DOI:10.19476/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2018.06.08
基于电化学模型的锂空气电池仿真
杜双龙1,赖延清1,贾明1,程壮1,艾立华2,艾亮2
(1. 中南大学 冶金与环境学院,长沙 410000;
2. 湖南艾华集团股份有限公司,益阳 413000)
摘 要:基于COMSOL仿真平台,建立一维电化学模型,研究放电电流密度、氧气浓度、氧气扩散速率以及Li+扩散系数等因素对电池性能影响。结果表明:当放电电流密度从0.05 mA/cm2增大到0.5 mA/cm2时,锂空气电池的放电比容量由1256.4 mA·h/g下降到139.2 mA·h/g;在放电电流密度为0.1mA/cm2条件下,外界氧气浓度从4.73 mol/m3增加到18.92 mol/m3时,电池比容量从371.2 mA·h/g增加到1274.5 mA·h/g,表明提高外部环境的氧气浓度有助于提高电池比容量;氧气扩散速率为电池反应的速度控制步骤。当氧气扩散系数从3.5×10-10 m2/s 提高到7×10-9 m2/s时,电池的容量从373.0 mA·h/g增加到2352.1 mA·h/g;而提高Li+的扩散系数对电池的比容量几乎没有影响。
关键词:锂空气电池;电流密度;氧气浓度;扩散系数;数值仿真
文章编号:1004-0609(2018)-06-1143-08 中图分类号:TM911 文献标志码:A
近几年电动汽车的发展受到了人们的广泛关注,但是受限于锂离子电池比容量的限制,电动汽车的续航里程仍远远低于内燃机车[1]。因此,开发出新一代的高比容量储能体系对电动汽车有着重要意义。锂空气电池由于其超高理论比容量被视为是未来电动汽车的理想储能装置,已经受到各国研究者的广泛关注。但是由于放电产物Li2O2会沉积在多孔阴极的孔隙之内造成孔隙阻塞,阻断氧气与Li+接触,导致放电终止,对其的研究只能停滞在实验室阶段[2-3]。
不同于锂离子电池,锂空气电池是使用金属锂作为电池阳极,阴极反应物为空气中的氧气。由于来自外部的氧气可以不计入电池的质量,以Li2O2为唯一放电产物时,其理论比容量可达11000 W·h/kg[4-6]。基于电解质状态的不同,锂空气电池可以分为有机电解质体系、水系电解质体系、混合体系和全固态电解质体系。BARDENHAGEN等[7]使用XPS手段研究了锂空气电池正极内部在电极深度方向上反应产物的分布情况,结果表明,孔隙中由于氧气浓度存在,生成产物将附着正孔隙壁面上,并且生成位置首先集中在电极的顶部与底部;XU等[8]研究发现,锂空气电池正极上的催化剂对电池性能也有很大的影响,主要反映在提高电池的循环性能和电池容量以及降低电池充电电压三方面,这点与FREUNBERGER等[9]的研究成果类似。锂空气电池的放电容量在很大程度上取决于放电产物Li2O2的累积,所以可以通过控制催化剂的种类从而影响放电产物中Li2CO3与Li2O2的比例,提高放电产物中Li2O2所占的比例从而达到提高电池的循环性能[10]。其次,研究发现使用催化剂非均匀填充的空气电极比均匀填充电极得到的电池放电容量要更高[11]。
随着计算机水平的发展,仿真技术在传统电池研究领域也发挥了重要作用,建立数值模型研究电池,能够有效缩短设计周期,节约时间和成本[12-16],近年来在新型储能锂空气电池上也得到了广泛应用[17-20]。ALLEN等[11]基于二元电解质浓溶液理论,建立锂空气电池数值模型,模型考虑了电池系统时间与空间尺度物料传输的变化以及Li2O2膜的增长情况;研究表明,锂空气电池的容量发挥与放电电压不仅与氧气浓度相关,还与正极孔隙率有关。SAHAPATSOMBUT等[18]在前面一维模型研究的基础上,研究循环过程中的容量衰减,生成产物中考虑了Li2O2和Li2CO3的生成反应,其研究表明,锂空气电池的容量衰减来源于循环过程中反应产物的不断沉积。为进一步研究氧气浓度对锂空气电池的影响,SAHAPATSOMBUT等[19]比较了空气与纯氧气对锂空气电池的影响;结果表明,相比于纯氧环境,在电流密度为0.05 mA/cm2情况下,锂空气电池在空气环境中电池容量将由1240 mA·h/g下降到226 mA·h/g,采用一种具有氧气选择性膜,可以提升电池容量。LI[20]基于电化学模型与流体力学的耦合研究了颗粒粒径对电池容量的影响。综前所述,Li2O2产物的累积影响锂空气电池容量发挥,采用仿真手段进行锂空气电池模拟研究,可以节省人力物力,对于锂空气电池的设计优化等具有一定的指导作用。
