添加Ti对金属注射成形HK30不锈钢烧结致密化的影响
李大鹏,何浩,李益民,沈红仁,张翔
(中南大学 粉末冶金国家重点实验室,湖南 长沙,410083)
摘要:在HK30粉末中分别添加质量分数为0.4%,0.8%和1.2%的Ti粉,采用粉末注射成形工艺制备试样,对制得的试样进行密度、显微组织、显微硬度和收缩率检测。基于黏弹性理论对烧结致密化过程进行分析,推导出烧结过程中致密化速率的表达式。研究结果表明:添加Ti会加快烧结初期的致密化速率,降低烧结激活能,但使最终的烧结密度下降;Ti颗粒周围的奥氏体硬度下降。在烧结过程中Ti具有更高的亲和力,优先结合材料中的碳氧等元素,减少奥氏体中的杂质含量,在烧结初始阶段有利于致密化的进行。在烧结后期,超固相线液相烧结对致密化的贡献最大,因为碳含量的减少,使液相生成量减少,从而阻碍了密度的继续提高。
关键词:烧结致密化;HK30不锈钢;黏弹性理论;金属注射成形
中图分类号:TF121 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2013)08-3151-08
Effect of Ti addition on sintering densification of MIM HK30 stainless steel
LI Dapeng, HE Hao, LI Yimin, SHEN Hongren, ZHANG Xiang
(State Key Laboratory of Powder Metallurgy, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China)
Abstract: The HK30 stainless steel powder was mixed with 0.4%, 0.8%, 1.2% (mass fraction) Ti, and the samples were prepared by powder injection molding. The density, microstructure, microhardness and shrinkage rate of the samples were measured. The densification process was modeled based on viscoelasticity theory. The equation of densification rate was established. The results show that Ti addition reduces the sintering activation-energy and improves the sintering densification in initial stage, but it reduces the final density. The microhardness of austenite near Ti particle is lower than that of other areas. Because Ti has a higher affinity for C and O, which reduces the impurity levels in the austenite. The reduction of impurities is conducive for densification during the initial stage of sintering. In the final stage, supersolidus liquid-phase sintering has the largest contribution on densification. Because carbon is combined with Ti, the amount of liquid phase is reduced and therefore the sintering densification is hindered.
