锅炉燃烧系统鲁棒控制研究
恒庆海,鲁婧,周海,路阳
(北京信息科技大学 自动化学院,北京,100192)
摘 要:
火电厂锅炉燃烧过程中,主蒸汽压力控制系统的H∞混合灵敏度鲁棒控制问题进行研究。在工况大范围变化时,该被控对象模型有很大的变化。为了解决1常规的H∞鲁棒性能设计不能保证系统具有较好性能,且在系统运行初期有高频振荡和控制量超出正常工作范围的问题,提出通过修改不确定性权函数和性能权函数,可以进行H∞鲁棒控制方法设计,给出不确定性权函数和性能权函数的选择方法。进行改进的H∞混合灵敏度鲁棒控制器设计,求解H∞混合灵敏度鲁棒PI控制器。仿真结果表明,设计的控制系统具有较好的鲁棒性能。
关键词:
中图分类号:TP273 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2011)S1-0213-06
Robust control of a boiler combustion system
HENG Qing-hai, LU Jing, ZHOU Hai, LU Yang
(School of Automation, Beijing Information Science and Technology University, Beijing 100192, China)
Abstract: The design of H∞ robust performance of a boiler combustion system with the perturbations of the controlled members was presented. It can be used to solve H∞ robustness problems, which can’t be done by the conventional H∞ robust performance designs. In the initial stage of system operation, high frequency oscillation and large amplitude of output and control variable of the control system are exhibited by a conventional H∞ robust performance design method. It is pointed out that the design of the robust performance can be formulated as an optimization H∞ mixed sensitivity method, if the uncertainty weighting function and the performance weighting function are revised appropriately. The selections of the weighting functions are studied and the optimization H∞ mixed sensitivity robust PI controller is solved. The simulation results show that the proposed method is valid. The realization of the controllers doesn’t involve extra cost to the control equipment in existence.
