DOI:10.19476/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2018.12.13
特殊环境用无铅钎料可靠性研究进展
王剑豪1,薛松柏1,马超力1,龙伟民2,钟素娟2
(1. 南京航空航天大学 材料科学与技术学院,南京 211106;
2. 郑州机械研究所新型钎焊材料与技术国家重点实验室,郑州450002)
摘 要:
随着无铅钎料性能的提升和人们环保意识的提高,无铅钎料也逐渐被应用在特殊环境中。介绍特殊环境用无铅钎料可靠性的研究进展及趋势,分析特殊环境中无铅钎料焊点失效的原因,探讨各种特殊环境中提高无铅钎料可靠性的方法和机理,如微合金化、颗粒强化和基板改善,总结目前无铅钎料可靠性研究存在的不足,对无铅钎料未来的研究方向提出建议。
关键词:
文章编号:1004-0609(2018)-12-2499-13 中图分类号:TG425 文献标志码:A
21世纪以来信息技术的快速发展,不仅推动了电子产业的转型和升级,更对电子封装材料提出了更为严苛的要求[1]。随着各国禁铅法令的相继出台,开发性能优异的无铅钎料以替代含铅钎料成为热点。目前行业较为认可的主要有SnCu系[2]、SnAg系[3]、SnAgCu系[4]等无铅钎料。但是它们都存在着润湿性不足,熔点过高以及可靠性差等问题,难以满足生产的需要。
近年来,针对无铅钎料的研究不断深入,在改善钎料润湿性[5],降低熔点[6]等方面都取得了丰富的成果,使得无铅钎料也开始被应用在某些特殊环境中。随着无铅化的发展和人们环保意识的提高,无铅化也成为了特殊环境用电子材料的发展趋势。但是在某些特殊环境中,无铅钎料不仅要经受热场、电场和磁场等的耦合作用[7],还可能处于一些如极低温、腐蚀等环境中,大大降低焊点的可靠性。因此,研究特殊环境下无铅钎料组织性能变化的机理及可靠性改善措施势在必行。目前提升焊点可靠性的措施主要有3种:1) 微合金化,即向无铅钎料中添加微量合金元素来改善焊点性能[8];2) 添加纳米颗粒,通过颗粒强化增强可靠性[9];3) 改善基板,通过表面镀层等提高可靠 性[10]。目前特殊环境用无铅钎料可靠性的研究还比较少,本文作者通过介绍各种特殊环境对焊点的影响机理,对改善焊点可靠性取得的最新进展做出全面的总结,力图为未来特殊环境用无铅钎料可靠性的研究提供一些建议和指导。
1 高温时效
1.1 影响机理
随着电子元件功率的提高,焊点的服役温度不断上升[11]。焊点界面金属间化合物层Cu6Sn5的生长驱动力满足:
 (1)
(1)
式中:R为摩尔气体常数;T为绝对温度;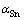 为Sn的活度。
为Sn的活度。
温度上升,焊点内部金属原子扩散加剧,Cu6Sn5生长驱动力增加。如图1所示,高温促进了界面金属间化合物(IMC)层粗化[12],也会形成明显的孔洞[13]。同时界面处Cu含量上升,界面处发生如下反应:Cu6Sn5+9Cu=5Cu3Sn。
经过一段时间的时效界面IMC层出现双层结构,Cu6Sn5与Cu3Sn相互竞争长大不仅导致界面层变厚,同时上述两种金属间化合物热膨胀系数(CTE)的不同使得时效过程中界面处极易形成应力集中,从而成为裂纹高发区[14]。
1.2 改善措施
1.2.1 微合金化
已有研究表明[15],在相同的时效条件下,添加0.025%Sm(质量分数)可以显著提高SnAgBi钎料焊点的可靠性。Nd能在SnAgCu钎料中形成弥散分布的NdSn3强化相,提高了焊点的力学性能[16]。但稀土元素含量不宜过多,否则钎料中粗大的稀土相组织会恶化钎料的力学性能[17]。Ce对SnAgCu钎料也有类似的作用[18]。
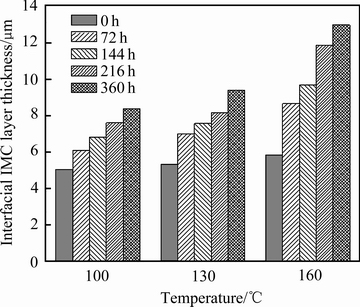
图1 时效过程SnAgCu305/Cu焊点界面层厚度变化
Fig. 1 Interfacial IMC layer thickness of SnAgCu305/Cu joint during isothermal aging
加入适量的Mn元素能够抑制焊点界面层的生长,即使经过长时间时效,SnAgCu-0.15%Mn的界面层厚度仍小于SnAgCu的[19],如图2所示。但是Mn含量超过0.2%时,由于Mn对Cu6Sn5的“诱导作用”[20],IMC层再次粗化。Bi元素的加入能够提高钎料的抗热疲劳性能[21],而复合添加Fe与Bi更能够使SnAgCu105钎料组织在时效过程中始终保持稳定均匀,如图3所示[22]。

图2 Sn-0.3Ag-0.7Cu-xMn焊点界面IMC层厚度与时效时间平方根t1/2的关系
Fig. 2 Relationship between interfacial IMC layer thickness of Sn-0.3Ag-0.7Cu-xMn/Cu joint and square root of isothermal aging time t1/2

图3 SnAgCu-Fe-xBi的FESEM像
Fig. 3 FESEM images of as-cast samples
1.2.2 纳米颗粒添加
已有研究表明[23],纳米颗粒的添加可以显著改善钎料性能。纳米Sb颗粒可以有效细化SnAgCu焊点组织[24]。根据吸附理论[25],界面Cu6Sn5的表面自由能可以表示为
 (2)
(2)
式中:Ak为Cu6Sn5颗粒k的表面积; 是Cu6Sn5颗粒k吸附纳米Sb后的表面张力;
是Cu6Sn5颗粒k吸附纳米Sb后的表面张力;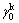 为Cu6Sn5颗粒k尚未吸附纳米Sb的表面张力;c为纳米锑颗粒的浓度;
为Cu6Sn5颗粒k尚未吸附纳米Sb的表面张力;c为纳米锑颗粒的浓度; 为Cu6Sn5颗粒k吸附纳米Sb的数量;R为气体常数;T为热力学温度。Cu6Sn5吸附适量纳米Sb后表面自由能降低,IMC生长受到抑制。
为Cu6Sn5颗粒k吸附纳米Sb的数量;R为气体常数;T为热力学温度。Cu6Sn5吸附适量纳米Sb后表面自由能降低,IMC生长受到抑制。
纳米Ag3Sn能够吸附在Sn-0.7Cu钎料界面处,细化焊点组织。在元素含量相同的情况下,Sn- 0.7Cu(Ag3Sn)的界面层厚度远低于SnAgCu钎料[26]。SnAgCu-xTiO2/Cu界面层厚度与时效时间的关系可以表示为[27]:
SnAgCu/Cu: 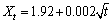 (3)
(3)
SnAgCu-TiO2/Cu: 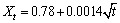 (4)
(4)
即时效过程中SnAgCu-TiO2复合钎料的平均扩散系数为0.0374 μm2/s,低于SnAgCu的0.0447 μm2/s,说明纳米TiO2可以阻碍元素扩散,抑制IMC的形成。但是TiO2含量不宜过高,否则会“团聚”而导致组织粗化[28],如图4所示。

图4 TiO2颗粒含量对SnAgCu钎料的树枝晶尺寸的影响
Fig. 4 Effect of TiO2 content on dendrite-arm spacing of SnAgCu solders
石墨烯纳米片(Graphenenanosheets,简称GNSs)具备超强的力学、热学和电学性能[29],是现在最为热门的新型材料。GNSs具有二维纳米结构和极大的比表面积,添加进钎料后不仅能够改善钎料的润湿性能和力学性能[30],而且对钎料内部原子的扩散起到强烈的阻碍作用[31],显著抑制钎焊及时效过程中界面层的生长,从而提高焊点的可靠性。