本文作者以锂空气电池为研究对象,基于COMSOL仿真平台,建立一维电化学模型,通过仿真手段研究不同放电电流密度,不同氧气浓度以及不同扩散系数下锂空气电池的有关容量等性能变化,研究结论可为锂空气电池工程化提供指导。
1 模型建立
1.1 研究对象
本研究以有机电解液体系电池为实验对象,假定生成产物只有Li2O2。电池放电时,负极的Li被氧化成Li+进入到电解液中,电子通过外电路流入阴极,O2在正极在催化剂的作用下与Li+结合生成Li2O2沉积在多孔阴极的孔隙之内,电极反应如下所示:1) 负极Li→Li++e;2) 正极Li++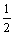 O2+e→
O2+e→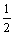 Li2O2;3) 总反应Li+
Li2O2;3) 总反应Li+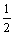 O2→
O2→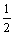 Li2O2。
Li2O2。
1.2 一维电化学模型的建立
1.2.1 几何模型
图1所示为锂空气电池一维等温模型的的几何模型。该模型包括隔膜与多孔电极两部分,锂金属负极在模型中被设置为边界。整个电池模型浸没在有机电解质中,如下所示:
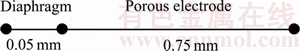
图1 锂空气电池一维几何模型
Fig. 1 One-dimensional geometric model of lithium-air battery
1.2.2 模型假设
为简化模型,提高模型的实用性,模型建立过程使用如下假设:
1) Li2O2是电池放电时的唯一产物且只生成于多孔阴极之内;
2) 该电池的电解质是基于二元电解质浓溶液理论的单一盐均匀有机溶剂混合物;
3) Li+的扩散使用浓溶液电解质理论,多孔阴极中充满了液相电解质;
4) 溶剂中氧气始终饱和;
5) 电极内的物质对流传递可以忽略。
1.2.3 一维电化学模型建立
锂空气电池在放电过程中,多孔碳电极为氧气的电化学还原提供反应场所。电池放电时,外部的氧气通过多孔电极的孔隙与电解液中的Li+接触,生成的Li2O2膜沉积在多孔阴极的孔隙内部的活性壁面。氧气在正极的扩散遵从Fick定律,如式(1)所示:
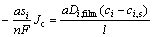 (1)
(1)
式中:a为电极单位体积的实际反应面积;si为化学计量数;Di,film为物质i的实际扩散系数;Jc为电解质与电极界面的局部电流转移密度; F为法拉第常数,96485 C/mol;n为反应转移电子数;ci为物质i的电解液相浓度;ci,s为物质i的表面浓度;l为计算的放电产物理论膜厚度。
不考虑电池电解液内的对流传质的影响,电池内Li+与氧气扩散与迁移的通量方程为
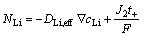 (2)
(2)
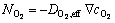 (3)
(3)
式中: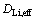 为Li的实际扩散系数;J2为溶液相中的电流密度;
为Li的实际扩散系数;J2为溶液相中的电流密度;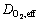 为氧气的实际扩散系数,电解质溶液电势为
为氧气的实际扩散系数,电解质溶液电势为
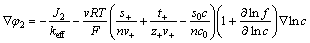 (4)
(4)
