网络首发时间: 2019-09-04 14:55
稀有金属2021年第1期
丝网印刷制备银/氯化银电极研究与应用进展
万甦伟 陈家林 李燕华 李俊鹏
昆明贵金属研究所稀贵金属综合利用新技术国家重点实验室
摘 要:
随着电化学传感器、生物传感器以及医用电极应用环境的发展,对银/氯化银参比电极和银/氯化银医用电极的可设计性、柔韧性、适应工业大批量生产等方面有了新要求。采用丝网印刷工艺制备再经低温固化成型的银/氯化银电极作为一种具备以上优点的低成本电极,已经成为了传感检测领域研究与应用的热点。从3个方面综述了丝网印刷制备银/氯化银电极的研究与应用进展:(1)丝网印刷制备银/氯化银电极的制备过程和优点、种类和区别以及电极的表征方法;(2)粘合剂选择、盐基层中氯化钾的浓度以及盐基层的层数等因素对丝网印刷制备银/氯化银电极氯离子敏感性、水合时间以及使用寿命等性能的影响;(3)丝网印刷制备银/氯化银电极在电化学生物传感器和医用电极方面的研究进展与应用。并对银/氯化银浆料影响电极灵敏性、稳定性的探究方向以及柔性衬底生物医用电极的接触阻抗提升途径进行了展望。
关键词:
丝网印刷银/氯化银电极 ;电化学传感器 ;生物传感器 ;生物医用电极 ;
中图分类号: TS871.1;O646.5;TP212
作者简介: 万甦伟(1995-),男,四川乐山人,硕士研究生,研究方向:银/氯化银电子浆料,E-mail:394386354@qq.com;; *李俊鹏,研究员,电话:13008692991,E-mail:lijunpeng@ipm.com.cn;
收稿日期: 2019-06-21
基金: 云南省重大科技专项项目(202002AB080001-1,2018ZE001)资助;
Progress in Research and Application of Silver/Silver Chloride Electrodes Prepared by Screen Printing
Wan Suwei Chen Jialin Li Yanhua Li Junpeng
State Key Laboratory of Advanced Technologies for Comprehensive Utilization of Platinum Metals,Kunming Institute of Precious Metals
Abstract:
Silver/silver chloride electrodes are widely used in many fields such as health and medical treatment,food and environ-mental protection because of their good environmental compatibility and the advantage of a very low half-cell potential compared to bio-logical tissues.However,with the development of the application environment of electrochemical sensors,biosensors and medical elec-trodes,higher requirements are put forward for the corresponding reference electrodes and medical electrodes in terms of performance,designability,flexibility and industrial mass production.Therefore,in order to meet the needs of corresponding applications,it has be-come a trend to develop screen-printed electrodes to replace traditional electrodes.At present,the silver/silver chloride electrode pre-pared by the screen-printed process and then solidified at a low temperature,as a low-cost electrode that meets the above requirementshas become a hot spot in the field of sensor detection and application.This paper reviewed the progress in research and application ofscreen-printed silver/silver chloride electrode from three aspects:(1)The advantages of screen-printed silver/silver chloride elec-trodes,the types and differences of screen-printed silver/silver chloride electrodes,and characterization method of screen-printed sil-ver/silver chloride electrodes.Firstly,the shortcomings of different methods for preparing silver/silver chloride electrodes were intro-duced,but the screen-printed silver/silver chloride electrodes filled the shortcomings of these methods,with low production cost,fastresponse speed,good repeatability,and automatic production.Screen-printed silver/silver chloride electrodes could be pided intomedical electrodes and reference electrodes according to application:when used as medical electrode,contact impedance and signalto-noise ratio could also characterize electrode performance;When used as a reference electrode,it was characterized by potential sta-bility,potential drift rate,service life,hydration period and shelf life.The reference electrode was pided into reference electrodeand quasi-or pseudo-reference electrode according to whether it contained chloride ion functional layer.The function of chloride ionfunctional layer was to ensure the stability of chloride ion concentration of the electrode,so that the potential was not easy to fluctuatedue to environmental influence.(2)Choice of adhesive,concentration of potassium chloride in the salt layer,the number of layers ofthe salt layer and other factors affected the chloride ion sensitivity and service life of the screen-printed silver/silver chloride elec-trodes.By summarizing the influence of two different types of potassium chloride layers on the performance of the electrode,it was con-cluded that when the slurry composed of potassium chloride and siloxane-based polymer had an optimal value,the response of the elec-trode to the concentration was not obvious,and the service life would also increase.The potassium chloride layer was a hydrogel elec-trode,and the higher the concentration,the shorter the service life.Then,by summarizing the effects of different concentrations of po-tassium chloride salt base layer and printing two different layers of potassium chloride salt base layer on the performance of screenprinted silver/silver chloride electrode,it was concluded that the conductivity of the electrode would increase with the increase of po-tassium chloride percentage within a certain range,and when it exceeded a certain percentage,the dissolution of potassium chloridewould lead to the increase of chloride sensitivity of the electrode.However,two different potassium chloride base layers would signifi-cantly reduce the sensitivity of the electrode.(3)Research and application of screen-printed silver/silver chloride electrodes in thefields of electrochemical biosensors and biomedical electrodes.The reference electrode was an important part of the electrochemical bi-osensor system,so starting from the structure of the reference electrode,the internal electrolyte of the electrode was studied,and a sta-ble,reliable,sensitive,and accurate reference electrode was successfully prepared.The performance of the prepared reference elec-trode was verified by cyclic voltammetry and amperometric analysis.The test results showed that the prepared electrode had excellentperformance and could provide reliable signals for accurate measurement of biosensors.The performance and human body fitted of thescreen-printed silver/silver chloride flexible substrate electrode met the requirements of medical electrodes after testing.Finally,the re-search direction of the silver/silver chloride slurry ratio affecting the sensitivity and stability of the electrodes and the contact imped-ance improvement path of the flexible substrate biomedical electrodes were prospected.