Key words: sintering densification; HK30 stainless steel; viscoelasticity theory; metal injection molding
HK30属于高铬镍奥氏体不锈钢,由于其在高温下优异的抗蚀性能和抗氧化性能,在汽车、化工和工程机械等领域获得了广泛的应用。因为奥氏体不锈钢硬度较低,加工时黏刀严重,采用机加工方法制备复杂形状中小型HK30零部件很困难。金属注射成形(metal injection molding,MIM)是传统粉末冶金与现代塑料注射成形相结合而产生的一种新型近净形成形技术,具有材料利用率高、成本低、组织均匀等优势,使用MIM生产小型HK30零部件可以有效解决以上问题。但HK30烧结窗口较窄,MIM工艺的添加黏结剂和脱脂2个步骤容易导致最终产品的碳含量增加,虽然碳含量的增加会降低液线,可以加快物质迁移,提高致密化速率[1],但液相的出现会导致较大的收缩与变形,尤其对于复杂形状零部件不利于保持尺寸及形状稳定性[2]。目前对HK30烧结过程的研究未见报道,但与其具有相似成分的316L不锈钢已经得到了广泛研究,主要通过添加合金元素来改善其烧结性能。Shu等[3]研究发现MIM316L不锈钢尺寸稳定性变差主要原因是液相的出现,并通过在其中添加Mo和Ni使其在适宜的烧结温度下不出现液相而改善产品烧结后的尺寸稳定性。果世驹等[4]在316L不锈钢中添加Fe-Mo-B烧结助剂,发现添加Mo可以提高Fe在固相中的扩散系数,加快烧结速率,但形成的FeMo2B2相会使材料变脆。Lal等[5]研究添加P和Si的316L不锈钢烧结过程,结果显示在1 100 ℃左右时P加速致密化而Si阻碍致密化,在1 300 ℃左右时P和Si均加速致密化。Ti是一种常用的合金钢添加元素,具有细化晶粒、吸收碳氧杂质、提高材料强度等明显作用。沈继程等[6]认为Ti在不锈钢中的作用主要通过形成TiN和TiC等体现,而固溶Ti的作用较小。研究发现TiN在奥氏体中溶解度很低,细小的TiN颗粒具有强烈的钉扎晶界的作用,可以抑制奥氏体晶粒长大,细化晶粒,同时细小的TiC颗粒具有明显析出强化作用[7-8]。杨才福等[9]还发现在Ti含量较高时,Ti还与硫结合, 生成颗粒状分布的Ti4C2S2,同时具有细化晶粒、析出强化、沉淀强化和改善夹杂物形态的作用。在HK30不锈钢中添加不同含量的Ti,通过Ti与碳结合,可以降低HK30不锈钢基体的碳含量,解决过烧和尺寸稳定性差的问题。但添加Ti对HK30烧结致密化的影响未见报道,因此,本文作者建立致密化过程模型并推导致密化方程,通过理论和实验分析不同Ti含量对HK30不锈钢的烧结致密化行为的影响。
1 实验
实验采用气雾化HK30不锈钢粉末(英国Osprey公司)和氢化脱氢Ti粉(北京浩运)为原料,HK30粉末的成分见表1,Ti粉中氧的质量分数小于0.4%,碳的质量分数小于0.02%。HK30和Ti粉末的扫描电镜照片如图1所示。HK30不锈钢粉末平均粒径为12.3μm,为球形颗粒,分散良好;Ti粉平均粒径为38.4 μm,为不规则形状,粒径分布范围较广。在HK30粉末中分别添加质量分数为0.4%,0.8%和1.2%的钛粉,干混3 h。喂料的制备使用油基黏结剂,以57%的粉末装载量进行配比,用捏合机捏合2.5 h,在XSMY密炼机上密炼3 h,设定温度为155 ℃,再通过V68型制粒机进行制粒。注射使用日精NEX-50注塑机,注射温度为159 ℃,注射时间为2.8 s。使用CH2Cl2进行溶剂脱脂,在40 ℃下脱脂3 h。在高纯氩气保护下进行热脱脂,最终温度为900 ℃,保温1.5 h。
