准一维无序体系电子局域化及输运特性
宋招权,徐慧, 马松山,刘小良
(中南大学 物理科学与技术学院,湖南 长沙,410083)
摘 要:
摘 要:在单电子紧束缚近似下,利用多对角全随机厄米矩阵算法,结合负本征值理论和无限阶微扰理论及传输矩阵方法,研究准一维多链无序体系中电子波函数局域化特性及其电子输运特性。研究结果表明:由于格点能量无序,准一维多链无序体系电子波函数呈现出局域化特性;格点能量无序度减小会导致在中间能区发生退局域化现象,表现为在中间能区电子波函数的局域长度大于体系格点数,即出现扩展态,且出现扩展态的能量区间随着无序度的减小而增大的趋势;同时,随着链数的增加,体系有向退局域化方向发展的趋势;在中间能区电子输运透射系数较大,而在低能区及高能区透射系数较小,同时,格点能量无序与维度效应对体系的电子输运存在竞争效应,当体系格点数及链数一定时,体系的透射系数随着格点能量无序度的增大而减小,而当体系格点数及格点能量无序度一定时,准一维多链无序体系的透射系数随着体系链数的增大而增大。
关键词:
中图分类号:O482.4,TB303 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2011)01-0125-05
Characteristics of electronic localization and transportation in quasi-one-dimensional disordered systems
SONG Zhao-quan, XU Hui, MA Song-shan, LIU Xiao-liang
(School of Physical Science and Technology, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China)
Abstract: Based on a tight-binding disordered model describing a single electron band, a model of quasi-one- dimensional disordered systems with several chains was established using the negative eignvalue theory, infinite order perturbation theory and transfer matrix method. The characteristics of electronic localization and transportation in quasi-one-dimensional disordered systems with several chains were discussed. The results indicate that the electronic states of the quasi-one-dimensional disordered systems are localized due to energy disorder of the lattices. The localization length increases with the decrease of the strength of energy disorder of the lattices. At the energy band center, there exist some extent states whose localization lengths are lager than that of the atoms of the chains in weak disorder. Meanwhile, with the increase of the number of the chains, the delocalization can be found. In addition, the transmission coefficient of electron transportion in quasi-one-dimensional disordered system is much higher in the energy band center than that in high and low energy region, and decreases with the increase of the energy disorder degree of the lattices, but increases with the increase of the number of the chains.
Key words: quasi-one-dimensional disordered systems; electronic localization; electronic transportation