Key words: H∞ mixed sensitivity; robust control; weighting function; boiler combustion system
对锅炉燃烧控制系统这样重要的设备,为了确保高效、准确、安全、稳定生产,锅炉燃烧的控制就显得更加重要[1-2]。锅炉燃烧系统被控对象不可避免的存在延迟摄动,鲁棒控制理论在一定范围内可有效解决摄动系统的鲁棒控制器设计问题[3-15]。常规的H∞鲁棒控制方法虽然能满足一些鲁棒性能指标,但其设计的锅炉燃烧控制系统在运行初期有高频振荡和控制量超出正常工作范围的问题[1],工程中难以实现。常规PID控制方法虽然结构简单、稳定性好、工作可靠、调整方便,但并不能完善而有效地解决系统的鲁棒性能问题。这个问题阻碍着所设计系统安全性和可靠性的提高。所以如果不改变现有锅炉燃烧控制系统鲁棒性能设计观念、理论和方法,很难解决这个问题。本文作者给出锅炉燃烧系统H∞鲁棒PID控制器设计方法及其求解方法。提出了通过修改不确定性权函数和性能权函数,可以进行H∞方法设计。给出了不确定性权函数和性能权函数的选择方法。进行了改进的H∞混合灵敏度鲁棒控制器设计,求解了H∞混合灵敏度鲁棒PI控制器,与常规PID控制器相比,具有较好的控制品质和鲁棒性,且具有结构简单、明确、实用等优 点。对锅炉燃烧系统设计结果进行的仿真表明,本文作者的设计方法是有效的。提高了锅炉燃烧系统对被控对象摄动时的鲁棒性,由于考虑到了串级系统的特点,求解简单、明了,并且不需要增加现有控制设备的投资。
1 锅炉燃烧控制问题
锅炉燃烧闭环系统形式[1]如图1所示。图中K1(s)和K2(s)分别为内控制器(燃烧率调节器)和主控制器(主蒸汽压力调节器),G1(s)和G2(s)分别为导前区(燃烧率)及惰性区(主蒸汽压力)被控对象的传递函数。r为参考输入,u1和u2分别为燃烧率调节器输出和主蒸汽压力调节器输出。
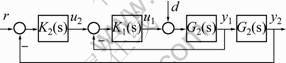
图1 锅炉燃烧控制系统
Fig.1 Boiler combustion control system
![]() (1)
(1)
![]() (2)
(2)
从式(1)和(2)可以看出:导前区与惰性区都存在相应的延迟,而且惰性区延迟是导前区延迟的6倍以上。
本文的设计问题是寻找鲁棒P控制器K1(s)和 H∞混合灵敏度鲁棒PI控制器K2(s),使得系统在 延迟摄动时仍具有较好的性能,即要求保证鲁棒性 能。
为便于设计结果比较,本文给出文献[1]常规H∞混合灵敏度的设计结果:
K1=69.65 (3)
![]() (4)
(4)
2 锅炉燃烧控制问题内控制器参数的整定
因为串级控制系统内、主回路带宽相差较大,所以内、主回路控制器参数可以按单回路分别来整定。
内回路可用临界比例带法设计,得比例(P)控制器为:
K1=42.499 8 (5)
3 锅炉燃烧控制问题的H∞鲁棒PI控制器设计
3.1 主控制器参数的整定
锅炉燃烧系统主回路设计框图如图2所示。可用H∞混合灵敏度方法进行鲁棒性能设计[13]。

图2 主回路H∞混合灵敏度
Fig.2 Main loop for H∞ mixed sensitivity design
根据文献[13],设计是求解稳定的控制器使
![]() (6)
(6)
![]() (7)
(7)
![]() (8)
(8)
实际上简单求
![]() (9)
(9)
即可[13]。式(9)可用于PID控制器参数寻优。
其中:WP和WI分别为性能和不确定性权函数。
根据式(2),其名义对象(标称对象)可取为:
![]() (10)
(10)
根据H∞控制理论,可取乘性不确定性权函数
![]() (11)
(11)
性能权函数可选取为:
![]() (12)
(12)