所有样品经过900 ℃(保温时间1 h)脱脂预烧后,分别在1 270 ℃和1 290 ℃下保温0~8 h获得不同致密度的样品,然后用排水法测量其密度,采用截线法测晶粒尺寸。样品经体积分数为4%的硝酸酒精溶液腐蚀后,在Polyvar-met金相显微镜上观察显微组织。粉末形貌观察和样品断口形貌在JSM-6360扫描电镜上进行。烧结收缩曲线测量使用STA449c/3/G型热分析仪(德国NETZSCH公司),将预烧坯加工成(长×宽×高)为3.5 mm×3.5 mm×20 mm的长方体试样,在高纯氩气气氛下保护下以5 ℃/min的升温速率升温至1 320 ℃。
表1 气雾化HK30不锈钢粉末的成分(质量分数)
Table 1 Composition and properties of gas-atomized HK30 stainless steel powder %
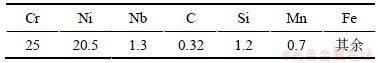
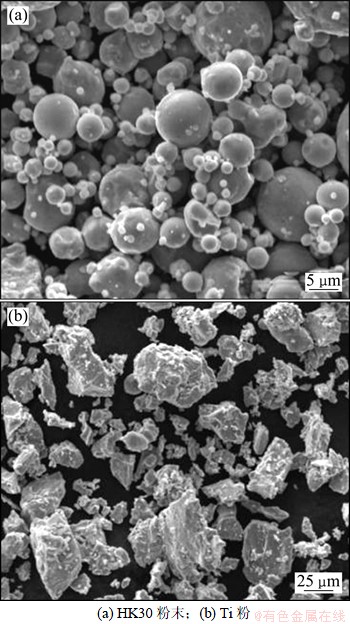
图1 原料粉末SEM照片
Fig. 1 SEM images of raw material powders
2 实验结果、致密化模型及数据拟合
2.1 实验结果
图2所示为不同烧结温度下样品密度随时间的变化。从图2可以看出:样品在900 ℃预烧后的相对密度为0.87~0.89,添加Ti样品的相对密度要高于纯HK30样品的相对密度,其中:含0.4%Ti样品的相对密度最高,达到0.89。但对比烧结时间为8 h的样品,含Ti样品的相对密度要低于纯HK30样品的相对密度,除含0.4%Ti样品的相对密度与纯HK30样品的相接近外,其他2种样品均只有0.92左右。样品的相对密度随烧结温度的升高而增大,但保温8 h的样品烧结密度相近。观察相对密度随时间的变化可以发现:添加Ti的样品在烧结初期相对密度提升较快,尤其在1 270 ℃下要比纯HK30样品的高。但随着烧结过程的进行,致密化速率的差异逐渐减小,烧结末段纯HK30样品的相对密度已经超过含Ti样品的相对密度。
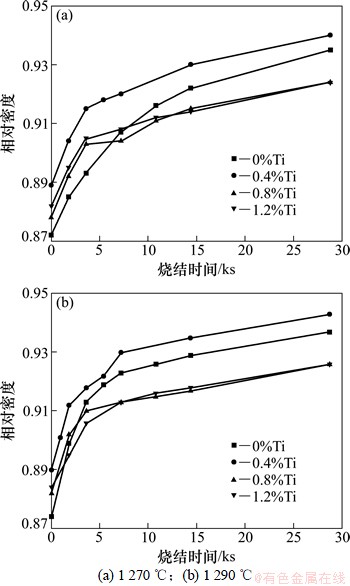
图2 不同烧结温度下样品密度曲线
Fig. 2 Density curves of samples at different temperatures
图3所示为样品烧结收缩曲线,不同Ti含量样品的收缩曲线和致密化速率曲线趋势一致。4种成分样品开始收缩的先后顺序依次为0.8%Ti,0.4%Ti,1.2%Ti和0%Ti,由图3可知:起始收缩温度分别为1 184 ℃,1 192 ℃,1 195 ℃和1 204 ℃。添加Ti样品较纯HK30样品起始收缩温度提前了9~20 ℃,且收缩速度明显高于纯HK30样品的收缩速度。在1 285~ 1 313 ℃区间收缩速度有异常增加,其中纯HK30样品最为明显。
图4所示为样品组织的显微硬度(HV0.01)测试照片。由图4可知:靠近Ti颗粒位置的压痕要比其他位置更大,说明Ti颗粒附近奥氏体的显微硬度小于奥氏体基体的显微硬度。图5所示为样品断口的能谱分析,结果证明存在Ti与C结合的颗粒。

图3 不同Ti含量的样品的烧结收缩曲线
Fig. 3 Shrinkage curves of samples with different Ti contents

图4 Ti颗粒周围的显微硬度压痕
Fig. 4 Indentation of microhardness for areas around Ti particle

图5 断口颗粒的SEM能谱分析
Fig. 5 SEM energy spectrum analysis of particles on fracture surface
2.2 致密化机理分析