1.2.3 基板改善
除了上述方法,在基板侧制备扩散阻挡层也可以提高时效条件下焊点的可靠性[32]。传统基板的镀层主要有Ni[33]、Au/Ni(ENIG)[34]、Au/Pd/Ni(ENEPIG)[35]等。Ni镀层能够有效阻碍界面间原子的互扩散,细化IMC层,提高焊点的性能[36]。在Ni表面喷Au,不仅可以防止Ni氧化,还有利于熔融钎料的润湿铺展[34]。在Ni/Au层间镀Pd能够抑制Ni对Au的置换作用,在提高了焊点可靠性的同时也满足了引脚间距减小的需求,因而具有比ENIG更为广阔的应用前景。
向铜基板中添加8%Zn或微量稀土元素Er能够有效细化焊点界面,保证焊点的可靠性[37-38]。轧制基板内部存在应力时,Cu原子倾向于从基板扩散至钎料中以降低晶格压力。钎焊前对基板进行退火处理能够有效消除基板的内应力和组织缺陷[39],减缓了Cu的扩散,从而抑制IMC过度生长[40]。
2 热循环
2.1 影响机理
电子产品服役过程中周期性的电流通断所引发的温度变化,会导致内部的焊点经受热循环作用。随着热循环周次的增加,焊点的强度也逐渐降低[41],界面Cu6Sn5由扇贝状逐渐粗化转变为层状,并有Cu3Sn层产生[42]。同时由于两者热膨胀系数不完全相同,热循环会导致焊点内应力升高,极易萌生微裂纹并沿Cu6Sn5与Cu3Sn界面处扩展[43],严重威胁焊点可靠性。
不仅如此,热循环也会导致含稀土的无铅钎料焊点出现“锡须”[44],如图5所示。目前“锡须”发生的机制尚不明确,不过很多学者认为是组织内应力诱发了“锡须”的产生[45]。在接触空气时钎料内部的稀土相RESn3容易发生如下的氧化反应:4RESn3+3O2=2RE2O3+12Sn。
形成稀土氧化物RE2O3,体积膨胀所产生的压应力促使反应产生Sn晶粒被“挤出表面”形成晶须[46]。在引脚间距减小的趋势下,锡须极有可能导致短路,从而大大降低产品寿命[47]。

图5 2000次热循环后焊点界面锡须花样
Fig. 5 Cross-section of plating around a whisker after 2000 thermal cycles
2.2 改善措施
2.2.1 微合金化
作为稀土元素,Ce和Pr由于“亲Sn性”会优先与Sn结合,减缓热循环过程中IMC层的生长[48-49],从而提高了焊点的可靠性。但是它们所引起的“锡须”问题仍然没有解决。目前防止“锡须”的办法主要有:1) 设置中间隔离层;2) 钎料合金化;3) 有机保护涂层。随着电子器件日趋微型化,充分了解“锡须”产生的机理,找到有效的抑制方法,制备更具可靠性的无铅钎料势在必行。
在SnAgCu钎料中,微量Al会与Cu形成Cu-Al硬质相,通过第二相强化的方式显著提高焊点强度,避免两侧材料的CTE失配而诱发裂纹,提高了焊点的可靠性[50],但是Al也会导致SnAgCu钎料抗腐蚀性能降低,因此,添加量限制在0.5%为宜[51]。
2.2.2 纳米颗粒添加
添加Al纳米颗粒可以显著提高无铅钎料焊点的可靠性[52]。纳米Al吸附在晶粒界面,不仅改善了焊点力学性能,而且降低了Cu的扩散系数,延缓了热循环过程中界面层的增厚,抑制了裂纹的萌生[53]。Al2O3纳米颗粒由于具有比TiO2更高的活性和表面能,对焊点可靠性的改善效果也更为明显[54]。纳米Fe2O3可以显著改善SnAgCu钎料的润湿性[55],同时降低了钎料与基板的CTE差值[56],提高了热循环条件下焊点的可靠性。
有机-无机笼型硅氧烷齐聚物(Polyhedral Oligomeric Silsesquioxane,简称POSS)以其特殊的结构成为广受关注的新型材料[57],如图6所示。作为增强相引入钎料,其活性官能团能够与基体形成可靠的键合,而其惰性核心又能够在复合材料服役时保持稳定,能够有效地提高钎料性能[58]。POSS颗粒会聚集在焊点金属间化合物晶界,阻碍原子沿晶扩散,从而细化了脆性界面层,提高了钎料的抗热循环性能[59]。同时,POSS颗粒也能降低热循环过程中焊点的内应力,抑制“锡须”的产生[60],如图7所示。
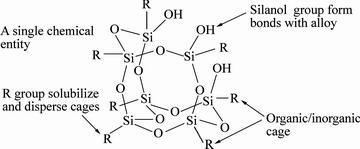
图6 POSS分子结构示意图
Fig. 6 Anatomy of POSS molecule
3 低温环境
对于民用电子产品来说,内部焊点的服役环境最低仅能达到-30 ℃,但是对在深空的低温环境运行的航天器来说,其服役温度可以达到-229 ℃(冥王星平均温度)甚至更低,因此这对空间设备内部元件的焊点在低温特殊环境下的可靠性提出了非常严苛的要求。
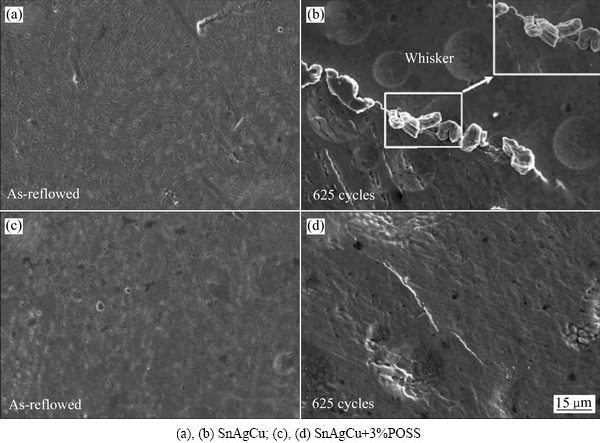
图7 热循环后钎料表面显微组织变化
Fig. 7 Surface microstructures evolution in specimens after cycles
3.1 影响机理
已有的研究表明[61],Sn在温度降至-13 ℃时会发生同素异构转变——灰锡转变,由四方晶系的β-Sn变成立方晶系的α-Sn,引起体积膨胀以及韧脆转变,使得钎料焊点力学性能下降[62-63],极易诱发断裂。将SnAgCu305/Cu焊点置于-196 ℃的极低温中存储25 d后,焊点内部出现了许多微裂纹,如图8所示[64],严重威胁焊点的可靠性。大多数航天器都采用主动热控来保证系统的安全可靠,但是这种方式大大增加了航天器的运行成本,限制了人类探索太空的步伐,因此,开发出具有良好耐低温性能的钎料是非常现实的需求。
3.2 改善措施
In基钎料以其优异的低温性能具有良好的应用前景[65]。目前,已经有一些针对低温环境的In基钎料投入使用[66],但铟基钎料不仅成本过高,而且其低熔点无法适应太空的大温变环境,具有很大的使用局限性。Sb能够抑制SnCuNi钎料发生灰锡转变,避免组织应力的产生[67]。目前,关于改善极低温下无铅钎料可靠性的研究还比较少,需要研究人员加以关注。
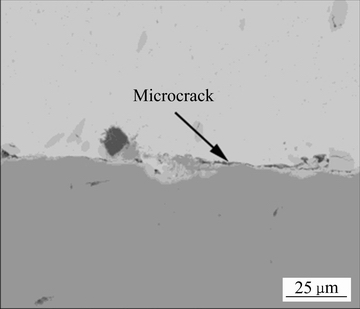
图8 -196 ℃存储后SnAgCu305/Cu焊点的微观组织
Fig. 8 Microstructure of SnAgCu305/Cu after storage at -196 ℃
4 电迁移
4.1 影响机理
由于电子器件的微小型化和功率的大幅提高,焊点所承受的电载荷也急剧增大,这对焊点是一个严峻的考验。高电流密度使金属原子能量上升到足够克服能垒,移动到相邻的空位上[68]。金属原子在电流作用下经过多次移动最终从一端迁移到另一端,这种现象被称为电迁移。当电流密度达到一定值时,在“电子风力”的作用下,单位时间迁移到焊点阳极的Cu原子激增,造成阳极界面层粗化,而阴极的空位由于无法得到原子补充而形成孔洞[69],在应力的作用下极易诱发裂纹[70],如图9所示。在电场与热场耦合的情况下,焊点失效速度会急剧增加[71]。Sn-9Zn焊点置于(150 ℃,5×103A/cm2)的条件下100 h即可导致阳极侧焊点Cu5Zn8层厚度大幅增加[72]。SAC305焊点经过热时效和5×103A/cm2的电迁移后,作为阴极的Cu焊盘逐渐溶解,空洞长大形成裂纹沿着界面层扩展,最终导致焊点失效[73]。电迁移效应严重阻碍了电子产品的更新换代,亟待解决。
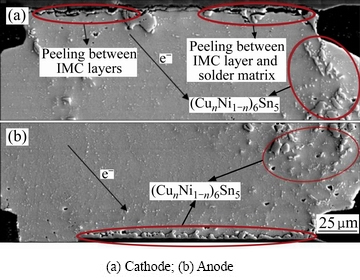
图9 经过电迁移后的SnAgCu305钎料焊点微观组织
Fig. 9 Microstructure of SnAgCu305 after electromigration