式中: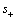 为阳离子的化学计量数;t+为Li+的迁移数;s0为溶剂的化学计量数;
为阳离子的化学计量数;t+为Li+的迁移数;s0为溶剂的化学计量数;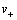 为阳离子的数量;v为离子的摩尔数;c和c0分别为电解液中溶质和溶剂的浓度。
为阳离子的数量;v为离子的摩尔数;c和c0分别为电解液中溶质和溶剂的浓度。
固相电子传导电流I1遵从欧姆定律,如式(5)所示:
 (5)
(5)
式中:J1为固相中的电流密度;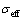 为固相电导率;
为固相电导率;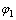 为固相电势。
为固相电势。
多孔碳电极为氧气的电化学还原提供反应场所,电池放电时,外部的氧气通过多孔电极的孔隙与电解液中的Li+接触,生成的Li2O2膜沉积在多孔阴极的孔隙内部的活性表面。正极电极反应的动力学表达式为:
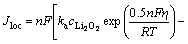
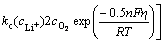 (6)
(6)
式中:Jloc是局部电流密度;ka为阳极传递系数;kc为阴极传递系数;ci为物质i的浓度。
反应过电势可以通过固相电势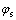 、电解液电势
、电解液电势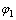 、表面膜电阻引起的电势降
、表面膜电阻引起的电势降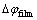 和平衡电势
和平衡电势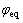 计算,计算公式如(7)所示:
计算,计算公式如(7)所示:
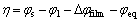 (7)
(7)
表面膜电阻引起的电势降如式(8)所示:
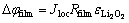 (8)
(8)
式中: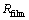 为产物Li2O2膜的电阻率;
为产物Li2O2膜的电阻率;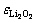 为固体产物Li2O2的体积分数。
为固体产物Li2O2的体积分数。
在模拟过程中假定负极锂金属端接地,电势为零。
1.2.4 正极中反应产物溶解过程孔隙变化描述
由于放电产物Li2O2在电解液中有一定的溶解度,因此反应过程中,生成产物在溶解度范围内时,产物将迅速溶解在溶液中,不会造成孔隙率的减小。此过程中液相中的浓度变化如公式(9)所示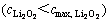 :
:
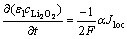 (9)
(9)
式中: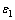 为正极的孔隙率;
为正极的孔隙率;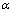 为正极的活性比表面积;
为正极的活性比表面积;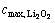 为Li2O2在电解液中的溶解度。
为Li2O2在电解液中的溶解度。
当放电产物Li2O2超过在电解液中的溶解度后,生成的Li2O2会附着在多孔正极内壁面上并呈薄膜状,随着反应继续进行,正极孔隙率将发生改变,此过程用公式(10)来描述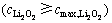 :
:
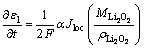 (10)
(10)
式中: 是放电产物中Li2O2的分子量;
是放电产物中Li2O2的分子量;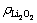 为产物密度。