HK30不锈钢是一种含有25%Cr和20%Ni(质量分数)的奥氏体不锈钢,其成分与316L不锈钢类似。German[10]使用基于黏弹性理论的烧结模型,研究了316L不锈钢的致密化行为,模拟结果与实验结果符合良好。因此,本研究采用黏弹性理论研究HK30不锈钢的致密化过程。黏弹性模型将粉末烧结体视为黏弹性流,在烧结过程中黏弹性体因为烧结力的作用产生黏性行为和弹性行为。Cai等[11]研究发现,在烧结的初始阶段,烧结体表现出一定弹性行为,随着温度的升高,弹性力作用减弱而黏性力作用增强,当温度超过500 ℃时,烧结力几乎完全为黏性力,烧结体表现为黏性行为。HK30不锈钢的烧结温度超过1 200 ℃时,黏性力对烧结起主要所用。因此,将弹性应变部分忽略,即将烧结体视为纯黏性体来建立黏性流动的致密化方程。采用黏弹性理论对不同成分的HK30不锈钢的烧结致密化行为进行研究,在无外力作用时,其本构方程为:
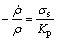 (1)
(1)
其中: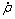 为密度随时间的变化率,即致密化速率;ρ为任意时间的密度;σs为烧结平均静水压力;KP为体积黏度。当材料的烧结力σs和体积黏度KP已知时,就可以根据上述方程求得烧结体在任意时刻的密度。
为密度随时间的变化率,即致密化速率;ρ为任意时间的密度;σs为烧结平均静水压力;KP为体积黏度。当材料的烧结力σs和体积黏度KP已知时,就可以根据上述方程求得烧结体在任意时刻的密度。
由于在烧结的不同阶段,粉末烧结体相对密度的不同,致密化表达式中有关的参数的表达式不同,故需要区分相对密度才能给出最终的表达式[12-13]。
对于开孔隙,σs的表达式为:
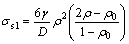 (2)
(2)
对于闭孔隙,σs的表达式为:
 (3)
(3)
其中:γ为表面能(J·m-2);D为晶粒粒径(m)。
一般认为,当相对密度达到0.92时,粉末烧结体中的开孔隙变为闭孔隙。然而,相关实验显示当粉末体的相对密度低于0.85时,粉末体的孔隙大部分为开孔隙,当相对密度高于0.85时,开孔隙开始减少,并且在相对密度达到0.95时开孔隙完全消失[14]。因此,相对密度ρ1=0.85和ρ2=0.95被分别当作闭孔隙和开孔隙的界限。当相对密度在这个过渡区间时,即ρ1<ρ<ρ2时,σs的表达式为:
 (4)
(4)
当相对密度ρ<0.92时,体积黏度KP的表达式为:
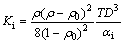 (5)
(5)
当相对密度ρ>0.92时,体积黏度KP的表达式为:
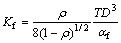 (6)
(6)
其中:材料参数αi和αf分别代表致密化初始阶段和最终阶段的有效扩散系数(m6·K·J-1·s-1)。
D的表达式采用如下晶粒长大模型[12]:
 (7)
(7)
其中:k和n为材料常数,该模型是由对生坯到完全烧结体的密度范围进行最小二乘回归分析推导而得。
材料参数αi和αf可以表示为:
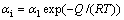 (8)
(8)
 (9)
(9)
其中:α1和α2为材料常数,能够通过在不同温度下相对密度随时间变化实验数据中测定;R为气体常数(J·mol-1·K-1);Q为晶界扩散激活能(J);T为热力学温度(K)。为了保证体积黏度在ρ=0.92处连续,α2可以用α1的形式表达:
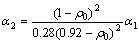 (10)
(10)
由于在烧结的不同阶段,粉末烧结体相对密度的不同,致密化表达式中有关的参数的表达式不同,故需要分相对密度的不同才能给出最终的表达式。最终得到致密化速率方程方程如下:
当ρ≤0.85时:
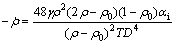 (11)
(11)
当0.85<ρ≤0.92时:
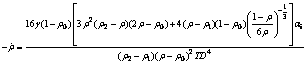 (12)