Keyword:
screen-printed silver/silver chloride electrodes; electrochemical sensors; biosensors; biomedical electrodes;
Received: 2019-06-21
随着化学传感器、生物传感器和医用电极在健康与医疗、食品与土壤质量、气候变换与环境保护等领域的不断发展
[1 ,2 ,3 ,4 ]
,对相应的参比电极、医用电极在性能可靠、低成本、可设计、具有柔韧性等方面提出了更高的要求
[5 ,6 ,7 ,8 ,9 ,10 ]
。目前常使用的玻璃外壳结构银/氯化银参比电极,虽然其具有优异的电位稳定性,但由于在保存和使用过程中需要经常更换电解液
[11 ]
,以及不可避免的存在液接电势影响检测准确性
[12 ,13 ]
。医用电极中应用最广的标准湿银/氯化银电极在使用过程中由于需要对皮肤进行预处理并涂抹导电膏,可能会造成人体的应激反应,同时标准湿银/氯化银电极在柔韧性等方面已不能满足可穿戴式检测设备的柔韧性要求,使得标准湿银/氯化银医用电极的应用陷入瓶颈。这些技术问题促进了银/氯化银电极的发展。
第一类电极(标准氢电极)和第二类电极(饱和甘汞电极、银/氯化银电极)都可用作参比电极
[11 ]
。标准氢电极由于氢气不易纯化、压强不易控制、铂黑容易中毒等原因,在实际应用中很少使用。甘汞电极在电位稳定性和光惰性方面相对银/氯化银电极具有优势,但其温度上限约为80℃,此外汞具有多种环境危害,其使用通常限于实验室检测
[14 ]
。银/氯化银(Ag/Ag Cl)电极因其环境相容性好,目前被广泛使用于化学传感器和生物传感器中用作参比电极
[15 ,16 ,17 ,18 ,19 ,20 ,21 ,22 ,23 ,24 ,25 ,26 ]
。此外银/氯化银具有相对生物组织而言非常低的半电池电位,是医用检测电极的首选。
研究人员针对不同的具体应用,开发可设计、小型化、低成本、便携式的丝网印刷电极来代替传统电极并满足相应应用需求已经成为了一种趋势。本文总结了近年来丝网印刷制备银/氯化银电极应用于电化学传感器、生物传感器和生物医用电极的最新研究进展,展望了影响丝网印刷银/氯化银参比电极性能因素的研究方向并提出了柔性衬底生物医用电极的接触阻抗等性能的提升途径。
1 丝网印刷银/氯化银电极及其表征方法
1.1 丝网印刷制备银/氯化银电极的优点
银/氯化银电极具有低极化、低阻抗、制造简便以及对低频电场敏感等优点,因此相对于标准氢电极和饱和甘汞电极有着更广的适用范围。银/氯化银电极的性能主要取决于微观上的界面情况,由于氯化银不导电,其比例过多会影响电极导电性,其比例过少无法与银颗粒形成均匀的银/氯化银分散界面会影响低极化的电化学特性。
银/氯化银电极的经典结构是玻璃外壳结构,采用电解氯化法制备
[27 ]
,这种电极具有优异的稳定性,电极电位可以精确到1 m V。但由于玻璃外壳银/氯化银电极保存与使用过程中需要经常更换电解液以保障电极电位的稳定、存在液接电势、柔韧性差、成本相对较高,对大多数环境和土壤传感器应用而言并不是一种优选等原因限制了进一步的应用
[11 ,12 ,13 ,28 ]
。粉末压片法制备的银/氯化银电极,由于其在一定温度压力下加强了银/氯化银粒子在微观上的紧密接触与分散,可以得到性能优异的电极
[29 ,30 ]
,但是这种方法工序复杂、成本较高、不易于大批量快速生产。此外还可通过热电解法
[31 ,32 ,33 ]
、热浸涂法
[34 ,35 ,36 ,37 ]
等方法制备银/氯化银电极,但都无法满足电极结构可灵活设计、低成本、柔韧性好等要求。
丝网印刷银/氯化银电极是丝网印刷技术与银/氯化银电极材料相结合而制备的电极。丝网印刷电极可以根据具体使用环境与条件设计电极图样,满足了电极的可设计性,具有制作成本低、样品用量少、响应速度快、重复性好以及制作自动化等优点
[38 ]
。银/氯化银电极浆料是由银粉、氯化银粉以及有机载体混合而成,丝网印刷银/氯化银电极是将银/氯化银电极浆料采用丝网印刷工艺,透过可设计的丝网印版印刷在特定的基底上,再经低温固化后制得成品电极,图1为丝网印刷原理图
[39 ]
。目前使用较多的刚性基底有硅、氧化铝、玻璃等,柔性基底有聚二甲基硅氧烷(PDMS)、聚对苯二甲酸乙二醇酯(PET)、聚酰亚胺(PI)、聚丙烯(PP)以及聚氨基甲酸酯(PU)等
[40 ,41 ]
。刚性基底主要用于制备参比电极,而柔性基底则是用于制备对电极柔韧性有要求的生物医用电极。PDMS由于其在化学惰性、广泛温度范围内的稳定性、透明度、可变的机械性能、低杨氏模量、优异的生物相容性等方面的优势,是目前在生物医用电极中应用最多的柔性基底
[40 ,41 ]
。
1.2 丝网印刷银/氯化银电极种类
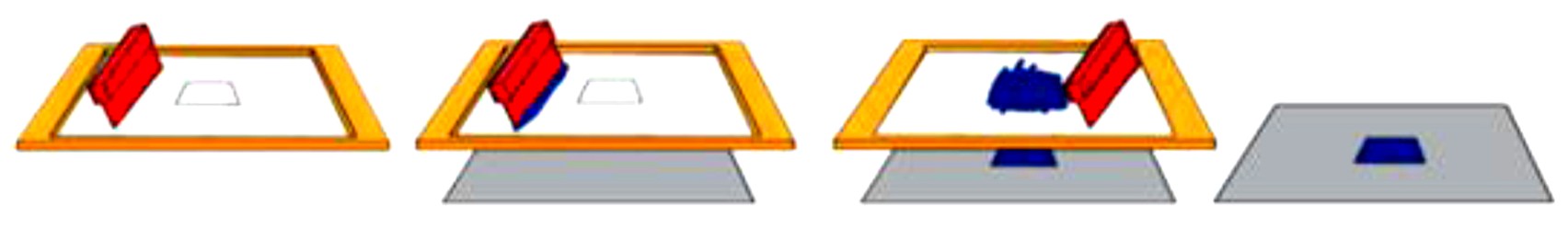
丝网印刷银/氯化银电极按应用分为医用电极与参比电极,其中参比电极按是否含氯离子功能层分为参比电极与准或伪参比电极(quasi-or pseudo-reference electrodes),如图2所示
[15 ]
。