近年来,随着纳米科技和分子电子学的发展,碳纳米管、纳米线及DNA分子导线等一维、准一维体系由于具有独特的电学性能而具有广阔的应用前景,如可用作纳米电子器件的导线、构筑特殊的纳电子元件(如场效应管、电子开关)及生物分子器件等,同时,由于在碳纳米管、纳米线及DNA分子导线等低维体系电子材料和器件的生产、制备过程中不可避免地会存在杂质态、缺陷等无序因素,而无序的引入会导致体系的电子波函数呈现局域化特性[1],从而对其电子输运特性产生影响;因此,对于一维、准一维等低维无序体系电子输运性质的研究已成为国内外研究的热点[2-6]。对于一维单链无序体系,其电子波函数是局域化的,电子只能通过热激发,在不同局域态之间跳跃输运,而对于准一维无序体系,在弱无序情况下,在能带中心出现退局域化现象[7-8];同时,由于现实的碳纳米管、纳米线及DNA分子导线等都有一定的宽度,准一维无序模型更能反映其真实特征。因此,很多研究者注重于准一维无序体系电学特性的研究。如Hjort等[9]利用传输矩阵方法研究了准一维聚乙烯、聚乙炔等无序体系的电子波函数局域化现象;徐慧 等[10-12]利用五对角随机厄米矩阵的求解方法,实现了对准一维无序体系的态密度及本征矢的数值计算;Gallos等[13]利用蒙特卡罗方法计算了准一维无序体系电子的平均迁移率对温度的依赖性;Ivanov等[14]计算研究了准一维无序体系中具有很小能量差的幺正对称态的局域态密度关联函数。然而,人们对于准一维体系中电子波函数的局域化特性的研究,特别是维度效应对准一维无序体系电子波函数局域化及电子输运的影响的研究很少。在此,本文作者通过构建准一维多链无序模型,在单电子紧束缚近似下,研究准一维多链无序体系中电子波函数局域化特性及其电子输运特性。
1 模型与方法
对1个有k条平行链的准一维无序系统(见图1),考虑到虽然次近邻格点间的相互作用对体系电子结构会产生附加的影响,但其影响相对最近邻格点间的相互作用来说小近1个数量级[15],因此,为了使问题简化,只计及最近邻格点间跳跃积分,即对第i个格点仅考虑它与i-k,i-1,i+1和i+k格点间的相互作用时,体系的哈密顿量可表示为[16]:
![]() (1)
(1)
其中:N为体系的格点总数;Z为格点i最近邻格点的数目;εi为第i格点的位能;tij为描述电子在i与j格点之间转移的跃迁矩阵元。本研究只考虑对角无序,即εi取一组均匀分布在区间[-W/2, W/2]的随机数,其中,W代表体系的格点能量无序度,非对角项tij取常数tij= -1。

图1 准一维多平行链无序模型
Fig.1 Model of quasi-one-dimensional disordered system
显然,上述准一维多链无序体系的哈密顿量可表示为一多对角的对称矩阵,即:
 (2)
(2)
利用多对角全随机厄米矩阵算法结合负本征值理论[17-18]和无限阶微扰理论[19]很容易求解其能量本征值及本征矢。对于每一能量本征值,其对应的本征矢扩展范围![]() 可表述示为:
可表述示为:
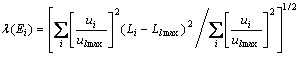 (3)
(3)
其中:![]() 为本征矢分量最大值;
为本征矢分量最大值;![]() 和
和![]() 分别为各本征矢分量和分量最大值对应的格点。若电子波函数是局域化的,其扩展范围通常称为波函数的局域长度;因此,对应于能量本征值Ei电子波函数局域长度,可以通过数值计算得出。
分别为各本征矢分量和分量最大值对应的格点。若电子波函数是局域化的,其扩展范围通常称为波函数的局域长度;因此,对应于能量本征值Ei电子波函数局域长度,可以通过数值计算得出。
同时,将体系重新编号。假定每条链所含原子个数都为l,且![]() ,则沿链方向和垂直于链的方向建立坐标后,体系中每个格点原子的坐标可记为(m, n),其中,1≤m≤k,1≤n≤l。体系的电子波函数表示为格点轨道波函数的线性组合
,则沿链方向和垂直于链的方向建立坐标后,体系中每个格点原子的坐标可记为(m, n),其中,1≤m≤k,1≤n≤l。体系的电子波函数表示为格点轨道波函数的线性组合![]() ,体系的哈密顿量作用在波函数
,体系的哈密顿量作用在波函数![]() 上则可以将薛定谔方程
上则可以将薛定谔方程![]() 表示为:
表示为:
![]() (4)
(4)
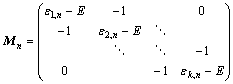 (5)
(5)
其中:![]() ;Ik和0k分别为
;Ik和0k分别为![]() 单位矩阵和零矩阵;Mn亦为k×k矩阵。
单位矩阵和零矩阵;Mn亦为k×k矩阵。
因此,在整个体系两端波函数的幅值可以表示为:
![]() (6)
(6)
![]() (7)
(7)
其中:T(E)为整个体系的总的透射系数[20-21];Tm,n为进入第m条链的电子从第n条链透射出来的概率。
2 计算结果与分析
对于无序体系,当格点数达2×103时,其电子结构已趋向稳定,其电子波函数局域化特性及其局域态分布都具有很好的稳定性[22],因此,选择包含3×103个格点的准一维多链,计算其电子波函数局域化特性及其输运特性。
2.1 电子波函数局域态
在准一维无序体系中,由于无序的存在,其电子波函数同样呈现出局域化特性。计算了格点数量N= 3 000,且格点能量无序度W=1.0的准一维三链无序体系电子波函数,如图2所示。从图2可见:对于本征能量为Ei= -0.993 39 eV的电子态,其电子波函数被局限在一个有限的范围内,在其局域中心位置(格点857处)的电子波函数的分量最大,但随着离局域中心位置距离的增大而迅速减小;因此,电子波函数分量的衰减快慢反映了其电子波函数的局域化程度,可以通过局域长度来描述。