4.2 改善措施
4.2.1 微合金化
稀土元素Ce能够细化钎料组织,从而在焊点内部形成众多的大角晶界,抑制了电载荷作用下Cu和Sn的迁移,从而延缓了孔洞和裂纹的产生[74]。已有研究表明[75],Sn基无铅钎料中Sn晶粒的取向能够显著影响焊点的抗电迁移性能,具有c取向的Sn晶粒具有更强的电迁移抗力。Co在Sn中的扩散系数比较大,在Sn晶粒表面聚集从而对Cu的扩散形成阻碍,同时细化焊点组织,增加c取向的Sn晶粒,提高焊点电迁移寿命[76]。
4.2.2 纳米颗粒添加
POSS颗粒可以与基体金属形成良好的结合[77],阻碍了焊点内部物质的移动,使电迁移现象受到明显的抑制[78]。碳纳米管(Carbon nanotube,简称CNT)是由卷曲的石墨烯组成的中空圆柱结构,以其高强度,低密度以及导电性能优异等特点,被视为理想的钎料增强材料[79]。CNT可以细化Sn-58Bi钎料组织[80],并与钎料基体元素良好键合,在焊点受力学载荷时优先从键合界面滑出[81],避免裂纹尖端应力集中而扩展。由于CNT导电性能良好,能在焊点中形成高导电性通道,在承受电载荷的情况下电子会优先从CNT网络通过从而抑制“电子风力”对基体的影响[82]。不过CNT制备困难,极易发生团聚,掺杂CNT的复合钎料成本较高,暂时难以实际应用。
目前,针对无铅钎料焊点电迁移的研究还比较少,随着电子元器件功能度的提升,焊点所承受的电载荷将进一步提高,因此完善电迁移机理的基础理论研究,进而开发出抗电迁移性能优异的无铅钎料还需要研究人员的努力。
5 腐蚀环境
5.1 影响机理
焊点服役环境日趋复杂,在多场协同作用下,钎料对腐蚀介质也十分敏感。焊点受腐蚀会出现如图10所示的孔洞,甚至出现材料大量溶解的现象,如图11所示[83]。目前多采用电化学腐蚀的方法来评价钎料抗腐蚀性能[84]。作为常见的腐蚀介质,海水中的Cl-离子吸附在焊点缺陷处与焊点内部的阳离子反应产生可溶性氯化物,从而形成点蚀,在应力的作用下其进一步扩展将导致焊点发生穿孔断裂[85]。

图10 焊点腐蚀孔洞
Fig. 10 Cavity of solder joints after corrosion
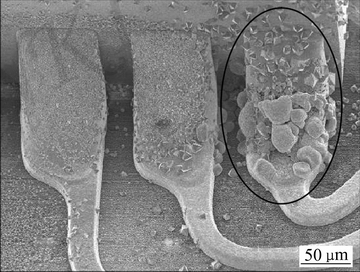
图11 焊点腐蚀溶解
Fig. 11 Diffluence of solder joints after corrosion
5.2 改善措施
Sn-Zn钎料耐蚀性能较差,但是向其中添加Y元素能够细化组织内部易氧化的富Zn相,降低了腐蚀原电池形成的概率,从而增大了Sn-9Zn的腐蚀电位值,提高了钎料的耐蚀性能,如图12所示[86]。Cu也能在一定程度上细化富Zn相[87],提高Sn-Zn耐蚀性能[88]。但是已有的研究表明[89],添加Cr与Ni的效果要优于添加Cu的。

图12 合金在3.5%NaCl溶液中腐蚀极化曲线
Fig. 12 Polarization curves of alloys in NaCl 3.5% solution
In能够在Sn-9Zn钎料表面形成钝化层以抑制腐蚀向组织内部进行[90]。由于具有较强的“亲氧集肤效应”[91],Ge会在钎料表面形成隔离层,阻碍Sn2+的扩散,进一步延缓了焊点氧化。但是Ge含量过多又会增加组织中脆性相聚集的风险。由于Ni可以细化组织,降低钎料的脆性,也可以通过复合添加Ge和Ni来改善钎料的耐腐蚀性能[92]。
6 跌落
电子产品在使用中都存在跌落的可能,其经受的力学冲击极易导致内部焊点断裂失效[93]。已有的研究表明[94],在经受跌落冲击时,无铅钎料焊点的可靠性弱于锡铅钎料。因此,了解跌落时焊点的失效机理及改善措施,进而开发出具有优异抗冲击性能的无铅钎料尤为重要。
6.1 影响机理
在跌落冲击时,芯片和PCB板由于弹性模量差异而发生不同程度的变形,使焊点承受较大的拘束应力,其内部的缺陷易产生应力集中而成为裂纹源[95],且裂纹最容易在较脆的IMC层中扩展[96]。WLCSP器件焊点在(1500 g,0.5 ms)的条件下跌落150次后,裂纹开始萌生。随着跌落次数的增加,裂纹长度以线性增长[97]。跌落时芯片与PCB板在芯片边角处产生的错配度最大,因而成为裂纹高发区。
6.2 改善措施
为了满足产品的服役要求,研究人员已经提出了一些改善焊点抗冲击性能的措施,比如向钎料中加入SiC纳米颗粒[98],降低SnAgCu钎料中的Ag含量[99]等,但是这些措施还不能满足要求。在无铅化的大背景下,急需适应现有生产模式的、抗冲击性能良好的无铅钎料。
7 辐照
除了极低温、大温变环境外,空间辐射也是航天器在轨运行所面临的另一个非常严峻的挑战。空间辐照会致材料内部产生大量缺陷,引起辐照脆化[100]。航天器在变轨、降落过程中会承受非常很大的振动载荷,这些缺陷极易形成裂纹,引发断裂失效。空间复杂的粒子辐射会导致电子元器件和材料性能衰退或者漂 移[101],严重威胁航天器的安全运行[102]。目前,多采用“抗辐射加固”对电子线路整体进行保护[103-104],但抗辐射加固装置具有一定的体积和质量,大大增加了航天器的发射及运行成本。在航天器“体积减小”和“有效载荷比提高”的大趋势下,对电子线路整体进行抗辐射加固已经越来越难以满足需求,急需从改善材料自身抗辐射性能的角度入手,提高航天器整体在辐照环境下的可靠性。目前,国内外关于辐照环境对钎料焊点影响机理的研究鲜有报道,在我国大力发展空间研究的大背景下,开展辐射环境对电子器件焊点可靠性的影响研究十分必要。
8 总结与展望
随着电子行业的发展,无铅钎料的应用日趋广泛,近年无铅钎料的研究成果十分丰富。不过关于特殊环境用无铅钎料焊点失效机理的研究还不成熟,而提升焊点可靠性的方法研究也主要局限在文中所提出的3个方面:钎料合金化是主要的研究方向,不过目前添加的多为单一元素,对钎料改性的效果并不理想,同时添加稀土元素所造成的“锡须”问题仍然没有解决;添加纳米颗粒虽然也能起到改善效果,但纳米颗粒极易“团聚”且成本过高,大规模生产应用较为困难;改善基板则是现在较为新颖的研究方向,有可能成为焊点可靠性研究的趋势。
综合来看,特殊环境用无铅钎料可靠性的发展方向主要集中在以下几个方面:1) 从多元化角度设计无铅钎料的成分,考虑复合添加多种元素来共同改善钎料性能;2) 降低纳米颗粒复合钎料制备成本,保证服役过程中纳米颗粒稳定不发生团聚,为纳米颗粒复合钎料的实际应用做好准备;3) 在实际应用中,钎料服役环境往往比较复杂,会同时面临多场的作用,因此针对多场耦合条件下无铅钎料焊点可靠性的研究十分必要;4) 无论是合金化、颗粒添加还是改善基板,单一方法只能在一定程度上起到作用,难以满足生产要求,可以考虑同时采用多种方法来协同作用,使焊点可靠性得到进一步的提高;5) 在国家大力发展航天事业的大环境下,急需具有优异的“抗极低温性能”、“抗大温变性能”和“抗辐射性能”的航天器用高可靠性钎料来满足太空探索的需求,但是现在国内外针对空间环境下焊点演变机理的研究还是一片空白,需要研究人员加以关注。
REFERENCES
[1] LI Yang, GE Jing-guo, ZHANG Yao-cheng, DAI Jun, JING Yan-feng. Effect of BaTiO3 on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Sn1.0Ag0.5Cu lead-free solder[J]. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics, 2015, 26(1): 613-619.
