒸馏温度的升高,精Cd的挥发量和挥发率大大增加,可知蒸馏温度对精Cd的挥发影响较大。
2.2 Tl含量分析
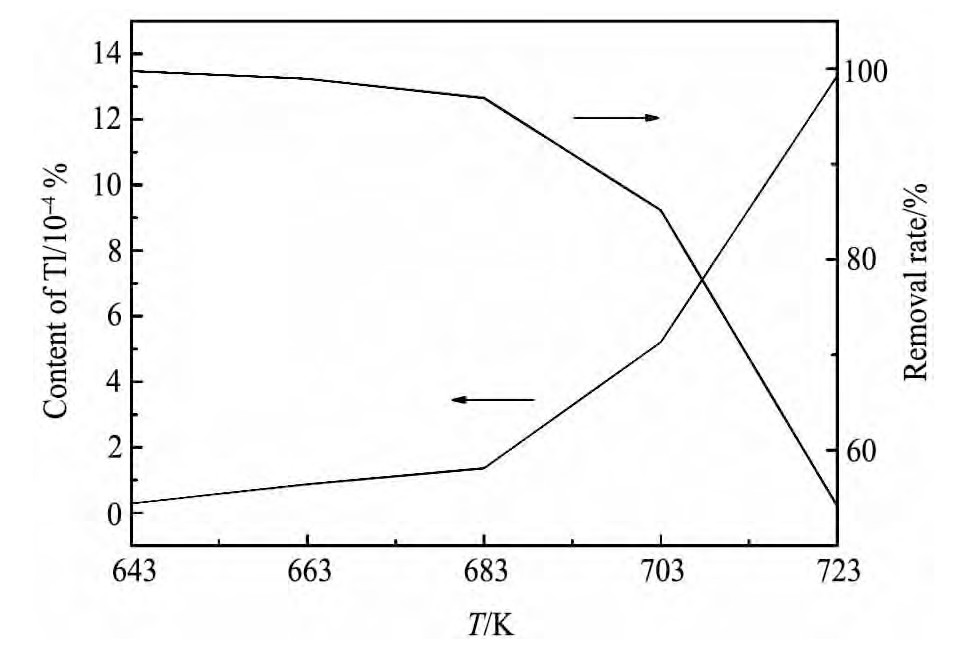
在其他实验条件相同的情况下,考察了蒸馏温度对Tl挥发的影响,实验结果如图4所示。
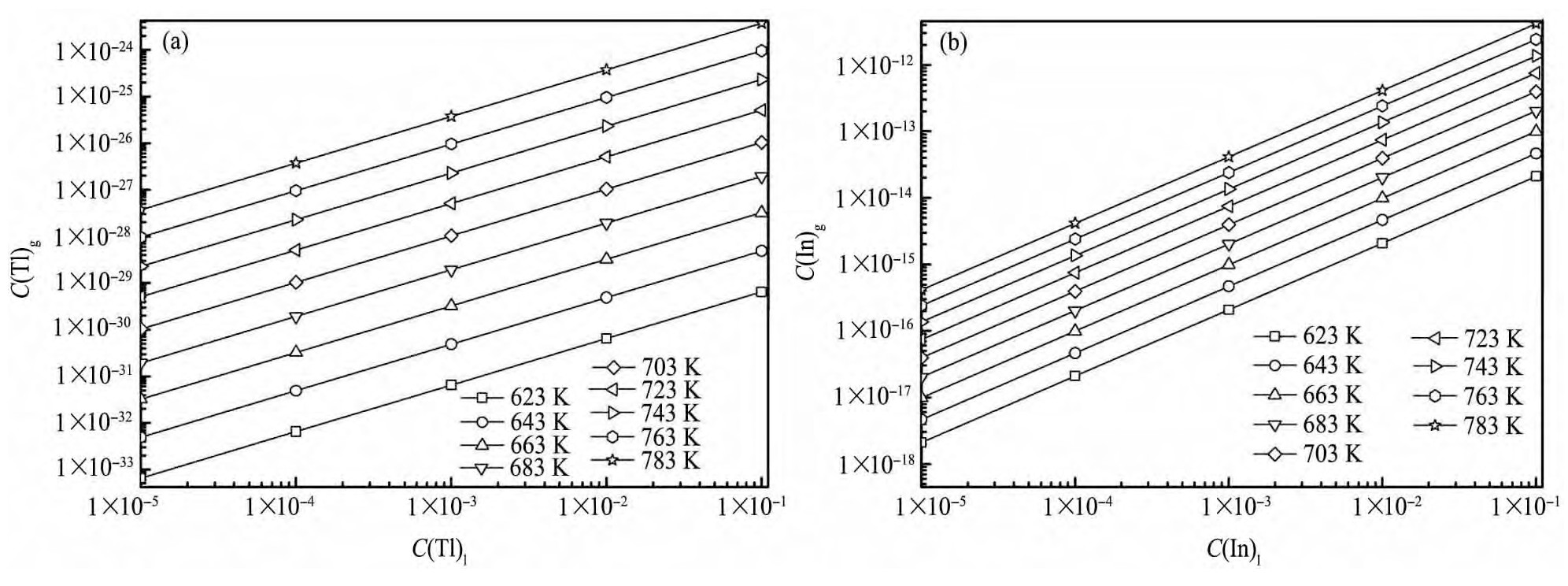
图3 Cd-Tl系和Cd-In系气液相平衡图Fig.3 Vapor-liquid equilibrium diagrams of Cd-Tl system(a)and Cd-In system(b)at different temperatures
表2 不同温度条件下的挥发情况Table 2 Volatilization under different temperature conditions 下载原图
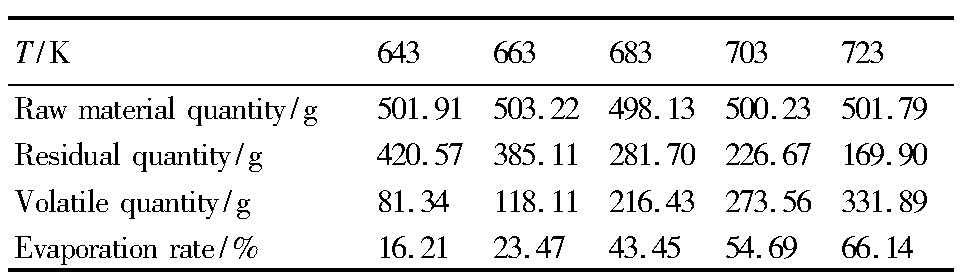
表2 不同温度条件下的挥发情况Table 2 Volatilization under different temperature conditions
由图4可知,蒸馏温度较低时,Tl脱除很彻底,在643 K时,挥发物中的Tl含量可低至28.3×10-7,Tl的脱除率可达99.76%,在643 K至683 K温度范围内,随着蒸馏温度的上升,挥发物中的Tl含量呈缓慢上升趋势,Tl的脱除率呈缓慢下降趋势;当蒸馏温度高于683 K,挥发物中的Tl含量随蒸馏温度呈快速上升趋势,相应的Tl的脱除率快速降低,在723 K时,挥发物中的Tl含量增至1.333×10-5,较643 K时增加了近47倍,而Tl的脱除率仅为54.13%。