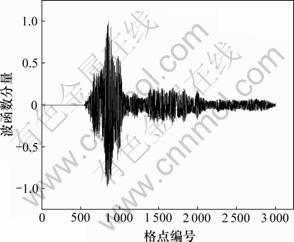
图2 准一维多平行链电子波函数的局域化
Fig.2 Electronic localization of quasi-one-dimensional disordered system
2.2 电子波函数局域长度
准一维多平行链无序体系电子局域长度与能量的关系如图3所示。
由图3(a)可知:当格点原子数及链数确定时,随着格点能量无序度的减小,在能区中间电子波函数的局域化程度减弱,局域长度增大;当W<2.0时,在能区中央开始出现电子波函数局域长度大于链长现象(对格点总数为N=3 000,链数为k=3体系,每条链所含原子个数为1 000),即出现了扩展态,并且随着格点能量无序度的进一步减小,电子波函数扩展长度进一步扩大,出现扩展态的能量区间也呈增大的趋势。由图3(b)可知:在格点原子数及格点能量无序度一定时,当链数较小时(如图中k<3的情况),在整个能量范围内电子波函数的局域长度均小于系统的格点数,电子波函数局域化程度比较强。而对于k=5的多链无序体系,在中间一定的能量区间内,存在着局域长度大于链长的扩展态。可见,随着链数的增加,体系有向退局域化方向发展的趋势。这是因为:在多链体系中,相邻格点原子之间的交叠积分的数目增加,扩大了格点间短程关联相互作用,而关联的引入会导致体系出现退局域化现象[7-8]。虽然存在无序,体系电子波函数具有局域化的倾向,但当无序度一定时,随着关联引入,中间能区可以出现扩展态,体现了维度效应的影响。

图3 准一维无序体系的局域长度随能量的变化
Fig.3 Relationship between localization length and energy of quasi-one-dimensional system
2.3 准一维多链无序体系的电子输运特性
准一维多平行链无序体系透射系数与能量的关系如图4所示。
由图4可知,准一维多链无序体系的透射系数总体上都呈现出在中间能区透射系数较大,而在低能区及高能区透射系数较小的特性。这是因为在准一维多链无序体系的中间能区电子波函数局域化程度弱,电子波函数扩展范围大,所以,电子输运的透射系数也大。同时,由图4(a)可知:当体系格点数及链数一定时,准一维多链无序体系的透射系数随着格点能量无序度的增大而减小。正是由于存在无序,体系电子波函数呈现局域化的特性,无序度越大,电子波函数局域化程度越大;因此,随着体系格点能量无序度的增大,体系电子输运的透射系数减小。而由图4(b)可知:当体系格点数及格点能量无序度一定时,准一维多链无序体系的透射系数随着体系链数的增大而增大,同样体现了维度效应的影响。一方面,随着体系链数的增加,体系电子波函数发生退局域化现象,其局域化程度降低,扩展范围增大;另一方面,随着体系链数的增加,体系电子输运的通道增加,同时,在格点数一定的情况下,链数越多,每条链上的格点原子数目越小,电子透射的距离越短,所以,体系电子输运透射系数随着链数的增大而增大。可见,在准一维无序体系,格点能量无序与维度效应对体系的电子输运存在竞争特性。
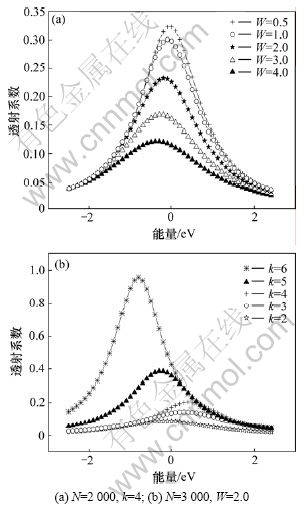
图4 准一维无序体系的透射系数随能量的变化
Fig.4 Relationship between transmission coefficient and energy of quasi-one-dimensional system
3 结论
(1) 准一维多链无序体系中由于格点能量无序的存在,其电子波函数同样呈现出局域化特性。
(2) 当体系格点数及链数确定时,格点能量无序度的减小会导致在中间能区发生退局域化现象,表现为在中间能区电子波函数的局域长度大于体系格点数,即出现扩展态,且出现扩展态的能量区间随着无序度的减小而呈增大的趋势;同时,随着链数的增加,体系有向退局域化方向发展的趋势。
(3) 准一维多链无序体系的透射系数在中间能区较大,而在低能区及高能区透射系数较小;同时,格点能量无序与维度效应对体系的电子输运存在竞争效应,当体系格点数及链数一定时,准一维多链无序体系的透射系数随着格点能量无序度的增大而减小,当体系格点数及格点能量无序度一定时,准一维多链无序体系的透射系数随着体系链数的增大而增大。
参考文献:
[1] Anderson P W. Absence of diffusion in certain Random lattices[J]. Phys Rev, 1958, 109(5): 1492-1505.
[2] Rodin A S, Fogler M M. Numerical studies of variable-range hopping in one-dimensional systems[J]. Phys Rev B, 2009, 80(15): 155435-12.
[3] Maul R, Wenzel W. Influence of structural disorder and large-scale geometric fluctuations on the coherent transport of metallic junctions and molecular wires[J]. Phys Rev B, 2009, 80(4): 045424-11.
