
Preparation and dielectric properties of compositionally graded (Ba,Sr)TiO3 thin film by sol-gel technique
ZHANG Tian-jin(章天金), WANG Jun(王 军), ZHANG Bai-shun(张柏顺),
WANG Jin-zhao(王今朝), WAN Neng(万 能), HU Lan(胡 兰)
Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Hubei University, Wuhan 430062, China
Received 10 April 2006; accepted 25 April 2006
Abstract:
Compositional graded BaxSr1-xTiO3 (x=0.6, 0.7, 0.8, 0.9, 1.0) (BST) thin films (less than 400 nm) were fabricated on Si and Pt/Ti/SiO2/Si substrates by sol-gel technique. A special heating treatment was employed to form the uniform composition gradients at 700 ℃. The microstructures of the films were studied by means of X-ray diffraction, atomic force microscope and field emission scanning electron microscopy. The results show that the films have uniform and crack-free surface morphology with perovskite structure phase. The small signal dielectric constant (εr) and dielectric loss (tan δ) are found to be 335 and 0.045 at room temperature and 200 kHz. The dielectric properties change significantly with applied dc bias, and the graded thin film show high tunability of 42.3% at an applied field of 250 kV/cm. All the results indicate that the graded BST thin films prepared by sol-gel technique have a promising candidate for microelectronic device.
Key words:
compositional gradient; sol-gel technique; microstructure; dielectric constant; tunability;
1 Introduction
Thin films of perovskite-type titanates, such as BaTiO3 and BaxSr1-xTiO3 (BST), are used widely on a variety of integrated devices, such as dynamic random acess memory (DRAM), decoupling capacitors, pyroelectric infrared (IR) sensors and piezoelectric microactuators [1-5]. BST thin films were produced by a variety of thin film deposition techniques including sputtering, laser ablation, MOCVD and sol-gel. However, using most of the above techniques, it is difficult to fabricate homogeneous films on a large substrate. In contrast, the sol-gel technique has the advantage of large-area deposition in addition to low cost and convenience in process control.
Recently, the attention of researchers has been focused on compositionally graded ferroelectric thin films. These multilayer film systems consist of smooth chemical composition gradients normal to the substrate. Such films have been reported to exhibit new properties not observed in conventional ferroelectric materials (uniform of hetero-structure) [6-8]. This heterogeneous system possesses internal stressed and polarization gradients, which may help to improve the tenability. Among these graded thin films mentioned above, there exist some problems in integrating the films with conventional IC processing, because the graded thin films should be reheated at different temperatures between 800 and 1 000 ℃ for 10-30 min. The high treating temperature for the graded thin films will deteriorate the quality of the films due to the strong diffusion between the thin films and the substrate. What is worse, the heat treating above 800 ℃ will damage the structure of the bottom electrode.
In this research work, BaxSr1-xTiO3 (BST) thin films with a compositional gradient of x=0.6 to 1 (in 0.1 mole fraction increments) were fabricated on Si and Pt/Ti/SiO2/Si substrates using modified sol-gel technique, and the emphasis was focused on structure, surface morphology and dielectric characterization.
2 ExperimentalThe precursor solutions for the BST were prepared by sol-gel method using barium acetate (Ba(CH3COO)2),strontium acetate (Sr(CH3COO)2) and titanium (IV) isopropoxide (Ti(C4H9O)4) as starting materials. Appropriate amounts of barium acetate and strontium acetate were mixed in heated glacial acetic acid and the solution was stirred until all the particles were dissolved. Then, a stoichiometric amount of titanium (IV) isopropoxide was dissolved in 2-methoxyethanol and added to the solution while stirring. Stirring was continued more than one hour. The dust and other suspended particles were removed by filtering the solution. Finally, five solution in the mole ratio of Ba∶Sr=60∶40, 70∶30, 80∶20, 90∶10, 100∶ 0 were obtained.
Thin films were fabricated on clean Si and Pt/Ti/SiO2/Si substrates by a multilayer spin-coating technique at 4 000 r/min for 30 s. Graded BST thin films were formed by sequentially depositing two layers of each composition onto the substrates. The process and ideally final configuration of the graded thin film is shown in Fig.1. It indicates the structure evolution of the BST thin film before (see the left part) and after (see the right part) heat treatment, the multilayer thin film will be transformed into uniform compositional gradient of barium an strontium.