设所求主回路PI控制器的形式为:
![]() (13)
(13)
对锅炉燃烧主回路采用H∞混合灵敏度指标设计。将式(13)代入式(9),并采用单纯形调优法。求解式(9),得主回路次最优H∞鲁棒PI控制器:
![]() (14)
(14)
3.2 仿真研究
为了检验本文设计方法的有效性,对锅炉燃烧控制系统的系统响应进行了仿真。r作单位阶跃变化、d作0.1单位阶跃变化时系统输出y1响应曲线见图3。r作单位阶跃变化、d作0.1单位阶跃变化时输出y2响应曲线见图4。r作单位阶跃变化、d作0.1单位阶跃变化时控制输出u1响应曲线见图5。r作单位阶跃变化、d作0.1单位阶跃变化时控制输出u2响应曲线见图6。图3~6中,曲线1对应于本文设计的控制器式(5)和式(14)。曲线2对应于文献[1]设计的控制器式(3)和式(4)。
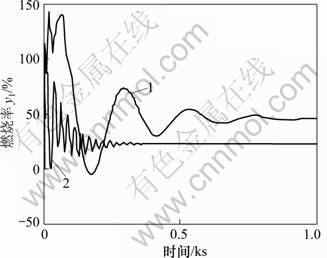
图3 系统输出y1(燃烧率)
Fig.3 System responses y1 (combustion rate)
图3所示为系统输出y1(燃烧率)。从图3可以看出:当主蒸汽压力发生阶跃变化时,文献[1]组成的锅炉燃烧控制系统稳态时燃烧率较低;且在刚开始变化时,有明显的振荡,燃烧率最大值甚至超过100%,在现实中很难采用。采用控制器式(5)和式(14)设计的系统,虽然能解决刚开始变化时,有明显振荡的问题;但刚开始变化时,幅值较大,在现实中较难采用。
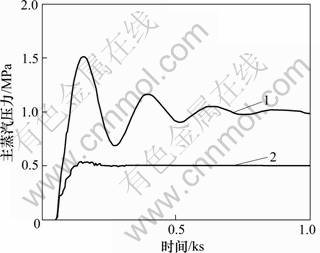
图4 系统输出y2 (主蒸汽压力)
Fig.4 System responses y2 (main steam pressure)
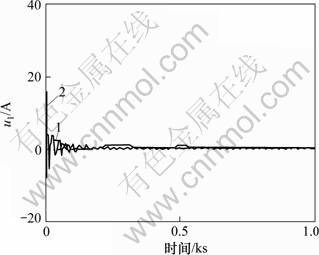
图5 燃烧率调节器输出u1
Fig.5 Control laws u1
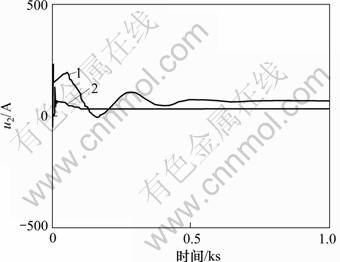
图6 主蒸汽压力调节器输出u2
Fig.6 Control laws u2
图4所示为系统输出y2。从图4可以看出:当主蒸汽压力发生阶跃变化时,文献[1]组成的锅炉燃烧控制系统,输出的稳态值为0.5,不是1。采用控制器式(5)和(14)设计的系统,虽然能解决输出的稳态值为 1的问题;但超调量较大,在现实中较难采用。
图5所示为燃烧率调节器输出u1。从图5可以看出:当主蒸汽压力发生阶跃变化时,文献[1]组成的锅炉燃烧控制系统,燃烧率调节器输出u1的幅值达到30 A以上;且在刚开始变化时,有明显的振荡,在现实中很难采用。采用控制器式(5)、式(14)设计的系统性能较好。
图6所示为主蒸汽压力调节器输出u2。从图6可以看出:当主蒸汽压力发生阶跃变化时,文献[1]组成的锅炉燃烧控制系统,主蒸汽压力调节器输出u2的幅值达到0.4 A以上;且在刚开始变化时,有振荡现象,在现实中很难采用。采用控制器式(5)和(14)设计的系统,性能较好。
由图3~6可以看出:文献[1]组成的锅炉燃烧控制系统,其性能较差,现实中不能使用。采用控制器式(5)和(14)设计的系统,虽然性能较文献[1]的性能好,但应用于实际工程,效果不好。因此,需要对控制器式(5)和(14)的H∞鲁棒PI控制器设计方法进行改进。
4 锅炉燃烧控制问题的改进H∞鲁棒PI控制器设计
4.1 主控制器参数的整定
根据H∞控制理论和鲁棒控制指标,可修改乘性不确定性权函数为:
![]() (15)
(15)
修改性能权函数可选取为:
![]() (16)
(16)
设所求主回路PI控制器的形式为:
![]() (17)
(17)
对锅炉燃烧主回路采用改进H∞混合灵敏度指标设计。将式(17)代入式(7),并采用单纯形调优法。求解式(7),得主回路次最优H∞鲁棒PI控制器