可知,在实验条件范围内,Tl的脱除效果对温度较敏感,因此选择较低的温度有利于Tl的脱除。
2.3 In含量分析
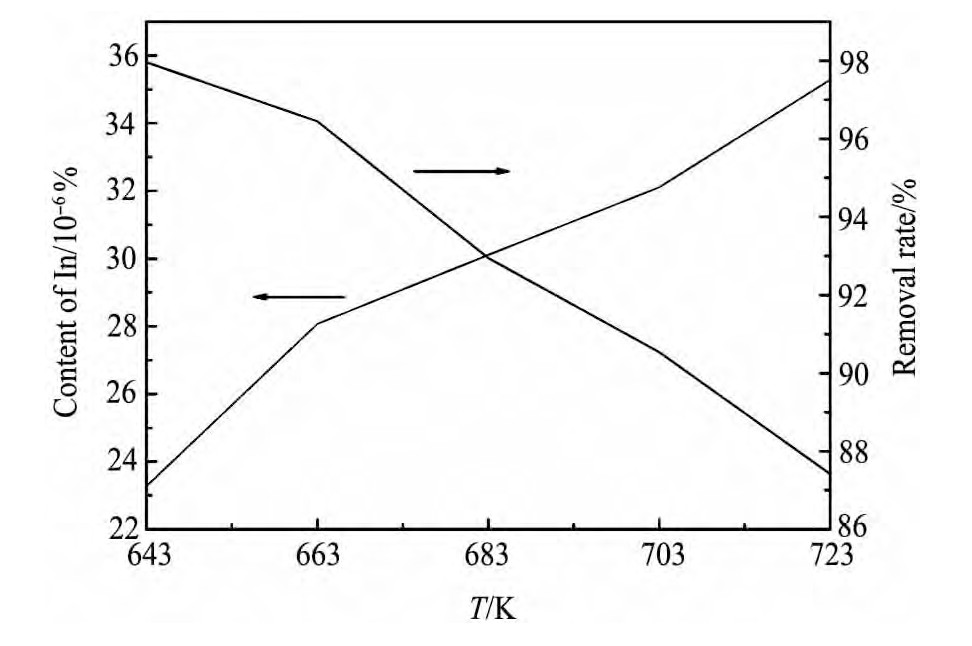
在其他条件不变的情况下,考察了蒸馏温度对In挥发的影响,实验结果如图5所示。
由图5可知,在整个温度段内,In脱除效果较好,当温度为643 K时,挥发物中的In含量为2.33×10-7,In的脱除率为97.97%,随着蒸馏温度的上升,挥发物中的In含量呈缓慢上升趋势,但增加不明显,当温度为723 K时,In的含量增加为3.528×10-7,仅增加了1.5倍,相应的In的脱除率降为87.41%。
图4 挥发物中的Tl含量与蒸馏温度的关系曲线Fig.4 Relationship between Tl content and distillation temper-ature in volatiles
图5 挥发物中的In含量与蒸馏温度的关系曲线Fig.5 Relationship between In content and distillation temper-ature in volatiles
可知,在实验条件范围内,蒸馏温度对In的脱除效果影响相对较小,In的脱除效果一直较好。
2.4 铁含量分析
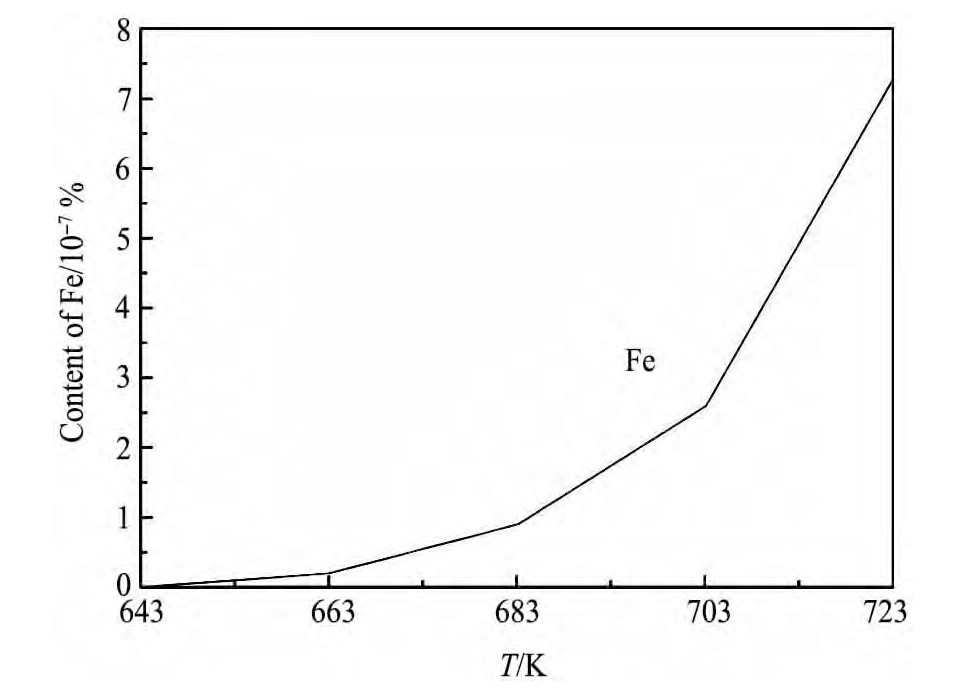
在其他条件不变的情况下,考察了收集产物中Fe含量的变化,实验结果如图6所示。