(12)
当0.92<ρ≤0.95时:
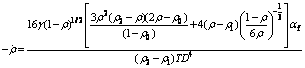 (13)
(13)
当ρ>0.95时:
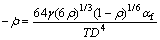 (14)
(14)
2.3 方程中参数的拟合
含有0%,0.4%,0.8%和1.2%Ti样品经过预烧后的相对密度依次为0.794 6,0.868 4,0.765 2和0.758 7,将此相对密度作为各成分样品的初始相对密度ρ0。图6所示为900 ℃预烧的金相照片,观察可发现没有出现明显的烧结颈。此次实验的气雾化HK30粉末原料的平均粒径为12.3 μm,80%的粉末粒径小于22 μm,属于小粒径粉末。对于小粒径粉末,一般假设其粉末平均粒径为初始晶粒尺寸,故此次实验中4种不同成分的初始晶粒尺寸均假设为12.3 μm。致密化速率方程中存在2个未知项,其一为晶粒尺寸D的长大方程,方程已经确定但需要求解方程中的常数项n和k;其二为材料参数αi和αf;另外,从αi和αf的方程表达式来看,材料常数α1,α2和烧结激活能Q未知,2个未知数至少需要2个方程来求解。
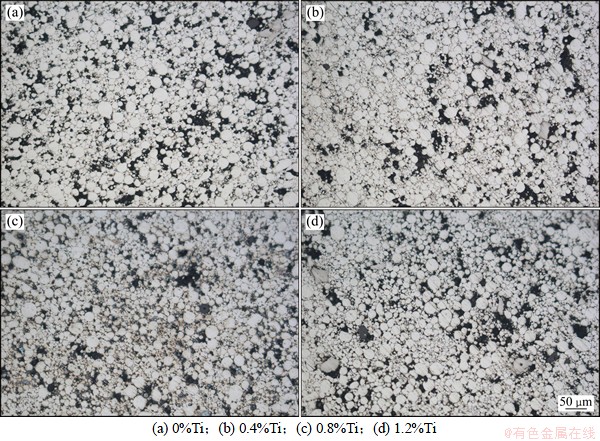
图6 不同Ti含量样品在900 ℃预烧时的样品金相照片
Fig. 6 Metallograph of samples with different contents of Ti at 900 ℃
将4种成分样品按式(7)进行拟合,得到结果如图7及表2所示。将表2中的参数代入式(7),即可得到晶粒长大方程的表达式。从致密化速率的表达式可以看出:都是 关于αi和αf的一次线性函数,方程可简写为:
关于αi和αf的一次线性函数,方程可简写为:
 或
或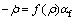 (15)
(15)
密度函数f(ρ)与ρ0,ρ1,ρ2,ρ,T,D和γ有关。粉末比表面能γ采用German 研究中316L不锈钢的比表面能,其值为1.5[10],其他参数均在实验中已测得。在计算密度函数f(ρ)时,根据其相对密度的区间不同采用了不同密度区间的密度函数f(ρ),最终拟合某一成分在某一温度下致密化速率随密度函数变化的直线时,也要根据相对密度区间的不同而分开拟合分别得到不同区间的αi和αf。
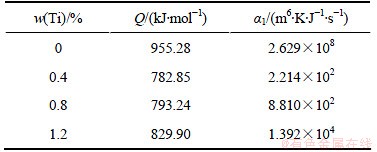
将图2中不同含钛量样品相对密度随烧结时间的变化曲线求导即得到致密化速率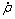 ,观察数据发现相对密度主要集中于0.92~0.95区间,根据式(12)计算得到αi。考虑不同温度下的αi,得到材料常数α1和烧结激活能Q,结果如表3所示。
,观察数据发现相对密度主要集中于0.92~0.95区间,根据式(12)计算得到αi。考虑不同温度下的αi,得到材料常数α1和烧结激活能Q,结果如表3所示。
Kwon等[12]计算出注射成形17-4PH不锈钢粉的烧结激活能为327.7 kJ/mol,α1=6.32×10-13 m6·K·J-1·s-1;钛铝扩散激活能为80~400 kJ/mol;何浩[13]计算出装载量为75%的铜粉压坯的扩散激活能为96.7 kJ/mol,α1=6.2×10-8 m6·K·J-1·s-1,装载量为85%的铜粉压坯的扩散激活能为386.6 kJ/mol,α1=2.353×10-9 m6·K·J-1·s-1。本文通过计算拟合得出的各成分扩散激活能Q与相关文献报道的激活能的数量级基本相同。从表3可以看出:添加Ti后烧结激活能下降,其中含0.4%Ti的样品烧结激活能最低,超过0.4%后烧结激活能随Ti含量的增加有微弱的提高。
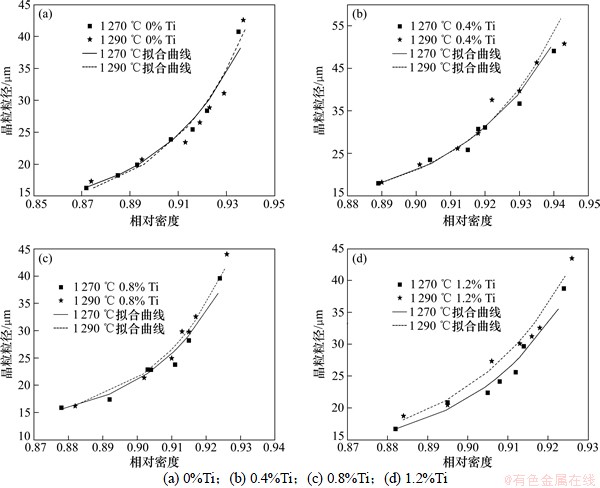