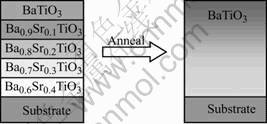
Fig.1 Schematic diagram of BST graded thin film (As- deposited thin film structure (left) and configuration model after heat treatment (right))
A special heating procedure was employed to form the compositional gradient thin films. For each spun-on coating, the as-deposited BST thin films were heated at 400 ℃ for 15 min to evaporate the organic solvent in the precursors by rapidly thermal annealing. After we deposited each composition, we heated the films at 600 ℃ for 5 min by rapidly thermal annealing. This process repeated five times. Then the BST films were annealed at 700 ℃ for 1.5 h in oxygen atmosphere for crystalli- zation by conventional heating process. In order to gain the crack-free films, an additional pre-annealing was used at 600 ℃ for 30 min in the furnace. A key issue in the formation of the smooth composition gradients was based on the long time annealing, which are responsible for the formation of composition gradients.
The film crystal structure was examined using X-ray diffraction (XRD) with Cu Kα radiation. The surface morphology of the graded film was quantified using an atomic force microscope(AFM) and field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM). To study the dielectric properties, 0.3 mm diameter Pt circular electrodes were deposited through a shadow mask to form a metal-ferroelectric-metal(MFM) configuration. The bottom Pt electric was exposed by etching a small portion of the film using dilute hydrofluoric acid. The dielectric propertied were measured using a Hewlett-Packard 4292A impedance/ gain phase analyzer.
3 Results and discussionFig.2 shows the glancing incidence X-ray diffraction pattern of the compositionally graded BST thin film and two uniform single composition films annealed at 700 ℃. It indicates a pseudo-cubic or perovskite phase without preferred orientation. The splitting peaks of the uniform composition are not observed, and the peaks of the graded film are broadened. In order to discuss furtherly, the (110) peaks of the three samples were chosen to investigate the crystalline phase evolution. As shown in the inset, the peak of the graded thin film is between the peak of BaTiO3 and Ba0.6Sr0.4TiO3. The XRD results indicate that uniform composition gradient is formed in the graded BST film using our process.
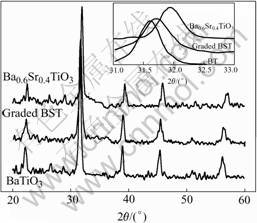
Fig.2 XRD patterns of single and graded BST thin film deposited on Si substrate (Inset is (110) peak of three films)
The surface morphology and grain structure of the graded thin film was analyzed using an atomic force microscope(AFM) and a scanning electron microscope (SEM). Fig.3 shows the AFM and SEM micrographs of the graded film. The graded film consists of a fully grown and crack-free grain structure. The approximate average grain size determined from the SEM is about 80 nm. The surface roughness of the film was estimated to be 5.6 nm by the AFM analysis. The grain size of the graded film is larger than the reported grain size [9]. Due to the present of larger grains, a relatively higher roughness was observed.
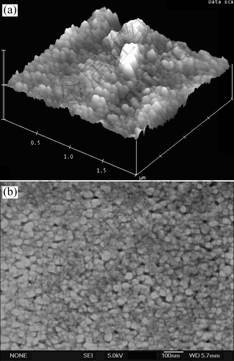
Fig.3 Surface morphologies of compositionally graded BST thin film: (a) Atomic force microcopy of 3-D surface; (b) SEM image
The dielectric properties of the films were measured using a capacitor configuration with the bottom Pt and top Pt electrodes at room temperature. The variations in the dielectric constant and loss factors with the frequency of the film are shown in Fig.4. It is seen that the dielectric constant of the graded film decreases with a power law in the frequency range below 1 kHz. This may be ascribed to the effects of space-charge polarization or Maxwell-Wagner type interfacial polarization[10]. The space-charge polarization inherently relates to non- uniform charge accumulation and the multi-interfaces within the graded films. In the high frequency region (1 kHz-1 MHz), the dielectric constant and dielectric loss almost slightly decreases and shows no noticeable dispersion with frequency.