[2] WANG Y W, LIN Y W, KAO C R. Inhibiting the formation of microvoids in Cu3Sn by additions of Cu to solders[J]. Journal of Alloys & Compounds, 2010, 493(1/2): 233-239.
[3] GARCIA L R, OSORIO W R, GARCIA A. The effect of cooling rate on the dendritic spacing and morphology of Ag3Sn intermetallic particles of a SnAg solder alloy[J]. Materials & Design, 2011, 32(5): 3008-3012.
[4] SU Y A, TAN L B, TEE T Y, TAN V B C. Rate-dependent properties of Sn-Ag-Cu based lead free solder joints[J]. Microelectronics Reliability, 2010, 50(4): 564-576.
[5] 轩庆庆, 龙伟民, 张青科, 路全彬. 稀土对Al-Si-Zn-Cu钎料工艺性能的影响[J]. 焊接, 2017(2): 31-36.
XUAN Qing-qing, LONG Wei-min, ZHANG Qing-ke, LU Quan-bin. Effect of rare earth elements on brazing process performance of Al-Si-Zn-Cu filler metal[J]. Welding & Joining, 2017(2): 31-36.
[6] 赵 杰, 钟海峰, 刘 平, 周 飞, 经敬楠. SnIn钎料与Au/Ni/Cu钎焊界面金属间化合物的研究[J]. 焊接, 2016(3): 18-21.
ZHAO Jie, ZHONG Hai-feng, LIU Ping, ZHOU Fei, JING Jing-nan. Intermetallic compounds formed on brazed interface between SnIn solder and Au/Ni/Cu[J]. Welding & Joining, 2016(3): 18-21.
[7] TU K N. Recent advances on electromigration in very-large- scale-integration of interconnects[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2003, 94(9): 5451-5473.
[8] ZHANG Q K, LONG W M, YU X Q, PEI Y Y. Effects of Ga addition on microstructure and properties of Sn-Ag-Cu/Cu solder joints[J]. Journal of Alloys & Compounds, 2015, 622: 973-978.
[9] GAIN A K, CHAN Y C. Growth mechanism of intermetallic compounds and damping properties of Sn-Ag-Cu-1wt% nano- ZrO2composite solders[J]. Microelectronics Reliability, 2014, 54(5): 945-955.
[10] LIU Yang, SUN Feng-lian, LUO Liang-liang, YUAN C A, ZHANG Guo-qi. Microstructure evolution and shear behavior of the solder joints for flip-chip LED on ENIG substrate[J]. Journal of Electronic Materials, 2015, 44(7): 2450-2457.
[11] 赵 宁, 钟 毅, 黄明亮, 马海涛. 微焊点中金属原子的热迁移及其对界面反应影响的研究进展[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2015, 25(8): 2157-2166.
ZHAO Ning, ZHONG Yi, HUANG Ming-liang, MA Hai-tao. Research progress in thermomigration of metal atoms inmicro solder joints and its effect on interfacial reaction[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2015, 25(8): 2157-2166.
[12] 马运柱, 罗辉庭, 李永君, 刘文胜, 黄国基. 等温时效对In-3Ag/Cu焊接界面组织演变特征的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2015, 25(5): 1256-1263.
MA Yun-zhu, LUO Hui-ting, LI Yong-jun, LIU Wen-sheng, HUANG Guo-ji. Effects of isothermal aging on In-3Ag/Cu interface microstructure evolution characteristics[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2015, 25(5): 1256-1263.
[13] ZHAO Guo-ji, SHENG Guang-min, WU Li-li, YUAN Xin-jian. Interfacial characteristics and microstructural evolution of Sn-6.5Zn solder/Cu substrate joints during aging[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2012, 22(8): 1954-1960.
[14] LIU Yang, MEERWIJK J, LUO Liang-liang, ZHANG Hong-lin, SUN Feng-lian, YUAN C A, ZHANG Guo-qi. Formation and evolution of intermetallic layer structures at SAC305/Ag/Cu and SAC0705-Bi-Ni/Ag/Cu solder joint interfaces after reflow and aging[J]. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics, 2014, 25(11): 4954-4959.
[15] 仇爱梅. SnAgBi-xSm钎料组织及性能的研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨理工大学, 2016: 1-48.
CHOU Ai-mei. Study on microstructure and properties of SnAgBi-xSm solder[D]. Harbin: Harbin University of Science and Technology, 2016: 1-48.
[16] 皋利利. 稀土Pr和Nd对SnAgCu无铅钎料组织与性能影响研究[D]. 南京: 南京航空航天大学, 2012: 1-130.
GAO Li-li. Effect of Pr and/or Nd on the Microstructures and Properties of Sn Ag Cu Solder[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2012: 1-130
[17] WANG He, XUE Song-bai, WANG Jian-xin. Study on the microstructure and properties of low-Ag Sn-0.3Ag-0.7Cu-0.5Ga solder alloys bearing Pr[J]. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics, 2017, 28(11): 8246-8254.
[18] YOON J W, NOH B I, JUNG S B. Effect of rare earth metal Ce addition to Sn-Ag solder on interfacial reactions with Cu substrate[J]. Metals and Materials International, 2014, 20(3): 515-519.
[19] 潘英才. 锰掺杂对无铅焊料Sn-0.3Ag-0.7Cu界面反应及力学性能的影响[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2014: 1-55.
PAN Ying-cai. Effects of Mn doping on interfacial reaction and mechanical properties of Sn-0.3Ag-0.7Cu lead-free solder[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2014: 1-55.
[20] 谭 淇. Fe或Mn对SAC0307钎料性能的影响[D]. 哈尔滨:哈尔滨工业大学, 2014: 1-55.
TAN Qi. Effect of iron or manganese on the properties of SAC0307 solder[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2014: 1-55.
[21] 刘 洋, 孙凤莲. Ni和Bi元素对SnAgCu钎焊界面金属化合物生长速率的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2012, 22(2): 460-464.
LIU Yang, SUN Feng-lian. Effect of Ni and Bi addition on growth rate of intermetallic compound of SnAgCu soldering[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2012, 22(2): 460-464.
[22] ALI B, SABRI M F M, SUKIMAN N L, JAUHARI I. Microhardness and shear performance of Fe/Bi-bearing SAC105 solder alloys under high temperature aging[J]. Journal of Materials Science Materials in Electronics, 2016: 1-10.
[23] EL-DALY A A, AL-GANAINY G S, FAWZY A, YOUNIS M J. Structural characterization and creep resistance of nano-silicon carbide reinforced Sn-1.0Ag-0.5Cu lead-free solder alloy[J]. Materials & Design, 2014, 55(6): 837-845.