目前被广泛研究与使用的丝网印刷银/氯化银参比电极一般由3个功能层组成,每个功能层具有不同的作用。第一层是导体层,负责电子的传输。第二层是离子对电子层,这一层是银/氯化银层,负责与离子相互作用产生电子流。最后的功能层是负责控制电极周围氯离子浓度的KCl层,因为根据能斯特方程,银/氯化银电极的电极电位主要受氯离子浓度影响,用作参比电极时为保证电极电位稳定,氯离子浓度就要保持不变。伪参比电极由于其没有氯离子功能层来保证电极的氯离子浓度稳定,使得电位容易受环境影响而波动。伪参比电极对银离子和氯离子具有高敏感性,通常只在实验室内使用,在使用环境复杂的环境传感器的具体应用中几乎不适用,因为其他阴离子或蛋白质会极大地干扰其电势稳定性。此外伪参比电极还经常用于使用循环伏安法或电流分析法的传感器中,因为这些情况下环境介质是已知的。Carrara等
[16 ]
研究了一种高灵敏度胆固醇生物传感器,其中包含了丝网印刷的银/氯化银伪参比电极,使用循环伏安法作为传感方法。而Hernández等
[17 ]
同样也对检测胆固醇的生物传感器有所研究,他们研究的一次性丝网印刷传感器上同样使用了银/氯化银伪参比电极。
生物医用电极作为一种可以有效地将生物体表面的离子电流转换为电信号的传感器,是生物医学系统中的关键组成部分
[9 ]
。银/氯化银电极是一种不极化电极,满足生物医用电极对导电性好、稳定性强、电位波动小、极化电位小等要求,常用作生物测量用电极。目前银/氯化银电极广泛地应用于临床监测以及生物医学的相关测量,如肌电图(EMG)、脑电图(EEG)、心电图(ECG)以及眼电图(EOG)等
[40 ,42 ,43 ,44 ,45 ]
。标准湿银/氯化银电极是目前在临床心电检测中最常用的生物医用电极,具有信号稳定性好、检测再现性好以及涂抹导电凝胶后可以获得低的皮肤阻抗等优点,可以测量得到较为精确的生物电信号以辅助医务人员对患者病情进行诊断。其结构如图3所示,由Ag/Ag Cl层、电极芯、导电凝胶、无纺布等部件组成
[40 ]
。目前针对丝网印刷银/氯化银生物电极的研究较少,大多数研究集中在纺织柔性电极和微针电极方面
[46 ,47 ,48 ]
,但由于银/氯化银可以制备成浆料形式,印刷在柔性基底上后能够制备出完美贴合人类皮肤的柔性化生物电极来代替传统的生物电极,具有极大的应用潜力与研究价值。
图1 丝网印刷原理图
Fig.1 Screen-printing schematic
[39]
图2 参比电极与伪参比电极的差异
Fig.2 Difference between a RE and a QRE
[15]
1.3 丝网印刷银/氯化银电极的表征方法
丝网印刷银/氯化银电极用作参比电极时,其性能一般通过电位稳定性、电位漂移率、使用寿命、水合期、保质期等来表征。此外由于银/氯化银电极还可用作生物医用电极,所以当丝网印刷银/氯化银电极用作医用电极时,接触阻抗、信噪比等也可对电极性能进行表征。电位稳定性是指其电位随时间的波动性,波动性越小稳定性越好,参比电极和医用电极的稳定性都直接影响着测量的准确性与可靠性。电极的漂移率指的是其电势在恒定条件下改变的速率,漂移率越低,电极性能越好。使用寿命是指银/氯化银电极在维持工作状态下的有效时间。使用寿命根据应用而存在不同,所需寿命通常可以在几分钟到一年的范围内。如在分析化学中所需电极是一次性的,则其使用寿命可能是几分钟,而对于某些需长期检测的应用而言,其使用寿命应至少几个月。Idegami等
[18 ]
研究制备的一次性银/氯化银参比电极,其电位稳定时间约为60 min,而Shitanda等
[19 ]
研制的平面固体型银/氯化银丝网印刷参比电极,其电极潜在使用寿命到达1680 h。水合期即响应时间,指的是参比电极置于溶液中达到稳定电位所需要的时间,水合期越短越好。保质期是从生产到第一次使用且能保证其应用特性的最大允许时间。经典的银/氯化银玻璃外壳结构电极由于水分的蒸发导致了其保质期较短,而丝网印刷电极的保质期通常在一年以上
[28 ]
。接触阻抗在生物医用电极上指的是电极-皮肤的阻抗值,阻抗值越低,获得的生物电信号越精确。信号比是指电极采集到的有用信号与自身噪声的比值,反应了电极采集有效电信号的能力。
图3 Ag/Ag Cl电极的外观结构图
Fig.3 Appearance of Ag/Ag Cl electrode
[40]
(a)Front face;(b)Back face
2 影响丝网印刷银/氯化银电极的因素
Atkinson等
[20 ]
比较研究了两种不同类型的氯化钾层在连续十倍差梯度的氯化钾溶液(饱和氯化钾:去离子水的体积比为1∶10,1∶100,1∶1000)中的丝网印刷银/氯化银电极性能。两种不同氯化钾层,一种是含有6%,3%,0.6%(质量分数)浓度的氯化钾与硅氧烷基聚合物组成的浆料,另一种是水凝胶态,分别为饱和氯化钾溶液和饱和溶液与去离子水的体积比按1∶2和1∶10稀释的溶液。电极在p H值为7的磷酸二钠/磷酸二氢钾溶液稳定1 h后使用万用表测量其相对于商用参比电极的电位。实验发现,氯化钾层为氯化钾与硅氧烷基聚合物浆料的电极在连续十倍差氯化钾浓度梯度的测试溶液中,初始6%氯化钾浓度的电极,其在氯化钾浓度梯度变换中,电位差较小,将氯化钾浓度提升到一个最佳值,电极对变换的氯离子浓度的响应几乎是平坦的,其使用寿命也会相应增加;而氯化钾层为水凝胶态的电极,初始氯化钾浓度越高,其漂移越大,使用寿命越短,优点是水合期很短。在水合时间和漂移率之间存在关联,初始盐浓度水平和粘合剂类型对参比电极的实际使用寿命都有重大影响。一般而言,随着KCl基体浓度的增加,参比电极在一定范围的氯化物溶液环境中需要更长的时间来达到稳定电位,但同时表现出更长的使用寿命。
Glanc等
[15 ]