为产物密度。
此外,由于产物在多孔正极内部壁面的不断沉积,会导致正极孔隙率逐渐减小,正极内活性比表面积也随之有所下降。电极内单位体积的实际活性表面面积见公式(11)为
 (11)
(11)
式中: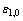 为正极初始孔隙率;
为正极初始孔隙率;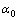 为正极初始活性比表面积,0、5的取值取决于放电产物Li2O2的形貌,其中0代表产物Li2O2在电解液溶解度范围内,5代表产物Li2O2超出溶解度范围[17]。
为正极初始活性比表面积,0、5的取值取决于放电产物Li2O2的形貌,其中0代表产物Li2O2在电解液溶解度范围内,5代表产物Li2O2超出溶解度范围[17]。
在反应产物Li2O2超出溶解度范围后,其在正极活性壁面上累积。在此过程中,产物Li2O2的体积分数如式(12):
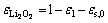 (12)
(12)
式中: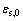 为正极初始固相体积分数。放电产物Li2O2膜厚度通过固相放电产物的体积分数计算,见方程(13):
为正极初始固相体积分数。放电产物Li2O2膜厚度通过固相放电产物的体积分数计算,见方程(13):
 (13)
(13)
式中:r0为正极初始粒径。
模拟过程中,金属锂负极接地,正极集流体电流为放电电流,电池的放电终止电压为2.5 V,分别研究电流密度为0.05、0.1、0.2和0.5 mA/cm2条件下电池容量的衰减情况。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 模型验证
通过将模拟得到的电池放电曲线与实验得到的放电曲线进行对比,可以验证该模型是否可靠。图2所示为放电电流密度为0.05 mA/cm2时实际放电曲线与模拟结果曲线的对比,其中实验数据来自文献[17],一维电化学模型网格剖分得到128个网格,网格数量足够。
从图2可以看出,在电池容量发挥在1100 mA·h/g之前,试验曲线与模拟均吻合较好,在实验容量大于1100 mA·h/g之后,两者稍有偏离,具体表现在模拟容量发挥大于实验结果。造成此现象的原因是由于模型建立过程中存在多种假设,以及部分参数的获取存在误差,这些均会在一定程度上影响电池容量的发挥。总体来看,两条曲线仍具有很高的吻合度,表明该模型可靠性较好,能够用来反映电池行为。
锂空气电池仿真研究在拥有两个四核处理器(Intel Core i7 CPU,2.93 GHz,总共8个处理器内核)和总共6 GB随机存取存储器(RAM)的戴尔高性能T1650工作站上进行,计算资源足够。
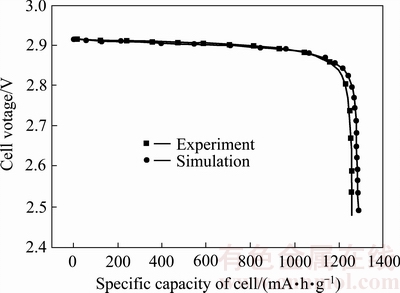
图2 锂空气电池的放电曲线与模拟结果对比
Fig. 2 Contrast between discharge curve and simulation results of lithium-air battery (Applied current density: 0.05 mA/cm2)
2.2 放电电流密度对电池性能的影响
电流是影响电池容量发挥的重要因素,图3所示为不同放电电流密度下电池的放电曲线。该电池的放电比容量与初始放电电压见表1。
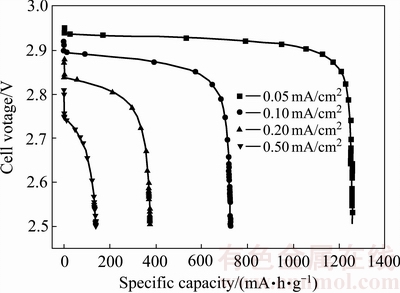
图3 不同放电电流密度下锂空气电池的放电曲线
Fig. 3 Discharge curves of lithium-air battery at different current densities
表1 锂空气电池初始放电电压与比容量
Table 1 Initial discharge voltage and specific capacity of lithium-air battery
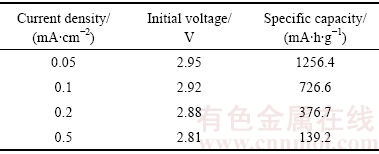