[24] EL-DALY A A, HAMMAD A E, FAWZY A, NASRALLH D A. Microstructure, mechanical properties, and deformation behavior of Sn-1.0Ag-0.5Cu solder after Ni and Sb additions[J]. Materials & Design, 2013,43: 40-49.
[25] TANG Y, LI G Y, PAN Y C. Influence of TiO2 nanoparticles on IMC growth in Sn-3.0Ag-0.5Cu-xTiO2 solder joints in reflow process[J]. Journal of Alloys & Compounds, 2013, 554(2): 195-203.
[26] 汪 源. 纳米Ag3Sn、Cu6Sn5颗粒对Sn基无铅焊料性能影响研究[D]. 北京: 北京理工大学, 2015: 1-92.
WANG Yuan. Effect of Ag3Sn, Cu6Sn5 nanoparticle on properties of Sn-based lead-free solder[D]. Beijing: Beijing Institute of Technology, 2015: 1-92.
[27] 张 亮, TU K N, 郭永环, 何成文, 张 剑. 时效对SnAgCu/SnAgCu-TiO2焊点界面与性能影响[J]. 焊接学报, 2013, 34(8): 43-46.
ZHANG Liang, TU K N, GUO Yong-huan, HE Cheng-wen, ZHANG Jian. Effect of aging on the interface and properties of SnAgCu/SnAgCu-TiO2 solder joints[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2013, 34(8): 43-46.
[28] 张 亮, 韩继光, 刘凤国, 郭永环, 何成文. 纳米TiO2颗粒对SnAgCu钎料组织与性能的影响[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2013, 42(9): 1897-1900.
ZHANG Liang, HAN Ji-guang, LIU Feng-guo, GUO Yong-huan, HE Cheng-wen. Effect of nano-particles TiO2 on the microstructures and properties of SnAgCu solders[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2013, 42(9): 1897-1900.
[29] MIRACLE D B. Metal matrix composites–From science to technological significance[J]. Composites Science & Technology, 2005, 65(15/16): 2526-2540.
[30] CHEN G, WU F, LIU C, SILBERSCHMIDT V V, CHAN Y C. Microstructures and properties of new Sn-Ag-Cu lead-free solder reinforced with Ni-coated graphene nanosheets[J]. Journal of Alloys & Compounds, 2016, 656: 500-509.
[31] KONG K J, CHOI Y, RYU B H, LEE J O, CHANG H. Investigation of metal/carbon-related materials for fuel cell applications by electronic structure calculations[J]. Materials Science & Engineering C, 2006, 26(5/7): 1207-1210.
[32] HO C E, HSU L H, YANG C H, YEH T C, LEE P T. Effect of Pd(P) thickness on the soldering reaction between Sn-3Ag-0.5Cu alloy and ultrathin-Ni(P)-type Au/Pd(P)/Ni(P)/Cu metallization pad[J]. Thin Solid Films, 2014, 584: 257-264.
[33] KOMIYAMA T, CHONAN Y, ONUKI J, OHTA T. The influence of phosphorus concentration of electroless plated NiP film on interfacial structures in the joints between SnAg solder and NiP alloy film[J]. Materials Transactions, 2002, 43(2): 227-231.
[34] CHEN Fei-jun, YAN Shi, YANG Zhen-guo. Failure analysis on electrolytic Ni/Au surface finish of PCB used for wire bonding and soldering[J]. Soldering & Surface Mount Technology, 2014, 26(4): 180-193.
[35] MA Rui, LI Ming-yu, FANG Lin, ZHU Shao-de, ZHENG Rui-sheng. Effect of the Ni/Pd/Au-Cu pre-plated finish lead frame surface structure treated by various surface roughening methods on packaging properties[J]. Journal of Adhesion Science and Technology, 2016, 30(4): 422-433.
[36] 朱奇农, 罗 乐, 肖 克, 杜黎光. Ni对Sn96.5Ag3.5/Cu之间扩散行为的阻挡作用[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2000, 10(2): 199-202.
ZHU Qi-nong, LUO Le, XIAO Ke, DU Li-guang. Ni as diffusion barriers between eutectic Sn-Ag solder and Cu[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2000, 10(2): 199-202.
[37] YU Xiao, HU Xiao-wu, LI Yu-long, ZHANG Ru-hua. Effect of alloying Cu substrate on microstructure and coarsening behavior of Cu6Sn5 grains of soldered joints[J]. Journal of Materials Science Materials in Electronics, 2015, 26(5): 2782-2794.
[38] 徐 涛, 胡小武, 江雄心. 基板稀土微合金化对Sn3Ag0.5Cu/Cu钎焊界面反应的影响[J]. 电子元件与材料, 2016, 35(2): 65-69.
XU Tao, HU Xiao-wu, JIANG Xiong-xin. Effect of RE microalloying in substrate on interface reaction of Sn3Ag0.5Cu/ Cu solder joint[J]. Electronic Components and Materials, 2016, 35(2): 65-69.
[39] 张尧武, 曾卫东, 史春玲, 康 超, 彭雯雯. 真空去应力退火对TC18钛合金残余应力及组织性能的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2011, 21(11): 2780-2785.
ZHANG Yao-wu, ZENG Wei-dong, SHI Chun-ling, KANG Chao, PENG Wen-wen. Influence of vacuum stress relieving annealing on residual stress and microstructure properties of TC18 titanium alloy[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2011,21(11): 2780-2785.
[40] 余 啸, 李玉龙, 胡小武, 张如华. Cu基板退火处理的Cu/Sn58Bi/Cu钎焊接头界面微结构[J]. 焊接学报, 2015, 36(10): 29-32.
YU Xiao, LI Yu-long, HU Xiao-wu, ZHANG Ru-hua. Study of interfacial microstructure of Cu/Sn58Bi/Cu solder joints with annealed Cu[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2015, 36(10): 29-32.
[41] SHARMA A, JANG Y J, KIM J B, JUNG J P. Thermal cycling, shear and insulating characteristics of epoxy embedded Sn-3.0Ag-0.5Cu (SAC305) solder paste for automotive applications[J]. Journal of Alloys & Compounds, 2017, 704: 795-803.
[42] SHNAWAH D A, SABRI M F M, BADRUDDIN I A. A review on thermal cycling and drop impact reliability of SAC solder joint in portable electronic products[J]. Microelectronics Reliability, 2012, 52(1): 90-99.
[43] XU Lu-hua, PANG J H L, CHE Fang-xin. Impact of thermal cycling on Sn-Ag-Cu solder joints and board-level drop reliability[J]. Journal of Electronic Materials, 2008, 37(6): 880-886.
[44] DUDEK M A, CHAWLA N. Mechanisms for Sn whisker growth in rare earth-containing Pb-free solders[J]. Acta Materialia, 2009, 57(15): 4588-4599.
[45] 石红昌, 冼爱平. 镀层表面锡晶须自发生长现象的研究进展[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2011, 21(5): 1021-1030.
SHI Hong-chang, XIAN Ai-ping. Research development of tin whisker spontaneous growth on plating surface[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2011, 21(5): 1021-1030.
[46] TU K N, CHEN C, WU A T. Stress analysis of spontaneous Sn whisker growth[M]. US: Springer, 2006.
[47] SUGANUMA K, BAATED A, Kim K S, HAMASAKI K, NEMOTO N, NAKAGAWA T, YAMADA T. Sn whisker growth during thermal cycling[J]. Acta Materialia, 2011, 59(19): 7255-7267.
[48] Zhang L, Xue S B, Zeng G, GAO L L, YE H. Interface reaction between SnAgCu/SnAgCuCe solders and Cu substrate subjected to thermal cycling and isothermal aging[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2012, 510(1): 38-45.
[49] WU Jie, XUE Song-bai, WANG Jing-wen, LIU Shuang, HAN Yi-long, WANG Liu-jue. Recent progress of Sn-Ag-Cu lead-free solders bearing alloy elements and nanoparticles in electronic packaging[J]. Journal of Materials Science Materials in Electronics, 2016: 1-35.