由图6可知,随蒸馏温度的上升,收集的产物中Fe含量有所增加,但增加量较少,含量始终保持在1×10-8以下,对产物的纯度影响较小,因此采用钢坩埚以及钢质收集器进行本实验是可行的。
因此为最大量降低挥发物中的Tl和In含量,并且保证Cd的挥发率,蒸馏温度选取最低温度643 K为最佳温度,在此温度条件下,精镉的挥发率为16.21%,挥发产物中Tl含量为2.83×10-7,Tl的脱除率为99.76%,In的含量为2.327×10-7,In的脱除率为97.97%,可获得纯度为99.9999%的金属Cd。
图6 挥发物中的Fe含量与蒸馏温度的关系曲线Fig.6Relationship between Fe content and distillation tem-perature in volatiles
3结论
1.理论计算可得利用真空蒸馏法脱除精Cd中Tl和In是可行的。
2.控制系统压力为2~5 Pa,保温时间7 h,在643~723 K温度范围内,随蒸馏温度的升高,挥发物中的Tl含量增加迅速,Tl的脱除率相应迅速降低,In含量增加缓慢,且保持在较低水平,In的脱除率减小幅度较小。
3.采用钢坩埚,钢质收集器对实验产物纯度影响较小,产物中Fe含量始终保持在1×10-8以下。
4.在真空度2~5 Pa范围内,蒸馏温度为643 K,保温时间为7 h,精Cd的挥发率为16.21%,挥发产物中Tl含量为2.83×10-7,Tl的脱除率为99.76%,In的含量为2.327×10-7,In的脱除率为97.97%,可获得纯度为99.9999%的金属Cd。
参考文献