研究了3种银/氯化银浆料、不同浓度氯化钾盐基层以及印刷两层不同氯化钾盐基层对丝网印刷银/氯化银电极性能的影响,电极性能通过在连续十倍差氯化钾浓度梯度的溶液(饱和氯化钾:去离子水的体积比为1∶10,1∶100,1∶1000)中电位变化差、不同p H缓冲液中的稳定性和电极可应用的工作浓度范围来表征。实验首先测试了含20%,66%和71%的3种不同质量分数的氯化钾盐基层对电极性能的影响,发现如果氯化钾含量太低,电极具有非常低的电导率,从而产生噪声响应影响检测,随着氯化钾百分比增加,电导率也会增加,但是氯化钾的浓度超过一定百分比时,粘合剂对其粘附能力会下降,氯化钾更容易溶解到溶液中,从而导致电极氯化物敏感性增加。根据实验数据可以推测,针对于不同的具体应用存在最佳氯化钾浓度范围的盐基层,使得电极具有最佳性能。在氯化钾盐基层上再添加另一层氯离子盐基层,会显著降低电极的敏感性,使电极电位足够稳定可以在任何氯离子浓度下使用。实验数据显示所有具有两层盐基层的电极,在氯化物10倍浓度梯度溶液中表现出+2~+4 m V/10倍的敏感性,但如果最外层的盐基层氯化钾浓度过高,使氯化钾溶于溶液中也会增加电极的灵敏度。此外使用一种聚合物基(银:氯化银为3∶2(质量比))以及两种玻璃基(银:氯化银都为1∶1(质量比))共3种银/氯化银浆料制备了的电极进行性能表征,实验结果显示出聚合物基与玻璃基在电极性能上存在差异,但并未进一步探究银/氯化银比值与所用粘合剂对电极性能的具体影响。
Sophocleous等
[21 ]
也同样研究了20%,50%,66%3种不同质量分数氯化钾浓度的盐基层对电极性能的影响,得出了与Glanc等相似的结论,即当电极中保持足够的氯化钾浓度时,电极的电位稳定性能非常好,但是一旦氯化钾溶解在溶液中,电极就会根据浸入溶液的浓度漂移到不同的电位。此外他们还研究了电极中不含银/氯化银层的情况,实验发现这种情况下电极的对氯离子浓度的敏感性会很低,虽然电极不含银/氯化银层,但是在银层上印刷盐基层的时候,部分银会转换为氯化银,盐基层浓度的不同会造成银/氯化银比例的改变,从而对电极的敏感性造成影响。
根据现有一些关于丝网印刷银/氯化银电极性能影响因素的文献报道,可以总结出银/氯化银的比率,是否有银/氯化银层、粘合剂的选择、盐基层中氯化钾的浓度以及印刷盐基层的层数等因素会对电极的氯离子敏感性、水合时间、使用寿命等性能造成影响。目前的研究大都直接使用成品银/氯化银浆料,很少涉及银/氯化银颗粒度与形貌以及树脂选择等因素对电极性能影响的研究,更深入的影响机理研究还有待进一步开展。
3 丝网印刷银/氯化银电极在电化学生物传感器方面的研究与应用
近年来,基于电位滴定法、伏安法和安培法的电化学生物传感器已经引起了大量研究人员的关注,因为这类电化学传感器结构简单、响应快、便携而且便宜,并且可用于检测特定的生物间的相互作用。参比电极是电化学生物传感器系统的重要组成部分,银/氯化银参比电极需要内部电解质以获得理想的性能,但大多数一次性用的传感器条的银/氯化银并没有内部电解质,因此有必要制造更精确的参比电极,以便可以用于开发高灵敏度的感测技术的应用
[49 ,50 ]
。
Idegami等
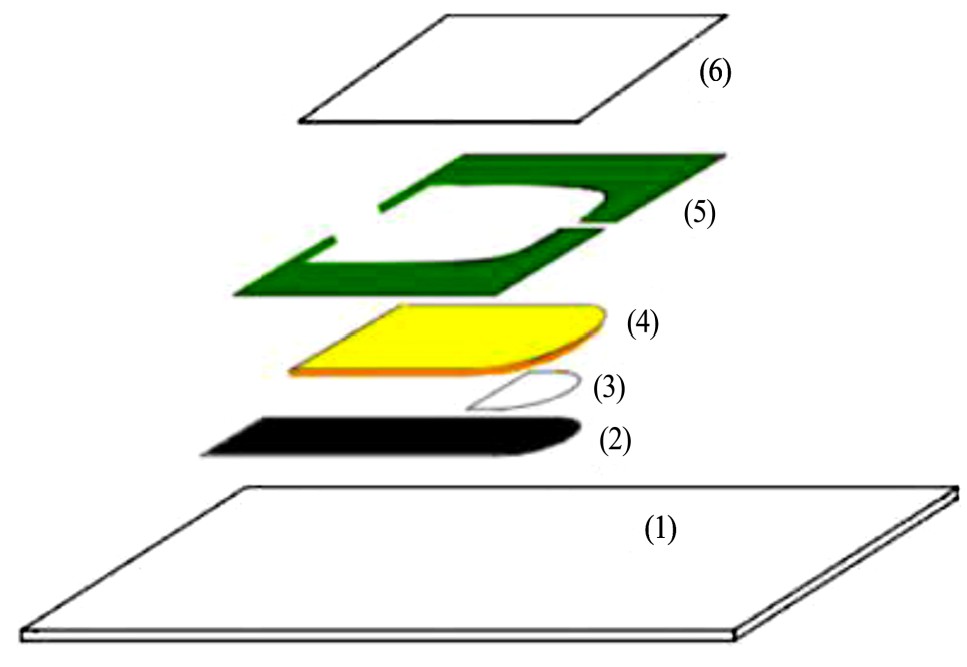
[18 ]
研究了可以快速响应的一次性银/氯化银丝网印刷参比电极,该一次性电极水合时间约为4 min,具有60 min的电极电位稳定性且电极对氯离子浓度不敏感,可以用于各类传感器的快速电化学检测。电极的结构由一层玻璃环氧树脂基底,一层导电层,一层银/氯化银,一层含2%海藻酸钠的饱和KCl的内部电解质层,一个带两个狭缝的绝缘层和一层亲水聚合物涂层的聚酯薄膜组成,其结构如图4。电解质层的表面通过施加重量3%的Ca Cl2 溶液而凝胶化。带两个狭缝的绝缘层,一个狭缝被制造成允许测试溶液与参比电极的内部组分接触,另一个被制成允许空气逸出。最后,涂有亲水聚合物的聚酯薄膜均匀覆盖在电极上。由于海藻酸盐在样品溶液中凝胶化的能力,使该一次性参比电极4 min后电位稳定,并具有60 min的电位稳定性且性能不依赖于Cl- 的浓度。作者采用丝网印刷工艺,成功地制备了一种稳定性能可靠含有内部电解质的一次性平面银/氯化银参比电极,可以将参比电极、工作电极和辅助电极制备一条传感器条上,并且可以满足低成本下大规模生产的要求,可用于制备电化学生物传感器用一次性传感器条带。
图4 参比电极结构
Fig.4 Structure of reference electrode
[18]
(a)Glass-epoxy substrate;(2)Conductive track;(3)Ag/Ag-Cl layer;(4)Internal electrolyte layer;(5)Insulating layerwith two slits;(6)Hydrophilic polymer-coated polyester film
Shitanda等
[22 ]
研发一种一次性的纸基丝网印刷的银/氯化银参比电极,其水合时间少于1 min,而寿命高达75 h,可在多种技术应用的得到广泛应用,包括用于制备一次性电化学传感器和p H传感器。通过在防水处理过的纸基材的一面印刷银浆、银/氯化银浆、KCl层等功能层来制备,纸基的厚度为800μm。以商用银/氯化银电极为参比电极测量该电极在0.1 mol·L-1 Na2 SO4 溶液中的开路电位,测试结果表明其电位在1 min内稳定,且电位稳定时间约为75 h。Hernández等
[17 ]