从图3可以看出,电池初始放电时,电压首先迅速降低,随后才开始进入平稳的放电平台,并且随着应用放电电流密度的增加这个下降幅度也在有所增加。当放电电流密度为0.05 mA/cm2增大到0.5 mA/cm2时,电池的初始放电电压从2.95 V下降到2.81 V;导致这一现象的原因是放电初始阶段,电池内部由于电阻存在,随着电流增大,欧姆极化也逐渐增大,因此导致了放电电压低于理论电压。
此外,从表1可以看出,当应用放电电流密度为0.05 mA/cm2增大到0.5 mA/cm2时,电池的放电比容量从1256.4 mA·h/g下降到只有139.2 mA·h/g;这也印证了放电电流越大,容量发挥越小,放电电流越小,放电容量则越大的规律。
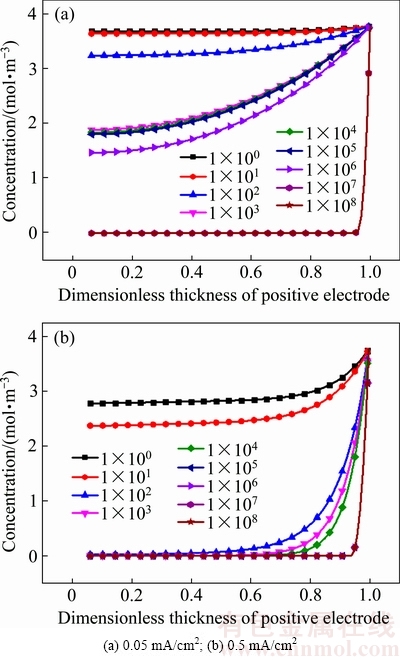
图4 不同电流密度下正极氧气浓度分布
Fig. 4 Distribution of positive oxygen concentration at different current densities
图4(a)和(b)所示分别为放电电流密度为0.05 mA/cm2、0.5 mA/cm2时电池正极内部氧气浓度演化规律。节选了从1×100到1×108等9个时间点电极内氧气浓度,横坐标为电池正极的无量纲厚度。电池放电初期,电极表面充足的Li+与O2在正极孔隙表面接触,迅速发生反应将电极表面的氧气快速消耗,致使1×100~1×102时间段内出现较大的氧气浓度梯度。放电中期,由于氧气扩散,氧气必然会在正极内部形成自外而内的浓度梯度;在小电流0.05 mA/cm2放电时(见图4(a)),氧气与Li+的反应速度相对较慢,因此在放电中期1×102~1×107时间内氧气浓度出现的梯度相对较小;在大电流0.5 mA/cm2放电时,氧气浓度则出现较大梯度。放电末期时,由于放电产物Li2O2在多孔正极的孔隙内部的不断沉积,导致氧气扩散通道变窄,扩散速率持续下降。这一现象在大电流放电时更为明显,由图4(b)可以看出,由于前中期放电产物在壁面的累积,造成孔隙堵塞,后期时仅有少量氧气能够到大电极内部,这也是大电流放电容量较小的原因之一。
电池的放电电流不仅影响电池内部氧气浓度分布,对电池的过电势也有直接影响。图5给出了不同放电电流密度下电池正极的过电势分布。可以看出,电流密度为小电流0.05 mA/cm2时,过电势曲线相对平稳,氧气侧与电解质侧过电势在前中期大抵相当,在放电末期迅速增大,这是由于末期电池内部活性物质消耗,导致内阻增大所致。大电流0.5 mA/cm2,氧气侧电压降基本保持不变,但是电解质过电势逐渐增大,最后时刻过电势达到0.37 V,这严重阻碍了电池整体的容量发挥。
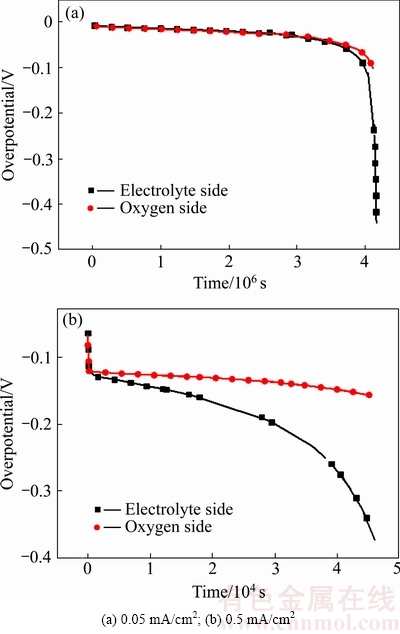
图5 不同电流密度下多孔正极过电势
Fig. 5 Overpotential of porous positive electrode at different current densities
2.3 氧气浓度对电池性能的影响
电池容量的发挥不仅与电池放电电流有关,正极氧气浓度也密切相关。图6给出放电电流密度为0.1 mA/cm2时不同氧气浓度下电池放电容量曲线。
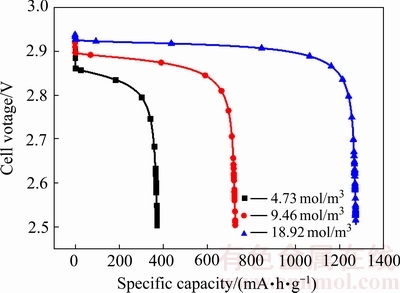
图6 不同氧气浓度下的电池容量
Fig. 6 Battery capacity at different oxygen concentrations
从图6中可以看出,正极所处的环境中氧气浓度越高,电池的放电容量越高,电池的放电电压也比较高。从表2可以看出,当外界氧气浓度从4.73 mol/m3增加到18.92 mol/m3时,电池容量从371.2 mA·h/g增加到1274.5 mA·h/g,增长近3.4倍。这是因为氧气浓度的增大,使得在多孔阴极处有大量的Li+与氧气结合生成了Li2O2,在未达到氧气浓度饱和之前,均会造成电池容量的大幅度提升。
表2 不同氧气浓度下电池容量
Table 2 Battery capacity at different oxygen concentrations