[50] 张志鑫. Cu-Al化合物对SnAgCu焊点可靠性的影响[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2014: 1-65.
ZHANG Zhi-xin. Effect of copper-aluminum intermetallics on the reliability of SnAgCu solder joints[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2014: 1-65.
[51] Fayeka M, Fazal M A, Haseeb A S M A. Effect of aluminum addition on the electrochemical corrosion behavior of Sn-3Ag-0.5Cu solder alloy in 3.5wt% NaCl solution[J]. Journal of Materials Science Materials in Electronics, 2016, 27(11): 1-8.
[52] Zhang Liang, Han Ji-guang, Guo Yong-huan, SUN Lei. Creep behavior of SnAgCu solders containing nano-Al particles[J]. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics, 2015, 26(6): 1-6.
[53] Gain A K, Zhang Liang-chi. Harsh service environment effects on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Sn-Ag-Cu-1wt% nano-Al solder alloy[J]. Journal of Materials Science Materials in Electronics, 2016, 27(11): 11273-11283.
[54] Tsao L C, Wu R W, Cheng T H, FAN K H, CHEN R S. Effects of nano-Al2O3 particles on microstructure and mechanical properties of Sn3.5Ag0.5Cu composite solder ball grid array joints on Sn/Cu pads[J]. Materials & Design, 2013, 50(17): 774-781.
[55] Gu Y, Zhao X, Li Y, LIU Y, WANG Y, LI Z Y. Effect of nano-Fe2O3additions on wettability and interfacial intermetallic growth of low-Ag content Sn-Ag-Cu solders on Cu substrates[J]. Journal of Alloys & Compounds, 2015, 627: 39-47.
[56] Chen Ping, Zhao Xiu-chen, Wang Yong, ZHENG Bing, LIU Cheng-liang, CHEN Si-qi. Effect of nano α-Fe2O3 additions on physical and mechanical properties of Sn-1.0Ag-0.7Cu- xFe2O3 low Ag lead-free solders[J]. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics, 2016, 27(2): 1507-1519.
[57] LI Gui-zhi, WANG Li-chang, NI Han-li, CHARLES U P Jr. Polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane(POSS) polymers and copolymers: A review[J]. Journal of Inorganic & Organometallic Polymers, 2001, 11(11): 123-154.
[58] SHEN Jun, PENG Chang-fei, YIN Heng-gang, CHEN Jie. Influence of minor POSS molecules additions on the microstructure and hardness of Sn3Ag0.5Cu-xPOSS composite solders[J]. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics, 2012, 23(9): 1640-1646.
[59] Shen Jun, Tang Qin-tang, Pu Ya-yun, ZHAI Da-jun, CAO Zhong-min, CHEN Jie. Influence of POSS nano-particles on Sn-3.0Ag-0.5Cu-xPOSS/Cu composite solder joints during isothermal aging[J]. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics, 2013, 24(12): 4881-4887.
[60] 刘思涵, 马立民, 舒雨田, 左 勇, 郭 福. Sn基无铅钎料晶须生长行为的研究[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2015(11): 2868-2872.
LIU Si-han, MA Li-min, SHU Yu-tian, ZUO Yong, GUO Fu. Growth behavior of whiskers in Sn-based lead-free solders[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2015(11): 2868-2872.
[61] Plumbridge W J. Tin pest issues in lead-free electronic solders[J]. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics, 2007, 18(1): 307-318.
[62] Tsui Y, Mahmoud R, Surrey E, HAMPSHIRE D. Superconducting and mechanical properties of low-temperature solders for joints[J]. IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 2016, 26(3): 1-4.
[63] Zhang Yu-ming, Zhu Hong-lai, Fujiwara M, XU Jin-quan, MING Dao. Low-temperature creep of SnPb and SnAgCu solder alloys and reliability prediction in electronic packaging modules[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2013, 68(8): 607-610.
[64] 赵 鑫. Sn63Pb37、Sn3.0Ag0.5Cu钎料及其焊点的低温可靠性研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2014: 1-87.
ZHAO Xin. Study on reliability of Sn63Pb37, Sn3.0Ag0.5Cu solders and solder joints under low temperature[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2014: 1-87.
[65] Noor E E M, Zuhailawati H, Radzali O. Low temperature In-Bi-Zn solder alloy on copper substrate[J]. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics, 2016, 8(2): 1-8.
[66] Shimizu K, Nakanishi T, Karasawa K, HASHIMOTO K, NIWA K. Solder joint reliability of indium-alloy interconnection[J]. Journal of Electronic Materials, 1995, 24(1): 39-45.
[67] 陈海燕, 曾键波, 谢 羽, 路美秀, 牛 艳, 李 霞. Sn-Sb-Cu-Ni焊料和焊点在低温条件下组织和性能研究[J]. 材料工程, 2015, 43(11): 57-64.
CHEN Hai-yan, ZENG Jian-bo, XIE Yu, LU Mei-xiu, NIU Yan, LI Xia. Research on microstructure and properties of Sn-Sb-Cu-Ni solder and its joints at low temperature[J]. Journal of Material Engineering, 2015,43(11): 57-64.
[68] Li Y, Lim A B Y, Luo K, CHEN Z, WU F S, CHAN Y C. Phase segregation, interfacial intermetallic growth and electromigration-induced failure in Cu/In-48Sn/Cu solder interconnects under current stressing[J]. Journal of Alloys & Compounds, 2016, 673: 372-382.
[69] Zuo Yong-zuo, Ma Li-min, Liu Si-han, SHU Yu-tian, GUO Fu. Evolution of microstructure across eutectic Sn-Bi solder joints under simultaneous thermal cycling and current stressing[J]. Journal of Electronic Materials, 2015, 44(1): 597-603.
[70] Yue Wu, Qin Hong-bo, Zhou Min-bo, XIAO M A, ZHANG Xin-ping. Electromigration induced microstructure evolution and damage in asymmetric Cu/Sn-58Bi/Cu solder interconnect under current stressing[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2014, 24(5): 1619-1628.
[71] LI Xue-mei, SUN Feng-lian, ZHANG Hao, XIN Tong. Effect of temperature on interface diffusion in micro solder joint under current stressing[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2015, 25(5): 1699-1703.
[72] 张 飞. 尺寸效应下时效及电迁移对Cu/Sn-9Zn(SAC305)/Cu拉伸性能的影响[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学, 2015: 1-61.
ZHANG Fei. Size effect on tensile properties of Cu/Sn-9Zn(SAC305)/Cu solder interconnects under aging and current stressing[D]. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology, 2015: 1-61.
[73] 叶 松. 倒装芯片Ni/Sn-3.0Ag-0.5Cu/ENEPIG(OSP)无铅焊点的电迁移行为[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学, 2011: 1-70.
YE Song. Electromigration behavior of Ni/Sn-3.0Ag- 0.5Cu/ENEPIG(OSP) solder joints in flip chip packaging[D]. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology, 2011: 1-70.
[74] Xie H X, Friedman D, Mirpuri K, CHAWLA N. Electromigration damage characterization in Sn-3.9Ag-0.7Cu and Sn-3.9Ag-0.7Cu-0.5Ce solder joints by three-dimensional X-ray tomography and scanning electron microscopy[J]. Journal of Electronic Materials, 2014, 43(1): 33-42.
[75] Lu M, Shih D Y, Lauro P, GOLDSMITH C, HENDERSON D W. Effect of Sn grain orientation on electromigration degradation mechanism in high Sn-based Pb-free solders[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2008, 92(21): 1335.
[76] Kim Y, Nagao S, Sugahara T, SUGANUMA K, UESHIMA M, ALBERCHT H J, WILKE K, STORGIES J. Enhanced reliability of Sn-Ag-Bi-In joint under electric current stress by adding Co/Ni elements[J]. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics, 2014, 25(7): 3090-3095.
[77] Lee A, Subramanian K N. Development of nano- composite lead-free electronic solders[J]. Journal of Electronic Materials, 2005, 34(11): 1399-1407.
[78] 张睿竑, 徐广臣, 邰 枫, 郭 福, 夏志东, 雷永平. 具有纳米结构的增强颗粒对SnBi焊点电迁移的影响[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2011(S2): 45-50.