还报道了以聚二甲基硅氧烷(PDMS)乳液作为内部电解质层组分和液体接点材料的平面固体型丝网印刷银/氯化银参比电极,该电极的潜在稳定性达到了1680 h,同时对Na+ ,K+ ,Cl- 和PO4 2- 等重要离子物质不敏感,可应用在一次性电化学传感器、生物传感器等多种技术设备中。
循环伏安法与电流分析法是电化学检测的常用方法,使用伏安法和分析法进行检测时,由于环境介质是已知的,所以银/氯化银参比电极可以为没有内部电解质的裸露银/氯化银,即伪参比电极。Musa等
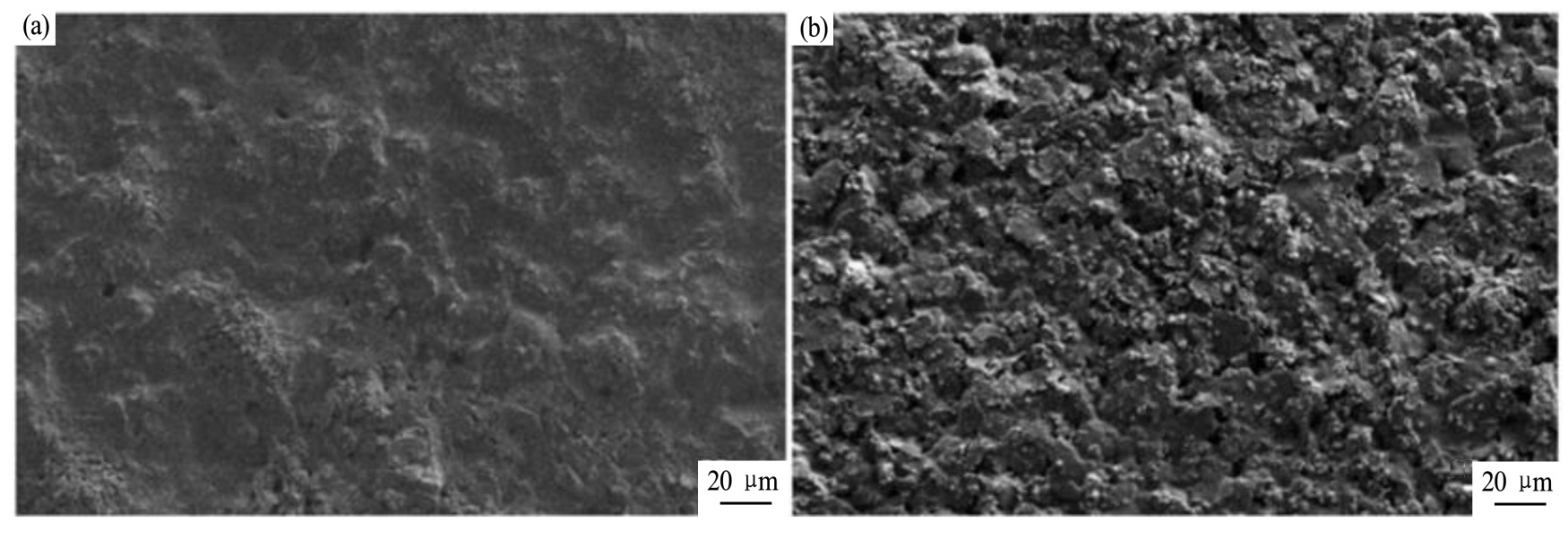
[23 ]
通过对丝网印刷、电极处理、离子选择性膜的配方等材料和制备工艺的优化,开发了一套用于监测p H值的小型化电位系统,该系统包括了一个丝网印刷银/氯化银伪参比电极,与固态离子选择性电极耦合。电极通过在500μm厚的PET膜上印刷石墨工作电极、银/氯化银伪参比电极(由Electrodag 6037 SS银/氯化银浆料印刷)、绝缘层以及离子选择性膜制备,用循环伏安法检测了石墨电极的性质并研究了不同固化温度与时间对电极性能的影响。图5显示了银/氯化银伪参比电极在90℃固化30 min与120℃固化20 min的形貌差异,作者推测较高的固化温度很可能会去除浆料中含有的更多的非金属成分,使得电极表面更加粗糙,但是同时也降低了电极的电阻。对120℃固化20 min的3个银/氯化银伪参比电极样品进行了7天的开路电位测量,7 d内电极的开路电位标准偏差为±1.2 m V,表现出良好的电位稳定性。最终的小型电位系统包括银/氯化银伪参比电极与p H电极,在7.00~7.63的p H范围内达到了(-60.8±1.7)m V/p H的p H灵敏度。
Silva等
[24 ]
通过喷墨印刷方式研发了PET或色谱纸为基底的固态银/氯化银伪参比电极。使用印刷机将含20%乙二醇的银纳米粒子浆料印刷在PET或纸基上,在120℃固化20 min后,使用40mg·ml-1 的Na Cl O溶液对印刷好的部分银层进行短时间浸泡以形成氯化银层,然后用去离子水清洗并用氮气流干燥。对比研究了浸泡法与电化学处理法,得到了相似的结果,实现了通过更为简单的化学氯化法来获得氯化银层,可应用于大规模生产不同结构和尺寸的固态银/氯化银伪参比电极。对所制备的电极进行电位可靠性以及黑暗存储30 d后的电极性能进行了测试,测试结果表明电极的开路电位值与商用银/氯化银电极没有显著差异,30 min内显示出良好的再现性与稳定性,黑暗条件下存储30 d后再使用同样具有效用。
图5 银/氯化银伪参比电极SEM照片
Fig.5 SEM images of an Ag/Ag Cl QRE
[23]
(a)Cured for 30 min at 90℃;(b)Cured for 20 min at 120℃
Jadav等
[25 ]
研发了一种可以现场快速检测果汁中维生素C含量的银-碳丝网印刷电极。自制了银纳米粒子与碳纳米粒子,将银/碳纳米粒子分别与热固性环氧树脂混合配置成了粘度为1500~4500c P适应于丝网印刷工艺的银浆、碳浆及银/氯化银浆。使用丝网印刷工艺,银浆印刷辅助电极,碳浆印刷工作电极,银/氯化银浆料印刷参比电极,制备了三电极体系的丝网印刷电极,并研究分析了该电极的线性范围、再现性、稳定性等电极性能,证明完全满足快速检测维生素C浓度的需要。通过循环伏安法测定并校准维生素C浓度与银-碳丝网印刷电极氧化峰电位的关系,建立了电极电位与维生素C浓度的函数关系,这样实际检测时只需测量电极电位,通过对应函数关系换算即可得到维生素C的含量。这种使用伏安法测定维生素C的方法与目前常用的光谱法或液相色谱法相比,不需要昂贵的仪器和专业的人员,但可以现场快速地检测出与实验室化学检测系统相似的结果。
在生物传感器中,一般各类酶作为检测的敏感元件,而银/氯化银电极作为参比电极为其提供可靠的电位信号。Carrara等
[16 ]
研究了一种高灵敏度胆固醇生物传感器,相较于之前公布的其他胆固醇氧化酶和酯酶的类似系统,该传感器的敏感性提高了几个数量级。他们通过将多壁碳纳米管印在工作电极上,再印刷细胞色素P450scc,银/氯化银作为参比电极,循环伏安法作为传感方法,并与使用金纳米颗粒的传感器进行了比较。实验结果表明,该传感器的电子转移效率是使用金纳米颗粒传感器的2.4倍,普通传感器的17.8倍,灵敏度为1.12μA·(mmol·L-1 )-1 ·mm-2 。Hernández等
[17 ]
同样也对检测胆固醇的生物传感器有所研究,以四氯化碳(TCNQ)、普鲁士蓝(PB)或铁氧体(Fe3 O4 )为介质或电催化剂,制备了3类丝网印刷电极,对3种类型的电化学传感器进行了评价,其中每种传感器都印刷了银/氯化银浆料作为参比电极。通过安倍实验,建立了游离胆固醇与电极电位之间的关系,通过校准曲线计算出TCNQ、PB和铁氧体的检测范围分别为1.56,1.29和0.29 mmol·L-1 ,灵敏度分别为221,41,132 n A·(mmol·L-1 )-1 ·mm-2 。
Liao和Chou
[26 ]