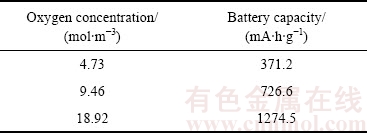
图7所示为不同氧气浓度下放电产物Li2O2膜厚度的变化。从图7中可以看出,电池内部产物在厚度方向上呈现一定的梯度变化,靠近正极表面,Li2O2厚度越大,远离表面则产物厚度越小;并且外部氧气浓度越大,厚度梯度越小,且任何位置的产物厚度均大于其它浓度的厚度。这是由于氧气浓度较大时,将形成较大氧气浓度梯度,在该梯度下氧气迅速向电池内部扩散,在梯度方向上发生反应,生成具有一定厚度的Li2O2产物;氧气浓度较低时,形成较小的浓度梯度,并且表面处先发生反应,使得表面区域孔隙率降低,该结果将导致更少的氧气扩散进入电池内部,因此将形成较大的Li2O2膜厚度梯度。
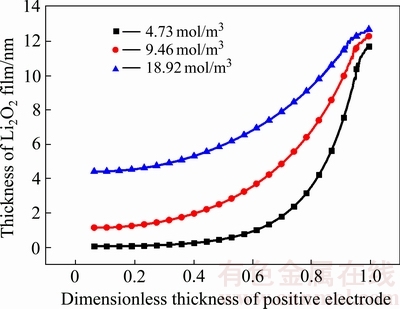
图7 不同氧气浓度下Li2O2膜厚度的变化
Fig. 7 Thickness change of Li2O2 film at different oxygen concentrations
2.4 扩散系数的影响
综前所述,放电电流、氧气浓度均对电池容量发挥具有重要影响。由于电池反应同时受Li+扩散以及氧气扩散双重影响,因此,研究扩散系数对电池性能发挥同样重要。图8所示为不同的Li+扩散系数下电池容量的变化,研究Li+的扩散系数分别为2.11×10-9、1.055×10-8和2.11×10-8 m2/s下电池的容量发挥情况,其中放电电流密度设置为0.1 mA/cm2。从图8可以看出,3条曲线几乎完全重合,表明Li+的扩散系数对电池容量没有明显影响,不是反应控制步骤。
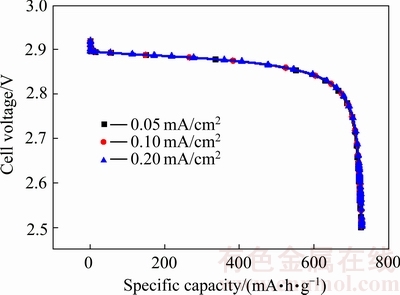
图8 Li+扩散系数对电池容量的影响
Fig. 8 Influence of Li+ diffusion coefficient on battery capacity
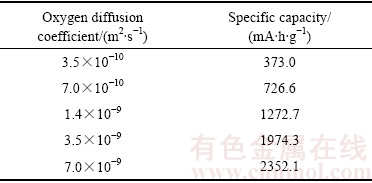
图9所示为放电电流密度设置为0.1 mA/cm2不同氧气扩散系数下的电池容量变化曲线。从图9可以看出,氧气扩散系数对电池容量发挥具有显著影响。具体表现为:氧气扩散系数越大,电池容量发挥越大,反之则较小。从表3可以看出,当氧气扩散系数从3.5×10-10 m2/s 提高到7×10-9 m2/s时,电池的容量从373.0 mA·h/g增加到2352.1 mA·h/g,增长近6.3倍,同时也表明氧气的扩散是电池反应的控制步骤。
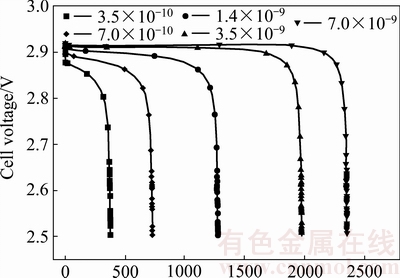
图9 不同氧气扩散系数下的电池容量
Fig. 9 Battery capacities at different oxygen diffusion coefficients
表3 不同氧气扩散系数下电池比容量
Table 3 Specific capacities at different oxygen diffusion coefficients
3 结论
1) 放电电流是影响电池容量发挥的重要因素。由于放电产物Li2O2在多孔正极孔隙内部的不断沉积,导致氧气扩散通道变窄,甚至造成孔隙堵塞。当放电电流密度从0.05 mA/cm2增大到0.5 mA/cm2时,锂空气电池的放电比容量由1256.4 mA·h/g下降到139.2 mA·h/g。
2) 外界氧气浓度是影响电池容量发挥的另一重要因素。在放电电流密度为0.1 mA/cm2条件下,外界氧气浓度从4.73 mol/m3增加到18.92 mol/m3,电池比容量从371.2 mA·h/g增加到1274.5 mA·h/g,增长近3.4倍,表明提高外部氧气浓度有助于提高电池比容量。
3) 氧气扩散速率为电池放电反应的速度控制步骤。当氧气扩散系数从3.5×10-10 m2/s 提高到7×10-9 m2/s时电池的容量从373.0 mA·h/g增加到2352.1 mA·h/g,增长近6.3倍,而提高Li+的扩散系数对电池的比容量几乎没有影响。
REFERENCES
[1] 李骄阳, 王 莉, 何向明. 动力锂电池的未来发展[J]. 新材料产业, 2016(3): 25-30.