图7 不同含Ti量样品的晶粒粒径-相对密度关系及拟合曲线
Fig. 7 Variation of grain size with relative density and fitting curve for samples with different Ti contents
表2 晶粒尺寸方程拟合曲线中的相关参数
Table 2 Related parameters in fitted line of particle size equation
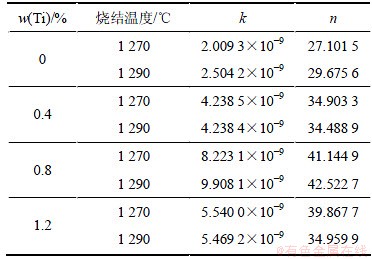
表3 不同成分下的材料参数Q和α1
Table 3 Q and α1 of samples with different contents of Ti
3 讨论
图2显示了不同烧结温度下样品相对密度随时间的变化。结果显示添加Ti的样品在烧结初期相对密度提升较快,在1 270 ℃下要明显高于纯HK30样品的相对密度。图3也显示出添加Ti样品较纯HK30样品起始收缩温度提前。从表3可以看出:添加Ti后晶界扩散激活能Qb降低,与实验所得结果相吻合。Nakajima等[15]发现铁在钛中有着较高的扩散速率。在烧结初期液相出现以前,体扩散和晶界扩散对致密化起决定性作用,钛的加入提供了新的扩散通道,有利于致密化过程。从图4可以看出:Ti颗粒周围的奥氏体的压痕面积更大,具有更低的硬度,表明其组织更软。在对断口表面颗粒SEM能谱分析中也发现了Ti和C原子比为近似1:1的颗粒,因此,可以确定在添加Ti后,有TiC形成。由此可推断烧结过程中Ti颗粒结合了周围奥氏体中的C和O等元素,导致其周围奥氏体中碳和氧含量的降低。梁良华等[16]认为致密化过程开始于900 ℃并形成烧结颈,同时开始发生与碳、氧反应。碳、氧一般集聚在粉末颗粒表面,阻碍颗粒黏接和烧结颈的形成。姜峰等[17]的研究发现:在烧结过程中氧会与Cr反应生成难以还原的Cr2O3,该氧化膜不利于固相阶段烧结颈的形成,阻碍原子扩散,从而阻碍烧结致密化过程。因此Ti颗粒造成的碳氧含量下降在烧结初期有利于致密化的进行,从而提高了致密化速率。但对比不同钛含量试样,添加1.2%Ti的样品致密化起始温度较高、致密化速率较低,这表明过高的钛含量反而会阻碍烧结致密化的进行。
对比图2中烧结时间为8 h时样品的密度,随着Ti含量的增加,烧结密度小幅度下降。观察图3中的烧结收缩曲线,在1 285~1 313 ℃区间,致密化速率异常增加,应有其他机制促进了致密化。本文作者推断在此温度区间内烧结过程中出现了液相,从而促进了烧结过程。随着烧结温度的升高和保温时间的延长,液相烧结对致密化起主导和决定性作用。烧结过程中,添加的Ti优先结合了HK30中的C,使其在烧结过程中生成的液相减少,进而使得致密化速率降低。因此在烧结后期,随Ti含量增加,样品的最终密度下降。章林等[18-19]的研究发现碳含量对烧结过程中的液相数量起决定性作用。Levenfeld等[20]在对MIM高速钢烧结过程的研究中发现,脱脂后若有大量残余碳,会使致密化速度在很窄的温度范围内快速增加。致密化速率过快是造成HK30过烧的主要原因,通过添加Ti来吸收脱脂后残余的碳可以有效减少液相生成量,从而防止过烧的产生。
烧结窗口为固相线烧结温度与碳化物溶解温度之差[19],良好的烧结性要求较宽的烧结窗口,既较低的固相烧结温度和较高的碳化物溶解温度。添加Ti有效地降低了起始致密化温度,提高了致密化速率,同时又延缓了液相的出现,减少液相生成量,因此能明显改善HK30不锈钢的烧结性能。
4 结论
(1) 在致密化初始阶段,添加Ti消除了Ti颗粒附近C和O等杂质,因而其致密化速率更快,促进了烧结。在低相对密度区间0.85~0.92所计算的扩散激活能表明添加Ti后较无添加Ti样品降低,热膨胀曲线分析所得的致密化速率也表明添加Ti后致密化速率降低,这两者都佐证了在初始阶段添加Ti后会促进 烧结。