The dc field dependence of capacitance and dielectric loss were measured at room temperature and 1 MHz to evaluate the tenability of the graded BST thin film. Fig.5 shows variation of capacitance and dielectric loss with voltage. The dielectric properties change significantly with de bias field. The tenability of the dielectric constant was calculated in terms of parameter ?C/C0, where ?C is the change in capacitance relative to zero bias capacitance C0. As expected, the tunability increases with the increasing electric field and a high
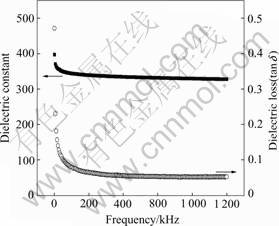
Fig. 4 Variation of dielectric constant and dielectric loss with frequency of graded BST thin film at room temperature
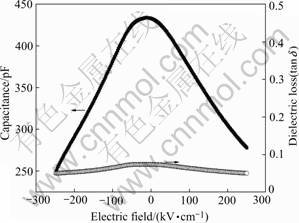
Fig.5 Variation of capacitance and dielectric loss with electric field at room temperature (at 1 MHz)
tunability of 42.3% can be obtained at an applied electric field of 250 kV/cm. The compositionally heterogeneous nature of our thin film and the presence of internal stress may have influence on improving the dielectric tenability[6]. However, the exact reason for the higher tunability and electric field distribution in graded BST film was not discussed. These results suggest that graded BST thin films are candidate to be developed as tunable microwave elements and integrated capacitors.
4 ConclusionsFerroelectric compositionally graded BST thin film with good crystalline structure and surface morphology is successfully fabricated using a modified sol-gel technique at 700 ℃. A significant dc field dependence of dielectric properties is observed which may due to the highly heterogeneous nature of the graded thin film and the presence of internal stress in the film. High dielectric tunability of 42.3% is achieved under an applied field of 250 kV/cm. The compositionally graded BST thin films by sol-gel technique have a promising candidate for microelectronic device.
References[1] CHEN B, YANG H, ZHAO L, MIAO J, XU B, QIU X G, ZHAO B R, QI X Y, DUAN X F. Thickness and dielectric constant of dead layer in Pt/Ba0.7Sr0.3TiO3 /YBa2Cu3O7-x capacitor [J]. Appl Phys Lett, 2004, 84(4): 583-585.
[2] PARK W Y, HWANG C S. Film-thickness-dependent curie-weiss behavior of Ba, Sr TiO3 thin-film capacitors having Pt electrodes [J]. Appl Phys Lett, 2004, 85(22): 5313-5315.
[3] JIN F, AUNER G W, NAIK R, SCHUBRING N W, MANTESE J V, CATALAN A B, MICHELI A L. Giant effective pyroelectric coefficients from graded ferroelectric devices [J]. Appl Phys Lett, 1998, 73(19): 2838-2840.
[4] ZAFAR S, JONES R E, JIANG B, WHITE B, KAUSHIK V, GILLESPIE S. The electronic conduction mechanism in barium strontium titanate thin films [J]. Appl Phys Lett, 1998, 73(24): 3533-3535.
[5] COLE M W, GEYER R G. The dependence of dielectric properties on compositional variation for tunable device applications [J]. Mech Mater, 2004, 36:1017-1026.
[6] ADIKARY S U, CHAN H L W. compositionally graded BaxSr1-xTiO3 thin films for tunable microwave applications [J]. Mater Chem Phys, 2003, 79: 157-160.
[7] ZHAI J, CHEN H. Nonlinear behaviors of the compositionally graded (Ba, Sr)TiO3 thin films derived by a sol-gel process [J]. Appl Phys Lett, 2004, 84(7): 1162-1164.
[8] TIAN H Y, CHAN H L W, CHOY C L, NO K S. The effects of composition gradients of BaxSr1-xTiO3 thin films on their microstructures, dielectric and optical properties [J]. Mat Sci Eng B, 2003,103: 246-252.
[9] WU Di, LI Ai-dong, LIU Zhi-guo, LING Hui-qin, GE Chuan-zhen, LIU Xiao-yong, WANG Hong, WANG Min, L? Peng, MING Nai-ben. Fabrication and electrical properties of sol-gel derived (Ba, Sr)TiO3 thin films with metallic LaNiO3 electrode [J]. Thin Solid Films, 1998, 336: 172-175.
[10] ZHU X, LU S, CHAN H L W, CHOY C L, WONG K H. Microstructures and dielectric properties of compositionally graded (Ba1-xSrx)TiO3 thin films prepared by pulsed laser deposition [J]. Appl Phys A, 2003, 76: 225-229.
Foundation item: Project(50372017/E0204) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project (2004ABA094) supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Hubei Province; Project supported by the Innovation Team Foundation of Education Bureau of Hubei Province, China
Corresponding author: ZHANG Tian-jin; Tel: +86-27-88661682; E-mail: zhangtj@hubu.edu.cn