LI Jiao-yang, WANG Li, HE Xiang-ming. Development of Power lithium battery in the future[J]. Advanced Materials Industry, 2016(3): 25-30.
[2] THOTIYL M M O, FREUNBERGER S A, PENG Z, BRUCE P G. The carbon electrode in nonaqueous Li-O2 cells[J]. Journal of American Chemical Society, 2013, 135(1): 494-500.
[3] 王倍洲, 王有伟, 刘建军, 陆文聪. 锂空气电池正极界面催化反应机理[J]. 中国材料进展, 2015, 12(34): 933-937.
WANG Bei-zhou, WANG You-wei, LIU Jian-jun, LU Wen-cong. Catalytic reaction mechanism in the positive electrode interface of lithium air battery[J]. Materials China, 2015, 12(34): 933-937.
[4] ZU Chen-xi, HONG Li. Thermodynamic analysis on energy densities of batteries[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2011, 4(8): 2614-2624.
[5] BRUCE P G, FREUNBERGER S A, HARDWICK L J. Li-O2 and Li-S batteries with high energy storage[J]. Nature Materials, 2012, 11(1): 19-29.
[6] GIRISHKUMAR G, MCCLOSKEY B, LUNTZ A C, SWANSON S, WILCKE W. Lithium-air battery: Promise and challenges[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 2010, 1(14): 2193-2203.
[7] BARDENHAGEN I, FENSKE M, FENSKE D, WITTSTOCK A,  M. Distribution of discharge products inside of the lithium/oxygen battery cathode[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2015, 299: 162-169.
M. Distribution of discharge products inside of the lithium/oxygen battery cathode[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2015, 299: 162-169.
[8] XU W, XU K, VISWANATHAN V V, TOWNE S A, HARDY J S, XIAO J, ZHANG J G. Reaction mechanisms for the limited reversibility of Li-O2 chemistry in organic carbonate electrolytes[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2011, 196(22): 9631-9639.
[9] FREUNBERGER S A, CHEN Y, PENG Z, GRIFFIN J M, HARDWICK L J,  F, BRUCE P G. Reactions in the rechargeable lithium-O2 battery with alkyl carbonate electrolytes[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2011, 133(20): 8040-8047.
F, BRUCE P G. Reactions in the rechargeable lithium-O2 battery with alkyl carbonate electrolytes[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2011, 133(20): 8040-8047.
[10] SERIANI N. Ab initio thermodynamics of lithium oxides: from bulk hases to nanoparticles[J]. Nanotechnology, 2009, 20(44): 445703-445710.
[11] ALLEN C J, MUKERJEE S, PLICHTA E J, HENDRICKSON M A, ABRAHAM K M. Oxygen electrode rechargeability in an ionic liquid for the Li-air battery[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 2011, 2(19): 2420-2424.
[12] 洪 树, 汤依伟, 贾 明, 艾立华, 殷宝华, 李 劼. 基于电化学模型的全固态锂离子电池的放电行为[J].中国有色金属学报, 2015, 25(8): 2176-2182.
HONG Shu,TANG Yi-wei,JIA Ming,AI Li-hua,YIN Bao-hua,LI Jie. Discharge behavior of all-solid-state Li-ion batteries based on electrochemical model[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2015, 25(8): 2176-2182.
[13] 程 昀, 李 劼, 贾 明, 汤依伟, 宋文锋, 张治安, 张 凯. 动力锂离子电池模块散热结构仿真研究[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2015, 25(6): 1607-1616.