(2) 在致密化后期,液相烧结对致密化起主导和决定性作用。添加的Ti优先结合了HK30中的C,使其在相同烧结条件下的生成液相减少,进而使得致密化速率降低。因而,在烧结后期随Ti含量增加,样品的最终密度有一定程度的下降。
参考文献:
[1] Hwang K S, German R M, Lenel F V. Capillary forces between spheres during agglomeration and liquid phase sintering[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 1987, 18(1): 11-17.
[2] German R M. Liquid phase sintering[M]. New York: Plenum Press, 1985: 181-199.
[3] Shu G J, Hwang K S, Pan Y T. Improvements in sintered density and dimensional stability of powder injection-molded 316L compacts by adjusting the alloying compositions[J]. Acta Materialia, 2006, 54(5): 1335-1342.
[4] 果世驹, 杨霞, 陈邦峰, 等. 粉末316L不锈钢的高密度强化烧结[J]. 机械工程材料, 2004, 28(7): 7-11.
GUO Shiju, YANG Xia, CHEN Bangfeng, et al. Enhanced sintering of P/M 316L stainless steel for high sintered density[J]. Materials for Mechanical Engineering, 2004, 28(7): 7-11.
[5] Lal S, Upadhyaya G S. Effect of phosphorus and silicon addition on the sintered properties of 316L austenitic stainless steel and its composites containing 4vol% yttria[J]. Journal of Materials Science 1989, 24(9): 3069-3075.
[6] 沈继程, 何慎, 郑宏光, 等. Ti含量对超低碳氮Cr18不锈钢冷轧板再结晶组织和织构的影响[J]. 上海金属, 2010(1): 30-33.
SHEN Jicheng, HE Shen, ZHENG Hongguang, et al. Influence of ti content on recrystallization microstructure and texture of cr18 stainless steel with ultra-low carbon and nitrogen[J]. Shanghai Metals, 2010(1): 30-33.
[7] 霍向东, 毛新平, 陈康敏. Ti含量对热轧带钢组织和力学性能的影响[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2009, 30(1): 23-28.
HUO Xiangdong, MAO Xinping, CHEN Kangmin. Influence of titanium content on microstructure and mechanical properties of hot-rolled strips[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2009, 30(1): 23-28.