![]() (18)
(18)
4.2 仿真研究
为了检验本文改进H∞混合灵敏度设计方法的有效性,对锅炉燃烧控制系统的系统响应进行了仿真。r作单位阶跃变化、d作0.1单位阶跃变化时系统输出y1响应曲线见图7。r作单位阶跃变化、d作0.1单位阶跃变化时输出y2响应曲线见图8。r作单位阶跃变化、d作0.1单位阶跃变化时控制输出u1响应曲线见图9。r作单位阶跃变化、d作0.1单位阶跃变化时控制输出u2响应曲线见图10。
其中,曲线1对应于本文改进H∞混合灵敏度设计的控制器式(5)和(18)。曲线2对应于文献[1]设计的控制器式(3)和(4)。
图7所示为系统输出y1(燃烧率)。从图7可以看出:当主蒸汽压力发生阶跃变化时,文献[1]组成的锅炉燃烧控制系统稳态时燃烧率较低;且在刚开始变化时,有明显的振荡,燃烧率最大值甚至超过100%。在现实中很难采用。改进H∞混合灵敏度设计组成的锅炉燃烧控制系统鲁棒性能较好。
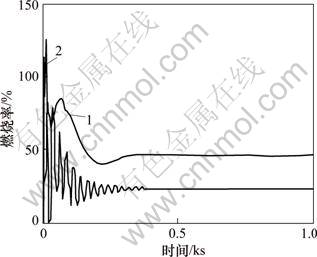
图7 燃烧率y1
Fig.7 System responses y1 (combustion rate)
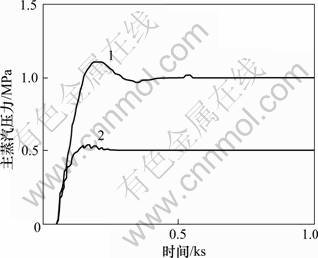
图8 系统输出y2(主蒸汽压力)
Fig.8 System responses y2 (main steam pressure)
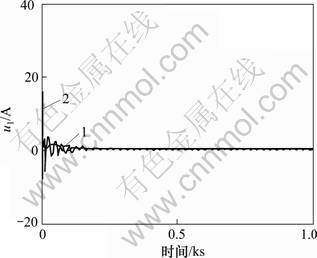
图9 燃烧率调节器输出u1
Fig.9 Control laws u1
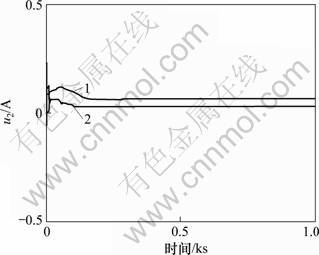
图10 主蒸汽压力调节器输出u2
Fig.10 Control laws u2
图8所示为系统输出y2。从图8可以看出:当主蒸汽压力发生阶跃变化时,文献[1]组成的锅炉燃烧控制系统,输出的稳态值为0.5,不是1,在现实中很难采用。改进H∞混合灵敏度设计组成的锅炉燃烧控制系统鲁棒性能较好。
图9所示为燃烧率调节器输出u1。从图9可以看出:当主蒸汽压力发生阶跃变化时,文献[1]组成的锅炉燃烧控制系统,燃烧率调节器输出u1的幅值达到 30 A以上;且在刚开始变化时,有明显的振荡,在现实中很难采用。改进H∞混合灵敏度设计组成的锅炉燃烧控制系统鲁棒性能较好。
图10所示为主蒸汽压力调节器输出u2。从图10可以看出:当主蒸汽压力发生阶跃变化时,文献[1]组成的锅炉燃烧控制系统,主蒸汽压力调节器输出u2的幅值达到0.4 A以上;且在刚开始变化时,有振荡现象,在现实中很难采用。改进H∞混合灵敏度设计组成的锅炉燃烧控制系统鲁棒性能较好。
由图7~10可以看出:本文提出的改进H∞混合灵敏度设计的锅炉燃烧系统鲁棒PI控制方法,设计所得系统具有较好的鲁棒性能,仿真结果证实了其有效性。且由于采用的是PI控制器,因此不需要增加现有设备的投资。
5 结论
对常规H∞鲁棒性能设计不能保证系统具有较好性能问题,提出了锅炉燃烧系统改进H∞鲁棒PI控制概念。给出了改进H∞混合灵敏度PI鲁棒控制器求解的一种设计方法。对具有大延迟的锅炉燃烧系统进行了改进H∞鲁棒PI控制器设计,所得系统具有较好的鲁棒性。提出的设计方法和步骤,对一般串级控制系统的H∞鲁棒PI控制器设计具有参考意义。
参考文献:
[1] Chen L J, Xue H. H∞ robust control of combustion based on the radiant energy signal[J]. Control and Instruments in Chemical Industry, 2010, 37 (10): 14-17.