[4] HU Dong-sheng, LU Xiu-juan, ZHANG Yong-mei, et al. Transport properties of a random binary side-coupled chain[J]. Chin Phys B, 2009, 18(6): 2498-2501.
[5] Bascones E, Estévez V, Trinidad J A, et al. Electronic correlations and disorder in transport through one-dimensional nanoparticle arrays[J]. Phys Rev B, 2008, 77(24): 245422-24.
[6] Ben-Naim E, Krapivsky P L. Strong mobility in weakly disordered systems[J]. Phys Rev Lett, 2009, 102(19): 190602-4.
[7] Brower P W, Mudry C, Simons B D, et al. Delocalization in coupled one-dimensional chains[J]. Phys Rev Lett, 1998, 81(4): 862-865.
[8] Sedrakyan T, Alexander O. Localization-delocalization transition in the quasi-one-dimensional ladder chain with correlated disorder[J]. Phys Rev B, 2004, 70(21): 214206-9.
[9] Hjort M, Stafstrom S. Localization in quasi-one-dimensional systems[J]. Phys Rev B, 2000, 62: 5245-5250.
[10] 徐慧. 准一维无序系统的电子结构[J]. 计算物理, 1997, 14(4): 574-576.
XU Hui. Electronic structure of quasi-one-dimensional disordered systems[J]. Chin J Comp Phys, 1997, 14(4): 574-576.
[11] 宋招权, 徐慧, 李燕峰, 等. 非对角无序和维数效应对低维无序系统电子结构的影响[J]. 物理学报, 2005, 54(5): 2198-2201.
SONG Zhao-quan, XU Hui, LI Yan-feng, et al. The effects of non-diagonal disorder and dimensions in low-dimensional disordered electronic system[J]. Acta Phys Sin, 2005, 54(5): 2198-2201.
[12] 刘小良, 徐慧, 马松山, 等. 准二维无序系统的电子结构[J]. 物理学报, 2006, 55(5): 2492-2497.
LIU Xiao-liang, XU Hui, MA Song-shan, et al. The electronic structure of quasi-two-dimensional disordered systems[J]. Acta Phys Sin, 2006, 55(5): 2492-2497.
[13] Gallos L K, Movaghar B, Siebbeles L D A. Temperature dependence of the charge carrier mobility in gated quasi-one- dimensional systems[J]. Phys Rev B, 2003, 67(16): 165417-8.
[14] Ivanov D A, Ostrovsky P M, Skvortsov M A. Correlations of the local density of states in quasi-one-dimensional wires[J]. Phys Rev B, 2009, 79(20): 205108-15.
[15] Kiwi M, Ramirez R, Trias A. Effects of overlap and next- nearest-neighbor interactions in tight-binding calculations[J]. Phys Rev B, 1978, 17(8): 3063-3069.
[16] Carpena P, Bemaola-Galvan P, Ivanov P C, et al. Metal-insulator transition in chains with correlated disorder[J]. Nature, 2002, 418: 955-959.
[17] Dean P. Vibrational spectra of diatomic chains[J]. Proc Roy Soc, 1960, 254: 507-521.
[18] Dean P. The vibrational properties of disordered systems: Numerical studies[J] Rev Mod Phys, 1972, 44(2): 127-168.
[19] WU Shi-yu, ZHENG Zhao-bo. Amplitude analysis of localization in one-dimensional disordered systems. Vibrational states of an isotopically disordered binary chain[J]. Phys Rev B, 1981, 24(8): 4787-4795.
[20] Buttiker M, Imry Y, Landauer R, et al. Generlized many channel conductance formula with application to small rings[J]. Phys Rev B, 1985, 31(10): 6207-6215.
[21] GUO Ai-min, XIONG Shi-jie. Effects of contact and efficient charge transport in G4-DNA molecules[J]. Phys Rev B, 2009, 80(3): 035115-5.
[22] 徐慧, 曾红涛. 无序系统中电子局域态分布[J]. 物理学报, 1992, 41(10): 1666-1671.
XU Hui, ZENG Hong-tao. Distribution of electronic localization in the disordered system[J]. Acta Phys. Sin., 1992, 41(10): 1666-1671.
收稿日期:2009-09-16;修回日期:2010-12-27
基金项目:高等学校博士点专项科研基金资助项目(20070533075);湖南省科技计划项目(2009FJ3004)
通信作者:徐慧(1958-),男,湖南常德人,博士,教授,从事材料性能计算模拟研究;电话:13907488179;E-mail: xuhui@mail.csu.edu.cn