采用丝网印刷工艺制备了平面式银/氯化银参比电极,可应用于电位生物传感器。他们对电解质层进行了改性,为了使电极的制备过程更为简便以及满足低成本的要求,使用琼脂凝胶作为内部电解质层,氯丁橡胶作为液体结与绝缘体。以所制备的丝网印刷电极为工作电极,商用银/氯化银电极为参比电极的双电极系统,连续测试了电极在溶液梯度为1×10-6 ~1×10-1 mol·L-1 以及0.3 mol·L-1 的KCl,Na Cl,Li Cl,Ca Cl2 ,Mg Cl2 以及NH4 Cl共6种溶液体系中的敏感情况。实验结果表明,他们所研发的平面式银/氯化银参比电极对大多数生理重要离子物质不敏感,包括Na+ ,K+ ,Li+ ,Ca2+ ,NH4+ 和Cl- 。此外该电极在琼脂凝胶干燥前可以表现出与商用银/氯化银电极相似的电极可逆响应,只要电解质层保持凝胶水合状态,电极就能保持稳定的电位。将研制的银/氯化银丝网印刷参比电极与氧化铱改性的铂基p H指示电极集成为p H生物传感器,与含商用银/氯化银电极的p H计对比发现两者性能相当,对人体血清、人体血液、可口可乐、自来水、橙汁、低脂牛奶等多种真实样品都能给出准确的p H值测量。
4 丝网印刷银/氯化银电极在医用电极方面的研究与应用
生物电是生物体的生理现象之一,医用电极作为一种可以有效地将生物体表的离子电流转换为电信号从而实现对生物电测量的传感器,是生物医学检测系统中的关键组成部分。由于生物电信号较弱、频率低接近直流等特点以及医用电极使用过程中必须与人体直接接触等客观因素,医用电极必须满足导电性好、低极化、电位波动小、接触阻抗低、无毒无害等要求。
周伟等
[40 ]
综述了生物医用电极的类别,包括传统银/氯化银电极、微针电极、纺织柔性电极、柔性衬底电极、泡沫结构电极、绝缘干电极以及在这些电极在心电图(ECG)、脑电图(EEG)、肌电图(EMG)以及电阻抗成像(EIT)等方面的应用。传统银/氯化银电极是目前使用最多的商用电极,但导电凝胶的使用使得传统银/氯化银电极存在着固有缺陷,促进了微针电极、纺织柔性电极、柔性衬底电极、泡沫结构电极、绝缘干电极等新式医用电极的发展,其中使用丝网印刷工艺制备的柔性衬底电极可以实现与人体皮肤高度贴合,满足不同部位的穿戴要求,目前已经成为了生物医用电极的重点研究方向。
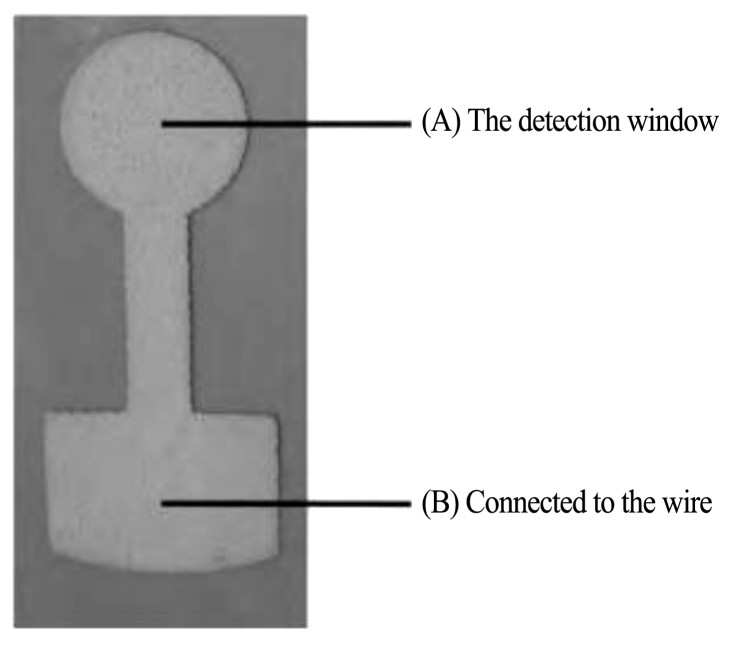
秦路丹等
[41 ]
就对柔性衬底的生物医用电极进行了研究,采用丝网印刷工艺,在聚酰亚胺(PI)柔性塑料基底上印刷银/氯化银浆料制备了银/氯化银柔性脑电电极,电极如图6所示。他们对电极表面涂层进行了SEM形貌表征,并对电极进行了电位稳定性、电化学阻抗、电极表面的附着性等性能测试。实验结果表明,电极涂层呈多孔结构,电极稳定电位为(0.97±0.20)m V,电极电位稳定性良好最大极差电位小于0.7 m V,4 h后的电极电位飘逸值小于10μV/4 min,皮肤经GT5导电膏处理后该电极的电极-皮肤阻抗值低于5 kΩ,符合脑电图记录要求。
图6 柔性脑电电极实物图
Fig.6 Photo of flexible EEG electrodes
[41]
5 总结与展望
采用丝网印刷工艺制备的丝网印刷银/氯化银电极,实现了银/氯化银电极的可设计性、柔韧性、低成本和适合工业大批量生产等方面的应用需求。尽管目前已经有研究人员对丝网印刷银/氯化银电极的电极性能影响因素和柔性脑电电极的应用等课题进行了探究,但还存在着银/氯化银电极浆料对电极敏感性和稳定性等性能影响机理研究不足,丝网印刷银/氯化银医用电极不使用导电膏情况下接触阻抗较高等问题,需要进一步探究。
1.银/氯化银层作为丝网印刷银/氯化银电极的核心部分,银/氯化银浆料直接影响着电极性能,但目前并没有研究人员研究银/氯化银电极浆料对电极电位、敏感性和稳定性等电极性能的影响机理。银粉和氯化银粉作为银/氯化银电极浆料的重要组成部分,银/氯化银活性界面可能会影响电极的电极电位、敏感性和稳定性。因为对于银/氯化银电极,由于氯化银不导电,如果氯化银含量过多,会影响电极的导电性和敏感性,氯化银含量过少,微观上不能形成均匀的银/氯化银活性界面,会影响电极的低极化特性和稳定性。探究银/氯化银活性界面对电极电位、敏感性和稳定性的影响机制,有利于根据应用需求调制银/氯化银电极浆料。
2.相对于传统医用电极,柔性电极可以实现电极与人体皮肤的高度贴合,获得更为精确的生物电信号。采用丝网印刷技术,将电极浆料印刷在柔性基底上制备柔性医用电极,已经成为了新式生物医用电极的研究热点。不使用导电膏情况下高的电极-皮肤接触阻抗是目前制约丝网印刷银/氯化银柔性医用电极发展的主要因素。树脂作为银/氯化银浆料的有机载体,其介电特性可能会影响电极-皮肤的接触阻抗值,探究树脂介电性能对接触阻抗的影响机制,采用介电性能更好的树脂制备银/氯化银电极浆料,有利于实现柔性生物电极“低接触阻抗”性能的目标。此外银/氯化银比例、电极的固化工艺以及柔性基底的选择等因素也可能影响电极的接触阻抗。
随着5G时代的逐步临近,电化学生物传感器以及生物医用电极领域的不断发展,作为数据实时监测终端的传感器和医用电极会迎来飞速发展的机遇,丝网印刷银/氯化银电极更多的应用需求与应用价值也会不断地被挖掘。相信随着影响丝网印刷银/氯化银电极性能因素的内在机制不断被发现并理解,会出现更多低成本、高效能的丝网印刷银/氯化银参比电极以及可穿戴、低接触阻抗的丝网印刷银/氯化银生物电极,在环境监测、医疗健康等领域带来更多的应用。
参考文献
[1] Soleimani M,Sophocleous M,Glanc M,Atkinson J K,Wang L,Wood R,Taylor R I.Engine oil acidity detection using solid state ion selective electrodes[J].Tribology International,2013,65:48.