ZHANG Rui-hong, XU Guang-chen, TAI Feng, GUO Fu, XIA Zhi-dong, LEI Yong-ping. Effects of nano-structured reinforcements on the electromigration behavior of SnBi solder joints[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2011(S2): 45-50.
[79] Niranjani V L, Rao B S S C, Singh V, KAMAT S V. Influence of temperature and strain rate on tensile properties of single walled carbon nanotubes reinforced Sn-Ag-Cu lead free solder alloy composites[J]. Materials Science & Engineering A, 2011, 529(1): 257-264.
[80] 何 鹏, 安 晶, 马 鑫, 陈 胜, 钱乙余, 林铁松. 含碳纳米管的Sn-58Bi钎料的制备及其钎焊性[J]. 焊接学报, 2011, 32(9): 9-12.
HE Peng, AN Jing, MA Xin, CHEN Sheng, QIAN Yi-yu, LIN Tie-song. Investigation preparation method and soldering behaviors of Sn-58Bi lead-free solder with carbon nanotubes[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2011, 32(9): 9-12.
[81] 安 晶. 含碳纳米管的Sn-58Bi无铅钎料的制备及其性能研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2010: 1-45.
AN Jing. Investigation on the preparation method and properties of Sn-58Bi lead-free solder with carbon nanotubes[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2010: 1-45.
[82] Xu S, Chan Y C, Zhang K, YUNG K C. Interfacial intermetallic growth and mechanical properties of carbon nanotubes reinforced Sn3.5Ag0.5Cu solder joint under current stressing[J]. Journal of Alloys & Compounds, 2014, 595(15): 92-102.
[83] 白鹏飞. SnAgCu无铅焊点水相环境腐蚀行为和预防措施的研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2008: 1-57.
BAI Peng-fei. Study on the corrosion and prevention of SnAgCu lead-free solder joint in aqua environment[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2008: 1-57.
[84] Gao Yan-fang, Cheng Cong-qian, Zhao Jie, WANG Li-hua, LI Xiao-gang. Electrochemical corrosion of Sn-0.75Cu solder joints in NaCl solution[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2012, 22(4): 977-982.
[85] Liu J C, Park S W, Nagao S, NOGI S, KOGA H, MA J S, ZHANG G, SUGANUMA K. The role of Zn precipitates and Cl- anions in pitting corrosion of Sn-Zn solder alloys[J]. Corrosion Science, 2015, 92: 263-271.
[86] 赵国际, 赵 平. 微量Y对Sn-9Zn钎料合金组织与腐蚀性能的影响[J]. 热加工工艺, 2014(21): 177-178.
ZHAO Guo-ji, ZHAO Ping. Influence of minor Y additions on microstructure and corrosion property of Sn-9Zn alloy[J]. Hot Working Technology, 2014(21): 177-178.
[87] Peng H T, Che C S, Kong G. Effect of minor Cu addition on corrosion behavior of Sn-Zn-xCu touch-up solder alloys[J]. Materials & Corrosion, 2017, 68(7): 791-798.
[88] Ma Li, Hu Qiang, Sun Yan-bin. Effect of Cu on the electrochemical corrosion behavior of Sn-8Zn-3Bi lead-free solder alloy[J]. Advanced Materials Research, 2015,1095: 95-98.
[89] Liu Jian-chun, Wang Zheng-hong, Xie Jing-yang, MA Ju-sheng, SHI Qing-yu, ZHANG Gong, SUGANUMA K. Effects of intermetallic-forming element additions on microstructure and corrosion behavior of Sn-Zn solder alloys[J]. Corrosion Science, 2016, 112: 150-159.
[90] Nazeri M F M, Mohamad A A. Corrosion resistance of ternary Sn-9Zn-xIn solder joint in alkaline solution[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2016, 661: 516-525.
[91] 贡国良, 洗爱平. 微量Ge对大气下液态Sn抗氧化性能的影响[J]. 金属学报, 2007, 43(7): 759-763.
GONG Guo-liang, XIAN Ai-ping. Influence of trace on oxidation of liquid Tin in atmosphere[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2007, 43(7): 759-763.
[92] 孙玉萍. Ge、Ni等元素对Al-Si-Cu钎料性能的影响[D]. 合肥: 合肥工业大学, 2014: 1-51.
SUN Yu-ping. Effect of Ge, Ni elements on the properties of Al-Si-Cu filler metal[D]. Hefei: Hefei University of Technology, 2014: 1-51.
[93] Huang Ming-liang, Zhao Ning, Liu Shuang, HE Yi-qian. Drop failure modes of Sn-3.0Ag-0.5Cu solder joints in wafer level chip scale package[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2016, 26(6): 1663-1669.
[94] Hokka J, Mattila T T, Li J, TEERI J, KIVILAHTI J K. A novel impact test system for more efficient reliability testing[J]. Microelectronics Reliability, 2010, 50(8): 1125-1133.
[95] Peng W, Marques M E. Effect of thermal aging on drop performance of chip scale packages with SnAgCu solder joints on Cu pads[J]. Journal of Electronic Materials, 2007, 36(12): 1679-1690.
[96] Kim J Y, Yu J, Kim S H. Effects of sulfide-forming element additions on the Kirkendall void formation and drop impact reliability of Cu/Sn-3.5Ag solder joints[J]. Acta Materialia, 2009, 57(17): 5001-5012.
[97] Che F X, Pang J H. Study on reliability of PQFP assembly with lead free solder joints under random vibration test[J]. Microelectronics Reliability, 2015, 55(12): 2769-2776.
[98] El-Daly A A, Fawzy A, Mansour S F,YOUNIS M J. Novel SiC nanoparticles-containing Sn-1.0Ag-0.5Cu solder with good drop impact performance[J]. Materials Science & Engineering A, 2013, 578: 62-71.
[99] Lee T K, Kim C U, Bieler T R. Influence of high-G mechanical shock and thermal cycling on localized recrystallization in Sn-Ag-Cu solder interconnects[J]. Journal of Electronic Materials, 2014, 43(1): 69-79.
[100] 赵大为. 空间热循环和辐照环境对LF6铝合金焊接组织及性能的影响[D]. 焦作: 河南理工大学, 2010: 1-63.
ZHAO Da-wei. Effect of space thermal cycling and radiation environment on the microstructures and properties of welded LF6 aluminum alloy[D].Jiaozuo: Henan Polytechnic University, 2010: 1-63.
[101] 陈学永, 张晓光, 陈杰. 宇航环境电连接器的失效机理及应用研究[J]. 测控技术, 2015, 34(2): 154-156.
CHEN Xue-yong, ZHANG Xiao-guang, CHEN Jie. Failure mechanism and application of electrical connectors used in aerospace[J]. Measurement & Control Technology, 2015, 34(2): 154-156.
[102] 周 飞, 李 强, 信太林, 韦锡峰, 张 华. 空间辐射环境引起在轨卫星故障分析与加固对策[J]. 航天器环境工程, 2012, 29(4): 392-396.
ZHOU Fei, LI Qiang, XIN Tai-lin, WEI Xi-feng, ZHANG Hua. Analyses and countermeasures of in-orbit satellite failures caused by space radiation environment[J]. Spacecraft Environment, 2012, 29(4): 392-396.
[103] 罗雁横, 张瑞君. 空间辐射环境与光器件抗辐射加固技术进展[J]. 电子与封装, 2009, 9(8): 43-47.
LUO Yan-heng, ZHANG Rui-jun. Space radiation environment and resist-radiation hardening technology progress of optical devices[J]. Electronics & Packaging, 2009, 9(8): 43-47.
[104] 贾向红, 邹 鸿, 许 峰, 于向前, 吴大尉, 杨成佳, 蒋 睿, 马洪波, 宗秋刚. 空间电子辐射风险及其防护策略研究进展[J]. 航天医学与医学工程, 2014, 27(6): 453-457.
JIA Xiang-hong, ZOU Hong, Xu Feng, YU Xiang-qian, WU Da-wei, YANG Cheng-jia, JIANG Rui, MA Hong-bo, ZONG Qiu-gang. Research progress of space electrons radiation risk and its protection strategy[J]. Space Medicine & Medical Engineering, 2014, 27(6): 453-457.