CHENG Yun, LI Jie, JIA Ming, TANG Yi-wei, SONG Wen-feng, ZHANG Zhi-an, ZHANG Kai. Simulation research of heat dissipation structure for automotive lithium-ion battery packs[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2015, 25(6): 1607-1616.
[14] 杜双龙, 赖延清, 贾 明, 程 昀, 张红亮, 张 凯, 刘业翔. 圆柱锂离子动力电池电热特性仿真[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2014, 24(7): 1823-1830.
DU Shuang-long, LAI Yan-qing, JIA Ming, CHENG Yun, ZHANG Hong liang, ZHANG Kai, LIU Ye-xiang. Electrothermal characteristics simulation of cylindrical automotive lithium-ion battery[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2014, 24(7): 1823-1830.
[15] LI Jie, CHENG Yun, JIA Ming, TANG Yi-wei, LIN Yue, ZHANG Zhi-an, LIU Ye-xiang. An electrochemical-thermal model based on dynamic responses for lithium iron phosphate battery[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2014, 255: 130-143.
[16] LI Jie, CHENG Yun, AI Liang, JIA Ming, DU Shuang-long, YIN Bao-hua, STANLEY Woob, ZHANG Hong-liang. 3D simulation on the internal distributed properties of lithium-ion battery with planar tabbed configuration[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2015, 293: 993-1005.
[17] SAHAPATSOMBUT U, CHENG H, SCOTT K. Modelling the micro-macro homogeneous cycling behaviour of a lithium-air battery[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2013, 227: 243-253.
[18] SAHAPATSOMBUT U, CHENG H, SCOTT K. Modelling of electrolyte degradation and cycling behavior in a lithium air battery[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2013, 243: 409-418.
[19] SAHAPATSOMBUT U, CHENG H, SCOTT K. Modelling of operation of a lithium-air battery with ambient air and oxygen-selective membrane[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2014 249: 418-430.
[20] LI Xiang-lin. A modeling study of the pore size evolution in lithium-oxygen battery electrodes[J]. Journal of The Electrochemical Society, 2015, 162(8): A1636-A1645.
Simulation for lithium air batteries based on electrochemical model
DU Shuang-long1, LAI Yan-qing1, JIA Ming1, CHENG Zhuang1, AI Li-hua2, AI Liang2
(1. School of Metallurgy and Environment, Central South University, Changsha 410000, China;
2. Aihua Group Co., Ltd., Yiyang 413000, China)
Abstract: Based on COMSOL simulation platform, a one-dimensional electrochemical model was established to study the effect of applied current density, oxygen concentration, diffusion of oxygen and lithium-ion on the performance of lithium air battery. The results show that the specific capacity reduces from 1256.4 mA·h/g to 139.2 mA·h/g with the applied current density increasing from 0.05 mA/cm2 to 0.5 mA/cm2; and the specific capacity is improved from 371.2 mA·h/g to 1274.5 mA·h/g with the oxygen concentration increasing from 4.73 mol/m3 to 18.92 mol/m3 when the applied current is set as 0.1mA/cm2. It is suggested that the specific capacity can be improved by increasing the oxygen concentration. The diffusion rate of oxygen is the rate-determining step during the discharge process. When the diffusion coefficient of oxygen increases from 3.5×10-10 m2/s to 7×10-9 m2/s, the specific capacity is improved from 373.0 mA·h/g to 2352.1 mA·h/g. The diffusion coefficient of Li+ has almost no effect on the specific capacity.
Key words: lithium air battery; current density; oxygen concentration; diffusion coefficient; numerical simulation
Foundation item: Projects(51204211, 51222403) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project(0714-EMTC02-5271/6) supported by the Special Foundation of Industrial Upgrading Transformation and Strengthen, Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, China
Received date: 2016-04-07; Accepted date: 2017-05-27
Corresponding author: JIA Ming; Tel: +86-13975127722; E-mail: jiamingsunmoon@aliyun.com
(编辑 何学锋)
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(51204211,51222403);工信部工业转型升级强基工程专项(0714-EMTC02-5271/6)
收稿日期:2016-04-07;修订日期:2017-05-27
通信作者:贾明,副教授,博士;电话:13975127722;E-mail: jiamingsunmoon@aliyun.com