[2] Cranny A,Harris N R,Nie M,Wharton J,Wood R,Stokes K.Screen-printed potentiometric Ag/Ag Cl chloride sensors:lifetime performance and their use in soil salt measurements[J].Sensors&Actuators A Physical,2011,169(2):288.
[3] Tu H L,Zhao H B,Wei F,Zhang Q Z,Fan Y Y,Du J.Research progress in advanced sensing materials and related devices[J].Chinese Journal of Rare Metals,2019,43(1):1.(屠海令,赵鸿滨,魏峰,张青竹,樊彦艳,杜军.新型传感材料与器件研究进展[J].稀有金属,2019,43(1):1.)
[4] Huang H P,Xu L,Yue Y F,Xu F.Nitrite electrochemical sensor based on graphene quantum dots modified electrode[J].Nonferrous Metals Science and Engineering,2017,8(2):47.(黄海平,徐亮,岳亚锋,许芳.基于石墨烯量子点修饰电极的亚硝酸根电化学传感器[J].有色金属科学与工程,2017,8(2):47.)
[5] Wang Z D,Deng M,Chen K,Wang M,Zhang Q S,Zeng D.Development and evaluation of an ultralownoise sensor system for marine electric field measurements[J].Sensors and Actuators A:Physical,2014,213(7):70.
[6] Zai J Z,Fu Y B,Zai X R,Ji H W,Liu A,Chai F G.Fabrication of novel Ag/Ag Cl electrode pair on the template of carbon foam as marine electric field sensor and its electrochemical performances[J].Ionics,2017,23(8):2213.
[7] Brown R J C,Brewer P J,Brett D J L.Long-term equilibrium potential and electrochemical impedance study of Ag/Ag Cl electrodes used in Harned cell measurements of p H[J].Accreditation and Quality Assurance,2009,14(3):139.
[8] Brewer P J,Brown R J.Effect of structural design of silver/silver chloride electrodes on stability and response time and the implications for improved accuracy in p Hmeasurement[J].Sensors,2009,9(1):118.
[9] Yu Y,Zhang J,Liu J.Biomedical implementation of liquid metal ink as drawable ECG electrode and skin circuit[J].PLo S ONE,2013,8(3):e58771.
[10] Chen P.Study on Biosensors on Screen Printing Techniques[D].Changsha:Central South University,2013.1.(陈平.基于丝网印刷技术的生物传感器的研究[D].长沙:中南大学,2013.1.)
[11] Allen J B,Larry R F.Electrochemical Methods:Fundamentals and Applications[M].Beijing:Chemical Industry Press,2005.1.(阿伦·J·巴德,拉里·R·福克纳.电化学方法:原理与应用.第2版[M].北京:化学工业出版社,2005.1.)
[12] Xiang B,Su J,Li Y,Zhang S T,Hou B R.Research on the properties of an Ag/Ag Cl solid reference electrode[J].Chinese High Technology Letters,2006,16(12):1265.(向斌,粟京,李焰,张胜涛,侯保荣.Ag/Ag Cl固体参比电极性能研究[J].高技术通讯,2006,16(12):1265.)
[13] Zhang Y,Wang Y S,Song Y S.Preparation of steady solid Ag/Ag Cl electrode by Ag Cl nano-powders[J].Journal of Wuhan University of Technology,2008,30(9):32.(张燕,王源升,宋玉苏.纳米Ag Cl粉末制备高稳全固态Ag/Ag Cl电极[J].武汉理工大学学报,2008,30(9):32.)
[14] Ma Y F,Yang M L,Fang L Y,Li D Y.Electroanalytical chemistry of bismuth-based electrodes:composition,substrates and fabrication[J].Chinese Journal of Rare Metals,2019,43(4):428.(马颖菲,杨民力,方绿叶,李东阳.铋基电极的电分析化学:构成、载体与制备方法[J].稀有金属,2019,43(4):428.)
[15] Glanc M,Sophocleous M,Atkinson J K,García E.The effect on performance of fabrication parameter variations of thick-film screen printed silver/silver chloride potentiometric reference electrodes[J].Sensors and Actuators A:Physical,2013,197:1.
[16] Carrara S,Shumyantseva V V,Archakov A I,SamorìB.Screen-printed electrodes based on carbon nanotubes and cytochrome P450scc for highly sensitive cholesterol biosensors[J].Biosensors and Bioelectronics,2009,24(1):148.
[17] Hernández M,Galán C A,?lvarez G A,Ramírez M T,Páez M E,González J L.Behavior of two and three electrode configuration and different mediators inworking electrode on development of disposable screen-printing biosensors for determination of free cholesterol[J].Journal of the Mexican Chemical Society,2013,57(1):47.
[18] Idegami K,Chikae M,Nagatani N,Tamiya E,Takamura Y.Fabrication and characterization of planar screenprinted Ag/Ag Cl reference electrode for disposable sensor strip[J].Japanese Journal of Applied Physics,2010,49(9):097003.
[19] Shitanda I,Kiryu H,Itagaki M.Improvement in the long-term stability of screen-printed planar type solidstate Ag/Ag Cl reference electrode by introducing poly(dimethylsiloxane)liquid junction[J].Electrochimica Acta,2011,58:528.
[20] Atkinson J K,Glanc M,Boltryk P,Sophocleous M A,García E.An investigation into the effect of fabrication parameter variation on the characteristic of screen-printed thick-film silver/silver chloride reference electrodes[J].Microelectronics International,2011,28(2):49.
[21] Sophocleous M A,Glanc M,Atkinson J K,García E.An experimental analysis of thick-film solid-state reference electrodes[A].IEEE SENSORS 2012-Proceedings[C].Taipei,China:Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc.,2012:6411137.
[22] Shitanda I,Komoda M,Hoshi Y,Itagaki M.An instantly usable paper-based screen-printed solid-state KCl/Ag/Ag Cl reference electrode with long-term stability[J].Analyst,2015,140(19):6481.
[23] Musa A E,Campo F J,Abramova N,Alonso M A,Domínguez O,Arcos J,Brivio M,Snakenborg D,Geschke O,Kutter J P.Disposable miniaturized screenprinted p H and reference electrodes for potentiometric systems[J].Electroanalysis,2011,23(1):115.
[24] Silva E,Miserere S,Kubota L T,Merkoci A.Simple onplastic/paper inkjet-printed solid-state Ag/Ag Cl pseudoreference electrode[J].Analytical Chemistry,2014,86(21):10531.
[25] Jadav J K,Umrania V V,Rathod K J,Golakiya B A.Development of silver/carbon screen-printed electrode for rapid determination of vitamin C from fruit juices[J].LWT-Food Science and Technology,2018,88:152.