[8] HOU Wentai, Honeycombe R W K. Structure of centrifugally cast austenitic stainless steels: Part 2. Effects of Nb, Ti, and Zr[J]. Materials Science and Technology, 1985, 1(5): 390-397.
[9] 杨才福, 张永权, 王宇杰. Ti含量对热轧带钢力学性能的影响[J]. 钢铁, 1995, 30(8): 48-51.
YANG Caifu, ZHANG Yongquan, WANG Yujie. Effect of Ti content on mechanical properties of hot-rolled strip steel[J]. Iron and Steel, 1995, 30(8): 48-51.
[10] German R M. Supersolidus liquid-phase sintering of prealloyed powders[J]. Metallurgical and Meterials Transactions A, 1997, 28(7): 1553-1567.
[11] Cai P Z, Green D J, Messing G L. Constrained densification of aluminum/zirconia hybrid laminates. I: Experimental observations of processing defects[J]. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 1997, 80(8): 1929-1939.
[12] Kwon Y S, Wu Y, Suri P. Simulation of the sintering densification and shrinkage behavior of powder- injection-molded 17-4PH stainless steel[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2004, 35: 257-263.
[13] 何浩. 粉末共注射成形及共烧结过程的研究[D]. 长沙: 中南大学粉末冶金研究院, 2010: 100-115.
HE Hao. A study on powder co-injection and co-sintering[D]. Changsha: Central South University Powder Metallurgy Research Institute, 2010: 100-115.
[14] German R M. Sintering theory and practice[M]. New York: John Wiley & Sons Inc, 1996: 80.
[15] Nakajima H, Ohshida S, Nonaka K, et a1. Diffusion of iron in Ti-Fe alloys[J].Scripta Mater, 1996, 34(6): 949-953.
[16] 梁良华, 李笃信, 李昆. 金属注射成形440C不锈钢的性能及其变形控制[J]. 粉末冶金工业, 2008, 18(5): 5-10.
LIANG Lianghua, LI Duxin, LI Kun. Performance and deformation control of 1njection molded 440c stainless steel compacts[J]. Powder Metallurgy Industry, 2008, 18(5): 5-10.
[17] 姜峰, 李益民, 李松林. 烧结气氛对MIM316L不锈钢微观组织和性能的影响[J]. 粉末冶金工业, 2003, 13(6): 18-22.
JIANG Feng, LI Yimin, LI Songlin. Influence of sintering atmosphere on microstructure and properties of MIM316l stainless steel[J]. Powder Metallurgy Industry, 2003, 13(6): 18-22.
[18] 章林, 刘芳, 李志友, 等. 高合金含量铁基烧结材料的致密化及性能[J]. 粉末冶金材料科学与工程, 2005, 10(3): 172-176.
ZHANG Lin, LIU Fang, LI Zhiyou, et al. Densification and properties of iron-based sintering material with high content of alloying elements[J]. Materials Science and Engineering of Powder Metallurgy, 2005, 10(3): 172-176.
[19] 章林, 刘芳, 李志友, 等. 粉末高速钢SLPS的研究进展[J]. 材料导报, 2005, 19(3): 52-55.
ZHANG Lin, LIU Fang, LI Zhiyou, et al. Overview of the supersolidous liquid phase singtering of powder metallurgy high speed steel[J]. Materials Review, 2005, 19(3): 52-55.
[20] Levenfeld B, Varez A, Torralba J M. Effect of residual carbon on the sintering process of M2 high speed steel parts obtained by a modified metal injection molding process[J]. Metallurgical and Meterials Transactions A, 2002, 33(6): 1843-1851.
(编辑 何运斌)
收稿日期:2012-07-27;修回日期:2012-09-15
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(51075);中南大学博士后基金资助项目(760413008)
通信作者:何浩(1982-),男,宁夏中宁人,博士;从事金属粉末注射成形技术研究;电话:0731-88836113;E-mail:he_hao555@yahoo.com.cn