Research progress on reliability of lead-free solders under special conditions
WANG Jian-hao1, XUE Song-bai1, MA Chao-li1, LONG Wei-min2, ZHONG Su-juan2
(1. College of Materials Science and Technology, Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, Nanjing 211106,China;
2. State Key Laboratory of Advanced Brazing Filler Metals and Technology, Zhengzhou Research Institute of Mechanical Engineering, Zhengzhou450002, China)
Abstract:Lead-free solders are applied under special conditions with the improvement of property of the solders and people's awareness of environmental protection. The research status and development trend of lead-free solders used under special conditions were reviewed synthetically. First of all, the failure mechanism of solder joints under different special conditions was discussed. Moreover, the ways to enhance the reliability of lead-free solders under several special conditions were reported and analyzed, such as microalloying, particle strength and substrate improvement. In addition, the defects of the current reliability research of lead-free solders were summarized, and the further research was prospected.
Key words: special condition; lead-free solder; microalloying; particle strength; substrate improvement; reliability
Foundation item: Project(51675269) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project supported by the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions, China
Received date: 2017-08-24; Accepted date: 2017-11-15
Corresponding author: XUE Song-bai; Tel: +86-25-84896070; E-mail: xuesb@nuaa.edu.cn
(编辑 王 超)
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(51675269);江苏高校优势学科建设工程资助项目
收稿日期:2017-08-24;修订日期:2017-11-15
通信作者:薛松柏,教授,博士;电话:025-84896070;E-mail:xuesb@nuaa.edu.cn
摘 要:随着无铅钎料性能的提升和人们环保意识的提高,无铅钎料也逐渐被应用在特殊环境中。介绍特殊环境用无铅钎料可靠性的研究进展及趋势,分析特殊环境中无铅钎料焊点失效的原因,探讨各种特殊环境中提高无铅钎料可靠性的方法和机理,如微合金化、颗粒强化和基板改善,总结目前无铅钎料可靠性研究存在的不足,对无铅钎料未来的研究方向提出建议。
[5] 轩庆庆, 龙伟民, 张青科, 路全彬. 稀土对Al-Si-Zn-Cu钎料工艺性能的影响[J]. 焊接, 2017(2): 31-36.
[6] 赵 杰, 钟海峰, 刘 平, 周 飞, 经敬楠. SnIn钎料与Au/Ni/Cu钎焊界面金属间化合物的研究[J]. 焊接, 2016(3): 18-21.
[11] 赵 宁, 钟 毅, 黄明亮, 马海涛. 微焊点中金属原子的热迁移及其对界面反应影响的研究进展[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2015, 25(8): 2157-2166.
[12] 马运柱, 罗辉庭, 李永君, 刘文胜, 黄国基. 等温时效对In-3Ag/Cu焊接界面组织演变特征的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2015, 25(5): 1256-1263.
[15] 仇爱梅. SnAgBi-xSm钎料组织及性能的研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨理工大学, 2016: 1-48.
[16] 皋利利. 稀土Pr和Nd对SnAgCu无铅钎料组织与性能影响研究[D]. 南京: 南京航空航天大学, 2012: 1-130.
[19] 潘英才. 锰掺杂对无铅焊料Sn-0.3Ag-0.7Cu界面反应及力学性能的影响[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2014: 1-55.
[20] 谭 淇. Fe或Mn对SAC0307钎料性能的影响[D]. 哈尔滨:哈尔滨工业大学, 2014: 1-55.
[21] 刘 洋, 孙凤莲. Ni和Bi元素对SnAgCu钎焊界面金属化合物生长速率的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2012, 22(2): 460-464.
[26] 汪 源. 纳米Ag3Sn、Cu6Sn5颗粒对Sn基无铅焊料性能影响研究[D]. 北京: 北京理工大学, 2015: 1-92.
[27] 张 亮, TU K N, 郭永环, 何成文, 张 剑. 时效对SnAgCu/SnAgCu-TiO2焊点界面与性能影响[J]. 焊接学报, 2013, 34(8): 43-46.
[28] 张 亮, 韩继光, 刘凤国, 郭永环, 何成文. 纳米TiO2颗粒对SnAgCu钎料组织与性能的影响[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2013, 42(9): 1897-1900.
[36] 朱奇农, 罗 乐, 肖 克, 杜黎光. Ni对Sn96.5Ag3.5/Cu之间扩散行为的阻挡作用[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2000, 10(2): 199-202.
[38] 徐 涛, 胡小武, 江雄心. 基板稀土微合金化对Sn3Ag0.5Cu/Cu钎焊界面反应的影响[J]. 电子元件与材料, 2016, 35(2): 65-69.
[39] 张尧武, 曾卫东, 史春玲, 康 超, 彭雯雯. 真空去应力退火对TC18钛合金残余应力及组织性能的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2011, 21(11): 2780-2785.
[40] 余 啸, 李玉龙, 胡小武, 张如华. Cu基板退火处理的Cu/Sn58Bi/Cu钎焊接头界面微结构[J]. 焊接学报, 2015, 36(10): 29-32.
[45] 石红昌, 冼爱平. 镀层表面锡晶须自发生长现象的研究进展[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2011, 21(5): 1021-1030.
[50] 张志鑫. Cu-Al化合物对SnAgCu焊点可靠性的影响[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2014: 1-65.
[60] 刘思涵, 马立民, 舒雨田, 左 勇, 郭 福. Sn基无铅钎料晶须生长行为的研究[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2015(11): 2868-2872.
[64] 赵 鑫. Sn63Pb37、Sn3.0Ag0.5Cu钎料及其焊点的低温可靠性研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2014: 1-87.
[67] 陈海燕, 曾键波, 谢 羽, 路美秀, 牛 艳, 李 霞. Sn-Sb-Cu-Ni焊料和焊点在低温条件下组织和性能研究[J]. 材料工程, 2015, 43(11): 57-64.
[72] 张 飞. 尺寸效应下时效及电迁移对Cu/Sn-9Zn(SAC305)/Cu拉伸性能的影响[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学, 2015: 1-61.
[73] 叶 松. 倒装芯片Ni/Sn-3.0Ag-0.5Cu/ENEPIG(OSP)无铅焊点的电迁移行为[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学, 2011: 1-70.
[78] 张睿竑, 徐广臣, 邰 枫, 郭 福, 夏志东, 雷永平. 具有纳米结构的增强颗粒对SnBi焊点电迁移的影响[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2011(S2): 45-50.
[80] 何 鹏, 安 晶, 马 鑫, 陈 胜, 钱乙余, 林铁松. 含碳纳米管的Sn-58Bi钎料的制备及其钎焊性[J]. 焊接学报, 2011, 32(9): 9-12.
[81] 安 晶. 含碳纳米管的Sn-58Bi无铅钎料的制备及其性能研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2010: 1-45.
[83] 白鹏飞. SnAgCu无铅焊点水相环境腐蚀行为和预防措施的研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2008: 1-57.
[86] 赵国际, 赵 平. 微量Y对Sn-9Zn钎料合金组织与腐蚀性能的影响[J]. 热加工工艺, 2014(21): 177-178.
[91] 贡国良, 洗爱平. 微量Ge对大气下液态Sn抗氧化性能的影响[J]. 金属学报, 2007, 43(7): 759-763.
[92] 孙玉萍. Ge、Ni等元素对Al-Si-Cu钎料性能的影响[D]. 合肥: 合肥工业大学, 2014: 1-51.
[100] 赵大为. 空间热循环和辐照环境对LF6铝合金焊接组织及性能的影响[D]. 焦作: 河南理工大学, 2010: 1-63.
[101] 陈学永, 张晓光, 陈杰. 宇航环境电连接器的失效机理及应用研究[J]. 测控技术, 2015, 34(2): 154-156.
[102] 周 飞, 李 强, 信太林, 韦锡峰, 张 华. 空间辐射环境引起在轨卫星故障分析与加固对策[J]. 航天器环境工程, 2012, 29(4): 392-396.
[103] 罗雁横, 张瑞君. 空间辐射环境与光器件抗辐射加固技术进展[J]. 电子与封装, 2009, 9(8): 43-47.