[2] Keshav S. Feedback combustion control using chemi-ionization probe in supersonic flow of combustion products[J]. Journal of Propulsion and Power, 2010, 26(1): 67-73.
[3] Ian P, Turner Matthew C, Herrmann G. Robust control applications[J]. Annual Reviews in Control, 2007, 31(1): 27-39.
[4] KIM J H, OH D C. Robust and non-fragile H∞ control for descriptor systems with parameter uncertainties and time delay[J]. International Journal of Control, Automation and Systems, 2007, 5(1): 8-14.
[5] Kim J M, Park J B, Choi Y H. Non-fragile guaranteed cost control of time-delayed uncertain systems[C]//Proceedings of ICCAS 2007-International Conference on Control, Automation and Systems. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2007: 1651-1655.
[6] Kim J K, Lim D H, Kim W K. Stability condition of robust and non-fragile H∞ hovering control with real-time tuning available fuzzy compensator [J]. International Journal of Control, Automation and Systems, 2007, 5(4): 364-371.
[7] Oya H, Hagino K. Trajectory-based design of robust non-fragile controllers for a class of uncertain linear continuous-time systems[J]. International Journal of Control, 2007, 80(12): 1849-1862.
[8] Patre B M, Deore P J. Robust stability and performance for interval process plants[J]. ISA Transactions, 2007, 46(3): 343-349.
[9] Keviczky L, Banyasz C. Robust stability and performance of time-delay control systems[J]. ISA Transactions, 2007, 46(2): 233-237.
[10] Daniel M A, Niculescu S I. Computing non-fragile PI controllers for delay models of TCP/AQM networks[J]. International Journal of Control, 2009, 82(12): 2249-2259.
[11] HENG Qing-hai, LU Jing. The selections of nominal plant and weighting functions for robust control design[C]// Proceedings of the 8th World Congress on Intelligent Control and Automation. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2010: 771-775.
[12] HENG Qing-hai, LU Jing. Non-fragile robust control for a paper basis weight control system[C]//Proceedings of the 8th World Congress on Intelligent Control and Automation. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2010: 781-784.
[13] HENG Qing-hai, LU Jing. H∞ non-fragile robust controller and its application to the paper basis weight control[C]//Proceedings of the 29th Chinese Control Conference. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2010: 1939-1942.
[14] Zotov M G. An approach to robust control design[J]. Automation and Remote Control, 2010, 71(11): 2395-2404.
[15] HENG Qing-hai, LU Jing. Non-fragile robust multi-performance optimization design for control system of heating furnace[J]. Journal of Central South University: Science and Technology, 2009, 40(S1): 164-168.
(编辑 陈爱华)
收稿日期:2011-04-15;修回日期:2011-06-15
通信作者:恒庆海(1964-),男,天津人,博士,教授,从事鲁棒控制和热工过程控制系统研究;电话:13051730929;E-mail:qhheng@126.com
摘要:对具有大延迟的火电厂锅炉燃烧过程中,主蒸汽压力控制系统的H∞混合灵敏度鲁棒控制问题进行研究。在工况大范围变化时,该被控对象模型有很大的变化。为了解决1常规的H∞鲁棒性能设计不能保证系统具有较好性能,且在系统运行初期有高频振荡和控制量超出正常工作范围的问题,提出通过修改不确定性权函数和性能权函数,可以进行H∞鲁棒控制方法设计,给出不确定性权函数和性能权函数的选择方法。进行改进的H∞混合灵敏度鲁棒控制器设计,求解H∞混合灵敏度鲁棒PI控制器。仿真结果表明,设计的控制系统具有较好的鲁棒性能。