[26] Liao W Y,Chou T C.Fabrication of a planar-form screen-printed solid electrolyte modified Ag/Ag Cl reference electrode for application in a potentiometric biosensor[J].Analytical Chemistry,2006,78(12):4219.
[27] Zhang W Z,Zhang X K.Preparation and performance measurement of Ag/Ag Cl electrode[J].Journal of North China University of Science and Technology (Natural Science Edition),2016,38(3):53.(张雯昭,张新坤.Ag/Ag Cl电极的制备与性能测试[J].华北理工大学学报(自然科学版),2016,38(3):53.)
[28] Sophocleous M,Atkinson J K.A review of screen-printed silver/silver chloride(Ag/Ag Cl)reference electrodes potentially suitable for environmental potentiometric sensors[J].Sensors and Actuators A Physical,2017,267:106.
[29] Wei Y G,Cao Q X,Huang Y X,Wang Y P.Preparation and performance of Ag/Ag Cl electrode with low noise for marine electric field sensor[J].Journal of Synthetic Crystals,2009,(s1):394.(卫云鸽,曹全喜,黄云霞,王毓鹏.海洋电场传感器低噪声Ag/Ag Cl电极的制备及性能[J].人工晶体学报,2009,(s1):394.)
[30] Song Y S,Zhang K,Zuo P,Zhou L Q.Effect of sintering technology on ag/agcl electrode potential stability[J].Journal of Naval University of Engineering,2011,23(6):49.(宋玉苏,张坤,左攀,周立清.烧结工艺对Ag/Ag Cl电极电位稳定性的影响[J].海军工程大学学报,2011,23(6):49.)
[31] Brewer P J,Leach A S,Brown R J C.The role of the electrolyte in the fabrication of Ag|Ag Cl reference electrodes for p H measurement[J].Electrochimica Acta,2015,161:80.
[32] Brewer P J,Brown R J C.Effect of silver annealing conditions on the performance of electrolytic silver/silver chloride electrodes used in Harned cell measurements of p H[J].Sensors,2010,10(3):2202.
[33] Brown R J C,Milton M J T.The microporous structure of silver/silver chloride electrodes and the implications for Harned cell operation[J].Accreditation&Quality Assurance,2005,10(7):352.
[34] He L,Xu L K,Wang J T,Yin P F.Performance of Ag/Ag Cl reference electrode prepared by hot dip coating method[J].Corrosion Science and Protection Technology.2009,21(5):482.(何霖,许立坤,王均涛,尹鹏飞.热浸涂银/氯化银参比电极性能研究[J].腐蚀科学与防护技术,2009,21(5):482.)
[35] Yin P F,Hou W T,Xu L K,Wang J T,Xin Y L.Comparative study on Ag/Ag Cl and Ag/Ag X reference electrodes prepared by hot dip coating method[J].Corrosion Science and Protection Technology,2010,22(5):407.(尹鹏飞,侯文涛,许立坤,王均涛,辛永磊.热浸涂银/氯化银和银/卤化银参比电极对比研究[J].腐蚀科学与防护技术,2010,22(5):407.)
[36] Xin Y L,Xu L K,Yin P F,Wang J T,Li X B.Factors influencing potential stability of a solid Ag/Ag Cl reference electrode[J].Journal of Chinese Society for Corrosion and Protection,2013,33(3):231.(辛永磊,许立坤,尹鹏飞,王均涛,李相波.全固态Ag/Ag Cl参比电极电位稳定性的影响因素[J].中国腐蚀与防护学报,2013,33(3):231.)
[37] Yin P F,Xu L K.Life evaluation of Ag/Ag Cl reference electrode[J].Total Corrosion Control,2014,(2):68.(尹鹏飞,许立坤.银/氯化银参比电极寿命评价[J].全面腐蚀控制,2014,(2):68.)
[38] Wang Y Q.Application of screen printed electrodes on electrochemical biosensors[J].Screen Printing Industry,2018,3:50.(王永秋.丝网印刷电极在电化学生物传感器上的应用研究[J].网印工业,2018,3:50.)
[39] Sinha S K,Noh Y,Rrljin N,Treich G M,Hajeb S,Guo Y,Chon K H,Sotzing G A.Screen printed PEDOT:PSS electrodes on commercial finished textiles for electrocardiography[J].ACS Applied Materials and Interfaces,2017,9(43):37524.
[40] Zhou W,Liu W,Qiu Q F,Liu R L,Jiang L L,Song R.Development,fabrication,and application of biomedical electrodes[J].Chinese Science Bulletin,2015(15):1352.(周伟,刘伟,邱清富,刘瑞亮,蒋乐伦,宋嵘.生物医用电极制造技术及应用研究进展[J].科学通报,2015(15):1352.)
[41] Qin L D,Li M Z,Li G L,Duan Y W.Preparation and evaluation of flexible silver-silver chloride EEG electrodes[J].Journal of Analytical Science,2016,32(4):445.(秦路丹,李明哲,李广利,段晏文.银-氯化银柔性脑电电极的制备及其评价[J].分析科学学报,2016,32(4):445.)
[42] Chi Y M,Jung T P,Cauwenberghs G.Dry-contact and noncontact biopotential electrodes:methodological review[J].IEEE Reviews in Biomedical Engineering,2010,3:106.
[43] Spinelli E,Haberman M.Insulating electrodes:a review on biopotential front ends for dielectric skin-electrode interfaces[J].Physiological Measurement,2010,31(10):S183.
[44] Bodenstein M,David M,Markstaller K.Principles of electrical impedance tomography and its clinical application[J].Critical Care Medicine,2009,37(2):713.
[45] Windmiller J R,Wang J.Wearable electrochemical sensors and biosensors:a review[J].Electroanalysis,2013,25(1):29.
[46] Marozas V,Petrenas A,Daukantas S,Lukosevicius A.A comparison of conductive textile-based and silver/silver chloride gel electrodes in exercise electrocardiogram recordings[J].Journal of Electrocardiology,2011,44(2):189.
[47] Liu R,Wang X H,Zhou Z Y.Application of MEMS microneedles array in biomedicine[J].Journal of Biomedical Engineering,2004,21(3):482.(刘冉,王晓浩,周兆英.MEMS微针阵列及其在生物医学上的应用[J].生物医学工程学杂志,2004,21(3):482.)
[48] Márquez J C,Seoane F,V?lim?ki E,Lindecrantz K.Comparison of dry-textile electrodes for electrical bioimpedance spectroscopy measurements[J].Journal of Physics:Conference Series,2010,224(1):012140.
[49] Chikae M,Fukuda T,Kerman K,Idegami K,Miura Y,Tamiya E.Amyloid-βdetection with saccharide immobilized gold nanoparticle on carbon electrode[J].Bioelectrochemistry,2008,74(1):118.
[50] Ahmed M U,Idegami K,Chikae M,Kerman K,Chaumpluk P,Yamamura S,Tamiya E.Electrochemical DNA biosensor using a disposable electrochemical printed(DEP)chip for the detection of SNPs from unpurified PCR amplicons[J].The Analyst,2007,132(5):431.